基于多反应堆的高并发服务器【C/C++/Reactor】(中)完整代码
Buffer.h
#pragma oncestruct Buffer {// 指向内存的指针char* data;int capacity;int readPos;int writePos;
};// 初始化
struct Buffer* bufferInit(int size);// 销毁
void bufferDestroy(struct Buffer* buf);// 扩容
void bufferExtendRoom(struct Buffer* buf, int size);// 得到剩余的可写的内存容量
int bufferWriteableSize(struct Buffer* buf);// 得到剩余的可读的内存容量
int bufferReadableSize(struct Buffer* buf);// 写内存 1.直接写
int bufferAppendData(struct Buffer* buf, const char* data, int size);
int bufferAppendString(struct Buffer* buf, const char* data); // 写内存 2.接收套接字数据
int bufferSocketRead(struct Buffer* buf,int fd);// 根据\r\n取出一行,找到其在数据块中的位置,返回该位置
char* bufferFindCRLF(struct Buffer* buf);// 发送数据
int bufferSendData(struct Buffer* buf,int socket);Buffer.c
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include "Buffer.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/uio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <strings.h>// 初始化
struct Buffer* bufferInit(int size) {struct Buffer* buffer = (struct Buffer*)malloc(sizeof(struct Buffer));if(buffer!=NULL) {buffer->data = (char*)malloc(size);buffer->capacity = size;buffer->readPos = buffer->writePos = 0;memset(buffer->data, 0, size);}return buffer;
}// 销毁
void bufferDestroy(struct Buffer* buf) {if(buf!=NULL) {if(buf->data!=NULL) { //指向有效的堆内存free(buf->data); // 释放}}free(buf);
}// 扩容
void bufferExtendRoom(struct Buffer* buf, int size) {// 1.内存够用 - 不需要扩容if(bufferWriteableSize(buf)>= size) {return;}// 2.内存需要合并才够用 - 不需要扩容// 已读的内存 + 剩余的可写的内存>= sizeelse if(buf->readPos + bufferWriteableSize(buf) >= size) {// 得到已写但未读的内存大小int readableSize = bufferReadableSize(buf);// 移动内存实现合并memcpy(buf->data, buf->data + buf->readPos, readableSize);// 更新位置buf->readPos = 0;buf->writePos = readableSize;}// 3.内存不够用 - 需要扩容else{void* temp = realloc(buf->data, buf->capacity + size);if(temp ==NULL) {return;// 失败了} memset(temp + buf->capacity, 0, size);// 只需要对拓展出来的大小为size的内存块进行初始化就可以了// 更新数据buf->data = temp;buf->capacity += size;}
}// 得到剩余的可写的内存容量
int bufferWriteableSize(struct Buffer* buf) {return buf->capacity - buf->writePos;
}// 得到剩余的可读的内存容量
int bufferReadableSize(struct Buffer* buf) {return buf->writePos - buf->readPos;
}// 写内存 1.直接写
int bufferAppendData(struct Buffer* buf, const char* data, int size) {// 判断传入的buf是否为空,data指针指向的是否为有效内存,以及数据大小是否大于零if(buf == NULL || data == NULL || size <= 0) {return -1;}// 扩容(试探性的)bufferExtendRoom(buf,size);// 数据拷贝memcpy(buf->data + buf->writePos, data, size);// 更新写位置buf->writePos += size;return 0;
}// 写内存 1.直接写
int bufferAppendString(struct Buffer* buf, const char* data) {int size = strlen(data);int ret = bufferAppendData(buf, data, size);return ret;
}// 写内存 2.接收套接字数据
/*当调用这个bufferSocketRead函数之后,一共接收到了多少个字节在这个函数里边,通过malloc申请了一块临时的堆内存(tmpbuf),这个堆内存是用来接收套接字数据的。当buf里边的数组容量不够了,那么就使用这块临时内存来存储数据,还需要把tmpbuf这块堆内存里边的数据再次写入到buf中。当用完了之后,需要释放内存。read/recv/readv:在接收数据的时候,- read/recv 只能指定一个数组- readv 能指定多个数组(也就是说第一个用完,用第二个...)
*/
int bufferSocketRead(struct Buffer* buf,int fd) {struct iovec vec[2]; // 根据自己的实际需求// 初始化数组元素int writeableSize = bufferWriteableSize(buf); // 得到剩余的可写的内存容量// 0号数组里的指针指向buf里边的数组,记得 要加writePos,防止覆盖数据vec[0].iov_base = buf->data + buf->writePos;vec[0].iov_len = writeableSize;char* tmpbuf = (char*)malloc(40960); // 申请40k堆内存vec[1].iov_base = buf->data + buf->writePos;vec[1].iov_len = 40960;// 至此,结构体vec的两个元素分别初始化完之后就可以调用接收数据的函数了int result = readv(fd, vec, 2);// 表示通过调用readv函数一共接收了多少个字节if(result == -1) {return -1;// 失败了}else if (result <= writeableSize) { // 说明在接收数据的时候,全部的数据都被写入到vec[0]对应的数组里边去了,全部写入到// buf对应的数组里边去了,直接移动writePos就好buf->writePos += result;}else {// 进入这里,说明buf里边的那块内存是不够用的,// 所以数据就被写入到我们申请的40k堆内存里边,还需要把tmpbuf这块// 堆内存里边的数据再次写入到buf中。// 先进行内存的扩展,再进行内存的拷贝,可调用bufferAppendData函数// 注意一个细节:在调用bufferAppendData函数之前,通过调用readv函数// 把数据写进了buf,但是buf->writePos没有被更新,故在调用bufferAppendData函数// 之前,需要先更新buf->writePosbuf->writePos = buf->capacity; // 需要先更新buf->writePosbufferAppendData(buf, tmpbuf, result - writeableSize);}free(tmpbuf);return result;
}// 根据\r\n取出一行,找到其在数据块中的位置,返回该位置
/*char *strstr(const char *haystack, const char *needle);void *memmem(const void *haystack, size_t haystacklen,const void *needle, size_t needlelen);
*/// CRLF表示\r\n
char* bufferFindCRLF(struct Buffer* buf) {// strstr --> 从大字符串中去匹配子字符串(遇到\0结束)// memmem --> 从大数据块中去匹配子数据块(需要指定数据块大小)char* ptr = memmem(buf->data + buf->readPos,bufferReadableSize(buf),"\r\n",2);return ptr;
}// 发送数据
int bufferSendData(struct Buffer* buf,int socket) {// 判断有无数据int readableSize = bufferReadableSize(buf);// 这些未读的数据就是待发送的数据if(readableSize > 0) {int count = send(socket,buf->data + buf->readPos,readableSize,MSG_NOSIGNAL);if(count > 0) {buf->readPos += count;usleep(1);}return count;} return 0;
}Channel.h
#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
// 定义函数指针
typedef int(*handleFunc)(void* arg);// 定义文件描述符的读写事件
enum FDEvent {TimeOut = 0x01,ReadEvent = 0x02,WriteEvent = 0x04
};struct Channel {// 文件描述符int fd;// 事件int events;// 回调函数handleFunc readCallback;// 读回调handleFunc writeCallback;// 写回调handleFunc destroyCallback;// 销毁回调// 回调函数的参数void* arg;
};// 初始化一个Channel
struct Channel* channelInit(int fd, int events, handleFunc readFunc, handleFunc writeFunc,handleFunc destroyFunc, void* arg);// 修改fd的写事件(检测 or 不检测)
void writeEventEnable(struct Channel* channel, bool flag);// 判断是否需要检测文件描述符的写事件
bool isWriteEventEnable(struct Channel* channel);Channel.c
#include "Channel.h"
#include <stdlib.h>struct Channel* channelInit(int fd, int events, handleFunc readFunc, handleFunc writeFunc, handleFunc destroyFunc, void* arg) {struct Channel* channel = (struct Channel*)malloc(sizeof(struct Channel));channel->fd = fd;channel->events = events;channel->readCallback = readFunc;channel->writeCallback = writeFunc;channel->destroyCallback = destroyFunc;channel->arg = arg;return channel;
}void writeEventEnable(struct Channel* channel, bool flag) {if(flag) {channel->events |= WriteEvent;}else{channel->events = channel->events & ~WriteEvent;}
}bool isWriteEventEnable(struct Channel* channel) {return channel->events & WriteEvent;
}ChannelMap.h
#pragma once
#include "Channel.h"
struct ChannelMap {struct Channel** list;int size;// 记录指针指向的数组的元素总个数
};// 初始化
struct ChannelMap* channelMapInit(int size);// 清空map
void ChannelMapClear(struct ChannelMap* map);// 重新分配内存空间
bool makeMapRoom(struct ChannelMap* map,int newSize,int unitSize);ChannelMap.c
#include "ChannelMap.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>struct ChannelMap* channelMapInit(int size) {struct ChannelMap* map = (struct ChannelMap*)malloc(sizeof(struct ChannelMap));map->size = size;map->list = (struct Channel**)malloc(sizeof(struct Channel*) * size);return map;
}void ChannelMapClear(struct ChannelMap* map) {if(map != NULL) {for(int i=0;i<map->size;++i) {if(map->list[i] != NULL) {free(map->list[i]);}}free(map->list);map->list = NULL;}map->size=0;
}bool makeMapRoom(struct ChannelMap* map,int newSize,int unitSize) {if(map->size < newSize) {int curSize = map->size;// 容量每次扩大原来的一倍while(curSize < newSize) {curSize*=2;}// 扩容 reallocstruct Channel** temp = realloc(map->list,curSize * unitSize);if(temp == NULL) {return false;}map->list = temp;memset(&map->list[map->size],0,(curSize - map->size) * unitSize);map->size = curSize;}return true;
}Dispatcher.h
#pragma once
#include "Channel.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"// 声明(不管这个结构体有无被定义出来,先告诉编译器有这么一种类型)
struct EventLoop;
struct Dispatcher {/* init 初始化epoll、select、或者poll需要的数据块最后需要把这个数据块的内存地址给到函数的调用者所以它的返回值肯定是一个指针另外epoll、select、或者poll它们需要的数据块对应的内存类型一样吗?不一样,如果想要一种类型来兼容三种不同的类型,怎么做到呢?在C语言里就是使用泛型,故返回值类型为void**/void* (*init)();// 添加int (*add)(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);// 删除int (*remove)(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);// 修改int (*modify)(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);// 事件检测int (*dispatch)(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int timeout); // 单位:s// 清除数据(关闭fd或者释放内存)int (*clear)(struct EventLoop* evLoop);
};EpollDispatcher.c
#include "Dispatcher.h"
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>#define Max 520struct EpollData {int epfd;//epoll树的根节点struct epoll_event* events;// 数组指针
};static void* epollInit();
static int epollAdd(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int epollRemove(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int epollModify(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int epollDispatch(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int timeout); // 单位:s
static int epollClear(struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int epollCtl(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop,int op);// EpollDispatcher 是 Dispatcher 的一个实例
struct Dispatcher EpollDispatcher = {// 把函数地址指定给它epollInit,epollAdd,epollRemove,epollModify,epollDispatch,epollClear
};static void* epollInit() {struct EpollData* data = (struct EpollData*)malloc(sizeof(struct EpollData));data->epfd = epoll_create(10);if(data->epfd == -1) {perror("epoll_create");exit(0);}data->events=(struct epoll_event*)calloc(Max,sizeof(struct epoll_event));return data;
}static int epollCtl(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop,int op) {struct EpollData* data = (struct EpollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;struct epoll_event ev;// 先把要检测的文件描述符存储到类型为epoll_event 的ev中ev.data.fd = channel->fd;// 指定要检测的这个fd的事件/*channel里边的事件,它的读和写对应的值使我们自己定义的epoll里边的,EPOLLIN和EPOLLOUT是linux操作系统定义的*/int events = 0;if(channel->events & ReadEvent) {events |= EPOLLIN;}if(channel->events & WriteEvent) {events |= EPOLLOUT;}ev.events = events;int ret = epoll_ctl(data->epfd,op,channel->fd,&ev);return ret;
}static int epollAdd(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {int ret = epollCtl(channel,evLoop,EPOLL_CTL_ADD);if(ret == -1) {perror("epoll_ctl add");exit(0);}return ret;
}
static int epollRemove(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {int ret = epollCtl(channel,evLoop,EPOLL_CTL_DEL);if(ret == -1) {perror("epoll_ctl delete");exit(0);}// 通过 channel 释放对应的 TcpConnection 资源channel->destroyCallback(channel->arg); // (已续写)return ret;
}
static int epollModify(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {int ret = epollCtl(channel,evLoop,EPOLL_CTL_MOD);if(ret == -1) {perror("epoll_ctl modify");exit(0);}return ret;
}
static int epollDispatch(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int timeout) {struct EpollData* data = (struct EpollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;int count = epoll_wait(data->epfd,data->events,Max,timeout * 1000);for(int i=0;i<count;++i) {int events = data->events[i].events;int fd = data->events[i].data.fd;if(events & EPOLLERR || events & EPOLLHUP) {// 对方断开了连接,删除 fd// epollRemove(Channel, evLoop);continue;}if(events & EPOLLIN) {// 已续写...eventActivate(evLoop,fd,ReadEvent);}if(events & EPOLLOUT) {// 已续写...eventActivate(evLoop,fd,WriteEvent);}}return 0;
