3DGS渐进式渲染 - 离线生成渲染视频
总览
输入:环绕Object拍摄的RGB视频
输出:自定义相机路径的渲染视频(包含渐变效果)
实现过程
首先,编译3DGS的C++代码,并跑通convert.py、train.py和render.py。教程如下:
- github网址:https://github.com/graphdeco-inria/gaussian-splatting
- 新手教程:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UXtuigy_wYc
- 训练自己的视频数据-教程:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wuKhEGCt6ks
在掌握训练自己的视频后,可以生成一组input图像对应的render图像,但点云和参数都是固定的,如:
- 渲染的scaling_modifier参数固定为1.0。
- 渲染时使用的点云 始终是train得到的完整点云。
因此,我们为了得到上面视频中的渐变效果,需要调整这两个地方(scaling_modifier参数和点云采样)。
1 调整scaling_modifier参数
- 修改render.py中的调用的render函数,向里面传入scaling_modifier参数。
# 对每一帧进行渲染
for idx, view in enumerate(tqdm(views, desc="Rendering progress")):rendering = render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, scaling_modifier=scaling_modifier)["render"]
- 进入该render函数,将scaling_modifier传入GaussianRasterizationSettings方法中。
def render(viewpoint_camera, pc : GaussianModel, pipe, bg_color : torch.Tensor, scaling_modifier = 1.0, override_color = None):# Create zero tensor. We will use it to make pytorch return gradients of the 2D (screen-space) meansscreenspace_points = torch.zeros_like(pc.get_xyz, dtype=pc.get_xyz.dtype, requires_grad=True, device="cuda") + 0try:screenspace_points.retain_grad()except:pass# Set up rasterization configurationtanfovx = math.tan(viewpoint_camera.FoVx * 0.5)tanfovy = math.tan(viewpoint_camera.FoVy * 0.5)raster_settings = GaussianRasterizationSettings(image_height=int(viewpoint_camera.image_height),image_width=int(viewpoint_camera.image_width),tanfovx=tanfovx,tanfovy=tanfovy,bg=bg_color,scale_modifier=scaling_modifier,viewmatrix=viewpoint_camera.world_view_transform,projmatrix=viewpoint_camera.full_proj_transform,sh_degree=pc.active_sh_degree,campos=viewpoint_camera.camera_center,prefiltered=False,debug=pipe.debug)
通过上面的方式,即可对每一帧在不同的scaling_modifier下进行渲染,该参数在SIBR Viewer中也可以修改,修改位置如下:
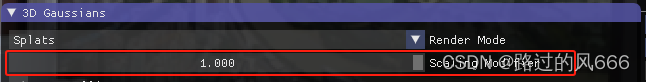
如下左图为scaling_modifier=0.01、右图为scaling_modifier=1.0

