【HashSet】| 深度剥析Java SE 源码合集Ⅲ
目录
- 一. 🦁 HashSet介绍
- 1.1 特点
- 1.2 底层实现
- 二. 🦁 结构以及对应方法分析
- 2.1 结构组成
- 2.1.1 源码实现
- 2.1.2 成员变量及构造方法
- 2.2 常用的方法
- 2.2.1 添加add(E e)方法
- 2.2.2 删除remove(Object o)方法
- 三. 最后想说
一. 🦁 HashSet介绍
1.1 特点
HashSet 是一个不保证元素的顺序且没有重复元素的集合,是线程不安全的。HashSet
允许有 null 元素。
1.2 底层实现
- HashSet底层使用 HashMap 存储元素的。
- HashMap 底层使用的是数组与链表实现元素的存储。
- 元素在数组中存放时,并不是有序存放的也不是随机存放的,而是
对元素的哈希值进行运算决定元素在数组中的位置。- 当两个元素的哈希值进行运算后得到相同的在数组中的位置时,会调用元素的 equals()方法判断两个元素是否相同。如果元素相同则不会添加该元素,如果不相同则会使用单向链表保存该元素。
二. 🦁 结构以及对应方法分析
2.1 结构组成
2.1.1 源码实现
HashSet的源码并没有很多,因为其基本是调用HashMap的方法来实现的。
package java.util;import java.io.InvalidObjectException;
import jdk.internal.access.SharedSecrets;public class HashSet<E>extends AbstractSet<E>implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Mapprivate static final Object PRESENT = new Object();/*** Constructs a new, empty set; the backing {@code HashMap} instance has* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).*/public HashSet() {map = new HashMap<>();}/*** Constructs a new set containing the elements in the specified* collection. The {@code HashMap} is created with default load factor* (0.75) and an initial capacity sufficient to contain the elements in* the specified collection.** @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this set* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));addAll(c);}/*** Constructs a new, empty set; the backing {@code HashMap} instance has* the specified initial capacity and the specified load factor.** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive*/public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);}/*** Constructs a new, empty set; the backing {@code HashMap} instance has* the specified initial capacity and default load factor (0.75).** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash table* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less* than zero*/public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);}/*** Constructs a new, empty linked hash set. (This package private* constructor is only used by LinkedHashSet.) The backing* HashMap instance is a LinkedHashMap with the specified initial* capacity and the specified load factor.** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map* @param dummy ignored (distinguishes this* constructor from other int, float constructor.)* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is less* than zero, or if the load factor is nonpositive*/HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);}/*** Returns an iterator over the elements in this set. The elements* are returned in no particular order.** @return an Iterator over the elements in this set* @see ConcurrentModificationException*/public Iterator<E> iterator() {return map.keySet().iterator();}/*** Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality).** @return the number of elements in this set (its cardinality)*/public int size() {return map.size();}/*** Returns {@code true} if this set contains no elements.** @return {@code true} if this set contains no elements*/public boolean isEmpty() {return map.isEmpty();}/*** Returns {@code true} if this set contains the specified element.* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this set* contains an element {@code e} such that* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)}.** @param o element whose presence in this set is to be tested* @return {@code true} if this set contains the specified element*/public boolean contains(Object o) {return map.containsKey(o);}/*** Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.* More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if* this set contains no element {@code e2} such that* {@code Objects.equals(e, e2)}.* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set* unchanged and returns {@code false}.** @param e element to be added to this set* @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified* element*/public boolean add(E e) {return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;}/*** Removes the specified element from this set if it is present.* More formally, removes an element {@code e} such that* {@code Objects.equals(o, e)},* if this set contains such an element. Returns {@code true} if* this set contained the element (or equivalently, if this set* changed as a result of the call). (This set will not contain the* element once the call returns.)** @param o object to be removed from this set, if present* @return {@code true} if the set contained the specified element*/public boolean remove(Object o) {return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;}/*** Removes all of the elements from this set.* The set will be empty after this call returns.*/public void clear() {map.clear();}/*** Returns a shallow copy of this {@code HashSet} instance: the elements* themselves are not cloned.