}
static int epollClear(struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct EpollData* data = (struct EpollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;free(data->events);close(data->epfd);free(data);return 0;
}PollDispatcher.c
#include "Dispatcher.h"
#include <poll.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/*对于poll来说,它的最大上限并不是1024,select的最大上限才是1024poll的文件描述符的最大上限取决于当前操作系统的配置,你的内存越大,那么它能检测的文件描述符得到数量就越多。但是有一点要说明,如果你让poll检测了很多个文件描述符,那么它的效率是非常低的,就是检测的文件描述符的数量越多,它的效率就越低如果你要检测的文件描述符特别多,建议用epoll,因为不管检测的文件描述符是上万还是上千,其实它的效率都是非常高的那什么时候使用select或者polls呢?其实是在需要检测的文件描述的数量并不多,且它们大多都是在激活的状态下,此时,效率是最高的总结为两点:1.检测的文件描述符数量并不多2.待检测出的文件描述符,大多都是激活的什么叫激活呢?假如说你登录了qq,你一天不说话,这叫激活吗?这不叫啊,就是如果你一天都在处于聊天状态。这叫激活所谓的聊天状态,就是进行数据的接收和发送。如果你只在这儿挂着,说明你只是保持了一个在线状态,你并没有做其他的事情,你现在是占用了网络资源。所以这种情况,不算激活。
*/
#define Max 1024
struct PollData {int maxfd;struct pollfd fds[Max];
};static void* pollInit();
static int pollAdd(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int pollRemove(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int pollModify(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int pollDispatch(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int timeout); // 单位:s
static int pollClear(struct EventLoop* evLoop);// PollDispatcher 是 Dispatcher 的一个实例
struct Dispatcher PollDispatcher = {// 把函数地址指定给它pollInit,pollAdd,pollRemove,pollModify,pollDispatch,pollClear
};static void* pollInit() {struct PollData* data = (struct PollData*)malloc(sizeof(struct PollData));data->maxfd = 0;for (int i = 0; i < Max; ++i) {data->fds[i].fd = -1;data->fds[i].events = 0;data->fds[i].revents = 0;}return data;
}static int pollAdd(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct PollData* data = (struct PollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;int events = 0;if (channel->events & ReadEvent) {events |= POLLIN;}if (channel->events & WriteEvent) {events |= POLLOUT;}int i=0;for(;i<Max;++i) {if(data->fds[i].fd == -1) {data->fds[i].fd = channel->fd;data->fds[i].events = events;data->maxfd = i > data->maxfd ? i : data->maxfd;break;}}if(i >= Max) {return -1;}return 0;
}static int pollRemove(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct PollData* data = (struct PollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;int i=0;for(;i<Max;++i) {if(data->fds[i].fd == channel->fd) {data->fds[i].fd = -1;data->fds[i].events = 0;data->fds[i].revents = 0;break;}}// 通过 channel 释放对应的 TcpConnection 资源channel->destroyCallback(channel->arg); // (已续写)if(i >= Max) {return -1;}return 0;
}
static int pollModify(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct PollData* data = (struct PollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;int events = 0;if (channel->events & ReadEvent) {events |= POLLIN;}if (channel->events & WriteEvent) {events |= POLLOUT;}int i=0;for(;i<Max;++i) {if(data->fds[i].fd == channel->fd) {data->fds[i].events = events;break;}}if(i >= Max) {return -1;}return 0;
}
static int pollDispatch(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int timeout) {struct PollData* data = (struct PollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;int count = poll(data->fds,data->maxfd + 1,timeout * 1000);if(count == -1) {perror("poll");exit(0);}for(int i=0;i<=data->maxfd;++i) {if(data->fds[i].fd == -1) {continue;}if(data->fds[i].revents & POLLIN) {// 已续写...eventActivate(evLoop,data->fds[i].fd,ReadEvent);}if(data->fds[i].revents & POLLOUT) {// 已续写...eventActivate(evLoop,data->fds[i].fd,WriteEvent);}}return 0;
}
static int pollClear(struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct PollData* data = (struct PollData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;free(data);return 0;
}SelectDispatcher.c
#include "Dispatcher.h"
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#define Max 1024
struct SelectData {fd_set readSet;fd_set writeSet;
};static void* selectInit();
static int selectAdd(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int selectRemove(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int selectModify(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static int selectDispatch(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int timeout); // 单位:s
static int selectClear(struct EventLoop* evLoop);
static void setFdSet(struct Channel* channel,struct SelectData* data);
static void clearFdSet(struct Channel* channel,struct SelectData* data);// SelectDispatcher 是 Dispatcher 的一个实例
struct Dispatcher SelectDispatcher = {// 把函数地址指定给它selectInit,selectAdd,selectRemove,selectModify,selectDispatch,selectClear
};static void* selectInit() {struct SelectData* data = (struct SelectData*)malloc(sizeof(struct SelectData));FD_ZERO(&data->readSet);FD_ZERO(&data->writeSet);return data;
}static void setFdSet(struct Channel* channel,struct SelectData* data) {if (channel->events & ReadEvent) {FD_SET(channel->fd,&data->readSet);}if (channel->events & WriteEvent) {FD_SET(channel->fd,&data->writeSet);}
}static void clearFdSet(struct Channel* channel,struct SelectData* data) {if (channel->events & ReadEvent) {FD_CLR(channel->fd,&data->readSet);}if (channel->events & WriteEvent) {FD_CLR(channel->fd,&data->writeSet);}
}static int selectAdd(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct SelectData* data = (struct SelectData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;if(channel->fd >= Max) {return -1;}setFdSet(channel,data);return 0;
}static int selectRemove(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct SelectData* data = (struct SelectData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;clearFdSet(channel,data);// 通过 channel 释放对应的 TcpConnection 资源channel->destroyCallback(channel->arg); // (已续写)return 0;
}
static int selectModify(struct Channel* channel,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct SelectData* data = (struct SelectData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;setFdSet(channel,data);clearFdSet(channel,data);return 0;
}
static int selectDispatch(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int timeout) {struct SelectData* data = (struct SelectData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;struct timeval val;val.tv_sec = timeout;val.tv_usec = 0;fd_set rdtmp = data->readSet;fd_set wrtmp = data->writeSet;int count = select(Max,&rdtmp,&wrtmp,NULL,&val);if(count == -1) {perror("select");exit(0);}for(int i=0;i<Max;++i) { if(FD_ISSET(i,&rdtmp)) {// 已续写...eventActivate(evLoop,i,ReadEvent);}if(FD_ISSET(i,&wrtmp)) {// 已续写...eventActivate(evLoop,i,WriteEvent);}}return 0;
}
static int selectClear(struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct SelectData* data = (struct SelectData*)evLoop->dispatcherData;free(data);return 0;
}EventLoop.h
#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "Dispatcher.h"
#include "ChannelMap.h"
#include <pthread.h>extern struct Dispatcher EpollDispatcher;
extern struct Dispatcher PollDispatcher;
extern struct Dispatcher SelectDispatcher;// 处理该节点中的channel的方式
enum ElemType{ADD, // 添加DELETE, // 删除MODIFY // 修改
};// 定义任务队列的节点
struct ChannelElement {int type;// 如何处理该节点中的channelstruct Channel* channel;struct ChannelElement* next;
};// 声明(不管这个结构体有无被定义出来,先告诉编译器有这么一种类型)
struct Dispatcher;
struct EventLoop{bool isQuit;// 开关struct Dispatcher* dispatcher;void* dispatcherData;// 任务队列struct ChannelElement* head;struct ChannelElement* tail;// 用于存储channel的mapstruct ChannelMap* channelMap;// 线程ID,Name,mutexpthread_t threadID;char threadName[32];pthread_mutex_t mutex;int socketPair[2]; //存储本地通信的fd 通过socketpair初始化
};// 初始化
struct EventLoop* eventLoopInit();
struct EventLoop* eventLoopInitEx(const char* threadName);// 启动反应堆模型
int eventLoopRun(struct EventLoop* evLoop);// 处理被激活的文件描述符fd
int eventActivate(struct EventLoop* evLoop,int fd,int event);// 添加任务到任务队列
int eventLoopAddTask(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel,int type);// 处理任务队列中的任务
int eventLoopProcessTask(struct EventLoop* evLoop);// 处理dispatcher中的任务
int eventLoopAdd(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel);
int eventLoopRemove(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel);
int eventLoopModify(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel);// 释放channel
int destroyChannel(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel);
EventLoop.c
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 初始化
struct EventLoop* eventLoopInit() {return eventLoopInitEx(NULL);
}// 写数据
void taskWakeup(struct EventLoop* evLoop) {const char* msg = "我是要成为海贼王的男人!";write(evLoop->socketPair[0],msg,strlen(msg));
}// 读数据
int readLocalMessage(void* arg) {struct EventLoop* evLoop = (struct EventLoop*)arg;char buffer[256];read(evLoop->socketPair[1],buffer,sizeof(buffer));return 0;
}struct EventLoop* eventLoopInitEx(const char* threadName) {struct EventLoop* evLoop = (struct EventLoop*)malloc(sizeof(struct EventLoop));evLoop->isQuit = false; // 没有运行// evLoop->dispatcher = &EpollDispatcher;evLoop->dispatcher = &PollDispatcher;// evLoop->dispatcher = &SelectDispatcher;evLoop->dispatcherData = evLoop->dispatcher->init(); // 任务队列(链表)evLoop->head = evLoop->tail = NULL;// 用于存储channel的mapevLoop->channelMap = channelMapInit(128);evLoop->threadID = pthread_self(); // 当前线程IDstrcpy(evLoop->threadName,threadName == NULL ? "MainThread" : threadName); // 线程的名字pthread_mutex_init(&evLoop->mutex, NULL); int ret = socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, evLoop->socketPair);if(ret == -1) {perror("socketpair");exit(0);}// 指定规则:evLoop->socketPair[0] 发送数据,evLoop->socketPair[1]接收数据struct Channel* channel = channelInit(evLoop->socketPair[1],ReadEvent, readLocalMessage,NULL,NULL,evLoop);// channel 添加到任务队列eventLoopAddTask(evLoop, channel,ADD);return evLoop;
}// 启动反应堆模型
int eventLoopRun(struct EventLoop* evLoop) {assert(evLoop != NULL);// 取出事件分发和检测模型struct Dispatcher* dispatcher = evLoop->dispatcher;// 比较线程ID是否正常if(evLoop->threadID != pthread_self()) {return -1;}// 循环进行事件处理while(!evLoop->isQuit) {/*dispatch指向的任务函数其实是动态的,由于在初始化的时候指向的是底层的IO模型用的是epoll模型,那么dispatcher->dispatch(evLoop,2);就是调用epollDispatch,里头的epoll_wait函数会随之被调用,每调用一次epoll_wait函数,就会得到一些被激活的文件描述符然后通过for循环,对被激活的文件描述符做一系列的处理 如果是poll,就是调用pollDispatch,里头的poll函数会随之被调用,每调用一次poll函数,就会得到一些被激活的文件描述符然后通过for循环,对被激活的文件描述符做一系列的处理 如果是select,就是调用selectDispatch,里头的select函数会随之被调用,每调用一次select函数,就会得到一些被激活的文件描述符然后通过for循环,对被激活的文件描述符做一系列的处理 */dispatcher->dispatch(evLoop,2); // 超时时长 2seventLoopProcessTask(evLoop);}return 0;
