Linux 多线程开发
第三章 Linux 多线程开发
- 3.1 线程
- 3.1.2 线程操作
- 3.1.2 线程属性
- 3.2 线程同步
- 3.2.1 互斥量/锁
- 3.2.2 死锁
- 3.2.3 读写锁
- 3.3 生产者消费者模型
- 3.3.1 条件变量
- 3.3.2 信号量/灯
网络编程系列文章:
第1章 Linux系统编程入门(上)
第1章 Linux系统编程入门(下)
第2章 Linux多进程开发(上)
第2章 Linux多进程开发(下)
第3章 Linux多线程开发
第4章 Linux网络编程
- 4.1 网络基础
- 4.2 socket 通信基础
- 4.3 TCP套接字通信
- 4.4 IO多路复用
- 4.5 UDP 通信
第5章 Web服务器
3.1 线程
-
线程概述
-
与进程(
process)类似,线程 (thread)是允许应用程序 并发执行 多个任务的一种机制。一个进程可以包含多个线程。同一个程序中的所有线程均会独立执行相同程序,且共享同一份全局内存区域 ,其中包括 初始化数据段、未初始化数据段,以及 堆内存段。(传统意义上的 UNIX 进程只是多线程程序的一个特例,该进程只包含一个线程) -
进程 是 CPU 分配资源的最小单位,线程是操作系统调度执行的最小单位。
-
线程是轻量级的进程(
LWP Light Weight Process),在 Linux 环境下线程的本质仍是进程。 -
查看指定进程的 LWP 号:
ps -Lf pid例如:打开火狐浏览器,查看进程所包含的线程
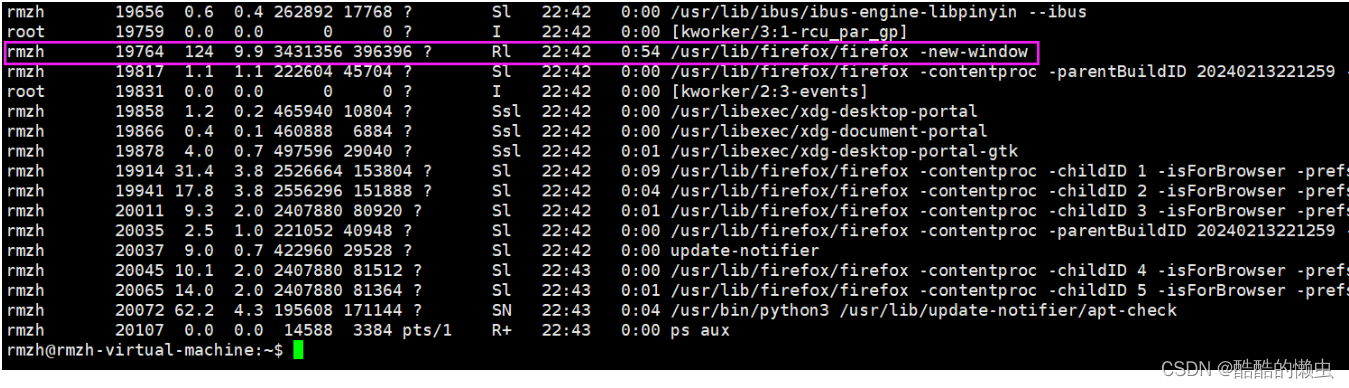
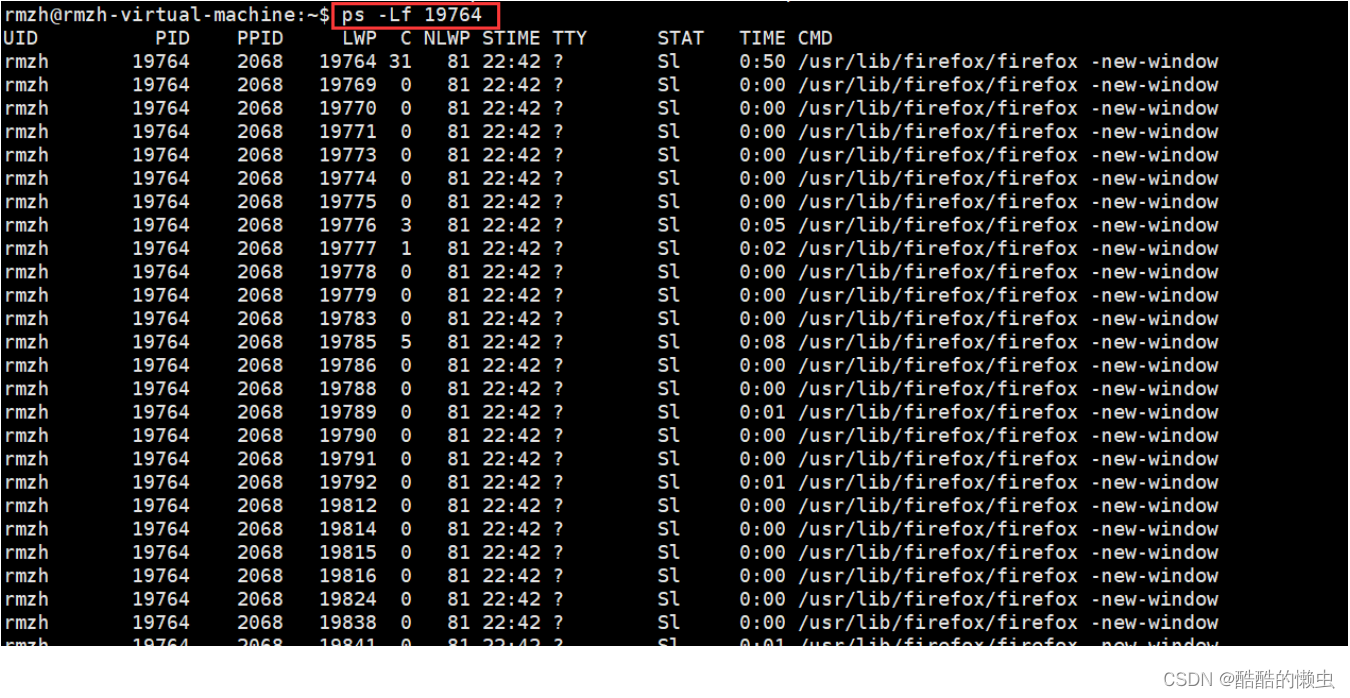
-
-
线程和进程区别
- 进程间的信息难以共享。由于除去只读代码段外,父子进程并未共享内存,因此必须采用一些进程间通信方式,在进程间进行信息交换。
- 调用
fork()来创建进程的代价相对较高,即便利用写时复制技术,仍然需要复制诸如 内存页表 和 文件描述符表 之类的多种 进程属性,这意味着fork()调用在时间上的开销依然不菲。 - 线程之间能够方便、快速地共享信息。只需将数据复制到 共享(全局或堆)变量 中即可。
- 创建线程比创建进程通常要快 10 倍甚至更多。线程间是共享虚拟地址空间的,无需采用写时复制来复制内存,也无需复制页表。
-
线程和进程虚拟地址空间
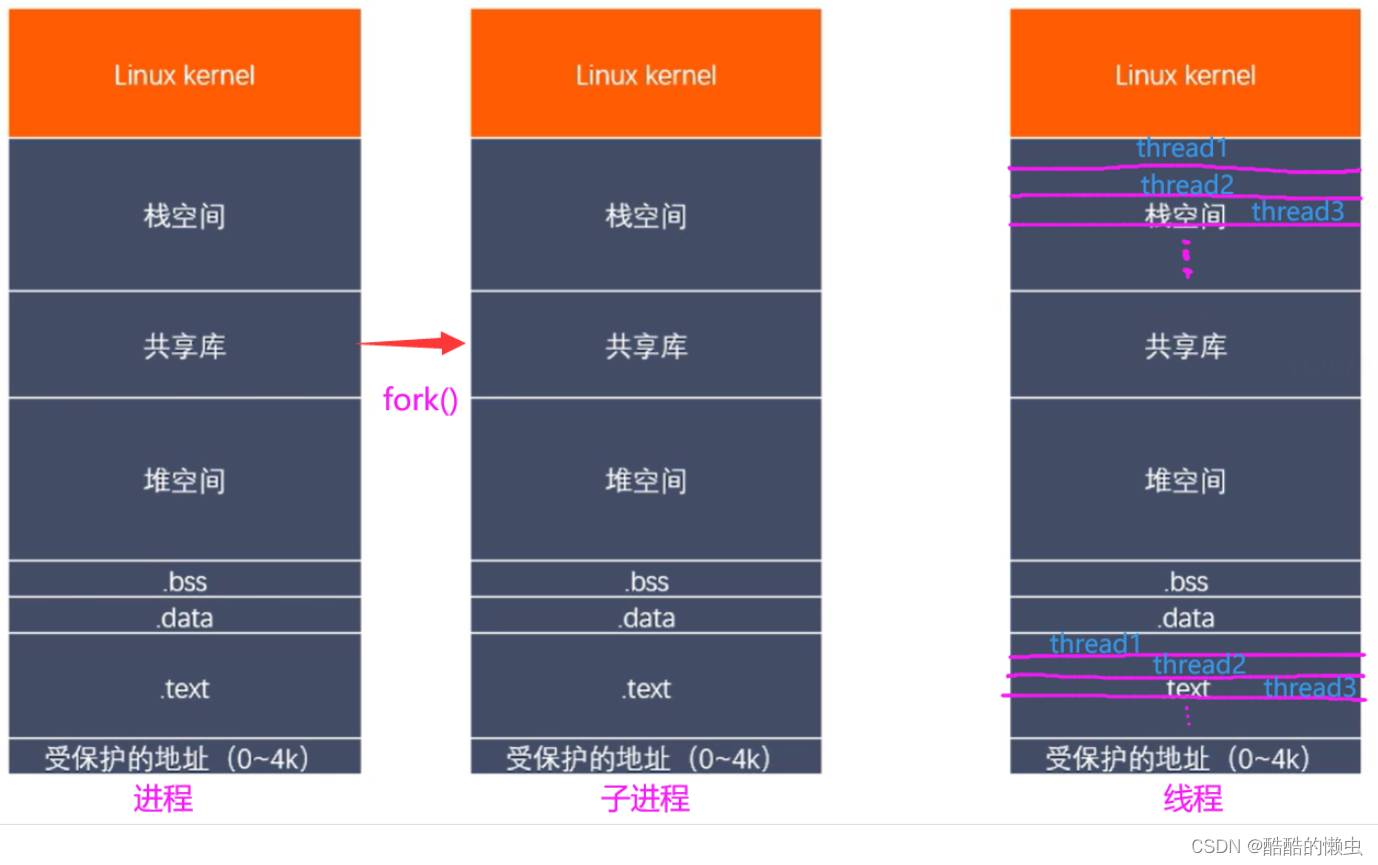
-
线程之间共享 和 非共享资源
-
共享资源
- 进程 ID 和父进程 ID
- 进程组 ID 和会话 ID
- 用户 ID 和 用户组 ID
- 文件描述符表 (这些都是内核中的数据)
- 信号处置
- 文件系统的相关信息:文件权限掩码 (
umask)、当前工作目录 - 虚拟地址空间(除
栈、.text)
-
非共享资源
- 线程 ID
- 信号掩码
- 线程特有数据
error变量- 实时调度策略和优先级
- 栈,本地变量和函数的调用链接信息
-
-
NPTL 简介
-
当 Linux 最初开发时,在内核中并不能真正支持线程。但是它的确可以通过
clone()系统调用将进程作为可调度的实体。这个调用创建了调用进程(calling process)的一个拷贝,这个拷贝与调用进程共享相同的地址空间。LinuxThreads项目使用这个调用来完成在用户空间模拟对线程的支持。不幸的是,这种方法有一些缺点,尤其是在信号处理、调度和进程间同步等方面都存在问题。另外,这个线程模型也不符合 POSIX 的要求。 -
要改进
LinuxThreads,需要内核的支持,并且重写线程库。有两个相互竞争的项目开始来满足这些要求。一个包括 IBM 的开发人员的团队开展了 NGPT ( Next Generation POSIX Threads )项目。同时Red Hat 的一些开发人员开展了 NPTL 项目。 NGPT 在 2003 年中期被放弃了,把这个领域完全留给了NPTL。 -
NPTL ,或称为
Native POSIX Thread Library,是 Linux 线程的一个新实现,它克服了 LinuxThreads 的缺点,同时也符合 POSIX 的需求。与 LinuxThreads 相比,它在性能和稳定性方面都提供了重大的改进。 -
查看当前
pthread库版本:getconf GNU_LIBPTHREAD_VERSION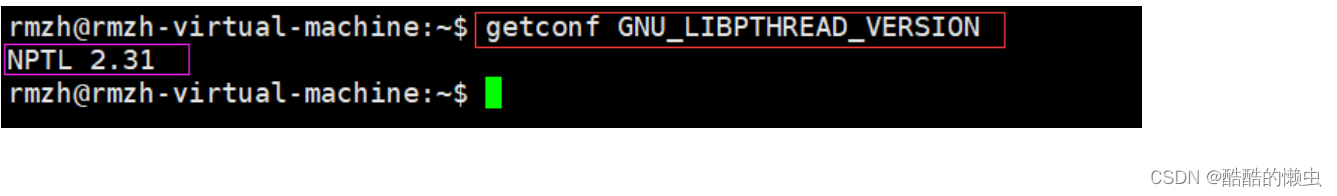
-
3.1.2 线程操作
// 创建一个子线程
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);// 获取当前的线程的线程ID
pthread_t pthread_self(void);// 比较两个线程ID是否相等
int pthread_equal(pthread_t t1, pthread_t t2);// 终止一个线程
void pthread_exit(void *retval);// 和一个已经终止的线程进行连接
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);// 分离一个线程。被分离的线程在终止的时候,会自动释放资源返回给系统
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);// 取消线程(让线程终止)
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);
-
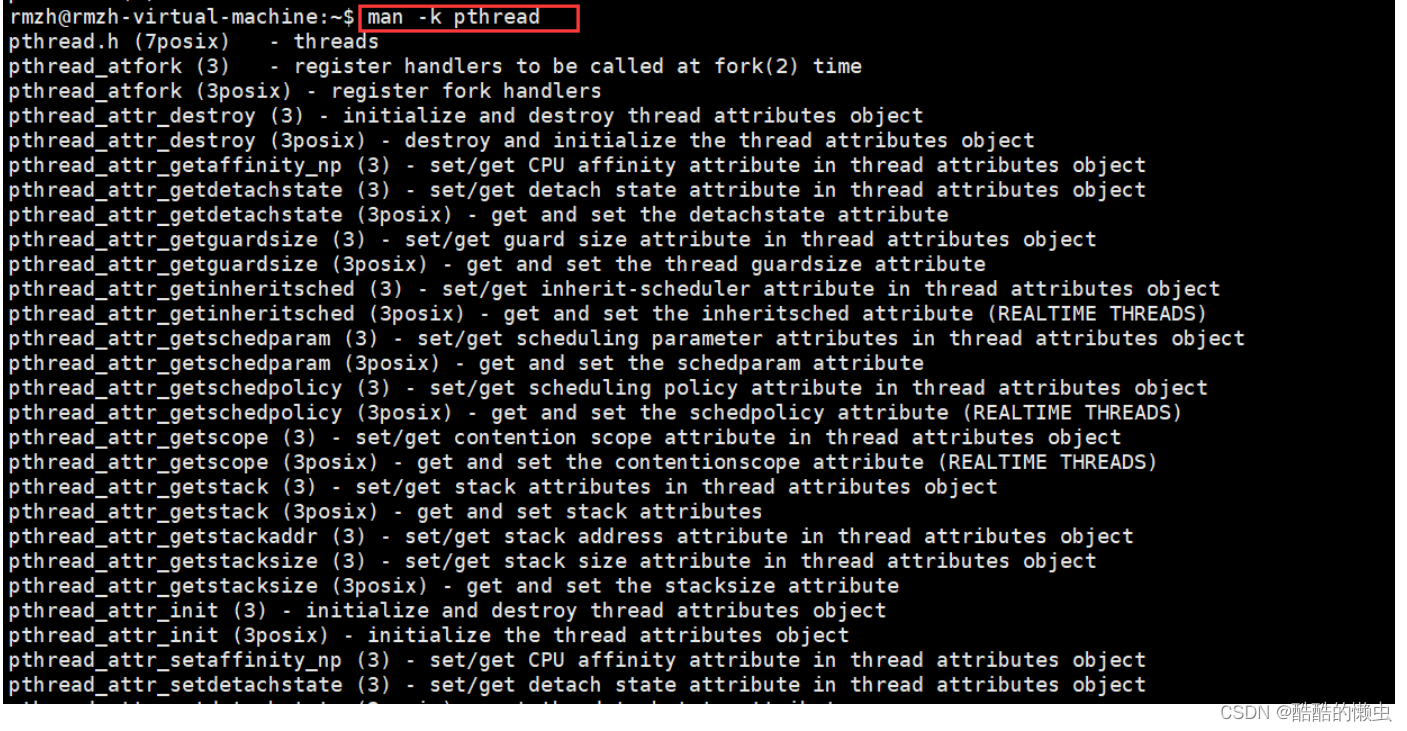
以上命令也可以使用
man pthread+按两次Tab键 / man -k pthread进行查询# 如果输入,显示 没有 pthread 的手册页条目 # 执行如下两条命令 sudo apt-get install glibc-doc sudo apt-get install manpages-posix manpages-posix-dev# 再输入 man pthread + 按两次Tab键 man -k pthread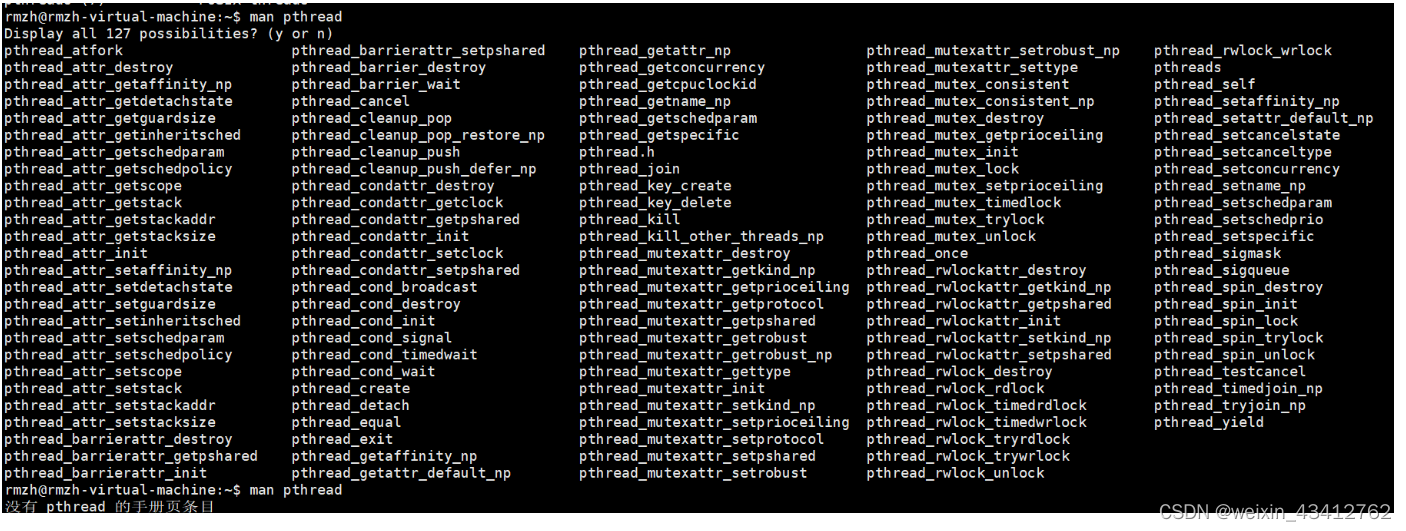
-
一般情况下,
main函数所在的线程我们称之为主线程(main线程),其余创建的线程称之为 子线程。- 程序中默认只有一个进程,
fork()函数调用,会有2进程。(主进程、子进程) - 程序中默认只有一个线程,
pthread_create()函数调用,2个线程。(主线程、子线程)
- 程序中默认只有一个进程,
-
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);-
功能:创建 一个子线程
-
参数:
thread:传出参数,线程创建成功后,子线程的线程ID 被写到该变量中。attr: 设置线程的属性,一般使用默认值,NULLstart_routine: 函数指针,这个函数是子线程需要处理的逻辑代码arg: 给第三个参数使用,传参
-
返回值:
- 成功:
0 - 失败:返回错误号。这个错误号和之前
errno不太一样。- 获取错误号的信息:
char * strerror(int errnum);
- 获取错误号的信息:
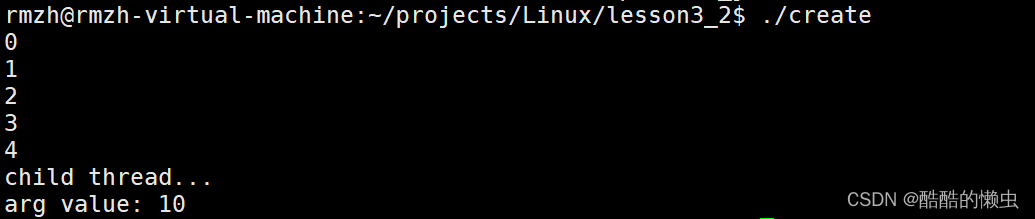
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h>// 子线程 void * callback(void * arg) {printf("child thread...\n");printf("arg value: %d\n", *(int *)arg);return NULL; }int main() { // 主线程pthread_t tid;int num = 10;// 创建一个子线程int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, (void *)&num);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error : %s\n", errstr);} for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {printf("%d\n", i);}sleep(1);return 0; // exit(0); 退出进程 }- 编译上面对的
pthread_create.c文件:gcc pthread_create.c -o create -lpthread,因为pthread.h是第三方库,所有要使用-l库名链接。⭐️⭐️⭐️
- 成功:
-
-
void pthread_exit(void *retval);- 功能:终止一个线程,在哪个线程中调用,就表示终止哪个线程
- 参数:
retval: 需要传递一个指针,作为一个返回值,可以在pthread_join()中获取到。
-
pthread_t pthread_self(void);- 功能:获取 当前的线程的 线程ID
-
int pthread_equal(pthread_t t1, pthread_t t2);- 功能:比较 两个线程ID是否相等
注意:不同的操作系统,
pthread_t类型的实现不一样,有的是 无符号的长整型,有的是使用 结构体 去实现的。#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h>void * callback(void * arg) {printf("child thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self());return NULL; // pthread_exit(NULL); } int main() {// 创建一个子线程pthread_t tid;int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error : %s\n", errstr);}// 主线程for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {printf("%d\n", i);}printf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid, pthread_self());// 让主线程退出,当主线程退出时,不会影响其他正常运行的线程。pthread_exit(NULL);printf("main thread exit\n"); // 该句不会运行return 0; // exit(0); } -
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);- 功能:和一个已经终止的线程进行 连接
回收子线程的资源
这个函数是阻塞函数,调用一次只能回收一个子线程
一般在主线程中使用 - 参数:
thread:需要回收的子线程的IDretval: 接收子线程退出时的返回值 (二级指针)
- 返回值:
0: 成功
非0: 失败,返回的错误号
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h>int value = 10; //全局变量(共享)void * callback(void * arg) {printf("child thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self());// sleep(3);// return NULL; // int value = 10; // 局部变量,该线程退出时就会销毁pthread_exit((void *)&value); //等同: return (void *)&value; } int main() {// 创建一个子线程pthread_t tid;int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error : %s\n", errstr);}// 主线程for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {printf("%d\n", i);}printf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid ,pthread_self());// 主线程调用pthread_join()回收子线程的资源int * thread_retval;ret = pthread_join(tid, (void **)&thread_retval);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error : %s\n", errstr);}printf("exit data : %d\n", *thread_retval); // 返回的全局变量 (如果是子线程中的局部变量,会返回随机值,因为子线程中的局部变量被收回)printf("回收子线程资源成功!\n");// 让主线程退出,当主线程退出时,不会影响其他正常运行的线程。pthread_exit(NULL);return 0; } - 功能:和一个已经终止的线程进行 连接
