Linux 软raid - - Barrier
什么是Barriers
在linux软raid中,用来处理正常IO和同步IO的并发问题,可以简单理解为专用于软raid的锁。
软raid在做resync/recovery,或者配置操作时需要raise 屏障,于此同时必须暂停正常IO。
barrier是可以被多次raise的一个计数器,来计算有多少个相关活动事件在发生,其中不包括正常IO。
raise 屏障的条件是没有pending的IO即nr_pending=0。
只有在没有人等待barrier down的情况下,才会选择raise barrier。这意味着,一旦IO请求准备就绪,在IO请求有机会之前,不会启动其他需要屏障的操作。
常规IO调用“wait_barrier”。当返回时,没有后台组IO发生,它必须安排在完成IO后调用allow_barrier。
后台组IO调用必须调用raise_barrier。一旦返回,就没有正常的IO发生。它必须安排在特定后台IO完成时调用lower_barrier。
/* Barriers....* Sometimes we need to suspend IO while we do something else,* either some resync/recovery, or reconfigure the array.* To do this we raise a 'barrier'.* The 'barrier' is a counter that can be raised multiple times* to count how many activities are happening which preclude* normal IO.* We can only raise the barrier if there is no pending IO.* i.e. if nr_pending == 0.* We choose only to raise the barrier if no-one is waiting for the* barrier to go down. This means that as soon as an IO request* is ready, no other operations which require a barrier will start* until the IO request has had a chance.** So: regular IO calls 'wait_barrier'. When that returns there* is no backgroup IO happening, It must arrange to call* allow_barrier when it has finished its IO.* backgroup IO calls must call raise_barrier. Once that returns* there is no normal IO happeing. It must arrange to call* lower_barrier when the particular background IO completes.*/
相关数据结构
用来描述软raid配置相关的所有信息。
struct r1conf {struct mddev *mddev;struct raid1_info *mirrors; /* twice 'raid_disks' to* allow for replacements.*/int raid_disks;spinlock_t device_lock;/* list of 'struct r1bio' that need to be processed by raid1d,* whether to retry a read, writeout a resync or recovery* block, or anything else.*/struct list_head retry_list;/* A separate list of r1bio which just need raid_end_bio_io called.* This mustn't happen for writes which had any errors if the superblock* needs to be written.*/struct list_head bio_end_io_list;/* queue pending writes to be submitted on unplug */struct bio_list pending_bio_list;int pending_count;/* for use when syncing mirrors:* We don't allow both normal IO and resync/recovery IO at* the same time - resync/recovery can only happen when there* is no other IO. So when either is active, the other has to wait.* See more details description in raid1.c near raise_barrier().*/wait_queue_head_t wait_barrier;spinlock_t resync_lock;atomic_t nr_sync_pending;atomic_t *nr_pending;atomic_t *nr_waiting;atomic_t *nr_queued;atomic_t *barrier;int array_frozen;/* Set to 1 if a full sync is needed, (fresh device added).* Cleared when a sync completes.*/int fullsync;/* When the same as mddev->recovery_disabled we don't allow* recovery to be attempted as we expect a read error.*/int recovery_disabled;/* poolinfo contains information about the content of the* mempools - it changes when the array grows or shrinks*/struct pool_info *poolinfo;mempool_t r1bio_pool;mempool_t r1buf_pool;struct bio_set bio_split;/* temporary buffer to synchronous IO when attempting to repair* a read error.*/struct page *tmppage;/* When taking over an array from a different personality, we store* the new thread here until we fully activate the array.*/struct md_thread *thread;/* Keep track of cluster resync window to send to other* nodes.*/sector_t cluster_sync_low;sector_t cluster_sync_high;};
在当前的例子中,我们需要关注3个成员。
- nr_pending
正在处理的正常IO - nr_waitting
等待同步完成的正常IO - barrier
正在处理的同步IO
相关内核函数
raise_barrier
raise_barrier只有在同步IO的场景下raid1_sync_request才会被调用,这就意味着,只有等待正常IO完成之后,才能把屏障加起来。
static sector_t raise_barrier(struct r1conf *conf, sector_t sector_nr)
{int idx = sector_to_idx(sector_nr); // 获取在bucket中的index。spin_lock_irq(&conf->resync_lock);/* Wait until no block IO is waiting */wait_event_lock_irq(conf->wait_barrier,!atomic_read(&conf->nr_waiting[idx]),conf->resync_lock);/* block any new IO from starting */atomic_inc(&conf->barrier[idx]);/** In raise_barrier() we firstly increase conf->barrier[idx] then* check conf->nr_pending[idx]. In _wait_barrier() we firstly* increase conf->nr_pending[idx] then check conf->barrier[idx].* A memory barrier here to make sure conf->nr_pending[idx] won't* be fetched before conf->barrier[idx] is increased. Otherwise* there will be a race between raise_barrier() and _wait_barrier().*/smp_mb__after_atomic(); // 内存屏障。/* For these conditions we must wait:* A: while the array is in frozen state* B: while conf->nr_pending[idx] is not 0, meaning regular I/O* existing in corresponding I/O barrier bucket.* C: while conf->barrier[idx] >= RESYNC_DEPTH, meaning reaches* max resync count which allowed on current I/O barrier bucket.*/wait_event_lock_irq(conf->wait_barrier,(!conf->array_frozen &&!atomic_read(&conf->nr_pending[idx]) &&atomic_read(&conf->barrier[idx]) < RESYNC_DEPTH) ||test_bit(MD_RECOVERY_INTR, &conf->mddev->recovery),conf->resync_lock);if (test_bit(MD_RECOVERY_INTR, &conf->mddev->recovery)) {atomic_dec(&conf->barrier[idx]);spin_unlock_irq(&conf->resync_lock);wake_up(&conf->wait_barrier);return -EINTR;}atomic_inc(&conf->nr_sync_pending);spin_unlock_irq(&conf->resync_lock);return 0;
