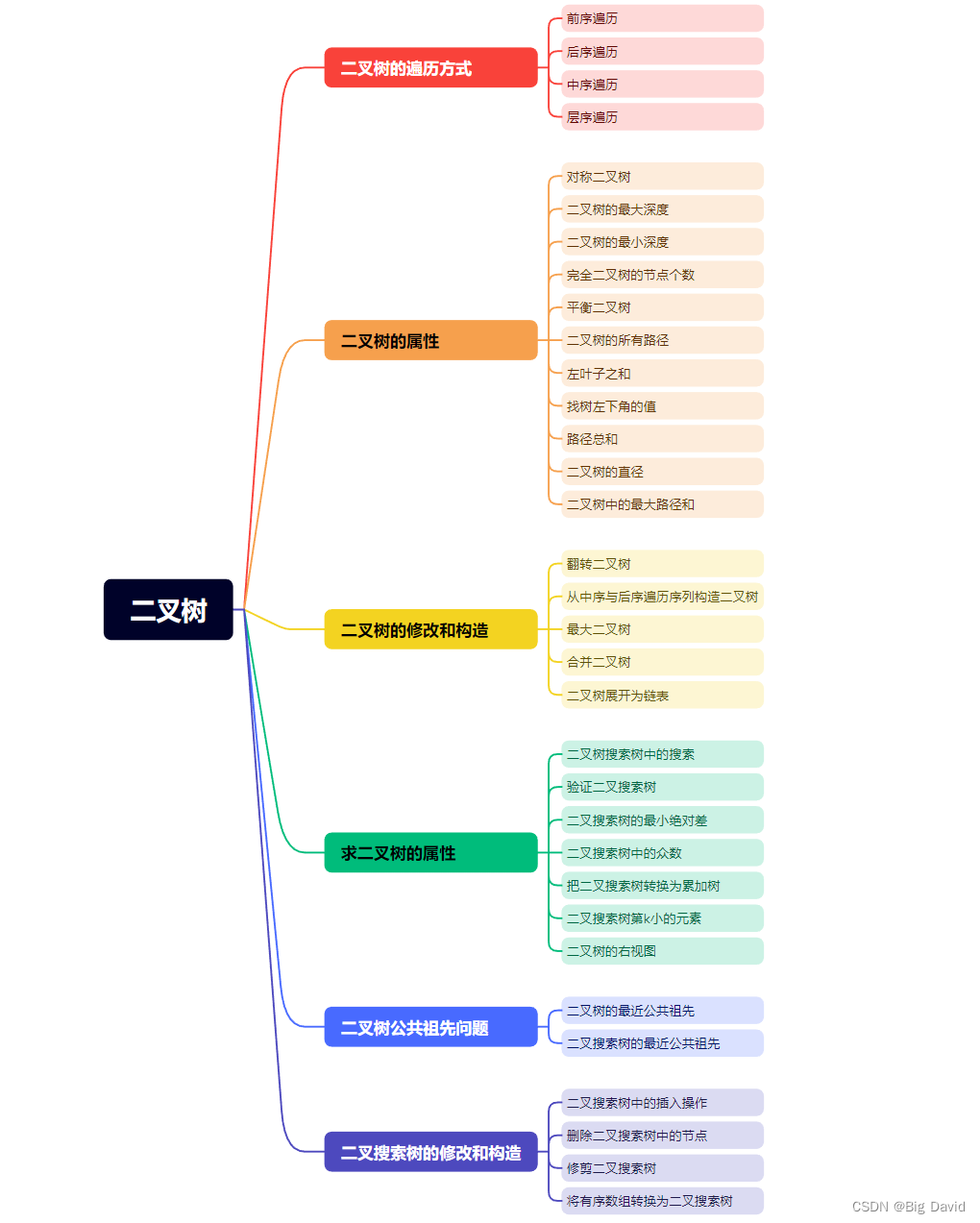
【数据结构刷题专题】—— 二叉树
二叉树
二叉树刷题框架
二叉树的定义:
struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode* left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL);
};
1 二叉树的遍历方式
【1】前序遍历
class Solution {
public:void traversal(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& vec) {if (node == NULL) return;vec.push_back(node->val);traversal(node->left, vec);traversal(node->right, vec);}vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;traversal(root, result);return result;}
};
【2】后序遍历
class Solution {
public:void traversal(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& vec) {if (node == NULL) return;traversal(node->left, vec);traversal(node->right, vec);vec.push_back(node->val);}vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;traversal(root, result);return result;}
};
【3】中序遍历
class Solution {
public:void traversal(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& vec) {if (node == NULL) return;traversal(node->left, vec);vec.push_back(node->val);traversal(node->right, vec);}vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;traversal(root, result);return result;}
};
【4】层序遍历
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> result;queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root != NULL) que.push(root);while (!que.empty()) {vector<int> vec;int size = que.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();vec.push_back(node->val);if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);}result.push_back(vec);}return result;}
};
2 二叉树的属性
【1】101. 对称二叉树
class Solution {
public:bool compare(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return false;else if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return false;else if (left == NULL && right == NULL) return true;else if (left->val != right->val) return false;bool outside = compare(left->left, right->right);bool inside = compare(left->right, right->left);return outside && inside;}bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return true;return compare(root->left, root->right);}
};
【2】104. 二叉树的最大深度
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return 0;int depth = 0;queue<TreeNode*> que;que.push(root);while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();depth++;while (size--) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);}}return depth;}
};
递归法:
class Solution {
public:int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0;int left = getDepth(node->left);int right = getDepth(node->right);return 1 + max(left, right);}int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {return getDepth(root);}
};
【3】111.二叉树的最小深度
递归法:
class Solution {
public:int getDepth(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0;int left = getDepth(node->left);int right = getDepth(node->right);if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) return 1 + left;if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) return 1 + right;return 1 + min(left, right);}int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {return getDepth(root);}
};
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root == NULL) return 0;que.push(root);int depth = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();depth++;while (size--) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return depth;}}return depth;}
};
【4】222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
递归法:
class Solution {
public:int getNum(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0;int left = getNum(node->left);int right = getNum(node->right);return 1 + left + right;}int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {return getNum(root);}
};
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root == NULL) return 0;que.push(root);int num = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();while (size--) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();num++;if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);}}return num;}
};
【5】110. 平衡二叉树
class Solution {
public:int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0;int left = getHeight(node->left);if (left == -1) return -1;int right = getHeight(node->right);if (right == -1) return -1;return abs(left - right) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(left, right);}bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;}
};
【6】257. 二叉树的所有路径
class Solution {
public:void traversal(TreeNode* node, string path, vector<string>& result) {path += to_string(node->val);if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) {result.push_back(path);return;}if (node->left) traversal(node->left, path + "->", result);if (node->right) traversal(node->right, path + "->", result);}vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) {vector<string> result;string path;if (root == NULL) return result;traversal(root, path, result);return result;}
};
【7】404. 左叶子之和
class Solution {
public:int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return 0;int left = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left);if (root->left && root->left->left == NULL && root->left->right == NULL) {left = root->left->val;}int right = sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);return left + right;}