** @return a shallow copy of this set*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Object clone() {try {HashSet<E> newSet = (HashSet<E>) super.clone();newSet.map = (HashMap<E, Object>) map.clone();return newSet;} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {throw new InternalError(e);}}/*** Save the state of this {@code HashSet} instance to a stream (that is,* serialize it).** @serialData The capacity of the backing {@code HashMap} instance* (int), and its load factor (float) are emitted, followed by* the size of the set (the number of elements it contains)* (int), followed by all of its elements (each an Object) in* no particular order.*/private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException {// Write out any hidden serialization magics.defaultWriteObject();// Write out HashMap capacity and load factors.writeInt(map.capacity());s.writeFloat(map.loadFactor());// Write out sizes.writeInt(map.size());// Write out all elements in the proper order.for (E e : map.keySet())s.writeObject(e);}/*** Reconstitute the {@code HashSet} instance from a stream (that is,* deserialize it).*/private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// Consume and ignore stream fields (currently zero).s.readFields();// Read capacity and verify non-negative.int capacity = s.readInt();if (capacity < 0) {throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal capacity: " +capacity);}// Read load factor and verify positive and non NaN.float loadFactor = s.readFloat();if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) {throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +loadFactor);}// Clamp load factor to range of 0.25...4.0.loadFactor = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);// Read size and verify non-negative.int size = s.readInt();if (size < 0) {throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal size: " + size);}// Set the capacity according to the size and load factor ensuring that// the HashMap is at least 25% full but clamping to maximum capacity.capacity = (int) Math.min(size * Math.min(1 / loadFactor, 4.0f),HashMap.MAXIMUM_CAPACITY);// Constructing the backing map will lazily create an array when the first element is// added, so check it before construction. Call HashMap.tableSizeFor to compute the// actual allocation size. Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to// what is actually created.SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, HashMap.tableSizeFor(capacity));// Create backing HashMapmap = (((HashSet<?>)this) instanceof LinkedHashSet ?new LinkedHashMap<>(capacity, loadFactor) :new HashMap<>(capacity, loadFactor));// Read in all elements in the proper order.for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")E e = (E) s.readObject();map.put(e, PRESENT);}}/*** Creates a <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em>* and <em>fail-fast</em> {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this* set.** <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED} and* {@link Spliterator#DISTINCT}. Overriding implementations should document* the reporting of additional characteristic values.** @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this set* @since 1.8*/public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return new HashMap.KeySpliterator<>(map, 0, -1, 0, 0);}
}2.1.2 成员变量及构造方法
- HashMap<E,Object> map:存储元素的容器
- Object PRESENT = new Object():充当map中的value
- 构造方法:这个无参构造方法里new了一个HashMap容器。说明了HashSet的底层是由HashMap实现的。
static final long serialVersionUID = -5024744406713321676L;private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Mapprivate static final Object PRESENT = new Object();/*** Constructs a new, empty set; the backing {@code HashMap} instance has* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).*/public HashSet() {map = new HashMap<>();}
2.2 常用的方法
2.2.1 添加add(E e)方法
/*** Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.* More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if* this set contains no element {@code e2} such that* {@code Objects.equals(e, e2)}.* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set* unchanged and returns {@code false}.** @param e element to be added to this set* @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified* element*/public boolean add(E e) {return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;}
由源码可以看到,添加方法是通过返回一个布尔类型,而有趣的是它的实现方法居然是直接调用map的put()方法,而参数e则是放在了key的位置,value位置则是前面看到的成员变量。这里很好的说明了HashSet的值为什么不能重复,而且是无序的,因为HashMap的key就是无序的,而且不能重复。
2.2.2 删除remove(Object o)方法
public boolean remove(Object o) {return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;}
这里的删除方法是调用了HashMap的remove(),这个方法在HashMap中是直接根据主键删除对应的元素,非常直观。
三. 最后想说
学习源码知识,有助于帮助我们扎实内功,提升程序员的涵养,如果您不想直接在idea查看源码,也想了解他,可以关注博主,都给您整理好啦,好了,文章到这里就结束啦,咱们下期见,喜欢可以一键三连哦😄
相关文章:

【HashSet】| 深度剥析Java SE 源码合集Ⅲ
目录一. 🦁 HashSet介绍1.1 特点1.2 底层实现二. 🦁 结构以及对应方法分析2.1 结构组成2.1.1 源码实现2.1.2 成员变量及构造方法2.2 常用的方法2.2.1 添加add(E e)方法2.2.2 删除remove(Object o)方法三. 最后想说一. 🦁 HashSet介绍 1.1 特…...
