大数据开发扩展shell--尚硅谷shell笔记
大数据开发扩展shell
学习目标
1 熟悉shell脚本的原理和使用
2 熟悉shell的编程语法
第一节 Shell概述

1)Linux提供的Shell解析器有:
查看系统中可用的 shell
[atguigu@hadoop101 ~]$ cat /etc/shells /bin/sh/bin/bash/sbin/nologin/bin/dash/bin/tcsh/bin/csh
2)bash和sh的关系(Bash是sh的改进版本,提供了更加丰富的功能)
[atguigu@hadoop101 bin]$ ll | grep bash-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 941880 5月 11 2016 bashlrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 4 5月 27 2017 sh -> bash
3)Centos默认的解析器是bash
[atguigu@hadoop101 bin]$ echo $SHELL/bin/bash
第二节 Shell脚本入门
(1)需求:创建一个Shell脚本,输出helloworld
(2)案例实操:
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch helloworld.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim helloworld.sh在helloworld.sh中输入如下内容#!/bin/bashecho "helloworld"
(3)脚本的常用执行方式
第一种:采用bash或sh+脚本的相对路径或绝对路径(不用赋予脚本+x权限)
sh+脚本的相对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ sh helloworld.sh Helloworld
sh+脚本的绝对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ sh /home/atguigu/datas/helloworld.sh helloworld
bash+脚本的相对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ bash helloworld.sh Helloworld
bash+脚本的绝对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ bash /home/atguigu/datas/helloworld.sh Helloworld
第二种:采用输入脚本的绝对路径或相对路径执行脚本(必须具有可执行权限+x)
(a)首先要赋予helloworld.sh 脚本的+x权限
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod +x helloworld.sh
(b)执行脚本
相对路径[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./helloworld.sh Helloworld绝对路径[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ /home/atguigu/datas/helloworld.sh Helloworld
注意:第一种执行方法,本质是bash解析器帮你执行脚本,所以脚本本身不需要执行权限。第二种执行方法,本质是脚本需要自己执行,所以需要执行权限。
【了解】第三种:在脚本的路径前加上“.”或者 source
(a)有以下脚本
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat test.sh #!/bin/bashA=5echo $A
(b) 分别使用sh,bash,./ 和 . 的方式来执行,结果如下:
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ bash test.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $A[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ sh test.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $A[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./test.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $A[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ . test.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $A5
原因:
前三种方式都是在当前shell中打开一个子shell来执行脚本内容,当脚本内容结束,则子shell关闭,回到父shell中。
第四种,也就是使用在脚本路径前加“.”或者 source的方式,可以使脚本内容在当前shell里执行,而无需打开子shell!这也是为什么我们每次要修改完/etc/profile文件以后,需要source一下的原因。
开子shell与不开子shell的区别就在于,环境变量的继承关系,如在子shell中设置的当前变量,父shell是不可见的。
第三节 变量
3.1 系统预定义变量
1)常用系统变量
H O M E 、 HOME、 HOME、PWD、 S H E L L 、 SHELL、 SHELL、USER等
2)案例实操
(1)查看系统变量的值
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $HOME/home/atguigu
(2)显示当前Shell中所有变量:set
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ setBASH=/bin/bashBASH_ALIASES=()BASH_ARGC=()BASH_ARGV=()
3**.2** 自定义变量
1)基本语法
(1)定义变量:变量名=变量值,注意=号前后不能有空格
(2)撤销变量:unset 变量名
(3)声明静态变量:readonly变量,注意:不能unset
2)变量定义规则
(1)变量名称可以由字母、数字和下划线组成,但是不能以数字开头,环境变量名建议大写。
(2)等号两侧不能有空格
(3)在bash中,变量默认类型都是字符串类型,无法直接进行数值运算。
(4)变量的值如果有空格,需要使用双引号或单引号括起来。
3)案例实操
(1)定义变量A
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ A=5[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $A5
(2)给变量A重新赋值
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ A=8[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $A8
(3)撤销变量A
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ unset A[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $A
(4)声明静态的变量B=2,不能unset
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ readonly B=2[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $B2[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ B=9-bash: B: readonly variable
(5)在bash中,变量默认类型都是字符串类型,无法直接进行数值运算
[atguigu@hadoop102 ~]$ C=1+2[atguigu@hadoop102 ~]$ echo $C1+2
(6)变量的值如果有空格,需要使用双引号或单引号括起来
[atguigu@hadoop102 ~]$ D=I love banzhang-bash: world: command not found[atguigu@hadoop102 ~]$ D="I love banzhang"[atguigu@hadoop102 ~]$ echo $DI love banzhang
(7)可把变量提升为全局环境变量,可供其他Shell程序使用
export 变量名
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim helloworld.sh
在helloworld.sh文件中增加echo $B
#!/bin/bashecho "helloworld"echo $B[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./helloworld.sh Helloworld
发现并没有打印输出变量B的值。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ export B[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./helloworld.sh helloworld2
3**.3** 特殊变量
3.3.1 $n
1)基本语法
$n (功能描述:n为数字,$0代表该脚本名称,$1- 9 代表第一到第九个参数,十以上的参数,十以上的参数需要用大括号包含,如 9代表第一到第九个参数,十以上的参数,十以上的参数需要用大括号包含,如 9代表第一到第九个参数,十以上的参数,十以上的参数需要用大括号包含,如{10})
2)案例实操
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch parameter.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim parameter.sh#!/bin/bashecho '==========$n=========='echo $0 echo $1 echo $2#!/bin/bash 是脚本的开头,指定了使用Bash解释器来执行该脚本。
echo '==========$n==========' 这行代码会输出字符串 '==========$n==========',其中 $n 是一个变量,它的值在脚本中没有定义,所以这里会显示为 $n。
echo $0 这行代码会输出当前脚本的文件名,即 $0 变量的值。
echo $1 这行代码会输出第一个命令行参数的值,即 $1 变量的值。
echo $2 这行代码会输出第二个命令行参数的值,即 $2 变量的值。[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 parameter.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./parameter.sh cls xz==========$n==========./parameter.shclsxz
3.3.2 $#
1)基本语法
$# (功能描述:获取所有输入参数个数,常用于循环)。
2)案例实操
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim parameter.sh#!/bin/bashecho '==========$n=========='echo $0 echo $1 echo $2echo '==========$#=========='echo $#[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 parameter.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./parameter.sh cls xz==========$n==========./parameter.shclsxz==========$#==========2
3.3.3 ∗ ∗ ∗ 、 ***、 ∗∗∗、@**
1)基本语法
∗ (功能描述:这个变量代表命令行中所有的参数, * (功能描述:这个变量代表命令行中所有的参数, ∗(功能描述:这个变量代表命令行中所有的参数,*把所有的参数看成一个整体)
@ (功能描述:这个变量也代表命令行中所有的参数,不过 @ (功能描述:这个变量也代表命令行中所有的参数,不过 @(功能描述:这个变量也代表命令行中所有的参数,不过@把每个参数区分对待)
2)案例实操
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim parameter.sh#!/bin/bashecho '==========$n=========='echo $0 echo $1 echo $2echo '==========$#=========='echo $#echo '==========$*=========='echo $*echo '==========$@=========='echo $@[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./parameter.sh a b c d e f g==========$n==========./parameter.shab==========$#==========7==========$*==========a b c d e f g==========$@==========a b c d e f g
3.3.4 $?
