leetcode 1 ~ 100
文章目录
- 1. 两数之和(用哈希表减少查找的时间复杂度)
- 2. 两数相加(高精度加法)
- 3.无重复字符的最长子串:(模板:经典的滑动窗口算法)
- 5. 最长回文子串(枚举)
- 6. Z 自形变换(找规律)
- 7.整数反转
- 8. 字符串转换整数(atoi)
- 9. 回文数
- 11.盛水最多的容器(贪心(基于双指针来实现))
- 12. 整数转罗马数字
- 13. 罗马数字转整数
- 14. 最长公共前缀
- 15. 三数之和(双指针 + 去重)
- 16. 最接近的三数之和(双指针算法)
- 17. 电话号码的字母组合(标准 DFS)
- 18. 四数之和(双指针算法)
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(前后双指针寻找结点 + dummy 避免特判)
- 20. 有效的括号(栈的简单应用)
- 21. 合并两个有序链表(模拟归并排序中的二路归并操作)
- 22. 括号生成(DFS)
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点(链表结点交换算法)
- 26. 删除有序数组中的重复项(经典双指针算法)
- 27. 移除元素(简单的双指针算法)
- 31. 下一个排列:
- 32. 最长有效括号
- 33.搜索旋转排序数组:
- 34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置:
- 35.搜索插入位置:
- 36.有效的数独:
- 37.解数独:
- 38.外观数列:
- 39.组合总和:
- 40.组合总和:
- 41.缺失的第一个正数:
- 42.接雨水:
- 43.字符串相乘:
- 44.通配符匹配:
- 45.跳跃游戏 II:
- 46.全排列:
- 47.全排列 II:
- 48.旋转图像:
- 49.字母异位词分组:
- 50.Pow(x, n):
- 51. N 皇后(DFS)
- 52. N 皇后 II(DFS,和 51 题完全一样,只是不需要记录方案是什么)
- 53. 最大子数组和(动态规划)
- 54. 螺旋矩阵
- 55.跳跃游戏:
- 56. 区间合并(模板:区间合并)
- 57. 插入区间
- 58. 最后一个单词的长度(模拟题)
- 59. 螺旋矩阵 II(方向数组的简单应用)
1. 两数之和(用哈希表减少查找的时间复杂度)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {unordered_map<int, int> dict; // val : indexfor (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if (dict.count(target - nums[i]))return {dict[target - nums[i]], i};elsedict[nums[i]] = i;}return {};}
};(注:本题也可以用双指针算法。)
2. 两数相加(高精度加法)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode* p = dummy;int t = 0;while (l1 || l2 || t){if (l1) {t += l1->val;l1 = l1->next;}if (l2) {t += l2->val;l2 = l2->next;}p->next = new ListNode(t % 10);p = p->next;t /= 10;}return dummy->next;}
};3.无重复字符的最长子串:(模板:经典的滑动窗口算法)
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {int res = 0;unordered_map<char, int> ht; // ht: hashtablefor (int l = 0, r = 0; r < s.size(); r++){ht[s[r]]++;while (ht[s[r]] > 1){ht[s[l]]--;l++;}res = max(res, r - l + 1);}return res;}
};
5. 最长回文子串(枚举)
class Solution {
public:string longestPalindrome(string s) {string res = "";for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {// 看回文串的长度是否是奇数int l = i - 1, r = i + 1;while (l >= 0 && r < s.size() && s[l] == s[r]) l--, r++;if (res.size() < r - (l + 1)) res = s.substr(l + 1, r - (l + 1));// 看回文串的长度是否是偶数l = i, r = i + 1;while (l >= 0 && r < s.size() && s[l] == s[r]) l--, r++;if (res.size() < r - (l + 1)) res = s.substr(l + 1, r - (l + 1));}return res;}
};6. Z 自形变换(找规律)
class Solution {
public:string convert(string s, int numRows) {if (numRows == 1) return s; // numRows = 1会导致base为0,需要特判string res = "";int base = 2 * numRows - 2;for (int k = 0; k < numRows; k++)for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)if ((i - k) % base == 0 || (i + k) % base == 0)res += s[i];return res;}
};// 每一趟会有 numRows + (nuRows - 2) = 2 * numRows - 2 = base 个数
// 故最终第0行应该是满足 (i + 0) % base == 0的数
// 第1行是 (i + 1) % base == 0的数
// 第 k 行是 (i + k) % base == 0的数
// k的范围是从 0 到 numRows - 17.整数反转
class Solution {
public:int reverse(int x) {int res = 0;bool is_minus = (x < 0);while (x){if (is_minus && res < (INT_MIN - x % 10) / 10) return 0;if (!is_minus && res > (INT_MAX - x % 10) / 10) return 0;res = res * 10 + x % 10;x /= 10;}return res;}
};
8. 字符串转换整数(atoi)
class Solution {
public:int myAtoi(string s) {int res = 0;bool is_minus = false;for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){if (s[i] == ' ') continue;else if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-'){is_minus = (s[i] == '-');if (i + 1 < s.size() && !isdigit(s[i + 1])) return res;else continue;}else if (isdigit(s[i])){while (i < s.size() && isdigit(s[i])){int t = s[i] - '0';if (is_minus && res > (INT_MAX - t) / 10) return INT_MIN;if (!is_minus && res > (INT_MAX - t) / 10) return INT_MAX;res = res * 10 + t;i++;}if (is_minus) return -res;else return res;}else return res;}return res;}
};9. 回文数
class Solution {
public:bool isPalindrome(int x) {if (x < 0) return false;if (!x) return true;long long res = 0; // 翻转后有可能会溢出int tmp = x;while (tmp){res = res * 10 + tmp % 10;tmp /= 10;}return res == x;}
};11.盛水最多的容器(贪心(基于双指针来实现))
class Solution {
public:int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {int res = 0;int i = 0, j = height.size() - 1;while (i < j){res = max(res, min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i));if (height[i] < height[j]) i++;else j--;}return res;}
};12. 整数转罗马数字
class Solution {
public:string intToRoman(int num) {unordered_map<int, string> dict{{1, "I"}, {4, "IV"}, {5, "V"}, {9, "IX"}, {10, "X"}, {40, "XL"}, {50, "L"}, {90, "XC"}, {100, "C"}, {400, "CD"}, {500, "D"}, {900, "CM"}, {1000, "M"}};vector<int> base{1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1};string res = "";for (auto b : base){if (!num) break;int cnt = num / b;num %= b;if (cnt){for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)res += dict[b];}}return res;}
};13. 罗马数字转整数
class Solution {
public:int romanToInt(string s) {// 从右往左遍历,定义一个哈希表表示大小关系,正常情况下右边小于等于左边;// 如果右边大于左边,说明出现了特殊规则// unordered_map<char, int> pri{{'I', 1}, {'V', 2}, {'X', 3}, {'L', 4}, \// {'C', 5}, {'D', 6}, {'M', 7}}; /* 后记:val表的功能可以替代pri,故可以不用专门定义pri */unordered_map<char, int> val{{'I', 1}, {'V', 5}, {'X', 10}, {'L', 50}, \{'C', 100}, {'D', 500}, {'M', 1000}};int res = 0;for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0;){if (i && val[s[i]] > val[s[i - 1]]) // e.g. IV{res += val[s[i]] - val[s[i - 1]];i -= 2;}else{res += val[s[i]];i--;}}return res;}
};14. 最长公共前缀
class Solution {
public:string longestCommonPrefix(vector<string>& strs) {string cp = strs[0];for (auto& s : strs)for (int i = 0; i < cp.size(); i++)if (cp[i] != s[i]) {cp.erase(cp.begin() + i, cp.end());break; }return cp;}
};15. 三数之和(双指针 + 去重)
本题双指针算法的判定依据:
对于每一个固定的 i,当 j 增大时,k 必减小。
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // sort是双指针算法和去重的前提vector<vector<int>> res;for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++){if (i && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue; // 对i去重for (int j = i + 1, k = nums.size() - 1; j < nums.size() - 1; j++){if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue; // 对j去重while (j < k && nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] > 0) k--;if (j == k) break; // 注意:两指针不能重合!if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0)res.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]});}}return res;}
};16. 最接近的三数之和(双指针算法)
class Solution {
public:int threeSumClosest(vector<int>& nums, int target) {sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());pair<int, int> res(INT_MAX, INT_MAX);for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 2; i++){if (i && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;for (int j = i + 1, k = nums.size() - 1; j < k; j++){if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue;while (j < k - 1 && nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k - 1] >= target) k--;int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k];res = min(res, make_pair(abs(sum - target), sum));if (j < k - 1){sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k - 1];res = min(res, make_pair(target - sum, sum));}}}return res.second;}
};17. 电话号码的字母组合(标准 DFS)
class Solution {
public:string s;unordered_map<char, string> dict{{'2', "abc"},{'3', "def"},{'4', "ghi"},{'5', "jkl"},{'6', "mno"},{'7', "pqrs"},{'8', "tuv"},{'9', "wxyz"}};vector<string> res;vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {if (digits.empty()) return {};dfs(digits, 0);return res;}void dfs(string digits, int idx){if (idx == digits.size()){res.push_back(s);return;}for (char c : dict[digits[idx]]){s += c;dfs(digits, idx + 1);s.pop_back();}}
};18. 四数之和(双指针算法)
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {vector<vector<int>> res;if (nums.size() < 4) return res;sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 3; i++){if (i && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.size() - 2; j++){if (j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) continue;for (int k = j + 1, m = nums.size() - 1; k < m; k++){if (k > j + 1 && nums[k] == nums[k - 1]) continue;while (k < m - 1 && (long)nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] + nums[m - 1] >= target) m--; // 注意:不加long会有数据溢出问题,下同if ((long)nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] + nums[m] == target)res.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[k], nums[m]});}}}return res;}
};19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点(前后双指针寻找结点 + dummy 避免特判)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);ListNode* left = dummy;ListNode* right = head;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)right = right->next;while (right != nullptr){left = left->next;right = right->next;}left->next = left->next->next;ListNode* res = dummy->next;delete dummy; // 删除哑节点,释放内存return res;}
