【Java】CompletableFuture 并发顺序调度
前言
Java CompletableFuture 提供了一种异步编程的方式,可以在一个线程中执行长时间的任务,而不会堵塞主线程。
和Future相比,CompletableFuture不仅实现了Future接口,也实现了 CompletionStage接口。Future接口不用多说,CompletionStage接口将多个CompletionStage执行顺序依赖给抽象了出来。
有了CompletableFuture接口,就能将多个异步事件的结果进行执行顺序编排。
使用
可数操作
一般使用 CompletableFuture的场景是有一个 a 操作,一个 b操作,还有一个 c 操作依赖 a、b两个操作的返回结果。可以直接使用 allOf()接受一长串的入参,也可以使用thenCombine()针对两个操作的特定情况。
public static void main(String[] argv) {CompletableFuture<String> c1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(second * 20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}return "1";});CompletableFuture<String> c2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(second * 20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}return "2";});CompletableFuture c9 = CompletableFuture.allOf(c1, c2);c9.thenApply(v -> {try {c1.get();c2.get();System.out.println("Everything is all right");} catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("Something error");}return v;});c9.join();}
可变操作
当想要处理的 CompletableFuture 是可变的,比如说根据数据库查出的数据每个都需要执行一个 CompletableFuture 操作,也就是 n 个 CompletableFuture。
CompletableFuture<Void> allFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(completableFutureList.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]));CompletableFuture<List<T>> result = allFuture.thenApply(v ->completableFutureList.stream().map(CompletableFuture::join).filter(Objects::nonNull).collect(Collectors.toList()));List<T> tList = result.get(50, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
源码实现
CompletableFuture 类成员变量
CompletableFuture中有一个 volatile 关键词修饰的成员变量,result,CompletableFuture.get()函数中的返回的就是这个变量。它会先检查result变量是否为null,不为null则直接返回,为null则会根据是否可中断进行一个while循环等。

