Spring El表达式官方文档学习
文章目录
- 推荐
- 一、概述
- 1、什么是SpEL
- 2、SpEL能做什么
- 二、SpEL表达式使用
- 1、文字表达式
- 2、属性, 数组, List, Map,和 索引
- (1)属性操作
- (2)数组和List
- (3)Map
- 3、内嵌List
- 4、内嵌Map
- 5、构建数组
- 6、调用类的方法
- 7、SpEL操作符
- (1)标准运算符
- (2)instanceof 和 正则表达式的匹配操作符
- (3)操作符的英文等价标识
- (4)逻辑运算符
- (5)数学运算符
- (6)赋值运算符
- 8、获取类的类型
- 9、调用类构造器
- 10、SpEL变量
- (1)基本使用
- (2)#this 和 #root变量
- 11、调用类静态方法
- 12、Bean引用
- 13、三元运算符(If-Then-Else)
- 14、Elvis操作符
- 15、安全导航操作员
- 16、集合选择
- 17、集合投影
- 18、表达式模板
- 三、练习实例
- 公用实体类
- Society
- Inventor
- PlaceOfBirth
- SPEL01
- Test01
- Demo类
- MyMessage类
- Simple类
- SPEL02
- xml配置文件中使用
- anno注解中使用
- SPEL03
- Test01
- SPEL04
- InlineListsTest
- InlineMaps
- ArrayConstructionTest
- MethodsTest
- OperatorsTest
- TypesTest
- ConstructorsTest
- VariablesTest
- FunctionTest
- BeanReferencesTest
- TernaryOperatorTest
- ElvisOperatorTest
- SafeNavigationOperator
- CollectionSelection
- CollectionProjectionTest
- ExpressionTemplatingTest
推荐
Spring SPEL表达式语言的深入学习与使用【一万字】
Spring SpEL表达式的使用
Spring-SpEL表达式超级详细使用全解
spring-expressions官方文档
下面文档基本就是官方文档的翻译,源自:Spring-SpEL表达式超级详细使用全解,做了一丢丢的练习实践补充(官方文档中的所有示例)
一、概述
1、什么是SpEL
SpEL(Spring Expression Language)是Spring框架中用于表达式语言的一种方式。它类似于其他编程语言中的表达式语言,用于在运行时计算值或执行特定任务。
SpEL提供了一种简单且强大的方式来访问和操作对象的属性、调用对象的方法,以及实现运算、条件判断等操作。它可以被用于XML和注解配置中,可以用于许多Spring框架中的特性,如依赖注入、AOP、配置文件等。
SpEL表达式可以在字符串中进行定义,使用特殊的语法和符号来表示特定的操作。例如,可以使用${expression}来表示一个SpEL表达式,其中expression是具体的SpEL语句。
SpEL支持各种操作和函数,包括算术运算、逻辑运算、条件判断、正则表达式匹配、集合操作等。它还支持访问上下文中的变量和参数,以及调用对象的方法。
2、SpEL能做什么
SpEL表达式具有广泛的功能,以下是一些SpEL表达式可以做的事情:
- 访问对象属性:SpEL表达式可以通过对象引用来访问对象的属性,例如${object.property}。
- 调用方法:SpEL表达式可以调用对象的方法,例如${object.method()}。
- 进行算术运算:SpEL表达式支持各种算术运算符,如加法、减法、乘法和除法。
- 进行逻辑运算:SpEL表达式支持逻辑运算符,如与、或、非等。
- 进行条件判断:SpEL表达式可以进行条件判断,例如通过if语句判断条件,并执行相应的操作。
- 访问集合元素和属性:SpEL表达式可以通过索引或键来访问集合中的元素或对象的属性。
- 执行正则表达式匹配:SpEL表达式可以执行正则表达式匹配,并返回匹配结果。
- 访问上下文变量和参数:SpEL表达式可以访问上下文中的变量和方法参数。
- 进行类型转换:SpEL表达式可以进行类型转换操作,将一个对象转换为另一种类型。
- 支持特殊操作符:SpEL表达式支持一些特殊的操作符,如Elvis操作符(?:)、安全导航操作符(?.)等。
总的来说,SpEL表达式可以用于在运行时计算值、执行任务和操作对象,提供了灵活且强大的表达能力,广泛应用于Spring框架中的各种功能和配置中。
二、SpEL表达式使用
1、文字表达式
支持的文字表达式类型有字符串、数值(int、real、hex)、布尔和null。字符串由单引号分隔。若要将单引号本身放在字符串中,请使用两个单引号字符。
通常来说,不会单纯的定义一个简单的文字表达式,而是通过方法调用等等复杂的操作,来完成一个功能:
// 定义Parser,可以定义全局的parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 获取字符串 "Hello World"
String helloWorld = (String) parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'").getValue();
// double类型 6.0221415E23
double avogadrosNumber = (Double) parser.parseExpression("6.0221415E+23").getValue();// int类型 2147483647
int maxValue = (Integer) parser.parseExpression("0x7FFFFFFF").getValue();
// true
boolean trueValue = (Boolean) parser.parseExpression("true").getValue();
// null
Object nullValue = parser.parseExpression("null").getValue();
2、属性, 数组, List, Map,和 索引
(1)属性操作
注意!属性名的第一个字母不区分大小写。
// 定义Parser,可以定义全局的parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 注意!属性名的第一个字母不区分大小写。 birthdate.year等效于Birthdate.Year
// 取出Inventor 中,birthdate属性的year属性
Inventor zhangsan = new Inventor("zhangsan", new Date(), "China");
// 定义StandardEvaluationContext ,传入一个操作对象
StandardEvaluationContext zhangsanContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(zhangsan);
int year = (Integer) parser.parseExpression("birthdate.year + 1900").getValue(zhangsanContext);
System.out.println(year); // 2023//取出Inventor的placeOfBirth的city属性
PlaceOfBirth placeOfBirth = new PlaceOfBirth("长沙", "中国");
zhangsan.setPlaceOfBirth(placeOfBirth);
String city = (String) parser.parseExpression("placeOfBirth.City").getValue(zhangsanContext);
System.out.println(city); // 长沙
(2)数组和List
数组和List的内容是通过使用方括号符号获得的。
// 定义Parser,可以定义全局的parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// 省略数据初始化// 取出tesla对象的inventions 第四个数据
String invention = parser.parseExpression("inventions[3]").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);// 取出ieee对象的第一个Member的name属性
String name = parser.parseExpression("Members[0].Name").getValue(context, ieee, String.class);// 取出ieee对象的第一个Member中的第七个Inventions
String invention = parser.parseExpression("Members[0].Inventions[6]").getValue(context, ieee, String.class);
(3)Map
Map操作是通过key来获取的
// 取出societyContext的Officers中的key为president的值
Inventor pupin = parser.parseExpression("Officers['president']").getValue(societyContext, Inventor.class);String city = parser.parseExpression("Officers['president'].PlaceOfBirth.City").getValue(societyContext, String.class);// Officers中key为advisors的值取第一个
parser.parseExpression("Officers['advisors'][0].PlaceOfBirth.Country").setValue(societyContext, "Croatia");
3、内嵌List
可以使用{}符号在表达式中直接表示List。{}本身意味着一个空列表。
// 定义Parser,可以定义全局的parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// [1, 2, 3, 4]
List numbers = (List) parser.parseExpression("{1,2,3,4}").getValue(context);
System.out.println(numbers);// 嵌套: [[a, b], [x, y]]
List listOfLists = (List) parser.parseExpression("{{'a','b'},{'x','y'}}").getValue(context);
System.out.println(listOfLists);
4、内嵌Map
使用{key:value}符号在表达式中表示Map。{:}意味着空Map。
// 定义Parser,可以定义全局的parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// {name=Nikola, dob=10-July-1856}
Map inventorInfo = (Map) parser.parseExpression("{name:'Nikola',dob:'10-July-1856'}").getValue(context);
System.out.println(inventorInfo);// 嵌套:{name={first=Nikola, last=Tesla}, dob={day=10, month=July, year=1856}}
Map mapOfMaps = (Map) parser.parseExpression("{name:{first:'Nikola',last:'Tesla'},dob:{day:10,month:'July',year:1856}}").getValue(context);
System.out.println(mapOfMaps);// List与Map可以嵌套使用,互相结合。
// 嵌套:[{name={first=Nikola, last=Tesla}}, {dob={day=10, month=July, year=1856}}]
List listOfMaps = (List) parser.parseExpression("{{name:{first:'Nikola',last:'Tesla'}},{dob:{day:10,month:'July',year:1856}}}").getValue(context);
System.out.println(listOfMaps);
5、构建数组
多维数组不提供初始化方式。
// 定义Parser,可以定义全局的parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();int[] numbers1 = (int[]) parser.parseExpression("new int[4]").getValue(context);// 数组并初始化
int[] numbers2 = (int[]) parser.parseExpression("new int[]{1,2,3}").getValue(context);// 多维数组
int[][] numbers3 = (int[][]) parser.parseExpression("new int[4][5]").getValue(context);
6、调用类的方法
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 调用substring方法
String bc = parser.parseExpression("'abc'.substring(1, 3)").getValue(String.class);// 调用societyContext中对象的isMember方法,并传值。
StandardEvaluationContext societyContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(society);
boolean isMember = parser.parseExpression("isMember('Mihajlo Pupin')").getValue(societyContext, Boolean.class);
7、SpEL操作符
(1)标准运算符
使用标准运算符表示法支持关系运算符(等于、不等于、小于、小于或等于、大于和大于或等于)。
null不被视为任何东西(即不为零)。因此,任何其他值总是大于null (X > null总是为真),并且没有任何其他值小于零(X < null总是为假)。
ExpressionParser parser = newSpelExpressionParser();// evaluates to true
boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression("2 == 2").getValue(Boolean.class);// evaluates to false
boolean falseValue = parser.parseExpression("2 < -5.0").getValue(Boolean.class);// evaluates to true
boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression("'black' < 'block'").getValue(Boolean.class);
(2)instanceof 和 正则表达式的匹配操作符
使用基本类型时要小心,因为它们会立即被装箱为包装器类型,所以1 instanceof T(int)会计算为false,而1 instanceof T(Integer)会计算为true。
// evaluates to false
boolean falseValue = parser.parseExpression("'xyz' instanceof T(Integer)").getValue(Boolean.class);// evaluates to true
boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression("'5.00' matches '^-?\\d+(\\.\\d{2})?$'").getValue(Boolean.class);//evaluates to false
boolean falseValue = parser.parseExpression("'5.0067' matches '^-?\\d+(\\.\\d{2})?$'").getValue(Boolean.class);
(3)操作符的英文等价标识
每个符号操作符也可以被指定为纯字母的等价物。这避免了所使用的符号对于嵌入表达式的文档类型具有特殊含义的问题(例如在XML文档中)。所有文本操作符都不区分大小写。对应的文本是: lt (<) gt (>) le (<=) ge (>=) eq (==) ne (!=) div (/) mod (%) not (!)
(4)逻辑运算符
SpEL支持以下逻辑运算符:and、or、not
// 结果: false
boolean falseValue = parser.parseExpression("true and false").getValue(Boolean.class);// 调用方法并根据方法返回值判断
String expression = "isMember('Nikola Tesla') and isMember('Mihajlo Pupin')";
boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression(expression).getValue(societyContext, Boolean.class);// -- OR --
boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression("true or false").getValue(Boolean.class);// 调用方法并根据方法返回值判断
String expression = "isMember('Nikola Tesla') or isMember('Albert Einstein')";
boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression(expression).getValue(societyContext, Boolean.class);// -- NOT --
// 取反
boolean falseValue = parser.parseExpression("!true").getValue(Boolean.class);// -- AND and NOT --
String expression = "isMember('Nikola Tesla') and !isMember('Mihajlo Pupin')";
boolean falseValue = parser.parseExpression(expression).getValue(societyContext, Boolean.class);
(5)数学运算符
可以对数字和字符串使用加法运算符。 只能对数字使用减法、乘法和除法运算符。 也可以使用模数(%)和指数幂(^)运算符。 强制执行标准运算符优先级。
// Addition
int two = parser.parseExpression("1 + 1").getValue(Integer.class); // 2String testString = parser.parseExpression("'test' + ' ' + 'string'").getValue(String.class); // 'test string'// Subtraction
int four = parser.parseExpression("1 - -3").getValue(Integer.class); // 4double d = parser.parseExpression("1000.00 - 1e4").getValue(Double.class); // -9000// Multiplication
int six = parser.parseExpression("-2 * -3").getValue(Integer.class); // 6double twentyFour = parser.parseExpression("2.0 * 3e0 * 4").getValue(Double.class); // 24.0// Division
int minusTwo = parser.parseExpression("6 / -3").getValue(Integer.class); // -2double one = parser.parseExpression("8.0 / 4e0 / 2").getValue(Double.class); // 1.0// Modulus
int three = parser.parseExpression("7 % 4").getValue(Integer.class); // 3int one = parser.parseExpression("8 / 5 % 2").getValue(Integer.class); // 1// Operator precedence
int minusTwentyOne = parser.parseExpression("1+2-3*8").getValue(Integer.class); // -21
(6)赋值运算符
若要给对象设置属性,请使用赋值运算符(=)。这通常在对setValue的调用中完成,但也可以在对getValue的调用中完成。
// 定义Parser,可以定义全局的parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Inventor inventor = new Inventor();
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();parser.parseExpression("Name").setValue(context, inventor, "Aleksandar Seovic");System.out.println(inventor.getName()); // Aleksandar Seovic// 或者这样赋值
String aleks = parser.parseExpression("Name = 'Aleksandar Seovic2'").getValue(context, inventor, String.class);
System.out.println(inventor.getName()); // Aleksandar Seovic2
8、获取类的类型
可以使用特殊的T运算符来指定java.lang.Class的实例(类型)。静态方法也是通过使用这个操作符来调用的。
StandardEvaluationContext使用TypeLocator来查找类型,StandardTypeLocator(可以替换)是基于对java.lang包的理解而构建的。所以java.lang中类型的T()引用不需要使用全限定名,但是其他包中的类,必须使用全限定名。
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Class dateClass = parser.parseExpression("T(java.util.Date)").getValue(Class.class);Class stringClass = parser.parseExpression("T(String)").getValue(Class.class);boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression("T(java.math.RoundingMode).CEILING < T(java.math.RoundingMode).FLOOR").getValue(Boolean.class);
9、调用类构造器
使用new运算符调用构造函数。除了基本类型(int、float等)和String之外,所有类型都应该使用完全限定的类名。
Inventor einstein = p.parseExpression("new org.spring.samples.spel.inventor.Inventor('Albert Einstein', 'German')").getValue(Inventor.class);//创建一个新的Inventor,并且添加到members的list中
p.parseExpression("Members.add(new org.spring.samples.spel.inventor.Inventor('Albert Einstein', 'German'))").getValue(societyContext);
10、SpEL变量
(1)基本使用
可以使用#variableName语法在表达式中引用变量。通过在EvaluationContext实现上使用setVariable方法来设置变量
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Inventor tesla = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", "Serbian");EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();
context.setVariable("newName", "Mike Tesla"); // 设置变量// 获取变量newName,并将其赋值给name属性
parser.parseExpression("Name = #newName").getValue(context, tesla);
System.out.println(tesla.getName()); // "Mike Tesla"
(2)#this 和 #root变量
this变量引用当前的评估对象(根据该评估对象解析非限定引用)。
root变量总是被定义并引用根上下文对象。虽然#this可能会随着表达式的组成部分的计算而变化,但是#root总是指根。
// 创建一个Integer数组