};20. 有效的括号(栈的简单应用)
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> stk;for (auto c : s){if (c == '(' || c == '{' || c == '[')stk.push(c);else{// if (stk.empty() || (c == ')' && stk.top() != '(') || (c == '}' && stk.top() != '{') || (c == ']' && stk.top() != '['))if (stk.empty() || abs(stk.top() - c) > 2) // (){}[] = 40 41 123 125 91 93return false;else stk.pop();}}return stk.empty();}
};21. 合并两个有序链表(模拟归并排序中的二路归并操作)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode* p = dummy;ListNode* p1 = list1;ListNode* p2 = list2;while (p1 && p2){if (p1->val <= p2->val){p->next = p1;p1 = p1->next;}else{p->next = p2;p2 = p2->next;}p = p->next;}if (p1) p->next = p1;if (p2) p->next = p2;return dummy->next;}
};22. 括号生成(DFS)
class Solution {
public:string s;vector<string> res;vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {// 左括号用了i个,右括号用了j个,当i == j == n时,即可dfs(n, 0, 0);return res;}void dfs(int n, int left, int right){if (left == n && right == n){res.push_back(s);return;}// 左分支的条件如果满足,就转向左分支if (left < n){s += '(';dfs(n, left + 1, right); // 在左分支里继续进行递归s.pop_back(); // 和回溯}//如果右分支的条件满足,就转向右分支if (right < left){s += ')';dfs(n, left, right + 1); // 在右分支里继续进行递归s.pop_back(); // 和回溯}}
};24. 两两交换链表中的节点(链表结点交换算法)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);ListNode* p = dummy;while (p->next && p->next->next){ListNode* left = p->next; // 必须要先用两个临时结点把p->nextListNode* right = p->next->next; // 和p->next->next保存起来p->next = right;left->next = right->next;right->next = left;p = left; // <=> p = p->next->next;}return dummy->next;}
};26. 删除有序数组中的重复项(经典双指针算法)
class Solution {
public:int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {int k = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if (!i || nums[i] != nums[i - 1])nums[k++] = nums[i];}return k;}
};27. 移除元素(简单的双指针算法)
第一种实现方式:两个指针都从左往右走
class Solution {
public:int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {int k = 0; // k是新数组的长度,初始时为0for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)if (nums[i] != val)nums[k++] = nums[i];return k;}
};第二种实现方式:两个指针从两头出发往中间走
class Solution {
public:int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {int n = nums.size();int i = -1, j = n;while (i < j){do i++; while (i < j && nums[i] != val);do j--; while (i < j && nums[j] == val);if (i < j) swap(nums[i], nums[j]);}return i;}
};
// 注:这种实现方式可以应对以下两种边界情况:
// (1)nums为空;
// (2)nums仅含1个元素
31. 下一个排列:
class Solution {
public:void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();// 从后往前找到第一对升序的元素int i = n - 1;while (i >= 1 && nums[i - 1] >= nums[i]) i--;if (i == 0) // 如果不存在升序元素对,reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 直接将降序翻转为升序else // 如果存在升序元素对,{int j = i; i--; // 此时nums[i - 1], nums[i]即为从后往前第一对升序元素// 再次从后往前,寻找第一个大于nums[i]的元素int k = n - 1;while (k > i && nums[i] >= nums[k]) k--;// 找到后将nums[i]和nums[k]交换swap(nums[i], nums[k]);// 此时[j, end)必降序,将其翻转为升序即可reverse(nums.begin() + j, nums.end());}}
};32. 最长有效括号
class Solution {
public:int longestValidParentheses(string s) {int res = 0;stack<int> stk;for (int i = 0, start = -1; i < s.size(); i++){if (s[i] == '(') stk.push(i);else // 来右括号{if (!stk.empty()) // 来右括号且栈不空,说明栈顶有左括号{stk.pop(); // 将左括号弹出,if (!stk.empty()) // 如果弹出后栈顶仍有左括号,res = max(res, i - stk.top()); // 则左括号的下一个位置到i的长度即为当前i对应的最大有效括号长度else res = max(res, i - start); // 如果将栈顶左括号弹出后栈空,则从start + 1到i皆为有效长度}else // 来右括号且栈空{start = i;}}}return res;}
};33.搜索旋转排序数组:
class Solution {
public:int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;while (l <= r){int mid = l + r >> 1;if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;// 我们要做的就是确定每次的mid到底是在左半段还是右半段中if (nums[l] <= nums[mid]) // 说明mid在左半段,则左半段可以二分{if (nums[l] <= target && target < nums[mid])r = mid - 1;elsel = mid + 1;}else // 说明mid在右半段,则右半段可以二分{if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[r])l = mid + 1;elser = mid - 1;}}return -1;}
};34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置:
class Solution {
public:vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {vector<int> res;if (nums.empty()) return {-1, -1};int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;while (l < r){int mid = l + r >> 1;if (nums[mid] >= target) r = mid;else l = mid + 1;}if (nums[l] != target) return {-1, -1};else{res.push_back(l);int l = 0, r = nums.size() - 1;while (l < r){int mid = l + r + 1 >> 1;if (nums[mid] <= target) l = mid;else r = mid - 1;}res.push_back(l);}return res;}
};35.搜索插入位置:
// 找到从前往后第一个大于等于target的位置
class Solution {
public:int searchInsert(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int l = 0, r = nums.size(); // 注意:此处不再是nums.size() - 1while (l < r){int mid = l + r >> 1;if (nums[mid] >= target) r = mid;else l = mid + 1;}return l;}
};36.有效的数独:
class Solution {
public:bool row[9][9], col[9][9], block[3][3][9];bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {memset(row, 0, sizeof row);memset(col, 0, sizeof col);memset(block, 0, sizeof block);for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++)if (board[i][j] != '.'){int t = board[i][j] - '1';if (row[i][t] || col[j][t] || block[i / 3][j / 3][t])return false;elserow[i][t] = col[j][t] = block[i / 3][j / 3][t] = true;}return true;}
};37.解数独:
class Solution {
public:bool row[9][9], col[9][9], block[3][3][9];void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {memset(row, 0, sizeof row);memset(col, 0, sizeof col);memset(block, 0, sizeof block);int n = board.size(), m = board[0].size();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)if (board[i][j] != '.'){int t = board[i][j] - '1';row[i][t] = col[j][t] = block[i / 3][j / 3][t] = true;}dfs(board, 0, 0);}bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int x, int y){int n = board.size(), m = board[0].size();if (y == m) { y = 0; x++; }if (x == n) return true;if (board[x][y] != '.') return dfs(board, x, y + 1);for (int num = 0; num < 9; num++){if (!row[x][num] && !col[y][num] && !block[x / 3][y / 3][num]){board[x][y] = num + '1';row[x][num] = col[y][num] = block[x / 3][y / 3][num] = true;if (dfs(board, x, y + 1)) return true;board[x][y] = '.';row[x][num] = col[y][num] = block[x / 3][y / 3][num] = false;}}return false;}
};38.外观数列:
class Solution {
public:string countAndSay(int n) {string s = "1";for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){string tmp = "";for (int j = 0; j < s.size();){int k = j + 1;while (k < s.size() && s[j] == s[k]) k++;tmp += to_string(k - j) + s[j];j = k;}s = tmp;}return s;}
};39.组合总和:
- 第一种 DFS:逐数字枚举
class Solution {
public:vector<int> path;vector<vector<int>> res;vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {dfs(candidates, 0, target);return res; }void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int u, int target){if (target == 0){res.push_back(path);return;} // 注意:此if与后面if的顺序不能颠倒!if (u == candidates.size()) return;// skip current positiondfs(candidates, u + 1, target);// choose current positionif (target - candidates[u] >= 0){path.push_back(candidates[u]);dfs(candidates, u, target - candidates[u]);path.pop_back();}}
};- 第二种 DFS:按第 i 个数选多少个来搜索
class Solution {
public:vector<int> path;vector<vector<int>> res;vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {dfs(candidates, 0, target);return res; }void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int u, int target){if (target == 0){res.push_back(path);return;} // 注意:此if与后面if的顺序不能颠倒!if (u == candidates.size()) return;for (int i = 0; i * candidates[u] <= target; i++){dfs(candidates, u + 1, target - i * candidates[u]);path.push_back(candidates[u]);}for (int i = 0; i * candidates[u] <= target; i++)path.pop_back();}
};40.组合总和:
class Solution {
public:vector<int> path;vector<vector<int>> res;vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());dfs(candidates, 0, target);return res; }void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int idx, int target){if (target == 0){res.push_back(path);return;}if (idx == candidates.size()) return;int prev = -1;for (int i = idx; i < candidates.size(); i++){if (prev != candidates[i] && candidates[i] <= target){prev = candidates[i];path.push_back(candidates[i]);dfs(candidates, i + 1, target - candidates[i]);path.pop_back();}}}
};41.缺失的第一个正数:
class Solution {
public:int firstMissingPositive(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i])swap(nums[nums[i] - 1], nums[i]);}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (nums[i] != i + 1)return i + 1;}return n + 1;}
};42.接雨水:
class Solution {
public:int trap(vector<int>& height) {int ans = 0;int l = 0, r = height.size() - 1;int lmax = 0, rmax = 0;while (l < r){lmax = max(lmax, height[l]);rmax = max(rmax, height[r]);if (lmax <= rmax){ans += lmax - height[l];l++;}else{ans += rmax - height[r];r--;}}return ans;}
};43.字符串相乘:
class Solution {
