Linux fork()系统调用流程解析
1. fork()函数介绍(百度百科)
fork系统调用用于创建一个新进程,称为子进程,它与进程(称为系统调用fork的进程)同时运行,此进程称为父进程。创建新的子进程后,两个进程将执行fork()系统调用之后的下一条指令。子进程使用相同的pc(程序计数器),相同的CPU寄存器,在父进程中使用的相同打开文件。
它不需要参数并返回一个整数值。下面是fork()返回的不同值。
负值:创建子进程失败。
零:返回到新创建的子进程。
正值:返回父进程或调用者。该值包含新创建的子进程的进程ID。
2. fork()使用示例(百度百科)
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[]){pid_t pid=fork();if ( pid < 0 ) {fprintf(stderr,"错误!");} else if( pid == 0 ) {printf("子进程空间");exit(0);} else {printf("父进程空间,子进程pid为%d",pid);}// 可以使用wait或waitpid函数等待子进程的结束并获取结束状态exit(0);
}
3. Linux中fork()代码实现分析
3.1 fork()系统调用定义
#ifdef __ARCH_WANT_SYS_FORK
SYSCALL_DEFINE0(fork)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_MMUstruct kernel_clone_args args = {.exit_signal = SIGCHLD,};return kernel_clone(&args);
#else/* can not support in nommu mode */return -EINVAL;
#endif
}
#endif
fork()函数不需要传递任何参数,因此他的系统调用声明为DEFINE0。我们继续跟踪fork()系统调用的实现,这里发现是直接调用kernel_clone()函数进行后续处理。
3.2 跟踪kernel_clone()函数实现
/** Ok, this is the main fork-routine.** It copies the process, and if successful kick-starts* it and waits for it to finish using the VM if required.** args->exit_signal is expected to be checked for sanity by the caller.*/
pid_t kernel_clone(struct kernel_clone_args *args)
{u64 clone_flags = args->flags;struct completion vfork;struct pid *pid;struct task_struct *p;int trace = 0;pid_t nr;/** For legacy clone() calls, CLONE_PIDFD uses the parent_tid argument* to return the pidfd. Hence, CLONE_PIDFD and CLONE_PARENT_SETTID are* mutually exclusive. With clone3() CLONE_PIDFD has grown a separate* field in struct clone_args and it still doesn't make sense to have* them both point at the same memory location. Performing this check* here has the advantage that we don't need to have a separate helper* to check for legacy clone().*/if ((args->flags & CLONE_PIDFD) &&(args->flags & CLONE_PARENT_SETTID) &&(args->pidfd == args->parent_tid))return -EINVAL;/** Determine whether and which event to report to ptracer. When* called from kernel_thread or CLONE_UNTRACED is explicitly* requested, no event is reported; otherwise, report if the event* for the type of forking is enabled.*/if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_UNTRACED)) {if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK)trace = PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK;else if (args->exit_signal != SIGCHLD)trace = PTRACE_EVENT_CLONE;elsetrace = PTRACE_EVENT_FORK;if (likely(!ptrace_event_enabled(current, trace)))trace = 0;}/* 通过copy_process()函数创建一个新的进程 */p = copy_process(NULL, trace, NUMA_NO_NODE, args);add_latent_entropy();if (IS_ERR(p))return PTR_ERR(p);/** Do this prior waking up the new thread - the thread pointer* might get invalid after that point, if the thread exits quickly.*/trace_sched_process_fork(current, p);pid = get_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID);nr = pid_vnr(pid);if (clone_flags & CLONE_PARENT_SETTID)put_user(nr, args->parent_tid);if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {p->vfork_done = &vfork;init_completion(&vfork);get_task_struct(p);}if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_LRU_GEN) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_VM)) {/* lock the task to synchronize with memcg migration */task_lock(p);lru_gen_add_mm(p->mm);task_unlock(p);}/* 唤醒新创建的进程 */wake_up_new_task(p);/* forking complete and child started to run, tell ptracer */if (unlikely(trace))ptrace_event_pid(trace, pid);if (clone_flags & CLONE_VFORK) {if (!wait_for_vfork_done(p, &vfork))ptrace_event_pid(PTRACE_EVENT_VFORK_DONE, pid);}put_pid(pid);return nr;
}
从kernel_clone()函数定义可以看出,新进程的创建是通过拷贝父进程来实现的,通过copy_process()完成拷贝动作;而新进程的调度运行是通过wake_up_new_task()函数进行处理的。
3.3 跟踪copy_process()函数实现
/** This creates a new process as a copy of the old one,* but does not actually start it yet.** It copies the registers, and all the appropriate* parts of the process environment (as per the clone* flags). The actual kick-off is left to the caller.*/
static __latent_entropy struct task_struct *copy_process(struct pid *pid,int trace,int node,struct kernel_clone_args *args)
{int pidfd = -1, retval;struct task_struct *p;struct multiprocess_signals delayed;struct file *pidfile = NULL;const u64 clone_flags = args->flags;struct nsproxy *nsp = current->nsproxy;/** Don't allow sharing the root directory with processes in a different* namespace*/if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_FS))return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWUSER|CLONE_FS)) == (CLONE_NEWUSER|CLONE_FS))return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);/** Thread groups must share signals as well, and detached threads* can only be started up within the thread group.*/if ((clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND))return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);/** Shared signal handlers imply shared VM. By way of the above,* thread groups also imply shared VM. Blocking this case allows* for various simplifications in other code.*/if ((clone_flags & CLONE_SIGHAND) && !