C++笔试-剑指offer
剑指offer
文章目录
- 剑指offer
- 数组
- [数组中重复的数据 ](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-all-duplicates-in-an-array/description/)
- 将元素交换到对应的位置
- 二维数组中的查找
- 二叉搜索树
- 旋转数组的最小数字
- 二分查找
- 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
- 相互抵消
- 连续子数组的最大和(二)
- 动态规划
- 链表
- 从尾到头打印链表
- 栈
- 反转链表(双指针、递归)
- 拓展:反转链表中间一部分
- 删除链表的节点
- 链表合并
- 链表中倒数最后k个结点
- 双指针思想
- 复杂链表的复制
- 哈希表
- 在每个旧节点后加上新节点
- 删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
- 双指针思想
- 删除链表中重复的结点
- 二叉树
- 二叉树的深度
- 递归
- 二叉树的最小深度
- 二叉树的镜像
- 队列、栈
- 用两个栈实现队列
- 动态规划
- 跳台阶
- DP(ACM模式)
- 递归(ACM模式)
数组
数组中重复的数据
将元素交换到对应的位置
class Solution {
public:vector<int> findDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {vector<int> result;for (int i = 0; i<nums.size();i++){while (nums[i] != nums[nums[i]-1]){swap(nums[i],nums[nums[i]-1]);}}for (int i = 0; i<nums.size();i++){if (nums[i]-1 != i){result.push_back(nums[i]);}}return result;}
};
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
二维数组中的查找
二叉搜索树
class Solution{
public:bool Find(int target, vector<vector><int> arr){if (arr.empty() || arr[0].empty()) return false;int i = 0;//行int j = arr.size()-1;//列while (i<=arr.size()-1 && j>=0){if (target == arr[i][j])return true;else if (tartget < arr[i][j])--j;else++i;}return false;}
}
类似于二叉搜索树:

旋转数组的最小数字
二分查找
最小值一定在右区域!
class Solution {
public:/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param nums int整型vector * @return int整型*/int minNumberInRotateArray(vector<int>& nums) {int left = 0, right = nums.size()-1;int mid;while (left<right){mid = (left + right)/2;if (nums[left]<nums[right])//left一定在左区域或最低点,right一定在右区域,左区域的数一定大于等于右区域的数return nums[left];if (nums[mid] > nums[right])//mid在左区域,最小的数字在mid右边{left = mid + 1;}else if (nums[mid] == nums[right])//mid在重复元素{--right;}else //mid在右区域, 最小数字要么是mid要么在mid左边{right = mid;}}return nums[left];}
};
数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
相互抵消
用不同数字相互抵消的方法,最后留下来的一定是超过一半的数字
int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(vector<int>& numbers) {// write code hereint num = numbers[0];int count = 1;for (int i = 1; i<numbers.size(); ++i){if (count > 0){if (numbers[i]==num){++count;}else {--count;}}else //count = 0{num = numbers[i];count = 1;}}return num;}
};
1287. 有序数组中出现次数超过25%的元素
由于这题是升序,可以直接用步长判断,也可以用上题的步骤判断
连续子数组的最大和(二)
根据剑指offer自己想的,待优化:
int最大值INT_MAX,最小值INT_MIN
int的最小值可以写成0x8000000,最大值可以写成0x7FFFFFFF
class Solution {
public:vector<int> FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(vector<int>& arr) {// write code hereint result = 0x80000000;vector<int> vresult;vector<int> temp;int sum = 0;for (int i =0;i<arr.size();++i){if (sum<0)//如果和为负数,那么前一个和一定是从那个元素开始算的最大和了{temp.clear();temp.push_back(arr[i]);sum=arr[i];}else {sum+=arr[i];temp.push_back(arr[i]);}if (sum>=result){result = sum;vresult = temp;}}return vresult;}
};
动态规划
//只需要保存最大值时:
int res = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++) {if (nums[i - 1] > 0) nums[i] += nums[i - 1];if (nums[i] > res) res = nums[i];
}
return res;
//需要保存对应的子数组时:求连续子数组的最大和(ACM模式)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main() {string str;cin>>str;//输入是个字符串int k =0;vector<int> numbers;while((k = str.find(',')) != str.npos){//注意输出的方法string temp = str.substr(0, k);numbers.push_back(stoi(temp));str = str.substr(k + 1);}numbers.push_back(stoi(str));int tempmax = 0;int result = 0x80000000;int sum = 0;for (int i =0; i<numbers.size();++i){if (sum<0){sum=numbers[i];}else {sum+=numbers[i];}result = max(sum,result);}if (result<0){result = 0;}printf("%d",result);
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
链表
从尾到头打印链表
栈
利用栈先入后出的特点,很好解决
class Solution {
public:vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {stack<int> stk;vector<int> result;int value = 0;while (head!=nullptr){stk.push(head->val);head = head->next;}while (!stk.empty()){value = stk.top();result.push_back(value);stk.pop();}return result;}
};
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(n)
反转链表(双指针、递归)
双指针:
class Solution {
public:vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {ListNode* preNode = nullptr;ListNode* curNode = head;while(curNode!=nullptr){ListNode* temp = curNode->next;curNode->next = preNode;preNode = curNode;curNode = temp;}vector<int> result;while(preNode!=nullptr){result.push_back(preNode->val);preNode = preNode->next;}return result;}
};
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
递归:
class Solution {
public:vector<int> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode* head) {ListNode* newhead = ReverseList(head);vector<int> result;while (newhead!=nullptr){result.push_back(newhead->val);newhead = newhead->next;}return result;}ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* head){if (head==nullptr || head->next==nullptr){return head;}ListNode* newhead = ReverseList(head->next);head->next->next = head;head->next = nullptr;return newhead;}
};
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(n)
拓展:反转链表中间一部分
92. 反转链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {if (head->next==nullptr || left==right){return head;}ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);dummyhead->next = head;ListNode* preleftEdge = dummyhead;ListNode* leftEdge = head;ListNode* rightEdge = head;for(int i = 1; i<left;++i){preleftEdge = preleftEdge->next;leftEdge = preleftEdge->next;}for(int i = 1; i<right;++i){rightEdge = rightEdge->next;}ListNode* nextrightEdge = rightEdge->next;ListNode* leftNode = leftEdge;ListNode* firstNode = leftNode;ListNode* rightNode = leftNode->next;while (rightNode!=nextrightEdge){ListNode* temp = rightNode->next;rightNode->next = leftNode;leftNode = rightNode;rightNode = temp;}preleftEdge->next = leftNode;firstNode->next = nextrightEdge;return dummyhead->next;}
};
删除链表的节点
class Solution {
public:/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param head ListNode类 * @param val int整型 * @return ListNode类*/ListNode* deleteNode(ListNode* head, int val) {// write code hereListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);dummyhead->next = head;ListNode* pre = dummyhead;ListNode* cur = head;while (cur!=nullptr){if (cur->val==val){pre->next = cur->next;break;}else {cur = cur->next;pre = pre->next;}}return dummyhead->next;}
};
还有一种不需要知道前驱结点就可以“删除”链表结点的方法,前提是不能删除最后一个结点:
class Solution {
public:void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {node->val = node->next->val;node->next = node->next->next;}
};
链表合并
ACM模式的话要注意输入输出,然后要注意cur指针的更新
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode
{int val;ListNode* next;ListNode(int val): val(val), next(nullptr){}