根据使用get() 或者 get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) 函数的不同,最终等待result结果的函数也不同。get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)函数会是用 timedGet(long nanos) 函数进行等待。
/*** Waits if necessary for this future to complete, and then* returns its result.** @return the result value* @throws CancellationException if this future was cancelled* @throws ExecutionException if this future completed exceptionally* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted* while waiting*/public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {Object r;return reportGet((r = result) == null ? waitingGet(true) : r);}
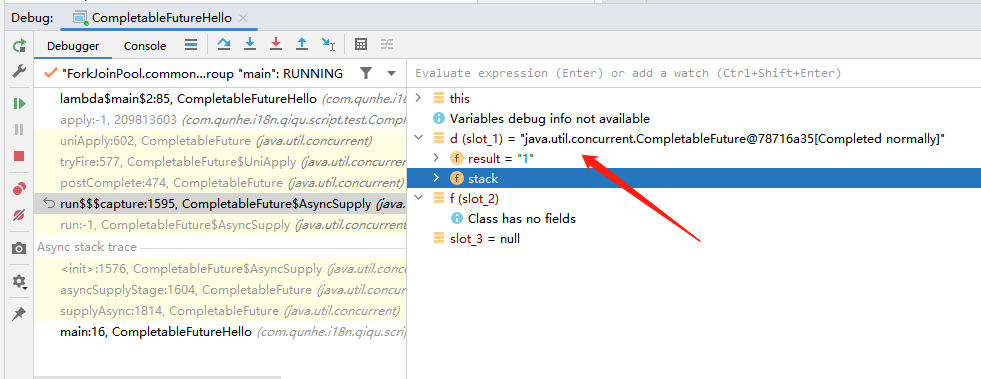
除了代表结果的 result 之外,还有一个 Completion 类 的变量 stack。从断点执行和代码的注解上看,这个stack代表者从属当前CompletableFuture的操作。当前CompletableFuture操作执行完毕后(result里有结果),会引动其他Completion进行处理。
/* * A CompletableFuture may have dependent completion actions,* collected in a linked stack. It atomically completes by CASing* a result field, and then pops off and runs those actions. This* applies across normal vs exceptional outcomes, sync vs async* actions, binary triggers, and various forms of completions.*/* 可以通过截图看出 在Idea 内存中有和没有 Completion stack的CompletableFuture相比,有比没有多了 1 dependents的标记
| Completion stack里没有东西的CompletableFuture | Completion stack里有东西的CompletableFuture |
|---|---|
 |  |
CompletableFuture 多个操作组织结构
CompletableFuture类能够通过 CompletableFuture.allOf()或者 CompletableFuture.anyOf()将多个CompletableFuture 对象组合在一起,等到满足条件时,再触发之后操作的执行。
以allOf方法为例,CompletableFuture.allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) 方法会整合作为入参的所有CompletableFuture,等到他们呢所有的都完成之后,才返回结果。
/* ------------- Arbitrary-arity constructions -------------- *//*** Returns a new CompletableFuture that is completed when all of* the given CompletableFutures complete. If any of the given* CompletableFutures complete exceptionally, then the returned* CompletableFuture also does so, with a CompletionException* holding this exception as its cause. Otherwise, the results,* if any, of the given CompletableFutures are not reflected in* the returned CompletableFuture, but may be obtained by* inspecting them individually. If no CompletableFutures are* provided, returns a CompletableFuture completed with the value* {@code null}.** <p>Among the applications of this method is to await completion* of a set of independent CompletableFutures before continuing a* program, as in: {@code CompletableFuture.allOf(c1, c2,* c3).join();}.** @param cfs the CompletableFutures* @return a new CompletableFuture that is completed when all of the* given CompletableFutures complete* @throws NullPointerException if the array or any of its elements are* {@code null}*/public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);}/** Recursively constructs a tree of completions. */static CompletableFuture<Void> andTree(CompletableFuture<?>[] cfs,int lo, int hi) {CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>();if (lo > hi) // emptyd.result = NIL;else {CompletableFuture<?> a, b;int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;if ((a = (lo == mid ? cfs[lo] :andTree(cfs, lo, mid))) == null ||(b = (lo == hi ? a : (hi == mid+1) ? cfs[hi] :andTree(cfs, mid+1, hi))) == null)throw new NullPointerException();if (!d.biRelay(a, b)) {BiRelay<?,?> c = new BiRelay<>(d, a, b);a.bipush(b, c);c.tryFire(SYNC);}}return d;}/** Pushes completion to this and b unless both done. */final void bipush(CompletableFuture<?> b, BiCompletion<?,?,?> c) {if (c != null) {Object r;while ((r = result) == null && !tryPushStack(c))lazySetNext(c, null); // clear on failureif (b != null && b != this && b.result == null) {Completion q = (r != null) ? c : new CoCompletion(c);while (b.result == null && !b.tryPushStack(q))lazySetNext(q, null); // clear on failure}}} /** Returns true if successfully pushed c onto stack. */final boolean tryPushStack(Completion c) {Completion h = stack;lazySetNext(c, h);return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, STACK, h, c);} boolean biRelay(CompletableFuture<?> a, CompletableFuture<?> b) {Object r, s; Throwable x;if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null ||b == null || (s = b.result) == null)return false;if (result == null) {if (r instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null)completeThrowable(x, r);else if (s instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult)s).ex) != null)completeThrowable(x, s);elsecompleteNull();}return true;}从源码上看是,是将整个CompletableFuture数组通过andTree()方法划分成了一颗二叉树,这个二叉树的叶子节点是传入的CompletableFuture对象,非叶子节点代表了它的子节点CompletableFuture的完成情况。
然后检测根节点的CompletableFuture的两个子节点是否完成。

cfs1、cfs2、cfs3、cfs4 是allOf的入参,四个CompletableFuture对象。
代码中通过a.bipush(b, c) 将 a、b串在一起。因为涉及到UNSAFE方法,不知道方法具体执行了什么操作。所以只能通过IDEA里内存里实际的值,去由结果推过程。
a.bipush(b,c) 前,内存各个变量实际值。

a.bipush(b,c) 后,内存各个变量实际值。

tryPushStack(Completion c) 方法前

tryPushStack(Completion c) 方法后 可以看到内存中 变量b 对应的内存地址为 75bd9247的 stack被赋值了成为了Completion c。
tryFire(int mode)方法执行前