};
【8】513. 找树左下角的值
迭代法:
class Solution {
public:int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {queue<TreeNode*> que;que.push(root);int val = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();if (i == 0) val = node->val;if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);}}return val;}
};
【9】112. 路径总和
class Solution {
public:bool pathSum(TreeNode* node, int count) {if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL && count == 0) return true;if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) return false;if (node->left) {count -= node->left->val;if (pathSum(node->left, count)) return true;count += node->left->val;}if (node->right) {count -= node->right->val;if (pathSum(node->right, count)) return true;count += node->right->val;}return false;}bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if (root == NULL) return false;return pathSum(root, targetSum - root->val);}
};
【10】543. 二叉树的直径
class Solution {
public:int ans;int Depth(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0;int left = Depth(node->left);int right = Depth(node->right);ans = max(ans, 1 + left + right);return 1 + max(left, right);}int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {ans = 1;Depth(root);return ans - 1;}
};
【11】124. 二叉树中的最大路径和
class Solution {
public:int ans = INT_MIN;int dfs(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return 0;ans = max(ans, node->val);int lSum = dfs(node->left);int rSum = dfs(node->right);lSum = max(0, lSum); rSum = max(0, rSum);ans = max(ans, node->val + lSum + rSum);return max(node->val + lSum, node->val + rSum);}int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {ans = max(ans, dfs(root));return ans;}
};
3 二叉树的修改和构造
【1】226. 翻转二叉树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return root;swap(root->left, root->right);if (root->left) invertTree(root->left);if (root->right) invertTree(root->right);return root;}
};
【2】106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1];TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue);if (postorder.size() == 1) return root;int qiege;for (qiege = 0; qiege <= inorder.size(); qiege++) {if (inorder[qiege] == root->val) break;}vector<int> leftInorder(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + qiege);vector<int> rightInorder(inorder.begin() + qiege + 1, inorder.end());postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1);vector<int> leftPostorder(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size());vector<int> rightPostorder(postorder.begin() + leftInorder.size(), postorder.end());root->left = traversal(leftInorder, leftPostorder);root->right = traversal(rightInorder, rightPostorder);return root;}TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {if (inorder.size() == 0 || postorder.size() == 0) return NULL;return traversal(inorder, postorder);}
};
【3】654. 最大二叉树
构造树一般采用的是前序遍历
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right) {if (left >= right) return NULL;int index = left;for (int i = left + 1; i < right; i++) {if (nums[i] > nums[index]) index = i;}TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[index]);root->left = traversal(nums, left, index);root->right = traversal(nums, index + 1, right);return root;}TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int>& nums) {return traversal(nums, 0, nums.size());}
};
【4】617. 合并二叉树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {if (root1 == NULL) return root2;if (root2 == NULL) return root1;root1->val += root2->val;root1->left = mergeTrees(root1->left, root2->left);root1->right = mergeTrees(root1->right, root2->right);return root1;}
};
【5】114. 二叉树展开为链表
class Solution {
public:void traversal(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return;traversal(node->left);traversal(node->right);TreeNode* left = node->left;TreeNode* right = node->right;node->left = NULL;node->right = left;while (node->right) node = node->right;node->right = right;return;}void flatten(TreeNode* root) {traversal(root);return;}
};
4 求二叉树的属性
【1】700. 二叉搜索树中的搜索
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* searchBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {while (root != NULL) {if (root->val > val) {root = root->left;} else if (root->val < val) {root = root->right;} else return root;}return root;}
};
【2】98. 验证二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:long long maxVel = LONG_MIN;bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return true;bool left = isValidBST(root->left);if (root->val > maxVel) maxVel = root->val;else return false;bool right = isValidBST(root->right);return left && right;}
};
【3】530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
遇到在二叉搜索树上求什么最值啊,差值之类的,就把它想成在一个有序数组上求最值,求差值
把二叉搜索树转换成有序数组,然后遍历一遍数组,就统计出来最小差值
class Solution {
public:vector<int> vec;int ans = INT_MAX;void traversal(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return;traversal(node->left);vec.push_back(node->val);traversal(node->right);}int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {traversal(root);for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) {ans = min(ans, vec[i] - vec[i - 1]);}return ans;}
