【读论文】【精读】3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering
文章目录
- 1. What:
- 2. Why:
- 3. How:
- 3.1 Real-time rendering
- 3.2 Adaptive Control of Gaussians
- 3.3 Differentiable 3D Gaussian splatting
- 4. Self-thoughts
1. What:
What kind of thing is this article going to do (from the abstract and conclusion, try to summarize it in one sentence)
To simultaneously satisfy the requirements of efficiency and quality, this article begins by establishing a foundation with sparse points using 3D Gaussian distributions to preserve desirable space. It then progresses to optimizing anisotropic covariance to achieve an accurate representation. Lastly, it introduces a cutting-edge, visibility-aware rendering algorithm designed for rapid processing, thereby achieving state-of-the-art results in the field.
2. Why:
Under what conditions or needs this research plan was proposed (Intro), what problems/deficiencies should be solved at the core, what others have done, and what are the innovation points? (From Introduction and related work)
Maybe contain Background, Question, Others, Innovation:
Three aspects of related work can explain this question.
-
Traditional reconstructions such as SfM and MVS need to re-project and
blend the input images into the novel view camera, and use the
geometry to guide this re-projection(From 2D to 3D).Sad: Cannot completely recover from unreconstructed regions, or from “over-reconstruction”, when MVS generates inexistent geometry.
-
Neural Rendering and Radiance Fields
Neural rendering represents a broader category of techniques that leverage deep learning for image synthesis, while radiance field is a specific technique within neural rendering focused on the scene representation of light and color in 3D spaces.
-
Deep Learning was mainly used on MVS-based geometry before, which is also its major drawback.
-
Nerf is along the way of volumetric representation, which introduced positional encoding and importance sampling.
-
Faster training methods focus on the use of spatial data structures to store (neural) features that are subsequently interpolated during volumetric ray-marching, different encodings, and MLP capacity.
-
Today, notable works include InstantNGP and Plenoxels both rely on Spherical Harmonics.
Understand Spherical Harmonics as a set of basic functions to fit a geometry in a 3D spherical coordinate system.
球谐函数介绍(Spherical Harmonics) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
- Point-Based Rendering and Radiance Fields
- The methods in human performance capture inspired the choice of 3D Gaussians as scene representation.
- Point-based and spherical rendering is achieved before.
3. How:

Through the Gradient Flow in this paper’s pipeline, we are trying to connect Part4, 5, and 6 in this paper.
Firstly, start from the loss function, which is combined by a L 1 {\mathcal L}_{1} L1 loss and a S S I M SSIM SSIM index, just as shown below:
L = ( 1 − λ ) L 1 + λ L D − S S I M . (1) {\mathcal L}=(1-\lambda){\mathcal L}_{1}+\lambda{\mathcal L}_{\mathrm{D-SSIM}}.\tag{1} L=(1−λ)L1+λLD−SSIM.(1)
It found a relation between the actual image and the rendering image. So to finish the optimization, we need to dive into the process of rendering. From the chapter on related work, we know Point-based α \alpha α-blending and NeRF-style volumetric rendering share essentially the same image formation model. That is
C = ∑ i = 1 N T i ( 1 − exp ( − σ i δ i ) ) c i w i t h T i = exp ( − ∑ j = 1 i − 1 σ j δ j ) . (2) C=\sum_{i=1}^{N}T_{i}(1-\exp(-\sigma_{i}\delta_{i}))c_{i}\quad\mathrm{with}\quad T_{i}=\exp\left(-\sum_{j=1}^{i-1}\sigma_{j}\delta_{j}\right).\tag{2} C=i=1∑NTi(1−exp(−σiδi))ciwithTi=exp(−j=1∑i−1σjδj).(2)
And this paper actually uses a typical neural point-based approach just like (2), which can be represented as:
C = ∑ i ∈ N c i α i ∏ j = 1 i − 1 ( 1 − α j ) (3) C=\sum_{i\in N}c_{i}\alpha_{i}\prod_{j=1}^{i-1}(1-\alpha_{j}) \tag{3} C=i∈N∑ciαij=1∏i−1(1−αj)(3)
From this formulation, we can know what the representation of volume should contain the information of color c c c and transparency α \alpha α. These are attached to the gaussian, where Spherical Harmonics was used to represent color, just like Plenoxels. The other attributes used are the position and covariance matrix. So, now we have introduced the four attributes to represent the scene, that is positions 𝑝, 𝛼, covariance Σ, and SH coefficients representing color 𝑐 of each Gaussian.
After knowing the basic elements we need to use, now let’s work backward, starting with rendering, which was addressed in the author’s previous paper.
3.1 Real-time rendering
This method is independent of the propagation of gradients but is critical for real-time performance, which was published in the author’s paper before.