可以看到 cfs 除了 cfs1 之外,其他的 cfs 中的 stack都被赋值了。通过观察IDEA中内存中对象实际值,可以发现stack中 的 src 是 自己的树上的兄弟节点, snd 是自己。

CompletableFuture 多个操作执行顺序控制
CompletableFuture 一个节点要开始执行的前提是他的子节点全部执行完毕之后,才能触发自己节点上的操作。
当调用CompletableFuture 异步执行方法 supplyAsync 会传递一个 Supplier 对象作为入参。这个Supplier 会被封装成为 一个Runnable 子类 AsyncSupply 对象,作为其抽象方法 run 中 执行的一部分。
CompletableFuture<String> c2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(second * 20);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}return "2";});---------------------------------------------------------------------------------/*** Returns a new CompletableFuture that is asynchronously completed* by a task running in the {@link ForkJoinPool#commonPool()} with* the value obtained by calling the given Supplier.** @param supplier a function returning the value to be used* to complete the returned CompletableFuture* @param <U> the function's return type* @return the new CompletableFuture*/public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);}static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e,Supplier<U> f) {if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>();e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f));return d;}-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------public void run() {// fn 就是 CompletableFuture.supplyAsync 传入的 Supplier CompletableFuture<T> d; Supplier<T> f;if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {dep = null; fn = null;if (d.result == null) {try {// 将 Supplier 处理结果赋值给 CompletableFuture 的 resultd.completeValue(f.get());} catch (Throwable ex) {d.completeThrowable(ex);}} // Pops and tries to trigger all reachable dependents. Call only when known to be done.d.postComplete();}}从源码中可以看到,当执行了CompletableFuture.supplyAsync()他的通知机制封装在实现Runnable抽象方法run里。当你传入的Supplier 有结果返回之后,会调用 CompletableFuture 中的 postComplete() 方法,通知 stack中其他可达的 从属 Completion,让他们各自完成自己的 action。
/*** Pops and tries to trigger all reachable dependents. Call only* when known to be done.*/final void postComplete() {/** On each step, variable f holds current dependents to pop* and run. It is extended along only one path at a time,* pushing others to avoid unbounded recursion.*/CompletableFuture<?> f = this; Completion h;while ((h = f.stack) != null ||(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {CompletableFuture<?> d; Completion t;if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) {if (t != null) {if (f != this) {pushStack(h);continue;}h.next = null; // detach}// 将 下一个需要执行的 Completion 弹出来后 执行 tryFiref = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;}}}static final class UniApply<T,V> extends UniCompletion<T,V> {Function<? super T,? extends V> fn;UniApply(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep,CompletableFuture<T> src,Function<? super T,? extends V> fn) {super(executor, dep, src); this.fn = fn;}final CompletableFuture<V> tryFire(int mode) {CompletableFuture<V> d; CompletableFuture<T> a;if ((d = dep) == null ||// uniApply 对封装的 Supplier 进行执行!d.uniApply(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this))return null;dep = null; src = null; fn = null;return d.postFire(a, mode);}} final <S> boolean uniApply(CompletableFuture<S> a,Function<? super S,? extends T> f,UniApply<S,T> c) {Object r; Throwable x;if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null)return false;tryComplete: if (result == null) {if (r instanceof AltResult) {if ((x = ((AltResult)r).ex) != null) {completeThrowable(x, r);break tryComplete;}r = null;}try {if (c != null && !c.claim())return false;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") S s = (S) r;// 这里实际执行 CompletableFuture 的 SuppliercompleteValue(f.apply(s));} catch (Throwable ex) {completeThrowable(ex);}}return true;}从Idea里的 栈帧中可以看出来,是由 CompletableFuture 1 执行完后的 postComplete 引发了接下来的CompletableFuture
相关文章:

【Java】CompletableFuture 并发顺序调度
前言 Java CompletableFuture 提供了一种异步编程的方式,可以在一个线程中执行长时间的任务,而不会堵塞主线程。 和Future相比,CompletableFuture不仅实现了Future接口,也实现了 CompletionStage接口。Future接口不用多说&#…...
职场人必备的6款实用办公app,每一款都是心头爱
打工人不容易啊,不提高工作效率怕是要被淘汰了。今天给大家分享6款职场人必备的实用办公APP,免费效率神器让工作事半功倍。这些APP每一款都是我的心头爱,肯定会让人大开眼界的,超级实用,直接往下看吧。1、向日葵远程控…...

小丑改造计划之复习一
1.函数重载 根据参数个数 参数顺序 参数类型 的不同 可以在同一个域存在多个同名函数 但是不可以根据返回值 缺省参数的不同去重载函数 2.指针和引用的区别 第一点 指针是内存地址,会开辟内存空间,而引用和它所引用的变量共享同一块内存 第二点 引用必须…...
final修饰符使用中遇到的一些问题
文章目录final修饰符1. final不能用来修饰构造方法2. final修饰变量的一些注意问题2.1 final修饰成员变量2.2 final修饰引用类型2.2.1 演示代码中lombok链式编程介绍final修饰符 final具有“不可改变”的含义,它可以修饰非抽象类、非抽象成员方法和变量。 用final…...
好记又实用的获取电脑型号方法
个人常用的方法 方法二最好记又好用。 方法一 dxdiag命令 按下键盘WINR调出运行在输入框输入dxdiag命令后,按下回车;进入DirectX诊断工具,便可查看系统型号等信息。 这里就会显示系统型号。 方法二 设备和打印机 控制面板-查看方式-小图…...

@Transactional配置详解
一:事务注解Transactional,属性propagation的7个配置 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED -- 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。,默认配置,也是常用的选择。 PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS -- 支持当前事务&#…...

性能测试面试题汇总
稳定性测试的怎么挑选的接口? 1、频繁使用的接口:选择那些被频繁使用的接口,因为这些接口可能会面临更大的负载和并发访问,从而可能导致性能问题。 2、核心功能接口:选择那些实现系统核心功能的接口,因为这…...

vue权限控制和动态路由
思路 登录:当用户填写完账号和密码后向服务端验证是否正确,验证通过之后,服务端会返回一个token,拿到token之后(我会将这个token存贮到localStore中,保证刷新页面后能记住用户登录状态)…...

利用正则表达式删掉代码中的所有注释-pycharm为例
首先删除注释 打开您想要删除注释的Python文件。 使用快捷键 Ctrl Shift R 打开 "Replace in Files"(在文件中替换)对话框。 在 "Find"(查找)框中输入以下正则表达式,以查找所有行中的注释内容…...