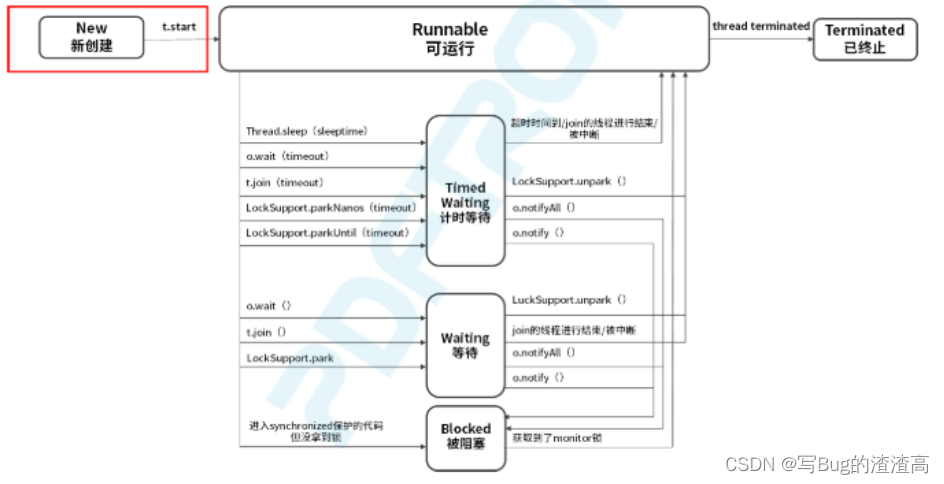
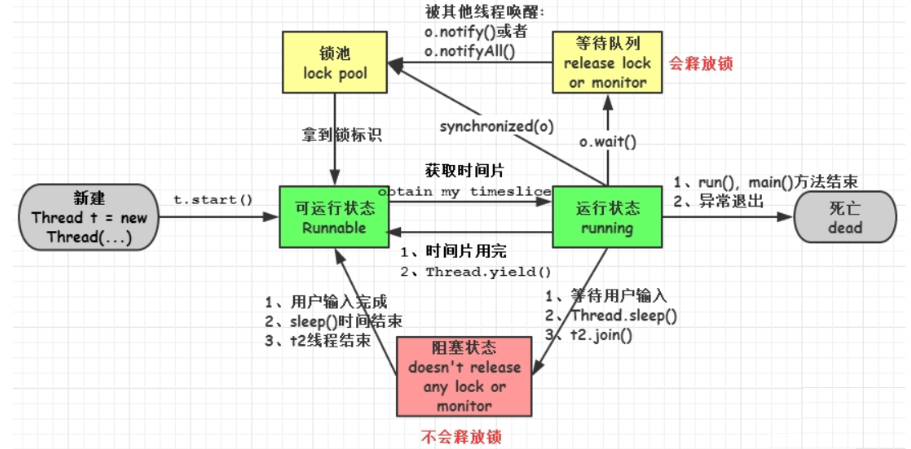
你了解线程的状态转换吗
本文概述: 讲述线程的六种状态. 你可能已经了解了六种状态, 但是你知道 sleep 被唤醒之后, wait ()被 notify 之后进入了什么状态吗? 本文只是开胃小菜, 你看看下一篇文章对你有没有帮助. 一共有六种状态: New 新建状态Runnable 运行状态Blocked 阻塞状态Waiting 等待状态Tim…...
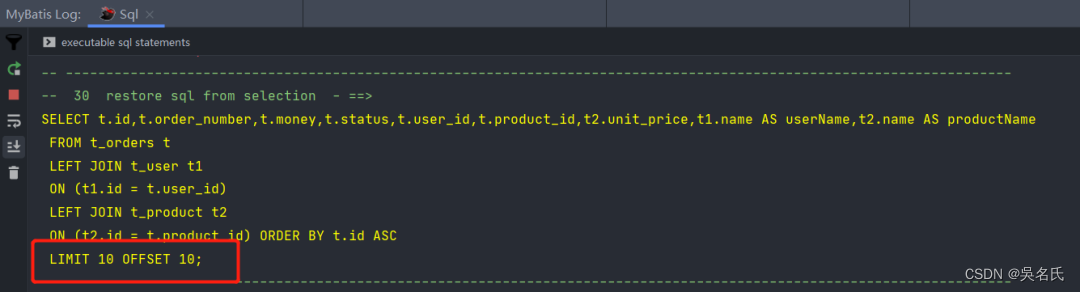
MyBatis-Plus联表查询的短板,该如何解决呢
mybatis-plus作为mybatis的增强工具,它的出现极大的简化了开发中的数据库操作,但是长久以来,它的联表查询能力一直被大家所诟病。一旦遇到left join或right join的左右连接,你还是得老老实实的打开xml文件,手写上一大段…...
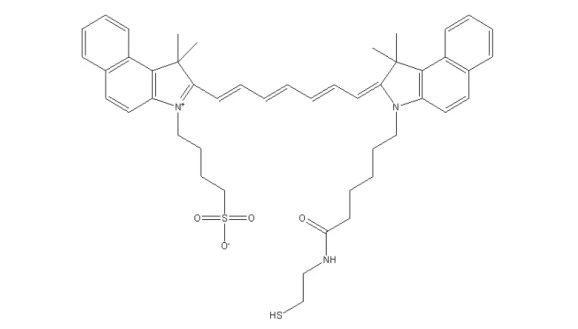
吲哚菁绿-巯基,ICG-SH,科研级别试剂,吲哚菁绿可用于测定心输出量、肝脏功能、肝血流量,和对于眼科血管造影术。
ICG-THIOL,吲哚菁绿-巯基 中文名称:吲哚菁绿-巯基 英文名称:ICG-THIOL 英文别名:ICG-SH 性状:绿色粉末 溶剂:溶于二氯甲烷等其他常规有机溶剂 稳定性:冷藏保存,避免反复冻融。 存储条件&…...

深度剖析JavaOptional类
Java Optional 类 Optional类在 Java 8中被加了进来,提供了一种处理业务逻辑想要的值可能没有出现(null)也可能出现的情况,可能直到目前,我们还是用null 来表示业务值不存在的情况,但是这可能导致空指针异常,Java 8新添加 Optional类可以从一定程度上来解决这个问题。 O…...
平面设计软件Corel CDR2023又开始放大招啦,CorelDRAW Graphics Suite 2023有哪些新增功能?