};int main() {int a;ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);ListNode* cur = dummyhead;ListNode* dummyhead1 = new ListNode(0);ListNode* cur1 = dummyhead1;ListNode* dummyhead2 = new ListNode(0);ListNode* cur2 = dummyhead2;while(cin>>a){ListNode* node = new ListNode(a);cur1->next = node;cur1 = cur1->next;if(cin.get()=='\n'){break;}}while(cin>>a){ListNode* node = new ListNode(a);cur2->next = node;cur2 = cur2->next;}cur1 = dummyhead1->next;cur2 = dummyhead2->next;while (cur1!=nullptr && cur2!=nullptr){if (cur1->val<=cur2->val){cur->next = cur1;cur1 = cur1->next;}else {cur->next = cur2;cur2 = cur2->next;}cur = cur->next;}if (cur1==nullptr){cur->next = cur2;}if (cur2==nullptr){cur->next = cur1;}cur = dummyhead->next;while (cur!=nullptr){printf("%d ",cur->val);cur = cur->next;}return 0;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")
链表中倒数最后k个结点
双指针思想
右指针指向左指针后k个元素,这样当右指针为最后一个节点后的元素时,左指针指向的就是所求元素
/*** struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pHead ListNode类 * @param k int整型 * @return ListNode类*/ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pHead, int k) {// write code hereif (pHead==nullptr){return nullptr;}ListNode* left = pHead;ListNode* right = left;for (int i =0; i<k;++i){if(right==nullptr){return nullptr;}right = right->next; }while (right!=nullptr){right = right->next;left = left->next;}return left;}
};
复杂链表的复制
LCR 154. 复杂链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
哈希表
键为旧指针,值为新指针。第一次遍历时初始化键和值的label,第二次赋上next和random指针
class Solution {
public:Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {if (head==nullptr){return nullptr;}unordered_map<Node*,Node*> mp;Node* cur = head;while (cur!=nullptr){Node* newNode = new Node(cur->val);mp[cur] = newNode;cur = cur->next;}cur = head;while (cur!=nullptr){mp[cur]->next = mp[cur->next];mp[cur]->random = mp[cur->random];cur = cur->next;}return mp[head];}
};
在每个旧节点后加上新节点
最后要记得把旧链表头结点断开连接
class Solution {
public:RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead) {if (pHead==nullptr){return nullptr;}//初始化nextRandomListNode* cur1 = pHead;while (cur1!=nullptr){RandomListNode* newNode = new RandomListNode(cur1->label);newNode->next = cur1->next;cur1->next = newNode;cur1 = cur1->next->next;}//赋值randomcur1 = pHead;RandomListNode* cur2 = pHead->next;while (cur1!=nullptr){if (cur1->random != nullptr){cur2->random = cur1->random->next;}cur1 = cur1->next->next;cur2 = cur2->next->next;}//拆分链表RandomListNode* newCloneHead = pHead->next;cur2 = newCloneHead;pHead->next = nullptr;while (cur2->next!=nullptr){cur2->next = cur2->next->next;cur2 = cur2->next;}cur2->next=nullptr;cur1 = pHead;cur2 = pHead->next;return newCloneHead;}
};
删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
双指针思想
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {// write code hereif (head==nullptr){return nullptr;}ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);ListNode* left = dummyhead;ListNode* right = head;while(right!=nullptr){while (right->next!=nullptr && right->val==right->next->val){right = right->next;}left->next = right;left = left->next;right = right->next;}return dummyhead->next;}
删除链表中重复的结点
比前面多了再将right右移一步的动作,以及最后要把left指向nullptr
class Solution {
public:ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead) {if (pHead==nullptr){return nullptr;}ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);ListNode* left = dummyhead;ListNode* right = pHead;while(right!=nullptr){if(right->next!=nullptr && right->val==right->next->val){while (right->next!=nullptr && right->val==right->next->val){right = right->next;}right = right->next;continue;}left->next = right;left = left->next;right = right->next;}left->next = nullptr;return dummyhead->next;}
};
二叉树
二叉树的深度
递归
返回左子树和右子树深度的最大值加上一(后序遍历)
class Solution {
public:int TreeDepth(TreeNode* pRoot) {if (pRoot==nullptr){return 0;}return max(TreeDepth(pRoot->left),TreeDepth(pRoot->right))+1;}
};
二叉树的最小深度
111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
和二叉树的(最大)深度的区别是,计算的是到叶子节点(左右孩子都为空)的最小深度,也用后序遍历实现
class Solution {
public:int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {if (root==nullptr){return 0;}if (root->left==nullptr && root->right!=nullptr){return minDepth(root->right)+1;}else if (root->right==nullptr && root->left!=nullptr){return minDepth(root->left)+1;}else{return min(minDepth(root->left),minDepth(root->right))+1;}}
};
二叉树的镜像
LCR 144. 翻转二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
前序遍历
TreeNode* Mirror(TreeNode* pRoot) {// write code hereif (pRoot==nullptr) return pRoot;swap(pRoot->left,pRoot->right);Mirror(pRoot->left);Mirror(pRoot->right);return pRoot;}
后序遍历
TreeNode* Mirror(TreeNode* pRoot) {// write code hereif (pRoot==nullptr) return pRoot;Mirror(pRoot->left);Mirror(pRoot->right);swap(pRoot->left,pRoot->right);return pRoot;}
队列、栈
用两个栈实现队列
每当要pop的时候就获取stack2的最上面的元素,如果stack2为空,则将stack1依次出栈到stack2。这样stack2上面的就是最先push进去的元素,最底下是最新push进去的元素。
class Solution
{
public:void push(int node) {stack1.push(node);}int pop() {while (!stack2.empty()){int result = stack2.top();stack2.pop();return result;}while (!stack1.empty()){int temp = stack1.top();stack2.push(temp);stack1.pop();}int result = stack2.top();stack2.pop();return result;}private:stack<int> stack1;stack<int> stack2;
};
动态规划
跳台阶
DP(ACM模式)
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>using namespace std;int main() {int a;cin>>a;unordered_map<int,int> dp;dp[0] = 1;dp[1] = 1;dp[2] = 2;if (a<=2){printf("%d",dp[a]);}else {for (int i=3;i<=a;i++){int temp = dp[2];dp[2] +=dp[1];dp[1] = temp;}printf("%d",dp[2]);}return 0;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")递归(ACM模式)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int Jump(int num)
{if (num==0) return 1;if (num==1) return 1;if (num==2) return 2;return Jump(num-1) + Jump(num-2);
}int main() {int a;cin>>a;int result = Jump(a);printf("%d",result);return 0;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")相关文章:

C++笔试-剑指offer
剑指offer 文章目录 剑指offer数组[数组中重复的数据 ](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-all-duplicates-in-an-array/description/)将元素交换到对应的位置 二维数组中的查找二叉搜索树 旋转数组的最小数字二分查找 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字相互抵消 连续子数组的最大…...
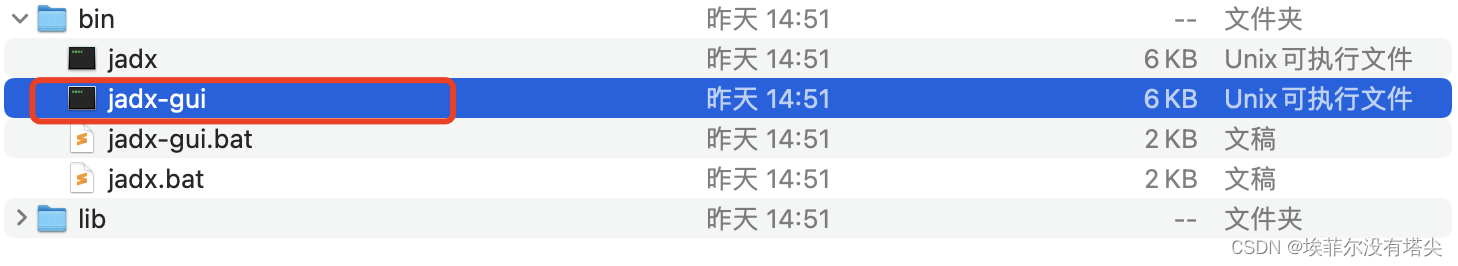
Mac安装jadx并配置环境
jadx官网:GitHub - skylot/jadx: Dex to Java decompiler 第一种: 安装jadx命令: brew install jadx 启动jadx-gui命令: jadx-gui 可能遇到的问题: Downloading https://formulae.brew.sh/api/formula.jws.json** h…...