-
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);-
功能:分离 一个线程。被分离的线程在终止的时候,会自动释放资源返回给系统。
- 不能多次分离,会产生不可预料的行为。
- 不能去连接一个已经分离的线程,会报错。
-
参数:需要分离的线程的ID
-
返回值:
成功:
0失败:返回错误号
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h>void * callback(void * arg) {printf("chid thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self());return NULL; }int main() {// 创建一个子线程pthread_t tid;int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error1 : %s\n", errstr);}// 输出主线程和子线程的idprintf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid, pthread_self());// 设置子线程分离,子线程分离后,子线程结束时对应的资源就不需要主线程释放ret = pthread_detach(tid);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error2 : %s\n", errstr);}// 设置分离后,对分离的子线程进行连接 pthread_join()// ret = pthread_join(tid, NULL);// if(ret != 0) {// char * errstr = strerror(ret);// printf("error3 : %s\n", errstr);// }pthread_exit(NULL);return 0; } -
-
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread);-
功能:取消 线程(让线程终止)
取消某个线程,可以终止某个线程的运行,
但是并不是立马终止,而是当子线程执行到一个取消点,线程才会终止。
- 取消点:系统规定好的一些 系统调用,我们可以粗略的理解为 从 用户区 到 内核区 的切换,这个位置称之为取消点。
-
返回值:(和上面的相同)
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h>void * callback(void * arg) {printf("chid thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self());for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {printf("child : %d\n", i); // 也是一个取消点}return NULL; }int main() {// 创建一个子线程pthread_t tid;int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, callback, NULL);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error1 : %s\n", errstr);}// 取消线程pthread_cancel(tid);for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {printf("%d\n", i);}// 输出主线程和子线程的idprintf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid, pthread_self());pthread_exit(NULL);return 0; } -
3.1.2 线程属性
// 线程属性类型: pthread_attr_t
// 初始化线程属性变量
int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t *attr);// 释放线程属性的资源
int pthread_attr_destroy(pthread_attr_t *attr);// 获取线程分离的状态属性
int pthread_attr_getdetachstate(const pthread_attr_t *attr, int *detachstate);// 设置线程分离的状态属性
int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *attr, int detachstate);
-
查看线程属性的操作:
man pthread_attr_+按两次Tab键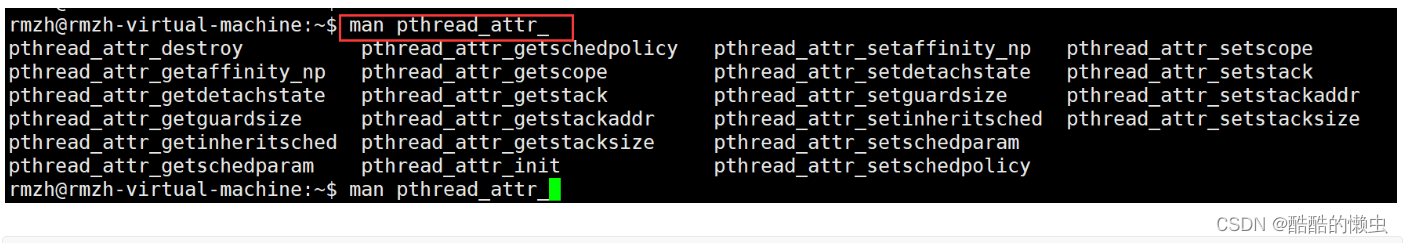
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h>void * callback(void * arg) {printf("chid thread id : %ld\n", pthread_self());return NULL; }int main() {// 创建一个线程属性变量pthread_attr_t attr;// 初始化属性变量pthread_attr_init(&attr);// 设置属性pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);// 创建一个子线程pthread_t tid;int ret = pthread_create(&tid, &attr, callback, NULL);if(ret != 0) {char * errstr = strerror(ret);printf("error1 : %s\n", errstr);}// 获取线程的栈的大小size_t size;pthread_attr_getstacksize(&attr, &size);printf("thread stack size : %ld\n", size);// 输出主线程和子线程的idprintf("tid : %ld, main thread id : %ld\n", tid, pthread_self());// 释放线程属性资源pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);pthread_exit(NULL);return 0; }
3.2 线程同步
- 线程的主要优势在于,能够通过 全局变量 来共享信息。不过,这种便捷的共享是有代价的:必须确保多个线程不会同时修改同一变量,或者某一线程不会读取正在由其他线程修改的变量。
- 临界区 是指访问某一 共享资源的代码片段,并且这段代码的执行应为 原子操作,也就是同时访问同一共享资源的其他线程 不应终断 该片段的执行。
- 线程同步:即当有一个线程在对内存进行操作时,其他线程都不可以对这个内存地址进行操作,直到该线程完成操作,其他线程才能对该内存地址进行操作,而其他线程则处于等待状态。
使用多线程实现买票的案例。
-
有3个窗口,一共是100张票。
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h>// 全局变量,所有的线程都共享这一份资源。 int tickets = 100;void * sellticket(void * arg) {// 卖票while(tickets > 0) {usleep(6000);printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets);tickets--;}return NULL; }int main() { // 主线程// 创建3个子线程pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3;pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL);pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL);pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL);// 回收子线程的资源,阻塞pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);pthread_join(tid3, NULL);// 或设置线程分离,子线程结束后资源自动回收// pthread_detach(tid1);// pthread_detach(tid2);// pthread_detach(tid3);pthread_exit(NULL); // 退出主线程return 0;// 如果不设置上一步,主线程结束后,子线程也会全结束。 }
3.2.1 互斥量/锁
-
为避免线程更新共享变量时出现问题,可以使用 互斥量(
mutex是mutual exclusion的缩写)来确保同时仅有一个线程可以访问某项共享资源。可以使用互斥量来保证对任意共享资源的 原子访问。 -
互斥量有两种状态: 已锁定(
locked)和 未锁定 (unlocked)。任何时候,至多只有一个线程可以锁定该互斥量。试图对已经锁定的某一互斥量再次加锁,将可能 阻塞线程 或者 报错失败,具体取决于加锁时使用的方法。 -
一旦线程锁定互斥量,随即成为该互斥量的所有者,只有所有者才能给互斥量解锁。一般情况下,对每一共享资源(可能由多个相关变量组成)会使用不同的互斥量,每一线程在访问同一资源时将采用如下协议:
- 针对共享资源 锁定互斥量
- 访问 共享资源
- 对互斥量 解锁
-
如果多个线程试图执行这一块代码(一个临界区),事实上只有一个线程能够持有该 互斥量(其他线程将遭到阻塞),即同时只有一个线程能够进入这段代码区域,如下图所示:
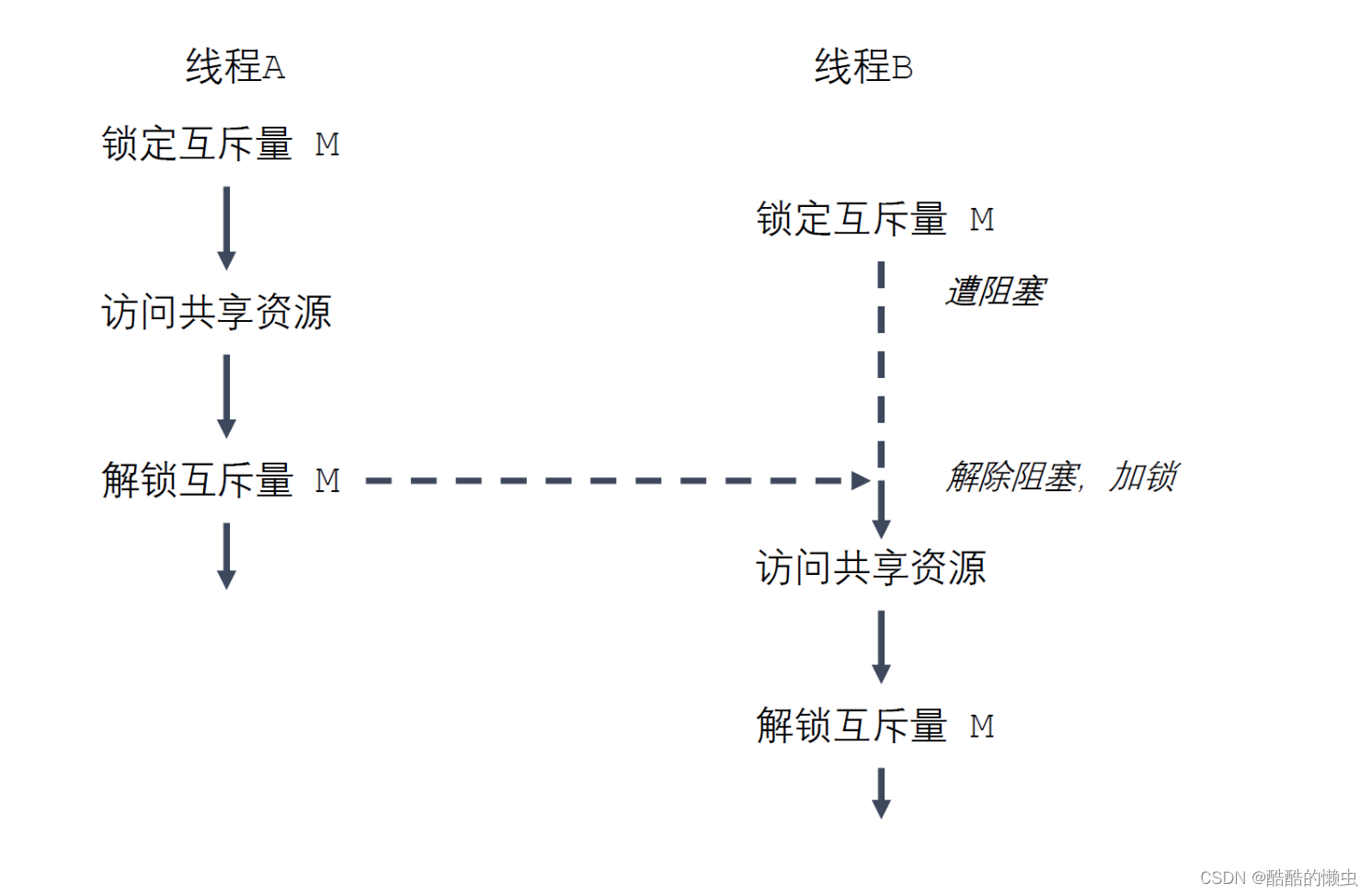
-
互斥量相关操作函数
- 互斥量的类型
pthread_mutex_t
// 初始化互斥量 int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);// 释放互斥量的资源 int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);// 加锁,阻塞的,如果有一个线程加锁了,那么其他的线程只能阻塞等待 int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);// 尝试加锁,如果加锁失败,不会阻塞,会直接返回。 int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); // 非阻塞// 解锁 int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);-
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);-
功能:初始化互斥量
-
参数:
mutex: 需要初始化的互斥量变量attr: 互斥量相关的属性,NULL
-
restrict: C语言的修饰符,被修饰的指针,不能由另外的一个指针进行操作。pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex = xxx; pthread_mutex_t *mutex1 = mutex; // 错误
解决上面买票的问题