CorelDRAW 2023中文版即将于2023年3月14日,在苏州举行线上直播的2023新品发布会,本次发布会主题为“设计新生力,矢量新未来”。 发布会邀请思杰马克丁公司领导、Corel 中国区总经理分享思杰与 Corel 的合作模式及在 CorelDRAW 产品上推动历程…...

初学torch【报错:expected scalar type double but found float、rmse】
目录 一、inout 二、expected scalar type double but found float 报错 三、pytorch中回归评价rmse: 一、inout torch网络训练,输入需要转换为tensor格式: import torch import numpy A torch.arange(12, dtypetorch.float32).reshape((…...
金三银四、金九银十 面试宝典 JAVASE八股文面试题 超级无敌全的面试题汇总(接近3万字的面试题,让你的JAVA语法基础无可挑剔)
JavaSE八股文 - 面试宝典 一个合格的 计算机打工人 ,收藏夹里必须有一份 JAVA八股文面试题 ,特别是即将找工作的计算机人,希望本篇博客对你有帮助! 本文参考了诸多大佬的面试题帖子,ps:白大锅、哪吒、英雄…...

数据结构:链式二叉树初阶
目录 一.链式二叉树的逻辑结构 1.链式二叉树的结点结构体定义 2.链式二叉树逻辑结构 二.链式二叉树的遍历算法 1.前序遍历 2.中序遍历 3.后序遍历 4.层序遍历(二叉树非递归遍历算法) 层序遍历概念: 层序遍历算法实现思路: 层序遍历代码实现: 三.链式二叉树遍历算…...

公式编写1000问9-12
9.问: 买入:日线创100日新高 ,周线(5周)BIAS>10 卖出:2日收盘在30线下方 注:买卖都只要单一信号即可,不要连续给出信号 我今天才开始学习编写,可是没有买入信号,不知道哪错了? B1…...

C++11:类的新功能和可变参数模板