(clone_flags & CLONE_VM))return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);/** Siblings of global init remain as zombies on exit since they are* not reaped by their parent (swapper). To solve this and to avoid* multi-rooted process trees, prevent global and container-inits* from creating siblings.*/if ((clone_flags & CLONE_PARENT) &¤t->signal->flags & SIGNAL_UNKILLABLE)return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);/** If the new process will be in a different pid or user namespace* do not allow it to share a thread group with the forking task.*/if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) {if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_NEWUSER | CLONE_NEWPID)) ||(task_active_pid_ns(current) != nsp->pid_ns_for_children))return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);}/** If the new process will be in a different time namespace* do not allow it to share VM or a thread group with the forking task.*/if (clone_flags & (CLONE_THREAD | CLONE_VM)) {if (nsp->time_ns != nsp->time_ns_for_children)return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);}if (clone_flags & CLONE_PIDFD) {/** - CLONE_DETACHED is blocked so that we can potentially* reuse it later for CLONE_PIDFD.* - CLONE_THREAD is blocked until someone really needs it.*/if (clone_flags & (CLONE_DETACHED | CLONE_THREAD))return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);}/** Force any signals received before this point to be delivered* before the fork happens. Collect up signals sent to multiple* processes that happen during the fork and delay them so that* they appear to happen after the fork.*/sigemptyset(&delayed.signal);INIT_HLIST_NODE(&delayed.node);spin_lock_irq(¤t->sighand->siglock);if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD))hlist_add_head(&delayed.node, ¤t->signal->multiprocess);recalc_sigpending();spin_unlock_irq(¤t->sighand->siglock);retval = -ERESTARTNOINTR;if (task_sigpending(current))goto fork_out;retval = -ENOMEM;/* 复制父进程的task_struct到新创建的进程,新进程的内核栈也在这个函数中分配 */p = dup_task_struct(current, node);if (!p)goto fork_out;p->flags &= ~PF_KTHREAD;if (args->kthread)p->flags |= PF_KTHREAD;if (args->io_thread) {/** Mark us an IO worker, and block any signal that isn't* fatal or STOP*/p->flags |= PF_IO_WORKER;siginitsetinv(&p->blocked, sigmask(SIGKILL)|sigmask(SIGSTOP));}p->set_child_tid = (clone_flags & CLONE_CHILD_SETTID) ? args->child_tid : NULL;/** Clear TID on mm_release()?*/p->clear_child_tid = (clone_flags & CLONE_CHILD_CLEARTID) ? args->child_tid : NULL;ftrace_graph_init_task(p);rt_mutex_init_task(p);lockdep_assert_irqs_enabled();
#ifdef CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKINGDEBUG_LOCKS_WARN_ON(!p->softirqs_enabled);
#endifretval = copy_creds(p, clone_flags);if (retval < 0)goto bad_fork_free;retval = -EAGAIN;if (is_rlimit_overlimit(task_ucounts(p), UCOUNT_RLIMIT_NPROC, rlimit(RLIMIT_NPROC))) {if (p->real_cred->user != INIT_USER &&!capable(CAP_SYS_RESOURCE) && !capable(CAP_SYS_ADMIN))goto bad_fork_cleanup_count;}current->flags &= ~PF_NPROC_EXCEEDED;/** If multiple threads are within copy_process(), then this check* triggers too late. This doesn't hurt, the check is only there* to stop root fork bombs.*/retval = -EAGAIN;if (data_race(nr_threads >= max_threads))goto bad_fork_cleanup_count;delayacct_tsk_init(p); /* Must remain after dup_task_struct() */p->flags &= ~(PF_SUPERPRIV | PF_WQ_WORKER | PF_IDLE | PF_NO_SETAFFINITY);p->flags |= PF_FORKNOEXEC;INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->children);INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->sibling);rcu_copy_process(p);p->vfork_done = NULL;spin_lock_init(&p->alloc_lock);init_sigpending(&p->pending);p->utime = p->stime = p->gtime = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_HAS_SCALED_CPUTIMEp->utimescaled = p->stimescaled = 0;
#endifprev_cputime_init(&p->prev_cputime);#ifdef CONFIG_VIRT_CPU_ACCOUNTING_GENseqcount_init(&p->vtime.seqcount);p->vtime.starttime = 0;p->vtime.state = VTIME_INACTIVE;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_IO_URINGp->io_uring = NULL;
#endif#if defined(SPLIT_RSS_COUNTING)memset(&p->rss_stat, 0, sizeof(p->rss_stat));
#endifp->default_timer_slack_ns = current->timer_slack_ns;#ifdef CONFIG_PSIp->psi_flags = 0;
#endiftask_io_accounting_init(&p->ioac);acct_clear_integrals(p);posix_cputimers_init(&p->posix_cputimers);p->io_context = NULL;audit_set_context(p, NULL);cgroup_fork(p);if (args->kthread) {if (!set_kthread_struct(p))goto bad_fork_cleanup_delayacct;}
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAp->mempolicy = mpol_dup(p->mempolicy);if (IS_ERR(p->mempolicy)) {retval = PTR_ERR(p->mempolicy);p->mempolicy = NULL;goto bad_fork_cleanup_delayacct;}
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CPUSETSp->cpuset_mem_spread_rotor = NUMA_NO_NODE;p->cpuset_slab_spread_rotor = NUMA_NO_NODE;seqcount_spinlock_init(&p->mems_allowed_seq, &p->alloc_lock);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TRACE_IRQFLAGSmemset(&p->irqtrace, 0, sizeof(p->irqtrace));p->irqtrace.hardirq_disable_ip = _THIS_IP_;p->irqtrace.softirq_enable_ip = _THIS_IP_;p->softirqs_enabled = 1;p->softirq_context = 0;
