十五、Object 类
文章目录
- Object 类
- 6.1 public Object()
- 6.2 toString方法
- 6.3 hashCode和equals(Object)
- 6.4 getClass方法
- 6.5 clone方法
- 6.6 finalize方法
Object 类
本文为书籍《Java编程的逻辑》1和《剑指Java:核心原理与应用实践》2阅读笔记
java.lang.Object类是类层次结构的根类,每个类(除了Object类本身)都使用Object类作为超类。一个类如果没有显式声明继承另一个类,则相当于默认继承了Object类。换句话说,Object类的变量可以接收任意类型的对象。Java规定Object[]可以接收任意类型对象的数组,但是不能接收基本数据类型的数组。
package com.ieening.learnCommonApi;public class TestObject {public static void main(String[] args) {Object foo = new Object();Object stringObj = "小姑";Object tesObject = new TestObject();Object arrayObject = new int[5]; // 编译通过,此时把数组对象当成一个普通对象赋值给arrayObjectObject[] objects = new Object[3];Object[] strings = new String[3];Object[] intArray = new int[3]; // 编译报错:Type mismatch: cannot convert from int[] to Object[]}
}
Object类是其他类的根父类,因此Object类的所有方法都会继承到子类中,包括数组对象,了解Object类的方法就非常重要。Object类中的主要方法如下所示。
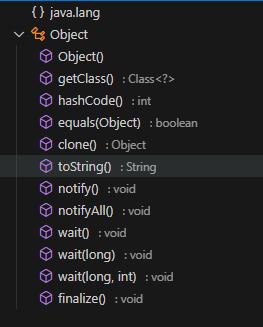
| 序号 | 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | public Object() | 无参构造器 |
| 2 | public final native Class<?> getClass() | 返回对象运行时的类型 |
| 3 | public native int hashCode() | 获取对象的 hash 值 |
| 4 | public boolean equals(Object obj) | 比较两个对象的内容是否相等 |
| 5 | protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException | 创建并返回对象的一个副本 |
| 6 | public String toString() | 对象字符串表示 |
| 7 | public final native void notify() | 唤醒当前对象监视器下等待的单个线程 |
| 8 | public final native void notifyAll() | 唤醒当前对象监视器下等待的所有线程 |
| 9 | public final void wait() throws InterruptedException | 当前线程等待直到被唤醒 |
| 10 | public final void wait(long timeoutMillis) throws InterruptedException | 当前线程等待直到被唤醒或时间结束 |
| 11 | public final void wait(long timeoutMillis, int nanos) throws InterruptedException | 当前线程等待直到被唤醒或时间结束 |
| 12 | protected void finalize() throws Throwable | 回收当前对象时,做一些清除操作 |
6.1 public Object()
Object类只有一个默认的空参构造器,所有类的对象创建最终都会通过super()语句调用到Object类的无参构造器中。如果一个类没有显式继承另一个类,那么在它的构造器中出现的super()语句表示调用的就是Object类的无参构造器。
6.2 toString方法
toString方法的作用是返回对象的字符串形式,也就是任意类型对象想转换成String类型,都可以调用toString方法。toString方法的原型返回的是一个类似地址值的字符串,不够简明并且对于开发人员来讲该字符串的信息没有意义,所以建议子类在重写该方法时,返回一个简明易懂的信息表达式,一般为对象的属性信息。
/*** Returns a string representation of the object.* @apiNote* In general, the* {@code toString} method returns a string that* "textually represents" this object. The result should* be a concise but informative representation that is easy for a* person to read.* It is recommended that all subclasses override this method.* The string output is not necessarily stable over time or across* JVM invocations.* @implSpec* The {@code toString} method for class {@code Object}* returns a string consisting of the name of the class of which the* object is an instance, the at-sign character `{@code @}', and* the unsigned hexadecimal representation of the hash code of the* object. In other words, this method returns a string equal to the* value of:* <blockquote>* <pre>* getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())* </pre></blockquote>** @return a string representation of the object.*/public String toString() {return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());}
6.3 hashCode和equals(Object)
1、hashCode
/*** Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is* supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by* {@link java.util.HashMap}.* <p>* The general contract of {@code hashCode} is:* <ul>* <li>Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during* an execution of a Java application, the {@code hashCode} method* must consistently return the same integer, provided no information* used in {@code equals} comparisons on the object is modified.* This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an* application to another execution of the same application.* <li>If two objects are equal according to the {@link* #equals(Object) equals} method, then calling the {@code* hashCode} method on each of the two objects must produce the* same integer result.* <li>It is <em>not</em> required that if two objects are unequal* according to the {@link #equals(Object) equals} method, then* calling the {@code hashCode} method on each of the two objects* must produce distinct integer results. However, the programmer* should be aware that producing distinct integer results for* unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables.* </ul>** @implSpec* As far as is reasonably practical, the {@code hashCode} method defined* by class {@code Object} returns distinct integers for distinct objects.** @return a hash code value for this object.* @see java.lang.Object#equals(java.lang.Object)* @see java.lang.System#identityHashCode*/@IntrinsicCandidatepublic native int hashCode();
hashCode方法的说明有以下几点:
hashCode方法用于返回对象的哈希码值。支持此方法是为了提高哈希表(如java.util.Hashtable提供的哈希表)的性能。hashCode在Object类中有native修饰,是本地方法,该方法的方法体不是Java实现的,是由C/C++实现的,最后编译为.dll文件,然后由Java调用。
hashCode方法重写时要满足如下几个要求。
- 如果两个对象调用
equals方法返回true,那么要求这两个对象的hashCode值一定是相等的。 - 如果两个对象的
hashCode值不相等,那么要求这两个对象调用equals方法一定是false。 - 如果两个对象的
hashCode值相等,那么这两个对象调用equals方法可能是true,也可能是false。
2、equals(Object)
判断引用相等使用==,两个对象内容相等使用equals,下面是Object equals代码:
/*** Indicates whether some other object is "equal to" this one.* <p>* The {@code equals} method implements an equivalence relation* on non-null object references:* <ul>* <li>It is <i>reflexive</i>: for any non-null reference value* {@code x}, {@code x.equals(x)} should return* {@code true}.* <li>It is <i>symmetric</i>: for any non-null reference values* {@code x} and {@code y}, {@code x.equals(y)}* should return {@code true} if and only if* {@code y.equals(x)} returns {@code true}.* <li>It is <i>transitive</i>: for any non-null reference values* {@code x}, {@code y}, and {@code z}, if* {@code x.equals(y)} returns {@code true} and* {@code y.equals(z)} returns {@code true}, then* {@code x.equals(z)} should return {@code true}.* <li>It is <i>consistent</i>: for any non-null reference values* {@code x} and {@code y}, multiple invocations of* {@code x.equals(y)} consistently return {@code true}* or consistently return {@code false}, provided no* information used in {@code equals} comparisons on the* objects is modified.* <li>For any non-null reference value {@code x},* {@code x.equals(null)} should return {@code false}.* </ul>** <p>* An equivalence relation partitions the elements it operates on* into <i>equivalence classes</i>; all the members of an* equivalence class are equal to each other. Members of an* equivalence class are substitutable for each other, at least* for some purposes.** @implSpec* The {@code equals} method for class {@code Object} implements* the most discriminating possible equivalence relation on objects;* that is, for any non-null reference values {@code x} and* {@code y}, this method returns {@code true} if and only* if {@code x} and {@code y} refer to the same object* ({@code x == y} has the value {@code true}).** In other words, under the reference equality equivalence* relation, each equivalence class only has a single element.** @apiNote* It is generally necessary to override the {@link #hashCode() hashCode}* method whenever this method is overridden, so as to maintain the* general contract for the {@code hashCode} method, which states* that equal objects must have equal hash codes.** @param obj the reference object with which to compare.* @return {@code true} if this object is the same as the obj* argument; {@code false} otherwise.* @see #hashCode()* @see java.util.HashMap*/public boolean equals(Object obj) {return (this == obj);}
从代码可以知道,Object的equals与==的效果是一样的。我们希望判断的是两个对象的属性内容是否相等,所以往往需要重写equals方法。
重写equals方法时,代码主要分为三个方面:
- 两个对象的地址一样,肯定返回
true。 - 两个对象的类型不一样,肯定返回
false。 - 两个对象被选择比较的属性信息完全一样,肯定返回
true,有不一样的则返回false。
关于equals方法的重写,Java规定一定要遵循如下几个原则。
- 自反性:
x.equals(x)返回true。 - 传递性:
x.equals(y)返回true,y.equals(z)返回true,则x.equals(z)也应该返回true。 - 一致性:只要参与
equals方法比较的属性值没有修改,那么无论何时调用equals方法的结果应该都是一致的。 - 对称性:
x.equals(y)与y.equals(x)的结果应该一致。 非空对象.equals(null)的结果一定是false。
关于==和equals方法的区别,总结如下。
==可用于判断两个基本数据类型变量,也可以用于判断两个引用类型变量。但都需要保证判断双方的类型一致或兼容,否则编译报错。equals方法只能用于判断引用类型的变量,因为只有对象才有方法,默认判断的是对象的内容,如果重写Object类的equals方法,则一般判断的是对象的内容是否相等。
6.4 getClass方法
我们知道对象有静态类型(编译时类型)和动态类型(运行时类型),静态类型和动态类型可能不一样。静态类型比较好判断,就是变量声明时的类型,那么动态类型呢?动态类型需要使用getClass方法。Object getClass代码方法如下:
/*** Returns the runtime class of this {@code Object}. The returned* {@code Class} object is the object that is locked by {@code* static synchronized} methods of the represented class.** <p><b>The actual result type is {@code Class<? extends |X|>}* where {@code |X|} is the erasure of the static type of the* expression on which {@code getClass} is called.</b> For* example, no cast is required in this code fragment:</p>** <p>* {@code Number n = 0; }<br>* {@code Class<? extends Number> c = n.getClass(); }* </p>** @return The {@code Class} object that represents the runtime* class of this object.* @jls 15.8.2 Class Literals*/@IntrinsicCandidatepublic final native Class<?> getClass();
6.5 clone方法
如果需要复制一个对象,则可以使用Object类提供的clone方法。该方法在Object类中的源码如下所示:
/*** Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning* of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general* intent is that, for any object {@code x}, the expression:* <blockquote>* <pre>* x.clone() != x</pre></blockquote>* will be true, and that the expression:* <blockquote>* <pre>* x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()</pre></blockquote>* will be {@code true}, but these are not absolute requirements.* While it is typically the case that:* <blockquote>* <pre>* x.clone().equals(x)</pre></blockquote>* will be {@code true}, this is not an absolute requirement.* <p>* By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling* {@code super.clone}. If a class and all of its superclasses (except* {@code Object}) obey this convention, it will be the case that* {@code x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()}.* <p>* By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent* of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence,* it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned* by {@code super.clone} before returning it. Typically, this means* copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure"* of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these* objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only* primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually* the case that no fields in the object returned by {@code super.clone}* need to be modified.** @implSpec* The method {@code clone} for class {@code Object} performs a* specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does* not implement the interface {@code Cloneable}, then a* {@code CloneNotSupportedException} is thrown. Note that all arrays* are considered to implement the interface {@code Cloneable} and that* the return type of the {@code clone} method of an array type {@code T[]}* is {@code T[]} where T is any reference or primitive type.* Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this* object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of* the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the* contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method* performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.* <p>* The class {@code Object} does not itself implement the interface* {@code Cloneable}, so calling the {@code clone} method on an object* whose class is {@code Object} will result in throwing an* exception at run time.** @return a clone of this instance.* @throws CloneNotSupportedException if the object's class does not* support the {@code Cloneable} interface. Subclasses* that override the {@code clone} method can also* throw this exception to indicate that an instance cannot* be cloned.* @see java.lang.Cloneable*/@IntrinsicCandidateprotected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