1)基本语法
$? (功能描述:最后一次执行的命令的返回状态。如果这个变量的值为0,证明上一个命令正确执行;如果这个变量的值为非0(具体是哪个数,由命令自己来决定),则证明上一个命令执行不正确了。)
2)案例实操
判断helloworld.sh脚本是否正确执行
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./helloworld.sh hello world[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $?0
第四节 运算符
1)基本语法
“ ( ( 运算式 ) ) ”或“ ((运算式))”或“ ((运算式))”或“[运算式]”
2)案例实操:
计算(2+3)* 4的值
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]# S=$[(2+3)*4][atguigu@hadoop101 datas]# echo $S
第五节 条件判断
1)基本语法
(1)test condition
(2)[ condition ](注意condition前后要有空格)
注意:条件非空即为true,[ atguigu ]返回true,[ ] 返回false。
2)常用判断条件
(1)两个整数之间比较
-eq 等于(equal) -ne 不等于(not equal)
-lt 小于(less than) -le 小于等于(less equal)
-gt 大于(greater than) -ge 大于等于(greater equal)
(2)按照文件权限进行判断
-r 有读的权限(read)
-w 有写的权限(write)
-x 有执行的权限(execute)
(3)按照文件类型进行判断
-e 文件存在(existence)
-f 文件存在并且是一个常规的文件(file)
-d 文件存在并且是一个目录(directory)
3)案例实操
(1)23是否大于等于22
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ [ 23 -ge 22 ][atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $?0
(2)helloworld.sh是否具有写权限
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ [ -w helloworld.sh ][atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $?0
(3)/home/atguigu/cls.txt目录中的文件是否存在
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ [ -e /home/atguigu/cls.txt ][atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $?1
(4)多条件判断(&& 表示前一条命令执行成功时,才执行后一条命令,|| 表示上一条命令执行失败后,才执行下一条命令)
[atguigu@hadoop101 ~]$ [ atguigu ] && echo OK || echo notOKOK[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ [ ] && echo OK || echo notOKnotOK
第六节 流程控制(重点)
6.1 if判断
1)基本语法
(1)单分支
if [ 条件判断式 ];then
程序
fi
或者
if [ 条件判断式 ]
then
程序
fi
(2)多分支
if [ 条件判断式 ]
then
程序
elif [ 条件判断式 ]
then
程序
else
程序
fi
注意事项:
(1)[ 条件判断式 ],中括号和条件判断式之间必须有空格
(2)if后要有空格
2)案例实操
输入一个数字,如果是1,则输出banzhang zhen shuai,如果是2,则输出cls zhen mei,如果是其它,什么也不输出。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch if.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim if.sh#!/bin/bashif [ $1 -eq 1 ]thenecho "banzhang zhen shuai"elif [ $1 -eq 2 ]thenecho "cls zhen mei"fi[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 if.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./if.sh 1banzhang zhen shuai
6.2 case语句
1)基本语法
case $变量名 in
“值1”)
如果变量的值等于值1,则执行程序1
;;
“值2”)
如果变量的值等于值2,则执行程序2
;;
…省略其他分支…
*)
如果变量的值都不是以上的值,则执行此程序
;;
esac
注意事项:
(1)case行尾必须为单词“in”,每一个模式匹配必须以右括号“)”结束。
(2)双分号“;;”表示命令序列结束,相当于java中的break。
(3)最后的“*)”表示默认模式,相当于java中的default。
2)案例实操
输入一个数字,如果是1,则输出banzhang,如果是2,则输出cls,如果是其它,输出renyao。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch case.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim case.sh!/bin/bashcase $1 in"1")echo "banzhang";;"2")echo "cls";;*)echo "renyao";;esac[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 case.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./case.sh 11
6.3 for循环
1)基本语法1
for (( 初始值;循环控制条件;变量变化 ))
do
程序
done
2)案例实操
从1加到100
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch for1.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim for1.sh#!/bin/bashsum=0for((i=0;i<=100;i++))dosum=$[$sum+$i]doneecho $sum[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 for1.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./for1.sh 5050
3)基本语法2
for 变量 in 值1 值2 值3…
do
程序
done
4)案例实操
(1)打印所有输入参数
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch for2.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim for2.sh#!/bin/bash#打印数字for i in cls mly wlsdoecho "ban zhang love $i"done[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 for2.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./for2.shban zhang love clsban zhang love mlyban zhang love wls
(2)比较 ∗ 和 *和 ∗和@区别
∗ 和 *和 ∗和@都表示传递给函数或脚本的所有参数,不被双引号“”包含时,都以$1 2 … 2 … 2…n的形式输出所有参数。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch for3.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim for3.sh#!/bin/bash echo '=============$*============='for i in $*doecho "ban zhang love $i"doneecho '=============$@============='for j in $@do echo "ban zhang love $j"done[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 for3.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./for3.sh cls mly wls=============$*=============banzhang love clsbanzhang love mlybanzhang love wls=============$@=============banzhang love clsbanzhang love mlybanzhang love wls
当它们被双引号“”包含时,$*会将所有的参数作为一个整体,以“$1 2 … 2 … 2…n”的形式输出所有参数;$@会将各个参数分开,以“$1” “ 2 ” … “ 2”…“ 2”…“n”的形式输出所有参数。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim for4.sh#!/bin/bash echo '=============$*============='for i in "$*" #$*中的所有参数看成是一个整体,所以这个for循环只会循环一次 do echo "ban zhang love $i"done echo '=============$@============='for j in "$@" #$@中的每个参数都看成是独立的,所以“$@”中有几个参数,就会循环几次 do echo "ban zhang love $j" done[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 for4.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./for4.sh cls mly wls=============$*=============banzhang love cls mly wls=============$@=============banzhang love clsbanzhang love mlybanzhang love wls
6.4 while循环
1)基本语法
while [ 条件判断式 ]
do
程序
done
2**)案例实操**
从1加到100
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch while.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim while.sh#!/bin/bashsum=0i=1while [ $i -le 100 ]dosum=$[$sum+$i]i=$[$i+1]doneecho $sum[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 while.sh [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./while.sh 5050
第七节 read读取控制台输入
1)基本语法
read (选项) (参数)
选项:
-p:指定读取值时的提示符;
-t:指定读取值时等待的时间(秒)。
参数
变量:指定读取值的变量名
2)案例实操
提示7秒内,读取控制台输入的名称
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch read.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim read.sh#!/bin/bashread -t 7 -p "Enter your name in 7 seconds :" NAMEecho $NAME[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./read.sh Enter your name in 7 seconds : atguiguatguigu
第八节 函数
8.1 系统函数
8.1.1 basename
1)基本语法
basename [string / pathname] [suffix] (功能描述:basename命令会删掉所有的前缀包括最后一个(‘/’)字符,然后将字符串显示出来。
选项:
suffix为后缀,如果suffix被指定了,basename会将pathname或string中的suffix去掉。
2)案例实操
截取该/home/atguigu/banzhang.txt路径的文件名称
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ basename /home/atguigu/banzhang.txt banzhang.txt[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ basename /home/atguigu/banzhang.txt .txtbanzhang
8.1.2 dirname
1)基本语法