In the previous game, someone had tried to model the world in ellipsoid and render it. This is the same as the render process of Gaussian splatting. But the latter uses lots of techniques in the utilization of threads and GPU.
- Firstly, it starts by splitting the screen into 16×16 tiles and then proceeds to cull 3D Gaussians against the view frustum and each tile, only keeping Gaussians with a 99% confidence interval intersecting the view frustum.
- Then instantiate each Gaussian according to the number of tiles they overlap and assign each instance a key that combines view space depth and tile ID.
- Then sort Gaussians based on these keys using a single fast GPU Radix sort.
- Finally, launching one thread block for each tile, for a given pixel, accumulate color and transparency values by traversing the lists front-to-back, until α \alpha α goes to one.
3.2 Adaptive Control of Gaussians
In the process of fitting gaussian to the scene, we should utilize the number and volume of gaussian to strengthen the representation of the scene. It contained two methods named clone and split, as shown below.

These were judged by the view-space positional gradients. Both under-reconstruction and over-construction have large view-space positional gradients. We will clone or split the gaussian according to different conditions.
3.3 Differentiable 3D Gaussian splatting
We have known the process of rendering and control of gaussian. Finally, we will talk about how to backward the gradients to where we can optimize. This is mainly about the processing of Gaussian function.
The basic simplified formulation of 3D Gaussain can be represented as:
G ( x ) = e − 1 2 ( x ) T Σ − 1 ( x ) . (4) G(x)=e^{-\frac{1}{2}(x)^{T}\Sigma^{-1}(x)}.\tag{4} G(x)=e−21(x)TΣ−1(x).(4)
We will use α \alpha α-blending to combine it to generate the rendering picture, so that we can calculate the loss function and finish the optimization. So now we need to know how to optimize and calculate the gradients of Gaussian.
When rasterizing, the three-dimensional scene needs to be transformed into a two-dimensional space. The author hopes that the 3D Gaussian will maintain its distribution during the transformation (otherwise, if the raster finish has nothing to do with Gaussian, all the efforts will be in vain). So we should choose a method to transfer the covariance matrix to camera coordinate without change the affine relation. That is
Σ ′ = J W Σ W T J T , (5) \Sigma'=JW\Sigma W^{T}J^{T},\tag{5} Σ′=JWΣWTJT,(5)
where J J J is the Jacobian of the affine approximation of the projective transformation.
Another problem is that the covariance matrix must be semi-definite. So we use a scaling matrix 𝑆 and rotation matrix 𝑅 to assure it. That is
Σ = R S S T R T (6) \Sigma=RSS^{T}R^{T}\tag{6} Σ=RSSTRT(6)
And then we can use a 3D vector 𝑠 for scaling and a quaternion 𝑞 to represent rotation. The gradients will backward to them. These are the whole process of optimization.
4. Self-thoughts
- Summary of different representation
- Explicit representation: Mesh, Point Cloud
- Implicit representation
-
Volumetric representation: Nerf
The density value returned by the sample points reflects whether there is geometric occupancy here.
-
Surface representation: SDF(Signed Distance Function)
Outputs the distance to the nearest surface in the space from this point, where a positive value indicates outside the surface, and a negative value indicates inside the surface.
-
Refer:
[1]: 3D Gaussian Splatting:用于实时的辐射场渲染-CSDN博客
[2]: 【三维重建】3D Gaussian Splatting:实时的神经场渲染-CSDN博客
[3]: 3D Gaussian Splatting中的数学推导 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
[4]: [NeRF坑浮沉记]3D Gaussian Splatting入门:如何表达几何 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
相关文章:

【读论文】【精读】3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering
文章目录 1. What:2. Why:3. How:3.1 Real-time rendering3.2 Adaptive Control of Gaussians3.3 Differentiable 3D Gaussian splatting 4. Self-thoughts 1. What: What kind of thing is this article going to do (from the a…...
JVM理解学习
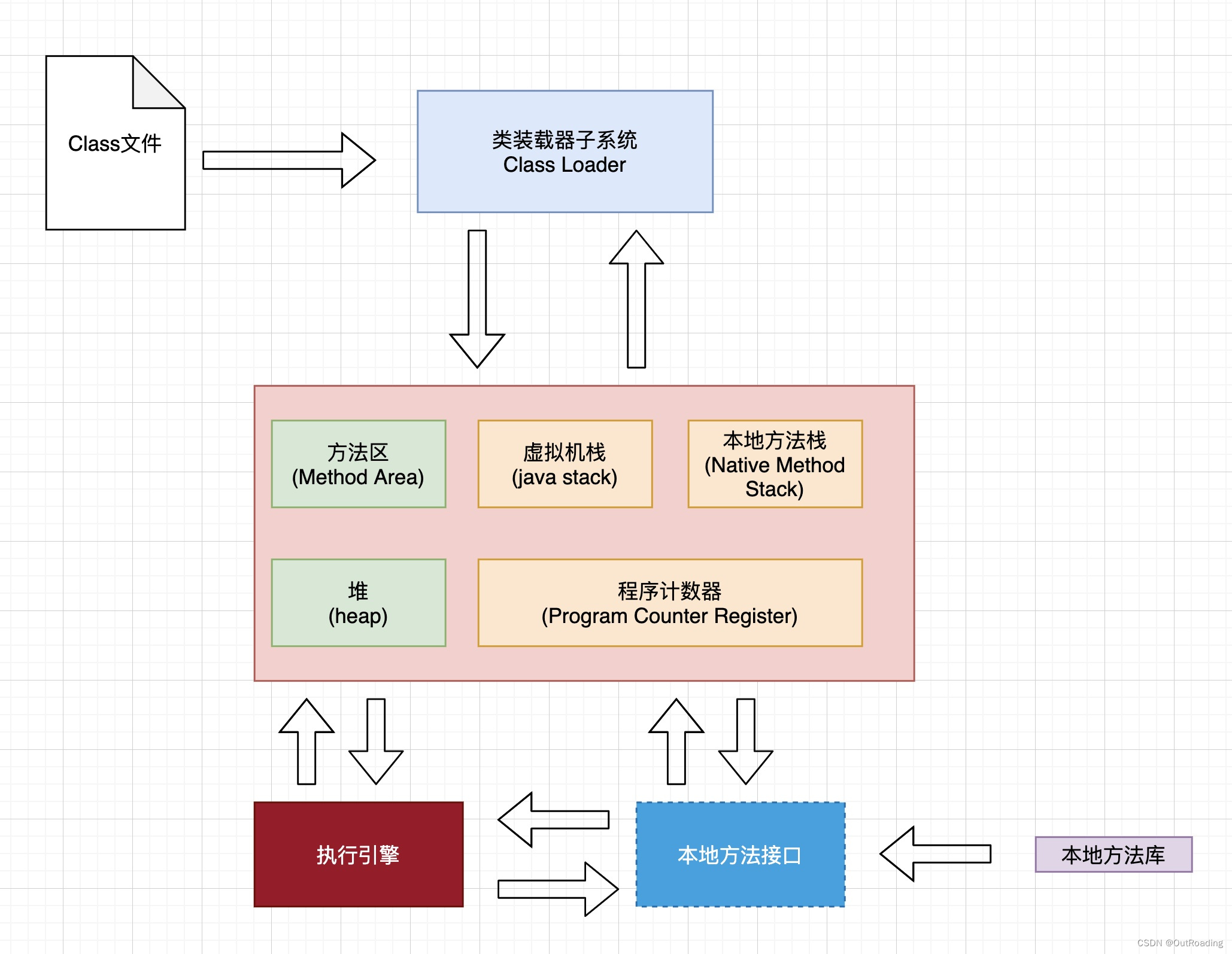
参考视频 JVM架构总览图 程序计数器 程序计数器,物理上用寄存器实现。 作用: 记住下一条JVM指令的执行地址 特点: 1 是线程私有的,随着线程的创建而创建,随着线程的消息而消息 2 是一小块内存 3 唯一不会内存溢出的地方…...