};
在递归中记录前一个节点的指针
class Solution {
public:int result = INT_MAX;TreeNode* pre = NULL;void traversal(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return;traversal(node->left);if (pre != NULL) result = min(result, node->val - pre->val);pre = node;traversal(node->right);}int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode* root) {traversal(root);return result;}
};
【4】501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
class Solution {
public:void traversal(TreeNode* cur, unordered_map<int, int>& map) {if (cur == NULL) return;map[cur->val]++;traversal(cur->left, map);traversal(cur->right, map);return;}static bool cmp(const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {return a.second > b.second;}vector<int> findMode(TreeNode* root) {unordered_map<int, int> map;vector<int> result;if (root == NULL) return result;traversal(root, map);vector<pair<int, int>> vec(map.begin(), map.end());sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), cmp);result.push_back(vec[0].first);for (int i = 1; i < vec.size(); i++) {if (vec[0].second == vec[i].second) result.push_back(vec[i].first);else break;}return result;}
};
【5】把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
class Solution {
public:int pre = 0;void traversal(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return;traversal(node->right);node->val += pre;pre = node->val;traversal(node->left);}TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {if (root == NULL) return root;traversal(root);return root;}
};
【6】230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
class Solution {
public:int maxVel = INT_MIN;vector<int> vec;void traversal(TreeNode* node) {if (node == NULL) return;traversal(node->left);if (node->val > maxVel) {vec.push_back(node->val);maxVel = node->val;}traversal(node->right);return;}int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {traversal(root);return vec[k - 1];}
};
【7】二叉树的右视图
class Solution {
public:vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> result;queue<TreeNode*> que;if (root == NULL) return result;que.push(root);while (!que.empty()) {int size = que.size();for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {TreeNode* node = que.front();que.pop();if (i == (size - 1)) result.push_back(node->val);if (node->left) que.push(node->left);if (node->right) que.push(node->right);}}return result;}
};
5 二叉树的公共祖先问题
【1】236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {if (root == p || root == q || root == NULL) return root;TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);if (left != NULL && right != NULL) return root;if (left != NULL && right == NULL) return left;else if (left == NULL && right != NULL) return right;else return NULL;}
};
【2】235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {while (root) {if (root->val > q->val && root->val > p->val) root = root->left;else if (root->val < q->val && root->val < p->val) root = root->right;else return root;}return NULL;}
};
6 二叉搜索树的修改和构造
【1】二叉搜索树的插入操作
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* insertIntoBST(TreeNode* root, int val) {if (root == NULL) {TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(val);return node;}if (root->val > val) root->left = insertIntoBST(root->left, val);if (root->val < val) root->right = insertIntoBST(root->right, val);return root;}
};
【2】450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {if (root == NULL) return root;if (root->val == key) {if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) {delete root;return NULL;} else if (root->left == NULL) {auto tmp = root->right;delete root;return tmp;} else if (root->right == NULL) {auto tmp = root->left;delete root;return tmp;} else {TreeNode* cur = root->right;while (cur->left != NULL) {cur = cur->left;}cur->left = root->left;TreeNode* tmp = root;root = root->right;delete tmp;return root;}}if (root->val > key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key);if (root->val < key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key);return root;}
};
【3】669. 修剪二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {if (root == NULL) return root;if (root->val < low) return trimBST(root->right, low, high);if (root->val > high) return trimBST(root->left, low, high);root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high);return root;}
};
【4】108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* traversal(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right) {if (left > right) return NULL;int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);root->left = traversal(nums, left, mid - 1);root->right = traversal(nums, mid + 1, right);return root;}TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {return traversal(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);}
};
二叉树刷题专题到此结束,读者对题目有更好的解答欢迎讨论。
相关文章:

【数据结构刷题专题】—— 二叉树
二叉树 二叉树刷题框架 二叉树的定义: struct TreeNode {int val;TreeNode* left;TreeNode* right;TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL); };1 二叉树的遍历方式 【1】前序遍历 class Solution { public:void traversal(TreeNode* node, vector&…...