调用该方法时可以创建并返回当前对象的一个副本。从源码中可以发现该方法的权限修饰符是protected,说明默认Object类中的clone方法只能在java.lang包或其他包的子类中调用。因此,如果在测试类中要通过自定义类的对象来调用clone方法,则必须重写该方法。这里要注意的是,如果要重写该方法,则子类必须实现java.lang.Cloneable接口,否则会抛出CloneNotSupportedException。
6.6 finalize方法
Object类中finalize方法的源码如下所示:
/*** Called by the garbage collector on an object when garbage collection* determines that there are no more references to the object.* A subclass overrides the {@code finalize} method to dispose of* system resources or to perform other cleanup.* <p>* <b>When running in a Java virtual machine in which finalization has been* disabled or removed, the garbage collector will never call* {@code finalize()}. In a Java virtual machine in which finalization is* enabled, the garbage collector might call {@code finalize} only after an* indefinite delay.</b>* <p>* The general contract of {@code finalize} is that it is invoked* if and when the Java virtual* machine has determined that there is no longer any* means by which this object can be accessed by any thread that has* not yet died, except as a result of an action taken by the* finalization of some other object or class which is ready to be* finalized. The {@code finalize} method may take any action, including* making this object available again to other threads; the usual purpose* of {@code finalize}, however, is to perform cleanup actions before* the object is irrevocably discarded. For example, the finalize method* for an object that represents an input/output connection might perform* explicit I/O transactions to break the connection before the object is* permanently discarded.* <p>* The {@code finalize} method of class {@code Object} performs no* special action; it simply returns normally. Subclasses of* {@code Object} may override this definition.* <p>* The Java programming language does not guarantee which thread will* invoke the {@code finalize} method for any given object. It is* guaranteed, however, that the thread that invokes finalize will not* be holding any user-visible synchronization locks when finalize is* invoked. If an uncaught exception is thrown by the finalize method,* the exception is ignored and finalization of that object terminates.* <p>* After the {@code finalize} method has been invoked for an object, no* further action is taken until the Java virtual machine has again* determined that there is no longer any means by which this object can* be accessed by any thread that has not yet died, including possible* actions by other objects or classes which are ready to be finalized,* at which point the object may be discarded.* <p>* The {@code finalize} method is never invoked more than once by a Java* virtual machine for any given object.* <p>* Any exception thrown by the {@code finalize} method causes* the finalization of this object to be halted, but is otherwise* ignored.** @apiNote* Classes that embed non-heap resources have many options* for cleanup of those resources. The class must ensure that the* lifetime of each instance is longer than that of any resource it embeds.* {@link java.lang.ref.Reference#reachabilityFence} can be used to ensure that* objects remain reachable while resources embedded in the object are in use.* <p>* A subclass should avoid overriding the {@code finalize} method* unless the subclass embeds non-heap resources that must be cleaned up* before the instance is collected.* Finalizer invocations are not automatically chained, unlike constructors.* If a subclass overrides {@code finalize} it must invoke the superclass* finalizer explicitly.* To guard against exceptions prematurely terminating the finalize chain,* the subclass should use a {@code try-finally} block to ensure* {@code super.finalize()} is always invoked. For example,* <pre>{@code @Override* protected void finalize() throws Throwable {* try {* ... // cleanup subclass state* } finally {* super.finalize();* }* }* }</pre>** @deprecated Finalization is deprecated and subject to removal in a future* release. The use of finalization can lead to problems with security,* performance, and reliability.* See <a href="https://openjdk.org/jeps/421">JEP 421</a> for* discussion and alternatives.* <p>* Subclasses that override {@code finalize} to perform cleanup should use* alternative cleanup mechanisms and remove the {@code finalize} method.* Use {@link java.lang.ref.Cleaner} and* {@link java.lang.ref.PhantomReference} as safer ways to release resources* when an object becomes unreachable. Alternatively, add a {@code close}* method to explicitly release resources, and implement* {@code AutoCloseable} to enable use of the {@code try}-with-resources* statement.* <p>* This method will remain in place until finalizers have been removed from* most existing code.** @throws Throwable the {@code Exception} raised by this method* @see java.lang.ref.WeakReference* @see java.lang.ref.PhantomReference* @jls 12.6 Finalization of Class Instances*/@Deprecated(since="9", forRemoval=true)protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
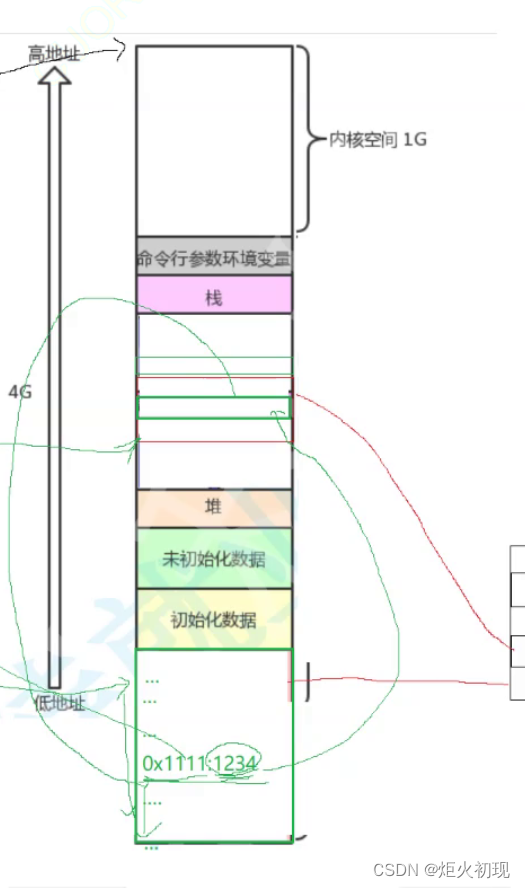
finalize方法是Object类中的protected方法,子类可以重写该方法以实现资源清理工作,GC在回收对象之前会调用该方法,即该方法不是由开发人员手动调用的。当对象变成不可达时,即对象成为需要被回收的垃圾对象时,GC会判断该对象是否覆盖了finalize方法,若未覆盖,则直接将其回收。若对象未执行过finalize方法,则将其放入F-Queue队列,由一个低优先级线程执行该队列中对象的finalize方法。执行完finalize方法后,GC会再次判断该对象是否可达,若不可达,则进行回收,否则对象复活,复活后的对象下次回收时,将不再放入F-Queue队列,即不再执行其finalize方法。Java语言规范并不能保证finalize方法会被及时执行,而且根本不能保证它们会被执行。所以不建议用finalize方法完成非内存资源清理工作以外的任务。
马俊昌.Java编程的逻辑[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2018. ↩︎
尚硅谷教育.剑指Java:核心原理与应用实践[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2023. ↩︎
相关文章:

十五、Object 类
文章目录 Object 类6.1 public Object()6.2 toString方法6.3 hashCode和equals(Object)6.4 getClass方法6.5 clone方法6.6 finalize方法 Object 类 本文为书籍《Java编程的逻辑》1和《剑指Java:核心原理与应用实践》2阅读笔记 java.lang.Object类是类层次结构的根…...
计算机网络——06分组延时、丢失和吞吐量
分组延时、丢失和吞吐量 分组丢失和延时是怎样发生的 在路由器缓冲区的分组队列 分组到达链路的速率超过了链路输出的能力分组等待排到队头、被传输 延时原因: 当当前链路有别的分组进行传输,分组没有到达队首,就会进行排队,从…...
[C#] 如何调用Python脚本程序
为什么需要C#调用python? 有以下几个原因需要C#调用Python: Python拥有丰富的生态系统:Python有很多强大的第三方库和工具,可以用于数据科学、机器学习、自然语言处理等领域。通过C#调用Python,可以利用Python的生态系…...

AlmaLinux更换鼠标样式为Windows样式
文章目录 前言先看看条件与依赖第一步:测试最终效果第二步:使用CursorXP修改鼠标样式CurosrXP安装CursorXP使用 第三步:Linux端环境搭建与命令执行UbuntuFedora其他系统均失败 第四步:应用主题 前言 只不过是突发奇想,…...
BUGKU-WEB 留言板
题目描述 题目无需登录后台!需要xss平台接收flag, http协议需要http协议的xss平台打开场景后界面如下: 解题思路 看到此类的题目,应该和存储型xss有关,也就是将恶意代码保存到服务器端即然在服务器端,那就…...
Linux之动静态库
今天我们来讲动静态库! 首先我们来粗粒度的划分一下动态库和静态库。 动态库就是只有一份库文件,所有想用该库的文件与改库文件建立链接,然后使用。这样可以提高代码复用率,避免重复拷贝产生没必要的内存消耗。 静态库…...