使用 Ruby 或 Python 在文件中查找
对于经常使用爬虫的我来说,在大多数文本编辑器都会有“在文件中查找”功能,主要是方便快捷的查找自己说需要的内容,那我有咩有可能用Ruby 或 Python实现类似的查找功能?这些功能又能怎么实现? 问题背景 许多流行的文本…...

python实现冒泡排序
冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法,它重复地遍历要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来。遍历数列的工作是重复地进行直到没有再需要交换,也就是说该数列已经排序完成。 以下是用Python实现冒泡排序的代…...
)
大数据开发(HBase面试真题-卷二)
大数据开发(HBase面试真题) 1、HBase读写数据流程?2、HBase的读写缓存?3、在删除HBase中的一个数据的时候,它什么时候真正的进行删除呢?4、HBase的一个region由哪些东西组成?5、HBase的rowkey为…...
基于springboot+vue的线上教育系统(源码+论文)
目录 前言 一、功能设计 二、功能实现 三、库表设计 四、论文 前言 现在大家的生活方式正在被计算机的发展慢慢改变着,学习方式也逐渐由书本走向荧幕,我认为这并不是不能避免的,但说实话,现在的生活方式与以往相比有太大的改变,人们的娱乐方式不仅仅…...

01-shell的自学课-基础变量学习
一、echo变量的一个坑 声明【临时变量】,然后打印出来;(拓展:env是linux的全局变量) [rootgong ~]# xinjizhiwashell [rootgong ~]# echo $xinjizhiwa shell [rootgong ~]# echo $xinjizhiwa-haha shell-haha [rootgo…...

鸿蒙Harmony应用开发—ArkTS声明式开发(基础手势:Span)
作为Text组件的子组件,用于显示行内文本的组件。 说明: 该组件从API Version 7开始支持。后续版本如有新增内容,则采用上角标单独标记该内容的起始版本。 该组件从API Version 10开始支持继承父组件Text的属性,即如果子组件未设置…...

前端框架的演进之路:从静态网页到现代交互体验的探索
前端框架的发展史 随着互联网的快速发展,前端技术也在不断进步,前端框架作为前端开发的重要工具,经历了从简单到复杂、从单一到多元的演变过程。本文将回顾前端框架的发展史,探讨其变迁背后的原因和趋势。 一、静态网页时代 在…...

在Linux/Ubuntu/Debian中设置字体
下载字体。 下载你喜欢的字体,双击并安装。 之后更新字体缓存: fc-cache -f -v安装 GNOME 调整。 GNOME Tweaks 是一个工具,允许你自定义 GNOME 桌面环境的各个方面,包括字体。 如果你还没有安装 GNOME Tweaks: …...

Python 常用内置函数,及实例演示
Python的内置函数非常强大,可以帮助你完成各种任务。以下是20个非常有用的Python内置函数及其使用实例: 1. abs() 返回数字的绝对值。 print(abs(-5)) # 输出:52. all() 如果迭代器的所有元素都为真(或迭代器为空)…...

C++标准输入输出和名字空间
C标准输入输出和名字空间 标准输入输出 在C中,标准输入输出(I/O)是通过标准库中的iostream库来实现的,它提供了一套流(stream)抽象来进行数据的输入和输出操作。这套流抽象包括输入流用于读取数据&#x…...

hive逗号分割行列转换
select * from ( select back_receipt_nos,order_no,reject_no from ods_oneplus.ods_us_wms_reject_order_match_all_d where order_no 10150501385980001 ) t1 lateral view explode(split(t1.back_receipt_nos, ,)) t as back_receipt_no where 1 1;...
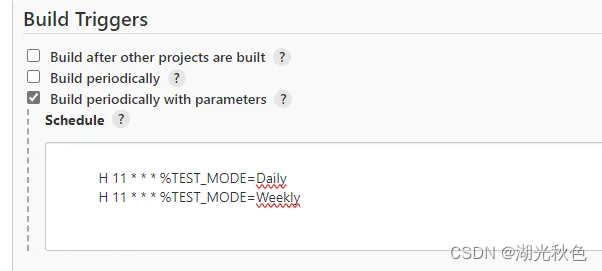
Jenkins插件Parameterized Scheduler用法
Jenkins定时触发构建的同时设定参数。可以根据不同的定时构建器设置不同参数或环境变量的值。可以设置多个参数。并结合when控制stage流程的执行。结合when和triggeredBy区分定时构建的stage和手动执行的stage。 目录 什么是Parameterized Scheduler?如何配置实现呢…...