2 点云采样
为了实现视频一开始由中心物体向四周扩散的渐变效果,我们需要通过点云采样的方式,实现点云数量渐变式增多
具体步骤如下:
- 计算原始点云中所有点的密度大小。
- 以密度最大的点作为中心点,计算每个点到该点的距离,得到升序排序后的索引。
- 根据该索引生成渐变式的点云。
对应在render.py中添加如下代码:
def get_indices(model_path, iteration):path = os.path.join(model_path, "point_cloud", "iteration_" + str(iteration), "point_cloud.ply")plydata = PlyData.read(path)xyz = np.stack((np.asarray(plydata['vertex']['x']),np.asarray(plydata['vertex']['y']),np.asarray(plydata['vertex']['z'])), axis=1)# 定义邻域半径neighbor_radius = 0.1 # 例如,这里假设邻域半径为0.1# 使用最近邻算法查找每个点的邻域内的点的数量nbrs = NearestNeighbors(radius=neighbor_radius, algorithm='auto').fit(xyz)densities = nbrs.radius_neighbors(xyz, return_distance=False)# 使用最近邻算法查找每个点的邻域内的点的数量nbrs = NearestNeighbors(radius=neighbor_radius, algorithm='auto').fit(xyz)densities = nbrs.radius_neighbors(xyz, return_distance=False)# 计算每个点的密度point_cloud_density = np.array([len(density) for density in densities])# 确定渲染顺序start_idx = np.argmax(point_cloud_density)start_point = xyz[start_idx]# 根据与起始点的距离对点云进行排序distances = np.linalg.norm(xyz - start_point, axis=1)sorted_indices = np.argsort(distances)return sorted_indices在render_set函数中调用get_indices函数:
def render_set(model_path, name, iteration, views, gaussians, pipeline, background, scene):render_path = os.path.join(model_path, name, "ours_{}".format(iteration), "renders")gts_path = os.path.join(model_path, name, "ours_{}".format(iteration), "gt")makedirs(render_path, exist_ok=True)# makedirs(gts_path, exist_ok=True)### 计算点的渲染顺序sorted_indices = get_indices(model_path, iteration)# 对给定的images.bin(相机外参)一帧帧图片进行渲染for idx, view in enumerate(tqdm(views, desc="Rendering progress")):# 修改点云切片if idx<120:indices = sorted_indices[:(len(sorted_indices)//120 * idx)]scene.change_pc_indice(indices=indices)scaling_modifier = 0.01elif scaling_modifier<1:scaling_modifier += 0.01else:scaling_modifier = 1rendering = render(view, gaussians, pipeline, background, scaling_modifier=scaling_modifier)["render"]torchvision.utils.save_image(rendering, os.path.join(render_path, '{0:05d}'.format(idx) + ".png"))
最后,运行render.py即可得到最后的渲染视频(包含渐变效果)。
3 自定义环绕Object的相机路径
render.py使用的相机外参和内参分别存储在images.bin和cameras.bin中。
cameras.bin(内参)
该文件解析(read_intrinsics_binary函数)后,得到如下key-value(int-Camera对象)组成的字典。
{...,
1: Camera(id=1, model='PINHOLE', width=1332, height=876, params=array([1035.49659905, 1034.97186374, 666. , 438.])),...}
images.bin(外参)
该文件解析(read_extrinsics_binary函数)后,得到如下key-value(int-Image对象)组成的字典
{...,
263: Image(id=263, qvec=array([-0.15935236, -0.46899572, 0.35922958, 0.79095129]), tvec=array([-0.68604342, -0.24766367, 1.17531395]), camera_id=1, name='IMG_6597.jpg', xys=array([[ 826.85421273, 3.56521302],[ 791.22610197, 6.24990826],[1318.28015465, 6.96729477],...,[1041.33873779, 316.22219915],[ 737.99930832, 487.77142606],[ 649.78058365, 72.14452395]]), point3D_ids=array([ -1, -1, 75770, ..., -1, -1, -1]))
,...}
在不考虑测试集的时候,我们不会使用该字典的xys和point3D_ids,相机外参仅由qvec和tvec构成。
修改images.bin(外参)
为了生成自定义的相机路径,我们仅需修改images.bin中每一帧的qvec和tvec。核心代码如下:
# 读取相机内外参
images = read_extrinsics_binary('../C4879_4/sparse/0/images_original.bin')
qvecs, tvecs = get_qvec_tvec('../C4879_4/sparse/0/images_original.bin') # 获取qvecs, tvecsqvecs = np.array(qvecs)
tvecs = np.array(tvecs)
mean_x = tvecs[:,0].sum() / len(tvecs)
mean_y = tvecs[:,1].sum() / len(tvecs)
mean_z = tvecs[:,2].sum() / len(tvecs)
print(mean_x,mean_y,mean_z)
#################################以二维平面中的一个圆的轨迹为例############################
# 定义圆形轨迹的参数
radius = 1.0 # 圆的半径
num_poses = len(qvecs) # 生成的外参数量
center = np.array([mean_x,mean_y,mean_z]) # 圆心坐标# 生成沿着圆形轨迹的外参
poses = []
for i in range(num_poses):angle = 2 * np.pi * i / num_poses # 在圆上均匀分布的角度position = center + np.array([radius * np.cos(angle), radius * np.sin(angle), 0]) # 根据角度计算位置q = R.from_euler('xyz', [0, angle, 0]).as_quat() # 根据角度计算旋转四元数tvec = position # 平移向量即为位置poses.append((q, tvec))new_images = {}
for i in range(len(images)):new_images[i+1] = Image(id=images[i+1].id, qvec=np.array(poses[i][0]), tvec=np.array(poses[i][1]),camera_id=images[i+1].camera_id, name='{:03d}'.format(i), xys=images[i+1].xys, point3D_ids=images[i+1].point3D_ids)# 写入相机内外参
write_images_binary(new_images, '../C4879_4/sparse/0/images.bin')
使用到的依赖库和函数:
import numpy as np
import struct
import collections
from PIL import Image
from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation
import pandas as pd
from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation as RCameraModel = collections.namedtuple("CameraModel", ["model_id", "model_name", "num_params"])
Camera = collections.namedtuple("Camera", ["id", "model", "width", "height", "params"])
BaseImage = collections.namedtuple("Image", ["id", "qvec", "tvec", "camera_id", "name", "xys", "point3D_ids"])
Point3D = collections.namedtuple("Point3D", ["id", "xyz", "rgb", "error", "image_ids", "point2D_idxs"])
CAMERA_MODELS = {CameraModel(model_id=0, model_name="SIMPLE_PINHOLE", num_params=3),CameraModel(model_id=1, model_name="PINHOLE", num_params=4),CameraModel(model_id=2, model_name="SIMPLE_RADIAL", num_params=4),CameraModel(model_id=3, model_name="RADIAL", num_params=5),CameraModel(model_id=4, model_name="OPENCV", num_params=8),CameraModel(model_id=5, model_name="OPENCV_FISHEYE", num_params=8),CameraModel(model_id=6, model_name="FULL_OPENCV", num_params=12),CameraModel(model_id=7, model_name="FOV", num_params=5),CameraModel(model_id=8, model_name="SIMPLE_RADIAL_FISHEYE", num_params=4),CameraModel(model_id=9, model_name="RADIAL_FISHEYE", num_params=5),CameraModel(model_id=10, model_name="THIN_PRISM_FISHEYE", num_params=12)