基于AWS云服务构建智能家居系统的最佳实践
在当今智能家居时代,构建一个安全、高性能、可扩展和灵活的智能家居系统已经成为许多公司的目标。亚马逊网络服务(AWS)提供了一系列云服务,可以帮助企业轻松构建和管理智能家居系统。本文将探讨如何利用AWS云服务构建一个智能家居系统,并分享相关的最佳实践。 系统架构概述 该…...

Java零基础-集合:Set接口
哈喽,各位小伙伴们,你们好呀,我是喵手。 今天我要给大家分享一些自己日常学习到的一些知识点,并以文字的形式跟大家一起交流,互相学习,一个人虽可以走的更快,但一群人可以走的更远。 我是一名后…...

数据结构与算法-排序算法
1.顺序查找 def linear_search(iters, val):for i, v in enumerate(iters):if v val:return ireturn 2.二分查找 # 升序的二分查找 def binary_search(iters, val):left 0right len(iters)-1while left < right:mid (left right) // 2if iters[mid] val:return mid…...
SpringBoot 文件上传(三)
之前讲解了如何接收文件以及如何保存到服务端的本地磁盘中: SpringBoot 文件上传(一)-CSDN博客 SpringBoot 文件上传(二)-CSDN博客 这节讲解如何利用阿里云提供的OSS(Object Storage Service)对象存储服务保存文件。…...

web渗透测试漏洞流程:红队目标信息收集之资产搜索引擎收集
web渗透测试漏洞流程 渗透测试信息收集---域名信息收集1.域名信息的科普1.1 域名的概念1.2 后缀分类1.3 多重域名的关系1.4 域名收集的作用1.5 DNS解析原理1.6 域名解析记录2. 域名信息的收集的方法2.1 基础方法-搜索引擎语法2.1.1 Google搜索引擎2.1.1.1 Google语法的基本使用…...
UI自动化_id 元素定位
## 导包selenium from selenium import webdriver import time1、创建浏览器驱动对象 driver webdriver.Chrome() 2、打开测试网站 driver.get("你公司的平台地址") 3、使浏览器窗口最大化 driver.maximize_window() 4、在用户名输入框中输入admin driver.find_ele…...

华为OD技术面算法题整理
LeetCode原题 简单 题目编号频次409. 最长回文串 - 力扣(LeetCode)3...

vmware虚拟机下ubuntu扩大磁盘容量
1、扩容: 可以直接在ubuntu setting界面里直接扩容,也可通过vmware命令,如下: vmware提供一个命令行工具,vmware-vdiskmanager.exe,位于vmware的安装目录下,比如 C:/Program Files/VMware/VMwar…...
秋招打卡算法题第一天
一年多没有刷过算法题了,已经不打算找计算机类工作了,但是思来想去,还是继续找吧。 1. 字符串最后一个单词的长度 public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in new Scanner(System.in);while(in.hasNextInt()){String itemin.nextL…...

BC98 序列中删除指定数字
题目 描述 有一个整数序列(可能有重复的整数),现删除指定的某一个整数,输出删除指定数字之后的序列,序列中未被删除数字的前后位置没有发生改变。 数据范围:序列长度和序列中的值都满足 1≤�≤…...