dirname 文件绝对路径 (功能描述:从给定的包含绝对路径的文件名中去除文件名(非目录的部分),然后返回剩下的路径(目录的部分))
2)案例实操
获取banzhang.txt文件的路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 ~]$ dirname /home/atguigu/banzhang.txt /home/atguigu
8.2 自定义函数
1)基本语法
[ function ] funname[()]
{
Action;
[return int;]
}
2)经验技巧
(1)必须在调用函数地方之前,先声明函数,shell脚本是逐行运行。不会像其它语言一样先编译。
(2)函数返回值,只能通过$?系统变量获得,可以显示加:return返回,如果不加,将以最后一条命令运行结果,作为返回值。return后跟数值n(0-255)
3)案例实操
计算两个输入参数的和
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch fun.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim fun.sh#!/bin/bashfunction sum(){s=0s=$[$1+$2]echo "$s"}read -p "Please input the number1: " n1;read -p "Please input the number2: " n2;sum $n1 $n2;[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ chmod 777 fun.sh[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ./fun.sh Please input the number1: 2Please input the number2: 57
第九节 Shell工具(重点)
9.1 cut
cut的工作就是“剪”,具体的说就是在文件中负责剪切数据用的。cut 命令从文件的每一行剪切字节、字符和字段并将这些字节、字符和字段输出。
1)基本用法
cut [选项参数] filename
说明:默认分隔符是制表符
2)选项参数说明
| 选项参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -f | 列号,提取第几列 |
| -d | 分隔符,按照指定分隔符分割列,默认是制表符“\t” |
| -c | 指定具体的字符 |
3)案例实操
(1)数据准备
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch cut.txt[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim cut.txtdong shenguan zhenwo wolai laile le
(2)切割cut.txt第一列
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cut -d " " -f 1 cut.txt dongguanwolaile
(3)切割cut.txt第二、三列
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cut -d " " -f 2,3 cut.txt shenzhenwolaile
(4)在cut.txt文件中切割出guan
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat cut.txt | grep "guan" | cut -d " " -f 1guan
(5)选取系统PATH变量值,第2个“:”开始后的所有路径:
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $PATH/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin:/home/atguigu/.local/bin:/home/atguigu/bin[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ echo $PATH | cut -d ":" -f 3-/usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin:/home/atguigu/.local/bin:/home/atguigu/bin
(6)切割ifconfig 后打印的IP地址
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ifconfig ens33 | grep netmask | cut -d "i" -f 2 | cut -d " " -f 2192.168.6.101
9.2 awk
一个强大的文本分析工具,把文件逐行的读入,以空格为默认分隔符将每行切片,切开的部分再进行分析处理。
1)基本用法
awk [选项参数] ‘/pattern1/{action1} /pattern2/{action2}…’ filename
pattern:表示awk在数据中查找的内容,就是匹配模式
action:在找到匹配内容时所执行的一系列命令
2)选项参数说明
| 选项参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -F | 指定输入文件折分隔符 |
| -v | 赋值一个用户定义变量 |
3)案例实操
(1)数据准备
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ sudo cp /etc/passwd ./
(2)搜索passwd文件以root关键字开头的所有行,并输出该行的第7列。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ awk -F : '/^root/{print $7}' passwd /bin/bash
(3)搜索passwd文件以root关键字开头的所有行,并输出该行的第1列和第7列,中间以“,”号分割。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ awk -F : '/^root/{print $1","$7}' passwd root,/bin/bash
注意:只有匹配了pattern的行才会执行action
(4)只显示/etc/passwd的第一列和第七列,以逗号分割,且在所有行前面添加列名user,shell在最后一行添加"dahaige,/bin/zuishuai"。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ awk -F : 'BEGIN{print "user, shell"} {print $1","$7} END{print "dahaige,/bin/zuishuai"}' passwduser, shellroot,/bin/bashbin,/sbin/nologin。。。atguigu,/bin/bashdahaige,/bin/zuishuai
注意:BEGIN 在所有数据读取行之前执行;END 在所有数据执行之后执行。
(5)将passwd文件中的用户id增加数值1并输出
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ awk -v i=1 -F : '{print $3+i}' passwd1234
4**)awk的内置变量**
| 变量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| FILENAME | 文件名 |
| NR | 已读的记录数(行号) |
| NF | 浏览记录的域的个数(切割后,列的个数) |
5)案例实操
(1)统计passwd文件名,每行的行号,每行的列数
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ awk -F : '{print "filename:" FILENAME ",linenum:" NR ",col:"NF}' passwd filename:passwd,linenum:1,col:7filename:passwd,linenum:2,col:7filename:passwd,linenum:3,col:7。。。
(2)查询ifconfig命令输出结果中的空行所在的行号
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ifconfig | awk '/^$/{print NR}'91826
(3)切割IP
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ ifconfig ens33 | grep netmask | awk -F "inet" '{print $2}' | awk -F " " '{print $1}' 192.168.6.101
9.3 sort
sort命令是在Linux里非常有用,它将文件进行排序,并将排序结果标准输出。
1)基本语法
Sort (选项) (参数)
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| -n | 依照数值的大小排序 |
| -r | 以相反的顺序来排序 |
| -t | 设置排序时所用的分隔字符 |
| -k | 指定需要排序的列 |
参数:指定待排序的文件列表
2)案例实操
(1)数据准备
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ touch sort.txt[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ vim sort.txtbb:40:5.4bd:20:4.2xz:50:2.3cls:10:3.5ss:30:1.6
(2)按照“:”分割后的第三列倒序排序。
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ sort -t : -nrk 3 sort.txt bb:40:5.4bd:20:4.2cls:10:3.5xz:50:2.3ss:30:1.6
9**.4 wc**
wc命令用来统计文件信息。利用wc指令我们可以计算文件的行数,字节数、字符数等。
1)基本语法
wc [选项参数] filename
| 选项参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -l | 统计文件行数 |
| -w | 统计文件的单词数 |
| -m | 统计文件的字符数 |
| -c | 统计文件的字节数 |
2)案例实操
统计/etc/profile文件的行数、单词数、字节数!
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ wc -l /etc/profile [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ wc -w /etc/profile [atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ wc -m /etc/profile
第十节 正则表达式入门
正则表达式使用单个字符串来描述、匹配一系列符合某个语法规则的字符串。在很多文本编辑器里,正则表达式通常被用来检索、替换那些符合某个模式的文本。在Linux中,grep,sed,awk等命令都支持通过正则表达式进行模式匹配。
10.1 常规匹配
一串不包含特殊字符的正则表达式匹配它自己,例如:
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep atguigu
就会匹配所有包含atguigu的行
10.2 常用特殊字符
1)特殊字符:^
^ 匹配一行的开头,例如:
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep ^a
会匹配出所有以a开头的行
2)特殊字符:$
$ 匹配一行的结束,例如
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep t$
会匹配出所有以t结尾的行
思考:^$ 匹配什么?
3)特殊字符:.
. 匹配一个任意的字符,例如
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep r..t
会匹配包含rabt,rbbt,rxdt,root等的所有行
4)特殊字符:*
- 不单独使用,他和上一个字符连用,表示匹配上一个字符0次或多次,例如
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep ro*t
会匹配rt, rot, root, rooot, roooot等所有行
思考:.* 匹配什么?
5)特殊字符:[ ]
[ ] 表示匹配某个范围内的一个字符,例如
[6,8]------匹配6或者8
[0-9]------匹配一个0-9的数字
[0-9]*------匹配任意长度的数字字符串
[a-z]------匹配一个a-z之间的字符
[a-z]* ------匹配任意长度的字母字符串
[a-c, e-f]-匹配a-c或者e-f之间的任意字符
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep r[a,b,c]*t
会匹配rt,rat, rbt, rabt, rbact,rabccbaaacbt等等所有行
6)特殊字符:\
\ 表示转义,并不会单独使用。由于所有特殊字符都有其特定匹配模式,当我们想匹配某一特殊字符本身时(例如,我想找出所有包含 ‘$’ 的行),就会碰到困难。此时我们就要将转义字符和特殊字符连用,来表示特殊字符本身,例如
[atguigu@hadoop101 datas]$ cat /etc/passwd | grep a\$b
就会匹配所有包含 a$b 的行。
相关文章:

大数据开发扩展shell--尚硅谷shell笔记
大数据开发扩展shell 学习目标 1 熟悉shell脚本的原理和使用 2 熟悉shell的编程语法 第一节 Shell概述 1)Linux提供的Shell解析器有: 查看系统中可用的 shell [atguiguhadoop101 ~]$ cat /etc/shells /bin/sh/bin/bash/sbin/nologin/bin/dash/bin/t…...
考研数学|《1800》《1000》《880》《660》最佳搭配使用方法
直接说结论:基础不好先做1800、强化之前660,强化可选880/1000题。 首先,传统习题册存在的一个问题是题量较大,但难度波动较大。《汤家凤1800》和《张宇1000》题量庞大,但有些题目难度不够平衡,有些过于简单…...
)
【GameFramework框架内置模块】17、声音(Sound)
推荐阅读 CSDN主页GitHub开源地址Unity3D插件分享简书地址QQ群:398291828大家好,我是佛系工程师☆恬静的小魔龙☆,不定时更新Unity开发技巧,觉得有用记得一键三连哦。 一、前言 【GameFramework框架】系列教程目录: https://blog.csdn.net/q764424567/article/details/1…...

视频记录历史播放位置效果
简介 每次打开页面视频从上一次的播放位置开始播放 利用lodash库做节流 代码 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang"en"><head><meta charset"UTF-8"><meta name"viewport" content"widthdevice-width, initial-sca…...