手机常亮屏不自动灭屏
一. 基础知识介绍 1. WakeLock(休眠锁) WakeLock用于保持设备的唤醒状态,有些情况下,即时用户不操作App,我们也需要保持屏幕处于唤醒状态,以保证用户体验,比如视频类APP和计步类APP,…...
JVM(1)基础篇
1 初始JVM 1.1 什么是JVM JVM 全称是 Java Virtual Machine,中文译名 Java虚拟机。JVM 本质上是一个运行在计算机上的程序,他的职责是运行Java字节码文件。 Java源代码执行流程如下: 分为三个步骤: 编写Java源代码文件。 使用…...

相机图像质量研究(12)常见问题总结:光学结构对成像的影响--炫光
系列文章目录 相机图像质量研究(1)Camera成像流程介绍 相机图像质量研究(2)ISP专用平台调优介绍 相机图像质量研究(3)图像质量测试介绍 相机图像质量研究(4)常见问题总结:光学结构对成像的影响--焦距 相机图像质量研究(5)常见问题总结:光学结构对成…...
[OPEN SQL] 删除数据
DELETE语句用于删除数据库表中的数据 本次操作使用的数据库表为SCUSTOM,其字段内容如下所示 航班用户(SCUSTOM) 需要删除以下数据 1.删除单条数据 语法格式 DELETE <dbtab> FROM <wa>. DELETE <dbtab> FROM TABLE <itab>. DELETE FROM &…...
C语言第二十五弹---字符函数和字符串函数(上)
✨个人主页: 熬夜学编程的小林 💗系列专栏: 【C语言详解】 【数据结构详解】 目录 1、字符分类函数 2、字符转换函数 3、strlen的使用和模拟实现 4、strcpy 的模拟实现 5、strcat 的模拟实现 6、strcmp 的模拟实现 7、strncpy 函数的使用 总结…...
)
寒假学习记录16:Express框架(Node)
后续会补充 1.引入express 1.先下载express框架 创建一个package.json格式的文件,里面写入 {"dependencies": {"express": "~4.16.1" //express版本号} } 然后打开终端输入 npm i 2.引入express模块 const express require(&quo…...
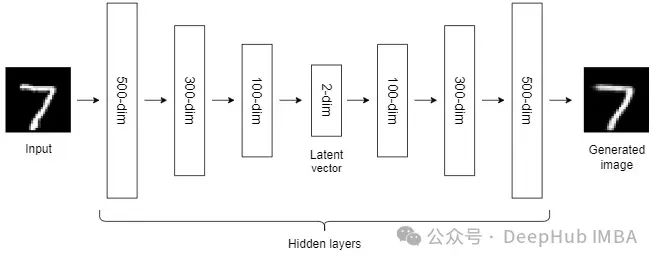
机器学习中的10种非线性降维技术对比总结
降维意味着我们在不丢失太多信息的情况下减少数据集中的特征数量,降维算法属于无监督学习的范畴,用未标记的数据训练算法。 尽管降维方法种类繁多,但它们都可以归为两大类:线性和非线性。 线性方法将数据从高维空间线性投影到低维空间(因此…...