}
CAMERA_MODEL_IDS = dict([(camera_model.model_id, camera_model)for camera_model in CAMERA_MODELS])def qvec2rotmat(qvec):return np.array([[1 - 2 * qvec[2]**2 - 2 * qvec[3]**2,2 * qvec[1] * qvec[2] - 2 * qvec[0] * qvec[3],2 * qvec[3] * qvec[1] + 2 * qvec[0] * qvec[2]],[2 * qvec[1] * qvec[2] + 2 * qvec[0] * qvec[3],1 - 2 * qvec[1]**2 - 2 * qvec[3]**2,2 * qvec[2] * qvec[3] - 2 * qvec[0] * qvec[1]],[2 * qvec[3] * qvec[1] - 2 * qvec[0] * qvec[2],2 * qvec[2] * qvec[3] + 2 * qvec[0] * qvec[1],1 - 2 * qvec[1]**2 - 2 * qvec[2]**2]])def rotmat2qvec(R):Rxx, Ryx, Rzx, Rxy, Ryy, Rzy, Rxz, Ryz, Rzz = R.flatK = np.array([[Rxx - Ryy - Rzz, 0, 0, 0],[Ryx + Rxy, Ryy - Rxx - Rzz, 0, 0],[Rzx + Rxz, Rzy + Ryz, Rzz - Rxx - Ryy, 0],[Ryz - Rzy, Rzx - Rxz, Rxy - Ryx, Rxx + Ryy + Rzz]]) / 3.0eigvals, eigvecs = np.linalg.eigh(K)qvec = eigvecs[[3, 0, 1, 2], np.argmax(eigvals)]if qvec[0] < 0:qvec *= -1return qvecclass Image(BaseImage):def qvec2rotmat(self):return qvec2rotmat(self.qvec)def read_next_bytes(fid, num_bytes, format_char_sequence, endian_character="<"):"""Read and unpack the next bytes from a binary file.:param fid::param num_bytes: Sum of combination of {2, 4, 8}, e.g. 2, 6, 16, 30, etc.:param format_char_sequence: List of {c, e, f, d, h, H, i, I, l, L, q, Q}.:param endian_character: Any of {@, =, <, >, !}:return: Tuple of read and unpacked values."""data = fid.read(num_bytes)return struct.unpack(endian_character + format_char_sequence, data)def read_extrinsics_binary(path_to_model_file):"""see: src/base/reconstruction.ccvoid Reconstruction::ReadImagesBinary(const std::string& path)void Reconstruction::WriteImagesBinary(const std::string& path)"""images = {}with open(path_to_model_file, "rb") as fid:num_reg_images = read_next_bytes(fid, 8, "Q")[0]for i in range(num_reg_images):binary_image_properties = read_next_bytes(fid, num_bytes=64, format_char_sequence="idddddddi")image_id = binary_image_properties[0]qvec = np.array(binary_image_properties[1:5])tvec = np.array(binary_image_properties[5:8])camera_id = binary_image_properties[8]image_name = ""current_char = read_next_bytes(fid, 1, "c")[0]while current_char != b"\x00": # look for the ASCII 0 entryimage_name += current_char.decode("utf-8")current_char = read_next_bytes(fid, 1, "c")[0]num_points2D = read_next_bytes(fid, num_bytes=8,format_char_sequence="Q")[0]x_y_id_s = read_next_bytes(fid, num_bytes=24*num_points2D,format_char_sequence="ddq"*num_points2D)xys = np.column_stack([tuple(map(float, x_y_id_s[0::3])),tuple(map(float, x_y_id_s[1::3]))])point3D_ids = np.array(tuple(map(int, x_y_id_s[2::3])))images[image_id] = Image(id=image_id, qvec=qvec, tvec=tvec,camera_id=camera_id, name=image_name,xys=xys, point3D_ids=point3D_ids)# if i>3:# breakreturn imagesdef write_next_bytes(fid, data, format_char_sequence, endian_character="<"):"""pack and write to a binary file.:param fid::param data: data to send, if multiple elements are sent at the same time,they should be encapsuled either in a list or a tuple:param format_char_sequence: List of {c, e, f, d, h, H, i, I, l, L, q, Q}.should be the same length as the data list or tuple:param endian_character: Any of {@, =, <, >, !}"""if isinstance(data, (list, tuple)):bytes = struct.pack(endian_character + format_char_sequence, *data)else:bytes = struct.pack(endian_character + format_char_sequence, data)fid.write(bytes)def write_images_binary(images, path_to_model_file):"""see: src/colmap/scene/reconstruction.ccvoid Reconstruction::ReadImagesBinary(const std::string& path)void Reconstruction::WriteImagesBinary(const std::string& path)"""with open(path_to_model_file, "wb") as fid:write_next_bytes(fid, len(images), "Q")for i, img in images.items():write_next_bytes(fid, img.id, "i")tmp_qvec = [q*1.01 for q in img.qvec.tolist()]write_next_bytes(fid, tmp_qvec, "dddd")tmp_tvec = [v*1.02 for v in img.tvec.tolist()]write_next_bytes(fid, tmp_tvec, "ddd")write_next_bytes(fid, img.camera_id, "i")for char in img.name:write_next_bytes(fid, char.encode("utf-8"), "c")write_next_bytes(fid, b"\x00", "c")write_next_bytes(fid, len(img.point3D_ids), "Q")for xy, p3d_id in zip(np.zeros_like(img.xys), np.zeros_like(img.point3D_ids)):write_next_bytes(fid, [*xy, p3d_id], "ddq")def get_qvec_tvec(path_to_model_file):qvecs = []tvecs = []with open(path_to_model_file, "rb") as fid:num_reg_images = read_next_bytes(fid, 8, "Q")[0]for i in range(num_reg_images):binary_image_properties = read_next_bytes(fid, num_bytes=64, format_char_sequence="idddddddi")image_id = binary_image_properties[0]qvec = np.array(binary_image_properties[1:5])qvecs.append(qvec)tvec = np.array(binary_image_properties[5:8])tvecs.append(tvec)camera_id = binary_image_properties[8]image_name = ""current_char = read_next_bytes(fid, 1, "c")[0]while current_char != b"\x00": # look for the ASCII 0 entryimage_name += current_char.decode("utf-8")current_char = read_next_bytes(fid, 1, "c")[0]num_points2D = read_next_bytes(fid, num_bytes=8,format_char_sequence="Q")[0]x_y_id_s = read_next_bytes(fid, num_bytes=24*num_points2D,format_char_sequence="ddq"*num_points2D)xys = np.column_stack([tuple(map(float, x_y_id_s[0::3])),tuple(map(float, x_y_id_s[1::3]))])point3D_ids = np.array(tuple(map(int, x_y_id_s[2::3])))return qvecs, tvecs
相关文章:

3DGS渐进式渲染 - 离线生成渲染视频
总览 输入:环绕Object拍摄的RGB视频 输出:自定义相机路径的渲染视频(包含渐变效果) 实现过程 首先,编译3DGS的C代码,并跑通convert.py、train.py和render.py。教程如下: github网址…...
chromium 协议栈 cronet ios 踩坑案例
1、请求未携带 Accept-Language http header 出现图片加载失败 现象: 访问 https://www.huawei.com/cn/?ic_mediumdirect&ic_sourcesurlent 时出现图片加载失败的问题 预期结果: 原因: 网络库删除了添加 Accept-Language header 的逻…...
)
Java快速排序知识点(含面试大厂题和源码)
快速排序(Quick Sort)是一种高效的排序算法,采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的策略来对一个数组进行排序。快速排序的平均时间复杂度为 O(n log n),在最坏的情况下为 O(n^2),但这种情况很少发生…...

SpringBoot整合Swagger2
SpringBoot整合Swagger2 1.什么是Swagger2?(应用场景)2.项目中如何使用2.1 导入依赖2.2 编写配置类2.3 注解使用2.3.1 controller注解:2.3.2 方法注解2.3.3 实体类注解2.3.4 方法返回值注解2.3.5 忽略的方法 3.UI界面 1.什么是Swa…...

C++算法题 - 矩阵
目录 36. 有效的数独54. 螺旋矩阵48. 旋转图像73. 矩阵置零289. 生命游戏 36. 有效的数独 LeetCode_link 请你判断一个 9 x 9 的数独是否有效。只需要 根据以下规则 ,验证已经填入的数字是否有效即可。 数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。 数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现…...

记录一个没测出来,有点严重的Bug
前提: 人物:若干个 部门:若干个 部门有一个人物选择框,可以选择所有的人物,且为非必填字段 bug现象: 部门中 的人物选择框每次都少一个人物 代码分析: F12接口后端没问题,定位为前端的问题。 前…...