【java基础】内部类、局部内部类、匿名内部类、静态内部类
内部类 内部类就是定义在另一个类中的类。我们使用内部类的原因主要有以下两点 内部类可以对同一个包中的其他类隐藏内部类方法可以访问定义这个类的作用域中的数据,包括原本私有的数据 public class A {class B {} }我们使用内部类可以访问外部类的所有属性&…...
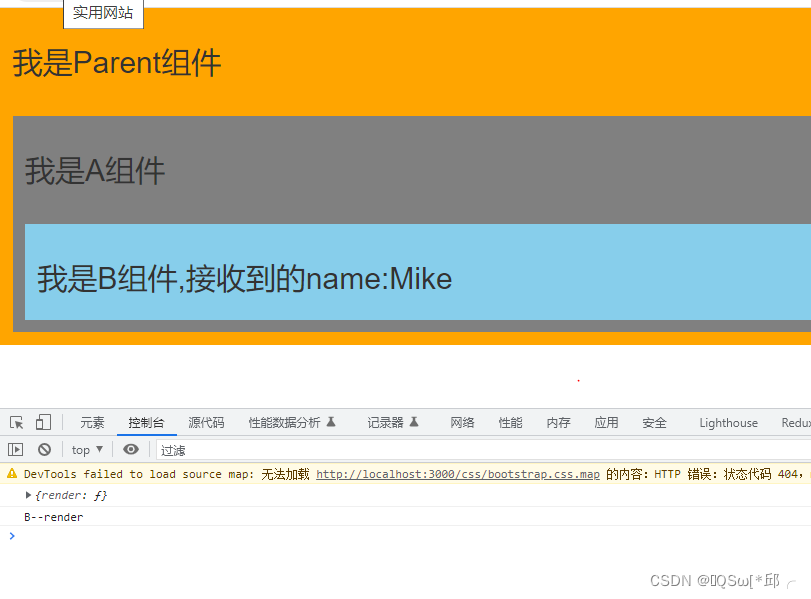
react renderProps学习记录
react renderProps学习记录1.引入2.改一下呢3.再改一下呢4.总结一下如何向组件内部动态传入带内容的结构(标签)?children propsrender props1.引入 上代码: import React, { Component } from react import ./index.css export default class Parent extends Com…...
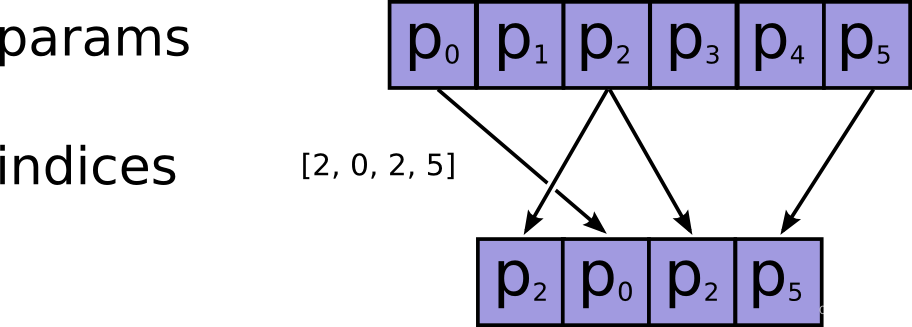
关于tf.gather函数batch_dims参数用法的理解
关于tf.gather函数batch_dims参数用法的理解0 前言1. 不考虑batch_dims2. 批处理(考虑batch_dims)2.1 batch_dims12.2 batch_dims02.3 batch_dims>22.4 batch_dims再降为12.5 再将axis降为12.6 batch_dims<02.7 batch_dims总结3. 补充4. 参数和返回值5. 其他相关论述6. 附…...

日常操作linux常用命令
cd /mnt/opt/cqstt/logs/stt-erp docker logs -f --tail1000 stt-erp # 查看物理CPU个数 cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep "physical id"| sort| uniq| wc -l # 查看每个物理CPU中core的个数(即核数) cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep "cpu cores"| uniq # 查看逻辑CPU的…...

【Java集合框架】篇二:Collection接口方法
JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现类,而是提供更具体的子接口(如:Set和List)去实现。 Collection 接口是 List和Set接口的父接口,该接口里定义的方法既可用于操作 Set 集合,也可用于操作 List 集合。方法如下…...

PHP入门指南:简单易学的语法和丰富的调试工具与安全性最佳实践
PHP是一种非常流行的服务器端编程语言,它被广泛地应用于Web开发中。如果您想学习Web开发,那么PHP是一个非常好的选择。在本文中,我将介绍PHP的一些基础知识,包括语法、变量、函数、数组、数据库连接、调试和安全性等。PHP的语法PH…...