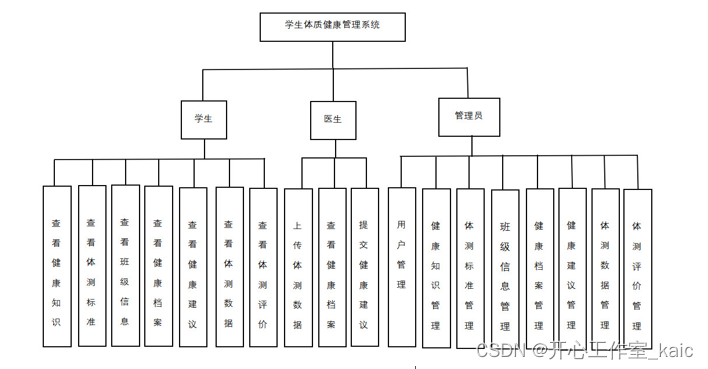
基于Java的学生体质健康管理系统的设计与实现(论文+源码)_kaic
摘 要 随着时代的进步,信息化也在逐渐深入融进我们生活的方方面面。其中也给健康管理带来了新的发展方向。通过对学生体质健康管理的研究与分析发现当下的管理系统还不够全面,系统的性能达不到使用者的要求。因此,本文结合Java的优势和流行性…...

【Linux系统】冯诺依曼与操作系统
什么是冯诺依曼体系结构? 如图即为冯诺依曼大致的体系结构图, 我们知道这些都是由我们的计算机硬件组成 输入设备:键盘, 鼠标, 摄像头, 话筒, 磁盘, 网卡... 输出设备:…...
——form表单的新增特性/h5的新特性)
前端理论总结(html5)——form表单的新增特性/h5的新特性
form表单的新增特性 range:范围 color:取色器 url:对url进行验证 tel:对手机号格式验证 email:对邮箱格式验证 novalidate :提交表单时不验证 form 或 input 域 numbe…...

基于TensorFlow的花卉识别(算能杯)%%%
Anaconda Prompt 激活 TensorFlow CPU版本 conda activate tensorflow_cpu //配合PyCharm环境 直接使用TensorFlow1.数据分析 此次设计的主题为花卉识别,数据为TensorFlow的官方数据集flower_photos,包括5种花卉(雏菊、蒲公英、玫瑰、向日葵…...

Android实现一周时间早中晚排班表
我们要做一个可以动态添加,修改一周早中晚时间排班表,需求图如下: one two 过程具体在这里不描述了,具体查看,https://github.com/yangxiansheng123/WorkingSchedule 上传数据格式: {"friday_plan":"…...
