【操作系统】操作系统实验02-生产者消费者程序改进
1. 说明文档中原有程序实现的功能、实现方法。(用语言、程序流程图、为原有程序添加注释等方式均可)
1.//const.h
2.//定义宏变量
3.#ifndef CONST_H
4.#define CONST_H
5.
6.#define TRUE 1
7.#define FALSE 0
8.#define ERROR 0
9.#define OVERFLOW -2
10.#define OK 1
11.#define MAXSIZE 20//队列中最多有20个元素
12.#define MAXLEN 100//字符串最大长度
13.
#endif1.//Typedefine.h
2.//定义结构体
3.#ifndef TYPEDEFINE_H
4.#define TYPEDEFINE_H
5.
6.#include "const.h"
7.//字符串结构体
8.typedef struct{
9. char data[MAXLEN];//数据
10. int len;//数据长度,不算字符串结束字符”\0”
11.}SString;
12.//元素类型结构体
13.typedef struct{
14. SString* strName;//数据
15. long INumber;//号码
16.}Elemtype;
17.//结点结构体
18.typedef struct node{
19. Elemtype data;//结点的数据域
20. struct node *next;//结点的指针域,指向下一个结点地址
21.}SNode;
22.//队列结构体
23.typedef struct{
24. Elemtype q[MAXSIZE];//存放队列元素
25. int front;//队列头指针
26. int rear;//队列尾指针,存放尾元素的下一个位置
27.}Queue;
28.//栈结构体
29.typedef struct st{
30. Elemtype data[MAXSIZE];//存放栈元素
31. int top;//栈顶指针
32.}Stack;
33.
34.typedef int BOOL;
35.typedef int Status;
36.
#endif1.//Queue.h
2.//定义队列的相关函数
3.#ifndef QUEUE_H_LY
4.#define QUEUE_H_LY
5.
6.#include "Typedefine.h"
7.#include <stdbool.h>
8.
9.Queue *InitQueue();//初始化队列函数
10.int EnQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype x);//入队函数
11.int DeQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype *x);//出队函数
12.int QueueEmpty(Queue Q);//判断队列是否为空,非空返回0,空返回1
13.int QueueCount(Queue *HQ);//统计队列元素个数
14.bool QueueFull(Queue Q);//判断队列是否满,满返回 TRUE,非满返回 FALSE
15.
#endif1.//Queue.c
2.//队列的相关函数实现代码
3.#include "stdio.h"
4.#include "malloc.h"
5.#include "const.h"
6.#include "Queue.h"
7.#include <stdbool.h>
8.//队列初始化函数
9.Queue *InitQueue(){
10. Queue *Q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));//申请空间
11. Q->front = Q->rear = 0;//头尾指针相等时说明队列为空
12. return Q;//返回队列指针
13.}
14.//入队函数
15.int EnQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype x){
16. if((Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == Q->front) return FALSE;//队满,入队失败,返回0
17. else{
18. Q->q[Q->rear] = x;//存放元素至队尾
19. Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;//队列尾指针指向下一位
20. return TRUE;
21. }
22.}
23.//出队函数
24.int DeQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype *x){
25. if(Q->rear == Q->front) return FALSE;//队空,出队失败,返回0
26. else{
27. *x = Q->q[Q->front];//从队头取出元素
28. Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;//队头指针指向下一位
29. return TRUE;
30. }
31.}
32.//判断队是否为空,非空返回0,空返回1
33.int QueueEmpty(Queue Q){
34. if(Q.rear == Q.front) return TRUE;//队空
35. else return FALSE;
36.}
37.//返回队列中的最后的一个元素
38.Elemtype Last(Queue *Q){
39. Elemtype *prElem = NULL;
40. Queue *prTempQueue;
41. prTempQueue = InitQueue();//初始化一个新的临时队列,用于暂存数据
42. while(QueueEmpty(*Q) == 1){//将Q中的元素依次取出放至prTempQueue中
43. DeQueue(Q, prElem);
44. EnQueue(prTempQueue, *prElem);
45. }
46. while(QueueEmpty(*prTempQueue) == 1){//将prTempQueue中的元素依次取出放至Q中
47. DeQueue(prTempQueue, prElem);
48. EnQueue(Q, *prElem);
49. }
50. return *prElem;//返回队列中的最后的一个元素
51.}
52.//判断队是否为满,满返回1,非满返回0
53.bool QueueFull(Queue Q){
54. if(((Q.rear + 1) % MAXSIZE) == Q.front) return TRUE;//队满
55. else return FALSE;
}1.//exp1.c
2.//主程序,实现三个生产者与两个消费者问题
3.//在30s内,生产者把产品放入缓冲区,消费者从缓冲区中拿走产品,缓冲区空间定义为5,因为队列中元素最大值设为了20,所以无需考虑队列满情况。生产者在缓冲区满时必须等待,直到缓冲区有空间才继续生产;消费者在缓冲区空时必须等待,直到缓冲区中有产品才能继续读取。共有三个生产者与两个消费者线程,并将生产的商品放入队列中(商品编号从1000开始,最多放五个),根据先生产先消费的原则进行消费。
4.#include <stdio.h>
5.#include <stdlib.h>
6.#include <unistd.h>
7.#include <pthread.h>
8.#include <errno.h>
9.#include <sys/ipc.h>
10.#include <semaphore.h>
11.#include <fcntl.h>
12.#include "Queue.h"
13.#include "const.h"
14.#include "Queue.c"
15.
16.#define N 5//定义可用资源数量
17.
18.time_t end_time;
19.sem_t mutex, full, empty;
20.int fd;
21.Queue *qt;
22.Elemtype p;
23.void consumer(void *arg);
24.void productor(void *arg);
25.
26.int main(){
27. pthread_t id1, id2, id3, id4, id5;//创建5个线程,分别对应三个生产者与两个消费者