西门子S7.NET通信库【读】操作详解
在使用西门子PLC进行工业自动化控制的过程中,经常需要与PLC进行数据交换。S7.NET是一款广泛应用于.NET平台的西门子PLC通信库,它为开发者提供了一系列的API函数,以便在C#、VB.NET等.NET语言中轻松实现与西门子PLC的数据交互。本文将详细介绍如…...

Qt/C++音视频开发69-保存监控pcm音频数据到mp4文件/监控录像/录像存储和回放/264/265/aac/pcm等
一、前言 用ffmpeg做音视频保存到mp4文件,都会遇到一个问题,尤其是在视频监控行业,就是监控摄像头设置的音频是PCM/G711A/G711U,解码后对应的格式是pcm_s16be/pcm_alaw/pcm_mulaw,将这个原始的音频流保存到mp4文件是会…...

闲聊Swift的枚举关联值
闲聊Swift的枚举关联值 枚举,字面上理解,就是把东西一件件列出来。 在许多计算机语言中,枚举都是一种重要的数据结构。使用枚举可以使代码更简洁,语义性更强,更加健壮。 Swift语言也不例外。但和其他语言相比…...

抓取Instagram数据:Fizzler库带您进入C#爬虫程序的世界
引言 在当今数字化的世界中,数据是无价之宝。社交媒体平台如Instagram成为了用户分享照片、视频和故事的热门场所。作为开发人员,我们可以利用爬虫技术来抓取这些平台上的数据,进行分析、挖掘和应用。本文将介绍如何使用C#编写一个简单的Ins…...