public:string multiply(string num1, string num2) {int n = num1.size(), m = num2.size();vector<int> A, B;for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) A.push_back(num1[i] - '0');for (int i = m - 1; i >= 0; i--) B.push_back(num2[i] - '0');vector<int> C(n + m);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)C[i + j] += A[i] * B[j];// 集中处理进位int t = 0;for (int i = 0; i < C.size(); i++){t += C[i];C[i] = t % 10;t /= 10;}while (C.size() > 1 && C.back() == 0) C.pop_back();string res;for (int i = C.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) res += C[i] + '0';return res;}
};44.通配符匹配:
class Solution {
public:bool isMatch(string s, string p) {int n = s.size(), m = p.size();s = ' ' + s, p = ' ' + p;vector<vector<bool>> f(n + 1, vector<bool>(m + 1));f[0][0] = true;for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) // i必须从0开始,因为f[0][j]是有意义的for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) // j可以从1开始,因为f[i][0]必为falseif (p[j] == '*')f[i][j] = f[i][j - 1] || (i && f[i - 1][j]);elsef[i][j] = (s[i] == p[j] || p[j] == '?') && (i && f[i - 1][j - 1]);return f[n][m];}
};45.跳跃游戏 II:
class Solution {
public:int jump(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();vector<int> f(n);for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < n; i++){while (j + nums[j] < i) j++;f[i] = f[j] + 1;}return f[n - 1];}
};46.全排列:
class Solution {
public:vector<int> path;vector<vector<int>> res;bool st[10];vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums) {dfs(nums, 0);return res;}void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int u){if (u == nums.size()){res.push_back(path);return;}for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if (!st[i]){path.push_back(nums[i]);st[i] = true;dfs(nums, u + 1);path.pop_back();st[i] = false;}}}
};
47.全排列 II:
class Solution {
public:vector<int> path;vector<vector<int>> res;bool st[10];vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int>& nums) {vector<int> tmp = nums;sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());dfs(tmp, 0);return res;}void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int u){if (u == nums.size()){res.push_back(path);return;}int prev = -11;for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if (prev != nums[i] && !st[i]){prev = nums[i];path.push_back(nums[i]);st[i] = true;dfs(nums, u + 1);path.pop_back();st[i] = false;}}}
};
48.旋转图像:
class Solution {
public:void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {/* 两次对称即可:先沿反对角线对称,再沿中轴左右对称*/int n = matrix.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++)swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[i][n - 1 - j]);}
};49.字母异位词分组:
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {unordered_map<string, vector<string>> map;for (auto& str : strs){string tmp = str;sort(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());map[tmp].push_back(str);}vector<vector<string>> res;for (auto& item : map) res.push_back(item.second);return res;}
};50.Pow(x, n):
class Solution {
public:double myPow(double x, int n) {typedef long long LL;bool is_minus = n < 0;double res = 1;for (LL k = abs(LL(n)); k; k >>= 1){if (k & 1) res *= x;x *= x;}if (is_minus) res = 1 / res;return res;}
};51. N 皇后(DFS)
class Solution {
public:bool col[10], dg[20], udg[20];vector<vector<string>> res;vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {// 初始化棋盘vector<string> g;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)g.push_back(string(n, '.'));dfs(0, n, g);return res;}void dfs(int u, int n, vector<string>& g){if (u == n){res.push_back(g);return;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (!col[i] && !dg[u - i + n] && !udg[u + i]){g[u][i] = 'Q';col[i] = dg[u - i + n] = udg[u + i] = true;dfs(u + 1, n, g);g[u][i] = '.';col[i] = dg[u - i + n] = udg[u + i] = false;}}}
};52. N 皇后 II(DFS,和 51 题完全一样,只是不需要记录方案是什么)
class Solution {
public:bool col[10], dg[20], udg[20];int res = 0;int totalNQueens(int n) {dfs(0, n);return res;}void dfs(int u, int n){if (u == n){res++;return;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (!col[i] && !dg[u - i + n] && !udg[u + i]){col[i] = dg[u - i + n] = udg[u + i] = true;dfs(u + 1, n);col[i] = dg[u - i + n] = udg[u + i] = false;}}}
};53. 最大子数组和(动态规划)
从动态规划的角度去理解:(更推荐)
class Solution {
public:int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {int res = INT_MIN;for (int i = 0, last = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){last = nums[i] + max(last, 0);res = max(res, last);}return res;}
};// 动态规划:
// f[i] 表示所有以nums[i]结尾的连续子数组的最大和
// f[i] = max(nums[i], f[i - 1] + nums[i]) = nums[i] + max(f[i - 1], 0);
// 由于只用到了两个状态,因此可以用一个变量保存f[i - 1],这样空间复杂度可以优化至O(1)从贪心的角度去理解:
class Solution {
public:int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {int res = -1e5, sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){sum += nums[i];if (sum < nums[i]) sum = nums[i];res = max(res, sum);}return res;}
};
// 贪心:
// 从左到右扫描,54. 螺旋矩阵
方法一:(迭代)利用方向数组(推荐)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {vector<int> res;int dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();vector<vector<bool>> st(m, vector<bool>(n));for (int i = 0, x = 0, y = 0, d = 0; i < m * n; i++){// 先判断上一步有没有走对,如果没有走对,就纠正上一步并让其走对if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || st[x][y]){x -= dx[d], y -= dy[d];d = (d + 1) % 4;x += dx[d], y += dy[d];}// 如果走对的话就记录res.push_back(matrix[x][y]);st[x][y] = true;x += dx[d], y += dy[d]; // 并继续往前走}return res;}
};方法二:(DFS)模拟
class Solution {
public:vector<int> res;vector<int> spiralOrder(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size();dfs(matrix, 0, 0, m - 1, n - 1); // 传入的是左上角和右下角的坐标(x1, y1)和(x2, y2)return res;}void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2){if (x1 > x2 || y1 > y2) return;int i = x1, j = y1;while (j <= y2){res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);j++;}j--,i++;while (i <= x2){res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);i++;}i--, j--;while (i > x1 && j >= y1) // i > x1的目的是防止出现回退,如第2个测试用例{res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);j--;}j++, i--;while (j < y2 && i > x1) // j < y2的目的也是防止出现回退,例如[[7], [9], [6]]{res.push_back(matrix[i][j]);i--;}dfs(matrix, x1 + 1, y1 + 1, x2 - 1, y2 - 1);}
};55.跳跃游戏:
class Solution {
public:bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if (j < i) return false;j = max(j, i + nums[i]);}return true;}
};56. 区间合并(模板:区间合并)
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {vector<vector<int>> res;sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end());int st = -1, ed = -1;for (auto seg : intervals){if (ed < seg[0]){if (st != -1) res.push_back({st, ed});st = seg[0], ed = seg[1];}else ed = max(ed, seg[1]);}if (st != -1) res.push_back({st, ed});return res;}
};57. 插入区间
方法一:先用二分查找找到插入位置,将新区间插入,再调用标准的区间合并算法
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> insert(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& newInterval) {// 先二分找到插入位置int l = 0, r = intervals.size();while (l < r){int mid = l + r >> 1;if (intervals[mid][0] >= newInterval[0]) r = mid;else l = mid + 1;}intervals.insert(intervals.begin() + l, newInterval);// 调用区间合并模板int st = -1, ed = -1;vector<vector<int>> res;for (int i = 0; i < intervals.size(); i++){if (ed < intervals[i][0]){if (st != -1) res.push_back({st, ed});st = intervals[i][0], ed = intervals[i][1];}else ed = max(ed, intervals[i][1]);}if (st != -1) res.push_back({st, ed});return res;}
};方法二:(Y总做法)模拟
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> insert(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& newInterval) {vector<vector<int>> res;// 首先寻找左侧没有交叠的区间int k = 0;while (k < intervals.size() && intervals[k][1] < newInterval[0]){res.push_back(intervals[k]);k++;}// 对中间有交叠的区间进行合并if (k < intervals.size()) // 这一条件可以处理intervals为空的情况{newInterval[0] = min(intervals[k][0], newInterval[0]);while (k < intervals.size() && intervals[k][0] <= newInterval[1]){newInterval[1] = max(intervals[k][1], newInterval[1]);k++;}}res.push_back(newInterval);// 右侧没有交叠的区间也照抄while (k < intervals.size()){res.push_back(intervals[k]);k++;}return res;}
};58. 最后一个单词的长度(模拟题)
class Solution {
public:int lengthOfLastWord(string s) {int k = s.size() - 1;while (s[k] == ' ') k--;int j = k;while (j >= 0 && s[j] != ' ') j--;return k - j;}
};59. 螺旋矩阵 II(方向数组的简单应用)
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> generateMatrix(int n) {vector<vector<int>> res(n, vector<int>(n));int dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};for (int i = 1, x = 0, y = 0, d = 0; i <= n * n; i++){if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= n || res[x][y] != 0){x -= dx[d], y -= dy[d];d = (d + 1) % 4;x += dx[d], y += dy[d];}res[x][y] = i;x += dx[d], y += dy[d];}return res;}
};相关文章:

leetcode 1 ~ 100
文章目录 1. 两数之和(用哈希表减少查找的时间复杂度)2. 两数相加(高精度加法)3.无重复字符的最长子串:(模板:经典的滑动窗口算法)5. 最长回文子串(枚举)6. Z…...

分享6个免费下载电子书的网站
着急看书的宝子们看这里! 收藏了一堆电子书网站终于能派上用场了~ 01/Z-Library https://zh.zlibrary-be.se/ 世界上最大的电子图书馆,拥有超千万的书籍和文章资源,99%的书籍资料都能在这里找到。 我给的这个网址现在还能正常打开使用&…...
typescript的入门到吐槽:看了typescript,发现前端真的卷,
typescript TypeScript 是一种由微软开发的自由和开源的编程语言。它是 JavaScript 的一个超集,而且本质上向这个语言添加了可选的静态类型和基于类的面向对象编程。 TypeScript 与 JavaScript 的区别 其实就是对JavaScript的封装,把一个弱类型语言封…...
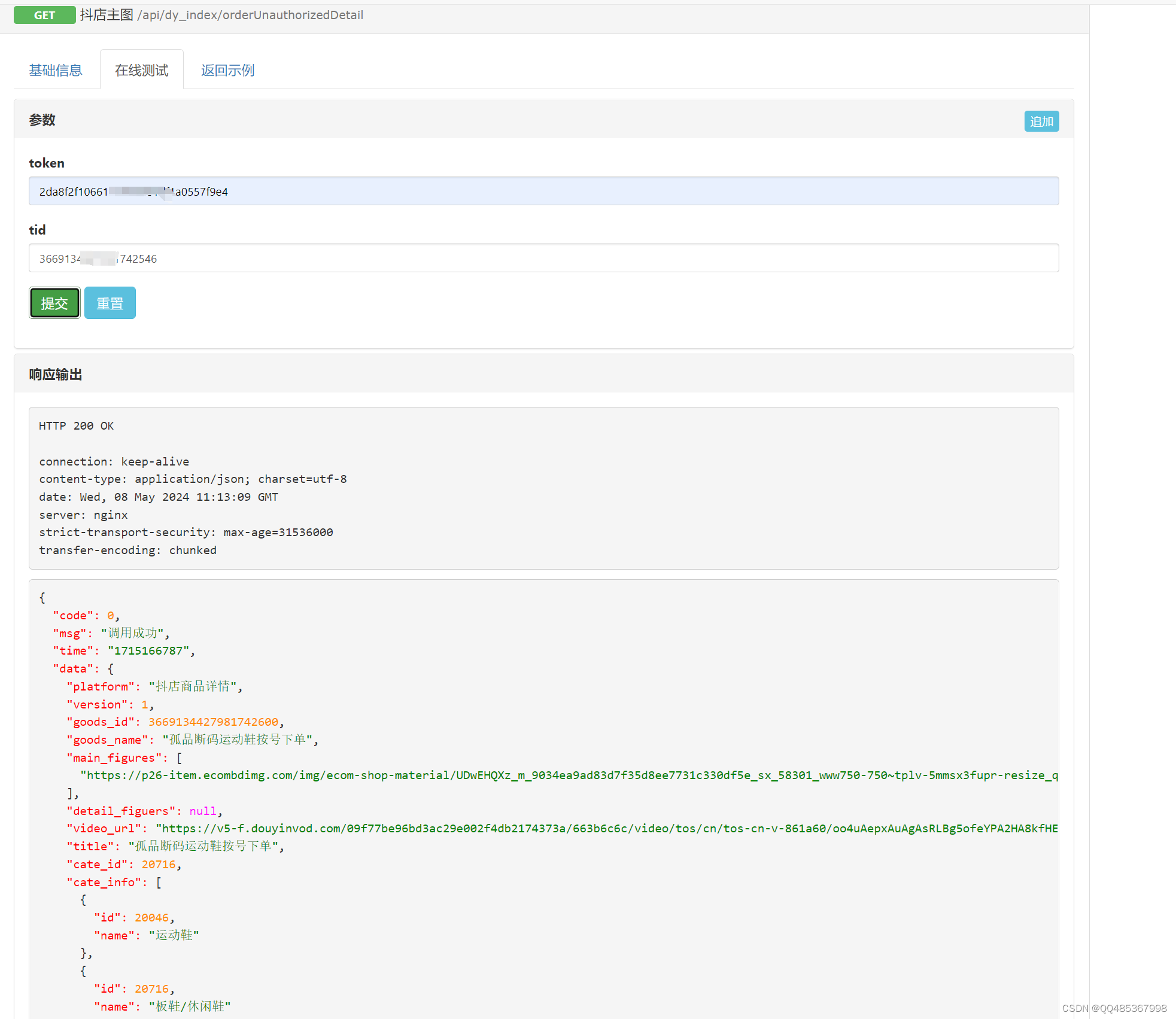
抖店商品详情API接口,商品上架(主图,价格,sku等属性,)item_get-获得抖店商品详情
抖店商品详情API接口,商品上架(主图,价格,sku等属性,)item_get-获得抖店商品详情 {"code": 0,"msg": "调用成功","time": "1715166889","data&quo…...
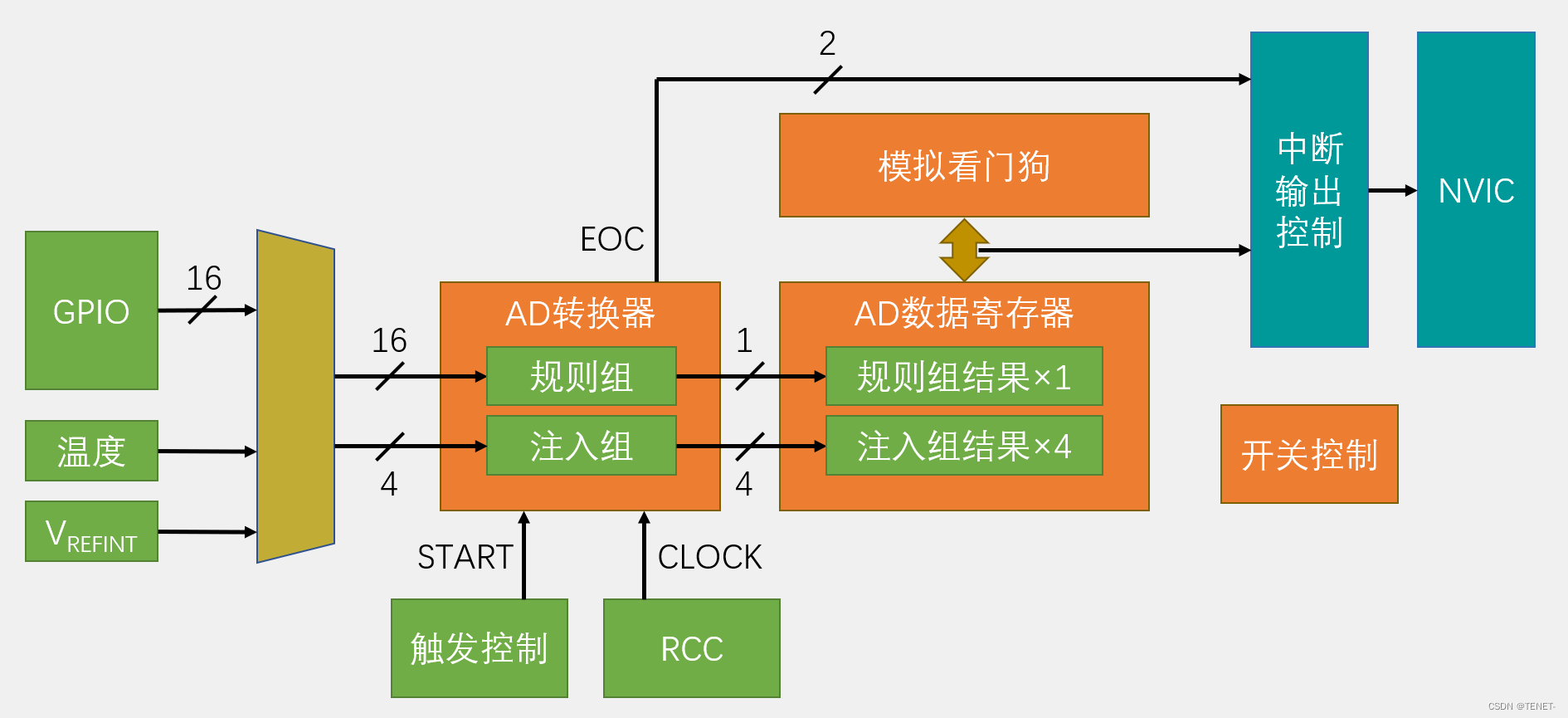
STM32使用ADC单/多通道检测数据
文章目录 1. STM32单片机ADC功能详解 2. AD单通道 2.1 初始化 2.2 ADC.c 2.3 ADC.h 2.4 main.c 3. AD多通道 3.1 ADC.c 3.2 ADC.h 3.3 main.c 3.4 完整工程文件 1. STM32单片机ADC功能详解 STM32单片机ADC功能详解 2. AD单通道 这个代码实现通过ADC功能采集三脚电…...
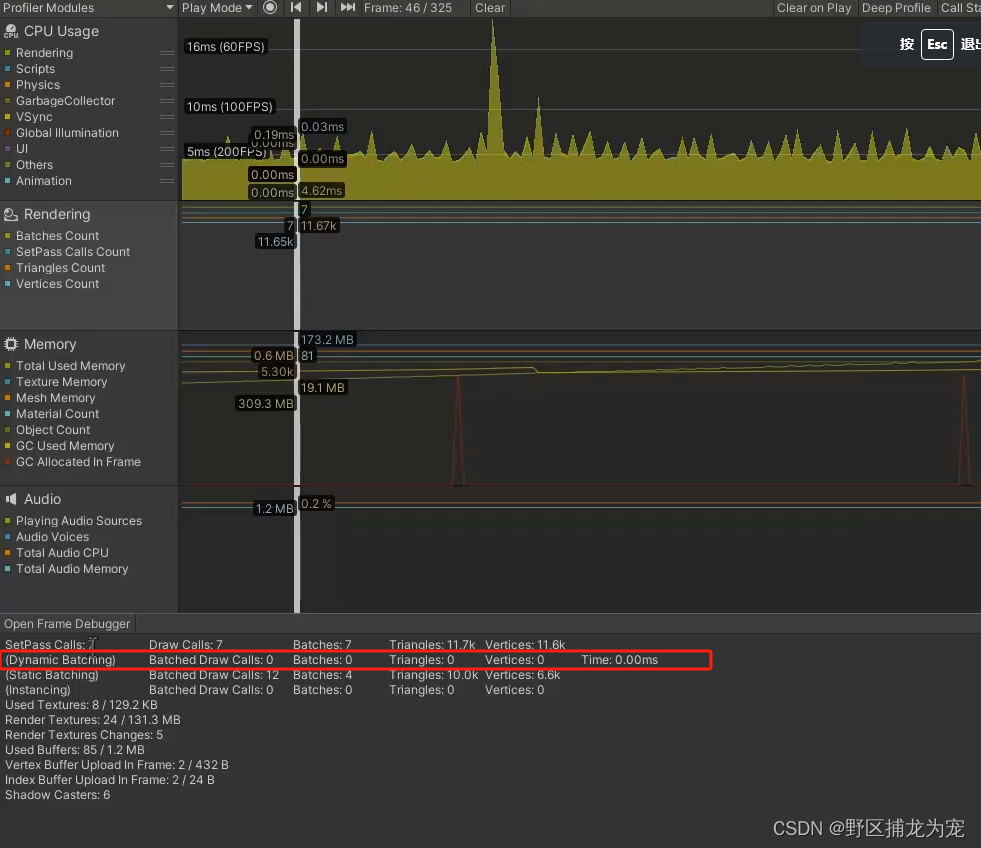
Unity 性能优化之动态批处理(四)
提示:仅供参考,有误之处,麻烦大佬指出,不胜感激! 文章目录 前言一、动态合批是什么?二、使用动态批处理1.打开动态合批2.满足条件 三、检查动态合批是否成功五、动态合批弊端总结 前言 动态批处理是常用优…...