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h>// 全局变量,所有的线程都共享这一份资源。 int tickets = 1000;// 创建一个互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex;void * sellticket(void * arg) {// 卖票while(1) {// 加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);if(tickets > 0) {usleep(6000);printf("%ld 正在卖第 %d 张门票\n", pthread_self(), tickets);tickets--;}else {// 解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);break;}// 解锁pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}return NULL; }int main() {// 初始化互斥量pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);// 创建3个子线程pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3;pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, sellticket, NULL);pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, sellticket, NULL);pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, sellticket, NULL);// 回收子线程的资源,阻塞pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);pthread_join(tid3, NULL);pthread_exit(NULL); // 退出主线程// 释放互斥量资源pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);return 0; } -
- 互斥量的类型
3.2.2 死锁
-
有时,一个线程需要同时访问两个或更多不同的共享资源,而每个资源又都由不同的互斥量管理。当超过一个线程 加锁 同一组互斥量 时,就有可能发生 死锁。
-
两个或两个以上的进程在执行过程中,因争夺共享资源而造成的一种 互相等待 的现象,若无外力作用,它们都将无法推进下去。此时称系统处于死锁状态或系统产生了死锁。
-
死锁的几种场景:
- 忘记 释放锁
- 重复 加锁
- 多线程多锁,抢占锁资源
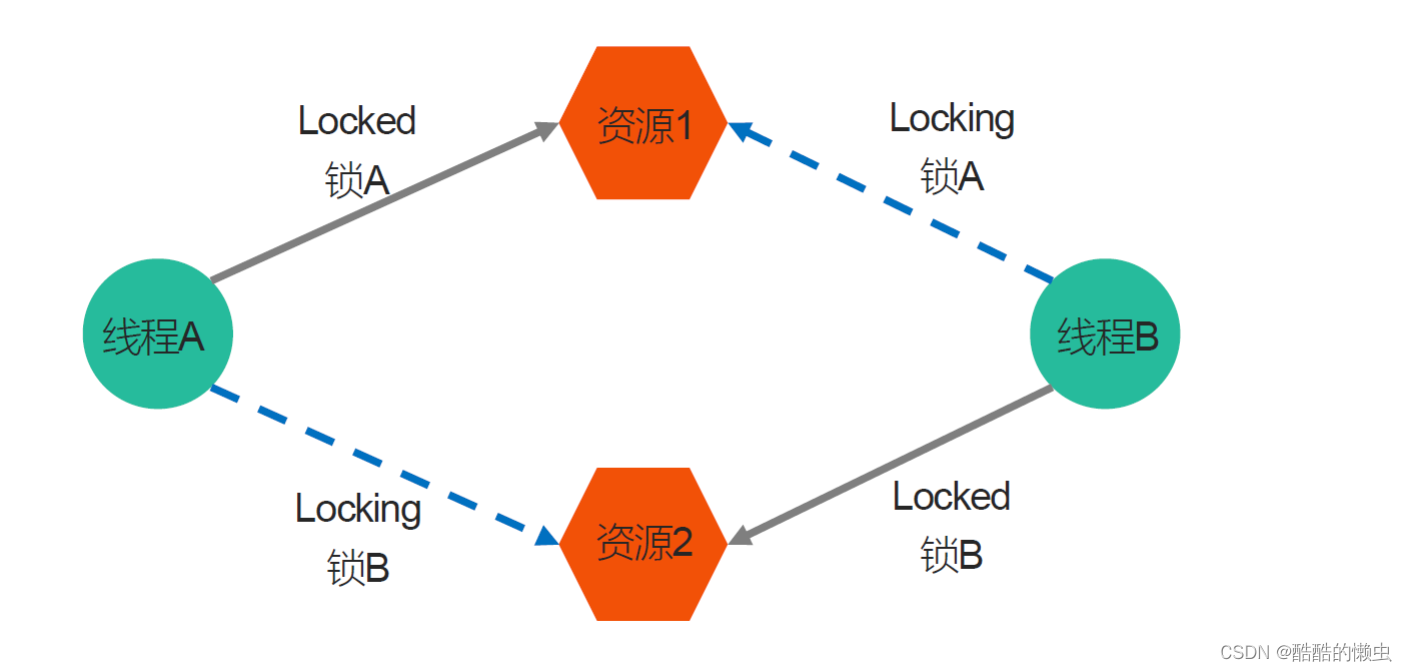
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h>// 创建2个互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex1, mutex2;void * workA(void * arg) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);sleep(1);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2);printf("workA....\n");pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);return NULL; }void * workB(void * arg) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex2);sleep(1);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);printf("workB....\n");pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex2);return NULL; }int main() {// 初始化互斥量pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL);pthread_mutex_init(&mutex2, NULL);// 创建2个子线程pthread_t tid1, tid2;pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, workA, NULL);pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, workB, NULL);// 回收子线程资源pthread_join(tid1, NULL);pthread_join(tid2, NULL);// 释放互斥量资源pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex1);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex2);return 0; }
3.2.3 读写锁
-
当有一个线程已经持有 互斥锁 时,互斥锁将所有试图进入临界区的线程都阻塞住。但是考虑一种情形,当前持有互斥锁的线程只是要 读访问 共享资源,而同时有其它几个线程也想 读取 这个共享资源,但是由于互斥锁的排它性,所有其它线程都无法获取锁,也就无法读访问共享资源了,但是实际上多个线程同时 读访问 共享资源并不会导致问题。
-
在对数据的读写操作中,更多的是 读操作,写操作较少,例如对数据库数据的读写应用。为了满足当前能够允许多个读出,但只允许一个写入的需求,线程提供了 读写锁 来实现。
-
读写锁 的特点:
- 如果有其它线程读数据,则允许其它线程执行读操作,但不允许写操作。
- 如果有其它线程写数据,则其它线程都不允许读、写操作。
- 写是独占的,写的优先级高。
-
读写锁相关操作函数
- 读写锁 的类型
pthread_rwlock_t
// 初始化 int pthread_rwlock_init(pthread_rwlock_t *restrict rwlock, const pthread_rwlockattr_t *restrict attr);// 释放资源 int pthread_rwlock_destroy(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock);// 加读锁 int pthread_rwlock_rdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); int pthread_rwlock_tryrdlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); // 尝试加读锁// 加写锁 int pthread_rwlock_wrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); int pthread_rwlock_trywrlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); // 尝试加写锁// 解锁 int pthread_rwlock_unlock(pthread_rwlock_t *rwlock); - 读写锁 的类型
案例:8个线程 操作 同一个全局变量。
3个线程不定时 写 这个全局变量,5个线程不定时的 读 这个全局变量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>// 创建一个共享数据
int num = 1;
// pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 定义互斥锁
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock; // 定义读写锁void * writeNum(void * arg) {while(1) {pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);num++;printf("++write, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num);pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);usleep(100);}return NULL;
}void * readNum(void * arg) {while(1) {pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);printf("===read, tid : %ld, num : %d\n", pthread_self(), num);pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);usleep(100);}return NULL;
}int main() {pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);// 创建3个写线程,5个读线程pthread_t wtids[3], rtids[5];for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {pthread_create(&wtids[i], NULL, writeNum, NULL);}for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {pthread_create(&rtids[i], NULL, readNum, NULL);}// 设置线程分离for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {pthread_detach(wtids[i]);}for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {pthread_detach(rtids[i]);}pthread_exit(NULL); // 主线程退出,子线程继续运行pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);return 0;
}
3.3 生产者消费者模型
- 生产者消费者模型中的对象:
- 生产者(多个)
- 消费者(多个)
- 容器
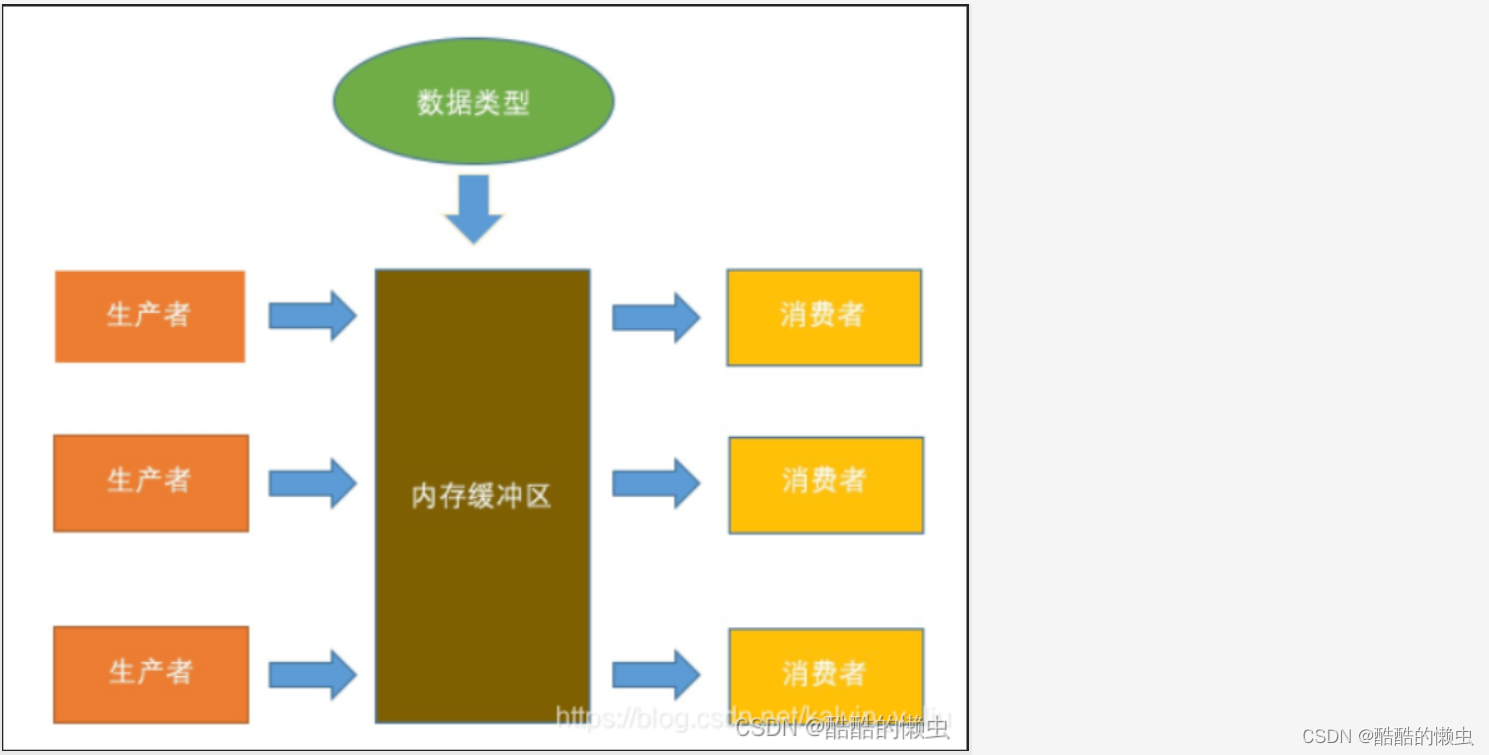
当容器中已满,生产者停止生产,并通知消费者消费产品;
当容器中为空,消费者停止消费,并通知生产者生产产品。
-
生产者消费者模型(粗略的版本,先不考虑容器的容量)