【Java八股面试系列】中间件-Redis
目录 Redis 什么是Redis Redis解决了什么问题 Redis的实现原理 数据结构 String 常用命令 应用场景 List(列表) 常用命令 应用场景 Hash(哈希) 常用命令 应用场景 set(集合) 常见命令编辑 应用场景 Sorted Set(有序集合) 常见命令编辑 应用场景 数据持…...

目前国内体验最佳的AI问答助手:kimi.ai
文章目录 简介图片理解长文档解析 简介 kimi.ai是国内初创AI公司月之暗面推出的一款AI助手,终于不再是四字成语拼凑出来的了。这是一个非常存粹的文本分析和对话工具,没有那些东拼西凑花里胡哨的AIGC功能,实测表明,这种聚焦是对的…...
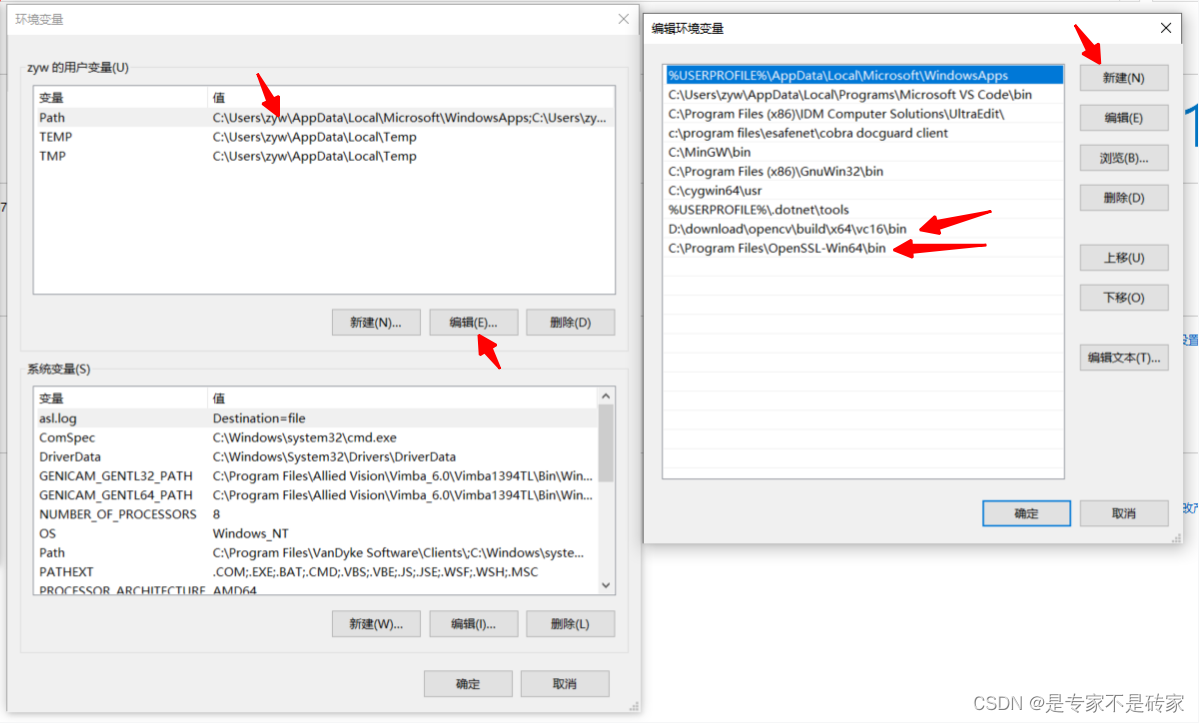
Visual Studio项目编译和运行依赖第三方库的项目
1.创建项目,这里创建的项目是依赖于.sln的项目,非CMake项目 2.添加第三方库依赖的头文件和库文件路劲 3.添加第三方依赖库文件 4.项目配置有2个,一个是Debug,一个是Release,如果你只配置了Debug,编译和运行…...

Rust 语言中 Vec 的元素的删除方法
在 Rust 中,Vec(向量)提供了多种删除元素的方法。以下是一些常用的删除方法: remove: 这是最常用的删除方法,它接受一个索引作为参数,并移除该索引处的元素,同时返回被移除的元素。所有后面的元…...
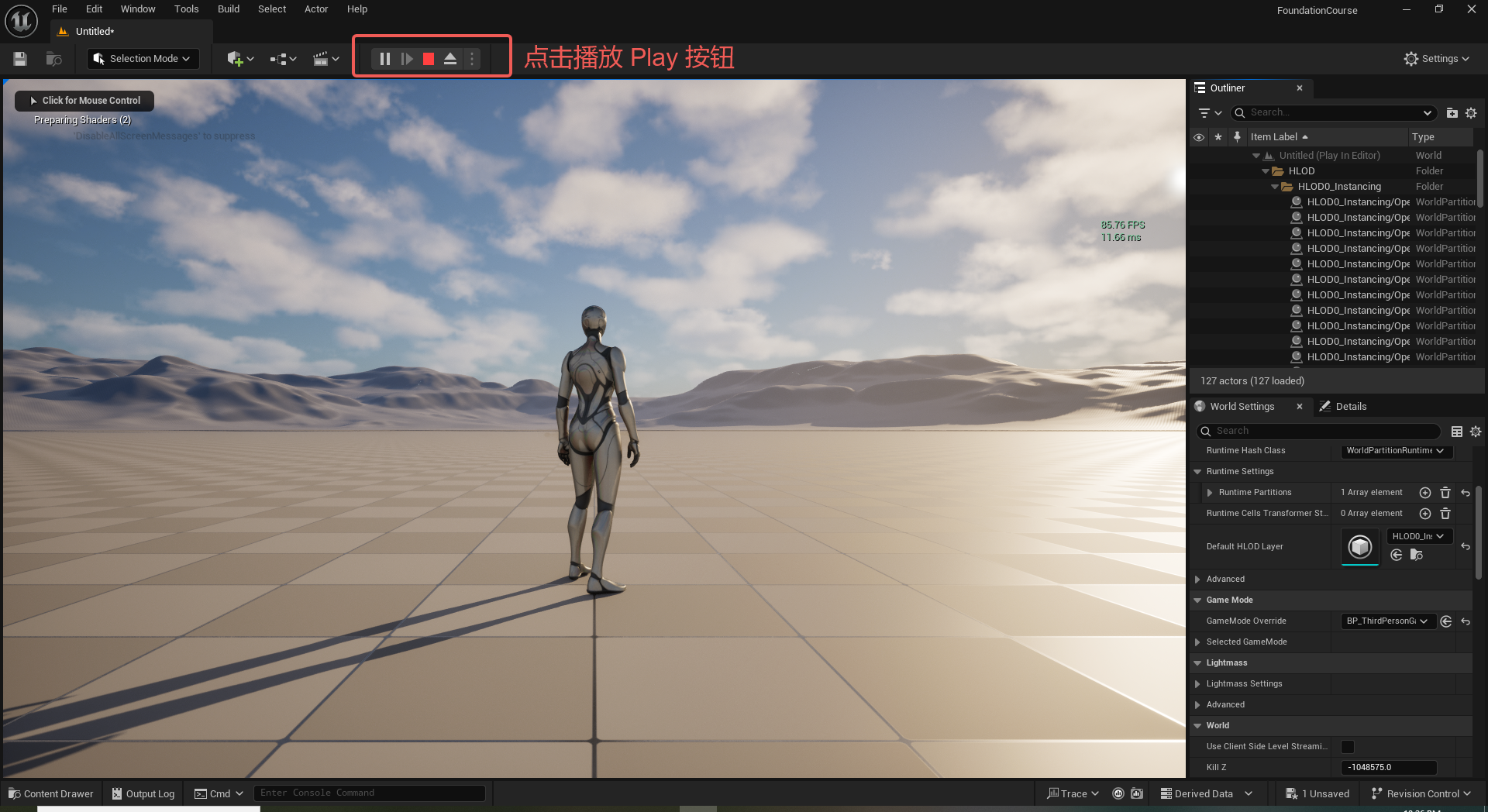
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...