List<Integer> primes = new ArrayList<Integer>();
primes.addAll(Arrays.asList(2,3,5,7,11,13,17));// create parser and set variable 'primes' as the array of integers
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();
context.setVariable("primes", primes);// numbers > 10 的 list
// evaluates to [11, 13, 17]
List<Integer> primesGreaterThanTen = (List<Integer>) parser.parseExpression("#primes.?[#this>10]").getValue(context);System.out.println(primesGreaterThanTen);
11、调用类静态方法
// 方法定义的方式
Method method = ...;EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();
context.setVariable("myFunction", method);
// 准备一个要调用的目标方法
public class StringUtils {public static String reverseString(String input) {StringBuilder backwards = new StringBuilder(input.length());for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) {backwards.append(input.charAt(input.length() - 1 - i));}return backwards.toString();}
}// 调用目标静态方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// 获取要调用的方法context.setVariable("reverseString",StringUtils.class.getDeclaredMethod("reverseString", String.class));// 调用String helloWorldReversed = parser.parseExpression("#reverseString('hello')").getValue(context, String.class);
}
12、Bean引用
如果已经用bean解析器配置了评估上下文,则可以使用@符号从表达式中查找bean。
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setBeanResolver(new MyBeanResolver());// 将调用MyBeanResolver 的 resolve(context,"something")
Object bean = parser.parseExpression("@something").getValue(context);
// 注意!MyBeanResolver 可以使用系统自带的BeanFactoryResolver,写成:
context.setBeanResolver(new BeanFactoryResolver(applicationContext));// BeanFactoryResolver的resolve方法,就是通过Bean的名称来获取Bean:
@Override
public Object resolve(EvaluationContext context, String beanName) throws AccessException {try {return this.beanFactory.getBean(beanName);}catch (BeansException ex) {throw new AccessException("Could not resolve bean reference against BeanFactory", ex);}
}
要访问工厂bean本身,应该在bean名称前加上&符号:
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setBeanResolver(new MyBeanResolver());// 将调用MyBeanResolver 的 resolve(context,"something")
Object bean = parser.parseExpression("&foo").getValue(context);
13、三元运算符(If-Then-Else)
// 使用示例
String falseString = parser.parseExpression("false ? 'trueExp' : 'falseExp'").getValue(String.class);
// name属性设置值
parser.parseExpression("Name").setValue(societyContext, "IEEE");
// 设置变量
societyContext.setVariable("queryName", "Nikola Tesla");// 三元运算符
expression = "isMember(#queryName)? #queryName + ' is a member of the ' " +"+ Name + ' Society' : #queryName + ' is not a member of the ' + Name + ' Society'";String queryResultString = parser.parseExpression(expression).getValue(societyContext, String.class);
// queryResultString = "Nikola Tesla is a member of the IEEE Society"
14、Elvis操作符
Elvis运算符是三元运算符语法的缩写,用于Groovy语言中。使用三元运算符语法时,通常需要将一个变量重复两次,如下例所示:
String name = "Elvis Presley";
String displayName = (name != null ? name : "Unknown");
可以使用Elvis运算符(因与Elvis的发型相似而得名)优化。以下示例显示了如何使用Elvis运算符:
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();String name = parser.parseExpression("name?:'Unknown'").getValue(String.class);
System.out.println(name); // 'Unknown'
更复杂的实例:
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();Inventor tesla = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", "Serbian");
String name = parser.parseExpression("Name?:'Elvis Presley'").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);
System.out.println(name); // Nikola Teslatesla.setName(null);
name = parser.parseExpression("Name?:'Elvis Presley'").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);
System.out.println(name); // Elvis Presley
15、安全导航操作员
安全导航操作符用于避免NullPointerException,来自Groovy语言。通常,当引用一个对象时,可能需要在访问该对象的方法或属性之前验证它不为null。为了避免这种情况,安全导航运算符返回null,而不是引发异常。以下示例显示了如何使用安全导航运算符:
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();Inventor tesla = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", "Serbian");
tesla.setPlaceOfBirth(new PlaceOfBirth("Smiljan"));String city = parser.parseExpression("PlaceOfBirth?.City").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);
System.out.println(city); // Smiljantesla.setPlaceOfBirth(null);
city = parser.parseExpression("PlaceOfBirth?.City").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);
System.out.println(city); // null - does not throw NullPointerException!!!
16、集合选择
// 语法.?[selectionExpression]
List<Inventor> list = (List<Inventor>) parser.parseExpression("Members.?[Nationality == 'Serbian']").getValue(societyContext);// 返回value小于27的值
Map newMap = parser.parseExpression("map.?[value<27]").getValue();
除了返回所有选定的元素之外,还可以只检索第一个或最后一个值。要获得匹配选择的第一个条目,语法是: .^[选择表达式].要获得最后一个匹配的选择,语法是: .$[选择表达式]。
17、集合投影
// 语法:.![projectionExpression]
// returns ['Smiljan', 'Idvor' ]
List placesOfBirth = (List)parser.parseExpression("Members.![placeOfBirth.city]");
18、表达式模板
// 通常使用#{}作为模板,与字符串拼接起来
String randomPhrase = parser.parseExpression("random number is #{T(java.lang.Math).random()}",new TemplateParserContext()).getValue(String.class);// evaluates to "random number is 0.7038186818312008"
// TemplateParserContext 的定义
public class TemplateParserContext implements ParserContext {public String getExpressionPrefix() {return "#{";}public String getExpressionSuffix() {return "}";}public boolean isTemplate() {return true;}
}
三、练习实例
公用实体类
Society
public class Society {private String name;public static String Advisors = "advisors";public static String President = "president";private List<Inventor> members = new ArrayList<Inventor>();private Map officers = new HashMap();public void setOfficers(Map map) {this.officers = map;}public List getMembers() {return members;}public Map getOfficers() {return officers;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public boolean isMember(String name) {for (Inventor inventor : members) {if (inventor.getName().equals(name)) {return true;}}return false;}}Inventor
public class Inventor {private String name;private String nationality;private String[] inventions;private Date birthdate;private PlaceOfBirth placeOfBirth;public Inventor(String name, String nationality) {GregorianCalendar c= new GregorianCalendar();this.name = name;this.nationality = nationality;this.birthdate = c.getTime();}public Inventor(String name, Date birthdate, String nationality) {this.name = name;this.nationality = nationality;this.birthdate = birthdate;}public Inventor() {}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getNationality() {return nationality;}public void setNationality(String nationality) {this.nationality = nationality;}public Date getBirthdate() {return birthdate;}public void setBirthdate(Date birthdate) {this.birthdate = birthdate;}public PlaceOfBirth getPlaceOfBirth() {return placeOfBirth;}public void setPlaceOfBirth(PlaceOfBirth placeOfBirth) {this.placeOfBirth = placeOfBirth;}public void setInventions(String[] inventions) {this.inventions = inventions;}public String[] getInventions() {return inventions;}
}PlaceOfBirth
public class PlaceOfBirth {private String city;private String country;public PlaceOfBirth(String city) {this.city=city;}public PlaceOfBirth(String city, String country) {this(city);this.country = country;}public String getCity() {return city;}public void setCity(String s) {this.city = s;}public String getCountry() {return country;}public void setCountry(String country) {this.country = country;}
}SPEL01
Test01
public class Test01 {@Testpublic void test01() {// 字面量表达式// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("'halo'");// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果Object value = expression.getValue();System.out.println(value);}@Testpublic void test02() {// 调用对象的方法// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.concat('!')");// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果String value = (String) exp.getValue();System.out.println(value);}@Testpublic void test03() {// 通过点操作符来访问对象的属性// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.bytes");// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果byte[] value = (byte[]) exp.getValue();System.out.println(value.length);}@Testpublic void test04() {// 通过点操作符来访问对象的多层属性// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.bytes.length");// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果int value = (int )exp.getValue();System.out.println(value);}@Testpublic void test05() {// 调用构造方法和成员方法// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("new String('hello world').toUpperCase()");// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果String value = (String )exp.getValue();System.out.println(value);// 这样就不用强转了String expValue = exp.getValue(String.class);System.out.println(expValue);}@Testpublic void test06() {// SpEL更常见的用法是提供一个字符串表达式,该字符串表达式针对特定的对象实例(也叫根对象)进行求值// 示例: 查询根对象属性, 并与字符串比较// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)// 这里会理解为root对象的name属性Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("name");// 创建1个对象, 后面把它作为rootObjectInventor rootObject = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", new GregorianCalendar(1856, 7, 9).getTime(), "Serbian");// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果// 这里传入了1个rootObject对象String value = (String)exp.getValue(rootObject);System.out.println(value);}@Testpublic void test07() {// spring el为EvaluationContext接口提供了2个实现:// SimpleEvaluationContext(功能受限)// StandardEvaluationContext(更加通用)// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 创建1个对象, 后面把它作为rootObjectSimple simple = new Simple();simple.booleanList.add(true);// 创建1个 SimpleEvaluationContext,并指定为只读属性绑定EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)//(这里完成对对simple对象的booleanList属性的第1个属性进行赋值)//(注意: 1. 使用Expression#setValue实现赋值// 2. 指定根对象, 其实就是表达式中没有限定的都从根对象上找// 3. 会完成自动类型转换, 其实就是false由字符串变成了布尔值)parser.parseExpression("booleanList[0]").setValue(context, simple, "false");Boolean b = simple.booleanList.get(0);System.out.println(b);}@Testpublic void test08() {// 可以使用SpelParserConfiguration来配置SpEl解析器// 1. 开启自动null初始化// 2. 开启自动集合扩容SpelParserConfiguration config = new SpelParserConfiguration(true,true);// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(config);// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("list[3]");// 显然, 这里的demo未初始化它的list属性Demo demo = new Demo();System.out.println(demo.list); // 输出: null// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果Object o = expression.getValue(demo);System.out.println(o);System.out.println(demo.list.size()); // 输出: 4}@Testpublic void test09() {// SpEl提供了3种编译模式: SpelCompilerMode 枚举类中// 在选定1种模式之后, 使用SpelParserConfiguration配置到SpelExpressionParser解析器中SpelParserConfiguration config = new SpelParserConfiguration(SpelCompilerMode.IMMEDIATE, this.getClass().getClassLoader());// 创建1个SpEl解析器SpelExpressionParser(它负责解析字符串)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(config);// 使用SpEl解析器解析1个字符串, 返回1个Expression表达式对象(它负责计算解析的字符串)Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("payload");// 使用Expression表达式对象的getValue方法获得结果MyMessage message = new MyMessage();Object payload = exp.getValue(message);System.out.println(payload);}}Demo类
class Demo {public List<String> list;
}
MyMessage类
public class MyMessage {public byte[] payload;}
Simple类
class Simple {public List<Boolean> booleanList = new ArrayList<Boolean>();
}
SPEL02
xml配置文件中使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!-- 在spring的配置文件中, 可以使用 #{ <expression string> } 的形式, 来使用el表达式 --><!-- 可以调用类的静态方法给bean的属性赋值 --><bean id="numberGuess" class="com.zzhua.spel02.NumberGuess"><property name="randomNumber" value="#{ T(java.lang.Math).random() * 100.0 }"/><!-- other properties --></bean><!-- 可以通过bean的名字来引用容器中的bean, 包括像: environment, systemProperties, systemEnvironment --><bean id="taxCalculator" class="com.zzhua.spel02.TaxCalculator"><property name="defaultLocale" value="#{ systemProperties['user.region'] }"/><!-- 也可以应用其它bean --><property name="initialShapeSeed" value="#{ numberGuess.randomNumber }"/><!-- other properties --></bean></beans>anno注解中使用