Request Response
简介 Request(请求) & Response(响应) 浏览器会向服务器发送请求数据,服务器也需要返回响应数据给浏览器,因此我们需要设置对应的类来代表请求数据和响应数据,且Servlet中的service方法就需…...

How to convert .py to .ipynb in Ubuntu 22.04
How to convert .py to .ipynb in Ubuntu 22.04 jupyter nbconvertp2j 最近看到大家在用jupyter notebook,我也试了一下,感觉还不错,不过,也遇到了一些问题,比方说,我有堆的.py文件,如果要一个一…...
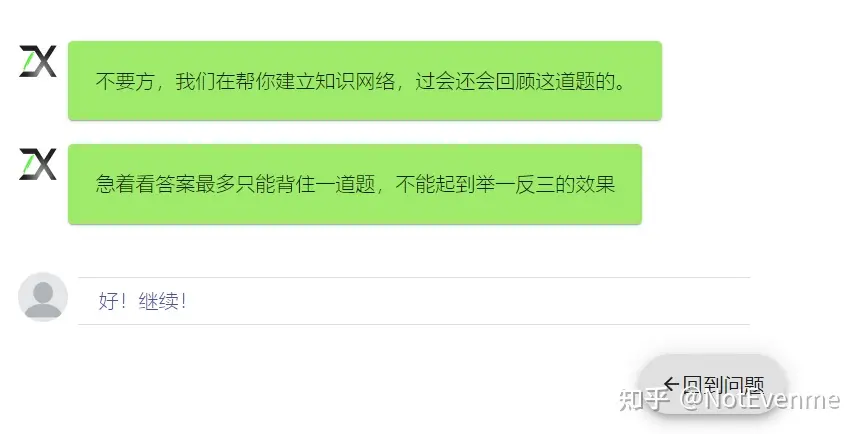
【prometheus-operator】k8s监控集群外redis
1、部署exporter GitHub - oliver006/redis_exporter: Prometheus Exporter for Redis Metrics. Supports Redis 2.x, 3.x, 4.x, 5.x, 6.x, and 7.x redis_exporter-v1.57.0.linux-386.tar.gz # 解压 tar -zxvf redis_exporter-v1.57.0.linux-386.tar.gz # 启动 nohup ./redi…...
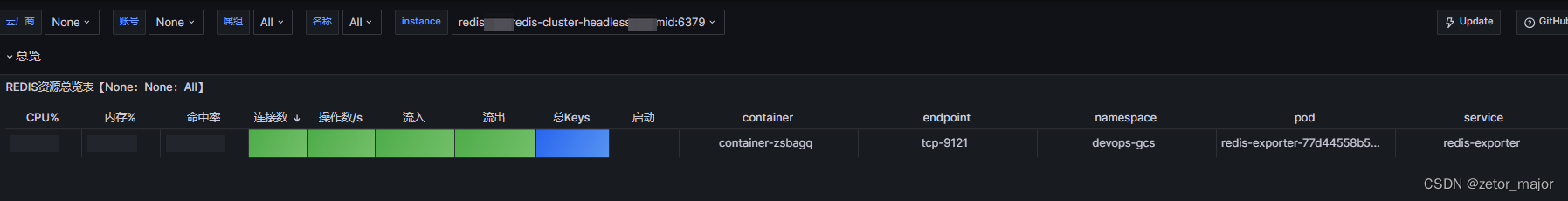
MySQL索引(图文并茂)
目录 一、索引的概念 二、索引的作用 三、创建索引的原则依据 四、索引的分类和创建 1、索引的分类 2、索引的创建 2.1 普通索引 2.1.1 直接创建索引 2.1.2 修改表方式创建 2.1.3 创建表的时候指定索引 2.2 唯一索引 2.2.1 直接创建唯一索引 2.2.2 修改表方式创建 …...
Redis 教程系列之Redis PHP 使用 Redis(十二)
PHP 使用 Redis 安装 开始在 PHP 中使用 Redis 前, 我们需要确保已经安装了 redis 服务及 PHP redis 驱动,且你的机器上能正常使用 PHP。 接下来让我们安装 PHP redis 驱动:下载地址为:https://github.com/phpredis/phpredis/releases。 P…...