#endifp->pagefault_disabled = 0;#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEPlockdep_init_task(p);
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXESp->blocked_on = NULL; /* not blocked yet */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BCACHEp->sequential_io = 0;p->sequential_io_avg = 0;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BPF_SYSCALLRCU_INIT_POINTER(p->bpf_storage, NULL);p->bpf_ctx = NULL;
#endif/* Perform scheduler related setup. Assign this task to a CPU. */retval = sched_fork(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_policy;retval = perf_event_init_task(p, clone_flags);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_policy;retval = audit_alloc(p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_perf;/* copy all the process information */shm_init_task(p);retval = security_task_alloc(p, clone_flags);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_audit;retval = copy_semundo(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_security;/* 将父进程的所有打开文件描述符表都复制到新创建的进程中 */retval = copy_files(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_semundo;retval = copy_fs(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_files;retval = copy_sighand(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_fs;retval = copy_signal(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_sighand;/* 将父进程的内存空间拷贝到新进程中,其实就是为新进程创建页表,把父进程的页表项拷贝到新进程中 */retval = copy_mm(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_signal;retval = copy_namespaces(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_mm;retval = copy_io(clone_flags, p);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_namespaces;retval = copy_thread(p, args);if (retval)goto bad_fork_cleanup_io;stackleak_task_init(p);if (pid != &init_struct_pid) {pid = alloc_pid(p->nsproxy->pid_ns_for_children, args->set_tid,args->set_tid_size);if (IS_ERR(pid)) {retval = PTR_ERR(pid);goto bad_fork_cleanup_thread;}}/** This has to happen after we've potentially unshared the file* descriptor table (so that the pidfd doesn't leak into the child* if the fd table isn't shared).*/if (clone_flags & CLONE_PIDFD) {retval = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);if (retval < 0)goto bad_fork_free_pid;pidfd = retval;pidfile = anon_inode_getfile("[pidfd]", &pidfd_fops, pid,O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);if (IS_ERR(pidfile)) {put_unused_fd(pidfd);retval = PTR_ERR(pidfile);goto bad_fork_free_pid;}get_pid(pid); /* held by pidfile now */retval = put_user(pidfd, args->pidfd);if (retval)goto bad_fork_put_pidfd;}#ifdef CONFIG_BLOCKp->plug = NULL;
#endiffutex_init_task(p);/** sigaltstack should be cleared when sharing the same VM*/if ((clone_flags & (CLONE_VM|CLONE_VFORK)) == CLONE_VM)sas_ss_reset(p);/** Syscall tracing and stepping should be turned off in the* child regardless of CLONE_PTRACE.*/user_disable_single_step(p);clear_task_syscall_work(p, SYSCALL_TRACE);
#if defined(CONFIG_GENERIC_ENTRY) || defined(TIF_SYSCALL_EMU)clear_task_syscall_work(p, SYSCALL_EMU);
#endifclear_tsk_latency_tracing(p);/* ok, now we should be set up.. */p->pid = pid_nr(pid);if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD) {p->group_leader = current->group_leader;p->tgid = current->tgid;} else {p->group_leader = p;p->tgid = p->pid;}p->nr_dirtied = 0;p->nr_dirtied_pause = 128 >> (PAGE_SHIFT - 10);p->dirty_paused_when = 0;p->pdeath_signal = 0;INIT_LIST_HEAD(&p->thread_group);p->task_works = NULL;clear_posix_cputimers_work(p);#ifdef CONFIG_KRETPROBESp->kretprobe_instances.first = NULL;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_RETHOOKp->rethooks.first = NULL;
#endif/** Ensure that the cgroup subsystem policies allow the new process to be* forked. It should be noted that the new process's css_set can be changed* between here and cgroup_post_fork() if an organisation operation is in* progress.*/retval = cgroup_can_fork(p, args);if (retval)goto bad_fork_put_pidfd;/** Now that the cgroups are pinned, re-clone the parent cgroup and put* the new task on the correct runqueue. All this *before* the task* becomes visible.** This isn't part of ->can_fork() because while the re-cloning is* cgroup specific, it unconditionally needs to place the task on a* runqueue.*/sched_cgroup_fork(p, args);/** From this point on we must avoid any synchronous user-space* communication until we take the tasklist-lock. In particular, we do* not want user-space to be able to predict the process start-time by* stalling fork(2) after we recorded the start_time but before it is* visible to the system.*/p->start_time = ktime_get_ns();p->start_boottime = ktime_get_boottime_ns();/** Make it visible to the rest of the system, but dont wake it up yet.* Need tasklist lock for parent etc handling!