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h>// 创建一个互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex;struct Node{ // 链表节点int num;struct Node *next; };// 头结点 struct Node * head = NULL;void * producer(void * arg) { // 生产者// 不断的创建新的节点,添加到链表中while(1) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);struct Node * newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newNode->next = head;head = newNode;newNode->num = rand() % 1000; // 随机数printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self());pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);usleep(100);}return NULL; }void * customer(void * arg) { // 消费者while(1) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);// 保存头结点的指针struct Node * tmp = head;// 判断是否有数据if(head != NULL) {// 有数据head = head->next;printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self());free(tmp);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);usleep(100);} else {// 没有数据pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}}return NULL; }int main() {pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);// 创建5个生产者线程,和5个消费者线程pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5];for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL);pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL);}for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // 线程分离pthread_detach(ptids[i]);pthread_detach(ctids[i]);}while(1) {sleep(10);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); // 线程退出,退出主线程pthread_exit(NULL);return 0; }存在的问题:当没有数据的时候,消费者 没有去通知 生产者生产,从而一直在循环加锁解锁,浪费了资源。
3.3.1 条件变量
条件变量 的类型 pthread_cond_t
- 条件变量 不是锁!
- 某个条件满足以后,可以 引起 / 解除 线程阻塞。
// 初始化
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
// 释放
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);// 等待,调用了该函数,线程会阻塞。 (当容器为空时,消费者停止消费,等待生产者生产)
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime); // 等待一定时间,调用了这个函数,线程会阻塞,直到指定的时间结束。// 唤醒一个或者多个等待的线程(发一个信号,告诉消费者可以消费了)
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);
// 广播,唤醒所有的等待的线程
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
-
生产者消费者模型改进
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h>// 创建一个互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 创建条件变量 pthread_cond_t cond;struct Node{int num;struct Node *next; };// 头结点 struct Node * head = NULL;void * producer(void * arg) {// 不断的创建新的节点,添加到链表中while(1) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);struct Node * newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newNode->next = head;head = newNode;newNode->num = rand() % 1000;printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self());// 只要生产了一个,就通知消费者消费pthread_cond_signal(&cond);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);usleep(100);}return NULL; }void * customer(void * arg) {while(1) {pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);// 保存头结点的指针struct Node * tmp = head;// 判断是否有数据if(head != NULL) {// 有数据head = head->next;printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self());free(tmp);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);usleep(100);} else {// 没有数据,需要等待// 当这个函数调用阻塞的时候,会对互斥锁进行解锁,当不阻塞的,继续向下执行,会重新加锁。pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); }}return NULL; }int main() {pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);// 创建5个生产者线程,和5个消费者线程pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5];for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL);pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL);}for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {pthread_detach(ptids[i]);pthread_detach(ctids[i]);}while(1) {sleep(10);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);pthread_exit(NULL);return 0; }
3.3.2 信号量/灯
-
和条件变量类似,信号量的类型
sem_t- 灯亮:资源可用(每个产品可以比作一个灯)
- 灯灭:资源不可用
// 初始化信号量 int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value); // 释放资源 int sem_destroy(sem_t *sem);// 对信号量加锁,调用一次对信号量的值-1,如果值为0,就阻塞。(不是立马阻塞) int sem_wait(sem_t *sem); int sem_trywait(sem_t *sem); // 尝试阻塞,如果值为0,就阻塞 int sem_timedwait(sem_t *sem, const struct timespec *abs_timeout); // 如果为0, 阻塞这么长(abs_timeout)时间// 对信号量解锁,调用一次对信号量的值+1 int sem_post(sem_t *sem); // 获取值 int sem_getvalue(sem_t *sem, int *sval);-
int sem_init(sem_t *sem, int pshared, unsigned int value);- 初始化信号量
- 参数:
sem: 信号量变量的地址pshared:0用在 线程 间 ,非0用在 进程 间value: 信号量中的值
查看说明文档:
man sem_init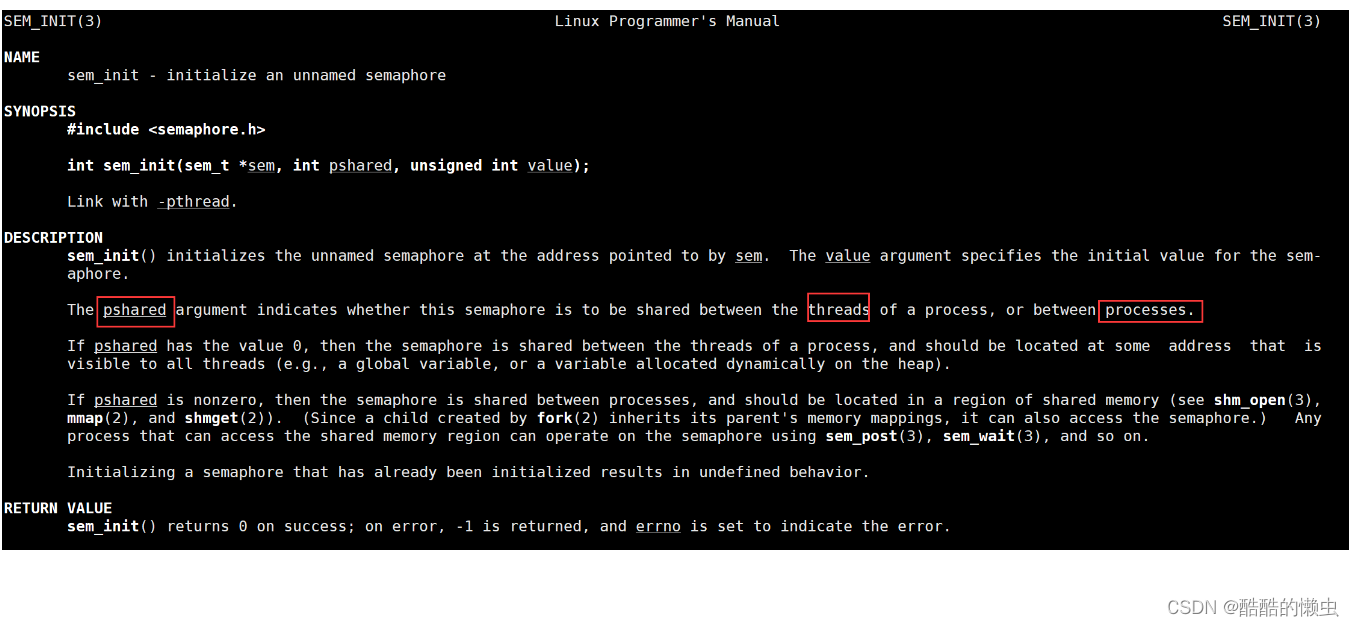
在开发程序时,一般采用 多线程开发,因为多线程比较 轻量。
/* 伪代码sem_t psem; // 生产者的信号量sem_t csem; // 消费者的信号量init(psem, 0, 8);init(csem, 0, 0);producer() {sem_wait(&psem); // -1sem_post(&csem); // +1,通知消费者,可以消费一个了}customer() {sem_wait(&csem); // -1sem_post(&psem); // +1,通知生产者,可以生产一个了}*/#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <semaphore.h>// 创建一个互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 创建两个信号量 sem_t psem; // 生产者的 sem_t csem; // 消费者的struct Node{int num;struct Node *next; };// 头结点 struct Node * head = NULL;void * producer(void * arg) {// 不断的创建新的节点,添加到链表中while(1) {sem_wait(&psem);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);struct Node * newNode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));newNode->next = head;head = newNode;newNode->num = rand() % 1000;printf("add node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", newNode->num, pthread_self());pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);sem_post(&csem);}return NULL; }void * customer(void * arg) {while(1) {sem_wait(&csem);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);// 保存头结点的指针struct Node * tmp = head;head = head->next;printf("del node, num : %d, tid : %ld\n", tmp->num, pthread_self());free(tmp);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);sem_post(&psem);}return NULL; }int main() {pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);sem_init(&psem, 0, 8);sem_init(&csem, 0, 0);// 创建5个生产者线程,和5个消费者线程pthread_t ptids[5], ctids[5];for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {pthread_create(&ptids[i], NULL, producer, NULL);pthread_create(&ctids[i], NULL, customer, NULL);}for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {pthread_detach(ptids[i]);pthread_detach(ctids[i]);}while(1) {sleep(10);}pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);pthread_exit(NULL);return 0; }
相关文章:

Linux 多线程开发
第三章 Linux 多线程开发 3.1 线程3.1.2 线程操作3.1.2 线程属性 3.2 线程同步3.2.1 互斥量/锁3.2.2 死锁3.2.3 读写锁 3.3 生产者消费者模型3.3.1 条件变量3.3.2 信号量/灯 网络编程系列文章: 第1章 Linux系统编程入门(上) 第1章 Linux系统…...

Android 9.0 关于在系统Launcher3中调用截图api总是返回null的解决方案
1.概述 在9.0的系统rom产品定制化开发中,在Launcher3的开发中,在某些时候需要调用截图接口来进行截屏功能实现,而在Launcher3中发现调用系统截屏接口SurfaceControl.screenshot进行截图的时候始终为null, 获取不到系统当前页面的截屏功能,所以需要找到当前截屏失败的原因然…...

openssl3.2 - exp - 用openssl命令行来模拟ECC加解密的全流程
文章目录 openssl3.2 - exp - 用openssl命令行来模拟ECC加解密的全流程概述笔记实验环境实验备注END openssl3.2 - exp - 用openssl命令行来模拟ECC加解密的全流程 概述 工程中要用到ECC加解密, 先去查了资料. 在网上能查到一些大佬们写的ECC加解密实现(基于openssl API), 不…...
【Linux进阶之路】HTTP协议
文章目录 一、基本概念1.HTTP2.域名3.默认端口号4.URL 二、请求与响应1.抓包工具2.基本框架3.简易实现3.1 HttpServer3.2 HttpRequest3.2.1 version13.2.2 version23.2.3 version3 总结尾序 一、基本概念 常见的应用层协议: HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Sec…...