}// 处理被激活的文件描述符fd
int eventActivate(struct EventLoop* evLoop, int fd, int event)
{if (fd < 0 || evLoop == NULL){return -1;}// 取出channelstruct Channel* channel = evLoop->channelMap->list[fd];assert(channel->fd == fd);if (event & ReadEvent && channel->readCallback){channel->readCallback(channel->arg);}if (event & WriteEvent && channel->writeCallback){channel->writeCallback(channel->arg);}return 0;
}// 添加任务到任务队列
int eventLoopAddTask(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel,int type) {/*为什么在上面添加链表节点的时候需要加互斥锁?- 因为有可能是当前线程去添加,也有可能是主线程去添加如果当前的线程是主线程,那么我们能够让主线程进行节点的处理吗?- 肯定不能,因为你当前主线程它只能负责和客户端建立连接,如果这个连接建立好了,剩下的事情都是需要由这个子线程来完成的。所以主线程肯定不会给你去处理任务队列里边的节点。在主线程里边,其实它是有一个反应堆模型的,在当前的这个子线程里边也有一个反应堆模型。每个反应堆模型里边都有一个Dispatcher。关于这个Dispatcher就是epoll、poll、或者select,所以主线程去处理的话,这个任务就放到主线程的那个Dispatcher里边了,这样很显然是不对的。故在子线程的任务队列里边有了任务之后,还需要交给子线程的Dispatcher去处理。因此这个节点的处理,还需要判断当前线程到底是什么线程。如果它是主线程不能让它去处理,如果是子线程,直接让它去处理。*/// 加锁,保护共享资源pthread_mutex_lock(&evLoop->mutex);// 创建新节点,后添加到任务队列中去struct ChannelElement* node = (struct ChannelElement*)malloc(sizeof(struct ChannelElement));node->channel = channel;node->type = type;node->next = NULL;// 链表为空if(evLoop->head == NULL) {evLoop->head = evLoop->tail = node;}else {evLoop->tail->next = node; // 添加evLoop->tail = node; // 后移}pthread_mutex_unlock(&evLoop->mutex);// 处理节点/*** 这个描述假设了一个前提条件,就是当前的EventLoop反应堆属于子线程* 细节:* 1.对于链表节点的添加:可能是当前线程也可能是其他线程(主线程)* 1).修改fd的事件,当前子线程发起,当前子线程处理* 2).添加新的fd(意味着和一个新的客户端建立连接,这是由主线程做的,故添加任务节点这个操作肯定是由主线程做的),* 添加任务节点的操作是由主线程发起的* 2.不能让主线程处理任务队列里边的节点,需要由当前的子线程去处理* * */if(evLoop->threadID == pthread_self()) {// 当前子线程eventLoopProcessTask(evLoop);}else{// 主线程 -- 告诉子线程处理任务队列中的任务// 1.子线程在工作 2.子线程被阻塞了:select、poll、epolltaskWakeup(evLoop);}/*小细节:假设说添加任务的是主线程,那么程序就会执行taskWakeup这个函数,主线程执行这个函数,对于子线程来说有两种情况,第一种情况它正在干活,对于子线程没有影响,充其量就是它检测的那个集合里边多出来了一个被激活的文件描述符。如果说此时子线程被select、poll、或epoll_wait阻塞了,调用taskWakeup可以解除其阻塞。如果解除阻塞了,我们希望子线程干什么事情呢?因为主线程是在子线程的任务队列里边添加了一个任务, 那么我们让子线程解除阻塞是需要让子线程去处理任务队列里边的任务。因此需要在eventLoopRun函数中调用eventLoopProcessTask(evLoop);因为这个反应堆模型只要开始运行(eventLoopRun)就会不停的调用dispatch函数,这个dispatch是一个函数指针,底层指向的是poll模型的poll函数,select模型的select函数,epoll模型的epoll_wait函数,如果当前的子线程正在被刚才的提到的这三个函数里边的其中一个阻塞着,此时正好被主线程唤醒了。需要在循环进行事件处理中添加一句eventLoopProcessTask(evLoop);总结:关于任务队列的处理有两个路径:第一个路径:子线程往任务队列里边添加一个任务,比如说修改文件描述符里边的事件,肯定是子线程自己修改自己检测的文件描述符的事件,修改完了之后,子线程就直接调用eventLoopProcessTask(evLoop);这个函数去处理任务队列里边的任务。第二个路径:主线程在子线程的任务队列里边添加了一个任务,主线程是处理不了的,并且主线程现在也不知道子线程是在工作还是在阻塞,所以主线程就默认子线程现在正在阻塞,因此主线程就调用了一个唤醒函数(taskWakeup),调用这个函数保证子线程肯定是在运行的,而子线程是eventLoopRun函数的dispatch函数的调用位置解除了阻塞,然后调用eventLoopProcessTask(evLoop);int eventLoopRun(struct EventLoop* evLoop) {...// 循环进行事件处理while(!evLoop->isQuit) {dispatcher->dispatch(evLoop,2); // 超时时长 2seventLoopProcessTask(evLoop);}...}*/return 0;
}// 处理任务队列中的任务
int eventLoopProcessTask(struct EventLoop* evLoop) {pthread_mutex_lock(&evLoop->mutex);// 取出头节点struct ChannelElement* head = evLoop->head;while (head!=NULL) {struct Channel* channel = head->channel;if(head->type == ADD) {// 添加eventLoopAdd(evLoop,channel);}else if(head->type == DELETE) {// 删除eventLoopRemove(evLoop,channel);}else if(head->type == MODIFY) {// 修改eventLoopModify(evLoop,channel);}struct ChannelElement* tmp = head;head = head->next;// 释放节点free(tmp);}evLoop->head = evLoop->tail = NULL;pthread_mutex_unlock(&evLoop->mutex);return 0;
}// 将任务队列中的任务添加到Dispatcher的文件描述符检测集合中
int eventLoopAdd(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel) {int fd = channel->fd;// 取出文件描述符fdstruct ChannelMap* channelMap = evLoop->channelMap;// channelMap存储着channel和fd之间的对应关系// 需要判断channelMap里边是否有fd 和 channel对应的键值对(其中,文件描述符fd对应的就是数组的下标)if(fd >= channelMap->size) {// 没有足够的空间存储键值对 fd->channel ==> 扩容if(!makeMapRoom(channelMap,fd,sizeof(struct Channel*))) {return -1;}}// 找到fd对应的数组元素位置,并存储if(channelMap->list[fd] == NULL) {// 把文件描述符fd和channel的对应关系存储到channelMap/*在dispatcher里边,还有dispatch函数指针,也就是dispatcher->dispatch(evLoop,timeout)这个是一个检测函数,通过调用dipatch函数,就可以得到激活的文件描述符,得到了激活的文件描述符之后,需要通过这个文件描述符找到它所对应的channel*/channelMap->list[fd] = channel;/*首先从evLoop里边把dispatcher这个实例给取出来:evLoop->dispatcher在dispatcher里边有一系列的函数指针,其中有一个叫做add。这个add就是把文件描述符添加到dispatcher对应的文件描述符检测集合中,函数指针add,指向的底层函数可能是不一样的,这个取决于我们选择的dispatcher模型,它有可能是poll,有可能是epoll,也有可能是select。选择的IO模型不一样,add这个函数指针指向的函数的处理动作也就不一样*/evLoop->dispatcher->add(channel,evLoop);} return 0;
}/*把任务队列里面的节点从dispatcher的检测集合中删除,调用dispatcher里边的remove函数,
*/
int eventLoopRemove(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel) {int fd = channel->fd;// 从evLoop中取出channelMap实例struct ChannelMap* channelMap = evLoop->channelMap;/*假设我们要删除的这个文件描述符并不在channelMap中存储着,说明我们要操作的这个文件描述符并不在dispatcher的检核集合中。因为它在检测集合里边,在添加的时候就会把文件描述符fd和channel的映射关系也存储到channelMap里边去了。故只要它在检测集合里边,它肯定就在channelMap里边。如果它不在channelMap里边,那么它就肯定不在检测集合里边。如果它不在检测集合里边,就无需做任何事情,直接返回-1*/if(fd >= channelMap->size) {return -1;}// 如果文件描述符fd在检测集合里,就从中把它删除int ret = evLoop->dispatcher->remove(channel,evLoop);return ret;
}// 修改检测集合里边文件描述符事件的函数
int eventLoopModify(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel) {int fd = channel->fd;struct ChannelMap* channelMap = evLoop->channelMap;if(fd >= channelMap->size || channelMap->list[fd] == NULL) {return -1;}int ret = evLoop->dispatcher->modify(channel,evLoop);return ret;
}// 释放channel
int destroyChannel(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel) {// 删除 channel 和 fd 的对应关系evLoop->channelMap->list[channel->fd] = NULL;// 关闭 fdclose(channel->fd);// 释放 channel 内存free(channel);return 0;
}HttpRequest.h
#pragma once
#include "Buffer.h"
#include "HttpResponse.h"
#include <stdbool.h>// 请求头键值对
struct RequestHeader{char* key;char* value;
};// 当前的解析状态
enum HttpRequestState {ParseReqLine, // 当前解析的是请求行ParseReqHeaders, // 当前解析的是请求头ParseReqBody, // 当前解析的是请求体ParseReqDone // 完成解析
};// 定义 http 请求结构体
struct HttpRequest {// 当前解析状态enum HttpRequestState curState; // 请求行char* method;char* url;char* version; // 请求头struct RequestHeader* reqHeaders;int reqHeadersNum;
};// 初始化
struct HttpRequest* httpRequestInit();// 重置
void httpRequestReset(struct HttpRequest* req);
void httpRequestResetEx(struct HttpRequest* req);
// 销毁
void httpRequestDestroy(struct HttpRequest* req);// 获取处理状态
enum HttpRequestState httpRequestState(struct HttpRequest* req);// 添加请求头
void httpRequestAddHeader(struct HttpRequest* req,const char* key,const char* value);// 根据key得到请求头的value
char* httpRequestGetHeader(struct HttpRequest* req,const char* key);// 解析请求行
bool parseHttpRequestLine(struct HttpRequest* req,struct Buffer* readBuf);// 解析请求头
bool parseHttpRequestHeader(struct HttpRequest* req,struct Buffer* readBuf);// 解析http请求协议
bool parseHttpRequest(struct HttpRequest* req,struct Buffer* readBuf,struct HttpResponse* response,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int socket);// 处理http请求协议
bool processHttpRequest(struct HttpRequest* req,struct HttpResponse* response);// 发送文件
void sendFile(const char* fileName,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int cfd);
// 判断文件扩展名,返回对应的 Content-Type(Mime-Type)
const char* getFileType(const char* name);// 发送目录
void sendDir(const char* dirName,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int cfd); // 解码字符串
void decodeMsg(char* to,char* from);
int hexToDec(char c);HttpRequest.c
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include "HttpRequest.h"
#include "TcpConnection.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <ctype.h> // isxdigit#define HeaderSize 12
// 初始化
struct HttpRequest* httpRequestInit() {struct HttpRequest* request = (struct HttpRequest*)malloc(sizeof(struct HttpRequest));httpRequestReset(request);request->reqHeaders = (struct RequestHeader*)malloc(sizeof(struct RequestHeader) * HeaderSize);return request;
}// 重置
void httpRequestReset(struct HttpRequest* req) {req->curState = ParseReqLine;req->method = NULL;req->url = NULL;req->version = NULL;req->reqHeadersNum = 0;
}void httpRequestResetEx(struct HttpRequest* req) {free(req->method);free(req->url);free(req->version);if(req->reqHeaders != NULL) {for(int i=0;i<req->reqHeadersNum;++i) {free(req->reqHeaders[i].key);free(req->reqHeaders[i].value);}free(req->reqHeaders);}httpRequestReset(req);
}void httpRequestDestroy(struct HttpRequest* req) {if(req != NULL) {httpRequestResetEx(req);free(req);}
}// 获取处理状态
enum HttpRequestState httpRequestState(struct HttpRequest* req) {return req->curState;
}// 添加请求头
void httpRequestAddHeader(struct HttpRequest* req,const char* key, const char* value) {req->reqHeaders[req->reqHeadersNum].key = (char*)key;req->reqHeaders[req->reqHeadersNum].value = (char*)value;req->reqHeadersNum++;
}// 根据key得到请求头的value
char* httpRequestGetHeader(struct HttpRequest* req,const char* key) {if(req!=NULL) {for(int i=0;i<req->reqHeadersNum;++i) {if(strncasecmp(req->reqHeaders[i].key,key,strlen(key)) == 0) {return req->reqHeaders[i].value;}}}return NULL;
}// 注意:传入指针的地址(二级指针),这个函数涉及给指针分配一块内存,
// 指针在作为参数的时候会产生一个副本,而把指针的地址作为参数传入
// 不会产生副本// 如果想要在一个函数里边给外部的一级指针分配一块内存,那么需要把
// 外部的一级指针的地址传递给函数.外部的一级指针的地址
// 二级指针,把二级指针传进来之后,对它进行解引用,让其指向我们申请的
// 一块堆内存,就可以实现外部的一级指针被初始化了,也就分配到了一块内存
char* splitRequestLine(const char* start,const char* end,const char* sub,char** ptr) {char* space = (char*)end;if(sub != NULL) {space = memmem(start,end-start,sub,strlen(sub));assert(space!=NULL);}int length = space - start;char* tmp = (char*)malloc(length+1);strncpy(tmp,start,length);tmp[length] = '\0';*ptr = tmp;// 对ptr进行解引用=>*ptr(一级指针),让其指向tmp指针指向的地址return space+1;
}// 解析请求行
bool parseHttpRequestLine(struct HttpRequest* req,struct Buffer* readBuf) {// 读取请求行char* end = bufferFindCRLF(readBuf);// 保存字符串起始位置char* start = readBuf->data + readBuf->readPos;// 保存字符串结束地址int lineSize = end - start;if(lineSize>0) {start = splitRequestLine(start,end," ",&req->method);// 请求方式start = splitRequestLine(start,end," ",&req->url);// url资源splitRequestLine(start,end,NULL,&req->version);// 版本
#if 0// get /xxx/xx.txt http/1.1// 请求方式char* space = memmem(start,lineSize," ",1);assert(space!=NULL);int methodSize = space - start;req->method = (char*)malloc(methodSize + 1);strncpy(req->method,start,methodSize);req->method[methodSize] = '\0';// 请求静态资源start = space + 1;space = memmem(start,end-start," ",1);assert(space!=NULL);int urlSize = space - start;req->url = (char*)malloc(urlSize + 1);strncpy(req->url,start,urlSize);req->url[urlSize] = '\0';// http 版本start = space + 1;req->version = (char*)malloc(end-start + 1);strncpy(req->version,start,end-start);req->version[end-start] = '\0';
#endif// 为解析请求头做准备readBuf->readPos += lineSize;readBuf->readPos += 2;// 修改状态req->curState = ParseReqHeaders;return true;}return false;
}// 该函数处理请求头中的一行