}
wait_barrier
wait_barrier只有在向下发写请求raid1_write_request时被调用,如果此时对应的磁盘扇区存在barrier,nr_waiting会被添加,表示同一时刻,同一扇区存在同步IO。
static void _wait_barrier(struct r1conf *conf, int idx)
{/** We need to increase conf->nr_pending[idx] very early here,* then raise_barrier() can be blocked when it waits for* conf->nr_pending[idx] to be 0. Then we can avoid holding* conf->resync_lock when there is no barrier raised in same* barrier unit bucket. Also if the array is frozen, I/O* should be blocked until array is unfrozen.*/atomic_inc(&conf->nr_pending[idx]);/** In _wait_barrier() we firstly increase conf->nr_pending[idx], then* check conf->barrier[idx]. In raise_barrier() we firstly increase* conf->barrier[idx], then check conf->nr_pending[idx]. A memory* barrier is necessary here to make sure conf->barrier[idx] won't be* fetched before conf->nr_pending[idx] is increased. Otherwise there* will be a race between _wait_barrier() and raise_barrier().*/smp_mb__after_atomic();/** Don't worry about checking two atomic_t variables at same time* here. If during we check conf->barrier[idx], the array is* frozen (conf->array_frozen is 1), and chonf->barrier[idx] is* 0, it is safe to return and make the I/O continue. Because the* array is frozen, all I/O returned here will eventually complete* or be queued, no race will happen. See code comment in* frozen_array().*/if (!READ_ONCE(conf->array_frozen) &&!atomic_read(&conf->barrier[idx]))return;/** After holding conf->resync_lock, conf->nr_pending[idx]* should be decreased before waiting for barrier to drop.* Otherwise, we may encounter a race condition because* raise_barrer() might be waiting for conf->nr_pending[idx]* to be 0 at same time.*/spin_lock_irq(&conf->resync_lock);atomic_inc(&conf->nr_waiting[idx]);atomic_dec(&conf->nr_pending[idx]);/** In case freeze_array() is waiting for* get_unqueued_pending() == extra*/wake_up(&conf->wait_barrier);/* Wait for the barrier in same barrier unit bucket to drop. */wait_event_lock_irq(conf->wait_barrier,!conf->array_frozen &&!atomic_read(&conf->barrier[idx]),conf->resync_lock);atomic_inc(&conf->nr_pending[idx]);atomic_dec(&conf->nr_waiting[idx]);spin_unlock_irq(&conf->resync_lock);
}static void wait_barrier(struct r1conf *conf, sector_t sector_nr)
{int idx = sector_to_idx(sector_nr);_wait_barrier(conf, idx);
}
wait_read_barrier
wait_read_barrier只有在下发IO读请求时被调用raid1_write_request,读请求入口将对应的bio状态置为pending状态,如果raid处于非frozen状态,直接返回。
static void wait_read_barrier(struct r1conf *conf, sector_t sector_nr)
{int idx = sector_to_idx(sector_nr);/** Very similar to _wait_barrier(). The difference is, for read* I/O we don't need wait for sync I/O, but if the whole array* is frozen, the read I/O still has to wait until the array is* unfrozen. Since there is no ordering requirement with* conf->barrier[idx] here, memory barrier is unnecessary as well.*/atomic_inc(&conf->nr_pending[idx]);if (!READ_ONCE(conf->array_frozen))return;spin_lock_irq(&conf->resync_lock);atomic_inc(&conf->nr_waiting[idx]);atomic_dec(&conf->nr_pending[idx]);/** In case freeze_array() is waiting for* get_unqueued_pending() == extra*/wake_up(&conf->wait_barrier);/* Wait for array to be unfrozen */wait_event_lock_irq(conf->wait_barrier,!conf->array_frozen,conf->resync_lock);atomic_inc(&conf->nr_pending[idx]);atomic_dec(&conf->nr_waiting[idx]);spin_unlock_irq(&conf->resync_lock);
}
lower_barrier
static void lower_barrier(struct r1conf *conf, sector_t sector_nr)
{int idx = sector_to_idx(sector_nr);BUG_ON(atomic_read(&conf->barrier[idx]) <= 0);atomic_dec(&conf->barrier[idx]);atomic_dec(&conf->nr_sync_pending);wake_up(&conf->wait_barrier);
}
相关文章:

Linux 软raid - - Barrier
什么是Barriers 在linux软raid中,用来处理正常IO和同步IO的并发问题,可以简单理解为专用于软raid的锁。 软raid在做resync/recovery,或者配置操作时需要raise 屏障,于此同时必须暂停正常IO。 barrier是可以被多次raise的一个计数…...
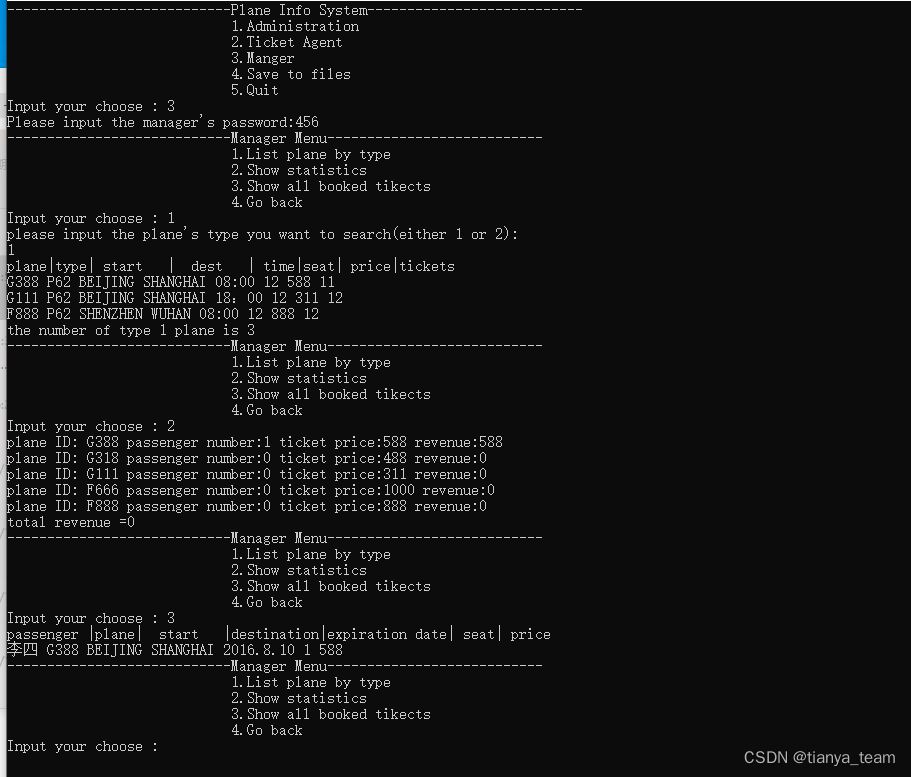
航空公司管理系统(迷你版12306)
要求 今天分享一个之前辅导留学生的作业,作业要求如下: Project E: Airways Management System Overall description: Your team is employed by an Airways company for the implementation of a computer system responsible for a large part of th…...