28. pthread_t mon_th_id;
29. int ret;
30. end_time = time(NULL) + 30;//程序执行30s停止
31. qt = InitQueue();//初始化队列qt
32. p.INumber = 1000;//号码从1000开始
33. ret = sem_init(&mutex, 0, 1);//初使化互斥信号量mutex为1
34. ret = sem_init(&empty, 0, N);//初使化empty信号量为N
35.
36. ret = sem_init(&full, 0, 0);//初使化full信号量为0
37. if(ret != 0) perror("sem_init");
38.
39. ret = pthread_create(&id1, NULL, (void*)productor, NULL);//生产者线程1
40. if(ret != 0) perror("pthread cread1");
41.
42. ret = pthread_create(&id3, NULL, (void*)productor, NULL);//生产者线程3
43. if(ret != 0) perror("pthread cread3");
44.
45. ret = pthread_create(&id2, NULL, (void*)consumer, NULL);//消费者线程2
46. if(ret != 0) perror("pthread cread2");
47.
48. ret = pthread_create(&id5, NULL, (void*)productor, NULL);//生产者线程5
49. if(ret != 0) perror("pthread cread5");
50.
51. ret = pthread_create(&id4, NULL, (void*)consumer, NULL);//消费者线程4
52. if(ret != 0) perror("pthread cread4");
53.
54. pthread_join(id1, NULL);//等待生产者线程1结束
55. pthread_join(id2, NULL);//等待消费者线程2结束
56. pthread_join(id3, NULL);//等待生产者线程3结束
57. pthread_join(id4, NULL);//等待消费者线程4结束
58. pthread_join(id5, NULL);//等待生产者线程5结束
59.
60. exit(0);
61.}
62.//生产者线程函数
63.void productor(void *arg){
64. int i, nwrite;
65. while(time(NULL) < end_time){//在规定时间内循环生产商品
66. sem_wait(&empty);//empty信号量P操作
67. sem_wait(&mutex);//互斥信号量P操作
68. if(TRUE == QueueFull(*qt)){//队满不操作
69. printf("Procuctor: buffer is full, please try to write later.\n");
70. }
71. else{//队不满
72. EnQueue(qt, p);//入队
73. printf("Productor: write [%d] to buffer\n",p.INumber);
74. p.INumber++;//编号加一
75. }
76. sem_post(&full);//full信号量V操作
77. sem_post(&mutex);//mutex信号量V操作
78. sleep(1);
79. }
80.}
81.
82.void consumer(void *arg){
83. int nolock = 0;
84. int ret, nread;
85. Elemtype p2;
86. while((time(NULL) < end_time) || (FALSE == (QueueEmpty(*qt)))){//在规定时间内或队列非空时,循环消费商品
87. sem_wait(&full);//full信号量P操作
88. sem_wait(&mutex);//互斥信号量P操作
89. if(TRUE == QueueEmpty(*qt)){//队列空,不能消费
90. printf("Consumer: the buffer is empty, please try to read later.\n");
91. }
92. else{//队列非空
93. DeQueue(qt, &p2);//出队
94. printf("Consumer: read [%d] from buffer.\n", p2.INumber);
95. }
96. sem_post(&empty);//empty信号量V操作
97. sem_post(&mutex);//互斥信号量V操作
98. sleep(2);
99. }
}2. 列出可改进的功能、实现方法等
可改进的功能:
- 将代码整理,去除掉了冗余代码。
- 显示缓冲区资源个数:创建全局变量n,统计生产者/消费者 生产/消费后缓冲区中剩余的资源个数,并予以显示。
- 提示生产者/消费者线程结束语句,如:Productor 1 is killed。
- 利用gettid()函数获得生产者、消费者的线程id,并显示是哪一个生产者/消费者 生产/消费 了哪一个商品。
- 编写了display()函数,根据生产者/消费者的动作,可视化了缓冲区中的商品状况,使商品变化情况更加简单直观。
- 利用for循环创建线程,实现可以自主输入想要创建的生产者与消费者个数(数值在1到10之间)、缓冲区大小(数值在1到20之间)与产品编号(数值在1到1000之间)。
- 编写了print()函数,优化了终端可视化界面,可在界面中选择功能并自定义赋值,使程序运行更灵活直观。
实现方法:
- 首先打印出终端可视化界面,让用户可以自主选择功能,可以进行自定义赋值、运行程序与退出系统操作,未进行自定义赋值的变量使用默认值。
- 自定义赋值后运行程序,根据用户的赋值给变量赋值,并创建生产者、消费者线程,运行生产者、消费者函数。
- 在生产者、消费者函数中,根据队列情况进行P、V操作与生产/消费操作,并利用gettid()函数获得生产者的线程id,显示是哪一个生产者/消费者 生产/消费了哪一件商品,并可视化生产/消费操作前后缓冲区中的产品变化情况与缓冲区中剩余的资源个数。
- 运行规定时间后生产者/消费者线程结束,退出系统。
3. 详细说明已完成的改进,附上程序代码,改进处加注释(注意代码格式)
1.//const.h
2.
3.#ifndef CONST_H
4.#define CONST_H
5.#define TRUE 1
6.#define FALSE 0
7.#define MAXSIZE 20
8.#define MAXLEN 100
#endif1.//Typedefine.h
2.
3.#ifndef TYPEDEFINE_H
4.#define TYPEDEFINE_H
5.#include "const.h"
6.
7.typedef struct{
8. char data[MAXLEN];
9. int len;
10.}SString;
11.
12.typedef struct{
13. SString* strName;
14. long INumber;
15.}Elemtype;
16.
17.typedef struct{
18. Elemtype q[MAXSIZE];
19. int front;
20. int rear;
21.}Queue;
22.
#endif1.//Queue.h
2.
3.#ifndef QUEUE_H_LY
4.#define QUEUE_H_LY
5.
6.#include "Typedefine.h"
7.#include <stdbool.h>
8.
9.Queue *InitQueue();
10.int EnQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype x);
11.int DeQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype *x);
12.int QueueEmpty(Queue Q);
13.bool QueueFull(Queue Q);
14.
#endif1.//Queue.c
2.
3.#include "stdio.h"
4.#include "malloc.h"
5.#include "const.h"
6.#include "Queue.h"