Windows 11 系统安装时如何跳过联网和逃避微软账号登录
问题描述 Windows 11 是从 22H2 版本之后开始强制联网何登录微软账号的。 这就带来两个问题: 1、如果我的电脑没有网络或者网卡驱动有问题,那就无法继续安装系统了。 2、如果我有强怕症,就是不想登录微软账号,害怕个人信息泄露…...
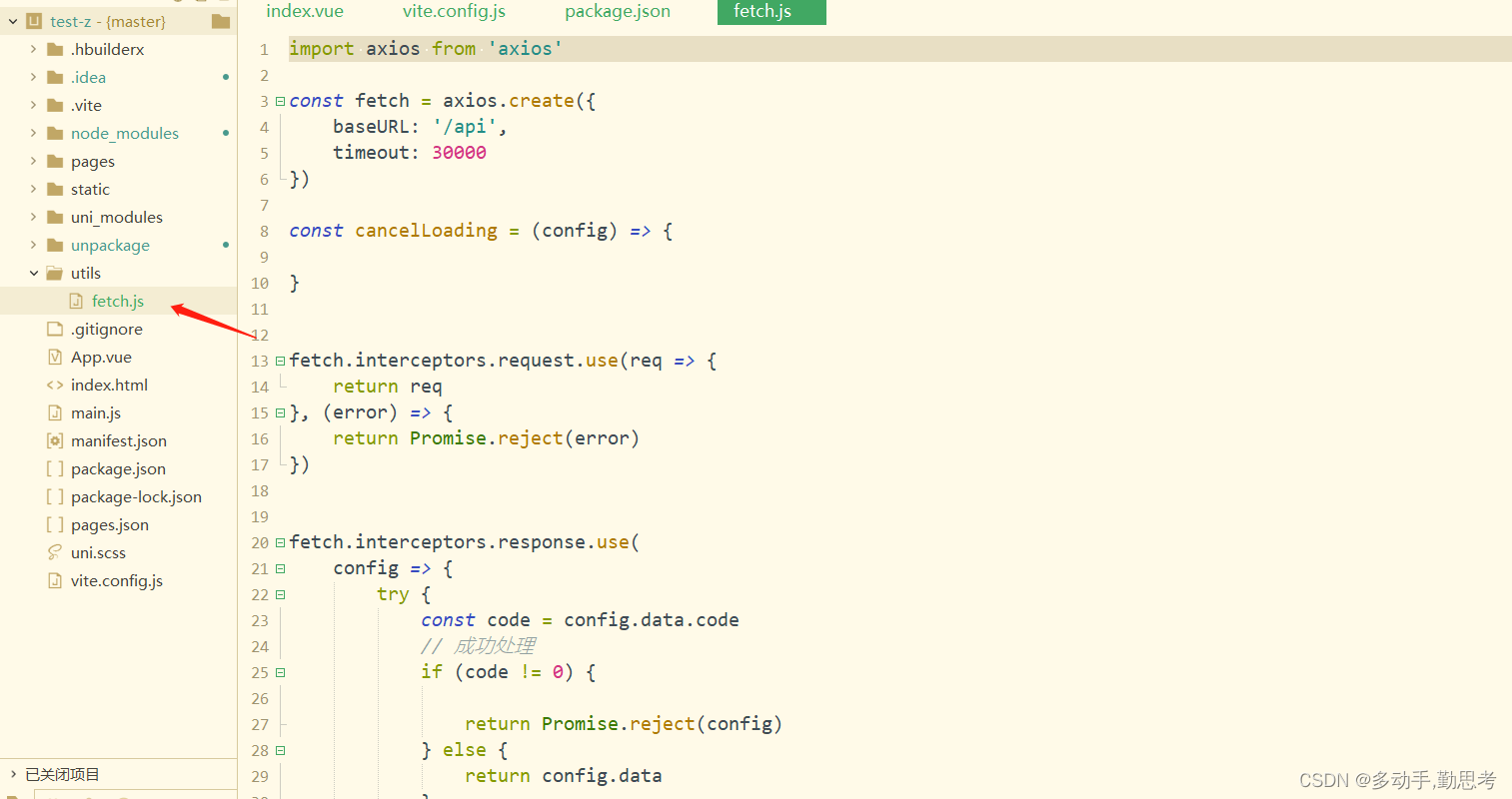
uniapp + vue3 使用axios
场景 uniapp自带的uni.request不太好用,也有可能是自己用axios用的太熟悉了,所以还是用axios趁手点,所以尝试在uniapp中使用axios。 操作 因为uniapp项目没有package.json,所以先在项目根目录下执行 npm init, 执行完毕后直接…...