科学突破可能开创6G通信新时代
格拉斯哥大学开发的火柴盒大小的天线可以为全息通话、改进自动驾驶和更好的医疗保健的世界铺平道路。 格拉斯哥大学表示,这种创新的无线通信天线将超材料的独特特性与复杂的信号处理相结合,有助于构建未来的 6G 网络。 数字编码动态超表面天线…...
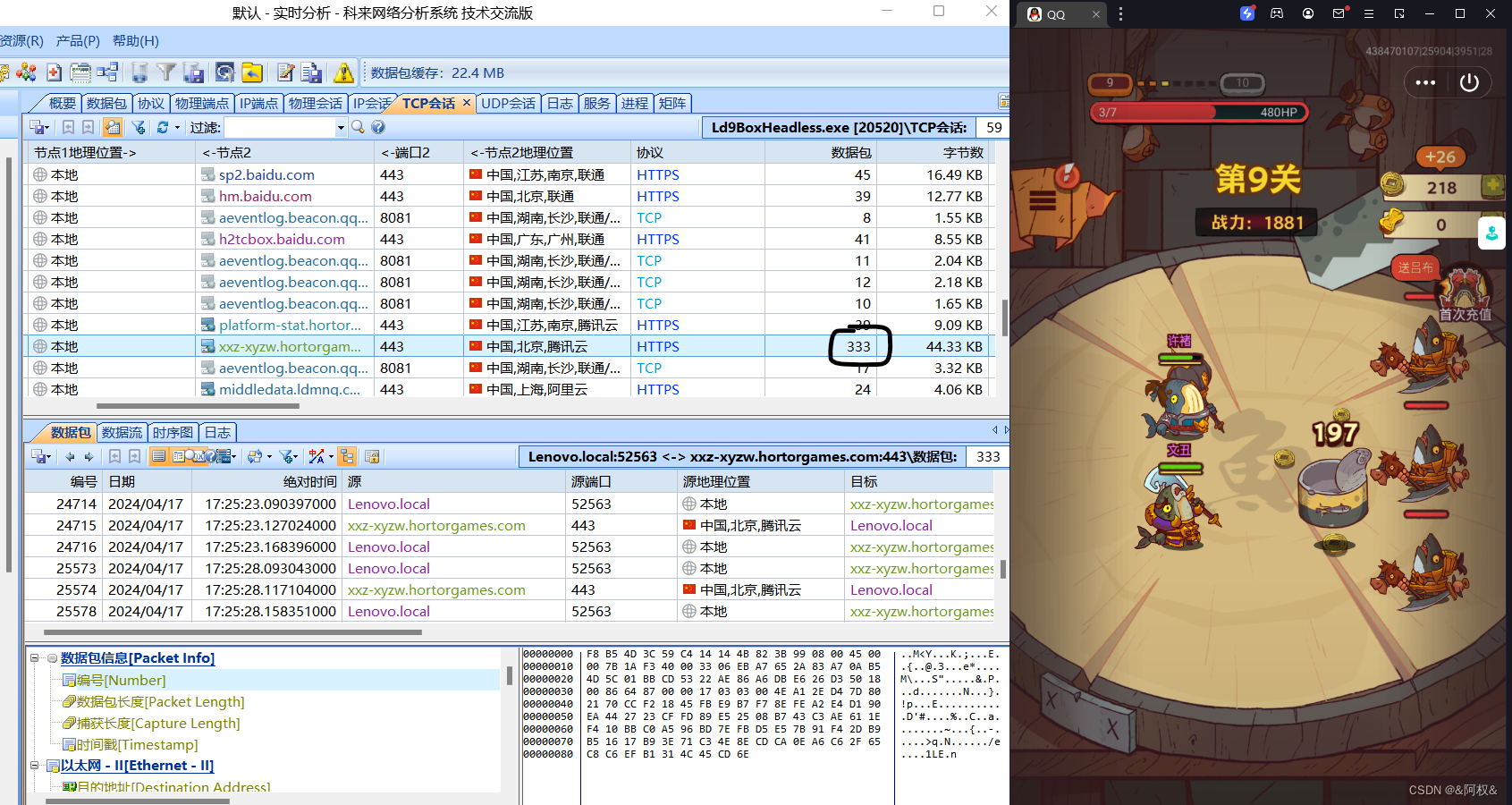
游戏、app抓包
文章目录 协议app抓包游戏抓包 协议 在抓包之前,首先我们要对每个程序使用什么协议有个大致的了解,比如网页这种就是走的http协议。 在一些app中我们通过发送一个请求,然后服务器接受,响应,返回一个数据包,…...
PACNet CellNet(代码开源)|bulk数据作细胞分类,评估细胞命运性能的一大利器
文章目录 1.前言2.CellNet2.1CellNet简介2.2CellNet结果 3.PACNet3.1安装R包与加载R包3.2加载数据3.3开始训练和分类3.4可视化分类过程3.5可视化分类结果 4.细胞命运分类和免疫浸润比较 1.前言 今天冲浪看到一个细胞分类性能评估的R包——PACNet,它与转录组分析方法…...