7.#include <stdbool.h>
8.
9.Queue *InitQueue(){
10. Queue *Q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
11. Q->front = Q->rear = 0;
12. return Q;
13.}
14.
15.int EnQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype x){
16. if((Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == Q->front) return FALSE;
17. else{
18. Q->q[Q->rear] = x;
19. Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
20. return TRUE;
21. }
22.}
23.
24.int DeQueue(Queue *Q, Elemtype *x){
25. if(Q->rear == Q->front) return FALSE;
26. else{
27. *x = Q->q[Q->front];
28. Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
29. return TRUE;
30. }
31.}
32.
33.int QueueEmpty(Queue Q){
34. if(Q.rear == Q.front) return TRUE;
35. else return FALSE;
36.}
37.
38.bool QueueFull(Queue Q){
39. if(((Q.rear + 1) % MAXSIZE) == Q.front) return TRUE;
40. else return FALSE;
}1.//exp1.c
2.
3.#include <stdio.h>
4.#include <stdlib.h>
5.#include <unistd.h>
6.#include <pthread.h>
7.#include <errno.h>
8.#include <sys/ipc.h>
9.#include <semaphore.h>
10.#include <fcntl.h>
11.#include "Queue.h"
12.#include "const.h"
13.#include "Queue.c"
14.#include <sys/syscall.h>//使用gettid()函数所需要的头文件
15.#define gettid() syscall(__NR_gettid)//使用gettid()函数所需要的头文件
16.#include <string.h>
17.
18.time_t end_time;
19.sem_t mutex, full, empty;
20.Queue *qt;
21.Elemtype p;
22.int n = 0;//缓冲区中资源个数
23.int x = 2, y = 2;//生产者与消费者个数(默认值)
24.int ret;
25.int N = 5;//缓冲区最大资源个数(默认值)
26.
27.void consumer(void *arg);
28.void productor(void *arg);
29.void display();//可视化缓冲区中商品状况
30.void print();//终端可视化界面
31.
32.int main(){
33. p.INumber = 1;//产品初始编号(默认值)
34. while(1){
35. print();//展示系统可视化选项
36. //接收用户需要的功能号
37. char number[100];
38. ret = scanf("%s", &number[0]);
39. if(strlen(number)!=1 || ret != 1 || number[0] < '0' || number[0] > '5'){
40. printf("\nplease input a number between 0 and 5!\n");
41. continue;
42. }
43. int num = number[0] - '0';
44. //输入想要创建的生产者个数,并确保数值在1到10之间
45. if(num == 1){
46. do{
47. printf("Please input the number of productor: ");
48. ret = scanf("%d",&x);
49. if(ret != 1 || x < 1 || x > 10){
50. printf("Please ensure the input between 1 and 10\n");
51. }
52. }while(ret != 1 || x < 1 || x > 10);
53. }
54. //输入想要创建的消费者个数,并确保数值在1到10之间
55. else if(num == 2){
56. do{
57. printf("Please input the number of consumer: ");
58. ret = scanf("%d",&y);
59. if(ret != 1 || y < 1 || y > 10){
60. printf("Please ensure the input between 1 and 10\n");
61. }
62. }while(ret != 1 || y < 1 || y > 10);
63. }
64. //输入想要创建的缓冲区大小,并确保数值在1到20之间
65. else if(num == 3){
66. do{
67. printf("Please input the size of buffer: ");
68. ret = scanf("%d",&N);
69. if(ret != 1 || N < 1 || N > 20){
70. printf("Please ensure the input between 1 and 20\n");
71. }
72. }while(ret != 1 || N < 1 || N > 20);
73. }
74. //输入想要生产的产品的初始编号,并确保数值在1到1000之间
75. else if(num == 4){
76. do{
77. printf("Please input the key of product: ");
78. ret = scanf("%d",&p.INumber);
79. if(ret != 1 || p.INumber < 1 || p.INumber > 1000){
80. printf("Please ensure the input between 1 and 1000\n");
81. }
82. }while(ret != 1 || p.INumber < 1 || p.INumber > 1000);
83. }
84. //运行程序
85. else if(num == 5){
86. pthread_t id;
87. end_time = time(NULL) + 10;
88. qt = InitQueue();
89. //p.INumber = 1000;
90. ret = sem_init(&mutex, 0, 1);
91. ret = sem_init(&empty, 0, N);
92.
93. ret = sem_init(&full, 0, 0);
94. if(ret != 0) perror("sem_init");
95. //创建线程
96. for(int i = 0; i < x; i++){
97. ret = pthread_create(&id, NULL, (void*)productor, NULL);
98. if(ret != 0) perror("Productor pthread create");
99. }
100.
101. for(int i = x; i < x + y; i++){
102. ret = pthread_create(&id, NULL, (void*)consumer, NULL);
103. if(ret != 0) perror("Consumer pthread create");
104. }
105. //等待线程结束
106. for(int i = 0; i < x; i++){
107. pthread_join(id, NULL);
108. printf("Productor %d is killed\n", i);//提示程序结束语句
109. }