股市新手福音:河北源达“财源滚滚”让投资变得更简单
在浩渺的股市海洋中,每一位投资者都渴望找到一把能够指引航向的罗盘。尤其是对于股市新手来说,面对复杂的市场环境、纷繁的个股信息以及不断变化的投资策略,如何快速入门、精准选股,无疑是一大挑战。而河北源达信息技术股份有限公…...

2024.02.14 校招 实习 内推 面经
绿*泡*泡VX: neituijunsir 交流*裙 ,内推/实习/校招汇总表格 1、校招&社招 | 中国电子信息产业集团有限公司校园招聘 校招&社招 | 中国电子信息产业集团有限公司校园招聘 2、校招&社招 | 中核光电2024年春季校园招聘开启! 校…...
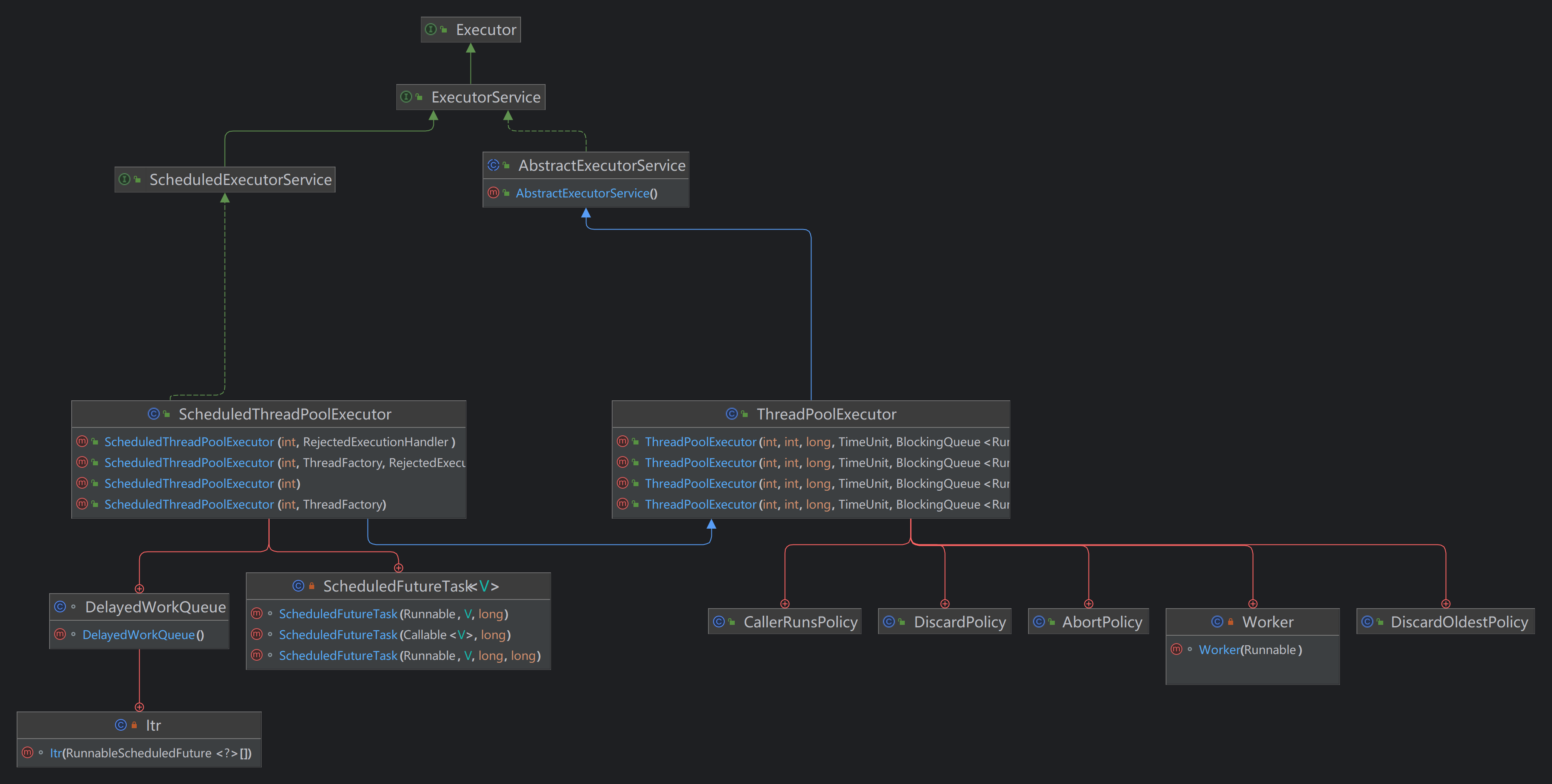
5.Java并发编程—JUC线程池架构
JUC线程池架构 在Java开发中,线程的创建和销毁对系统性能有一定的开销,需要JVM和操作系统的配合完成大量的工作。 JVM对线程的创建和销毁: 线程的创建需要JVM分配内存、初始化线程栈和线程上下文等资源,这些操作会带来一定的时间和…...
之forward、sample、decode)
llama2c(4)之forward、sample、decode
1、forward float* logits forward(transformer, token, pos); 输入transformer的参数,当前token,pos位置,预测出下一个token的预测值(用矩阵乘,加减乘除等运算构成Transformer) 其中,logits如…...