关于前后端的参数传递
以前端javascript,后端nodejsexpress为例,后端可以从前端发来的request里获取这些属性:header、query、url、params、body,其中params和query是从url中解析获得,不过express已帮我们做好了,就不用我们自己再…...
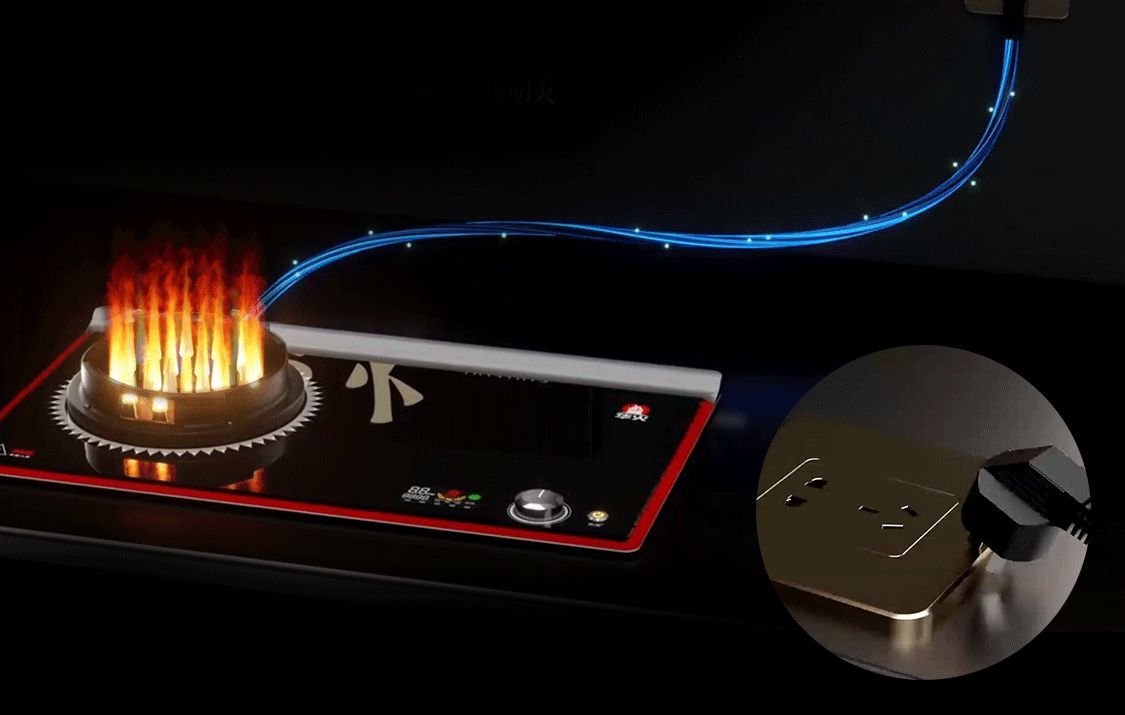