110. for(int i = x; i < x + y; i++){
111. pthread_join(id, NULL);
112. printf("Consumer %d is killed\n", i);//提示程序结束语句
113. }
114. break;
115. }
116. //退出系统
117. else if(num == 0){
118. break;
119. }
120. }
121. return 0;
122.}
123.
124.void productor(void *arg){
125. while(time(NULL) < end_time){
126. sem_wait(&empty);
127. sem_wait(&mutex);
128. if(TRUE == QueueFull(*qt)){
129. printf("Productor pthread %u: buffer is full, please try to write later.\n", gettid());
130. }
131. else{
132. EnQueue(qt, p);
133. display();//可视化缓冲区
134. n++;//缓冲区资源数加一
135. printf("------->");
136. display();//可视化缓冲区
137. printf("\n");
138. printf("Productor pthread %u: write [%d] to buffer.\n", gettid(), p.INumber);//利用gettid()函数获得生产者的线程id,并显示是哪一个生产者生产了哪一件商品
139. printf("There are %d left in buffer\n",n);//显示缓冲区中剩余的资源个数
140. printf("--------------------------------------------------\n");//生产者/消费者动作分隔符
141. p.INumber++;
142. }
143. sem_post(&full);
144. sem_post(&mutex);
145. sleep(1);
146. }
147.}
148.
149.void consumer(void *arg){
150. Elemtype p2;
151. while((time(NULL) < end_time) || (FALSE == (QueueEmpty(*qt)))){
152. sem_wait(&full);
153. sem_wait(&mutex);
154. if(TRUE == QueueEmpty(*qt)){
155. printf("Consumer pthread %u: the buffer is empty, please try to read later.\n", gettid());
156. }
157. else{
158. DeQueue(qt, &p2);
159. display();//可视化缓冲区
160. n--;//缓冲区资源数减一
161. printf("------->");
162. display();//可视化缓冲区
163. printf("\n");
164. printf("Consumer pthread %u: read [%d] from buffer.\n", gettid(), p2.INumber);//利用gettid()函数获得消费者的线程id,并显示是哪一个消费者消费了哪一件商品
165. printf("There are %d left in buffer\n",n);//显示缓冲区中剩余的资源个数
166. printf("--------------------------------------------------\n");//生产者/消费者动作分隔符
167. }
168. sem_post(&empty);
169. sem_post(&mutex);
170. sleep(2);
171. }
172.}
173.//可视化缓冲区中的商品状况
174.void display(){
175. printf("[");
176. for(int i = n; i > 0; i--){
177. printf(" P ");
178. }
179. printf("]");
180.}
181.//终端可视化界面
182.void print()
183.{
184. printf("\n");
185. printf("*********************************************************************************\n");
186. printf("--------------------[ Producer Consumer Program Function Bar ]-------------------\n");
187. printf("*********************************************************************************\n");
188. printf("* 1.Enter the number of producers you want to create (default value is 2) *\n");
189. printf("* 2.Enter the number of consumers you want to create (default value is 2) *\n");
190. printf("* 3.Enter the buffer size you want to create (default value is 5) *\n");
191. printf("* 4.Enter the initial product number you want to produce (default value is 1) *\n");
192. printf("* 5.run the program *\n");
193. printf("* 0.Exit the system *\n");
194. printf("---------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
195. printf("Please enter 0-5 to select a function: ");
}4. 运行结果截图
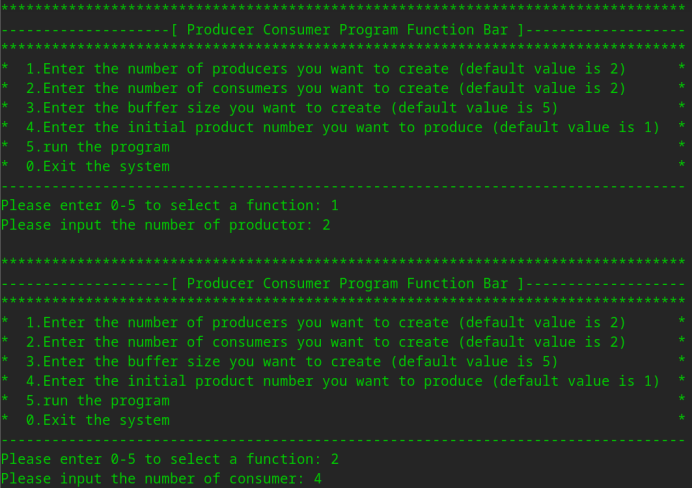
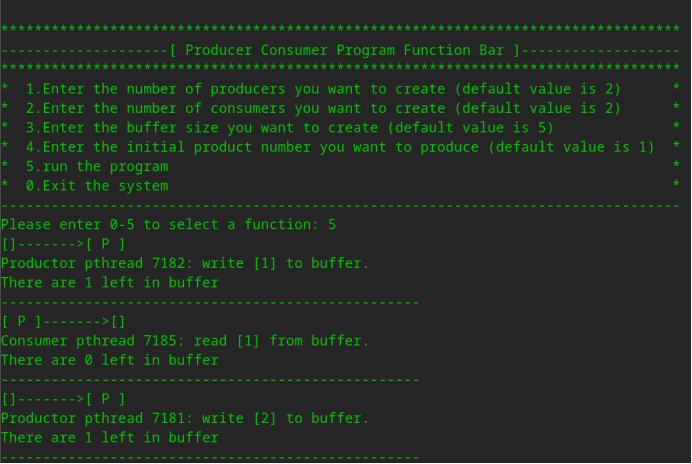
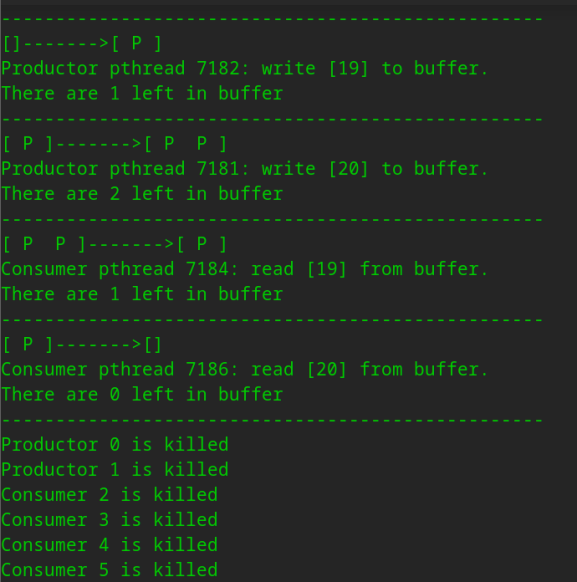
(1)示例一,这次运行我们想将生产者改为2个,消费者改为4个,其余选项为默认值,运行程序。
中间略
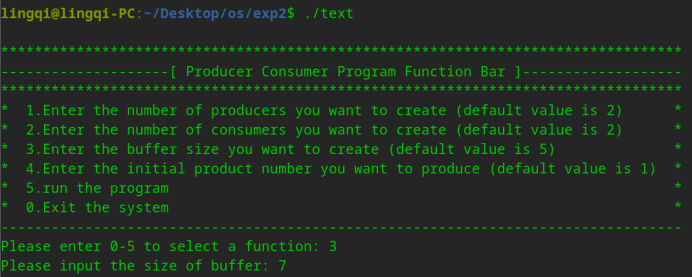
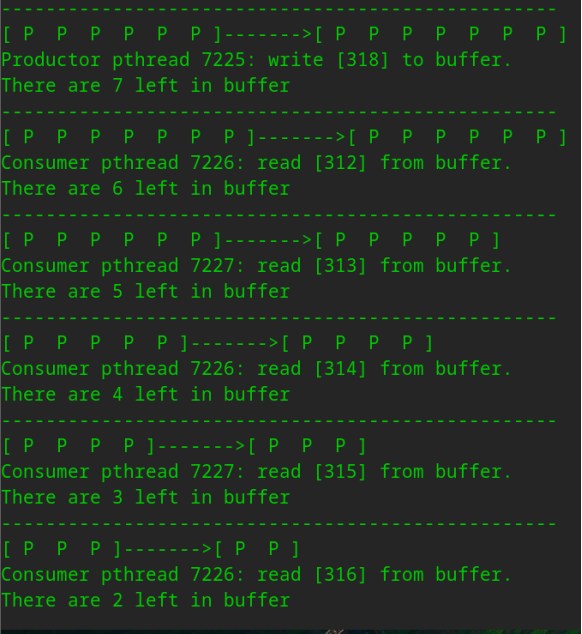
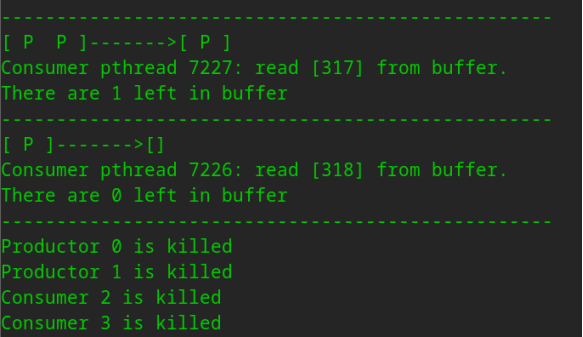
(2)示例二,这次运行我们想将缓冲区大小改为7,商品初始编号改为300,其余选项为默认值,运行程序。
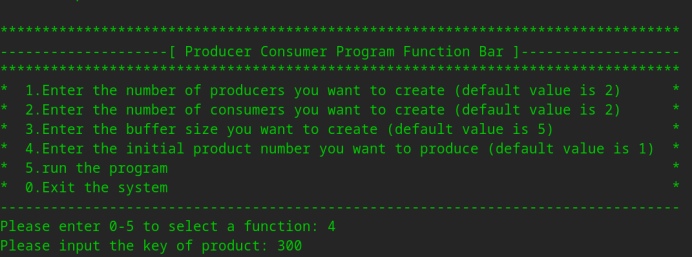
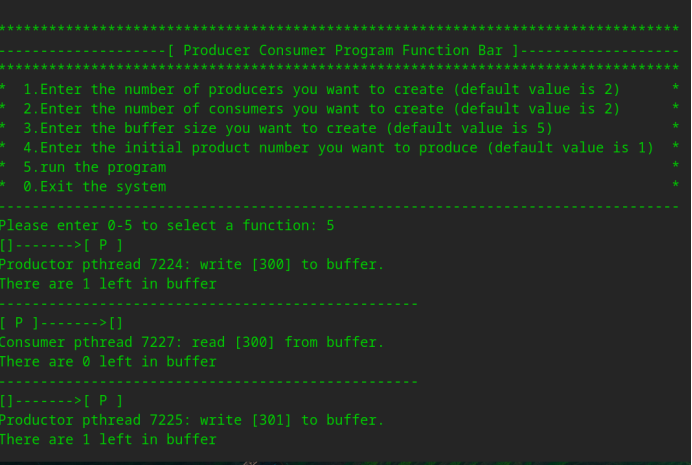
中间略
5. 总结
实验中遇到的问题与解决方法:
问题1:想要改进程序执行语句,使程序运行时能反映出具体是哪一位生产者/消费者 生产/消费 了哪一个商品。一开始我尝试在pthread_create()函数中给生产者/消费者函数传递生产者/消费者id变量,但是由于线程共享变量,无法在生产者-生产者、消费者-消费者之间作出区分。
解决方法:最终我决定使用gettid()函数获得生产者、消费者的线程id,作为每一位生产者/消费者的标志,来反映出具体是哪一位生产者/消费者 生产/消费 了商品。
问题2:在程序运行过程中,缓冲区中的产品变化并不能被很好的反映出来。
解决方法:我编写了display()函数,分别在生产/消费前后调用它,可视化了缓冲区中的商品状况。
问题3:程序不够灵活,并且界面对用户不够友好。想要实现用户能够简单自主地控制想要创建的生产者与消费者个数、缓冲区大小与产品编号。
解决方法:我使用了全局变量,在程序执行之初定义好默认值,并提供了与用户交互的接口,使用户能够自主改变程序运行的参数。编写了print()函数,优化了终端可视化界面,使用户能够自主选择想要改变何种参数,使程序运行更灵活直观。
相关文章:

【操作系统】操作系统实验02-生产者消费者程序改进
1. 说明文档中原有程序实现的功能、实现方法。(用语言、程序流程图、为原有程序添加注释等方式均可) 1.//const.h 2.//定义宏变量 3.#ifndef CONST_H 4.#define CONST_H 5. 6.#define TRUE 1 7.#define FALSE 0 8.#define ERROR 0 9.#define OVERFLOW -…...

TCP协议是安全的吗?
不安全 虽然 TCP 提供了一种可靠且高效的数据传输方式,但它不提供任何加密或身份验证机制来保护数据。因此,传输的数据可能会被未经授权的用户拦截和读取,而且其真实性无法验证。 因此,为了确保 TCP 通信的安全,必须…...
c语言回顾-结构体(2)
前言 前面讲了结构体的概念,定义,赋值,访问等知识,本节内容小编将讲解结构体的内存大小的计算以及通过结构体实现位段,话不多说,直接上干货!!! 1.结构体内存对齐 说到计…...
Prometheus常见exporter安装部署
Prometheus常见exporter安装部署 在稳定性环境的监控当中需要收集各种各样的数据,这样的数据收集是通过各种exporter进行的,在这里我们进行最常用稳定性数据的收集exporter安装部署介绍。 node_exporter安装部署 node_exporter主要监控服务器本身的一…...
DGit的使用
将Remix连接到远程Git仓库 1.指定克隆的分支和深度 2.清理,如果您不在工作区上工作,请将其删除或推送至 GitHub 或 IPFS 以确保安全。 为了进行推送和拉取,你需要一个 PAT — 个人访问令牌 当使用 dGIT 插件在 GitHub 上推送、拉取、访问私…...
ElasticSearch学习篇13_《检索技术核心20讲》进阶篇之LSM树
背景 学习极客实践课程《检索技术核心20讲》https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/215243,文档形式记录笔记。 内容 磁盘和内存数据读取特点 工业界中数据量往往很庞大,比如数据无法全部加载进内存,无法支持索引的高效实时更新&…...
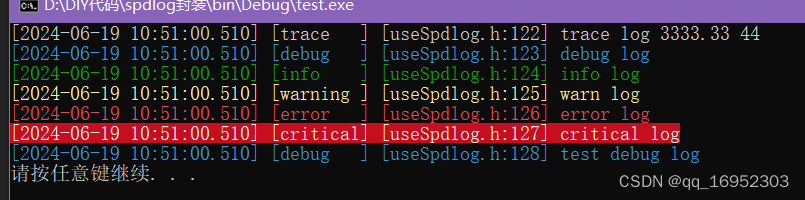
简单好用的C++日志库spdlog使用示例
文章目录 前言一、spdlog的日志风格fmt风格printf风格 二、日志格式pattern三、sink,多端写入四、异步写入五、注意事项六、自己封装了的代码usespdlog.h封装代码解释使用示例 前言 C日志库有很多,glog,log4cpp,easylogging, eas…...