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class FieldValueTestBean {// 可以在属性、方法、构造器参数 中使用@Value注解, 并使用SpEl表达式@Value("#{ systemProperties['user.region'] }")private String defaultLocale;private MovieFinder movieFinder;private final CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao;@Value("#{ systemProperties['user.region'] }")public void setDefaultLocale(String defaultLocale) {this.defaultLocale = defaultLocale;}public String getDefaultLocale() {return this.defaultLocale;}@Autowiredpublic void configure(MovieFinder movieFinder,@Value("#{ systemProperties['user.region'] }") String defaultLocale) {this.movieFinder = movieFinder;this.defaultLocale = defaultLocale;}public FieldValueTestBean(CustomerPreferenceDao customerPreferenceDao,@Value("#{systemProperties['user.country']}") String defaultLocale) {this.customerPreferenceDao = customerPreferenceDao;this.defaultLocale = defaultLocale;}}SPEL03
Test01
public class Test01 {@Testpublic void test01() {// 字面量表达式//(支持字符串、数字、布尔、null, 其中字符串使用前后共2个单引号声明, 如果要在字符串中包含单引号,那就要连续用2个单引号来表示)ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();String helloWorld = (String) parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'").getValue();String helloWorld2 = (String) parser.parseExpression("'''Hello World'").getValue();System.out.println(helloWorld); // Hello WorldSystem.out.println(helloWorld2);// 'Hello Worlddouble avogadrosNumber = (Double) parser.parseExpression("6.0221415E+23").getValue();System.out.println(avogadrosNumber); // 6.0221415E23int maxValue = (Integer) parser.parseExpression("0x7FFFFFFF").getValue();System.out.println(maxValue); // 2147483647boolean trueValue = (Boolean) parser.parseExpression("true").getValue();System.out.println(trueValue); // trueObject nullValue = parser.parseExpression("null").getValue();System.out.println(nullValue); // null}@Testpublic void test02() {// 访问属性//(注意: 属性名的首字母大小写随意, 因为首字母不敏感)ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Inventor rootObject = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", new GregorianCalendar(1856, 7, 9).getTime(), "Serbian");rootObject.setPlaceOfBirth(new PlaceOfBirth("北京", "中国"));SimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding()// 指定root对象.withRootObject(rootObject).build();// 字符串表达式中, 凡是不知道的属性, 就从context的rootObject中找int year = (Integer) parser.parseExpression("Birthdate.Year + 1900").getValue(context);System.out.println(year); // 1856String city = (String) parser.parseExpression("placeOfBirth.City").getValue(context);System.out.println(city); // 北京// 字符串表达式中, 凡是不知道的属性, 就从rootObject中找, 那干脆直接用rootObject就好了int year2 = (Integer) parser.parseExpression("Birthdate.Year + 1900").getValue(rootObject);System.out.println(year2); // 1856String city2 = (String) parser.parseExpression("placeOfBirth.City").getValue(rootObject);System.out.println(city2); // 北京}@Testpublic void test03() {// 通过中括号来访问数组、集合、mapExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 给rootObject的inventions属性赋值Inventor rootObject = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", new GregorianCalendar(1856, 7, 9).getTime(), "Serbian");String[] inventions = {"灯泡1", "灯泡2", "灯泡3"};rootObject.setInventions(inventions);SimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding()// 指定root对象.withRootObject(rootObject).build();// 访问 Inventor 的 inventions属性// 字符串表达式中, 凡是不知道的属性, 就从context的rootObject中找String invention2 = parser.parseExpression("inventions[2]").getValue(context, String.class);// 这里指定的rootObject参数, 比context中的rootObject优先级会更高String invention1 = parser.parseExpression("inventions[2]").getValue(context, rootObject, String.class);System.out.println(invention1); // 灯泡3System.out.println(invention2); // 灯泡3// 访问 society 的 members 属性, Member的 inventions 属性Society society = new Society();society.getMembers().add(rootObject);// 字符串表达式中, 凡是不知道的属性, 就从context的rootObject中找String name = parser.parseExpression("Members[0].Name").getValue(context, society, String.class);// 字符串表达式中, 凡是不知道的属性, 就从context的rootObject中找String invention = parser.parseExpression("Members[0].Inventions[1]").getValue(context, society, String.class);System.out.println(name); // Nikola TeslaSystem.out.println(invention); // 灯泡2// 访问 map 中的数据Inventor inventor = new Inventor("Idvor", new GregorianCalendar(1856, 7, 9).getTime(), "Serbian");inventor.setPlaceOfBirth(new PlaceOfBirth("cCity", "cCountry"));society.getOfficers().put("president", inventor);SimpleEvaluationContext societyContext = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().withRootObject(society).build();Inventor pupin = parser.parseExpression("Officers['president']").getValue(societyContext, Inventor.class);System.out.println(pupin); // com.zzhua.entity.Inventor@2a2d45baString city = parser.parseExpression("Officers['president'].PlaceOfBirth.City").getValue(societyContext, String.class);System.out.println(city); // cCityInventor tempInventor = new Inventor("kkk", new GregorianCalendar(1856, 7, 9).getTime(), "Serbian");tempInventor.setPlaceOfBirth(new PlaceOfBirth("zz", "kk"));society.getOfficers().put("advisors", Arrays.asList(tempInventor));Object contry = parser.parseExpression("Officers['advisors'][0].PlaceOfBirth.Country").getValue(societyContext);System.out.println(contry); // kk// 使用SpEl设置为jj, 注意使用SimpleEvaluationContext时, 一定要选择可读可写的那个方法, 才能使用setValue, 否则会报错parser.parseExpression("Officers['advisors'][0].PlaceOfBirth.Country").setValue(societyContext, "jj");System.out.println(parser.parseExpression("Officers['advisors'][0].PlaceOfBirth.Country").getValue(societyContext));System.out.println(contry); // jj}}
SPEL04
InlineListsTest
public class InlineListsTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 可以在字符串表达式中通过 {} 表示 list集合({}表达式代表个空集合)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();SimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("{1,2,3,4}");List<Object> numbers1 = (List<Object>) exp.getValue();System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers1.toArray())); // [1, 2, 3, 4]List<Object> numbers2 = (List<Object>) exp.getValue(context);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers2.toArray())); // [1, 2, 3, 4]List<Object> numbers3 = (List<Object>) exp.getValue((Object) null); // 指定rootObjectSystem.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers3.toArray())); // [1, 2, 3, 4]}}
InlineMaps
public class InlineMaps {@Testpublic void test01() {// 可以在字符串表达式中通过 {key:value} 表示 map 集合, 其中map的key可以不使用单引号({:}表达式代表个空的map集合)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();SimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("{name:'Nikola',dob:'10-July-1856'}");Map map = (Map)exp.getValue(context);System.out.println(map); // {name=Nikola, dob=10-July-1856}Map mapOfMaps = (Map) parser.parseExpression("{name:{first:'Nikola',last:'Tesla'},dob:{day:10,month:'July',year:1856}}").getValue(context);System.out.println(mapOfMaps); // {name={first=Nikola, last=Tesla}, dob={day=10, month=July, year=1856}}}}
ArrayConstructionTest
public class ArrayConstructionTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 可以使用与java相似的语法, 在字符串表达式中声明数组(最多构建二维数组, 不能声明多维数组)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();SimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// -- 1Expression exp1 = parser.parseExpression("new int[4]");int[] numbers1 = (int[])exp1.getValue(context);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers1)); // [0, 0, 0, 0]// --- 2Expression exp2 = parser.parseExpression("new int[]{1,2,3}");int[] numbers2 = (int[])exp2.getValue(context);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers2)); // [1, 2, 3]// --- 3Expression exp3 = parser.parseExpression("new int[4][5]");int[][] numbers3 = (int[][]) exp3.getValue(context);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers3)); // [[I@7ca48474, [I@337d0578, [I@59e84876, [I@61a485d2]}}
MethodsTest
public class MethodsTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 可以通过 字符串表达式 调用方法, 同时也支持方法参数SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();/*SimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().withMethodResolvers(DataBindingMethodResolver.forInstanceMethodInvocation()).build();*/StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'abc'.substring(1, 3)");Object value1 = exp.getValue();System.out.println(value1); // bc// 如果使用SimpleEvaluationContext的话, 这里会报错, 因此使用StandardEvaluationContext//(不过也可以给SimpleEvaluationContext配上1个DataBindingMethodResolver也可以解决这个报错问题)Object value2 = exp.getValue(context);System.out.println(value2); // bc// ---SimpleEvaluationContext societyContext = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().withMethodResolvers(DataBindingMethodResolver.forInstanceMethodInvocation()).withRootObject(new Society()).build();// 调用rootObject(即society对象)的isMember方法哦boolean isMember = parser.parseExpression("isMember('Mihajlo Pupin')").getValue(societyContext, Boolean.class);System.out.println(isMember); // false}}
OperatorsTest
public class OperatorsTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 支持 比较运算符(注意: 任何值都比null要大)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("2 == 2");// ---Boolean value1 = exp.getValue(Boolean.class);System.out.println(value1); // true// ---SimpleEvaluationContext context2 = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();Boolean value2 = exp.getValue(context2, Boolean.class);System.out.println(value2); // true// ---SimpleEvaluationContext context3 = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();Boolean value3 = exp.getValue(context3, null, Boolean.class);System.out.println(value3); // true// --------System.out.println(parser.parseExpression("2 < -5.0").getValue(Boolean.class)); // falseSystem.out.println( parser.parseExpression("'black' < 'block'").getValue(Boolean.class)); // true// -------- 验证: 任何值都比null要大System.out.println(parser.parseExpression("null").getValue()); // nullSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("null == null").getValue()); // trueSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("null > null").getValue()); // falseSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("null < -1").getValue()); // trueSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("null < 'a'").getValue()); // true}@Testpublic void test02() {// 支持 instanceof 和 正则表达式的matches匹配操作SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// ---// instanceof使用示例(注意原始类型会被包装, 如: 1 instanceof T(int) 是false, 而1 instanceof T(Integer)是true)Expression exp1 = parser.parseExpression("'xyz' instanceof T(Integer)");boolean value1 = exp1.getValue(Boolean.class);System.out.println(value1); // falseSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("1 instanceof T(int)").getValue()); // falseSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("1 instanceof T(Integer)").getValue()); // trueSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("1 instanceof T(com.zzhua.entity.Society)").getValue()); // false// ---// 正则匹配示例Expression exp2 = parser.parseExpression("'5.00' matches '^-?\\d+(\\.\\d{2})?$'");boolean value2 = exp2.getValue(Boolean.class);System.out.println(value2); // true// 补充说明: 符号都可以使用对应的字母组合符号, 可以避免一些问题, 并且不区分大小写// lt (<)// gt (>)// le (<=)// ge (>=)// eq (==)// ne (!=)// div (/)// mod (%)// not (!)}@Testpublic void test03() {// 支持逻辑操作符: and (&&)、or (||)、not (!)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// --- AND(可将下面的and换成or)Expression exp1 = parser.parseExpression("true and false");Object value1 = exp1.getValue();System.out.println(value1); // falseSimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();Object value2 = exp1.getValue(context);System.out.println(value2); // false// --Expression exp3 = parser.parseExpression("isMember('Nikola Tesla') and isMember('Mihajlo Pupin')");Society rootObject = new Society();rootObject.getMembers().add(new Inventor("Nikola Tesla",""));rootObject.getMembers().add(new Inventor("Mihajlo Pupin",""));SimpleEvaluationContext societyContext = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().withRootObject(rootObject).withMethodResolvers(DataBindingMethodResolver.forInstanceMethodInvocation()).build();boolean value3 = exp3.getValue(societyContext, Boolean.class);System.out.println(value3); // true// !