*/write_lock_irq(&tasklist_lock);/* CLONE_PARENT re-uses the old parent */if (clone_flags & (CLONE_PARENT|CLONE_THREAD)) {p->real_parent = current->real_parent;p->parent_exec_id = current->parent_exec_id;if (clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD)p->exit_signal = -1;elsep->exit_signal = current->group_leader->exit_signal;} else {p->real_parent = current;p->parent_exec_id = current->self_exec_id;p->exit_signal = args->exit_signal;}klp_copy_process(p);sched_core_fork(p);spin_lock(¤t->sighand->siglock);rv_task_fork(p);rseq_fork(p, clone_flags);/* Don't start children in a dying pid namespace */if (unlikely(!(ns_of_pid(pid)->pid_allocated & PIDNS_ADDING))) {retval = -ENOMEM;goto bad_fork_cancel_cgroup;}/* Let kill terminate clone/fork in the middle */if (fatal_signal_pending(current)) {retval = -EINTR;goto bad_fork_cancel_cgroup;}/* No more failure paths after this point. *//** Copy seccomp details explicitly here, in case they were changed* before holding sighand lock.*/copy_seccomp(p);init_task_pid_links(p);if (likely(p->pid)) {ptrace_init_task(p, (clone_flags & CLONE_PTRACE) || trace);init_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID, pid);if (thread_group_leader(p)) {init_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_TGID, pid);init_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PGID, task_pgrp(current));init_task_pid(p, PIDTYPE_SID, task_session(current));if (is_child_reaper(pid)) {ns_of_pid(pid)->child_reaper = p;p->signal->flags |= SIGNAL_UNKILLABLE;}p->signal->shared_pending.signal = delayed.signal;p->signal->tty = tty_kref_get(current->signal->tty);/** Inherit has_child_subreaper flag under the same* tasklist_lock with adding child to the process tree* for propagate_has_child_subreaper optimization.*/p->signal->has_child_subreaper = p->real_parent->signal->has_child_subreaper ||p->real_parent->signal->is_child_subreaper;list_add_tail(&p->sibling, &p->real_parent->children);list_add_tail_rcu(&p->tasks, &init_task.tasks);attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_TGID);attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PGID);attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_SID);__this_cpu_inc(process_counts);} else {current->signal->nr_threads++;current->signal->quick_threads++;atomic_inc(¤t->signal->live);refcount_inc(¤t->signal->sigcnt);task_join_group_stop(p);list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_group,&p->group_leader->thread_group);list_add_tail_rcu(&p->thread_node,&p->signal->thread_head);}attach_pid(p, PIDTYPE_PID);nr_threads++;}total_forks++;hlist_del_init(&delayed.node);spin_unlock(¤t->sighand->siglock);syscall_tracepoint_update(p);write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);if (pidfile)fd_install(pidfd, pidfile);proc_fork_connector(p);sched_post_fork(p);cgroup_post_fork(p, args);perf_event_fork(p);trace_task_newtask(p, clone_flags);uprobe_copy_process(p, clone_flags);copy_oom_score_adj(clone_flags, p);return p;bad_fork_cancel_cgroup:sched_core_free(p);spin_unlock(¤t->sighand->siglock);write_unlock_irq(&tasklist_lock);cgroup_cancel_fork(p, args);
bad_fork_put_pidfd:if (clone_flags & CLONE_PIDFD) {fput(pidfile);put_unused_fd(pidfd);}
bad_fork_free_pid:if (pid != &init_struct_pid)free_pid(pid);
bad_fork_cleanup_thread:exit_thread(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_io:if (p->io_context)exit_io_context(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_namespaces:exit_task_namespaces(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_mm:if (p->mm) {mm_clear_owner(p->mm, p);mmput(p->mm);}
bad_fork_cleanup_signal:if (!(clone_flags & CLONE_THREAD))free_signal_struct(p->signal);
bad_fork_cleanup_sighand:__cleanup_sighand(p->sighand);
bad_fork_cleanup_fs:exit_fs(p); /* blocking */
bad_fork_cleanup_files:exit_files(p); /* blocking */
bad_fork_cleanup_semundo:exit_sem(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_security:security_task_free(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_audit:audit_free(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_perf:perf_event_free_task(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_policy:lockdep_free_task(p);
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAmpol_put(p->mempolicy);
#endif
bad_fork_cleanup_delayacct:delayacct_tsk_free(p);
bad_fork_cleanup_count:dec_rlimit_ucounts(task_ucounts(p), UCOUNT_RLIMIT_NPROC, 1);exit_creds(p);
bad_fork_free:WRITE_ONCE(p->__state, TASK_DEAD);exit_task_stack_account(p);put_task_stack(p);delayed_free_task(p);
fork_out:spin_lock_irq(¤t->sighand->siglock);hlist_del_init(&delayed.node);spin_unlock_irq(¤t->sighand->siglock);return ERR_PTR(retval);
}
copy_process()函数内容较多,博主只介绍跟内存空间相关的复制动作,因此下面介绍copy_mm()的实现。
3.4 跟踪copy_mm()函数实现
static int copy_mm(unsigned long clone_flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
{struct mm_struct *mm, *oldmm;tsk->min_flt = tsk->maj_flt = 0;tsk->nvcsw = tsk->nivcsw = 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_DETECT_HUNG_TASKtsk->last_switch_count = tsk->nvcsw + tsk->nivcsw;tsk->last_switch_time = 0;