 Object Pascal 学习笔记---第10章第1节(定义属性))
(delphi11最新学习资料) Object Pascal 学习笔记---第10章第1节(定义属性)
第10章 属性和事件 在过去的三章中,我已经介绍了Object Pascal中面向对象编程(OOP)的基础知识,解释了这些概念并展示了大多数面向对象编程语言中通用特性是如何具体实现的。自Delphi的早期,Object Pascal语言就是一…...
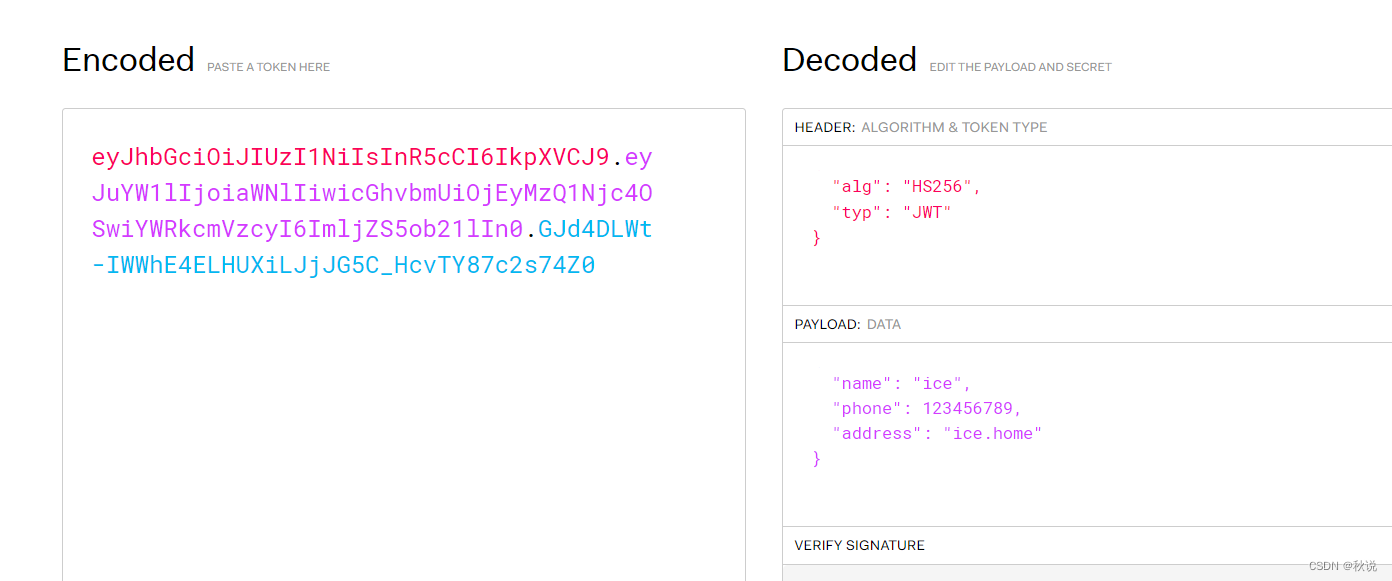
【网络安全 | 密码学】JWT基础知识及攻击方式详析
前言 JWT(Json Web Token)是一种用于在网络应用之间安全地传输信息的开放标准。它通过将用户信息以JSON格式加密并封装在一个token中,然后将该token发送给服务端进行验证,从而实现身份验证和授权。 流程 JWT的加密和解密过程如…...
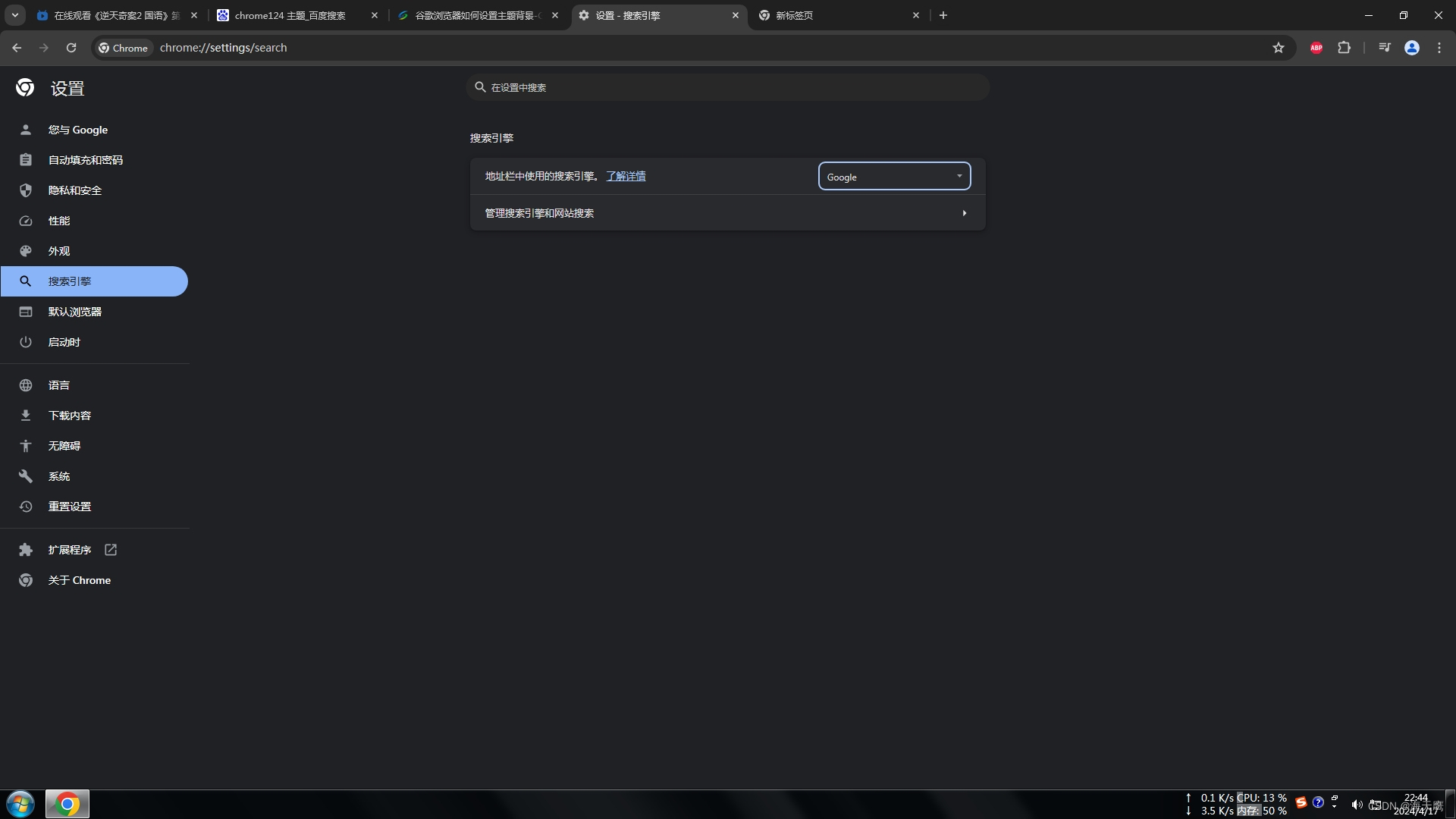
Chrome修改主题颜色
注意:自定义Chrome按钮只在搜索引擎为Google的时候出现。...