华火电焰灶,科技打造“新”厨房
家里最大的空气污染源其实来自厨房里的燃气灶!——斯坦福大学发表的《科学进展》期刊 厨房在家庭中占有举足轻重的地位,它不仅是一个烹饪美食的场所,更是家人情感交流的重要空间。厨房大致经历了两次变革,分别是以柴火灶为主体的厨…...

普通人副业要趁早,5种靠谱且持久的赚钱副业
中年危机、35岁被裁,这些听起来就让人焦虑的词汇,是否也让你感到不安?别担心,只要你早早开启副业之旅,这些都不是问题。 今天,我要为你介绍的这5种副业,不仅能帮你赚钱,还能让你的能…...
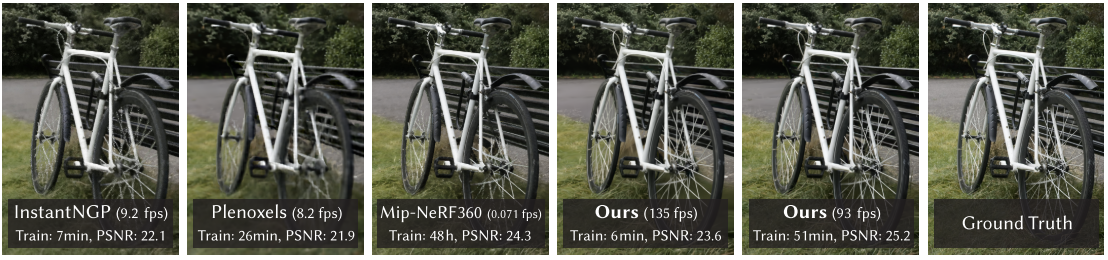
【文献解析】3D高斯抛雪球是个什么玩意
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.04079 项目:3D Gaussian Splatting for Real-Time Radiance Field Rendering 代码:git clone https://github.com/graphdeco-inria/gaussian-splatting --recursive 一、文章概述 1.1问题导向 辐射…...
嘎嘎好用的虚拟键盘第二弹之中文输入法
之前还在为不用研究输入中文而暗自窃喜 这不新需求就来了(新需求不会迟到 它只是在路上飞一会儿) 找到了个博主分享的代码 是好使的 前端-xyq 已经和原作者申请转载了 感谢~~ 原作者地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/linjiangxian/p/16223681.h…...
vue3使用el-autocomplete请求远程数据
服务器端 RestController RequestMapping("/teacher") public class TeacherController {Resourceprivate TeacherService teacherService;GetMapping({"/v1/getTop10TeacherByName/","/v1/getTop10TeacherByName/{name}"})public ResultBean&l…...
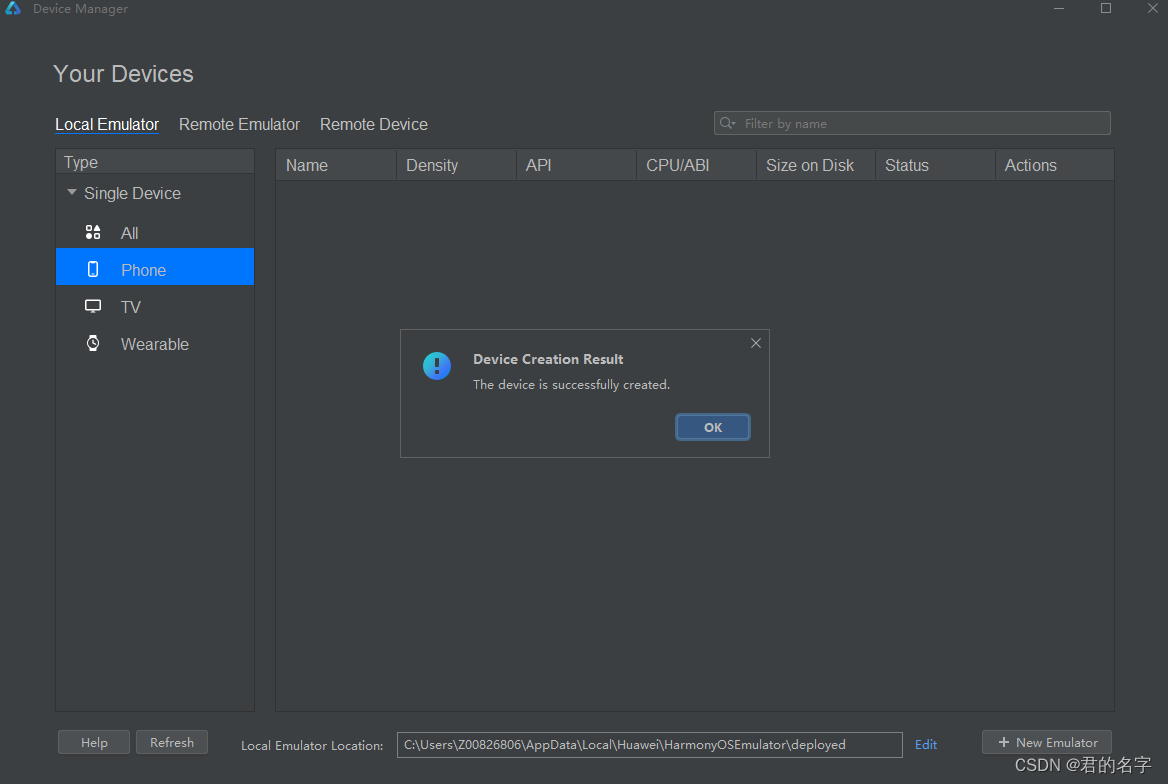
【学习笔记】HarmonyOS 4.0 鸿蒙Next 应用开发--安装开发环境
开发前的准备 首先先到官网去下载Devco Studio 这个开发工具,https://developer.harmonyos.com/cn/develop/deveco-studio/#download 提供了WIndows和Mac的开发环境,我自己是Windows的开发环境。 所以下载之后直接点击exe进行安装即可。 如果之前安装过…...

【PHP】计算两个时间戳之间相差的时间
目录 一、span方法概述 二、输出格式解析 三、方法执行流程 四、应用场景 五、注意事项 六、完整代码示例 时间跨度计算:PHP中的span方法解析 在Web开发中,我们经常需要对时间进行各种计算,尤其是在用户界面中展示时间差或倒计时等功能…...

Out-of-Distribution Detection with Semantic Mismatch under Masking
Out-of-Distribution Detection with Semantic Mismatch under Masking 摘要引言2 相关工作2.1 现有的OOD检测方法2.2基于重构的面向对象检测2.3利用外部OOD数据进行OOD检测2.4 开放集合识别Mismatch under Masking) 摘要 本文提出了一种名为MoodCat的新型分布之外(OOD)检测…...

嫦娥六号近月制动成功,建立月球基地又迈进一步!
嫦娥六号探测器在近月制动的关键时刻,北京航天飞行控制中心内弥漫着紧张而庄重的氛围。每一个航天科技工作者都屏息以待,他们的眼神中充满了期待与自豪。随着一系列精妙绝伦的指令如同琴弦上的音符般流畅地奏响,嫦娥六号探测器在万众瞩目的目…...

上位机图像处理和嵌入式模块部署(树莓派4b使用lua)
【 声明:版权所有,欢迎转载,请勿用于商业用途。 联系信箱:feixiaoxing 163.com】 lua是一个脚本语言,比c语言开发容易,也没有python那么重,整体使用还是非常方便的。一般当成胶水语言进行开发&a…...
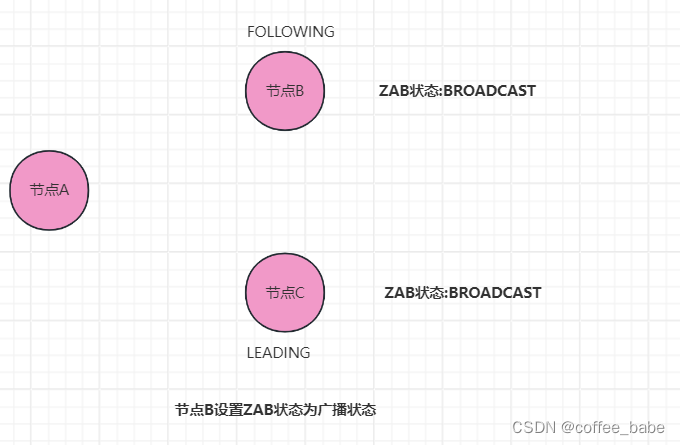
分布式与一致性协议之ZAB协议(五)
ZAB协议 ZAB集群如何从故障中恢复 如果我们想把ZAB集群恢复到正常状态,那么新领导者就必须确立自己的领导关系,成为唯一有效的领导者,然后作为主节点"领导"各备份节点一起处理读写请求 如何确立领导关系 前面提到,选…...
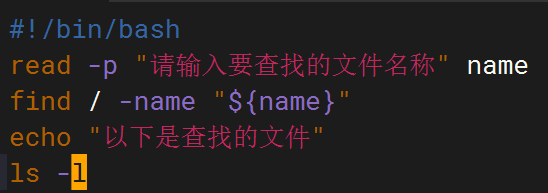
shell脚本--常见案例
1、自动备份文件或目录 2、批量重命名文件 3、查找并删除指定名称的文件: 4、批量删除文件 5、查找并替换文件内容 6、批量创建文件 7、创建文件夹并移动文件 8、在文件夹中查找文件...

macOS多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用
文章目录 问题现象问题原因解决办法 问题现象 macOS启动台(Launchpad)多出来了:Google云端硬盘、YouTube、表格、幻灯片、Gmail、Google文档等应用。 问题原因 很明显,都是Google家的办公全家桶。这些应用并不是通过独立安装的…...

如何为服务器生成TLS证书
TLS(Transport Layer Security)证书是确保网络通信安全的重要手段,它通过加密技术保护传输的数据不被窃听和篡改。在服务器上配置TLS证书,可以使用户通过HTTPS协议安全地访问您的网站。本文将详细介绍如何在服务器上生成一个TLS证…...

【AI学习】三、AI算法中的向量
在人工智能(AI)算法中,向量(Vector)是一种将现实世界中的数据(如图像、文本、音频等)转化为计算机可处理的数值型特征表示的工具。它是连接人类认知(如语义、视觉特征)与…...
)
Java入门学习详细版(一)
大家好,Java 学习是一个系统学习的过程,核心原则就是“理论 实践 坚持”,并且需循序渐进,不可过于着急,本篇文章推出的这份详细入门学习资料将带大家从零基础开始,逐步掌握 Java 的核心概念和编程技能。 …...