#endiftsk->mm = NULL;tsk->active_mm = NULL;/** Are we cloning a kernel thread?** We need to steal a active VM for that..*/oldmm = current->mm;if (!oldmm)return 0;/* 如果是线程的创建则不需要为新的线程task_struct创建新的mm_struct结构,和父线程共享即可,其实这也就是人们常说的多进程间是共享同一内存的原因(或者是多进程之间通信简单) */if (clone_flags & CLONE_VM) {mmget(oldmm);mm = oldmm;} else { /* 如果是需要创建新的进程,则需要去分配新的mm_struct */mm = dup_mm(tsk, current->mm);if (!mm)return -ENOMEM;}tsk->mm = mm;tsk->active_mm = mm;return 0;
}
对于多线程的copy_mm()到这里就结束了,子线程共享父线程的地址空间,但是对于创建新的进程来说,还需要去创建新的mm_struct,因此还需要跟踪dup_mm()的实现。
3.5 跟踪dup_mm()函数实现
/*** dup_mm() - duplicates an existing mm structure* @tsk: the task_struct with which the new mm will be associated.* @oldmm: the mm to duplicate.** Allocates a new mm structure and duplicates the provided @oldmm structure* content into it.** Return: the duplicated mm or NULL on failure.*/
static struct mm_struct *dup_mm(struct task_struct *tsk,struct mm_struct *oldmm)
{struct mm_struct *mm;int err;/* 分配一个新的mm_struct */mm = allocate_mm();if (!mm)goto fail_nomem;/* 拷贝父进程mm_struct的内容到子进程中 */memcpy(mm, oldmm, sizeof(*mm));/* 新进程的mm_struct初始化操作 */if (!mm_init(mm, tsk, mm->user_ns))goto fail_nomem;/* 拷贝父进程的所有vma到子进程,子进程的页表也是在此创建 */err = dup_mmap(mm, oldmm);if (err)goto free_pt;mm->hiwater_rss = get_mm_rss(mm);mm->hiwater_vm = mm->total_vm;if (mm->binfmt && !try_module_get(mm->binfmt->module))goto free_pt;return mm;free_pt:/* don't put binfmt in mmput, we haven't got module yet */mm->binfmt = NULL;mm_init_owner(mm, NULL);mmput(mm);fail_nomem:return NULL;
}
在dup_mm()函数内部,通过调用dup_mmap()函数来将父进程的所有vma拷贝到新创建的子进程的mm_struct中。
3.6 跟踪dup_mmap()函数实现
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
static __latent_entropy int dup_mmap(struct mm_struct *mm,struct mm_struct *oldmm)
{struct vm_area_struct *mpnt, *tmp;int retval;unsigned long charge = 0;LIST_HEAD(uf);MA_STATE(old_mas, &oldmm->mm_mt, 0, 0);MA_STATE(mas, &mm->mm_mt, 0, 0);uprobe_start_dup_mmap();if (mmap_write_lock_killable(oldmm)) {retval = -EINTR;goto fail_uprobe_end;}flush_cache_dup_mm(oldmm);uprobe_dup_mmap(oldmm, mm);/** Not linked in yet - no deadlock potential:*/mmap_write_lock_nested(mm, SINGLE_DEPTH_NESTING);/* No ordering required: file already has been exposed. */dup_mm_exe_file(mm, oldmm);mm->total_vm = oldmm->total_vm;mm->data_vm = oldmm->data_vm;mm->exec_vm = oldmm->exec_vm;mm->stack_vm = oldmm->stack_vm;retval = ksm_fork(mm, oldmm);if (retval)goto out;khugepaged_fork(mm, oldmm);retval = mas_expected_entries(&mas, oldmm->map_count);if (retval)goto out;/* 遍历父进程的所有vma */mas_for_each(&old_mas, mpnt, ULONG_MAX) {struct file *file;if (mpnt->vm_flags & VM_DONTCOPY) {vm_stat_account(mm, mpnt->vm_flags, -vma_pages(mpnt));continue;}charge = 0;/** Don't duplicate many vmas if we've been oom-killed (for* example)*/if (fatal_signal_pending(current)) {retval = -EINTR;goto loop_out;}if (mpnt->vm_flags & VM_ACCOUNT) {unsigned long len = vma_pages(mpnt);if (security_vm_enough_memory_mm(oldmm, len)) /* sic */goto fail_nomem;charge = len;}/* 为新进程创建vma,并拷贝父进程的vma内容到新创建的vma中 */tmp = vm_area_dup(mpnt);if (!tmp)goto fail_nomem;retval = vma_dup_policy(mpnt, tmp);if (retval)goto fail_nomem_policy;tmp->vm_mm = mm;retval = dup_userfaultfd(tmp, &uf);if (retval)goto fail_nomem_anon_vma_fork;if (tmp->vm_flags & VM_WIPEONFORK) {/** VM_WIPEONFORK gets a clean slate in the child.* Don't prepare anon_vma until fault since we don't* copy page for current vma.*/tmp->anon_vma = NULL;} else if (anon_vma_fork(tmp, mpnt))goto fail_nomem_anon_vma_fork;tmp->vm_flags &= ~(VM_LOCKED | VM_LOCKONFAULT);file = tmp->vm_file;if (file) { /* 如果是文件页映射的vma,则会对新创建的vma做如下操作 */struct address_space *mapping = file->f_mapping;get_file(file);i_mmap_lock_write(mapping);if (tmp->vm_flags & VM_SHARED)mapping_allow_writable(mapping);flush_dcache_mmap_lock(mapping);/* insert tmp into the share list, just after mpnt */vma_interval_tree_insert_after(tmp, mpnt,&mapping->i_mmap);flush_dcache_mmap_unlock(mapping);i_mmap_unlock_write(mapping);}/** Copy/update hugetlb private vma information.*/if (is_vm_hugetlb_page(tmp))hugetlb_dup_vma_private(tmp);/* Link the vma into the MT */mas.index = tmp->vm_start;mas.last = tmp->vm_end - 1;mas_store(&mas, tmp);if (mas_is_err(&mas))goto fail_nomem_mas_store;mm->map_count++;if (!(tmp->vm_flags & VM_WIPEONFORK))/* 将父进程vma的页表信息拷贝到子进程中 */retval = copy_page_range(tmp, mpnt);if (tmp->vm_ops && tmp->vm_ops->open)tmp->vm_ops->open(tmp);if (retval)goto loop_out;}/* a new mm has just been created */retval = arch_dup_mmap(oldmm, mm);
loop_out:mas_destroy(&mas);
out:mmap_write_unlock(mm);flush_tlb_mm(oldmm);mmap_write_unlock(oldmm);dup_userfaultfd_complete(&uf);
fail_uprobe_end:uprobe_end_dup_mmap();return retval;fail_nomem_mas_store:unlink_anon_vmas(tmp);
fail_nomem_anon_vma_fork:mpol_put(vma_policy(tmp));
fail_nomem_policy:vm_area_free(tmp);
fail_nomem:retval = -ENOMEM;vm_unacct_memory(charge);goto loop_out;
}
这里就是fork()系统调用的实现全部内容了,细节并没有全部展开,读者可自行阅读源码。
相关文章:
系统调用流程解析)
Linux fork()系统调用流程解析
1. fork()函数介绍(百度百科) fork系统调用用于创建一个新进程,称为子进程,它与进程(称为系统调用fork的进程)同时运行,此进程称为父进程。创建新的子进程后,两个进程将执行fork&…...
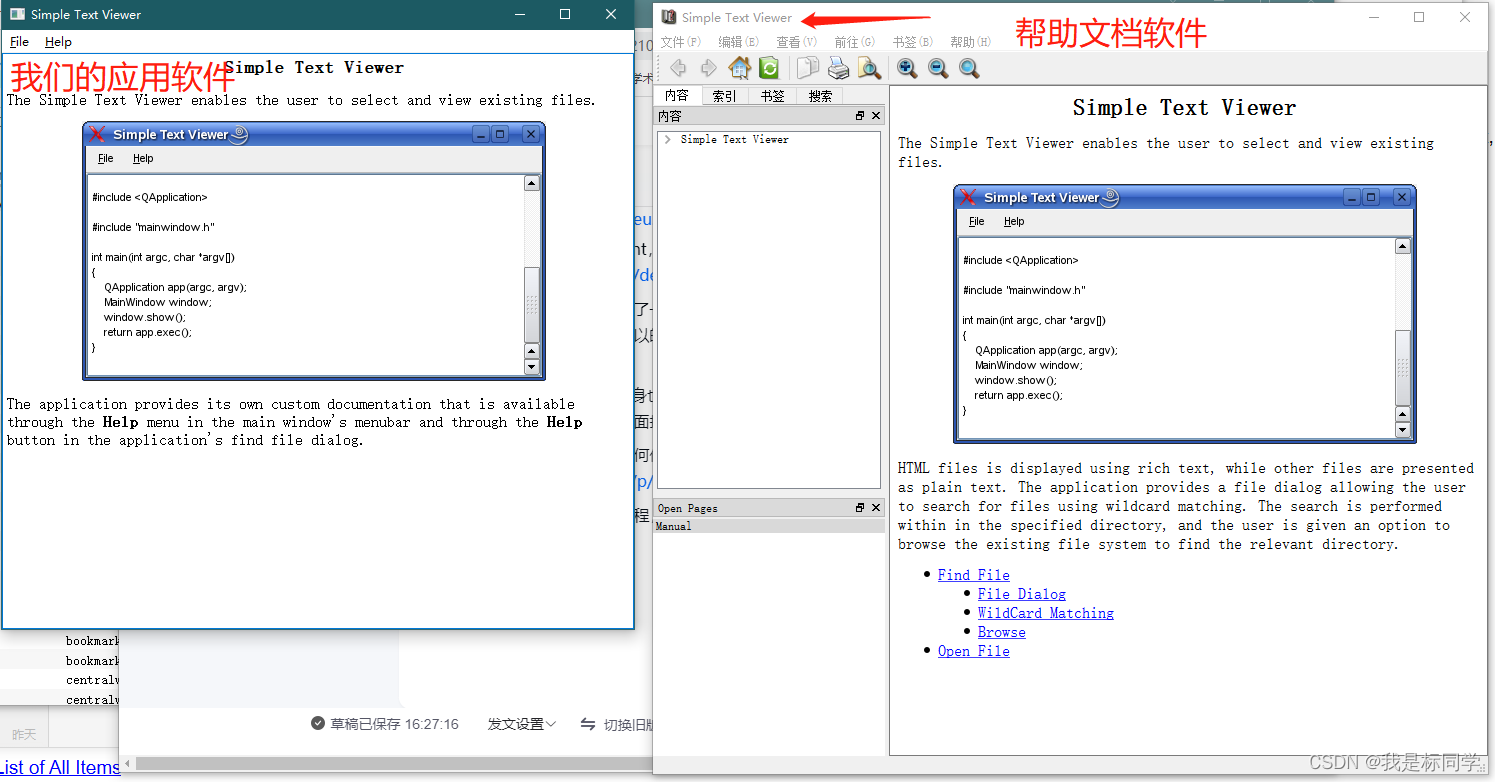
自定义软件帮助文档(qt assistant实现)
网上搜了一下,软件的帮助文档,三个都可以:https://github.com/zealdocs/zeal,https://zealdocs.org/,看看这个博客说的 https://blog.csdn.net/libaineu2004/article/details/125028913,这个也是开源的&…...