前端学习----css基础语法
CSS概述 CAscading Style Sheets(级联样式表) CSS是一种样式语言,用于对HTML文档控制外观,自定义布局等,例如字体,颜色,边距等 可将页面的内容与表现形式分离,页面内容存放在HTML文档中,而用于定义表现形式的CSS在一个.css文件中或HTML文档的某一部分 HTML与CSS的关系 HTM…...

超详解——python条件和循环——小白篇
目录 1. 缩进和悬挂else 2. 条件表达式 3. 和循环搭配的else 4. 可调用对象 总结: 1. 缩进和悬挂else 在Python中,代码块是通过缩进来表示的。条件判断和循环结构的代码块需要正确缩进。悬挂else指的是else子句和相应的if或循环在同一级别的缩进。 …...
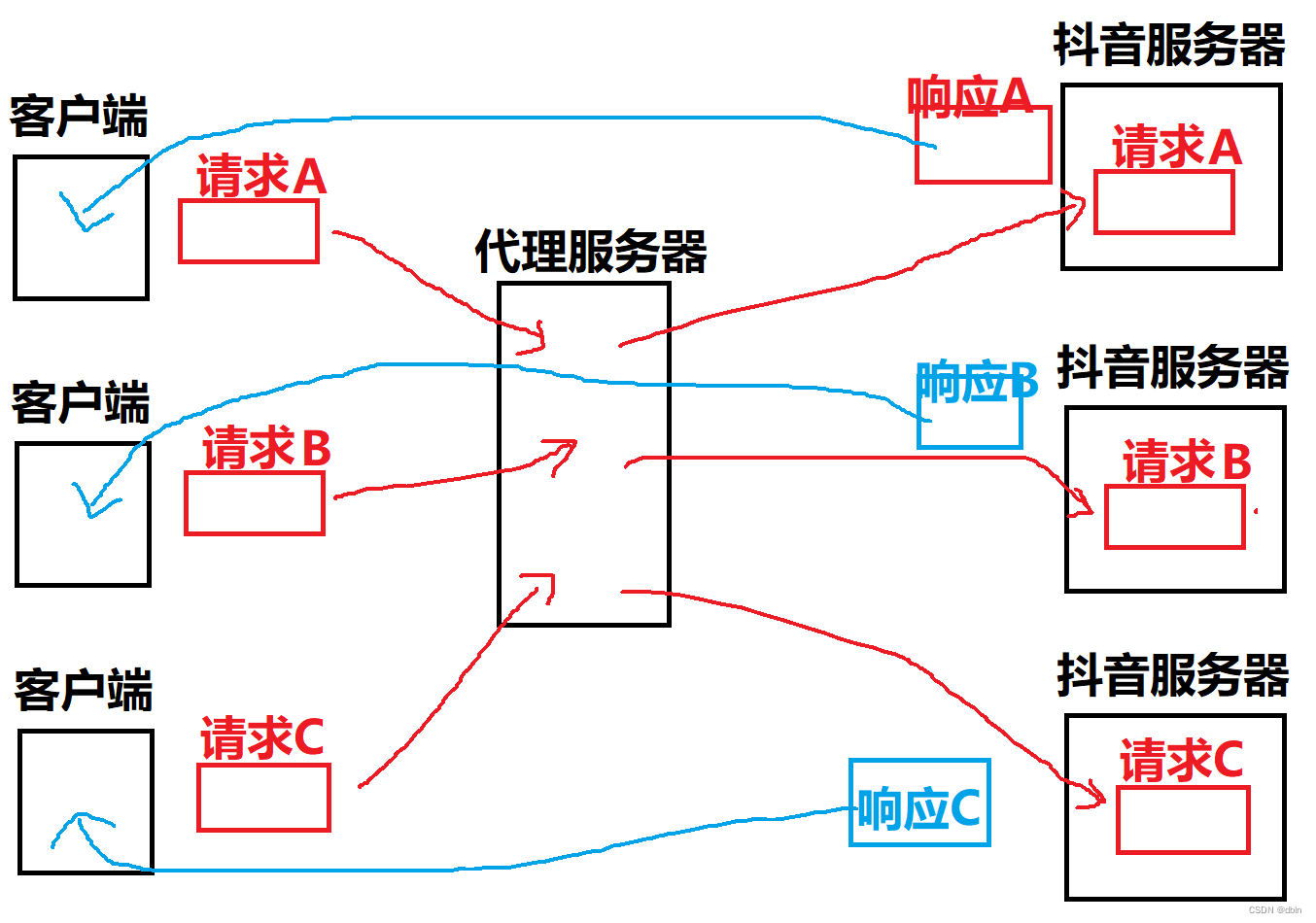
DNS协议 | NAT技术 | 代理服务器
目录 一、DNS协议 1、DNS背景 2、DNS协议 域名 域名解析 二、NAT技术 1、NAT技术 2、NAPT技术 3、NAT技术的缺陷 三、代理服务器 1、正向代理服务器 2、反向代理服务器 一、DNS协议 域名系统(Domain Name System,缩写:DNS&#…...