大数据:【学习笔记系列】Flink基础架构
Apache Flink 是一个开源的流处理框架,用于处理有界和无界的数据流。Flink 设计用于运行在所有常见的集群环境中,并且能够以高性能和可扩展的方式进行实时数据处理和分析。下面将详细介绍 Flink 的基础架构组件和其工作原理。 1. Flink 架构概览 Flink…...

Debezium系列之:部署Debezium采集Oracle数据库的详细步骤
Debezium系列之:部署Debezium采集Oracle数据库的详细步骤 一、部署Debezium Oracle连接器二、Debezium Oracle 连接器配置三、添加连接器配置四、可插拔数据库与不可插拔数据库一、部署Debezium Oracle连接器 部署的详细步骤可以参考博主这篇技术文章: Debezium系列之:安装…...

C语言通过键盘输入给结构体内嵌的结构体赋值——指针法
1 需求 以录入学生信息(姓名、学号、性别、出生日期)为例,首先通过键盘输入需要录入的学生的数量,再依次输入这些学生的信息,输入完成后输出所有信息。 2 代码 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h>//…...

AWS Key disabler:AWS IAM用户访问密钥安全保护工具
关于AWS Key disabler AWS Key disabler是一款功能强大的AWS IAM用户访问密钥安全保护工具,该工具可以通过设置一个时间定量来禁用AWS IAM用户访问密钥,以此来降低旧访问密钥所带来的安全风险。 工具运行流程 AWS Key disabler本质上是一个Lambda函数&…...
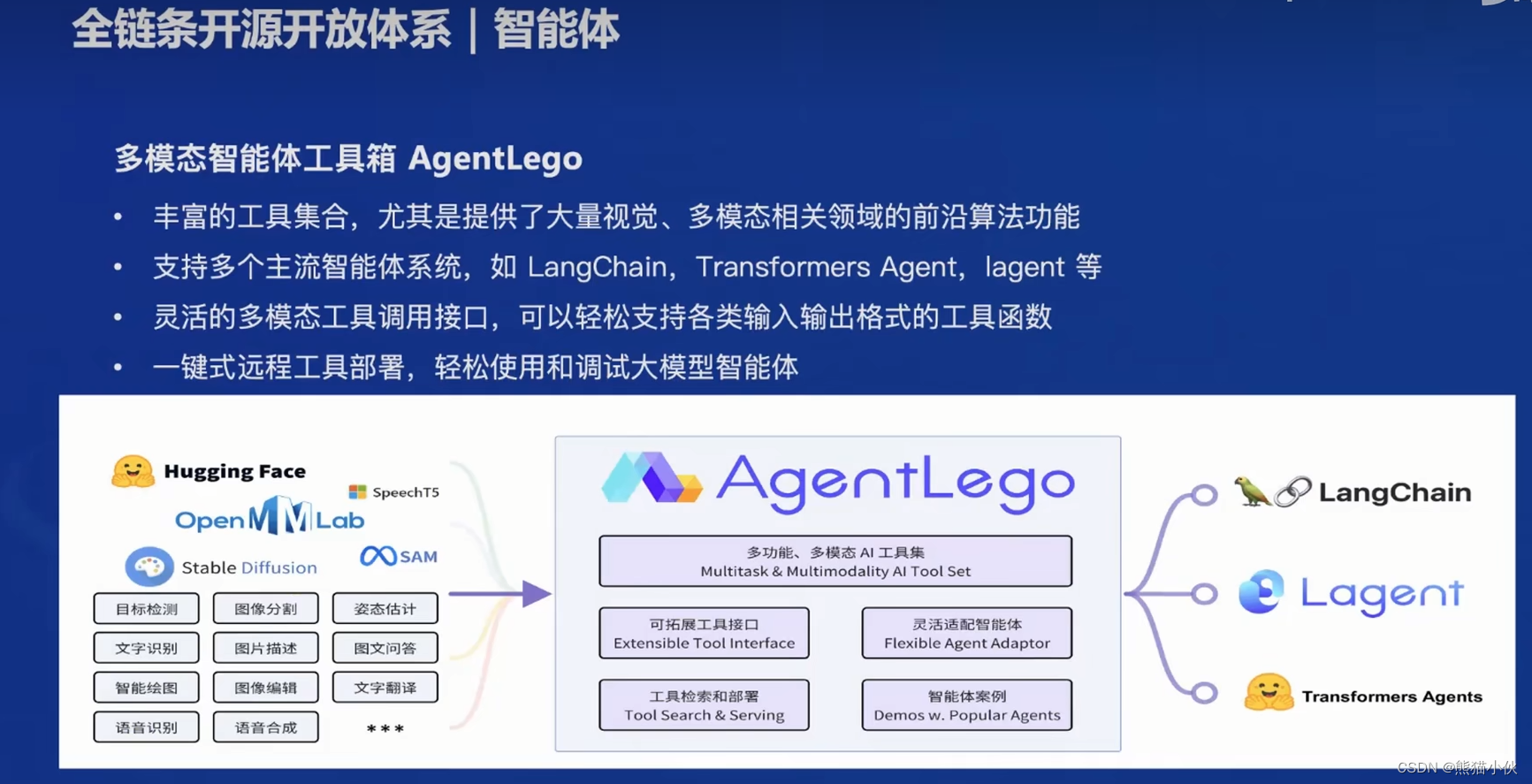
【第1节】书生·浦语大模型全链路开源开放体系
目录 1 简介2 内容(1)书生浦语大模型发展历程(2)体系(3)亮点(4)全链路体系构建a.数据b 预训练c 微调d 评测e.模型部署f.agent 智能体 3 相关论文解读4 ref 1 简介 书生浦语 InternLM…...