JavaScript语法和数据类型
基础 JavaScript 借鉴了 Java 的大部分语法,但同时也受到 Awk、Perl 和 Python 的影响。 JavaScript 是区分大小写的,并使用 Unicode 字符集。举个例子,可以将单词 Frh(在德语中意思是“早”)用作变量名。 var Frh …...
解决华为云服务器宝塔面板无法访问显示“此站点的连接不安全”问题
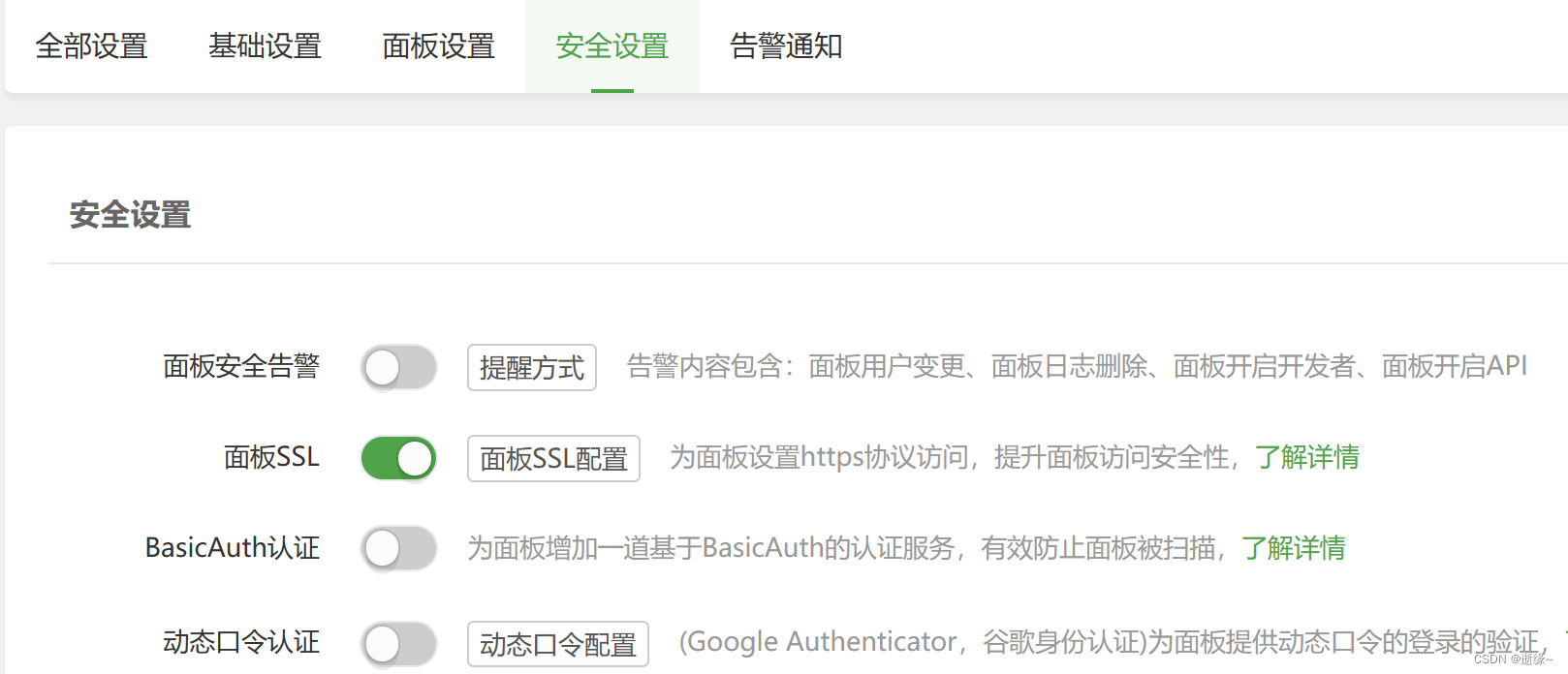
已经配置好安全组以及初始化宝塔面板,还是无法访问镜像管理页面,提示此站点的连接不安全。 解决方案 将地址https改为http即可进入。 成功登录后,开启面板SSL即可。...