[ubuntu]split命令分割文件
split 命令 $ split --help Usage: split [OPTION]... [INPUT [PREFIX]] Output fixed-size pieces of INPUT to PREFIXaa, PREFIXab, ...; default size is 1000 lines, and default PREFIX is x. With no INPUT, or when INPUT is -, read standard input.Mandatory argume…...

《小强升职记:时间管理故事书》阅读笔记
目录 前言 一、你的时间都去哪儿了 1.1 你真的很忙吗 1.2 如何记录和分析时间日志 1.3 如何找到自己的价值观 二、无压工作法 2.1 传说中的“四象限法则 2.2 衣柜整理法 三、行动时遇到问题怎么办? 3.1 臣服与拖延 3.2 如何做到要事第一? 3.…...
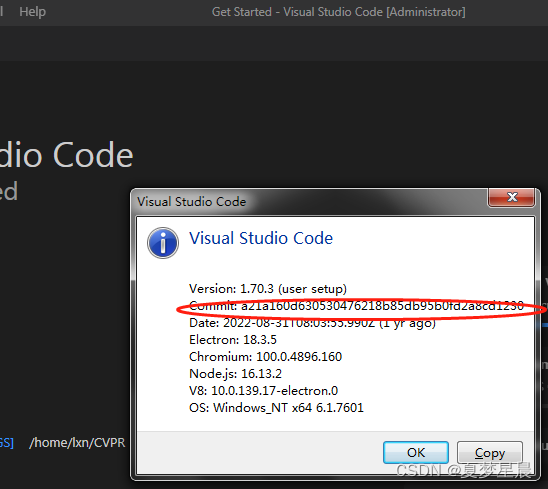
visual studio code could not establish connection to *: XHR failed
vscode远程连接服务器时,输入密码,又重新提示输入密码,就这样循环了好几次,然后会报上述的错误。由于我是window系统,我用cmd,然后ssh */你的IP地址/*发现可以远程到服务器上,但是通过Vscode就不…...

JVM-面试题
一、对象 1、对象创建 类加载检查 虚拟机遇到一条new指令时,首先将去检查这个指令的参数是否能在常量池定位到类的符号引用,并且检查这个符号引用代表的类是否被加载、解析和初始化过。若没有,必须先执行类加载过程。分配内存 类加载检查通过后,jvm将为新生对象分配内存,…...