ESP32设备驱动-GPIO外部中断
GPIO外部中断 文章目录 GPIO外部中断1、GPIO中断介绍2、GPIO中断使用步骤3、软件准备4、硬件准备5、代码实现在前面的文章 ESP32设备驱动-GPIO数字输入与输出中介绍如何对GPIO进行控制操作。本文将在该基础上使用GPIO中断进一步优化按键输入。即演示如何使用GPIO中断。 1、GPI…...
【安全】nginx反向代理+负载均衡上传webshel
Nginx负载均衡下上传webshell 什么是反向代理? 正向代理就是代替客户端进行各种服务的访问以及获取;那么反向代理自然就是代替服务器进行事务处理,就是此时的代理服务器负责将用户的各项请求做一个汇总、分类,将其分发到不同的服务…...
| 真题,思路,知识点)
华为OD机试 - 单词接龙(Python)| 真题,思路,知识点
单词接龙 题目 单词接龙的规则是: 可用于接龙的单词,首字母必须要与前一个单词的尾字母相同; 当存在多个首字母相同的单词时,取长度最长的单词; 如果长度也相等,则取字典序最小的单词; 已经参与接龙的单词不能重复使用; 现给定一组全部由小写字母组成的单词数组, 并指…...
[ 系统安全篇 ] window 命令禁用用户及解禁方法
🍬 博主介绍 👨🎓 博主介绍:大家好,我是 _PowerShell ,很高兴认识大家~ ✨主攻领域:【渗透领域】【数据通信】 【通讯安全】 【web安全】【面试分析】 🎉点赞➕评论➕收藏 养成习…...
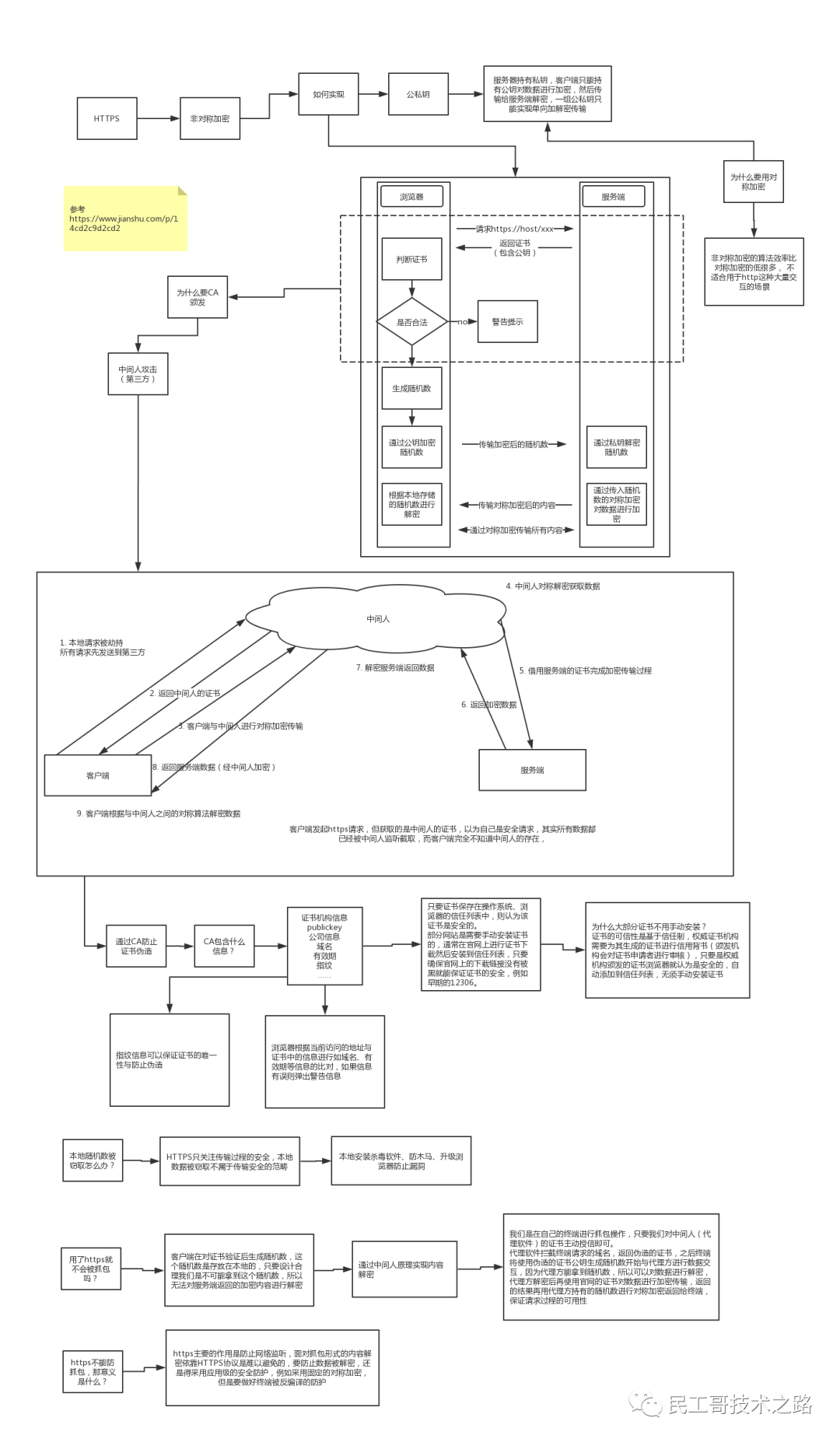
Https 协议超强讲解(二)
浏览器是如何确保 CA 证书的合法性? 1. 证书包含什么信息? 颁发机构信息 公钥 公司信息 域名 有效期 指纹 …… 2. 证书的合法性依据是什么? 首先,权威机构是要有认证的,不是随便一个机构都有资格颁发证书&am…...