文章目录1. 新增默认成员函数1.1 功能1.2 示例2. 类成员变量初始化3. 新关键字3.1 关键字default3.2 关键字delete补充3.3 关键字final和override4. 可变参数模板4.1 介绍4.2 定义方式4.3 展开参数包递归展开参数包优化初始化列表展开参数包逗号表达式展开参数包补充5. emplace…...
)
【Java学习笔记】15.Java 日期时间(1)
Java 日期时间 java.util 包提供了 Date 类来封装当前的日期和时间。 Date 类提供两个构造函数来实例化 Date 对象。 第一个构造函数使用当前日期和时间来初始化对象。 Date( )第二个构造函数接收一个参数,该参数是从 1970 年 1 月 1 日起的毫秒数。 Date(long …...
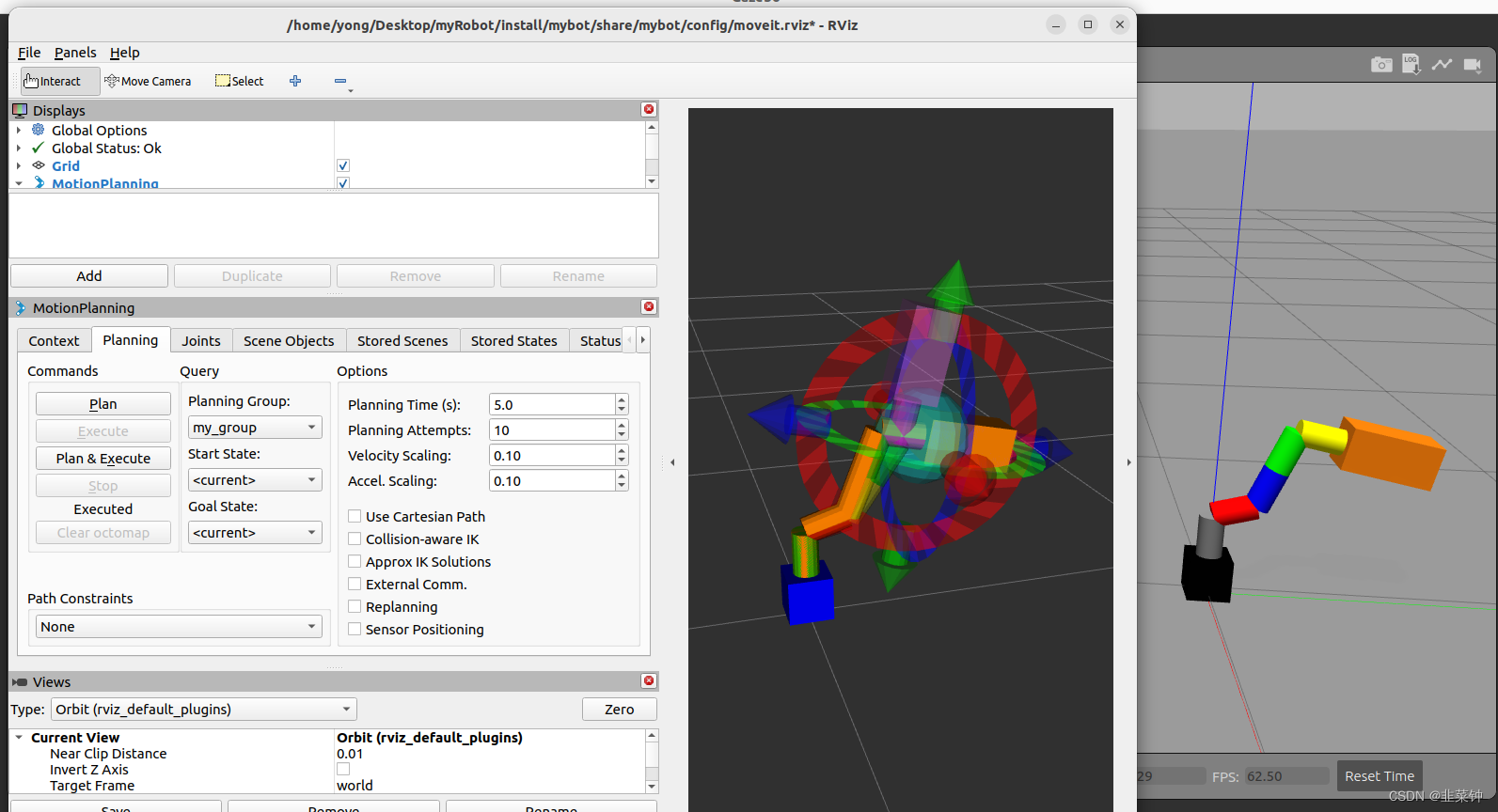
在ROS2中,通过MoveIt2控制Gazebo中的自定义机械手
目前的空余时间主要都在研究ROS2,最终目的是控制自己用舵机组装的机械手。 由于种种原因,先控制Gazebo的自定义机械手。 先看看目前的成果 左侧是rviz2中的moveit组件的机械手,右侧是gazebo中的机械手。在moveit中进行路径规划并执行后&#…...

Java-线程池 原子性 类
Java-线程池 原子性 类线程池构造方法调用Executors静态方法创建调用方法直接创建线程池对象原子性volatile-问题出现原因:volatile解决原子性AtomicInteger的常用方法悲观锁和乐观锁synchronized(悲)和CAS(乐)的区别并发工具类Hashtable集合ConcurrentHashMap原理:CountDownLa…...
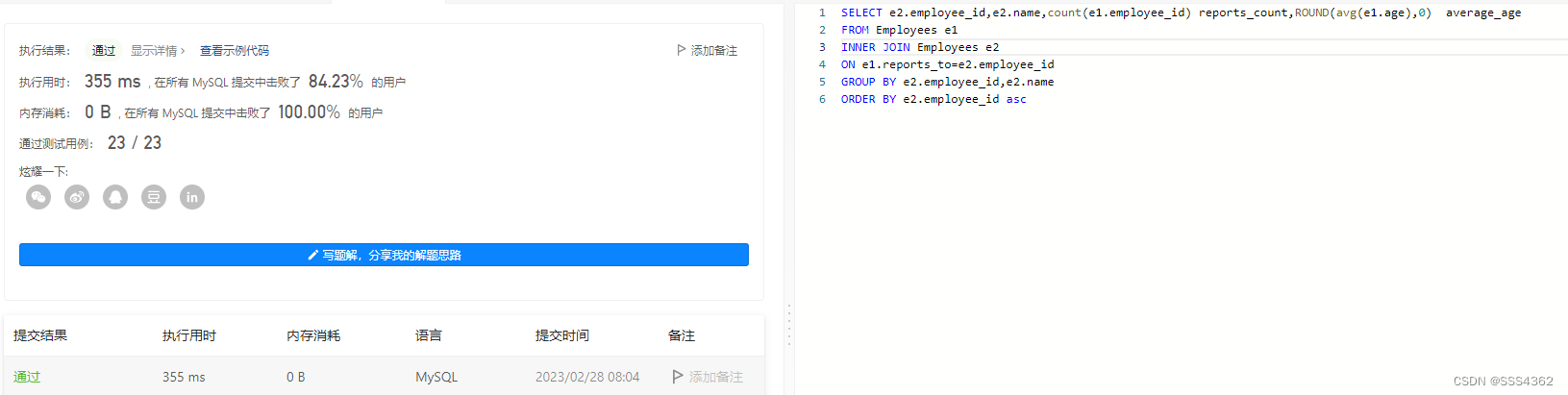
力扣sql简单篇练习(二十五)
力扣sql简单篇练习(二十五) 1 无效的推文 1.1 题目内容 1.1.1 基本题目信息 1.1.2 示例输入输出 1.2 示例sql语句 # Write your MySQL query statement below SELECT tweet_id FROM Tweets WHERE CHAR_LENGTH(content)>151.3 运行截图 2 求关注者的数量 2.1 基本题目内…...