深入ES6:解锁 JavaScript 类与继承的高级玩法
个人主页:学习前端的小z 个人专栏:JavaScript 精粹 本专栏旨在分享记录每日学习的前端知识和学习笔记的归纳总结,欢迎大家在评论区交流讨论! ES5、ES6介绍 文章目录 💯Class🍟1 类的由来🍟2 co…...

领域驱动设计:异常处理
一、异常的处理 异常处理是领域模型要考虑的一部分,原因在于模型的责任不可能无限大。在遇到自己处理能力之外的情况时,要采用异常机制报告错误,并将处理权转交。异常就是这样一种机制,某种程度上,它可以保证领域模型…...

网络网络层之(6)ICMPv6协议
网络网络层之(6)ICMPv6协议 Author: Once Day Date: 2024年6月2日 一位热衷于Linux学习和开发的菜鸟,试图谱写一场冒险之旅,也许终点只是一场白日梦… 漫漫长路,有人对你微笑过嘛… 全系列文章可参考专栏: 通信网络技术_Once-Day的博客-CS…...

《大道平渊》· 拾壹 —— 商业一定是个故事:讲好故事,员工奋发,顾客买单。
《大道平渊》 拾壹 "大家都在喝,你喝不喝?" 商业一定是个故事,人民群众需要故事。 比如可口可乐的各种故事。 可口可乐公司也只是被营销大师们, 作为一种故事载体,发挥他们的本领。 营销大师们开发故事…...

JavaScript 如何访问本地文件夹
在浏览器环境中的JavaScript(通常指的是前端JavaScript)由于安全限制,无法直接访问用户的本地文件或文件夹。这是为了防止恶意脚本访问并窃取用户的敏感数据。 但是,有几种方法可以间接地让用户选择并访问本地文件: 使…...

ArrayList顺序表简单实现
一、创建MyArrayList框架 1.1 MyArrayList 类中实现 arr 数组 import java.util.Arrays;public class MyArrayList {private int[] arr;private int usesize;private static final int P 10;public MyArrayList() {arr new int[P];} 在 MyArrayList 类内创建 arr 数组&…...
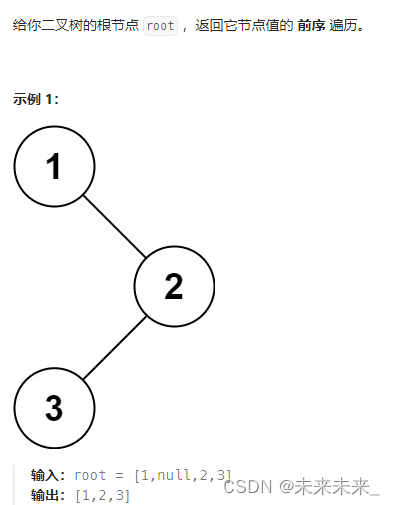
144、二叉树的前序递归遍历
题解: 递归书写三要素: 1)确定递归函数的参数和返回值。要确定每次递归所要用到的参数以及需要返回的值 2)确定终止条件。操作系统也是用栈的方式实现递归,那么如果不写终止条件或者终止条件写的不对,都…...

youtube 1080 分辨率 下载方式
YouTube 1080p Video Downloader 这张图像代表了Autodesk Maya中一个名为rocket_body_MAT的材质的着色器网络。下面是对节点及其连接的细分: 节点 place2dTexture12: 该节点用于控制2D纹理在表面上的位置映射。输出: Out UVrocket_body2.jpg: 该节点代表一个纹理文件,具体是…...