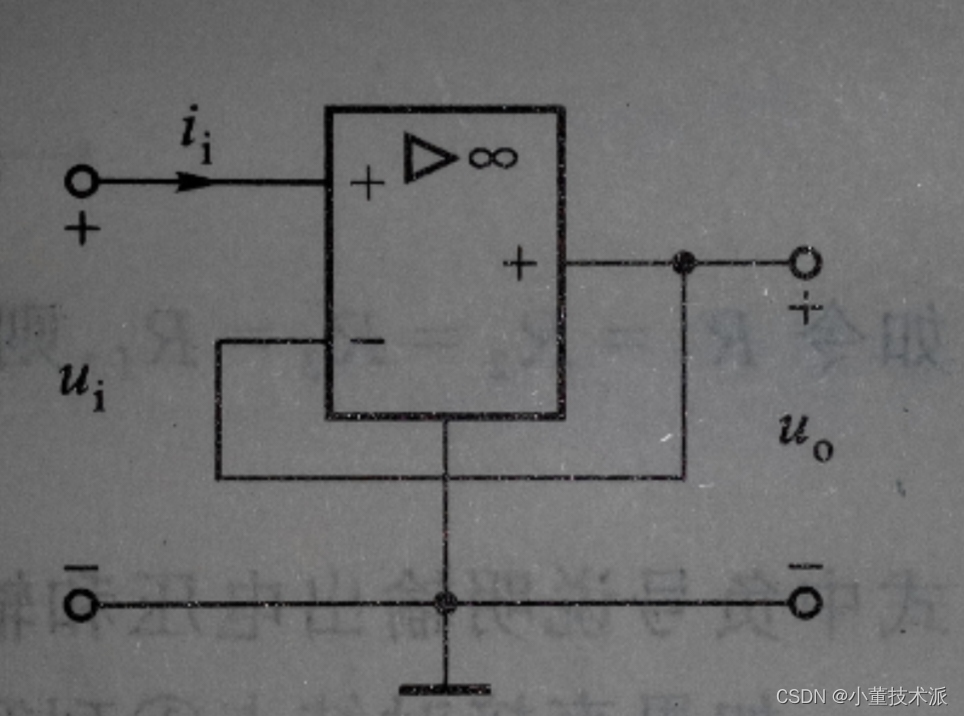
嵌入式硬件电路原理图之跟随电路
描述 电压跟随电路 电压跟随器是共集电极电路,信号从基极输入,射极输出,故又称射极输出器。基极电压与集电极电压相位相同,即输入电压与输出电压同相。这一电路的主要特点是:高输入电阻、低输出电阻、电压增益近似为…...

学习录
概述 这几年在迷茫中看了不少资料,有觉得写得很棒的,也有写的很糟糕的。所以一直想写这块的总结来进行归纳,同时也希望能给其他处于迷茫中的朋友提供一份高质量的资料列表(也许一个读者也没有),以下清单个人觉得值得反复看以及思…...
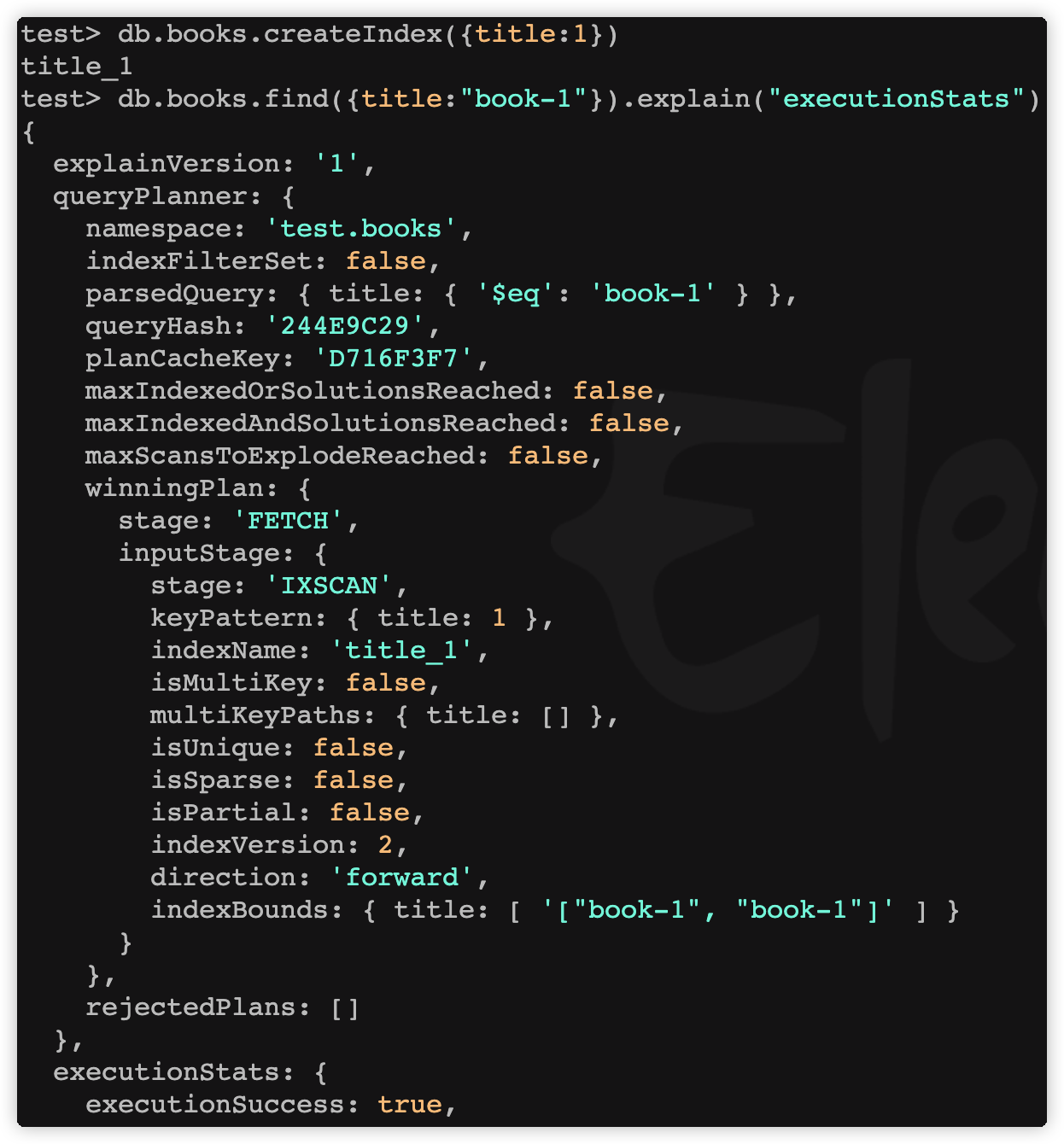
MongoDB索引详解
概述 索引是一种用来快速查询数据的数据结构。BTree 就是一种常用的数据库索引数据结构,MongoDB 采用 BTree 做索引,索引创建 colletions 上。MongoDB 不使用索引的查询,先扫描所有的文档,再匹配符合条件的文档。使用索引的查询&…...