前端面试题--HTML篇
一、src和href的区别src指向外部资源的位置,指向的内容会嵌入到文档中当前标签所在的位置;href指向网络资源的位置,建立和当前元素或当前文档之间的链接。二、对HTML语义化的理解根据内容的结构化,选择合适的标签。优点࿱…...
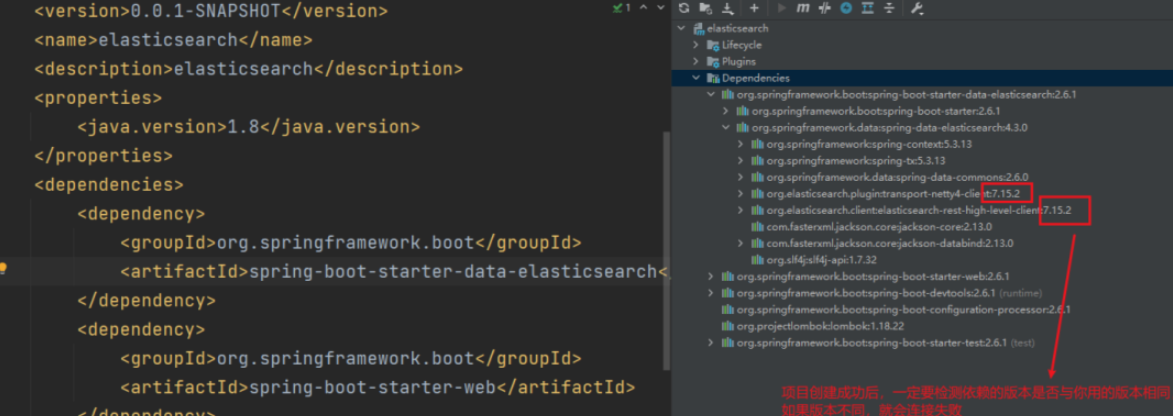
SpringBoot集成ElasticSearch,实现模糊查询,批量CRUD,排序,分页,高亮
导入elasticsearch依赖在pom.xml里加入如下依赖:<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId> </dependency>非常重要:检查依赖版本…...
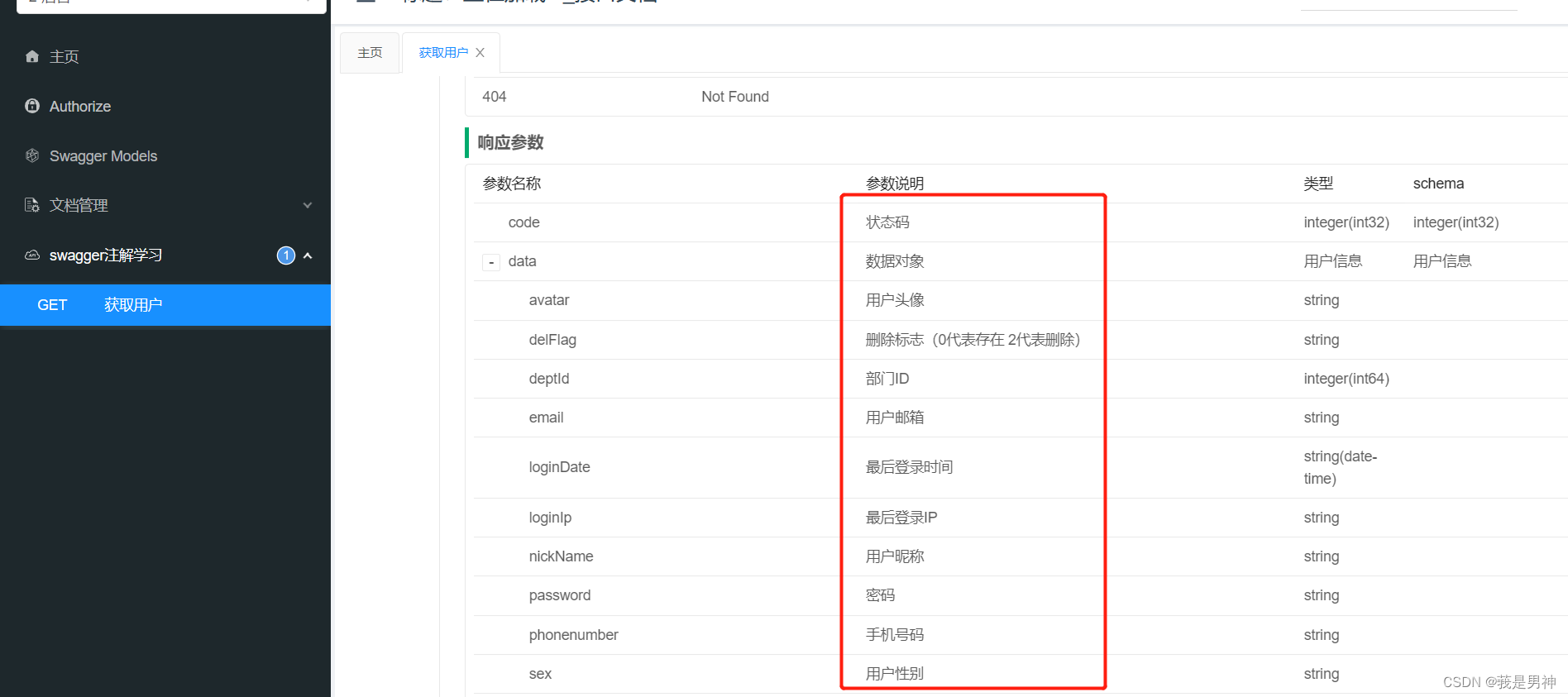
常用Swagger注解汇总
常用Swagger注解汇总 前言 在实际编写后端代码的过程中,我们可能经常使用到 swagger 注解,但是会用不代表了解,你知道每个注解都有什么属性吗?你都用过这些属性吗?了解它们的作用吗?本文在此带大家总结一下…...