bool parseHttpRequestHeader(struct HttpRequest* req,struct Buffer* readBuf) {char* end = bufferFindCRLF(readBuf);if(end!=NULL) {char* start = readBuf->data + readBuf->readPos;int lineSize = end - start;// 基于: 搜索字符串char* middle = memmem(start,lineSize,": ",2); if(middle!=NULL) {// 拿出键值对char* key = malloc(middle - start + 1);strncpy(key,start,middle - start);key[middle - start] = '\0';// 获得keychar* value = malloc(end - middle - 2 + 1);// end-(middle+2) + 1 = end - middle - 2 + 1strncpy(value,middle+2,end - middle - 2);value[end - middle - 2] = '\0';// 获得valuehttpRequestAddHeader(req,key,value);// 添加键值对// 移动读数据的位置readBuf->readPos += lineSize;readBuf->readPos += 2;}else {// 请求头被解析完了,跳过空行readBuf->readPos += 2;// 修改解析状态// 本项目忽略 post 请求,按照 get 请求处理req->curState = ParseReqDone;}return true;}return false;
}// 解析http请求协议
bool parseHttpRequest(struct HttpRequest* req,struct Buffer* readBuf,struct HttpResponse* response,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int socket) {bool flag = true;while(req->curState!=ParseReqDone) {switch(req->curState) {case ParseReqLine:// 解析请求行flag = parseHttpRequestLine(req,readBuf);break;case ParseReqHeaders:// 解析请求头flag = parseHttpRequestHeader(req,readBuf);break;case ParseReqBody:break;default:break;}if(!flag) {return flag;}// 判断是否解析完毕了,如果完毕了,需要准备回复的数据if(req->curState==ParseReqDone) {// 1.根据解析出的原始数据,对客户端的请求做出处理processHttpRequest(req,response);// 2.组织响应数据并发送给客户端httpResponsePrepareMsg(response,sendBuf,socket);}}req->curState = ParseReqLine;// 状态还原,保证还能继续处理第二条及以后的请求return flag;
}// 处理基于get的http请求
bool processHttpRequest(struct HttpRequest* req,struct HttpResponse* response) {if(strcasecmp(req->method,"get") != 0) {return -1;}decodeMsg(req->url,req->url); // 解码字符串// 处理客户端请求的静态资源(目录或者文件)char* file = NULL;if(strcmp(req->url,"/") == 0) {file = "./";}else {file = req->url + 1;}// 获取文件属性struct stat st;int ret = stat(file,&st);if(ret == -1) {// 文件不存在 -- 回复404// sendHeadMsg(cfd,404,"Not Found",getFileType(".html"),-1);// sendFile("404.html",cfd);strcpy(response->fileName,"404.html");response->statusCode = NotFound;strcpy(response->statusMsg,"Not Found");// 响应头httpResponseAddHeader(response,"Content-Type",getFileType(".html"));response->sendDataFunc = sendFile;return 0;}strcpy(response->fileName,file);response->statusCode = OK;strcpy(response->statusMsg,"OK!");// 判断文件类型if(S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)) {// 把这个目录中的内容发送给客户端// sendHeadMsg(cfd,200,"OK",getFileType(".html"),-1);// sendDir(file,cfd);// 响应头httpResponseAddHeader(response,"Content-Type",getFileType(".html"));response->sendDataFunc = sendDir;}else {// 把文件的内容发送给客户端// sendHeadMsg(cfd,200,"OK",getFileType(file),st.st_size);// sendFile(file,cfd);// 响应头char tmp[12] = {0};sprintf(tmp,"%ld",st.st_size);httpResponseAddHeader(response,"content-type",getFileType(file));httpResponseAddHeader(response,"content-length",tmp);response->sendDataFunc = sendFile;}return 0;
}// 将字符转换为整型数
int hexToDec(char c){if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')return c - '0';if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f')return c - 'a' + 10;if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'F')return c - 'A' + 10;return 0;
}// 解码字符串
// to 存储解码之后的数据, 传出参数, from被解码的数据, 传入参数
void decodeMsg(char* to,char* from) {for(;*from!='\0';++to,++from) {// isxdigit -> 判断字符是不是16进制格式, 取值在 0-f// Linux%E5%86%85%E6%A0%B8.jpgif(from[0] == '%' && isxdigit(from[1]) && isxdigit(from[2])){// 将16进制的数 -> 十进制 将这个数值赋值给了字符 int -> char// B2 == 178// 将3个字符, 变成了一个字符, 这个字符就是原始数据// *to = (hexToDec(from[1]) * 16) + hexToDec(from[2]);*to = (hexToDec(from[1]) << 4) + hexToDec(from[2]);// 跳过 from[1] 和 from[2] ,因此在当前循环中已经处理过了from += 2;}else{// 字符拷贝,赋值*to = *from;}}*to = '\0';
}const char* getFileType(const char* name) {// a.jpg a.mp4 a.html// 自右向左查找 '.' 字符,如不存在返回NULLconst char* dot = strrchr(name,'.');if(dot == NULL) return "text/plain; charset=utf-8";//纯文本if(strcmp(dot,".html") == 0 || strcmp(dot,".htm") == 0) return "text/html; charset=utf-8";if(strcmp(dot,".jpg")==0 || strcmp(dot,".jpeg")==0) return "image/jpeg";if(strcmp(dot,".gif")==0)return "image/gif";if(strcmp(dot,".png")==0)return "image/png";if(strcmp(dot,".css")==0) return "text/css";if(strcmp(dot,".au")==0)return "audio/basic";if(strcmp(dot,".wav")==0)return "audio/wav";if(strcmp(dot,".avi")==0)return "video/x-msvideo";if(strcmp(dot,".mov")==0 || strcmp(dot,".qt")==0)return "video/quicktime";if(strcmp(dot,".mpeg")==0 || strcmp(dot,".mpe")==0)return "video/mpeg";if(strcmp(dot,".vrml")==0 || strcmp(dot,".wrl")==0)return "model/vrml";if(strcmp(dot,".midi")==0 || strcmp(dot,".mid")==0)return "audio/midi";if(strcmp(dot,".mp3")==0)return "audio/mpeg";if(strcmp(dot,".ogg") == 0) return "application/ogg";if(strcmp(dot,".pac") == 0)return "application/x-ns-proxy-autoconfig";if(strcmp(dot,".pdf") == 0)return "application/pdf";return "text/plain; charset=utf-8";//纯文本
}void sendFile(const char* fileName,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int cfd) {// 打开文件int fd = open(fileName,O_RDONLY);if(fd < 0) {perror("open");return;}// assert(fd > 0);
#if 1while (1) {char buf[1024];int len = read(fd,buf,sizeof(buf));if(len > 0) {// send(cfd,buf,len,0);bufferAppendData(sendBuf,buf,len);
#ifndef MSG_SEND_AUTObufferSendData(sendBuf,cfd);
#endif}else if(len == 0) {break;}else{close(fd);perror("read");}}
#else// 把文件内容发送给客户端off_t offset = 0;int size = lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);// 文件指针移动到了尾部lseek(fd,0,SEEK_SET);// 移动到文件头部while (offset < size){int ret = sendfile(cfd,fd,&offset,size - offset);printf("ret value: %d\n",ret);if (ret == -1 && errno == EAGAIN) {printf("没数据...\n");}}
#endifclose(fd);
}void sendDir(const char* dirName,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int cfd) {char buf[4096] = {0};sprintf(buf,"<html><head><title>%s</title></head><body><table>",dirName);struct dirent** nameList;int num = scandir(dirName,&nameList,NULL,alphasort);for(int i=0;i<num;i++) {// 取出文件名 nameList 指向的是一个指针数组 struct dirent* tmp[]char* name = nameList[i]->d_name;struct stat st;char subPath[1024] = {0};sprintf(subPath,"%s/%s",dirName,name);stat(subPath,&st);if(S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)) {// 从当前目录跳到子目录里边,/sprintf(buf+strlen(buf),"<tr><td><a href=\"%s/\">%s</a></td><td>%ld</td></tr>",name,name,st.st_size);}else{sprintf(buf+strlen(buf),"<tr><td><a href=\"%s\">%s</a></td><td>%ld</td></tr>",name,name,st.st_size);}// send(cfd,buf,strlen(buf),0);bufferAppendString(sendBuf,buf);
#ifndef MSG_SEND_AUTObufferSendData(sendBuf,cfd);
#endifmemset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));free(nameList[i]); } sprintf(buf,"</table></body></html>");// send(cfd,buf,strlen(buf),0);bufferAppendString(sendBuf,buf);
#ifndef MSG_SEND_AUTObufferSendData(sendBuf,cfd);
#endiffree(nameList);
}HttpResponse.h
#pragma once
#include "Buffer.h"// 定义状态码枚举
enum HttpStatusCode {Unknown = 0,OK = 200,MovedPermanently = 301,MovedTemporarily = 302,BadRequest = 400,NotFound = 404
};// 定义响应的结构体
struct ResponseHeader {char key[32];char value[128];
};// 定义一个函数指针,用来组织要回复给客户端的数据块
typedef void (*responseBody) (const char* fileName,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int socket);// 定义结构体
struct HttpResponse {// 状态行:状态码,状态描述enum HttpStatusCode statusCode;char statusMsg[128];// 响应头 - 键值对struct ResponseHeader* headers;int headerNum;/*服务器回复给客户端的数据取决于客户端向服务器请求了什么类型的资源,有可能它请求的是一个目录,有可能请求的是一个文件,这个文件有可能是一个文本文件,也可能是一个图片,还可能是mp3...需要根据客户端的请求去回复相应的数据.所以如何去组织这个需要回复的数据块呢?- 定义一个函数指针,用来组织要回复给客户端的数据块fileName:分成两类,一类是目录类型,一类是非目录类型的文件如果是目录就去遍历目录,如果是文件,就读取其内容在进行套接字的通信过程中,如果要接收数据,它就是用来存储客户端发过来的数据块;如果要回复数据(给客户端发数据),发送的数据要先存储到sendBuf里边,再发送给客户端.socket:就是用来通信的文件描述符通过这个用于通信的文件描述符,就能够把写入到sendBuf里边的数据发送给客户端.sendBuf里边的数据就是我们组织好的Http响应的数据块*/responseBody sendDataFunc;// 文件名char fileName[128];
};// 初始化
struct HttpResponse* httpResponseInit();// 销毁
void httpResponseDestroy(struct HttpResponse* response);// 添加响应头
void httpResponseAddHeader(struct HttpResponse* response,const char* key,const char* value);// 组织http响应数据
void httpResponsePrepareMsg(struct HttpResponse* response,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int socket);HttpResponse.c
#include "HttpResponse.h"
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#define ResHeaderSize 16
// 初始化
struct HttpResponse* httpResponseInit() {struct HttpResponse* response = (struct HttpResponse*)malloc(sizeof(struct HttpResponse));// 状态行:状态码,状态描述response->statusCode = Unknown;bzero(response->statusMsg,sizeof(response->statusMsg));// 响应头 - 键值对int size = sizeof(struct ResponseHeader) * ResHeaderSize;response->headers = (struct ResponseHeader*)malloc(size);bzero(response->headers, size);response->headerNum = 0;// 函数指针response->sendDataFunc = NULL;// 文件名bzero(response->fileName,sizeof(response->fileName));return response;
}// 销毁
void httpResponseDestroy(struct HttpResponse* response) {if(response!=NULL) {free(response->headers);free(response);}
}// 添加响应头
void httpResponseAddHeader(struct HttpResponse* response,const char* key,const char* value){if(response == NULL || key == NULL || value == NULL) {return;}strcpy(response->headers[response->headerNum].key,key);strcpy(response->headers[response->headerNum].value,value);response->headerNum++;
}// 组织http响应数据
void httpResponsePrepareMsg(struct HttpResponse* response,struct Buffer* sendBuf,int socket) {// 状态行char tmp[1024] = {0};sprintf(tmp,"HTTP/1.1 %d %s\r\n",response->statusCode,response->statusMsg);bufferAppendString(sendBuf,tmp);// 响应头for(int i=0;i<response->headerNum;++i) {// memset(tmp,0,sizeof(tmp)); ?????????sprintf(tmp,"%s: %s\r\n",response->headers[i].key,response->headers[i].value);bufferAppendString(sendBuf,tmp);}// 空行bufferAppendString(sendBuf,"\r\n");#ifndef MSG_SEND_AUTObufferSendData(sendBuf,socket);
#endif// 回复的数据response->sendDataFunc(response->fileName,sendBuf,socket);
}TcpConnection.h
#pragma once
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "Buffer.h"
#include "Channel.h"
#include "HttpRequest.h"
#include "HttpResponse.h"// #define MSG_SEND_AUTOstruct TcpConnection {struct EventLoop* evLoop;struct Channel* channel;struct Buffer* readBuf;struct Buffer* writeBuf;char name[32];// http协议struct HttpRequest* request;struct HttpResponse* response;
};// 初始化
struct TcpConnection* tcpConnectionInit(int fd,struct EventLoop* evLoop);// 释放资源
int tcpConnectionDestroy(void* arg);TcpConnection.c
#include "TcpConnection.h"
#include "HttpRequest.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "Log.h"// 接收客户端数据