计算机网络ppt和课后题总结(下)
常用端口总结 计算机网络中,端口是TCP/IP协议的一部分,用于标识运行在同一台计算机上的不同服务。端口号是一个16位的数字,范围从0到65535。通常,0到1023的端口被称为“熟知端口”或“系统端口”,它们被保留给一些标准…...
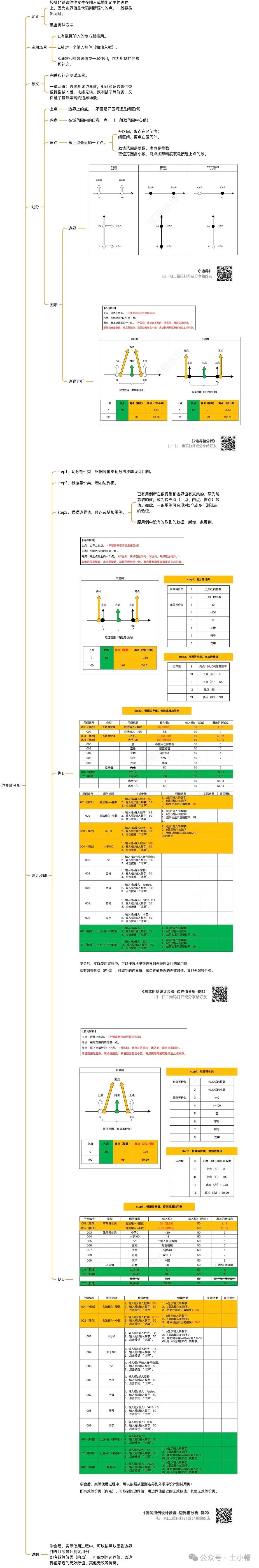
测试基础12:测试用例设计方法-边界值分析
课程大纲 1、定义 经验发现,较多的错误往往发生在输入或输出范围的边界上,因为边界值是代码判断语句的点,一般容易出问题(数值写错、多加或丢失等号、写错不等号方向…)。所以增加对取值范围的边界数据的测试ÿ…...

AI大模型在健康睡眠监测中的深度融合与实践案例
文章目录 1. 应用方案2. 技术实现2.1 数据采集与预处理2.2 构建与训练模型2.3 个性化建议生成 3. 优化策略4. 应用示例:多模态数据融合与实时监测4.1 数据采集4.2 实时监测与反馈 5. 深入分析模型选择和优化5.1 LSTM模型的优势和优化策略5.2 CNN模型的优势和优化策略…...

【西瓜书】9.聚类
聚类任务是无监督学习的一种用于分类等其他任务的前驱过程,作为数据清洗,基于聚类结果训练分类模型 1.聚类性能度量(有效性指标) 分类任务的性能度量有错误率、精度、准确率P、召回率R、F1度量(P-R的调和平均)、TPR、FPR、AUC回归…...

使用jemalloc实现信号驱动的程序堆栈信息打印
使用jemalloc实现信号驱动的程序堆栈信息打印 本文介绍应用如何集成jemalloc,在接收到SIGUSR1信号10时打印程序的堆栈信息。 1. 编译jemalloc 首先,确保你已经编译并安装了启用prof功能的jemalloc。以下是ubuntu18.04上的编译步骤: git c…...

树的4种遍历
目录 树的四种遍历方式的总结 1. 前序遍历(Pre-order Traversal) 2. 中序遍历(In-order Traversal) 3. 后序遍历(Post-order Traversal) 4. 层序遍历(Level-order Traversal 或 广度优先遍…...

深入探讨5种单例模式
文章目录 一、对比总览详细解释 二、代码1. 饿汉式2. 饱汉式3. 饱汉式-双检锁4. 静态内部类5. 枚举单例 三、性能对比 一、对比总览 以下是不同单例模式实现方式的特性对比表格。表格从线程安全性、延迟加载、实现复杂度、反序列化安全性、防反射攻击性等多个方面进行考量。 …...
无法与IP建立连接,未能下载VSCode服务器
如题,在远程连接服务器的时候突然遇到了这个提示。 查阅了一圈,发现是VSCode版本自动更新惹的祸!!! 在VSCode的帮助->关于这里发现前几天VSCode自动更新了,我的版本号变成了1.100.3 才导致了远程连接出…...