聊一聊接口测试的意义有哪些?
目录 一、隔离性 & 早期测试 二、保障系统集成质量 三、验证业务逻辑的核心层 四、提升测试效率与覆盖度 五、系统稳定性的守护者 六、驱动团队协作与契约管理 七、性能与扩展性的前置评估 八、持续交付的核心支撑 接口测试的意义可以从四个维度展开,首…...

智能分布式爬虫的数据处理流水线优化:基于深度强化学习的数据质量控制
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,数据已成为企业和研究机构的核心资产。智能分布式爬虫作为高效的数据采集工具,在大规模数据获取中发挥着关键作用。然而,传统的数据处理流水线在面对复杂多变的网络环境和海量异构数据时,常出现数据质…...
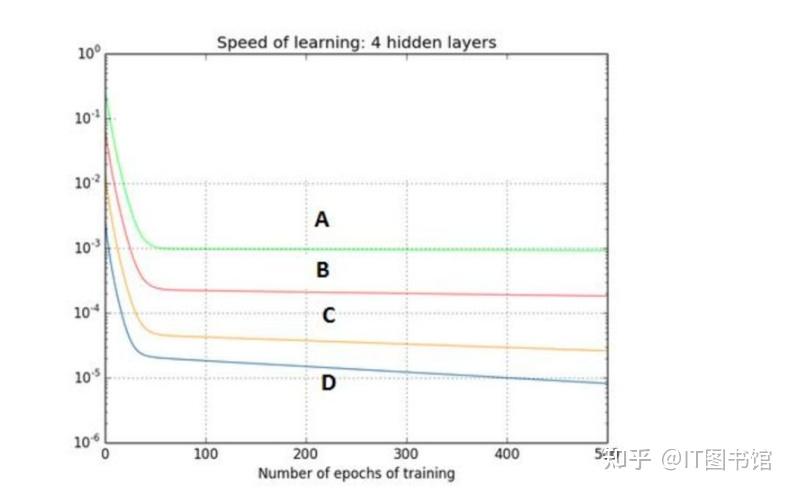
深度学习习题2
1.如果增加神经网络的宽度,精确度会增加到一个特定阈值后,便开始降低。造成这一现象的可能原因是什么? A、即使增加卷积核的数量,只有少部分的核会被用作预测 B、当卷积核数量增加时,神经网络的预测能力会降低 C、当卷…...
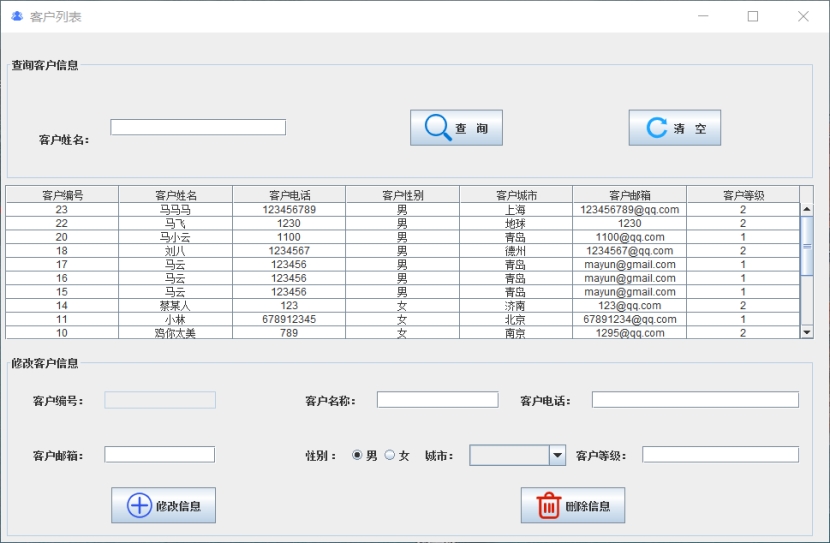
基于Java+MySQL实现(GUI)客户管理系统
客户资料管理系统的设计与实现 第一章 需求分析 1.1 需求总体介绍 本项目为了方便维护客户信息为了方便维护客户信息,对客户进行统一管理,可以把所有客户信息录入系统,进行维护和统计功能。可通过文件的方式保存相关录入数据,对…...
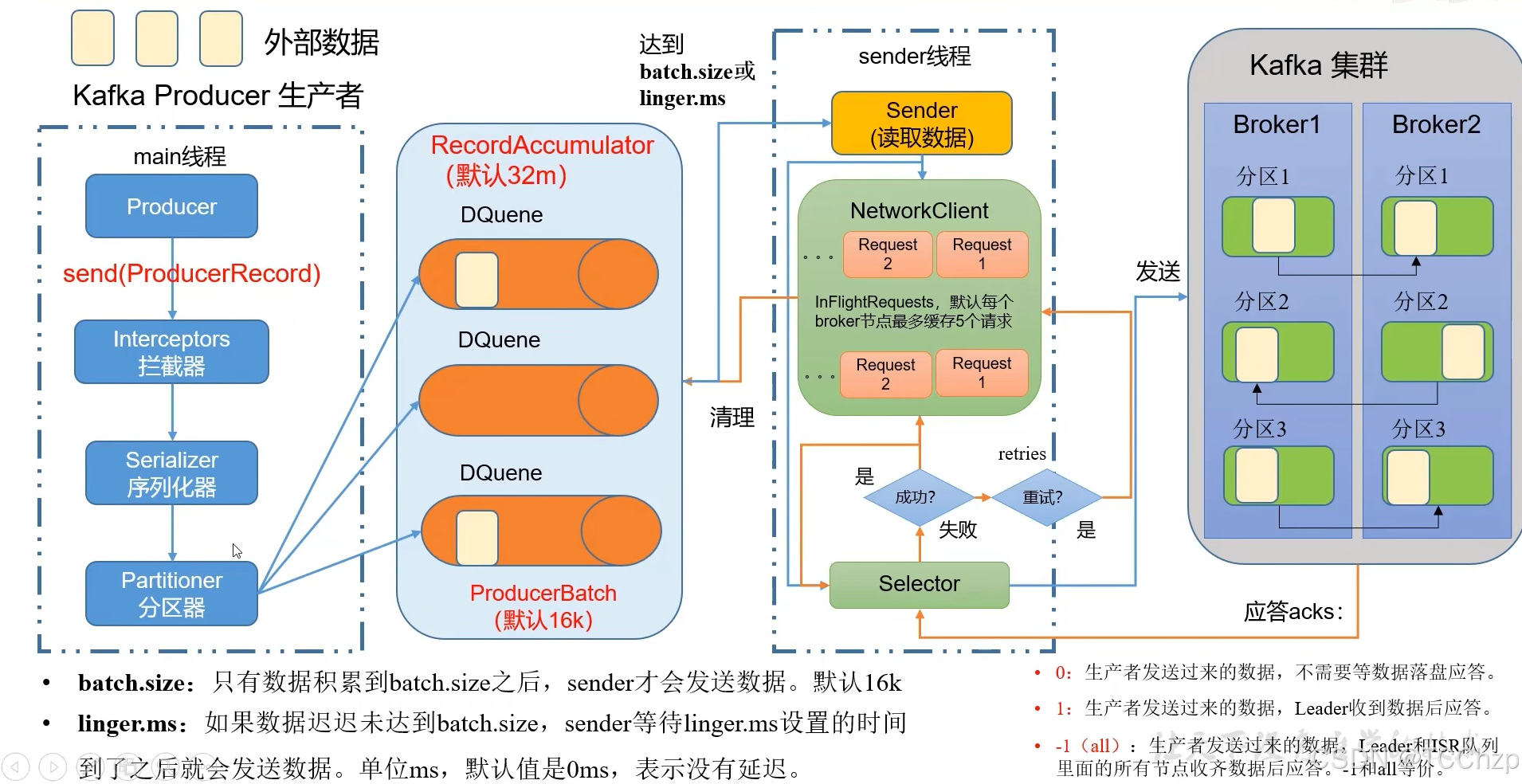
Kafka入门-生产者
生产者 生产者发送流程: 延迟时间为0ms时,也就意味着每当有数据就会直接发送 异步发送API 异步发送和同步发送的不同在于:异步发送不需要等待结果,同步发送必须等待结果才能进行下一步发送。 普通异步发送 首先导入所需的k…...