int processRead(void* arg) {struct TcpConnection* conn = (struct TcpConnection*)arg;// 接收数据int count = bufferSocketRead(conn->readBuf,conn->channel->fd);Debug("接收到的http请求数据: %s",conn->readBuf->data + conn->readBuf->readPos);if(count > 0) {// 接收到了Http请求,解析Http请求int socket = conn->channel->fd;
#ifdef MSG_SEND_AUTO writeEventEnable(conn->channel,true);eventLoopAddTask(conn->evLoop,conn->channel,MODIFY);
#endifbool flag = parseHttpRequest(conn->request,conn->readBuf,conn->response,conn->writeBuf,socket);if(!flag) {// 解析失败,回复一个简单的htmlchar* errMsg = "Http/1.1 400 Bad Request\r\n\r\n";bufferAppendString(conn->writeBuf,errMsg);}}else{
#ifdef MSG_SEND_AUTO// 断开连接eventLoopAddTask(conn->evLoop,conn->channel,DELETE);
#endif}
#ifndef MSG_SEND_AUTO// 断开连接eventLoopAddTask(conn->evLoop,conn->channel,DELETE);
#endifreturn 0;
}int processWrite(void* arg) {Debug("开始发送数据了(基于写事件发送)......");struct TcpConnection* conn = (struct TcpConnection*)arg;// 发送数据int count = bufferSendData(conn->writeBuf,conn->channel->fd);if(count > 0) {// 判断数据是否被全部发送出去了if(bufferReadableSize(conn->writeBuf) == 0){// 1.不再检测写事件 -- 修改channel中保存的事件writeEventEnable(conn->channel,false);// 2.修改dispatcher检测的集合 -- 添加任务节点eventLoopAddTask(conn->evLoop,conn->channel,MODIFY); // 3.删除这个节点eventLoopAddTask(conn->evLoop,conn->channel,DELETE);}}return 0;
}// 初始化
struct TcpConnection* tcpConnectionInit(int fd,struct EventLoop* evLoop) {struct TcpConnection* conn = (struct TcpConnection*)malloc(sizeof(struct TcpConnection));conn->evLoop = evLoop;struct Channel* channel = channelInit(fd,ReadEvent,processRead,processWrite,tcpConnectionDestroy,conn);conn->channel = channel;conn->readBuf = bufferInit(10240); // 10kconn->writeBuf = bufferInit(10240); // 10ksprintf(conn->name,"TcpConnection-%d",fd);// http协议conn->request = httpRequestInit();conn->response = httpResponseInit();// 把channel添加到事件循环对应的任务队列里边eventLoopAddTask(evLoop,conn->channel,ADD);Debug("和客户端建立连接, threadName: %s, threadID:%ld, connName: %s",evLoop->threadName, evLoop->threadID, conn->name);return conn;
}// 释放资源
int tcpConnectionDestroy(void* arg) {struct TcpConnection* conn = (struct TcpConnection*)arg;if(conn!=NULL) {if (conn->readBuf && bufferReadableSize(conn->readBuf) == 0 &&conn->writeBuf && bufferReadableSize(conn->writeBuf) == 0) {destroyChannel(conn->evLoop,conn->channel);bufferDestroy(conn->readBuf);bufferDestroy(conn->writeBuf);httpRequestDestroy(conn->request);httpResponseDestroy(conn->response);free(conn);}}Debug("连接断开, 释放资源, gameover, connName: %s", conn->name);return 0;
}TcpServer.h
#pragma once
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "ThreadPool.h"struct Listener {int lfd;unsigned short port;
};struct TcpServer {struct Listener* listener; // 监听套接字struct EventLoop* mainLoop; // 主线程的事件循环(反应堆模型)struct ThreadPool* threadPool; // 线程池int threadNum; // 线程数量
};// 初始化
struct TcpServer* tcpServerInit(unsigned short port,int threadNum);// 初始化监听
struct Listener* listenerInit(unsigned short port);// 启动服务器(不停检测有无客户端连接)
void tcpServerRun(struct TcpServer* server);TcpServer.c
#include "TcpServer.h"
#include "TcpConnection.h"
#include <arpa/inet.h> // 套接字函数的头文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Log.h"// 初始化
struct TcpServer* tcpServerInit(unsigned short port,int threadNum) {struct TcpServer* tcp = (struct TcpServer*)malloc(sizeof(struct TcpServer));tcp->listener = listenerInit(port); // 创建listenertcp->mainLoop = eventLoopInit(); // 主线程的事件循环(反应堆模型)tcp->threadPool = threadPoolInit(tcp->mainLoop,threadNum); // 创建线程池tcp->threadNum = threadNum; // 线程数量return tcp;
}// 初始化监听
struct Listener* listenerInit(unsigned short port) {// 创建一个Listner实例 -> listenerstruct Listener* listener = (struct Listener*)malloc(sizeof(struct Listener));// 1.创建一个监听的文件描述符 -> lfdint lfd = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); // AF_INET -> (网络层协议:Ipv4) ;SOCK_STREAM -> (传输层协议:流式协议) ;0 -> :表示使用Tcpif(lfd == -1) {perror("socket"); return NULL;} // 2.设置端口复用int opt = 1;int ret = setsockopt(lfd,SOL_SOCKET,SO_REUSEADDR,&opt,sizeof(opt)); if(ret == -1) {perror("setsockopt");return NULL;}// 3.绑定struct sockaddr_in addr;addr.sin_family = AF_INET;addr.sin_port = htons(port);// 主机字节序(小端)转成网络字节序(大端) 端口的最大数量:2^16=65536addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;// 0.0.0.0 ret = bind(lfd,(struct sockaddr*)&addr,sizeof(addr));if(ret == -1) {perror("bind");return NULL;}// 4.设置监听ret = listen(lfd,128);if(ret == -1) {perror("listen");return NULL;}listener->lfd = lfd;listener->port = port;return listener;
}int acceptConnection(void* arg) {struct TcpServer* server = (struct TcpServer*)arg;// 和客户端建立连接int cfd = accept(server->listener->lfd,NULL,NULL);if(cfd == -1) {perror("accept");return -1;}// 从线程池中去取出一个子线程的反应堆实例,去处理这个cfdstruct EventLoop* evLoop = takeWorkerEventLoop(server->threadPool);// 将cfd放到 TcpConnection中处理tcpConnectionInit(cfd, evLoop);// ...(已完,已补充)return 0;
}// 启动服务器(不停检测有无客户端连接)
void tcpServerRun(struct TcpServer* server) {Debug("服务器程序已经启动了...");// 启动线程池threadPoolRun(server->threadPool);/*线程池启动起来之后,需要让它处理任务,对于当前的TcpServer来说,是有任务可以处理的。在当前服务器启动之后,需要处理的文件描述符有且只有一个,就是用于监听的文件描述符,因此需要把待检测的文件描述符(用于监听的)添加到(mainLoop)事件循环里边。*/// 初始化一个channel实例struct Channel* channel = channelInit(server->listener->lfd,ReadEvent,acceptConnection,NULL,NULL,server);/*// 添加任务到任务队列int eventLoopAddTask(struct EventLoop* evLoop,struct Channel* channel,int type)如果把channel放到了mainLoop的任务队列里边,任务队列在处理的时候需要知道对这个节点做什么操作,是添加到检测集合里去,还是从检测集合里删除,还是修改检测集合里的文件描述符的事件那么对于监听的文件描述符,当然就是添加ADD*/// 添加检测的任务 eventLoopAddTask(server->mainLoop,channel,ADD);// 启动反应堆模型eventLoopRun(server->mainLoop);
}ThreadPool.h
#pragma once
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "WorkerThread.h"
#include <stdbool.h>// 定义线程池
struct ThreadPool {/*在线程池里边的这个mainLoop主要是做备份用的,主线程里边的mainLoop主要负责和客户端建立连接,只负责这一件事情,只有当线程池没有子线程这种情况下,mainLoop才负责处理和客户端的连接,否则的话它是不管其他事情的。*/struct EventLoop* mainLoop; // 主线程的反应堆模型int index; bool isStart;int threadNum; // 子线程总个数struct WorkerThread* workerThreads;
};// 初始化线程池
struct ThreadPool* threadPoolInit(struct EventLoop* mainLoop, int threadNum);// 启动线程池
void threadPoolRun(struct ThreadPool* pool);// 取出线程池中的某个子线程的反应堆实例
struct EventLoop* takeWorkerEventLoop(struct ThreadPool* pool);ThreadPool.c
#include "ThreadPool.h"
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>/*threadPoolInit函数、threadPoolRun函数、takeWorkerEventLoop函数都需要在主线程里边进行依次调用。首先调用threadPoolInit函数得到pool实例,之后调用threadPoolRun函数启动线程池(意味着里边的子线程会启动)。接着调用takeWorkerEventLoop函数取出线程池中的某个子线程的反应堆实例,再把这个实例给到调用者,调用者就可以通过这个实例,往它的任务队列里边添加任务,这个任务添加到evLoop的任务队列里边去了之后,就开始处理任务队列。然后再根据任务队列里边的节点类型来处理Dispatcher的检测集合。有三种情况:情况1.往检测集合里边添加新的节点 情况2.从检测集合里边删除一个节点情况3.修改检测集合里边某个文件描述符对应的事件Dispatcher这个检测集合被处理完之后,这个反应堆模型开始进行一个循环,它需要循环调用底层的poll/epoll_wait/select函数来检测这个集合里边是否有激活的文件描述符。如果有激活的文件描述符,那么就通过这个文件描述符找到它所对应的channel。找到这个channel之后,再基于激活的事件调用事件对应的回调函数。这个函数调用完成之后,对应的事件也就处理完毕。这就走完了整个的处理流程
*/// 初始化线程池(主线程)
struct ThreadPool* threadPoolInit(struct EventLoop* mainLoop, int threadNum) {struct ThreadPool* pool = (struct ThreadPool*)malloc(sizeof(struct ThreadPool));pool->mainLoop = mainLoop; // 主线程的反应堆模型pool->index = 0;pool->isStart = false;pool->threadNum = threadNum; // 子线程总个数pool->workerThreads = (struct WorkerThread*)malloc(sizeof(struct WorkerThread) * threadNum);// 子线程数组return pool;
}// 启动线程池 (主线程)
void threadPoolRun(struct ThreadPool* pool) {/*线程池被创建出来之后,接下来就需要让线程池运行起来,其实就是让线程池里的若干个子线程运行起来*/// 确保线程池未运行 assert(pool && !pool->isStart);// 比较主线程的ID和当前线程ID是否相等 // 相等=>确保执行线程为主线程;不相等=>exit(0)if(pool->mainLoop->threadID != pthread_self()) {exit(0);}pool->isStart = true; // 标记为启动if(pool->threadNum > 0) { // 线程数量大于零for(int i=0;i<pool->threadNum;++i) {workerThreadInit(&pool->workerThreads[i], i);// 初始化子线程workerThreadRun(&pool->workerThreads[i]); // 启动子线程}}
}/*这个函数是主线程调用的,因为主线程是拥有线程池的因此主线程可以遍历线程池里边的子线程,从中挑选一个子线程,得到它的反应堆模型,再将处理的任务放到反应堆模型里边
*/
// 取出线程池中的某个子线程的反应堆实例
struct EventLoop* takeWorkerEventLoop(struct ThreadPool* pool) {assert(pool->isStart); // 确保线程池是运行的// 比较主线程的ID和当前线程ID是否相等 // 相等=>确保执行线程为主线程;不相等=>exit(0)if(pool->mainLoop->threadID != pthread_self()) { exit(0);}// 从线程池中找到一个子线程,然后取出里边的反应堆实例struct EventLoop* evLoop = pool->mainLoop; // 初始化if(pool->threadNum > 0) { // 线程数量大于零evLoop = pool->workerThreads[pool->index].evLoop;/*整个处理流程需要确保每个任务都能被雨露均沾地分配给各个子线程,避免所有任务都由同一个线程处理,还确保了index在合适的取值范围。*/pool->index = ++pool->index % pool->threadNum;}return evLoop;
}WorkerThread.h
#pragma once
#include <pthread.h>
#include "EventLoop.h"/*工作线程:线程ID,线程名字(可选),互斥锁(线程同步),条件变量(线程阻塞),EventLoop(在每个子线程里边都有一个反应堆模型)
*/// 定义子线程对应的结构体
struct WorkerThread {pthread_t threadID;// 线程IDchar name[24];// 线程名字pthread_mutex_t mutex;// 互斥锁(线程同步)pthread_cond_t cond;// 条件变量(线程阻塞)struct EventLoop* evLoop;// 事件循环(反应堆模型)// 在每个子线程里边都有一个反应堆模型
};// 初始化
int workerThreadInit(struct WorkerThread* thread, int index);// 启动线程
void workerThreadRun(struct WorkerThread* thread);WorkerThread.c
#include "WorkerThread.h"
#include <stdio.h>
// 初始化
int workerThreadInit(struct WorkerThread* thread, int index) {thread->threadID = 0;// 线程IDsprintf(thread->name, "SubThread-%d", index);// 线程名字// 指定为NULL,表示使用默认属性pthread_mutex_init(&thread->mutex, NULL);// 互斥锁pthread_cond_init(&thread->cond, NULL);// 条件变量thread->evLoop = NULL;// 事件循环(反应堆模型)return 0;
}// 子线程的回调函数
void* subThreadRunning(void* arg) {struct WorkerThread* thread = (struct WorkerThread*)arg;// 还有子线程里边的evLoop是共享资源,需要添加互斥锁pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex);// 加锁thread->evLoop = eventLoopInitEx(thread->name);pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex);// 解锁pthread_cond_signal(&thread->cond);// 发送信号(唤醒主线程,通知主线程解除阻塞)eventLoopRun(thread->evLoop);// 启动反应堆模型return NULL;
}// 启动线程
void workerThreadRun(struct WorkerThread* thread) {// 创建子线程pthread_create(&thread->threadID, NULL, subThreadRunning, thread);/*在这里阻塞主线程的原因是:在于子线程的反应堆模型是否被真正的创建出来了?因此,可以判断一下thread->evLoop是否为NULL,如果等于NULL,说明子线程反应堆模型还没有被初始化完毕,没有初始化完毕,我们就阻塞主线程*/// 阻塞主线程,让当前函数不会直接结束pthread_mutex_lock(&thread->mutex);while(thread->evLoop == NULL) { // 多次判断pthread_cond_wait(&thread->cond, &thread->mutex);// 子线程的回调函数(subThreadRunning)里调用pthread_cond_signal(&thread->cond)可以解除这里的阻塞}pthread_mutex_unlock(&thread->mutex);
}相关文章:
完整代码)
基于多反应堆的高并发服务器【C/C++/Reactor】(中)完整代码
Buffer.h #pragma oncestruct Buffer {// 指向内存的指针char* data;int capacity;int readPos;int writePos; };// 初始化 struct Buffer* bufferInit(int size);// 销毁 void bufferDestroy(struct Buffer* buf);// 扩容 void bufferExtendRoom(struct Buffer* buf, int siz…...
Fluids —— Fluid sourcing
目录 FLIP Boundary: None FLIP Boundary: Velocity FLIP Boundary: Pressure Other methods SOP FLIP流体为生成粒子提供三种Boundary方式(None、Velocity、Pressure); 注,源对象必须是封闭且实体3D或体积对象,开…...
)
MongoDB相关问题及答案(2024)
1、MongoDB是什么,它与其他传统关系型数据库的主要区别是什么? MongoDB是一种开源文档型数据库,它属于NoSQL数据库的一个分支。NoSQL数据库提供了一种存储和检索数据的机制,这种机制的建模方式与传统的关系型数据库不同。而Mongo…...