代码随想录-链表 | 707设计链表
代码随想录-数组 | 707设计链表 LeetCode 707-设计链表解题思路代码复杂度难点总结 LeetCode 707-设计链表 题目链接 题目描述 你可以选择使用单链表或者双链表,设计并实现自己的链表。 单链表中的节点应该具备两个属性:val 和 next 。val 是当前节点…...
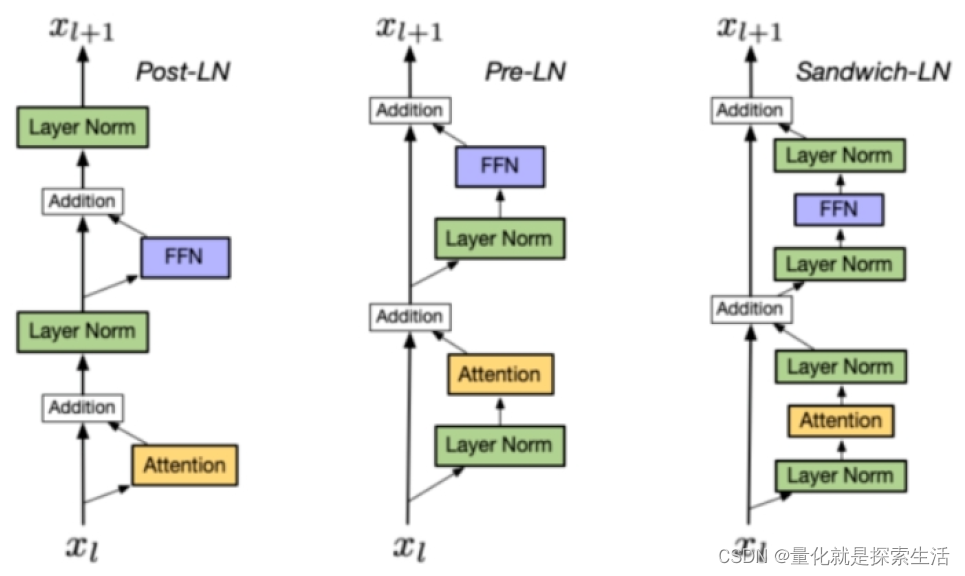
AIGC算法1:Layer normalization
1. Layer Normalization μ E ( X ) ← 1 H ∑ i 1 n x i σ ← Var ( x ) 1 H ∑ i 1 H ( x i − μ ) 2 ϵ y x − E ( x ) Var ( X ) ϵ ⋅ γ β \begin{gathered}\muE(X) \leftarrow \frac{1}{H} \sum_{i1}^n x_i \\ \sigma \leftarrow \operatorname{Var}(…...

【C语言】——字符串函数的使用与模拟实现(下)
【C语言】——字符串函数的使用与模拟实现(下) 前言五、长度受限类字符串函数5.1、 s t r n c p y strncpy strncpy 函数5.2、 s t r n c a t strncat strncat 函数5.3、 s t r n c m p strncmp strncmp 函数 六、 s t r s t r strstr strstr 函数6.1、函…...
:にする)
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする
日语学习-日语知识点小记-构建基础-JLPT-N4阶段(33):にする 1、前言(1)情况说明(2)工程师的信仰2、知识点(1) にする1,接续:名词+にする2,接续:疑问词+にする3,(A)は(B)にする。(2)復習:(1)复习句子(2)ために & ように(3)そう(4)にする3、…...

在rocky linux 9.5上在线安装 docker
前面是指南,后面是日志 sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo sudo dnf install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y docker version sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl status docker …...

汽车生产虚拟实训中的技能提升与生产优化
在制造业蓬勃发展的大背景下,虚拟教学实训宛如一颗璀璨的新星,正发挥着不可或缺且日益凸显的关键作用,源源不断地为企业的稳健前行与创新发展注入磅礴强大的动力。就以汽车制造企业这一极具代表性的行业主体为例,汽车生产线上各类…...

linux 错误码总结
1,错误码的概念与作用 在Linux系统中,错误码是系统调用或库函数在执行失败时返回的特定数值,用于指示具体的错误类型。这些错误码通过全局变量errno来存储和传递,errno由操作系统维护,保存最近一次发生的错误信息。值得注意的是,errno的值在每次系统调用或函数调用失败时…...

AI,如何重构理解、匹配与决策?
AI 时代,我们如何理解消费? 作者|王彬 封面|Unplash 人们通过信息理解世界。 曾几何时,PC 与移动互联网重塑了人们的购物路径:信息变得唾手可得,商品决策变得高度依赖内容。 但 AI 时代的来…...
混合(Blending))
C++.OpenGL (20/64)混合(Blending)
混合(Blending) 透明效果核心原理 #mermaid-svg-SWG0UzVfJms7Sm3e {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg-SWG0UzVfJms7Sm3e .error-icon{fill:#552222;}#mermaid-svg-SWG0UzVfJms7Sm3e .error-text{fill…...

【Linux】Linux 系统默认的目录及作用说明
博主介绍:✌全网粉丝23W,CSDN博客专家、Java领域优质创作者,掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域✌ 技术范围:SpringBoot、SpringCloud、Vue、SSM、HTML、Nodejs、Python、MySQL、PostgreSQL、大数据、物…...

NPOI操作EXCEL文件 ——CAD C# 二次开发
缺点:dll.版本容易加载错误。CAD加载插件时,没有加载所有类库。插件运行过程中用到某个类库,会从CAD的安装目录找,找不到就报错了。 【方案2】让CAD在加载过程中把类库加载到内存 【方案3】是发现缺少了哪个库,就用插件程序加载进…...

在 Spring Boot 项目里,MYSQL中json类型字段使用
前言: 因为程序特殊需求导致,需要mysql数据库存储json类型数据,因此记录一下使用流程 1.java实体中新增字段 private List<User> users 2.增加mybatis-plus注解 TableField(typeHandler FastjsonTypeHandler.class) private Lis…...

在golang中如何将已安装的依赖降级处理,比如:将 go-ansible/v2@v2.2.0 更换为 go-ansible/@v1.1.7
在 Go 项目中降级 go-ansible 从 v2.2.0 到 v1.1.7 具体步骤: 第一步: 修改 go.mod 文件 // 原 v2 版本声明 require github.com/apenella/go-ansible/v2 v2.2.0 替换为: // 改为 v…...