的用法示例System.out.println(parser.parseExpression("!true").getValue()); // falseSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("!false").getValue()); // trueSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("! false").getValue()); // trueSystem.out.println(parser.parseExpression("!! false").getValue()); // true}@Testpublic void test04() {// 支持算术运算符SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();int two = parser.parseExpression("1 + 1").getValue(Integer.class);System.out.println(two); // 2String testString = parser.parseExpression("'test' + ' ' + 'string'").getValue(String.class);System.out.println(testString); // test stringdouble d = parser.parseExpression("1000.00 - 1e4").getValue(Double.class);System.out.println(d); // -9000.0int six = parser.parseExpression("-2 * -3").getValue(Integer.class); // 6System.out.println(six); // 6double twentyFour = parser.parseExpression("2.0 * 3e0 * 4").getValue(Double.class);System.out.println(twentyFour);int minusTwo = parser.parseExpression("6 / -3").getValue(Integer.class); // -2System.out.println(minusTwo);double one = parser.parseExpression("8.0 / 4e0 / 2").getValue(Double.class); // 1.0System.out.println(one);int three = parser.parseExpression("7 % 4").getValue(Integer.class); // 3System.out.println(three);int one2 = parser.parseExpression("8 / 5 % 2").getValue(Integer.class); // 1System.out.println(one2);int minusTwentyOne = parser.parseExpression("1+2-3*8").getValue(Integer.class); // -21System.out.println(minusTwentyOne);}@Testpublic void test05() {// 支持赋值运算符//(如果需要给1个属性赋值, 可以使用=这个操作符;// 可以通过调用Expression#setValue方法来实现;// 也可以在Expression#getValue中使用=操作符来实现;)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Inventor inventor = new Inventor();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();// 给inventor(即rootObject)的name属性赋值parser.parseExpression("Name").setValue(context, inventor, "Aleksandar Seovic");System.out.println(inventor.getName()); // Aleksandar Seovic// 给inventor(即rootObject)的name属性赋值的第二种方式String aleks = parser.parseExpression("Name = 'Aleksandar Seovic2'").getValue(context, inventor, String.class);System.out.println(inventor.getName()); // Aleksandar Seovic2}
}
TypesTest
public class TypesTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 可以使用 T 这个操作符来指定1个实例对象所属的类, 也可以通过这个操作符来调用这个类的静态方法// (StandardEvaluationContext 使用TypeLocator 来查找类, 对于在java.lang包下的类,不需要使用全限定名, 其他类则须使用全限定名)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Class dateClass = parser.parseExpression("T(java.util.Date)").getValue(Class.class);System.out.println(dateClass); // class java.util.DateClass stringClass = parser.parseExpression("T(String)").getValue(Class.class);System.out.println(stringClass); // class java.lang.Stringboolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression("T(java.math.RoundingMode).CEILING < T(java.math.RoundingMode).FLOOR").getValue(Boolean.class);System.out.println(trueValue); // true}}
ConstructorsTest
public class ConstructorsTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 支持使用new操作符来调用构造器, 应该都要使用全限定名除了基本类型和String之外SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Inventor einstein = parser.parseExpression("new com.zzhua.entity.Inventor('Albert Einstein', 'German')").getValue(Inventor.class);System.out.println(einstein.getName()); // Albert Einstein}}
VariablesTest
public class VariablesTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 可以使用 #变量名 的方式来引用对应的变量//(变量名可以通过调用EvaluationContext#setVariable方法来设置)//(合理的变量名应当由字母、数字、下划线、$组成)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Inventor rootObject = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", "Serbian");EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();// 这里设置变量名context.setVariable("newName", "Mike Tesla");// 这里在表达式中使用 #变量名 来引用 设置到context中的变量parser.parseExpression("Name = #newName").getValue(context, rootObject);System.out.println(rootObject.getName()); // Mike Tesla}@Testpublic void test02() {// #this 总是引用当前计算对象// #root 总是引用rootObjectSpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();List<Integer> primes = new ArrayList<Integer>();primes.addAll(Arrays.asList(2,3,5,7,11,13,17));EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// 设置变量context.setVariable("primes", primes);// 找出所有大于10的List<Integer> primesGreaterThanTen = (List<Integer>) parser.parseExpression("#primes.?[#this>10]").getValue(context);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(primesGreaterThanTen.toArray())); // [11, 13, 17]}}
FunctionTest
public class FunctionTest {@Testpublic void test01() throws NoSuchMethodException {// 支持 用户自定义方法,// 具体来说就是可以通过EvaluationContext#setVariable来注册1个方法, 然后在字符串表达式中调用ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();// 注册1个方法(与注册变量使用的是同一个方法)context.setVariable("reverseString",StringUtils.class.getDeclaredMethod("reverseString", String.class));// 在表达式中通过 #注册的方法名 来调用对应的方法String helloReversed = parser.parseExpression("#reverseString('hello')").getValue(context, String.class);System.out.println(helloReversed); // olleh}}
BeanReferencesTest
public class BeanReferencesTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 如果EvaluationContext配置了BeanResolver, 那么可以使用 @符号来查找容器中的bean//(如果是1个FactoryBean, 并且需要访问bean本身, 那么需要使用 &符号来引用这个bean)SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();StandardEvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();applicationContext.registerBean("society", Society.class);applicationContext.refresh();context.setBeanResolver(new BeanResolver() {@Overridepublic Object resolve(EvaluationContext context, String beanName) throws AccessException {return applicationContext.getBean(beanName);}});System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean(Society.class).getName()); // null// 通过 @bean的名字 来引用从BeanResolver中解析出来的对象parser.parseExpression("@society.name = 'zzhua'").getValue(context);System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean(Society.class).getName()); // zzhua}}
TernaryOperatorTest
public class TernaryOperatorTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 支持使用三元运算符SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();String falseString = parser.parseExpression("false ? 'trueExp' : 'falseExp'").getValue(String.class);System.out.println(falseString); // falseExp// ---SimpleEvaluationContext societyContext = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().withRootObject(new Society()).withMethodResolvers(DataBindingMethodResolver.forInstanceMethodInvocation()).build();// 给societyContext中, 指定的rootObject的name属性, 赋值为IEEEparser.parseExpression("Name").setValue(societyContext, "IEEE");// 注册变量societyContext.setVariable("queryName", "Nikola Tesla");// 凡是没有限定的, 都从rootObject中找; #变量名 从注册的变量中找;String expression = "isMember(#queryName)? #queryName + ' is a member of the ' + Name + ' Society' : #queryName + ' is not a member of the ' + Name + ' Society'";String queryResultString = parser.parseExpression(expression).getValue(societyContext, String.class);System.out.println(queryResultString); // Nikola Tesla is not a member of the IEEE Society}}
ElvisOperatorTest
public class ElvisOperatorTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 可以使用Elvis 操作符 ?: 来简化 变量是否为null的三元表达式的语法//(可以在@Value注解中使用elvis操作符, 比如: @Value("#{systemProperties['pop3.port'] ?: 25}"))ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Inventor rootObject = new Inventor();// rootObject的name属性是否为null, 为null的话就取Unknown, 不为null的话就取rootObject的name属性String name = parser.parseExpression("name?:'Unknown'").getValue(rootObject, String.class);System.out.println(name); // Unknown}}
SafeNavigationOperator
public class SafeNavigationOperator {@Testpublic void test01() {// 支持使用安全导航符, 用于避免空指针异常。// (当访问引用对象的属性或方法时, 又不能确定这个被引用的对象是否为null时, 可以使用安全导航符,// 如果引用对象是null, 那么会返回null, 而不是抛出空指针异常)ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();Inventor tesla = new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", "Serbian");tesla.setPlaceOfBirth(new PlaceOfBirth("Smiljan"));String city = parser.parseExpression("PlaceOfBirth?.City").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);System.out.println(city); // Smiljan// 将rootObject的placeOfBirth置为nulltesla.setPlaceOfBirth(null);// rootObject的placeOfBirth是否为空, 如果为空, 则返回null, 如果不为空, 则访问它的city属性city = parser.parseExpression("PlaceOfBirth?.City").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);System.out.println(city); // null - 没有抛出NullPointerException!!!String value = parser.parseExpression("placeOfBirth?.city?.length").getValue(context, tesla, String.class);System.out.println(value); // null}}
CollectionSelection
public class CollectionSelection {@Testpublic void test01() {// 集合选择能够从1个集合中过滤某些元素添加到1个新的集合中;// 可以使用 .?[选择表达式] 来实现集合选择;// 对于list集合, 选择表达式中获取的是每个元素;// 对于map集合, 选择表达式中获取的是每个entry(即key-value对);// 如果只需要新集合中的第1个元素, 则使用 .^[selectionExpression];// 如果只需要新集合中的末位元素, 则使用 .$[selectionExpression];SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Society society = new Society();society.getMembers().add(new Inventor("Nikola Tesla", "Serbian"));society.getMembers().add(new Inventor("Nikola Tesla2", "Serbian2"));SimpleEvaluationContext societyContext = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().withRootObject(society).build();// rootObject的members属性是个集合, 然后对这个集合中的元素作筛选, 中括号里面的上下文其实就是#this, 筛选出国籍为SerbianList<Inventor> list = (List<Inventor>) parser.parseExpression("Members.?[Nationality == 'Serbian']").getValue(societyContext);System.out.println(list.size()); // 1List<Inventor> list2 = (List<Inventor>) parser.parseExpression("Members.?[#this.Nationality == 'Serbian']").getValue(societyContext);System.out.println(list2.size()); // 1// ---Society society2 = new Society();society2.getOfficers().put("a", 26);society2.getOfficers().put("b", 27);society2.getOfficers().put("c", 28);SimpleEvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().withRootObject(society2).build();Map newMap1 = (Map) parser.parseExpression("officers.?[value<27]").getValue(context);System.out.println(newMap1); // {a=26}Map newMap2 = (Map) parser.parseExpression("officers.?[key=='b']").getValue(context);System.out.println(newMap2); // {b=27}society2.setOfficers(null);// rootObject的officers属性是null, 这里会抛出空指针异常/*Map newMap3 = (Map) parser.parseExpression("officers?.?[key=='b']").getValue(context);System.out.println(newMap3); */// 这样写就对了, 使用安全导航符, 当rootObject的officers属性是null, 直接返回nullMap newMap3 = (Map) parser.parseExpression("officers?.?[key=='b']").getValue(context);System.out.println(newMap3); // null}}
CollectionProjectionTest
public class CollectionProjectionTest {@Testpublic void test() {// 集合投影就是将集合中的每个元素 都作 同样的处理 , 然后组合到1个新的集合里SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Society society = new Society();Inventor inventor1 = new Inventor("", "");inventor1.setPlaceOfBirth(new PlaceOfBirth("sh", "ch"));Inventor inventor2 = new Inventor("", "");inventor2.setPlaceOfBirth(new PlaceOfBirth("sz", "ch"));society.getMembers().add(inventor1);society.getMembers().add(inventor2);// 针对rootObject中的members属性, 中的每1个元素, 都获取他们的placeOfBirth属性, 然后city属性List list = (List) parser.parseExpression("Members.![placeOfBirth.city]").getValue(society);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(list.toArray())); // [sh, sz]}}
ExpressionTemplatingTest
public class ExpressionTemplatingTest {@Testpublic void test01() {// 支持表达式模板, 允许将字面量的字符串和 计算块 混在一起使用, 计算块定义的前后分隔符可以自定义, 最常用的是 #{ }SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();// 需要指定ParserContext为TemplateParserContext实现Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("random number is #{T(java.lang.Math).random()}",new TemplateParserContext("#{","}"));Object value = exp.getValue();System.out.println(value); // random number is 0.5179806528476545}相关文章:

Spring El表达式官方文档学习
文章目录 推荐一、概述1、什么是SpEL2、SpEL能做什么 二、SpEL表达式使用1、文字表达式2、属性, 数组, List, Map,和 索引(1)属性操作(2)数组和List(3)Map 3、内嵌List4、内嵌Map5、构建数组6、调用类的方法…...
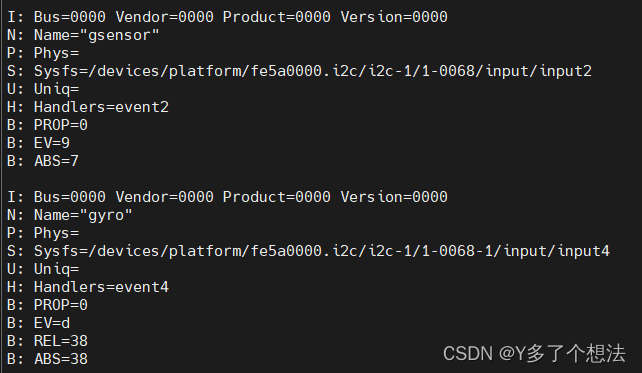
RK3568 android11 调试陀螺仪模块 MPU6500
一,MPU6500功能介绍 1.简介 MPU6500是一款由TDK生产的运动/惯性传感器,属于惯性测量设备(IMU)的一种。MPU6500集成了3轴加速度计、3轴陀螺仪和一个板载数字运动处理器(DMP),能够提供6轴的运动…...
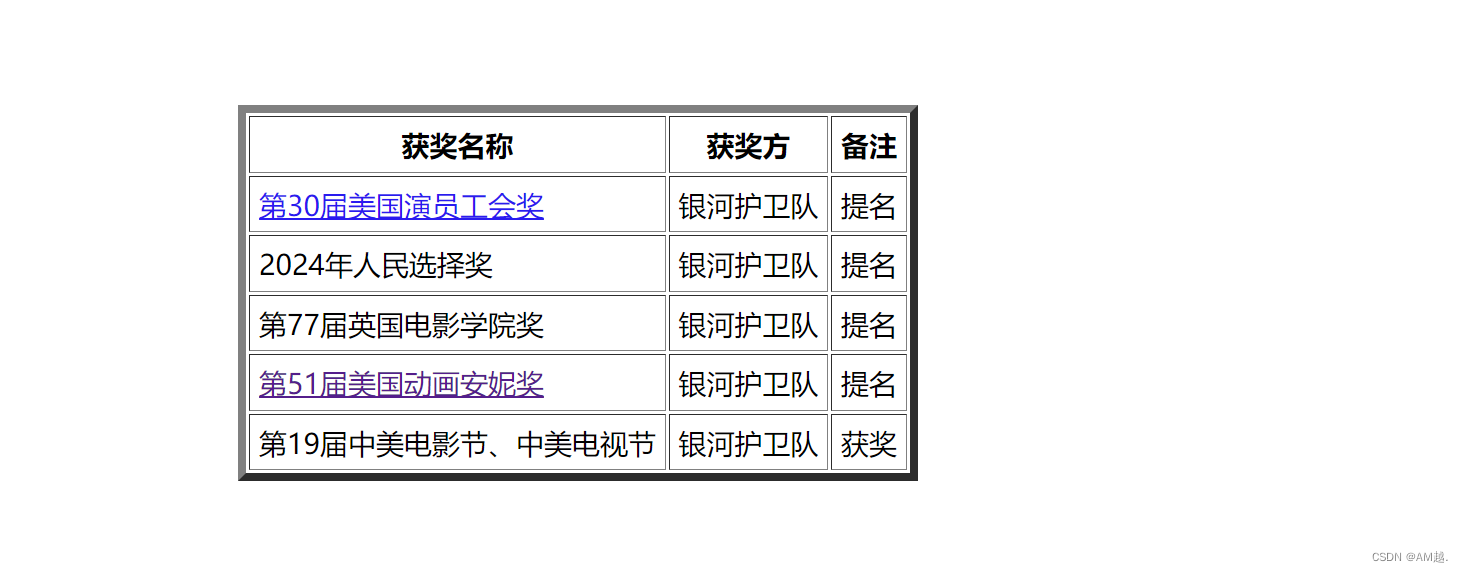
【HTML】HTML基础6.1(表格以及常见属性)
目录 表格介绍 表格标签 表格标签的常见属性 案例 知识点总结 表格介绍 在浏览器中,我们经常见到形如 这样的表格形式,一般来说,表格是为了让数据看起来更加清晰,增强数据的可读性 有的程序员也会用表格进行排版 表格标签 &…...