前端系列:ES6-ES12新语法
文章目录 ECMAScript系列:简介ECMAScript系列:ES6新特性let 关键字const 关键字变量的解构赋值模板字符串简化对象写法箭头函数参数默认值rest 参数spread扩展运算符Symbol迭代器生成器PromiseSetMapclass类数值扩展对象扩展模块化 ECMAScript系列&#…...
】精准核酸检测(并查集-JavaPythonC++JS实现))
226.【2023年华为OD机试真题(C卷)】精准核酸检测(并查集-JavaPythonC++JS实现)
🚀点击这里可直接跳转到本专栏,可查阅顶置最新的华为OD机试宝典~ 本专栏所有题目均包含优质解题思路,高质量解题代码(Java&Python&C++&JS分别实现),详细代码讲解,助你深入学习,深度掌握! 文章目录 一. 题目-精准核酸检测二.解题思路三.题解代码Python题解…...

浅谈MySQL之索引
1.什么是索引 索引是一种数据结构,用于提高数据库的查询性能。它类似于书籍的目录,通过预先排序和存储一定列(或多列)的值,使数据库引擎能够更快速地定位和访问特定行的数据。索引的作用是加速数据检索的速度ÿ…...
Rust类型之字符串
字符串 Rust 中的字符串类型是String。虽然字符串只是比字符多了一个“串”字,但是在Rust中这两者的存储方式完全不一样,字符串不是字符的数组,String内部存储的是Unicode字符串的UTF8编码,而char直接存的是Unicode Scalar Value…...