一文搞定JVM内存模型
鲁大猿,寻精品资料,帮你构建Java全栈知识体系 www.jiagoujishu.cn 运行时数据区 内存是非常重要的系统资源,是硬盘和 CPU 的中间仓库及桥梁,承载着操作系统和应用程序的实时运行。JVM 内存布局规定了 Java 在运行过程中内存申请、…...

月报总结|Moonbeam 12月份大事一览
一转眼已经到年底啦。本月,Moonbeam基金会发布四个最新战略重点:跨链解决方案、游戏、真实世界资产(RWA)、新兴市场。其中在新兴市场方面,紧锣密鼓地推出与巴西公司Grupo RO的战略合作。 用户教育方面,为了…...
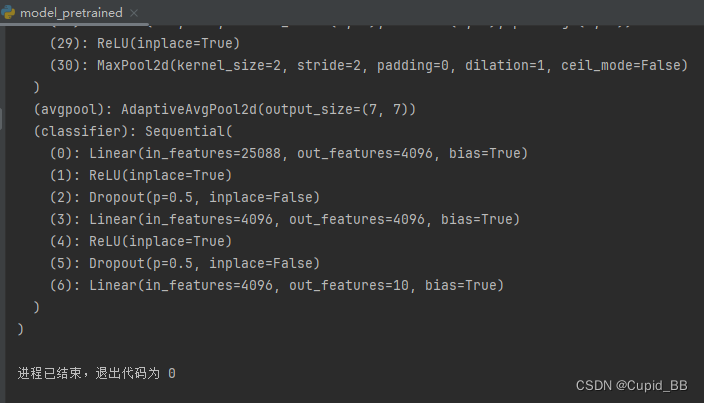
现有网络模型的使用及修改(VGG16为例)
VGG16 修改默认路径 import os os.environ[TORCH_HOME] rD:\Pytorch\pythonProject\vgg16 # 下载位置太大了(140多G)不提供直接下载 train_set torchvision.datasets.ImageNet(root./data_image_net, splittrain, downloadTrue, transformtorchvis…...
MacOS M1/M2 Go Debug 配置
前言 换电脑,Go 环境带来一些麻烦,耽误很多时间,稍作记录。 原始电脑是 Mac 旧款,CPU x86 构型,新电脑 M2,因为旧电脑里本地文件很多,为了简化搬迁,还是用了 Mac 自带的迁移&#x…...

paddlehub 文本检测使用
PaddleHub负责模型的管理、获取和预训练模型的使用。 参考:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleHub/tree/develop/modules/image/text_recognition/chinese_text_detection_db_server import paddlehub as hub import cv2 # from utils import cv_show import…...
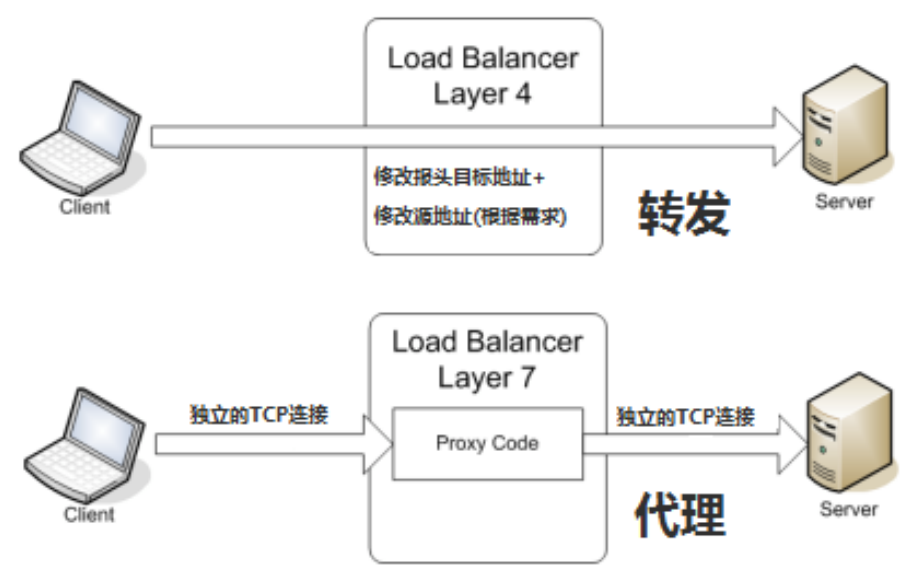
负载均衡概述
负载均衡 负载均衡 建立在现有网络结构之上,它提供了一种廉价有效透明的方法扩展网络设备和服务器的带宽、增加吞吐量、加强网络数据处理能力、提高网络的灵活性和可用性。 四层负载均衡 vs 七层负载均衡 四层负载均衡(目标地址和端口交换)…...