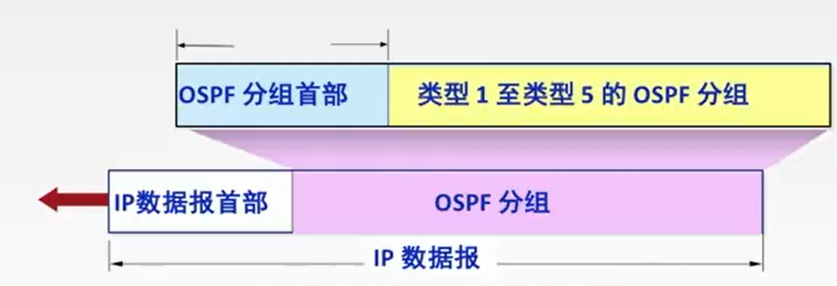
计算机网络:OSPF协议和链路状态算法
OSPF协议 开放最短路经优先OSPF协议是基于最短路径算法SPF,其主要特征就是使用分布式的链路状态协议OSPF协议的特点: 1.使用泛洪法向自治系统中的所有路由器发送信息,即路由器通过输出端口向所有相邻的路由器发送信息,而每一个相邻的路由器又…...

利用表驱动法+策略模式优化switch-case
1.前言 我有一个需求:有四个系统需要处理字段,一开始利用switch-case进行区分编码,后期字段处理越来越多,导致switch-case代码冗余,不太好,然后想通过java单继承多实现的性质进行优化。 2.实现 2.1定义S…...
SpringBoot创建和使用
目录 什么是SpringBoot SpringBoot的优点 SpringBoot项目的创建 1、使用idea创建 2、项目目录介绍和运行 Spring Boot配置文件 1、配置文件 2、配置文件的格式 3、properties 3.1、properties基本语法 3.2、读取配置文件 3.3、缺点 4、yml 4.1、优点 4.2、yml基本…...

which、whereis、locate文件查找命令
Linux下查找文件的命令有which、whereis、locate和find,find命令因要遍历文件系统,导致速度较慢,而且还会影响系统性能,而且命令选项较多,就单独放一篇介绍,可参见find命令——根据路径和条件搜索指定文件_…...
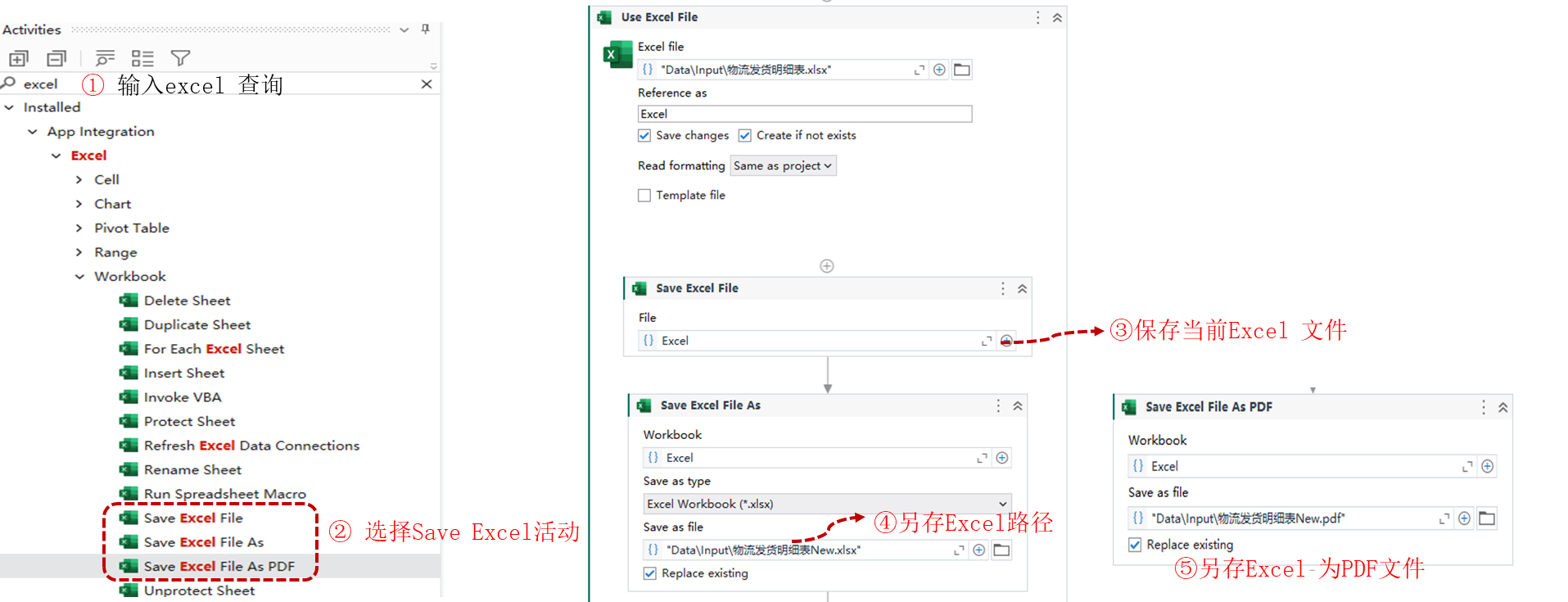
Uipath Excel 自动化系列14-SaveExcelFile(保存Excel)
活动描述 SaveExcelFile 保存Excel:保存工作簿,在修改 Excel 文件的用户界面自动化活动之后使用此活动,以保存对文件的更改 SaveExcelFile As 另存Excel : 将workbook 另存为文件 SaveExcelFile As PDF :将Excel 另存为PDF文件。该三个活…...