Shell - 学习笔记 - 2.1 - Shell变量:Shell变量的定义、赋值和删除
第2章 Shell编程 这一章我们正式进入 Shell 脚本编程,重点讲解变量、字符串、数组、数学计算、选择结构、循环结构和函数。 Shell 的编程思想虽然和 C、Java、Python、C# 等其它编程语言类似,但是在语法细节方面差异还是比较大的,有编程经验的…...

【OCR】实战使用 - 如何提高识别文字的精准度?
实战使用 - 如何提高文字识别的精准度 我们在平常使用OCR的时候,经常会出现文字识别不精准的情况,我们改如何提高文字识别的精度呢? 以下是一些提高OCR(Optical Character Recognition,光学字符识别)文字识…...

css3浮动定位
css3浮动定位 前言浮动float的基本概念浮动的使用浮动的顺序贴靠特性浮动的元素一定能设置宽高 使用浮动实现网页布局BFC规范和浏览器差异如何创建BFCBFC的其他作用浏览器差异 清除浮动相对定位 relative绝对定位 absolute绝对定位脱离标准文档流绝对定位的参考盒子绝对定位的盒…...
Linux 上 Nginx 配置访问 web 服务器及配置 https 访问配置过程记录
目录 一、前言说明二、配置思路三、开始修改配置四、结尾 一、前言说明 最近自己搭建了个 Blog 网站,想把网站部署到服务器上面,本文记录一下搭建过程中 Nginx 配置请求转发的过程。 二、配置思路 web项目已经在服务器上面运行起来了,运行的端…...