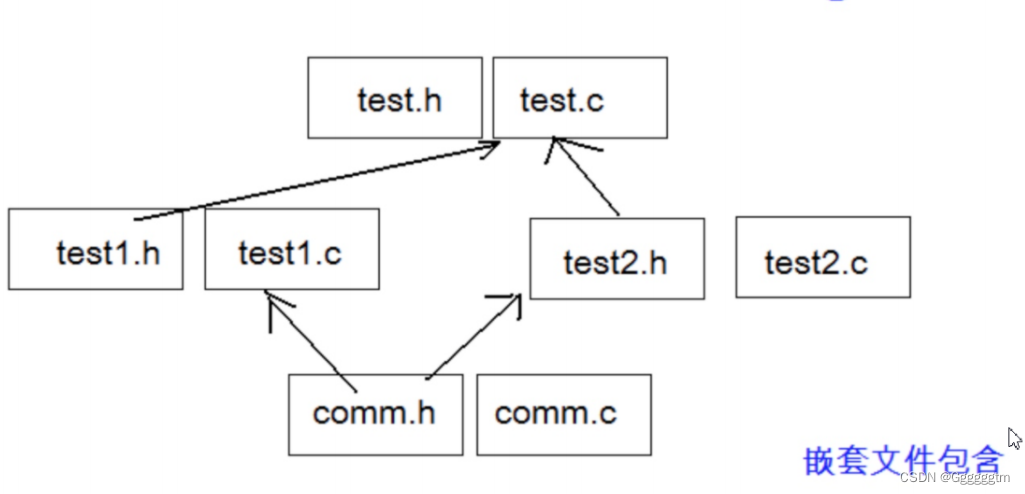
C语言的程序环境和预处理详解
目录 一、程序的翻译环境和执行环境 二、编译和链接详解 2、1 翻译环境 2、2 编译过程详解 2、3 执行环境 三、预处理详解 3、1 预定义符号 3、2 #define 3、2、1 #define定义的符号 3、2、2 #define 定义宏 3、2、3 #define 替换规则 3、3 宏和函数的对比 3、4 条件编译 3、5…...
3.JUC【Java面试第三季】
3.JUC【Java面试第三季】前言推荐3.JUC06_闲聊AQS面试1.题目说明07_可重入锁理论2.可重入锁说明“可重入锁”这四个字分开来解释可重入锁的种类08_可重入锁的代码验证-上09_可重入锁的代码验证-下3.LockSupport10_LockSupport是什么LockSupport是什么11_waitNotify限制线程等待…...
Linux防火墙(7)
实验目的 通过该实验了解Linux防火墙iptables实现原理,掌握iptables基本使用方法,能够利用iptables对操作系统进行加固。预备知识基本原理 netfilter/iptables(简称为iptables)组成Linux平台下的包过滤防火墙,具有完成…...
(主要关于teacher forcing))
2.11整理(2)(主要关于teacher forcing)
teacher forcing 训练迭代过程早期的RNN预测能力非常弱,几乎不能给出好的生成结果。如果某一个unit产生了垃圾结果,必然会影响后面一片unit的学习。RNN存在着两种训练模式(mode): free-running mode:就是常见的那种训练网络的方式: 上一个sta…...
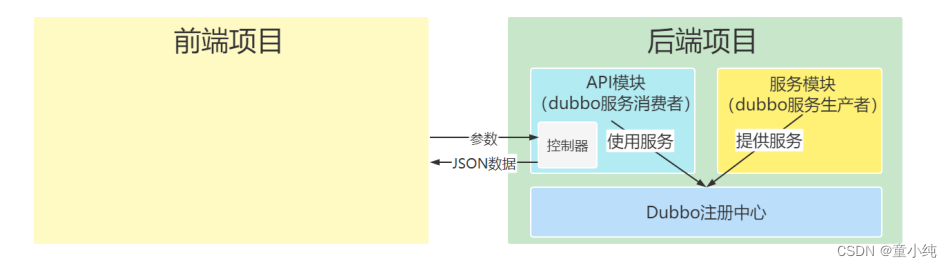
亿级高并发电商项目-- 实战篇 --万达商城项目 三(通用模块、商品服务模块、后台API模块、IDEA忽略文件显示等开发工作
专栏:高并发项目 👏作者简介:大家好,我是小童,Java开发工程师,CSDN博客博主,Java领域新星创作者 📕系列专栏:前端、Java、Java中间件大全、微信小程序、微信支付、若依框…...

IDEA下java程序的调试(简易实例图示版)
在线排版不太好看,介意的读者可下载word下来看:https://download.csdn.net/download/xijinno1/87441301IDEA下java程序的简单调试-System.out.println首先本次进行调试的一个程序是实现从1累加到100的功能,是在IDEA下进行编写的。如图所示&am…...
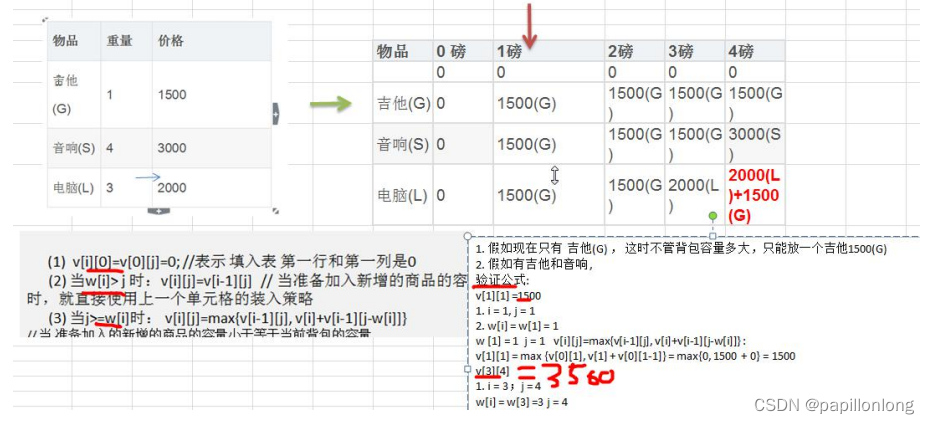
动态规划算法
1.应用场景-背包问题 背包问题:有一个背包,容量为 4 磅 , 现有如下物品 要求达到的目标为装入的背包的总价值最大,并且重量不超出要求装入的物品不能重复 2.动态规划算法介绍 动态规划(Dynamic Programming)算法的核心思想是&…...