python 方法运行计时装饰模式实现
在代码开发过程中,需要记录方法的执行时间,每个方法都硬代码也可以实现,但是不是最好的方式,考虑到设计模式和模版代码,通过装饰模式实现方法运行计时 在Python中,装饰器可以接受参数,这样可以…...

【权威出版/投稿优惠】2024年水利水电与能源环境科学国际会议(WRHEES 2024)
2024 International Conference on Water Resources, Hydropower, Energy and Environmental Science 2024年水利水电与能源环境科学国际会议 【会议信息】 会议简称:WRHEES 2024 大会时间:点击查看 截稿时间:点击查看 大会地点:…...

阿赵UE引擎C++编程学习笔记——场景加载和切换
大家好,我是阿赵。 继续学习UE引擎,这次来学习一下切换和加载场景的各种做法。 一、 蓝图实现 1、 切换关卡 所谓切换关卡,就是从当前关卡进入到一个新的关卡, 旧关卡的数据将会被放弃。进入新的关卡后,将会执行…...
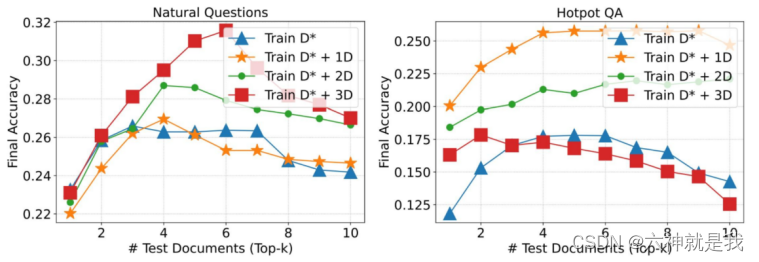
【LLM之RAG】RAFT论文阅读笔记
研究背景 论文针对的主要问题是如何将预训练的大型语言模型(LLMs)适应特定领域的检索增强生成(RAG)。这些模型通常在广泛的文本数据上进行预训练,已经表现出在广义知识推理任务上的优越性能。然而,在特定领…...
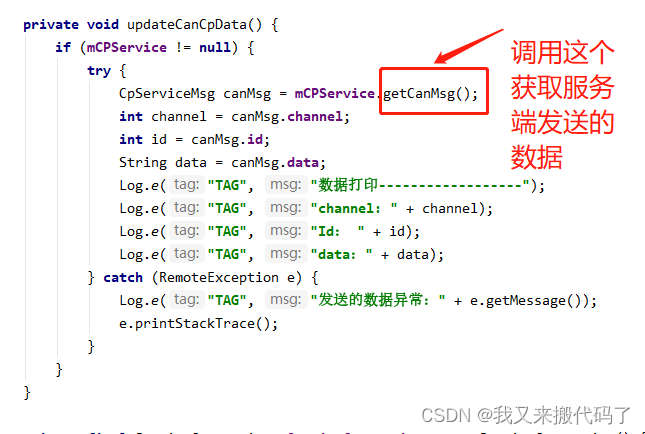
【Android】使用Binder(AIDL)实现利用自定义Bean进行的进程间通信(二)
项目前置 这是我之前写的关于Binder的一些知识点和使用基本数据类型在通信的文章,感兴趣的可以看一下: Binder(一)Binder的介绍和AIDL使用Binder的实例 项目目标 在两个APP之间进行数据传递,使用Android推荐的Binder通讯&#…...