数字电路三宝:锁存器、寄存器和触发器
在数字电路设计中,很多电子工程师经常会用到锁存器、寄存器和触发器,它们各自承担着不同的功能,但共同为数字电路的稳定性和高效性提供了坚强保障,下面将谈谈这三大元件,希望对小伙伴们有所帮助。 1、锁存器࿰…...

VLC相关资源及使用方法
资源 VLC源码: VLC的源码,与VLC Contrib配合使用可以编译相应的库、程序等,如果没有Contrib,可以使用源码下面的contrib文件夹下对应程序自动下载,单独编译,但是速度很慢。 下载地址: 官网&…...
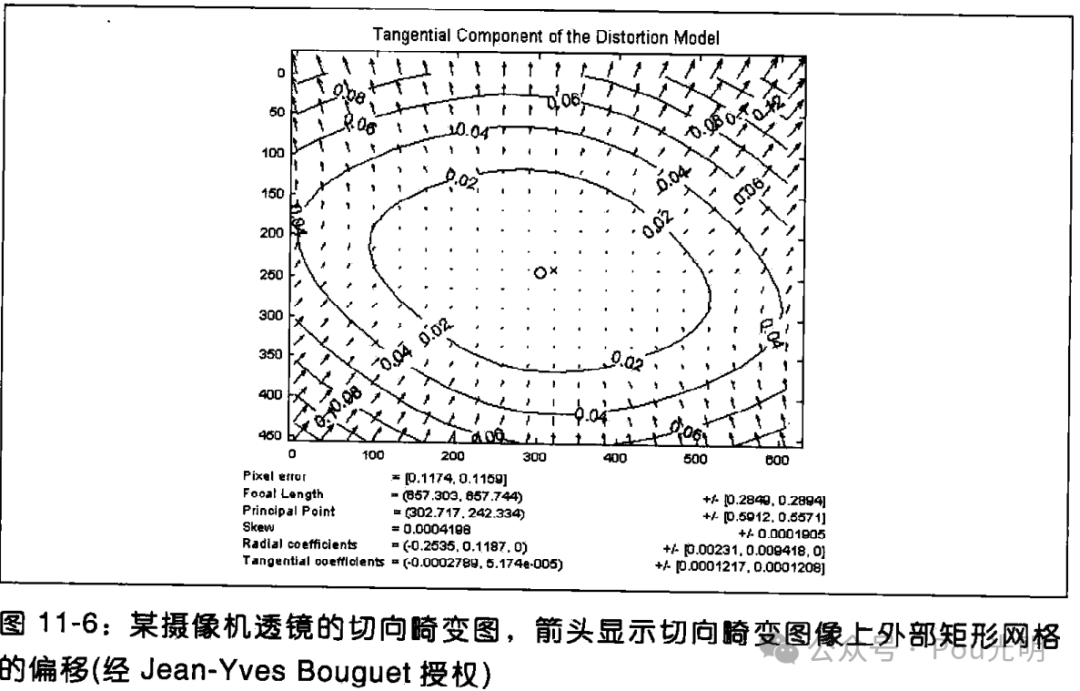
4_相机透镜畸变
理论上讲,是可能定义一种透镜而不引入任何畸变的。然而现实世界没有完美的透镜。这主要是制造上的原因,因为制作一个“球形”透镜比制作一个数学上理想的透镜更容易。而且从机械方面也很难把透镜和成像仪保持平行。下面主要描述两种主要的透镜畸变并为他…...
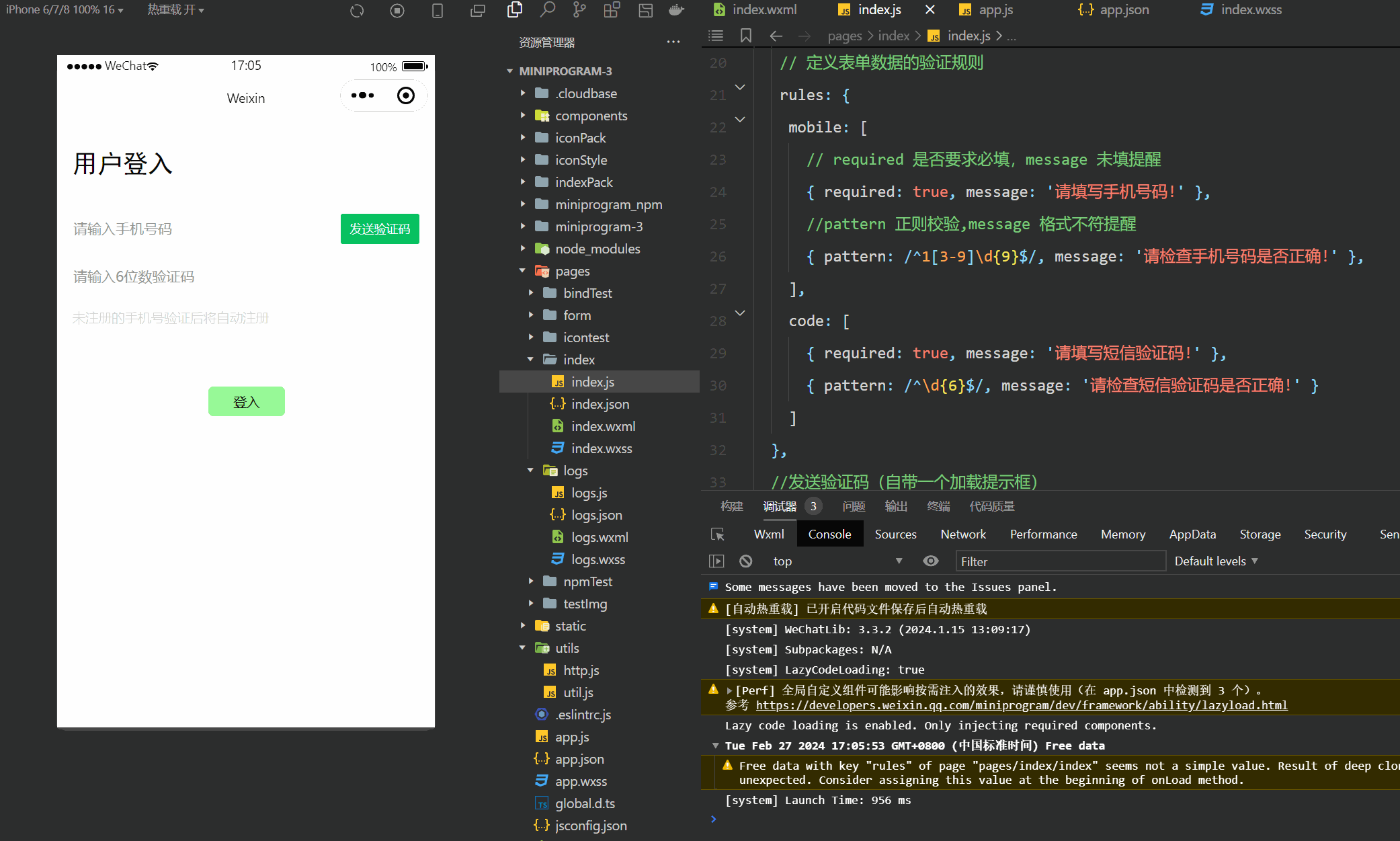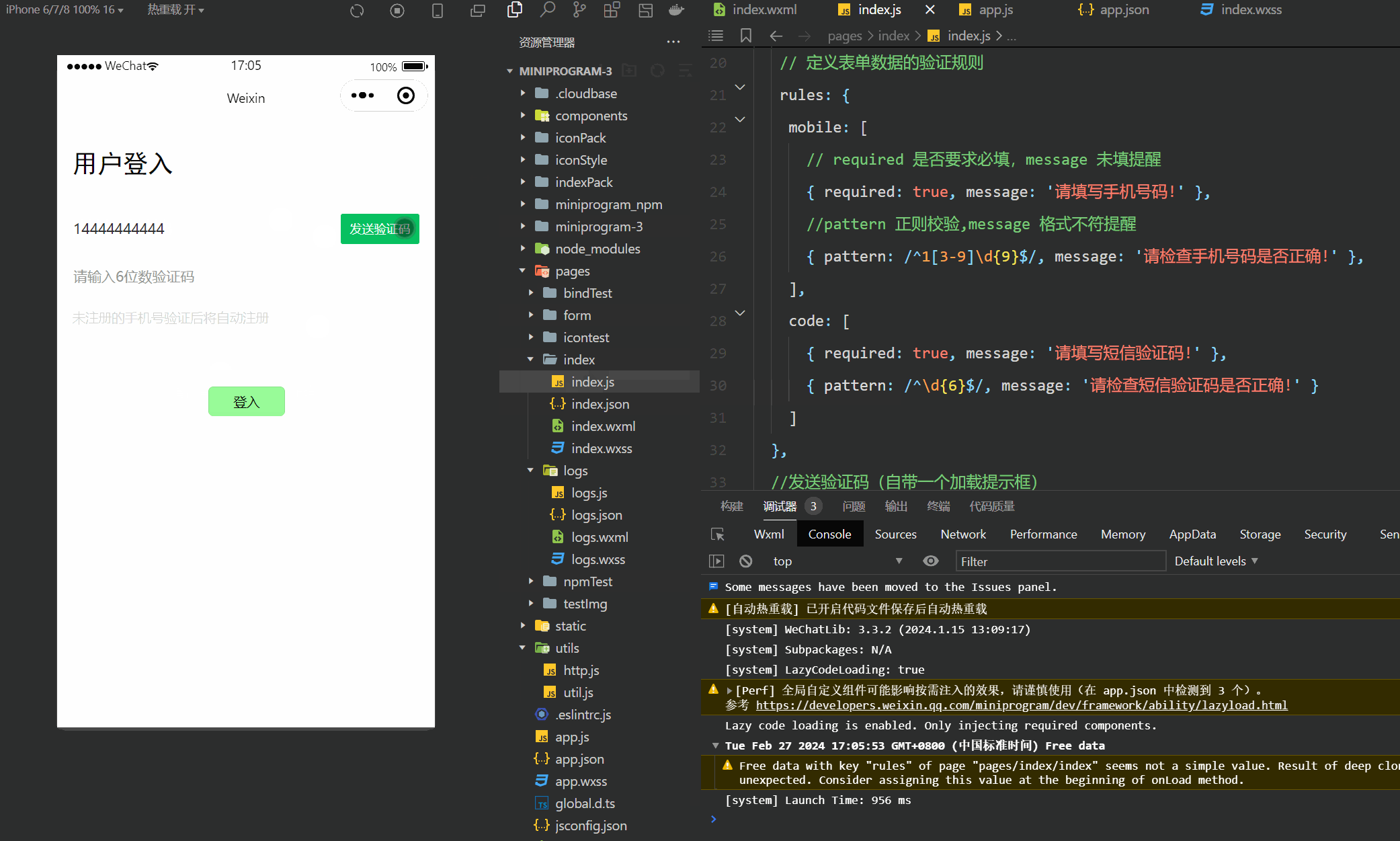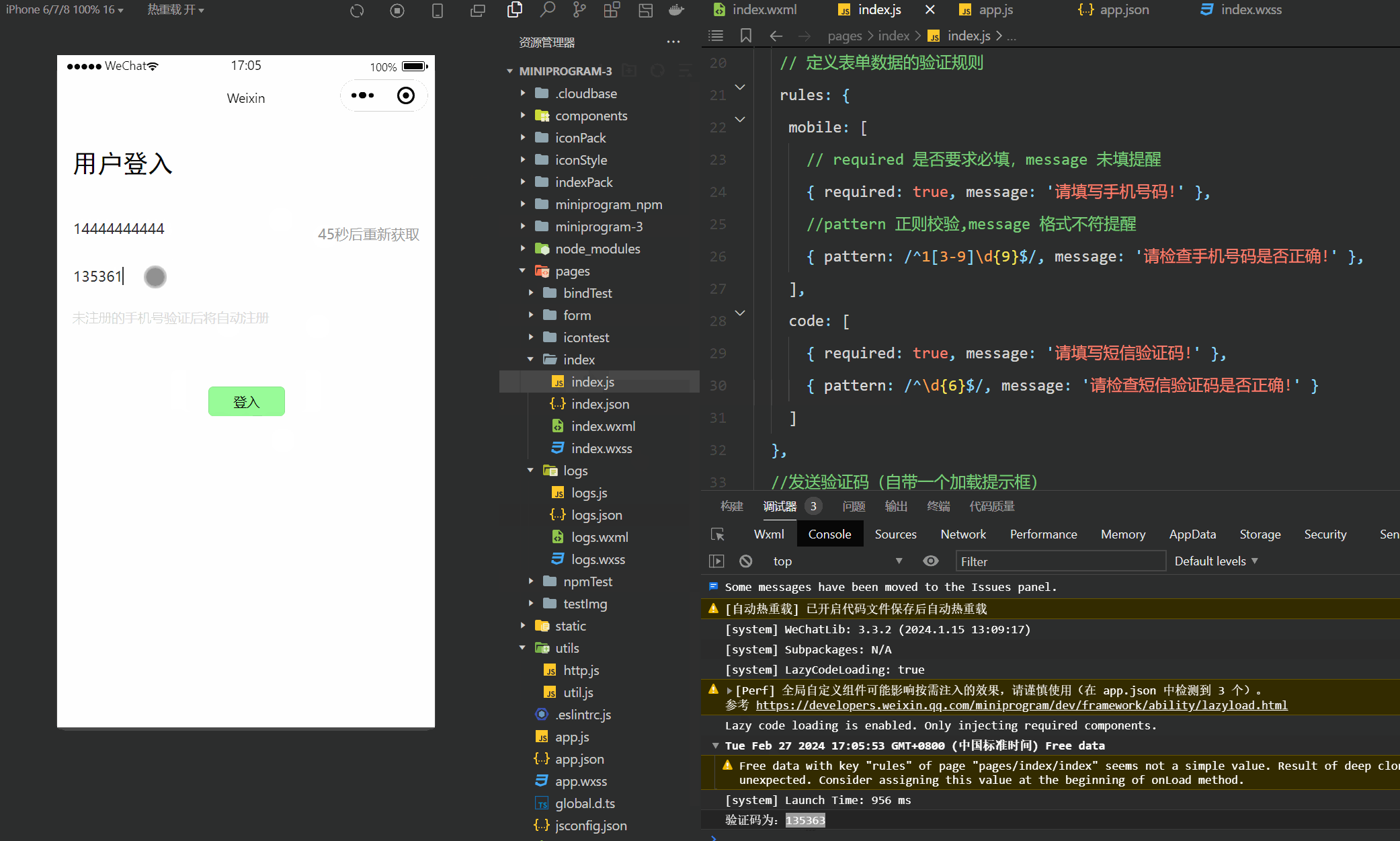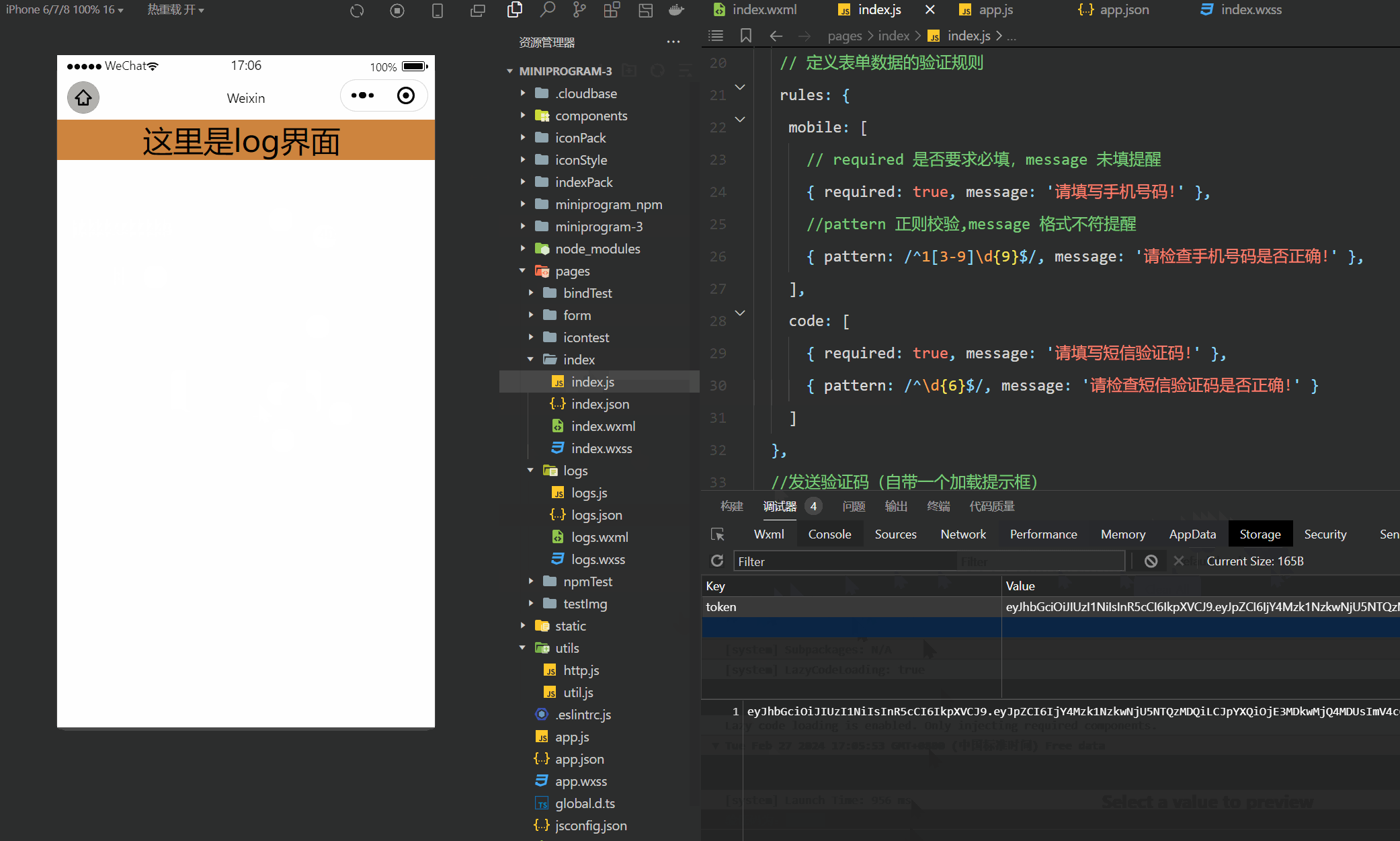
微信小程序(四十六)登入界面-进阶版
注释很详细,直接上代码 上一篇 此文使用了vant组件库,没有安装配置的可以参考此篇vant组件的安装与配置 新增内容: 1.手机号与验证码格式验证 2.验证码的网络申请和校验 wechat-http模块在好几篇以前已经讲了咋安装的,不记得的友…...