测试markdown--肇兴
day1: 1、去程:7:04 --11:32高铁 高铁右转上售票大厅2楼,穿过候车厅下一楼,上大巴车 ¥10/人 **2、到达:**12点多到达寨子,买门票,美团/抖音:¥78人 3、中饭&a…...
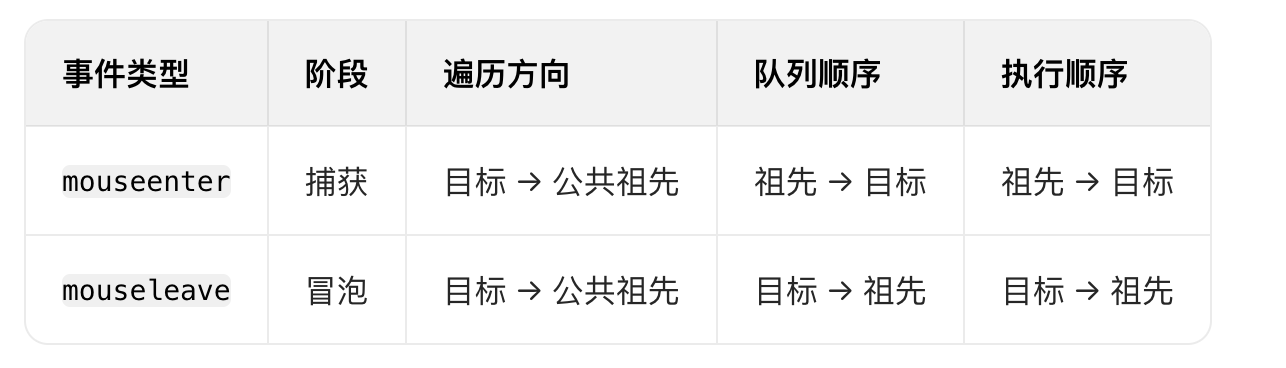
React19源码系列之 事件插件系统
事件类别 事件类型 定义 文档 Event Event 接口表示在 EventTarget 上出现的事件。 Event - Web API | MDN UIEvent UIEvent 接口表示简单的用户界面事件。 UIEvent - Web API | MDN KeyboardEvent KeyboardEvent 对象描述了用户与键盘的交互。 KeyboardEvent - Web…...

【HTML-16】深入理解HTML中的块元素与行内元素
HTML元素根据其显示特性可以分为两大类:块元素(Block-level Elements)和行内元素(Inline Elements)。理解这两者的区别对于构建良好的网页布局至关重要。本文将全面解析这两种元素的特性、区别以及实际应用场景。 1. 块元素(Block-level Elements) 1.1 基本特性 …...

使用Matplotlib创建炫酷的3D散点图:数据可视化的新维度
文章目录 基础实现代码代码解析进阶技巧1. 自定义点的大小和颜色2. 添加图例和样式美化3. 真实数据应用示例实用技巧与注意事项完整示例(带样式)应用场景在数据科学和可视化领域,三维图形能为我们提供更丰富的数据洞察。本文将手把手教你如何使用Python的Matplotlib库创建引…...
LINUX 69 FTP 客服管理系统 man 5 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
FTP 客服管理系统 实现kefu123登录,不允许匿名访问,kefu只能访问/data/kefu目录,不能查看其他目录 创建账号密码 useradd kefu echo 123|passwd -stdin kefu [rootcode caozx26420]# echo 123|passwd --stdin kefu 更改用户 kefu 的密码…...

【无标题】路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论
路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论 一、传统路径模型的根本缺陷 在经典正方形路径问题中(图1): mermaid graph LR A((A)) --- B((B)) B --- C((C)) C --- D((D)) D --- A A -.- C[无直接路径] B -…...

多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现
多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现 1. 系统概述 本系统使用多模态大模型(Stable Diffusion Inpainting)实现图像修复功能,结合文本描述和图片输入,对指定区域进行内容修复。系统包含完整的数据处理、模型训练、推理部署流程。 import torch import numpy …...

MinIO Docker 部署:仅开放一个端口
MinIO Docker 部署:仅开放一个端口 在实际的服务器部署中,出于安全和管理的考虑,我们可能只能开放一个端口。MinIO 是一个高性能的对象存储服务,支持 Docker 部署,但默认情况下它需要两个端口:一个是 API 端口(用于存储和访问数据),另一个是控制台端口(用于管理界面…...
Python 实现 Web 静态服务器(HTTP 协议)
目录 一、在本地启动 HTTP 服务器1. Windows 下安装 node.js1)下载安装包2)配置环境变量3)安装镜像4)node.js 的常用命令 2. 安装 http-server 服务3. 使用 http-server 开启服务1)使用 http-server2)详解 …...