HTTP中get与post的区别?在传输数据类型上有什么区别?【面试】
HTTP中的GET和POST是两种最常见的请求方法,它们在数据传输和使用场景上有一些关键的区别: GET请求: 数据传输方式:GET请求将数据附加在URL之后,形成查询字符串(namevalue的形式),数…...

「51媒体-年中大促」天津有哪些媒体资源-媒体宣传服务公司
传媒如春雨,润物细无声,大家好,我是51媒体网胡老师。 天津的媒体资源相当丰富,涵盖了报纸、电视、广播、新闻门户网站、央媒驻天津机构、视频媒体以及全国媒体资源等多个方面。以下是详细的媒体资源分类和具体信息: 一…...
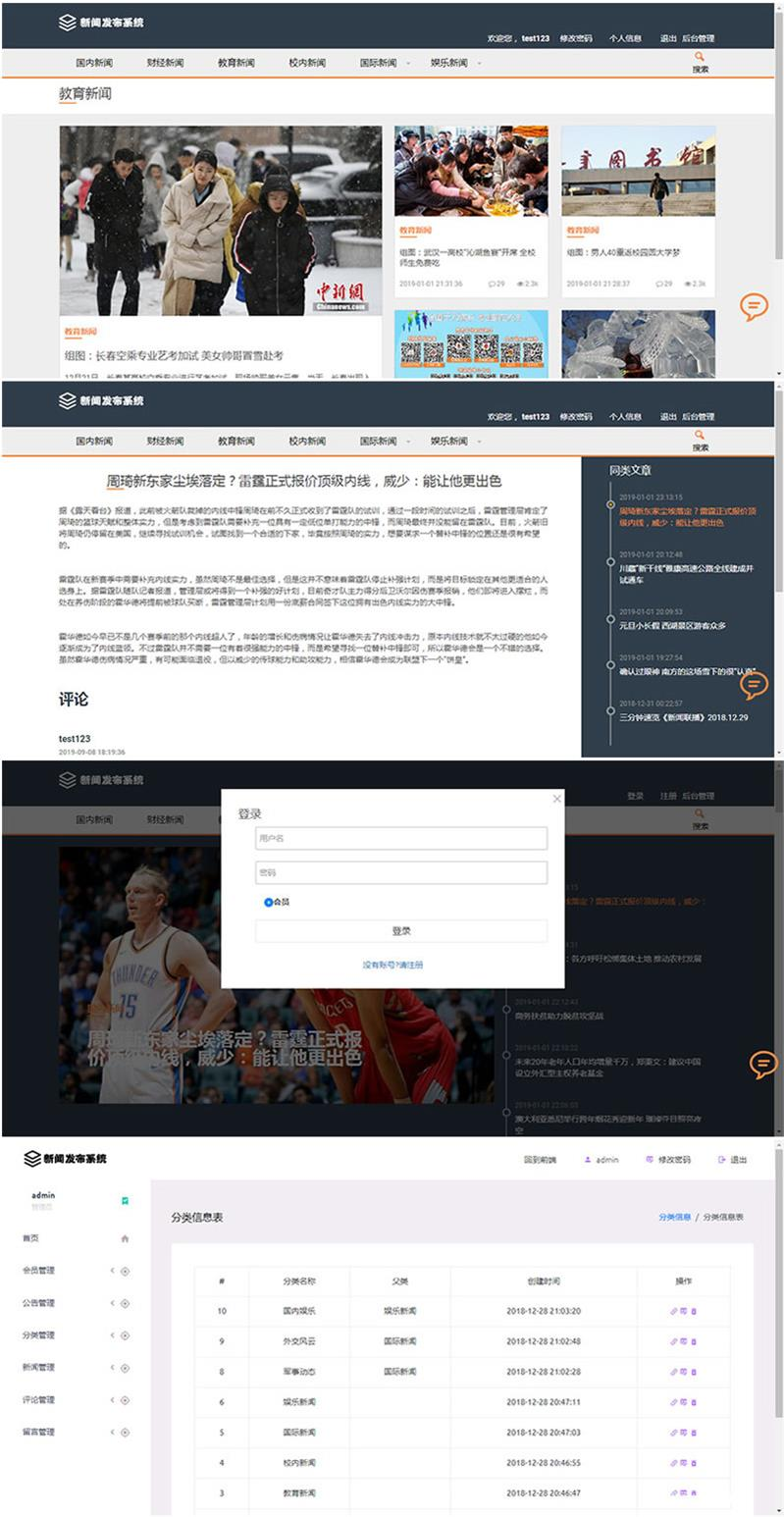
Thinkphp校园新闻发布系统源码 毕业设计项目实例
Thinkphp校园新闻发布系统源码 毕业设计项目实例 校园新闻发布系统模块: 用户模块:注册,登陆,查看个人信息,修改个人信息,站内搜索,新闻浏览等功能, 后台管理员模块:会员…...