CSP-201712-2-游戏
CSP-201712-2-游戏 解题思路 初始化变量:定义整数变量n和k,分别用来存储小朋友的总数和淘汰的特定数字。然后定义了num(用来记录当前报的数)和peopleIndex(用来记录当前报数的小朋友的索引)。 初始化小朋…...

记录SSM项目集成Spring Security 4.X版本 之 加密验证和记住我功能
目录 前言 一、用户登录密码加密认证 二、记住我功能 前言 本次笔记的记录是接SSM项目集成Spring Security 4.X版本 之 加入DWZ,J-UI框架实现登录和主页菜单显示-CSDN博客https://blog.csdn.net/u011529483/article/details/136255768?spm1001.2014.3001.5502 文章之后补…...

[AutoSar]BSW_Com09 CAN driver 模块FULL(BASIC)CAN、FIFO选择
目录 关键词平台说明一、FULL CAN 和Basic CAN 关键词 嵌入式、C语言、autosar、OS、BSW 平台说明 项目ValueOSautosar OSautosar厂商vector ,芯片厂商TI 英飞凌编程语言C,C编译器HighTec (GCC)autosar版本4.3.1 >>>>>回到总目录<&…...

WPF真入门教程30--顺风物流单据管理系统
1、教程回顾 到现在为止,真入门系列教程已完成了29刺由浅入深地讲解,当然不可能讲到了WPF的所有技能点,但读者看到了wpf的内部各种功能及之间的联系,在此基础上,提供一个完整有效的综合项目,本项目采用的是…...
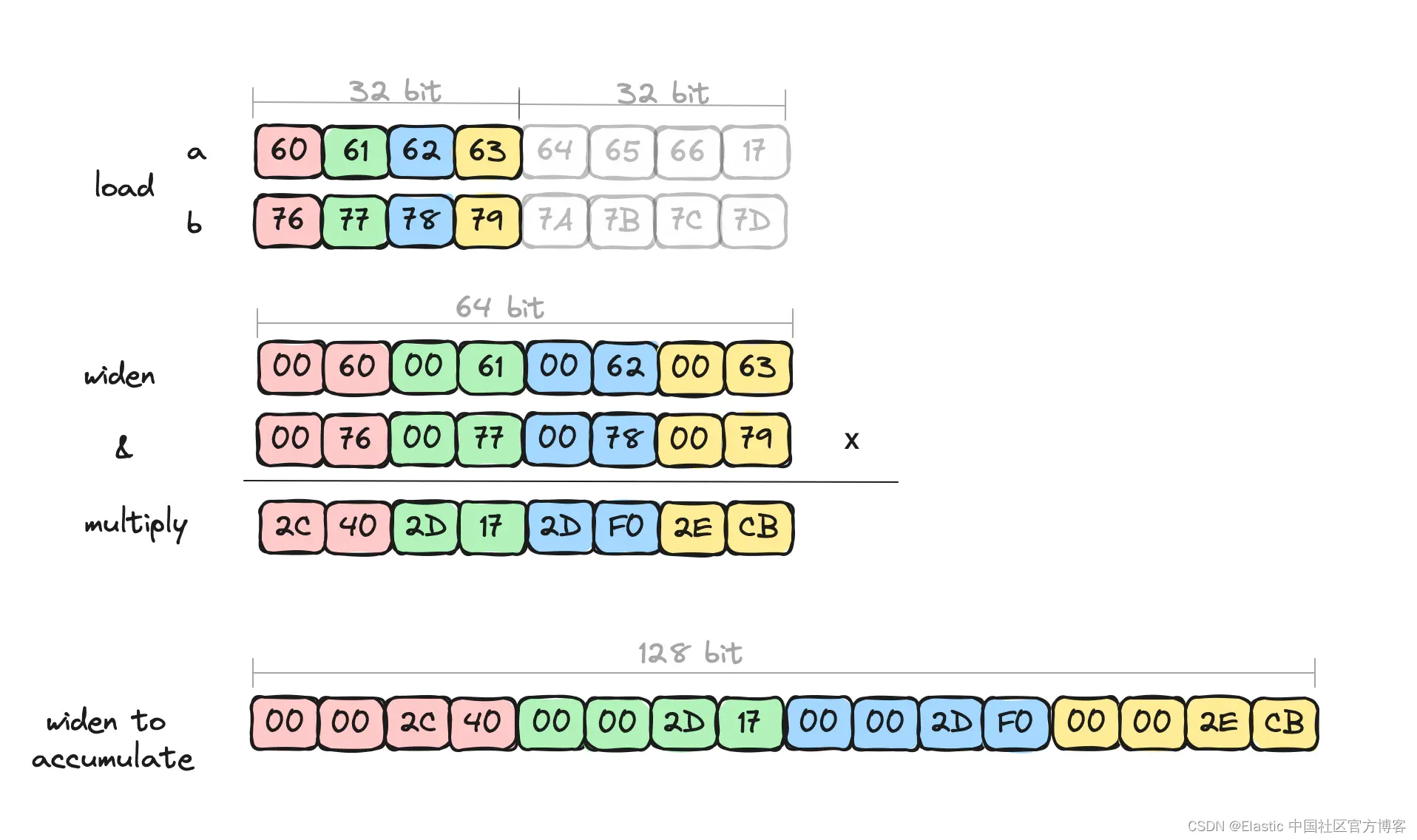
Elasticsearch:向量相似度计算 - 可笑的速度
作者:Chris Hegarty 任何向量数据库的核心都是距离函数,它确定两个向量的接近程度。 这些距离函数在索引和搜索期间执行多次。 当合并段或在图表中导航最近邻居时,大部分执行时间都花在比较向量的相似性上。 对这些距离函数进行微观优化是值…...

两数相加的问题
题目是:给两个非空的链表,表示两个非负整数。它们每位数都是按照逆序的方式存储,并且每一个节点只能存储一位数字。现在两个数相加,并且以相同的形式返回一个表示和的链表。 首先回顾一下,什么是链表?链表…...

微信小程序的单位
在小程序开发中,rpx是一种相对长度单位,用于在不同设备上实现自适应布局。它是微信小程序特有的单位,表示屏幕宽度的 1/750。 rpx单位的好处在于可以根据设备的屏幕宽度进行自动换算,使得页面在不同设备上保持一致的显示效果。例…...

软考通过率真的低吗?
软考通过率有多少?高项有必要找培训机构吗? 相对来说软考的通过率的确比其他考试要低,因为它的知识点有点杂,专业知识、政策、计算机系统各个方面的知识都需要去掌握。根据以往的数据来说高项(信息系统项目管理师&…...

国际视频编解码标准提案下载地址
H.266 相关提案下载地址:http://phenix.it-sudparis.eu/jvet/ 更新的地址:https://jvet-experts.org/ H.265 提案下载地址:http://phenix.int-evry.fr/jct/ 标准文档下载地址:http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-H.265 H.264 提案下载…...