关于 TypeScript 声明文件
declare var 声明全局变量declare function 声明全局方法declare class 声明全局类declare enum 声明全局枚举类型declare namespace 声明(含有子属性的)全局对象interface 和 type 声明全局类型export 导出变量export namespace 导出(含有子…...

SpringBoot学习-原理篇
SpringBoot原理篇springboot技术本身就是为了加速spring程序的开发的,可以大胆的说,springboot技术没有自己的原理层面的设计,仅仅是实现方案进行了改进。将springboot定位成工具,你就不会去想方设法的学习其原理了。就像是将木头…...
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程
Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认证教程一、说明二、环境准备三、编写 Docker Compose 和 jaas文件docker-compose.yml代码说明:server_jaas.conf 四、启动服务五、验证服务六、连接kafka服务七、总结 Docker 运行 Kafka 带 SASL 认…...

《Playwright:微软的自动化测试工具详解》
Playwright 简介:声明内容来自网络,将内容拼接整理出来的文档 Playwright 是微软开发的自动化测试工具,支持 Chrome、Firefox、Safari 等主流浏览器,提供多语言 API(Python、JavaScript、Java、.NET)。它的特点包括&a…...

vue3 定时器-定义全局方法 vue+ts
1.创建ts文件 路径:src/utils/timer.ts 完整代码: import { onUnmounted } from vuetype TimerCallback (...args: any[]) > voidexport function useGlobalTimer() {const timers: Map<number, NodeJS.Timeout> new Map()// 创建定时器con…...