计算机网络——多媒体网络
前些天发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站 通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家, 跳转到网站 小程一言 我的计算机网络专栏,是自己在计算机网络学习过程中的学习笔记与心得,在参考相关教材,网络搜素…...
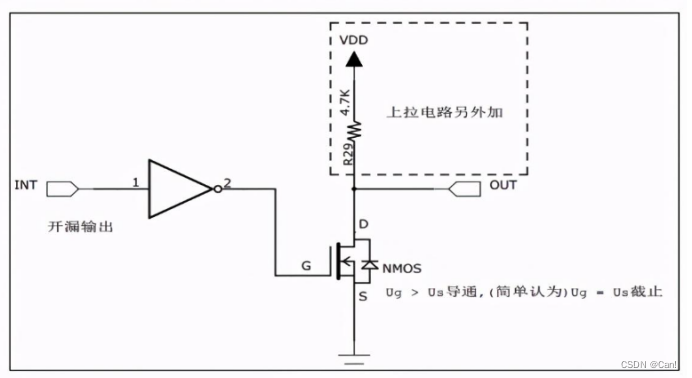
GPIO八种工作模式
目录 一、推挽输出 二、开漏输出 三、复用推挽输出 四、复用开漏输出 五、浮空输入 六、上拉输入 七、下拉输入 八、模拟输入 GPIO八种配置模式,原理和使用场景,硬件原理如下图: 一、推挽输出 1、 原理 当控制栅极为低电平时&#x…...
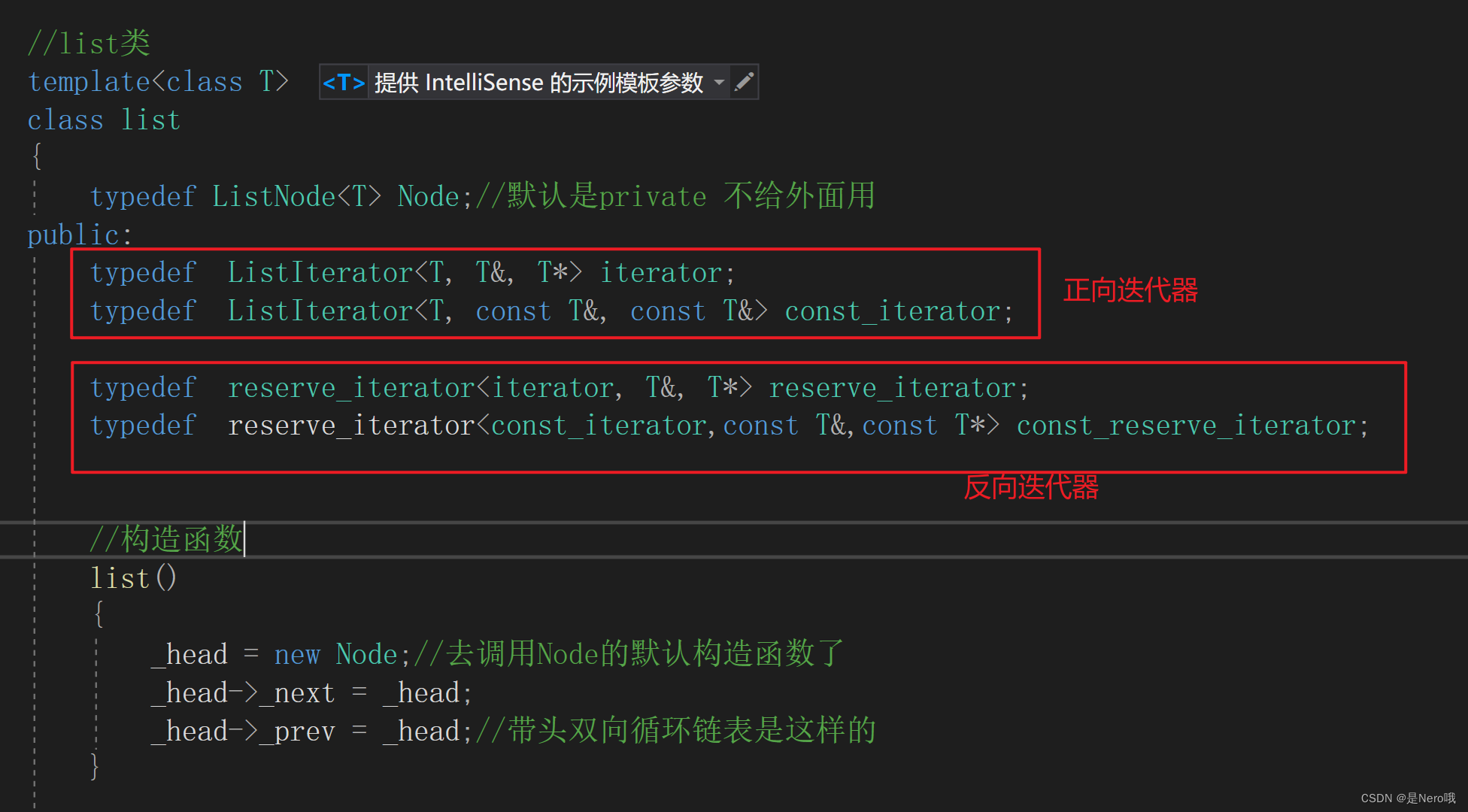
C++初阶:适合新手的手撕list(模拟实现list)
上次讲了常用的接口:今天就来进行模拟实现啦 文章目录 1.基本结构与文件规划2.空参构造函数(constructor)3.完善迭代器(iterator)(begin(),end())4.List Capacity(size(),empty())4.增删改查(push_back,pop_back,pop_f…...