Codeforces Round 933 (Div. 3) A~D
比赛链接 : codeforces.com/contest/1941 A . Rudolf and the Ticket 直接暴力即可 ; #include<bits/stdc.h> #define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); #define endl \n #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define sz(a) (int)a.size() #define p…...
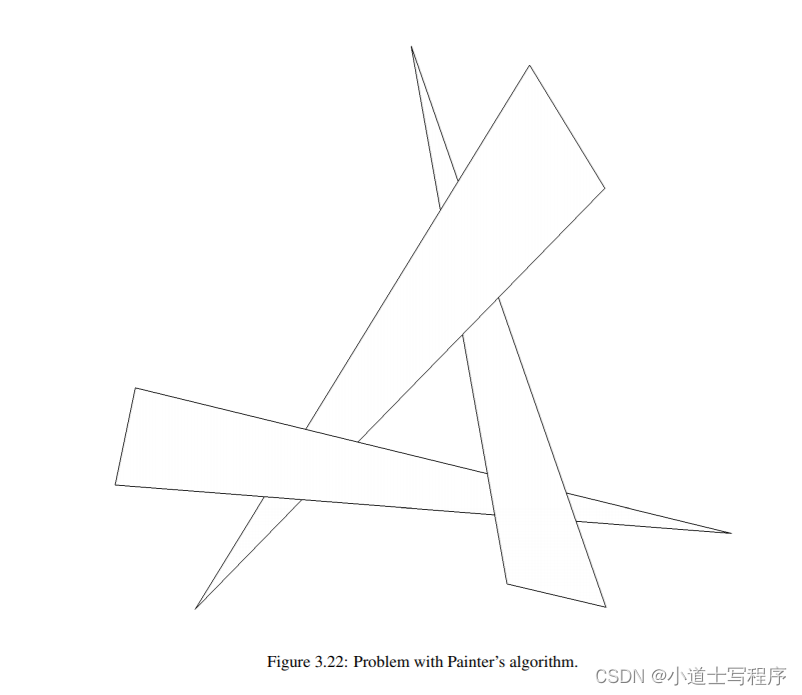
《vtk9 book》 官方web版 第3章 - 计算机图形基础 (3 / 5)
3.8 演员几何 我们已经看到了光照属性如何控制演员的外观,以及相机如何结合变换矩阵将演员投影到图像平面上。剩下的是定义演员的几何形状,以及如何将其定位在世界坐标系中。 建模 计算机图形学研究中的一个重要主题是建模或表示物体的几何形状。…...
cf2117E
原题链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/2117/problem/E 题目背景: 给定两个数组a,b,可以执行多次以下操作:选择 i (1 < i < n - 1),并设置 或,也可以在执行上述操作前执行一次删除任意 和 。求…...