C# WinForm MessageBox自定义按键文本 COM组件版
c# 更改弹窗MessageBox按钮文字_c# messagebox.show 字体-CSDN博客 需要用到大佬上传到百度云盘的Hook类,在大佬给的例子的基础上改动了点。 应用时自己加GUID和ProgID。 组件实现: using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.L…...
基于SpringBoot微信小程序的宠物美容预约系统设计与实现
博主介绍:✌全网粉丝30W,csdn特邀作者、博客专家、CSDN新星计划导师、Java领域优质创作者,博客之星、掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域和学生毕业项目实战,高校老师/讲师/同行交流合作✌ 主要内容:SpringBoot、Vue、SSM、HLM…...
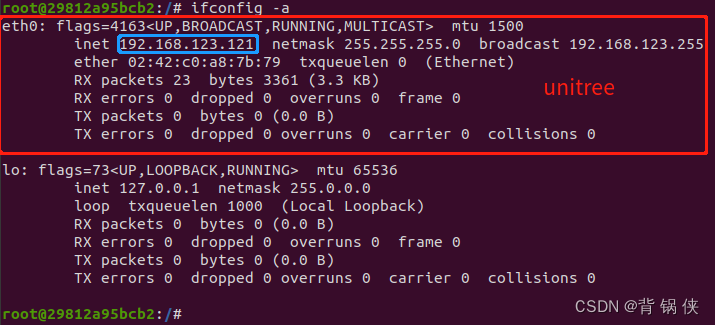
在 docker 容器中配置双网卡,解决通讯的问题
目录 1. 查看当前网络信息 2. 创建自定义网络桥 3. 创建双网卡模式 4. 删除默认网卡 已经创建好了的 Docker 容器,要修改它的IP比较麻烦,网上找了几种不同的方法,经过试验都没有成功,下面通过配置双网上来解决 IP 的问题。…...

uniapp中uview组件库CircleProgress 圆形进度条丰富的使用方法
目录 #内部实现 #平台差异说明 #基本使用 #设置圆环的动画时间 #API #Props 展示操作或任务的当前进度,比如上传文件,是一个圆形的进度环。 #内部实现 组件内部通过canvas实现,有更好的性能和通用性。 #平台差异说明 AppH5微信小程…...
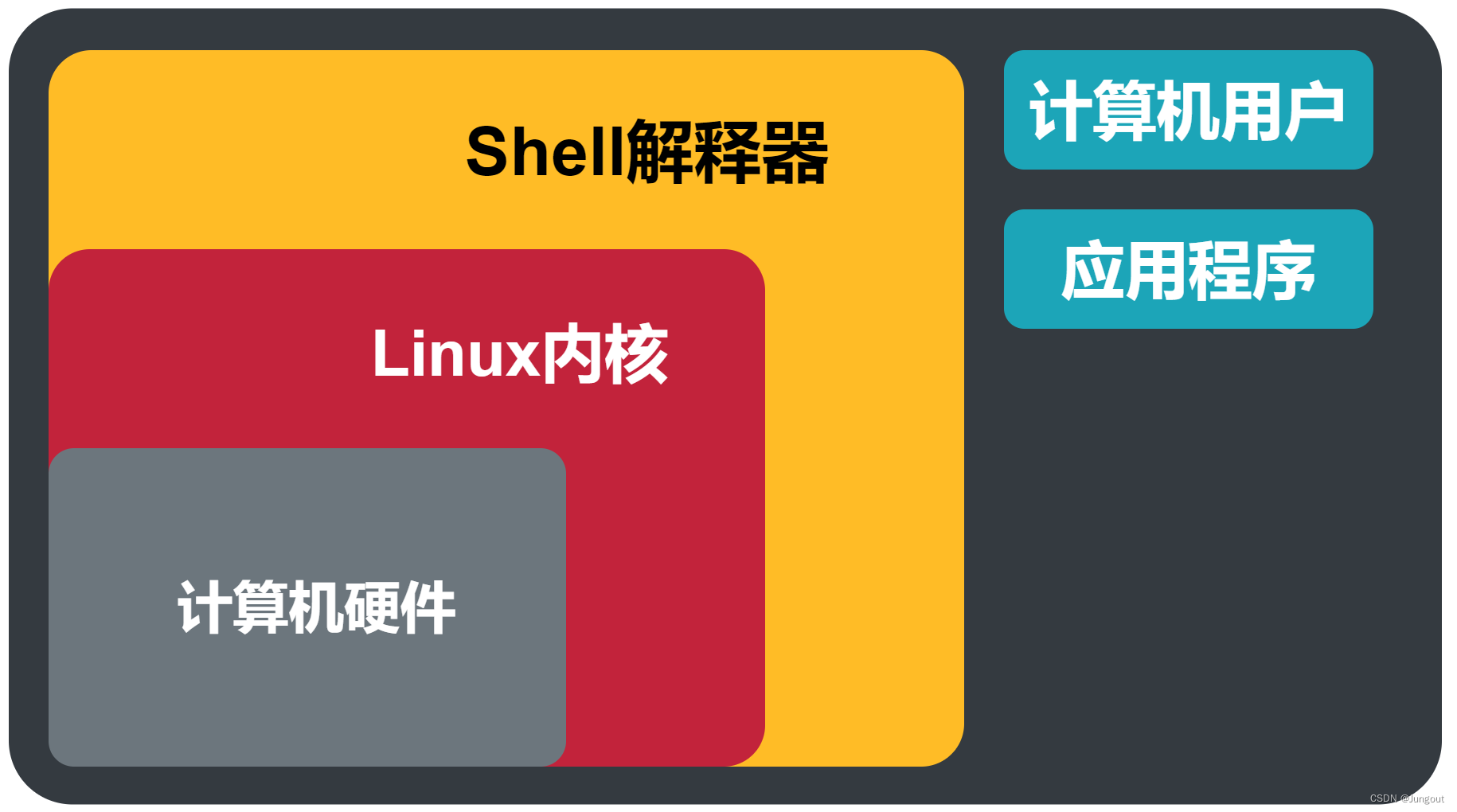
Linux操作系统基础(12):Linux的Shell解释器
1. Shell的介绍 在Linux中,Shell 是一种命令行解释器,它是用户与操作系统内核之间的接口,它负责解释用户输入的命令,并将其转换成系统调用或其他操作系统能够执行的指令。 Shell 提供了一种交互式的方式来与操作系统进行通信&am…...