css less sass 动态宽高
less height: ~"calc(100% - 30px)";若要需要按照某个比例固定高度可以用 min-height: e("calc(100vh - 184px)")css height: calc(100% - 50px);sass height:calc(100% - var(--height) );...

sqlserver导出数据为excel再导入到另一个数据库
要将SQL Server中的数据导出为Excel文件,然后再将该Excel文件导入到另一个数据库中,你可以按照以下步骤进行操作: 导出数据为Excel文件 echo offset SourceServer源服务器名称 set SourceDB数据库名称 set ExcelFilePath导出到的Excel文件路…...

异构微服务远程调用如何打jar包
1.服务提供方打 jar 包 RemoteUserService.java package com.finance.system.api;import com.finance.system.api.domain.dto.Enterprise; import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springfra…...

赋能智慧农业生产,基于YOLOv7开发构建农业生产场景下油茶作物成熟检测识别系统
AI赋能生产生活场景,是加速人工智能技术落地的有利途径,在前文很多具体的业务场景中我们也从实验的角度来尝试性地分析实践了基于AI模型来助力生产生活制造相关的各个领域,诸如:基于AI硬件实现农业作物除草就是一个比较熟知的场景…...

Docker入门介绍
【一】从 dotCloud 到 Docker——低调奢华有内涵 1、追根溯源:dotCloud 时间倒回到两年前,有一个名不见经传的小公司,他的名字叫做:dotCloud。 dotCloud 公司主要提供的是基于 PaaS(Platform as a Service,平台及服务) 平台为开发者或开发商…...
第四站:指针的进阶-(二级指针,函数指针)
目录 二级指针 二级指针的用途 多级指针的定义和使用 指针和数组之间的关系 存储指针的数组(指针数组:保存地址值) 指向数组的指针(数组指针) 传参的形式(指针) 数组传参时会退化为指针 void类型的指针 函数指针 定义: 调用:两种方式:(*指针名)(参数地址) 或者 指针…...
)
浏览器渲染原理(面试重点)
一、浏览器是如何渲染页面的 常见的简洁答案: 浏览器内核拿到内容后,渲染流程大致如下:解析HTML,构建Dom树;解析CSS,构建Render树;(将CSS代码解析成树形的数据结构,与D…...
将t指向的字符串复制到s指向的字符串的尾部。)
C //练习 5-3 用指针方式实现第2章中的函数strcat。函数strcat(s, t)将t指向的字符串复制到s指向的字符串的尾部。
C程序设计语言 (第二版) 练习 5-3 练习 5-3 用指针方式实现第2章中的函数strcat。函数strcat(s, t)将t指向的字符串复制到s指向的字符串的尾部。 注意:代码在win32控制台运行,在不同的IDE环境下,有部分可能需要变更。…...

深度剖析Redis:从基础到高级应用
目录 引言 1、 Redis基础 1.1 Redis数据结构 1.1.1 字符串(String) 1.1.2 列表(List) 1.1.3 集合(Set) 1.1.4 散列(Hash) 1.1.5 有序集合(Sorted Set)…...
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...
微信小程序之bind和catch
这两个呢,都是绑定事件用的,具体使用有些小区别。 官方文档: 事件冒泡处理不同 bind:绑定的事件会向上冒泡,即触发当前组件的事件后,还会继续触发父组件的相同事件。例如,有一个子视图绑定了b…...

工业自动化时代的精准装配革新:迁移科技3D视觉系统如何重塑机器人定位装配
AI3D视觉的工业赋能者 迁移科技成立于2017年,作为行业领先的3D工业相机及视觉系统供应商,累计完成数亿元融资。其核心技术覆盖硬件设计、算法优化及软件集成,通过稳定、易用、高回报的AI3D视觉系统,为汽车、新能源、金属制造等行…...
微信小程序云开发平台MySQL的连接方式
注:微信小程序云开发平台指的是腾讯云开发 先给结论:微信小程序云开发平台的MySQL,无法通过获取数据库连接信息的方式进行连接,连接只能通过云开发的SDK连接,具体要参考官方文档: 为什么? 因为…...
Docker 本地安装 mysql 数据库
Docker: Accelerated Container Application Development 下载对应操作系统版本的 docker ;并安装。 基础操作不再赘述。 打开 macOS 终端,开始 docker 安装mysql之旅 第一步 docker search mysql 》〉docker search mysql NAME DE…...
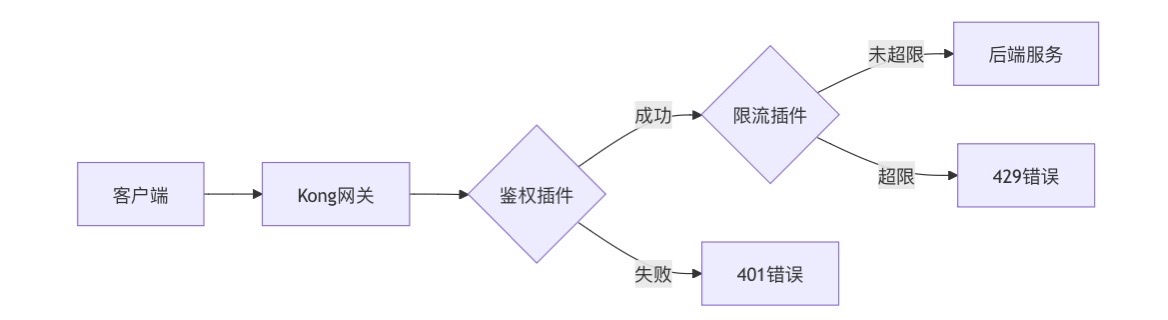
云原生安全实战:API网关Kong的鉴权与限流详解
🔥「炎码工坊」技术弹药已装填! 点击关注 → 解锁工业级干货【工具实测|项目避坑|源码燃烧指南】 一、基础概念 1. API网关(API Gateway) API网关是微服务架构中的核心组件,负责统一管理所有API的流量入口。它像一座…...

Spring Security 认证流程——补充
一、认证流程概述 Spring Security 的认证流程基于 过滤器链(Filter Chain),核心组件包括 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter、AuthenticationManager、UserDetailsService 等。整个流程可分为以下步骤: 用户提交登录请求拦…...
)
华为OD最新机试真题-数组组成的最小数字-OD统一考试(B卷)
题目描述 给定一个整型数组,请从该数组中选择3个元素 组成最小数字并输出 (如果数组长度小于3,则选择数组中所有元素来组成最小数字)。 输入描述 行用半角逗号分割的字符串记录的整型数组,0<数组长度<= 100,0<整数的取值范围<= 10000。 输出描述 由3个元素组成…...

二维FDTD算法仿真
二维FDTD算法仿真,并带完全匹配层,输入波形为高斯波、平面波 FDTD_二维/FDTD.zip , 6075 FDTD_二维/FDTD_31.m , 1029 FDTD_二维/FDTD_32.m , 2806 FDTD_二维/FDTD_33.m , 3782 FDTD_二维/FDTD_34.m , 4182 FDTD_二维/FDTD_35.m , 4793...

AD学习(3)
1 PCB封装元素组成及简单的PCB封装创建 封装的组成部分: (1)PCB焊盘:表层的铜 ,top层的铜 (2)管脚序号:用来关联原理图中的管脚的序号,原理图的序号需要和PCB封装一一…...