基于距离变化能量开销动态调整的WSN低功耗拓扑控制开销算法matlab仿真
目录 1.程序功能描述 2.测试软件版本以及运行结果展示 3.核心程序 4.算法仿真参数 5.算法理论概述 6.参考文献 7.完整程序 1.程序功能描述 通过动态调整节点通信的能量开销,平衡网络负载,延长WSN生命周期。具体通过建立基于距离的能量消耗模型&am…...

多种风格导航菜单 HTML 实现(附源码)
下面我将为您展示 6 种不同风格的导航菜单实现,每种都包含完整 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 代码。 1. 简约水平导航栏 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"zh-CN"> <head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport&qu…...

【C++从零实现Json-Rpc框架】第六弹 —— 服务端模块划分
一、项目背景回顾 前五弹完成了Json-Rpc协议解析、请求处理、客户端调用等基础模块搭建。 本弹重点聚焦于服务端的模块划分与架构设计,提升代码结构的可维护性与扩展性。 二、服务端模块设计目标 高内聚低耦合:各模块职责清晰,便于独立开发…...

LeetCode - 199. 二叉树的右视图
题目 199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 右视图是指从树的右侧看,对于每一层,只能看到该层最右边的节点。实现思路是: 使用深度优先搜索(DFS)按照"根-右-左"的顺序遍历树记录每个节点的深度对于…...

CSS设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整
width: fit-content 是 CSS 中的一个属性值,用于设置元素的宽度根据其内容自动调整,确保宽度刚好容纳内容而不会超出。 效果对比 默认情况(width: auto): 块级元素(如 <div>)会占满父容器…...

Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析
Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析 一、第一轮提问(基础概念问题) 1. 请解释Spring框架的核心容器是什么?它在Spring中起到什么作用? Spring框架的核心容器是IoC容器&#…...

安宝特案例丨Vuzix AR智能眼镜集成专业软件,助力卢森堡医院药房转型,赢得辉瑞创新奖
在Vuzix M400 AR智能眼镜的助力下,卢森堡罗伯特舒曼医院(the Robert Schuman Hospitals, HRS)凭借在无菌制剂生产流程中引入增强现实技术(AR)创新项目,荣获了2024年6月7日由卢森堡医院药剂师协会࿰…...
uniapp 小程序 学习(一)
利用Hbuilder 创建项目 运行到内置浏览器看效果 下载微信小程序 安装到Hbuilder 下载地址 :开发者工具默认安装 设置服务端口号 在Hbuilder中设置微信小程序 配置 找到运行设置,将微信开发者工具放入到Hbuilder中, 打开后出现 如下 bug 解…...

uniapp 实现腾讯云IM群文件上传下载功能
UniApp 集成腾讯云IM实现群文件上传下载功能全攻略 一、功能背景与技术选型 在团队协作场景中,群文件共享是核心需求之一。本文将介绍如何基于腾讯云IMCOS,在uniapp中实现: 群内文件上传/下载文件元数据管理下载进度追踪跨平台文件预览 二…...
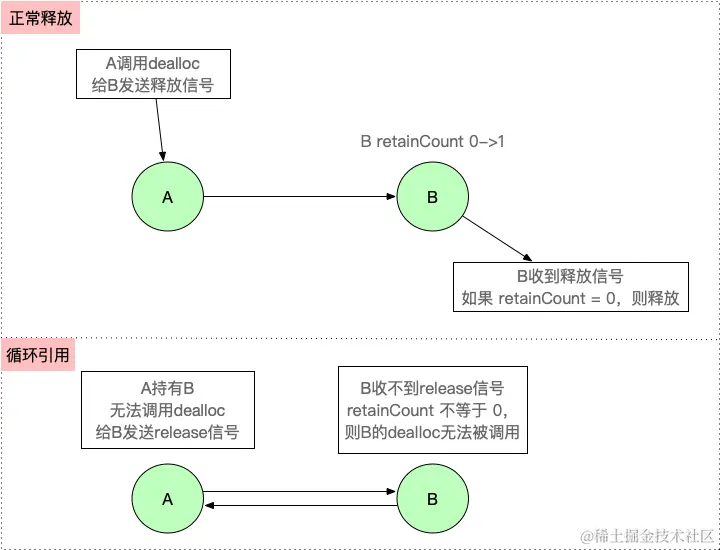
【iOS】 Block再学习
iOS Block再学习 文章目录 iOS Block再学习前言Block的三种类型__ NSGlobalBlock____ NSMallocBlock____ NSStackBlock__小结 Block底层分析Block的结构捕获自由变量捕获全局(静态)变量捕获静态变量__block修饰符forwarding指针 Block的copy时机block作为函数返回值将block赋给…...