Android开发编程从入门到精通,安卓技术从初级到高级全套教学
一、教程描述 本套教程基于JDK1.8版本,教学内容主要有,1、环境搭建,UI布局,基础UI组件,高级UI组件,通知,自定义组件,样式主题;2、四大组件,Intent࿰…...
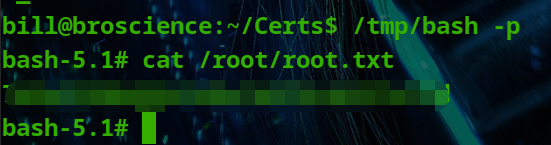
HackTheBox - Medium - Linux - BroScience
BroScience BroScience 是一款中等难度的 Linux 机器,其特点是 Web 应用程序容易受到“LFI”的攻击。通过读取目标上的任意文件的能力,攻击者可以深入了解帐户激活码的生成方式,从而能够创建一组可能有效的令牌来激活新创建的帐户。登录后&a…...

`nginx/conf/nginx.conf`最简配置说明
nginx/conf/nginx.conf最简配置说明 代码 nginx/conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; #工作进程个数;一般对应CPU内核对应一个worker_processes;太多反而让效率变差;# 事件驱动模块; events {worker_connections 1024;#设置每个worker_processes对应多少个联接; }# 网络请…...

商务智能|描述性统计分析与数据可视化
一、商务智能的三大方面 三个主要方面是描述性的统计分析、预测性的分析和指导性的数据分析。 A. 商务智能的知识体系下,数据分析包含了哪三个工作?商务智能体系架构里边关于数据分析的术语是什么? 商务智能的知识体系下,数据分析包含了三个工作,即描述性分析,预测性分析…...
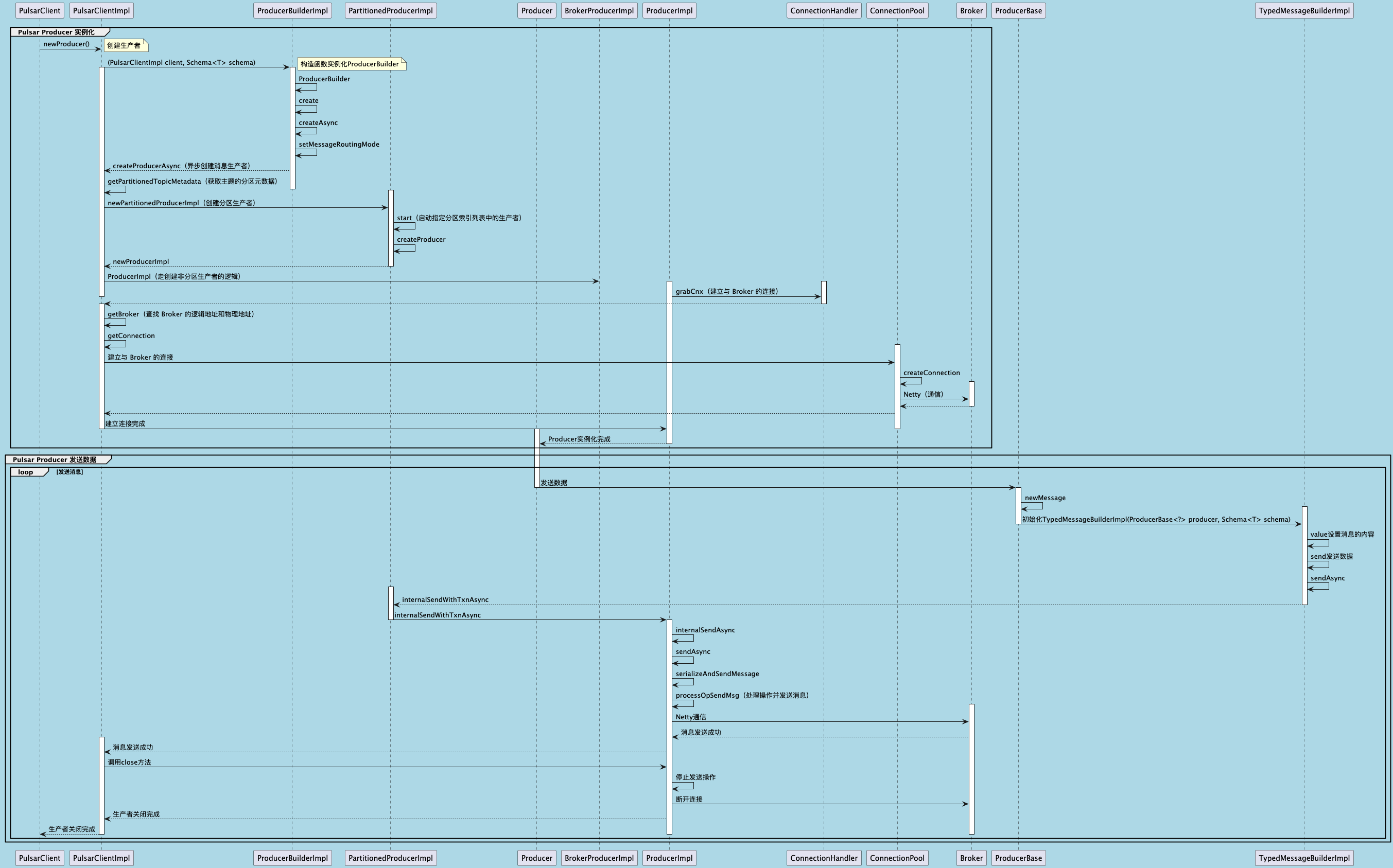
聊聊 Pulsar:Producer 源码解析
一、前言 Apache Pulsar 是一个企业级的开源分布式消息传递平台,以其高性能、可扩展性和存储计算分离架构在消息队列和流处理领域独树一帜。在 Pulsar 的核心架构中,Producer(生产者) 是连接客户端应用与消息队列的第一步。生产者…...