【Python】 Python脚本实现某平台视频流下载
亲爱的玛丽 我会想念着你 我是多么的讨厌分离 加油站旁的海鸥 机场路上的松柏 挥挥手眼泪就落下来 我多想和那些光阴永远住下来 我不能 我不能 🎵 赵雷《玛丽》 在视频内容的分发上,m3u8格式的视频流越来越常见。它将视频切分成多个…...

LangChain核心模块 Model I/O——Prompts
Prompts 语言模型的提示是用户提供的一组指令或输入,用于指导模型的响应,帮助模型理解上下文并生成相关且连贯的基于语言的输出,例如回答问题、完成句子或参与某项活动。对话。 关键问题 如何在LLMs中使用少量示例(few-shot examples)—…...

关于Docker守护程序未运行导致的错误
01 在启动Docker之前,确保你已经安装了Docker并且Docker服务是运行的。以下是一些步骤可以帮助你解决这个问题: 首先,确保Docker已经正确安装在你的系统上。你可以通过运行以下命令来检查Docker是否已安装: docker --version如果…...

Unity中关于SendMessage方法
在Unity中,SendMessage 方法用于在游戏对象及其所有子对象上调用指定名称的方法。这种方法可以用于在不需要知道接收方的确切类型的情况下,向游戏对象发送消息。 基本语法如下: void SendMessage(string methodName, object value null, S…...

C++ 修饰符类型
C 允许在 char、int 和 double 数据类型前放置修饰符。修饰符用于改变基本类型的含义,所以它更能满足各种情境的需求。 下面列出了数据类型修饰符: signedunsignedlongshort 修饰符 signed、unsigned、long 和 short 可应用于整型,signed …...
生产计划数据模型,实现能源企业数字化高效管理
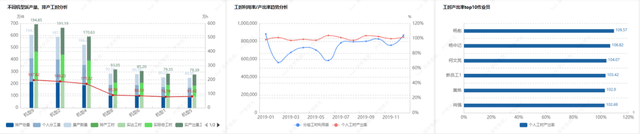
随着市场经济的快速发展,能源企业在经济发展中的地位也随之提高。但由于能源企业在生产计划经济管理上存在指标不平衡、市场观念落后和环保意识欠缺等问题,导致企业的经济效益降低。目前,提高企业的生产计划管理是改善能源企业现状最有利的途…...

【chemistry 2】蛋白质的共价结构
🌞欢迎来到生物化学的世界 🌈博客主页:卿云阁 💌欢迎关注🎉点赞👍收藏⭐️留言📝 🌟本文由卿云阁原创! 📆首发时间:🌹2024年3月26日&…...
什么是 UI ?设计师为你解答
用户界面(UI)它是人与机器互动的载体,也是用户体验(UX)一个组成部分。用户界面由视觉设计 (即传达产品的外观和感觉) 和交互设计 (即元素的功能和逻辑组织) 两部分组成。用户界面设计的目标是创建一个用户界面…...

pytest框架入门及环境配置
一、简介 pytest是python的专用测试框架,由于设计的巧妙性,使得pytest使用起来更加的灵活简单。pytest框架有着强大的功能,拥有很多的第三方插件,还具有良好的扩展性,可以与其他的框架进行结合使用。 pytest的优点: 1、可以与一些调度工具结合,实现持续集成 2、与allu…...

Ubuntu系统下交叉编译openssl
一、参考资料 OpenSSL&&libcurl库的交叉编译 - hesetone - 博客园 二、准备工作 1. 编译环境 宿主机:Ubuntu 20.04.6 LTSHost:ARM32位交叉编译器:arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc-11.1.0 2. 设置交叉编译工具链 在交叉编译之前&#x…...
docker详细操作--未完待续
docker介绍 docker官网: Docker:加速容器应用程序开发 harbor官网:Harbor - Harbor 中文 使用docker加速器: Docker镜像极速下载服务 - 毫秒镜像 是什么 Docker 是一种开源的容器化平台,用于将应用程序及其依赖项(如库、运行时环…...
:にする)
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする 1、前言(1)情况说明(2)工程师的信仰2、知识点(1) にする1,接续:名词+にする2,接续:疑问词+にする3,(A)は(B)にする。(2)復習:(1)复习句子(2)ために & ように(3)そう(4)にする3、…...

可靠性+灵活性:电力载波技术在楼宇自控中的核心价值
可靠性灵活性:电力载波技术在楼宇自控中的核心价值 在智能楼宇的自动化控制中,电力载波技术(PLC)凭借其独特的优势,正成为构建高效、稳定、灵活系统的核心解决方案。它利用现有电力线路传输数据,无需额外布…...

java调用dll出现unsatisfiedLinkError以及JNA和JNI的区别
UnsatisfiedLinkError 在对接硬件设备中,我们会遇到使用 java 调用 dll文件 的情况,此时大概率出现UnsatisfiedLinkError链接错误,原因可能有如下几种 类名错误包名错误方法名参数错误使用 JNI 协议调用,结果 dll 未实现 JNI 协…...

蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(2):进阶面试题与实战演练
前文覆盖了 BLE 扫描的基础概念与经典问题蓝牙 BLE 扫描面试题大全(1):从基础到实战的深度解析-CSDN博客,但实际面试中,企业更关注候选人对复杂场景的应对能力(如多设备并发扫描、低功耗与高发现率的平衡)和前沿技术的…...
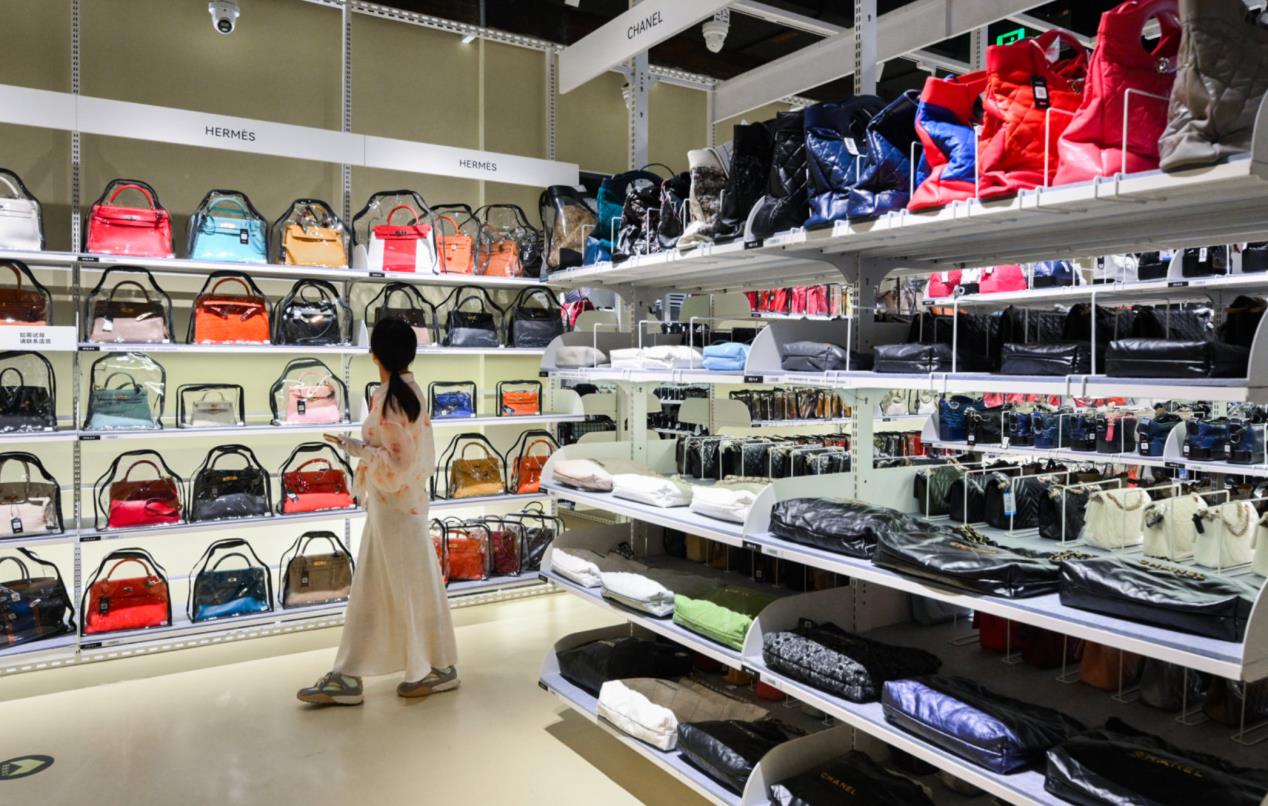

转转集团旗下首家二手多品类循环仓店“超级转转”开业
6月9日,国内领先的循环经济企业转转集团旗下首家二手多品类循环仓店“超级转转”正式开业。 转转集团创始人兼CEO黄炜、转转循环时尚发起人朱珠、转转集团COO兼红布林CEO胡伟琨、王府井集团副总裁祝捷等出席了开业剪彩仪式。 据「TMT星球」了解,“超级…...

大模型多显卡多服务器并行计算方法与实践指南
一、分布式训练概述 大规模语言模型的训练通常需要分布式计算技术,以解决单机资源不足的问题。分布式训练主要分为两种模式: 数据并行:将数据分片到不同设备,每个设备拥有完整的模型副本 模型并行:将模型分割到不同设备,每个设备处理部分模型计算 现代大模型训练通常结合…...
【Java_EE】Spring MVC
目录 Spring Web MVC 编辑注解 RestController RequestMapping RequestParam RequestParam RequestBody PathVariable RequestPart 参数传递 注意事项 编辑参数重命名 RequestParam 编辑编辑传递集合 RequestParam 传递JSON数据 编辑RequestBody …...
用docker来安装部署freeswitch记录
今天刚才测试一个callcenter的项目,所以尝试安装freeswitch 1、使用轩辕镜像 - 中国开发者首选的专业 Docker 镜像加速服务平台 编辑下面/etc/docker/daemon.json文件为 {"registry-mirrors": ["https://docker.xuanyuan.me"] }同时可以进入轩…...