20240312-2-贪心算法
贪心算法 是每次只考虑当前最优,目标证明每次是考虑当前最优能够达到局部最优,这就是贪心的思想,一般情况下贪心和排序一起出现,都是先根据条件进行排序,之后基于贪心策略得到最优结果。 面试的时候面试官一般不会出贪…...

前端 --- HTML
1. HTML 结构 1.1 HTML 文件基本结构 <html><head><title>第一个html程序</title></head><body>hello world!</body> </html> html 标签是整个 html 文件的根标签(最顶层标签)head 标签中写页面的属性.body 标签中写的是页…...

curl c++ 实现HTTP GET和POST请求
环境配置 curl //DV2020T环境下此步骤可省略 https://curl.se/download/ 笔者安装为7.85.0版本 ./configure --without-ssl make sudo make install sudo rm /usr/local/lib/curl 系统也有curl库,为防止冲突,删去编译好的curl库。 对以json数据的解析使…...
12、设计模式之代理模式(Proxy)
一、什么是代理模式 代理模式属于结构型设计模式。为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。 在某些情况下,一个对象不适合或者不能直接引用另一个对象,而代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用。 二、分类 代理模式分为三类&#…...

springboot集成Quartz定时任务组件
文章目录 前言一、Quartz 是什么?下面是对 Java 中 Quartz 的主要概念的简单描述: 二、使用步骤总结 前言 平时开发中相信大家都经常用到定时任务吧,最近简单的就是直接使用Scheduled注解标注到方法上用注解的方式在项目运行时无法去对任务进…...

代码随想录算法训练营第38天—动态规划06 | ● 完全背包 ● *518. 零钱兑换 II ● 377. 组合总和 Ⅳ
完全背包 视频讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1uK411o7c9 https://programmercarl.com/%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85%E9%97%AE%E9%A2%98%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80%E5%AE%8C%E5%85%A8%E8%83%8C%E5%8C%85.html 题目描述:有n件物品和一个最多能…...
复写零)
C语言每日一题(63)复写零
题目链接 力扣网 1089 复写零 题目描述 给你一个长度固定的整数数组 arr ,请你将该数组中出现的每个零都复写一遍,并将其余的元素向右平移。 注意:请不要在超过该数组长度的位置写入元素。请对输入的数组 就地 进行上述修改,不…...

ElasticSearch聚合查询
数据准备 索引创建 PUT product {"mappings": {"properties": {"createtime": {"type": "date"},"desc": {"type": "text","fields": {"keyword": {"type": …...
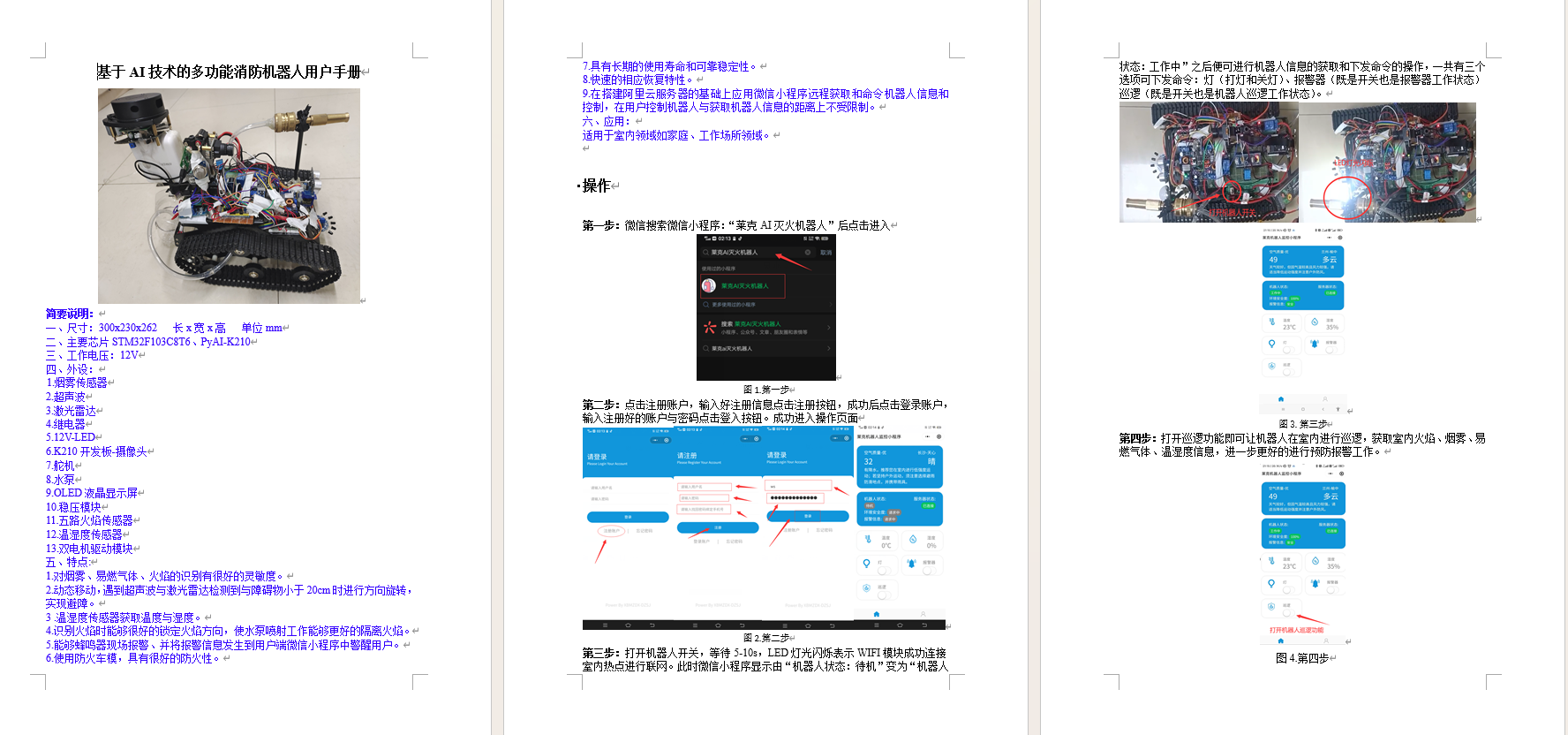
【毕设级项目】基于AI技术的多功能消防机器人(完整工程资料源码)
基于AI技术的多功能消防机器人演示效果 竞赛-基于AI技术的多功能消防机器人视频演示 前言: 随着“自动化、智能化”成为数字时代发展的关键词,机器人逐步成为社会经济发展的重要主体之一,“机器换人”成为发展的全新趋势和时代潮流。在可预见…...
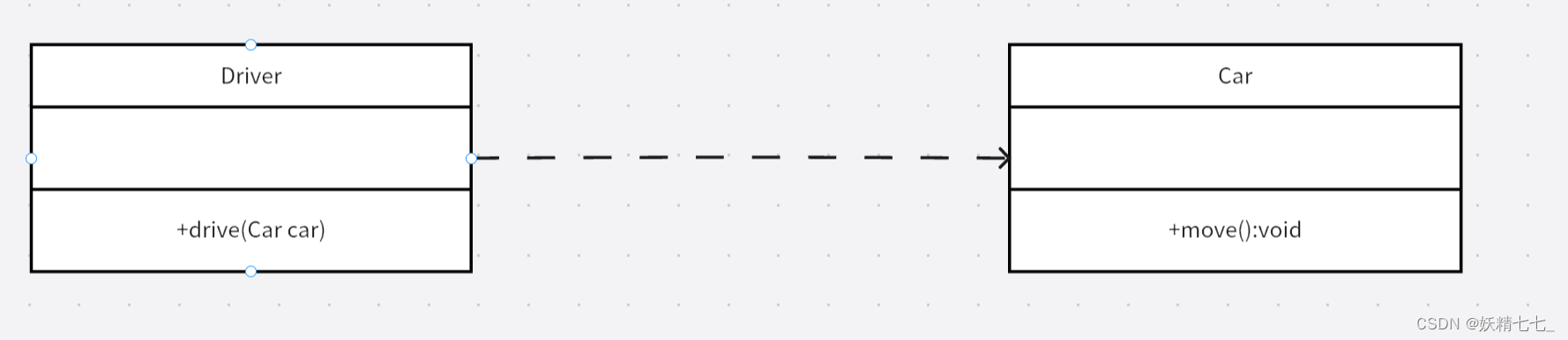
【一】【设计模式】类关系UML图
1. 继承(Generalization) 继承是对象间的一种层次关系,允许子类继承并扩展父类的功能。 UML线:带有空心箭头的直线,箭头指向基类(父类)。 class Parent {public void parentMethod() {System.…...