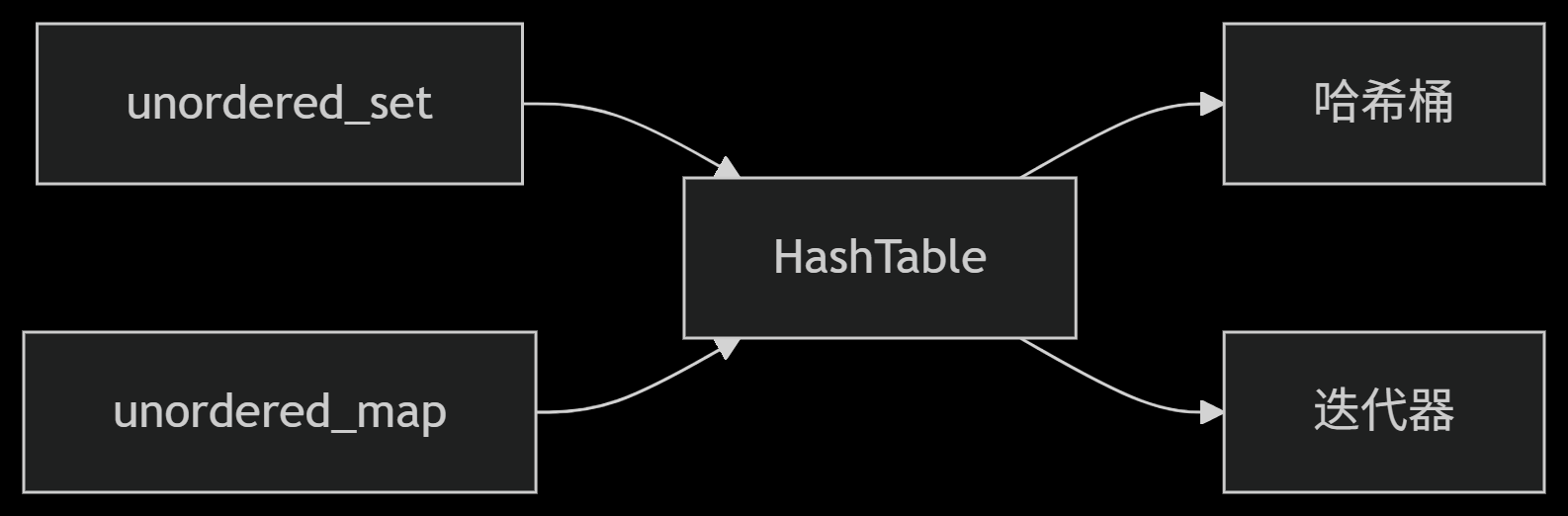
从零实现STL哈希容器:unordered_map/unordered_set封装详解
本篇文章是对C学习的STL哈希容器自主实现部分的学习分享 希望也能为你带来些帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、源码结构分析 1. SGISTL30实现剖析 // hash_set核心结构 template <class Value, class HashFcn, ...> class hash_set {ty…...
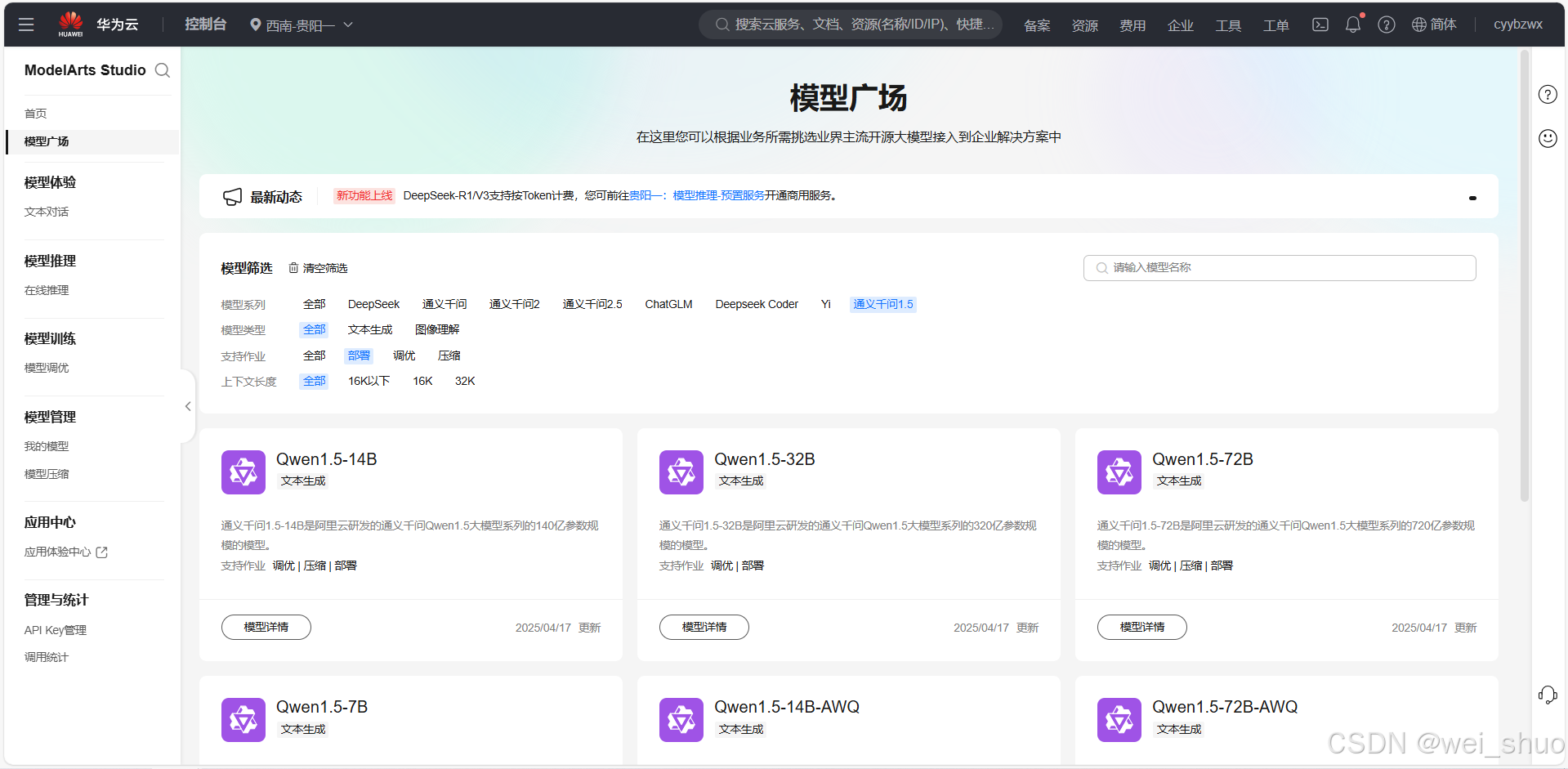
华为云Flexus+DeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建
华为云FlexusDeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建 前言 如今大模型其性能出色,华为云 ModelArts Studio_MaaS大模型即服务平台华为云内置了大模型,能助力我们轻松驾驭 DeepSeek-V3/R1,本文中将分享如何…...
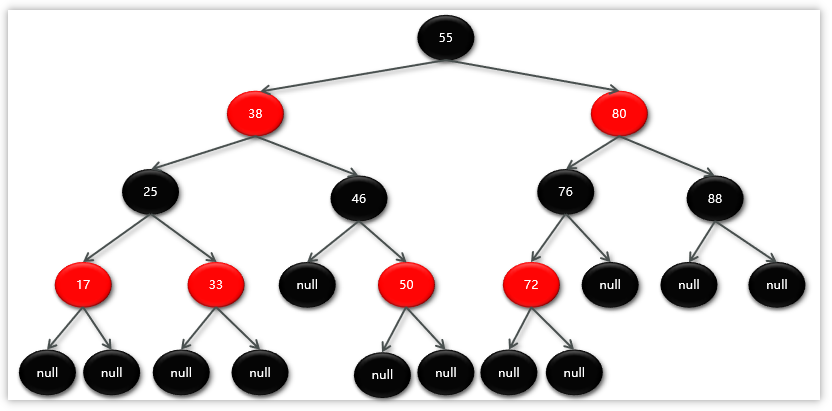
Map相关知识
数据结构 二叉树 二叉树,顾名思义,每个节点最多有两个“叉”,也就是两个子节点,分别是左子 节点和右子节点。不过,二叉树并不要求每个节点都有两个子节点,有的节点只 有左子节点,有的节点只有…...