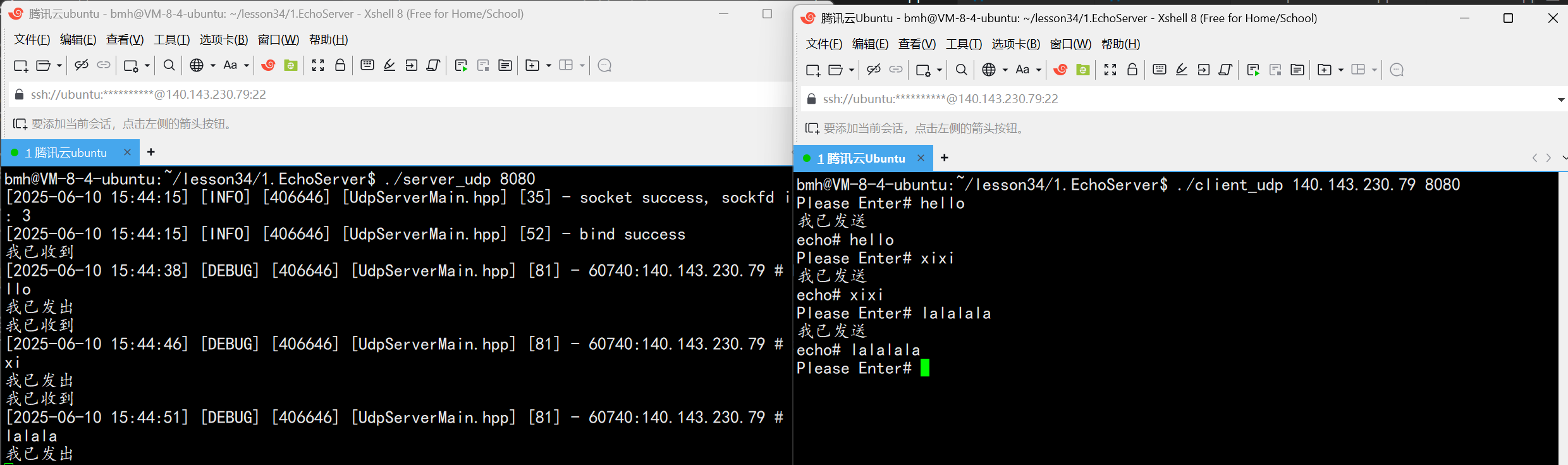
UDP(Echoserver)
网络命令 Ping 命令 检测网络是否连通 使用方法: ping -c 次数 网址ping -c 3 www.baidu.comnetstat 命令 netstat 是一个用来查看网络状态的重要工具. 语法:netstat [选项] 功能:查看网络状态 常用选项: n 拒绝显示别名&#…...
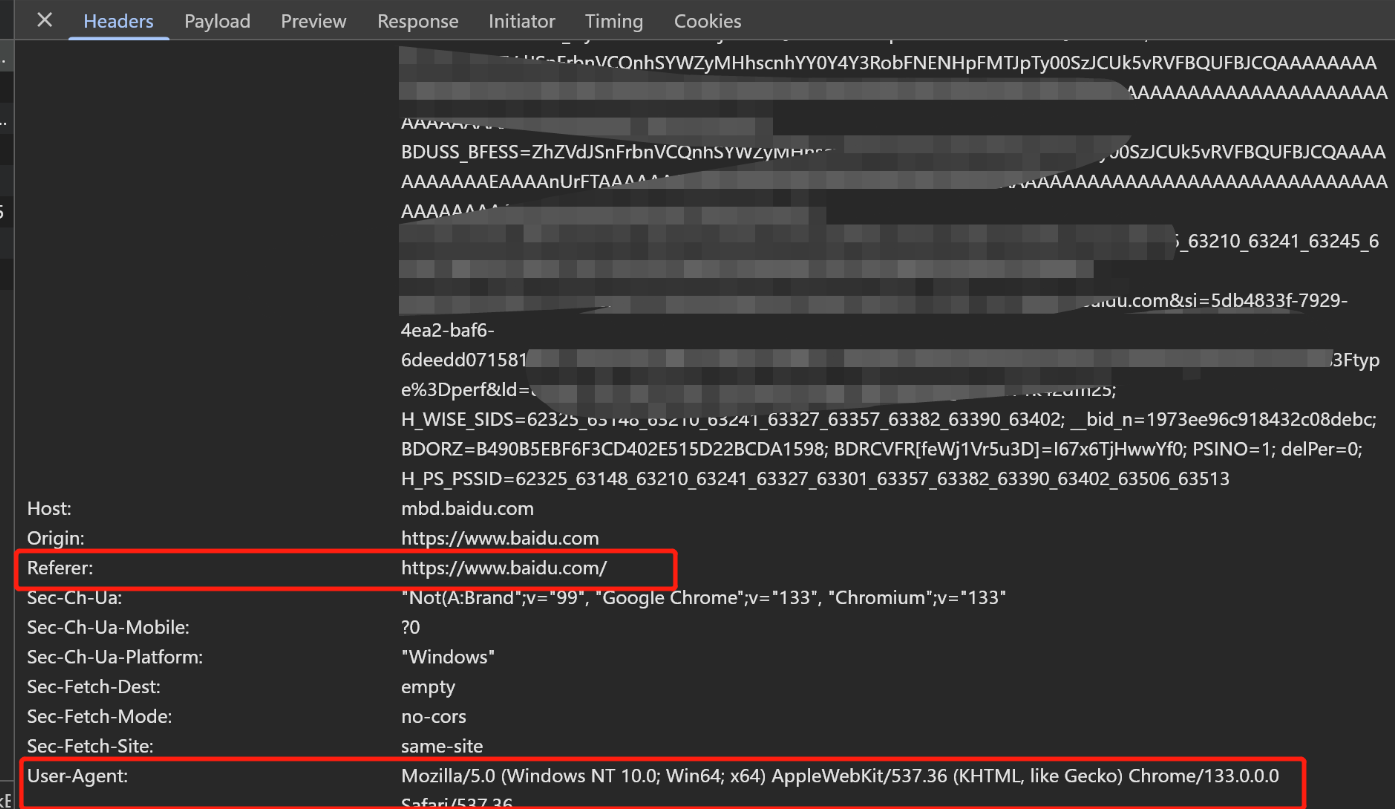
Python爬虫(一):爬虫伪装
一、网站防爬机制概述 在当今互联网环境中,具有一定规模或盈利性质的网站几乎都实施了各种防爬措施。这些措施主要分为两大类: 身份验证机制:直接将未经授权的爬虫阻挡在外反爬技术体系:通过各种技术手段增加爬虫获取数据的难度…...