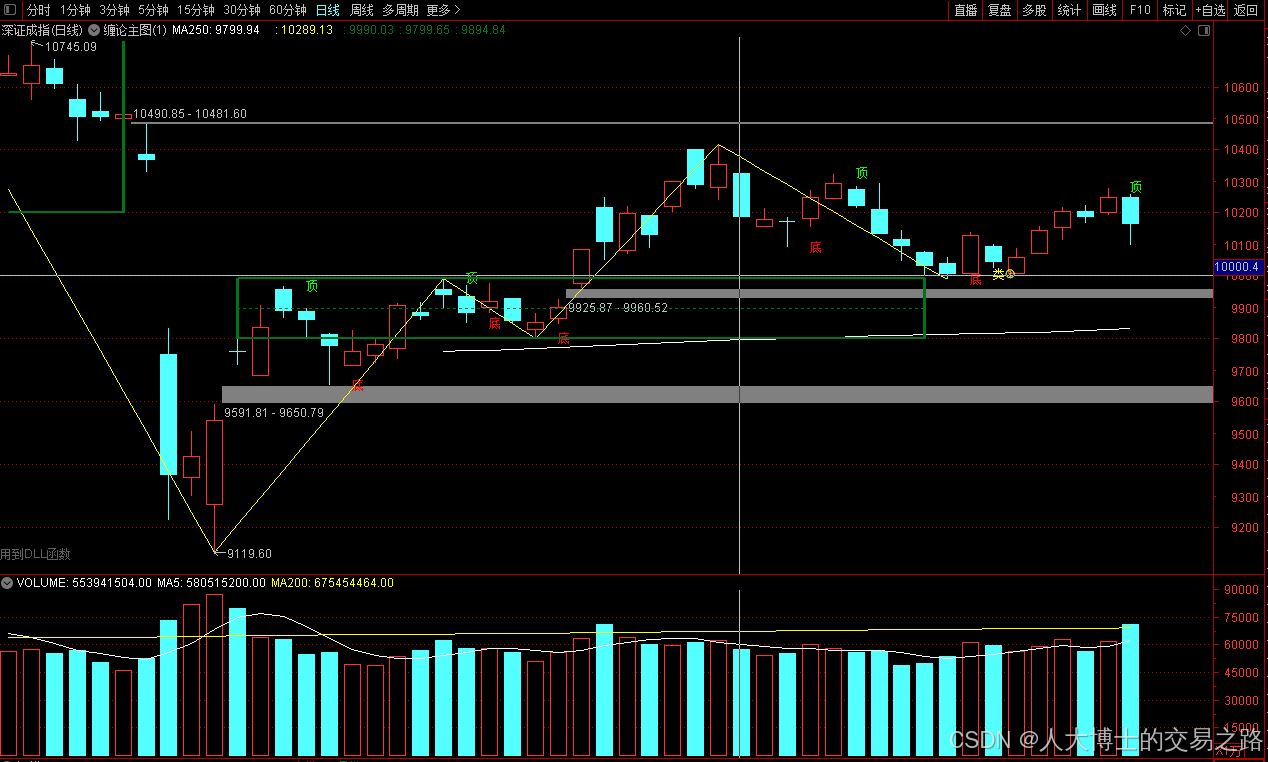
龙虎榜——20250610
上证指数放量收阴线,个股多数下跌,盘中受消息影响大幅波动。 深证指数放量收阴线形成顶分型,指数短线有调整的需求,大概需要一两天。 2025年6月10日龙虎榜行业方向分析 1. 金融科技 代表标的:御银股份、雄帝科技 驱动…...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...