【DevOps基础篇】容器化架构基础设施监控方案
【DevOps基础篇】容器化架构基础设施监控方案 目录 【DevOps基础篇】容器化架构基础设施监控方案要监视什么不同监控系统方案比较1. Datadog2. Prometheus3. ELK(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)4. Sysdig5. 自行打造!如何选择总结推荐超级课程: Docker快速入门到精通 当…...
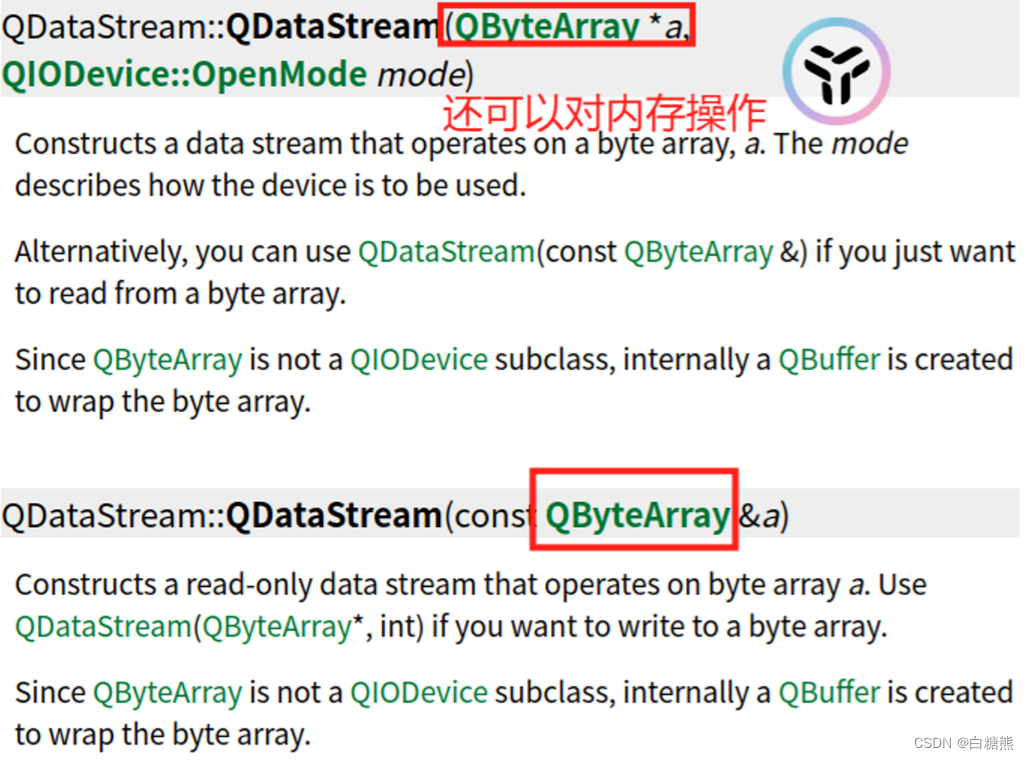
【QT】文件流操作(QTextStream/QDataStream)
文本流/数据流(二级制格式) 文本流 (依赖平台,不同平台可能乱码)涉及文件编码 #include <QTextStream>操作的都是基础数据类型:int float string //Image Qpoint QRect就不可以操作 需要下面的 …...

PHP和Node.js哪个更爽?
先说结论,rust完胜。 php:laravel,swoole,webman,最开始在苏宁的时候写了几年php,当时觉得php真的是世界上最好的语言,因为当初活在舒适圈里,不愿意跳出来,就好比当初活在…...

【Java学习笔记】Arrays类
Arrays 类 1. 导入包:import java.util.Arrays 2. 常用方法一览表 方法描述Arrays.toString()返回数组的字符串形式Arrays.sort()排序(自然排序和定制排序)Arrays.binarySearch()通过二分搜索法进行查找(前提:数组是…...

在HarmonyOS ArkTS ArkUI-X 5.0及以上版本中,手势开发全攻略:
在 HarmonyOS 应用开发中,手势交互是连接用户与设备的核心纽带。ArkTS 框架提供了丰富的手势处理能力,既支持点击、长按、拖拽等基础单一手势的精细控制,也能通过多种绑定策略解决父子组件的手势竞争问题。本文将结合官方开发文档,…...
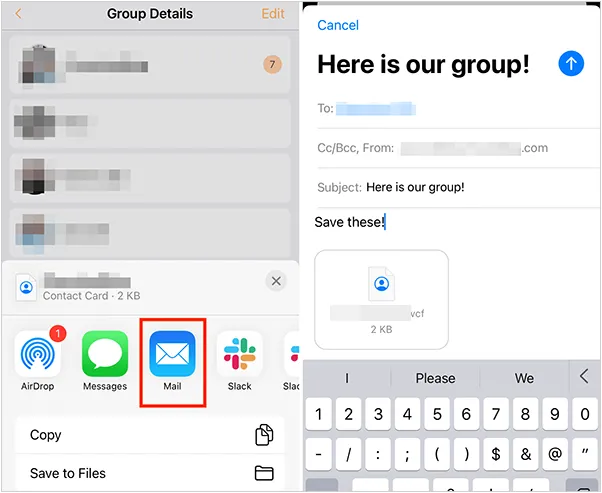
如何将联系人从 iPhone 转移到 Android
从 iPhone 换到 Android 手机时,你可能需要保留重要的数据,例如通讯录。好在,将通讯录从 iPhone 转移到 Android 手机非常简单,你可以从本文中学习 6 种可靠的方法,确保随时保持连接,不错过任何信息。 第 1…...

HTML前端开发:JavaScript 常用事件详解
作为前端开发的核心,JavaScript 事件是用户与网页交互的基础。以下是常见事件的详细说明和用法示例: 1. onclick - 点击事件 当元素被单击时触发(左键点击) button.onclick function() {alert("按钮被点击了!&…...
dify打造数据可视化图表
一、概述 在日常工作和学习中,我们经常需要和数据打交道。无论是分析报告、项目展示,还是简单的数据洞察,一个清晰直观的图表,往往能胜过千言万语。 一款能让数据可视化变得超级简单的 MCP Server,由蚂蚁集团 AntV 团队…...
)
Typeerror: cannot read properties of undefined (reading ‘XXX‘)
最近需要在离线机器上运行软件,所以得把软件用docker打包起来,大部分功能都没问题,出了一个奇怪的事情。同样的代码,在本机上用vscode可以运行起来,但是打包之后在docker里出现了问题。使用的是dialog组件,…...

AirSim/Cosys-AirSim 游戏开发(四)外部固定位置监控相机
这个博客介绍了如何通过 settings.json 文件添加一个无人机外的 固定位置监控相机,因为在使用过程中发现 Airsim 对外部监控相机的描述模糊,而 Cosys-Airsim 在官方文档中没有提供外部监控相机设置,最后在源码示例中找到了,所以感…...

什么是VR全景技术
VR全景技术,全称为虚拟现实全景技术,是通过计算机图像模拟生成三维空间中的虚拟世界,使用户能够在该虚拟世界中进行全方位、无死角的观察和交互的技术。VR全景技术模拟人在真实空间中的视觉体验,结合图文、3D、音视频等多媒体元素…...
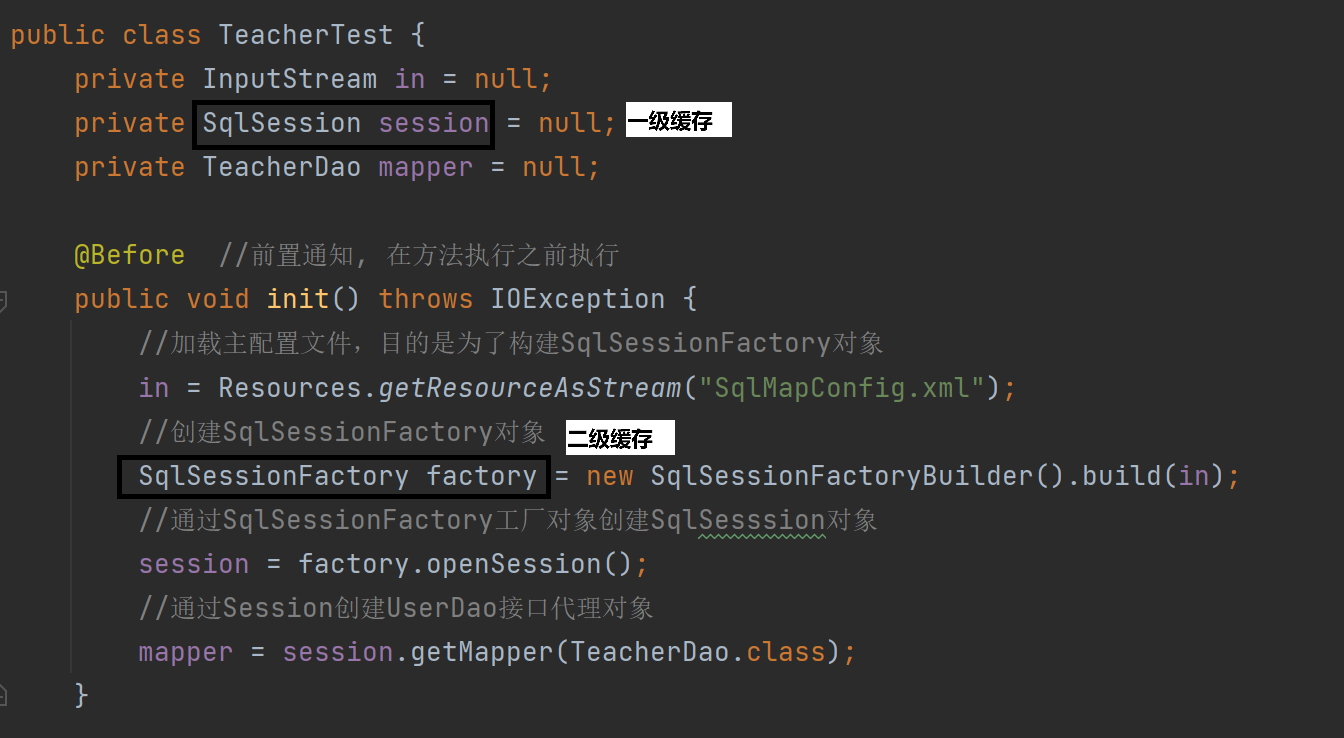
MyBatis中关于缓存的理解
MyBatis缓存 MyBatis系统当中默认定义两级缓存:一级缓存、二级缓存 默认情况下,只有一级缓存开启(sqlSession级别的缓存)二级缓存需要手动开启配置,需要局域namespace级别的缓存 一级缓存(本地缓存&#…...