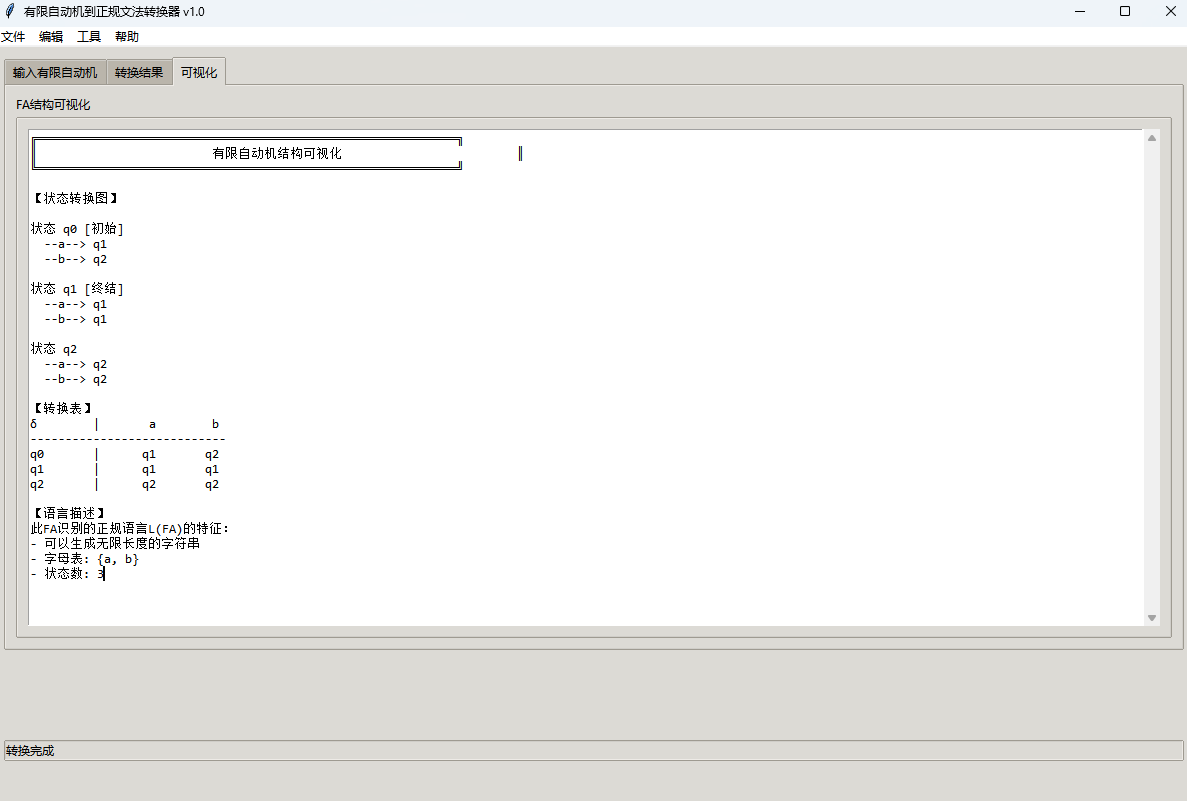
有限自动机到正规文法转换器v1.0
1 项目简介 这是一个功能强大的有限自动机(Finite Automaton, FA)到正规文法(Regular Grammar)转换器,它配备了一个直观且完整的图形用户界面,使用户能够轻松地进行操作和观察。该程序基于编译原理中的经典…...
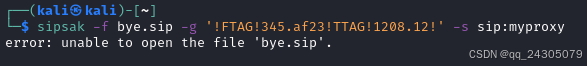
sipsak:SIP瑞士军刀!全参数详细教程!Kali Linux教程!
简介 sipsak 是一个面向会话初始协议 (SIP) 应用程序开发人员和管理员的小型命令行工具。它可以用于对 SIP 应用程序和设备进行一些简单的测试。 sipsak 是一款 SIP 压力和诊断实用程序。它通过 sip-uri 向服务器发送 SIP 请求,并检查收到的响应。它以以下模式之一…...

中医有效性探讨
文章目录 西医是如何发展到以生物化学为药理基础的现代医学?传统医学奠基期(远古 - 17 世纪)近代医学转型期(17 世纪 - 19 世纪末)现代医学成熟期(20世纪至今) 中医的源远流长和一脉相承远古至…...

智能AI电话机器人系统的识别能力现状与发展水平
一、引言 随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,AI电话机器人系统已经从简单的自动应答工具演变为具备复杂交互能力的智能助手。这类系统结合了语音识别、自然语言处理、情感计算和机器学习等多项前沿技术,在客户服务、营销推广、信息查询等领域发挥着越来越重要…...

MySQL 索引底层结构揭秘:B-Tree 与 B+Tree 的区别与应用
文章目录 一、背景知识:什么是 B-Tree 和 BTree? B-Tree(平衡多路查找树) BTree(B-Tree 的变种) 二、结构对比:一张图看懂 三、为什么 MySQL InnoDB 选择 BTree? 1. 范围查询更快 2…...

Redis上篇--知识点总结
Redis上篇–解析 本文大部分知识整理自网上,在正文结束后都会附上参考地址。如果想要深入或者详细学习可以通过文末链接跳转学习。 1. 基本介绍 Redis 是一个开源的、高性能的 内存键值数据库,Redis 的键值对中的 key 就是字符串对象,而 val…...
深入理解 C++ 左值右值、std::move 与函数重载中的参数传递
在 C 编程中,左值和右值的概念以及std::move的使用,常常让开发者感到困惑。特别是在函数重载场景下,如何合理利用这些特性来优化代码性能、确保语义正确,更是一个值得深入探讨的话题。 在开始之前,先提出几个问题&…...