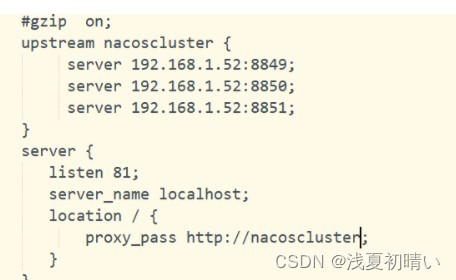
nacos的单机模式和集群模式
文章目录 目录 文章目录 前言 一、nacos数据库配置 二、单机模式 三、集群模式 四、使用nginx集群模式的负载均衡 总结 前言 一、nacos数据库配置 在数据库中创建nacos_config 编码格式utf8-mb4的数据库 把上面的数据库文件导入数据库 在 配置文件中添加如下 spring.datasour…...
Spring Boot 整合定时任务完成 从0 到1
Java 定时任务学习 定时任务概述 > 定时任务的应用场景非常广泛, 如果说 我们想要在某时某地去尝试的做某件事 就需要用到定时任务来通知我们 ,大家可以看下面例子 如果需要明天 早起,哪我们一般会去定一个闹钟去通知我们, 而在编程中 有许许多多的…...

Dialogue Transformers
Abstract 本文介绍了一种基于 Transformer 架构的 对话策略,其中自注意力机制被应用于对话轮次(dialogue turns)的序列上。近期的一些工作使用层次化的循环神经网络(hierarchical recurrent neural networks)在对话上下文中对多个话语(utterances)进行编码,但是我们认…...
【遇见青山】项目难点:缓存击穿问题解决方案
【遇见青山】项目难点:缓存击穿问题解决方案1.缓存击穿互斥锁🔒方案逻辑过期方案2.基于互斥锁方案的具体实现3.基于逻辑过期方案的具体实现1.缓存击穿 缓存击穿问题也叫热点Key问题,就是一个被高并发访问并且缓存重建业务较复杂的key突然失效…...
)
2023Flag具体实施计划(短期)
重新看了flag ,要做的事情太多,太杂,上周一周时间都在纠结和琢磨,该怎么下手。如何达成小目标。特别是沟通,汇报,演讲能力, 以及整体体系化的思维能力的训练。如何做到多思考,而不是瞎搞。这边重…...
研一寒假C++复习笔记--左值和右值的理解和使用
目录 1--左值和右值的定义 2--简单理解左值和右值的代码 3--非const引用只能接受左值 1--左值和右值的定义 左值:L-Value,L理解为 Location,表示可寻; 右值:R-Value,R理解为 Read,表示可读&a…...
业务系统对接大模型的基础方案:架构设计与关键步骤
业务系统对接大模型:架构设计与关键步骤 在当今数字化转型的浪潮中,大语言模型(LLM)已成为企业提升业务效率和创新能力的关键技术之一。将大模型集成到业务系统中,不仅可以优化用户体验,还能为业务决策提供…...

css实现圆环展示百分比,根据值动态展示所占比例
代码如下 <view class""><view class"circle-chart"><view v-if"!!num" class"pie-item" :style"{background: conic-gradient(var(--one-color) 0%,#E9E6F1 ${num}%),}"></view><view v-else …...

C# 类和继承(抽象类)
抽象类 抽象类是指设计为被继承的类。抽象类只能被用作其他类的基类。 不能创建抽象类的实例。抽象类使用abstract修饰符声明。 抽象类可以包含抽象成员或普通的非抽象成员。抽象类的成员可以是抽象成员和普通带 实现的成员的任意组合。抽象类自己可以派生自另一个抽象类。例…...
: 一刀斩断视频片头广告)
快刀集(1): 一刀斩断视频片头广告
一刀流:用一个简单脚本,秒杀视频片头广告,还你清爽观影体验。 1. 引子 作为一个爱生活、爱学习、爱收藏高清资源的老码农,平时写代码之余看看电影、补补片,是再正常不过的事。 电影嘛,要沉浸,…...
android RelativeLayout布局
<?xml version"1.0" encoding"utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"android:layout_width"match_parent"android:layout_height"match_parent"android:gravity&…...

破解路内监管盲区:免布线低位视频桩重塑停车管理新标准
城市路内停车管理常因行道树遮挡、高位设备盲区等问题,导致车牌识别率低、逃费率高,传统模式在复杂路段束手无策。免布线低位视频桩凭借超低视角部署与智能算法,正成为破局关键。该设备安装于车位侧方0.5-0.7米高度,直接规避树枝遮…...
【Veristand】Veristand环境安装教程-Linux RT / Windows
首先声明,此教程是针对Simulink编译模型并导入Veristand中编写的,同时需要注意的是老用户编译可能用的是Veristand Model Framework,那个是历史版本,且NI不会再维护,新版本编译支持为VeriStand Model Generation Suppo…...
CSS3相关知识点
CSS3相关知识点 CSS3私有前缀私有前缀私有前缀存在的意义常见浏览器的私有前缀 CSS3基本语法CSS3 新增长度单位CSS3 新增颜色设置方式CSS3 新增选择器CSS3 新增盒模型相关属性box-sizing 怪异盒模型resize调整盒子大小box-shadow 盒子阴影opacity 不透明度 CSS3 新增背景属性ba…...

命令行关闭Windows防火墙
命令行关闭Windows防火墙 引言一、防火墙:被低估的"智能安检员"二、优先尝试!90%问题无需关闭防火墙方案1:程序白名单(解决软件误拦截)方案2:开放特定端口(解决网游/开发端口不通)三、命令行极速关闭方案方法一:PowerShell(推荐Win10/11)方法二:CMD命令…...
UE5 音效系统
一.音效管理 音乐一般都是WAV,创建一个背景音乐类SoudClass,一个音效类SoundClass。所有的音乐都分为这两个类。再创建一个总音乐类,将上述两个作为它的子类。 接着我们创建一个音乐混合类SoundMix,将上述三个类翻入其中,通过它管理每个音乐…...