程序员是如何看待“祖传代码”的?
文章目录 每日一句正能量前言祖传代码的历史与文化价值祖传代码的技术挑战与机遇祖传代码与现代开发实践的融合祖传代码的管理与维护策略后记 每日一句正能量 黎明时怀着飞扬的心醒来,致谢爱的又一天,正午时沉醉于爱的狂喜中休憩,黄昏时带着感…...

Python爬虫之爬取并下载哔哩哔哩视频
亲自使用过,太好用了 # 导入requests模块,模拟发送请求 import requests # 导入json import json # 导入re import re# 定义请求头 headers {Accept: */*,Accept-Language: en-US,en;q0.5,User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_6…...

python 脚本设置输出颜色
在Python脚本中设置输出颜色,通常可以使用colorama库,它可以在Windows、Linux和macOS等平台上工作。colorama库扩展了Python的标准库,使得在控制台输出彩色文本更加简单。 首先,你需要安装colorama库。如果你还没有安装ÿ…...
 案例)
安卓websocket(客服端和服务端写在app端) 案例
废话不多说直接上代码 首选导入 implementation "org.java-websocket:Java-WebSocket:1.4.0" package com.zx.qnncpds.androidwbsocket;import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button;import a…...

超短脉冲激光自聚焦效应
前言与目录 强激光引起自聚焦效应机理 超短脉冲激光在脆性材料内部加工时引起的自聚焦效应,这是一种非线性光学现象,主要涉及光学克尔效应和材料的非线性光学特性。 自聚焦效应可以产生局部的强光场,对材料产生非线性响应,可能…...

大学生职业发展与就业创业指导教学评价
这里是引用 作为软工2203/2204班的学生,我们非常感谢您在《大学生职业发展与就业创业指导》课程中的悉心教导。这门课程对我们即将面临实习和就业的工科学生来说至关重要,而您认真负责的教学态度,让课程的每一部分都充满了实用价值。 尤其让我…...
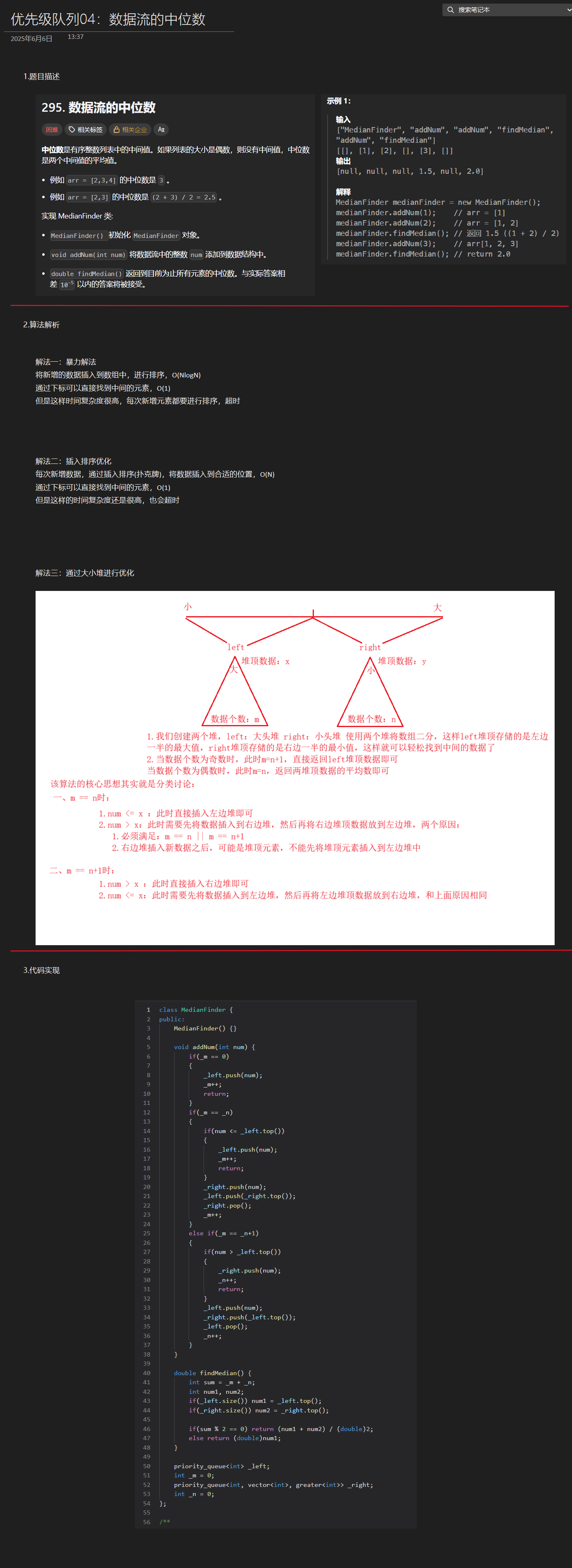
优选算法第十二讲:队列 + 宽搜 优先级队列
优选算法第十二讲:队列 宽搜 && 优先级队列 1.N叉树的层序遍历2.二叉树的锯齿型层序遍历3.二叉树最大宽度4.在每个树行中找最大值5.优先级队列 -- 最后一块石头的重量6.数据流中的第K大元素7.前K个高频单词8.数据流的中位数 1.N叉树的层序遍历 2.二叉树的锯…...
论文笔记——相干体技术在裂缝预测中的应用研究
目录 相关地震知识补充地震数据的认识地震几何属性 相干体算法定义基本原理第一代相干体技术:基于互相关的相干体技术(Correlation)第二代相干体技术:基于相似的相干体技术(Semblance)基于多道相似的相干体…...
短视频矩阵系统文案创作功能开发实践,定制化开发
在短视频行业迅猛发展的当下,企业和个人创作者为了扩大影响力、提升传播效果,纷纷采用短视频矩阵运营策略,同时管理多个平台、多个账号的内容发布。然而,频繁的文案创作需求让运营者疲于应对,如何高效产出高质量文案成…...
LabVIEW双光子成像系统技术
双光子成像技术的核心特性 双光子成像通过双低能量光子协同激发机制,展现出显著的技术优势: 深层组织穿透能力:适用于活体组织深度成像 高分辨率观测性能:满足微观结构的精细研究需求 低光毒性特点:减少对样本的损伤…...

Bean 作用域有哪些?如何答出技术深度?
导语: Spring 面试绕不开 Bean 的作用域问题,这是面试官考察候选人对 Spring 框架理解深度的常见方式。本文将围绕“Spring 中的 Bean 作用域”展开,结合典型面试题及实战场景,帮你厘清重点,打破模板式回答,…...
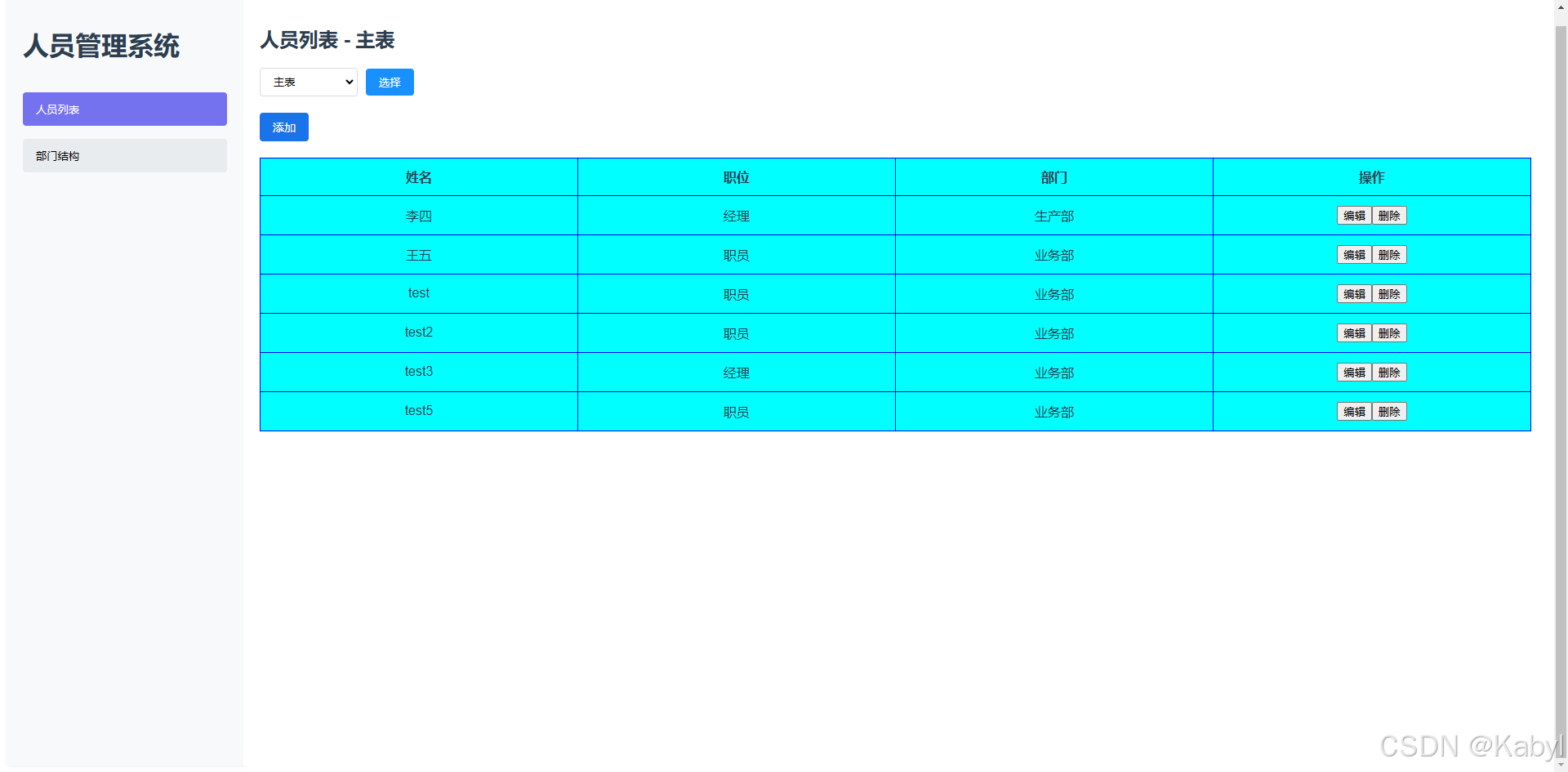
【1】跨越技术栈鸿沟:字节跳动开源TRAE AI编程IDE的实战体验
2024年初,人工智能编程工具领域发生了一次静默的变革。当字节跳动宣布退出其TRAE项目(一款融合大型语言模型能力的云端AI编程IDE)时,技术社区曾短暂叹息。然而这一退场并非终点——通过开源社区的接力,TRAE在WayToAGI等…...

【java】【服务器】线程上下文丢失 是指什么
目录 ■前言 ■正文开始 线程上下文的核心组成部分 为什么会出现上下文丢失? 直观示例说明 为什么上下文如此重要? 解决上下文丢失的关键 总结 ■如果我想在servlet中使用线程,代码应该如何实现 推荐方案:使用 ManagedE…...

RushDB开源程序 是现代应用程序和 AI 的即时数据库。建立在 Neo4j 之上
一、软件介绍 文末提供程序和源码下载 RushDB 改变了您处理图形数据的方式 — 不需要 Schema,不需要复杂的查询,只需推送数据即可。 二、Key Features ✨ 主要特点 Instant Setup: Be productive in seconds, not days 即时设置 :在几秒钟…...