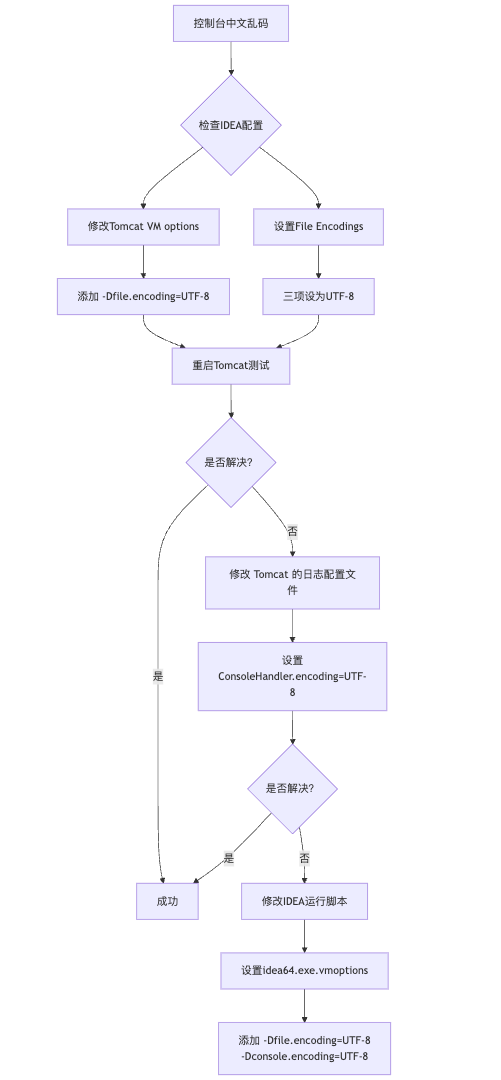
IDEA运行Tomcat出现乱码问题解决汇总
最近正值期末周,有很多同学在写期末Java web作业时,运行tomcat出现乱码问题,经过多次解决与研究,我做了如下整理: 原因: IDEA本身编码与tomcat的编码与Windows编码不同导致,Windows 系统控制台…...
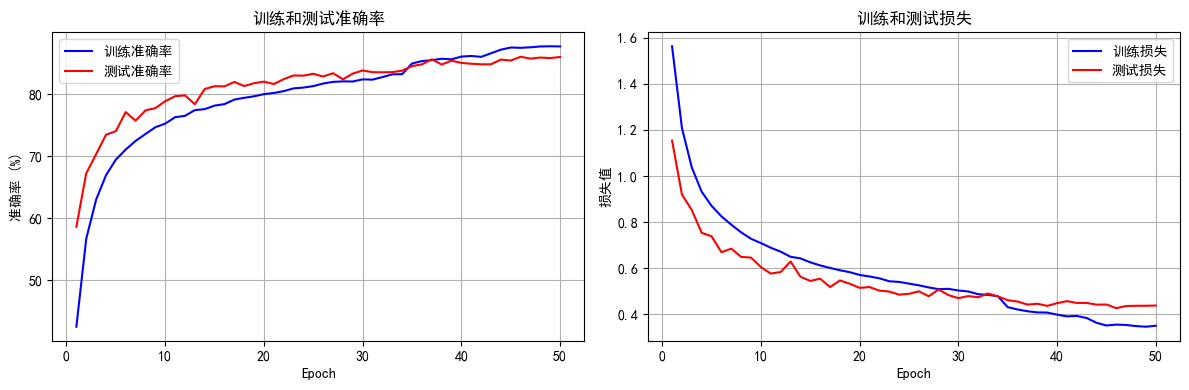
python打卡day49
知识点回顾: 通道注意力模块复习空间注意力模块CBAM的定义 作业:尝试对今天的模型检查参数数目,并用tensorboard查看训练过程 import torch import torch.nn as nn# 定义通道注意力 class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):def __init__(self,…...

Frozen-Flask :将 Flask 应用“冻结”为静态文件
Frozen-Flask 是一个用于将 Flask 应用“冻结”为静态文件的 Python 扩展。它的核心用途是:将一个 Flask Web 应用生成成纯静态 HTML 文件,从而可以部署到静态网站托管服务上,如 GitHub Pages、Netlify 或任何支持静态文件的网站服务器。 &am…...
苍穹外卖--缓存菜品
1.问题说明 用户端小程序展示的菜品数据都是通过查询数据库获得,如果用户端访问量比较大,数据库访问压力随之增大 2.实现思路 通过Redis来缓存菜品数据,减少数据库查询操作。 缓存逻辑分析: ①每个分类下的菜品保持一份缓存数据…...