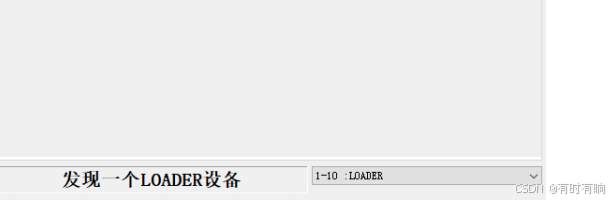
linux arm系统烧录
1、打开瑞芯微程序 2、按住linux arm 的 recover按键 插入电源 3、当瑞芯微检测到有设备 4、松开recover按键 5、选择升级固件 6、点击固件选择本地刷机的linux arm 镜像 7、点击升级 (忘了有没有这步了 估计有) 刷机程序 和 镜像 就不提供了。要刷的时…...
前端开发面试题总结-JavaScript篇(一)
文章目录 JavaScript高频问答一、作用域与闭包1.什么是闭包(Closure)?闭包有什么应用场景和潜在问题?2.解释 JavaScript 的作用域链(Scope Chain) 二、原型与继承3.原型链是什么?如何实现继承&a…...
:邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南)
精益数据分析(97/126):邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南
精益数据分析(97/126):邮件营销与用户参与度的关键指标优化指南 在数字化营销时代,邮件列表效度、用户参与度和网站性能等指标往往决定着创业公司的增长成败。今天,我们将深入解析邮件打开率、网站可用性、页面参与时…...
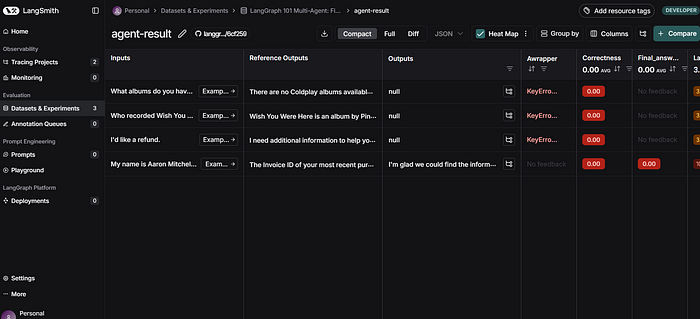
使用LangGraph和LangSmith构建多智能体人工智能系统
现在,通过组合几个较小的子智能体来创建一个强大的人工智能智能体正成为一种趋势。但这也带来了一些挑战,比如减少幻觉、管理对话流程、在测试期间留意智能体的工作方式、允许人工介入以及评估其性能。你需要进行大量的反复试验。 在这篇博客〔原作者&a…...
宇树科技,改名了!
提到国内具身智能和机器人领域的代表企业,那宇树科技(Unitree)必须名列其榜。 最近,宇树科技的一项新变动消息在业界引发了不少关注和讨论,即: 宇树向其合作伙伴发布了一封公司名称变更函称,因…...

第一篇:Liunx环境下搭建PaddlePaddle 3.0基础环境(Liunx Centos8.5安装Python3.10+pip3.10)
第一篇:Liunx环境下搭建PaddlePaddle 3.0基础环境(Liunx Centos8.5安装Python3.10pip3.10) 一:前言二:安装编译依赖二:安装Python3.10三:安装PIP3.10四:安装Paddlepaddle基础框架4.1…...
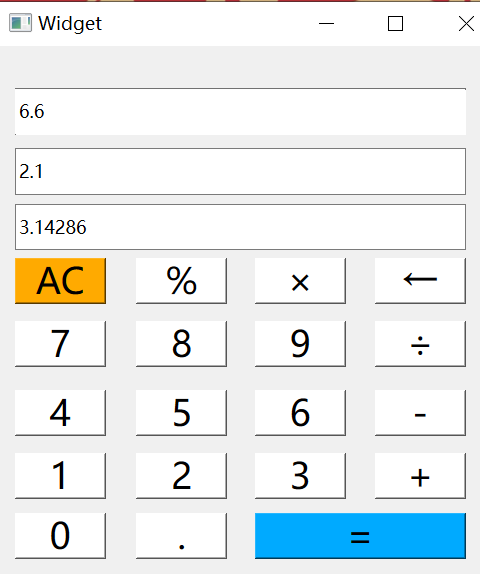
6.9-QT模拟计算器
源码: 头文件: widget.h #ifndef WIDGET_H #define WIDGET_H#include <QWidget> #include <QMouseEvent>QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE namespace Ui { class Widget; } QT_END_NAMESPACEclass Widget : public QWidget {Q_OBJECTpublic:Widget(QWidget *parent nullptr);…...