[Java恶补day16] 238.除自身以外数组的乘积
给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。 题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在 32 位 整数范围内。 请 不要使用除法,且在 O(n) 时间复杂度…...
集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join)
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join
纯 Java 项目(非 SpringBoot)集成 Mybatis-Plus 和 Mybatis-Plus-Join 1、依赖1.1、依赖版本1.2、pom.xml 2、代码2.1、SqlSession 构造器2.2、MybatisPlus代码生成器2.3、获取 config.yml 配置2.3.1、config.yml2.3.2、项目配置类 2.4、ftl 模板2.4.1、…...
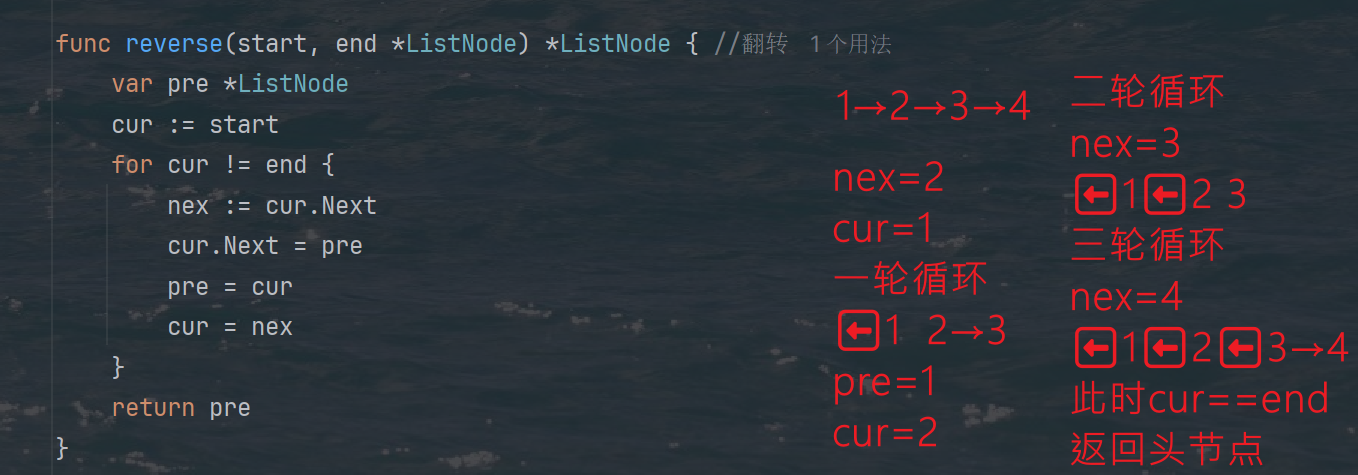
力扣热题100 k个一组反转链表题解
题目: 代码: func reverseKGroup(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode {cur : headfor i : 0; i < k; i {if cur nil {return head}cur cur.Next}newHead : reverse(head, cur)head.Next reverseKGroup(cur, k)return newHead }func reverse(start, end *ListNode) *ListN…...

Caliper 配置文件解析:fisco-bcos.json
config.yaml 文件 config.yaml 是 Caliper 的主配置文件,通常包含以下内容: test:name: fisco-bcos-test # 测试名称description: Performance test of FISCO-BCOS # 测试描述workers:type: local # 工作进程类型number: 5 # 工作进程数量monitor:type: - docker- pro…...

日常一水C
多态 言简意赅:就是一个对象面对同一事件时做出的不同反应 而之前的继承中说过,当子类和父类的函数名相同时,会隐藏父类的同名函数转而调用子类的同名函数,如果要调用父类的同名函数,那么就需要对父类进行引用&#…...
)
uniapp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息(地理位置/文件)
UniApp 集成腾讯云 IM 富媒体消息全攻略(地理位置/文件) 一、功能实现原理 腾讯云 IM 通过 消息扩展机制 支持富媒体类型,核心实现方式: 标准消息类型:直接使用 SDK 内置类型(文件、图片等)自…...

Neko虚拟浏览器远程协作方案:Docker+内网穿透技术部署实践
前言:本文将向开发者介绍一款创新性协作工具——Neko虚拟浏览器。在数字化协作场景中,跨地域的团队常需面对实时共享屏幕、协同编辑文档等需求。通过本指南,你将掌握在Ubuntu系统中使用容器化技术部署该工具的具体方案,并结合内网…...