【AI学习】三、AI算法中的向量
在人工智能(AI)算法中,向量(Vector)是一种将现实世界中的数据(如图像、文本、音频等)转化为计算机可处理的数值型特征表示的工具。它是连接人类认知(如语义、视觉特征)与…...
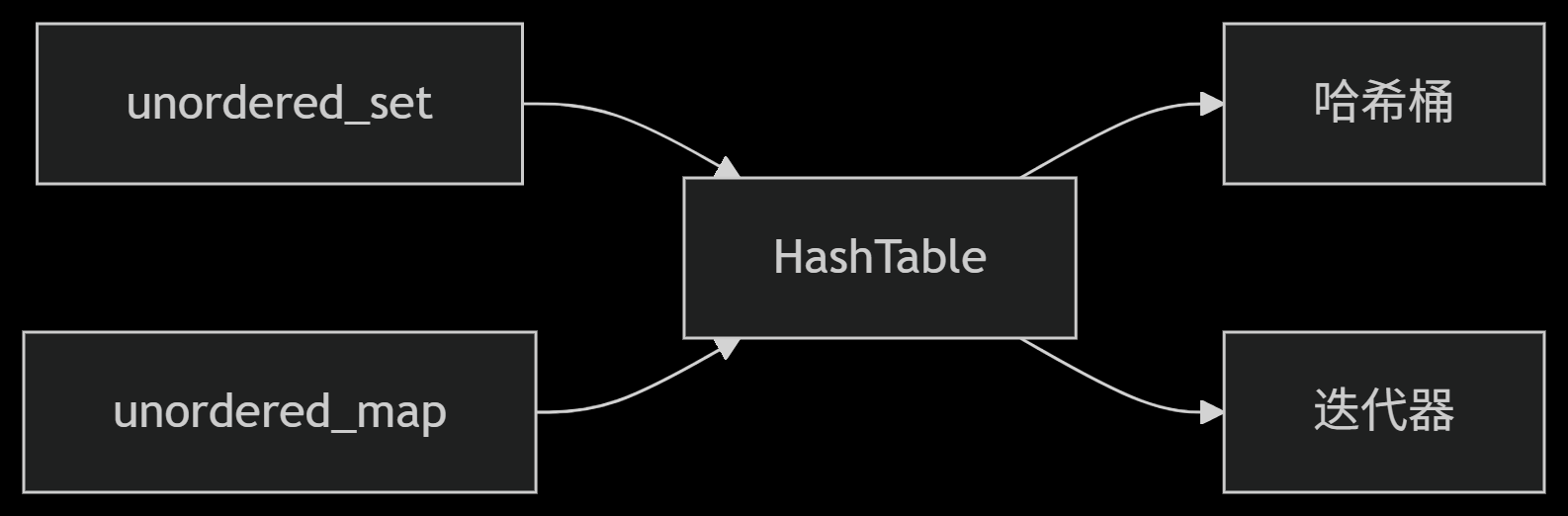
从零实现STL哈希容器:unordered_map/unordered_set封装详解
本篇文章是对C学习的STL哈希容器自主实现部分的学习分享 希望也能为你带来些帮助~ 那咱们废话不多说,直接开始吧! 一、源码结构分析 1. SGISTL30实现剖析 // hash_set核心结构 template <class Value, class HashFcn, ...> class hash_set {ty…...

Spring AI 入门:Java 开发者的生成式 AI 实践之路
一、Spring AI 简介 在人工智能技术快速迭代的今天,Spring AI 作为 Spring 生态系统的新生力量,正在成为 Java 开发者拥抱生成式 AI 的最佳选择。该框架通过模块化设计实现了与主流 AI 服务(如 OpenAI、Anthropic)的无缝对接&…...

【OSG学习笔记】Day 16: 骨骼动画与蒙皮(osgAnimation)
骨骼动画基础 骨骼动画是 3D 计算机图形中常用的技术,它通过以下两个主要组件实现角色动画。 骨骼系统 (Skeleton):由层级结构的骨头组成,类似于人体骨骼蒙皮 (Mesh Skinning):将模型网格顶点绑定到骨骼上,使骨骼移动…...

招商蛇口 | 执笔CID,启幕低密生活新境
作为中国城市生长的力量,招商蛇口以“美好生活承载者”为使命,深耕全球111座城市,以央企担当匠造时代理想人居。从深圳湾的开拓基因到西安高新CID的战略落子,招商蛇口始终与城市发展同频共振,以建筑诠释对土地与生活的…...
提供了哪些便利?)
现有的 Redis 分布式锁库(如 Redisson)提供了哪些便利?
现有的 Redis 分布式锁库(如 Redisson)相比于开发者自己基于 Redis 命令(如 SETNX, EXPIRE, DEL)手动实现分布式锁,提供了巨大的便利性和健壮性。主要体现在以下几个方面: 原子性保证 (Atomicity)ÿ…...