使用Matplotlib创建炫酷的3D散点图:数据可视化的新维度
文章目录 基础实现代码代码解析进阶技巧1. 自定义点的大小和颜色2. 添加图例和样式美化3. 真实数据应用示例实用技巧与注意事项完整示例(带样式)应用场景在数据科学和可视化领域,三维图形能为我们提供更丰富的数据洞察。本文将手把手教你如何使用Python的Matplotlib库创建引…...

Linux 中如何提取压缩文件 ?
Linux 是一种流行的开源操作系统,它提供了许多工具来管理、压缩和解压缩文件。压缩文件有助于节省存储空间,使数据传输更快。本指南将向您展示如何在 Linux 中提取不同类型的压缩文件。 1. Unpacking ZIP Files ZIP 文件是非常常见的,要在 …...

解读《网络安全法》最新修订,把握网络安全新趋势
《网络安全法》自2017年施行以来,在维护网络空间安全方面发挥了重要作用。但随着网络环境的日益复杂,网络攻击、数据泄露等事件频发,现行法律已难以完全适应新的风险挑战。 2025年3月28日,国家网信办会同相关部门起草了《网络安全…...

实战三:开发网页端界面完成黑白视频转为彩色视频
一、需求描述 设计一个简单的视频上色应用,用户可以通过网页界面上传黑白视频,系统会自动将其转换为彩色视频。整个过程对用户来说非常简单直观,不需要了解技术细节。 效果图 二、实现思路 总体思路: 用户通过Gradio界面上…...

Vue 模板语句的数据来源
🧩 Vue 模板语句的数据来源:全方位解析 Vue 模板(<template> 部分)中的表达式、指令绑定(如 v-bind, v-on)和插值({{ }})都在一个特定的作用域内求值。这个作用域由当前 组件…...
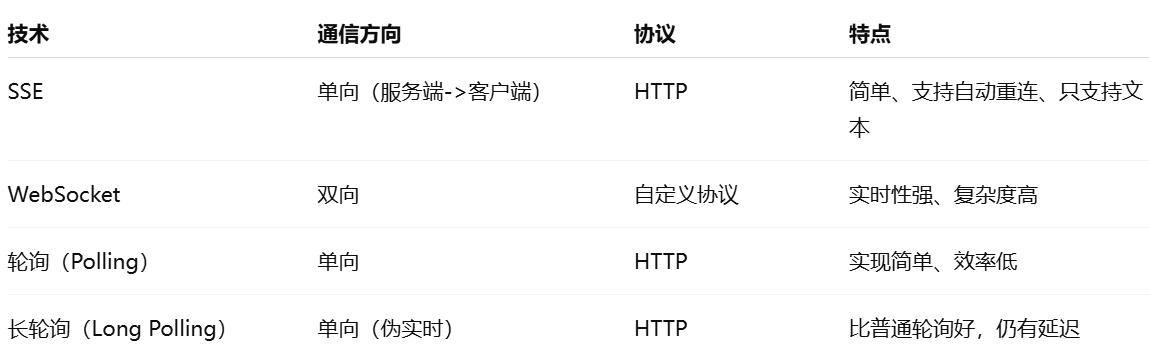
使用SSE解决获取状态不一致问题
使用SSE解决获取状态不一致问题 1. 问题描述2. SSE介绍2.1 SSE 的工作原理2.2 SSE 的事件格式规范2.3 SSE与其他技术对比2.4 SSE 的优缺点 3. 实战代码 1. 问题描述 目前做的一个功能是上传多个文件,这个上传文件是整体功能的一部分,文件在上传的过程中…...