前端老古董execCommand——操作 选中文本 样式
文章目录 ⭐前言⭐exe command api用法💖 example示例💖 测试效果 ⭐execommand和getSelection 的联系⭐总结⭐结束 ⭐前言 大家好,我是yma16,本文分享关于 前端老古董execCommand——操作选中文本。 execommand 当一个 HTML 文…...

elementui写一个自定义的rangeInput的组件
组件定义 使用el-row确保元素都在一行上对外暴露的prop是minValue和maxValue,但是不建议直接使用,使用计算属性minValueComputed和maxValueComputed更改计算属性的值的不要直接更改计算属性,也不要直接更改原本的prop,通知外层的父…...

护眼灯哪些牌子好?一文刨析护眼灯怎么选择!
护眼灯哪些牌子好?护眼台灯作为对抗视力挑战的一种方法,逐渐赢得了众多家长的青睐。这些台灯利用尖端光学技术,发出柔和且无刺激的照明,有助于保护眼睛不受伤害。它们不但可以调节亮度和色温,打造一个舒适且自然的阅读…...

抖音短剧看剧系统是怎么做的?怎么样搭建上线运营?
前言: 当前热门短剧已深入大家的日常,针对一些好的短剧更是吸金无数。今天给大家介绍一下短剧这个项目整个运作模式。 一、一部短剧是怎么样呈现到观众眼前的? 首先影视作品公司拍摄剪辑好短剧 ,弄好一切审核后,放到…...

2024.06.06校招 实习 内推 面经
绿*泡*泡VX: neituijunsir 交流*裙 ,内推/实习/校招汇总表格 1、校招 | 追觅科技2025届校园招聘/正式启动! 校招 | 追觅科技2025届校园招聘正式启动! 2、校招&实习&社招 | 博世海外招聘—德国/专场正式启动࿰…...

地震勘探——干扰波识别、井中地震时距曲线特点
目录 干扰波识别反射波地震勘探的干扰波 井中地震时距曲线特点 干扰波识别 有效波:可以用来解决所提出的地质任务的波;干扰波:所有妨碍辨认、追踪有效波的其他波。 地震勘探中,有效波和干扰波是相对的。例如,在反射波…...

在HarmonyOS ArkTS ArkUI-X 5.0及以上版本中,手势开发全攻略:
在 HarmonyOS 应用开发中,手势交互是连接用户与设备的核心纽带。ArkTS 框架提供了丰富的手势处理能力,既支持点击、长按、拖拽等基础单一手势的精细控制,也能通过多种绑定策略解决父子组件的手势竞争问题。本文将结合官方开发文档,…...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...

智能仓储的未来:自动化、AI与数据分析如何重塑物流中心
当仓库学会“思考”,物流的终极形态正在诞生 想象这样的场景: 凌晨3点,某物流中心灯火通明却空无一人。AGV机器人集群根据实时订单动态规划路径;AI视觉系统在0.1秒内扫描包裹信息;数字孪生平台正模拟次日峰值流量压力…...
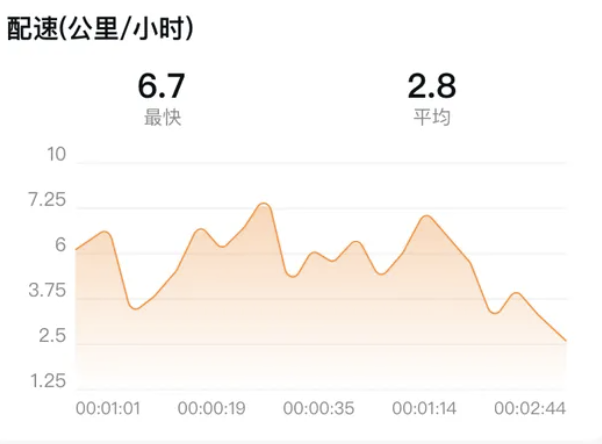
HarmonyOS运动开发:如何用mpchart绘制运动配速图表
##鸿蒙核心技术##运动开发##Sensor Service Kit(传感器服务)# 前言 在运动类应用中,运动数据的可视化是提升用户体验的重要环节。通过直观的图表展示运动过程中的关键数据,如配速、距离、卡路里消耗等,用户可以更清晰…...

华为OD机考-机房布局
import java.util.*;public class DemoTest5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in new Scanner(System.in);// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseSystem.out.println(solve(in.nextLine()));}}priv…...
mac 安装homebrew (nvm 及git)
mac 安装nvm 及git 万恶之源 mac 安装这些东西离不开Xcode。及homebrew 一、先说安装git步骤 通用: 方法一:使用 Homebrew 安装 Git(推荐) 步骤如下:打开终端(Terminal.app) 1.安装 Homebrew…...
免费数学几何作图web平台
光锐软件免费数学工具,maths,数学制图,数学作图,几何作图,几何,AR开发,AR教育,增强现实,软件公司,XR,MR,VR,虚拟仿真,虚拟现实,混合现实,教育科技产品,职业模拟培训,高保真VR场景,结构互动课件,元宇宙http://xaglare.c…...
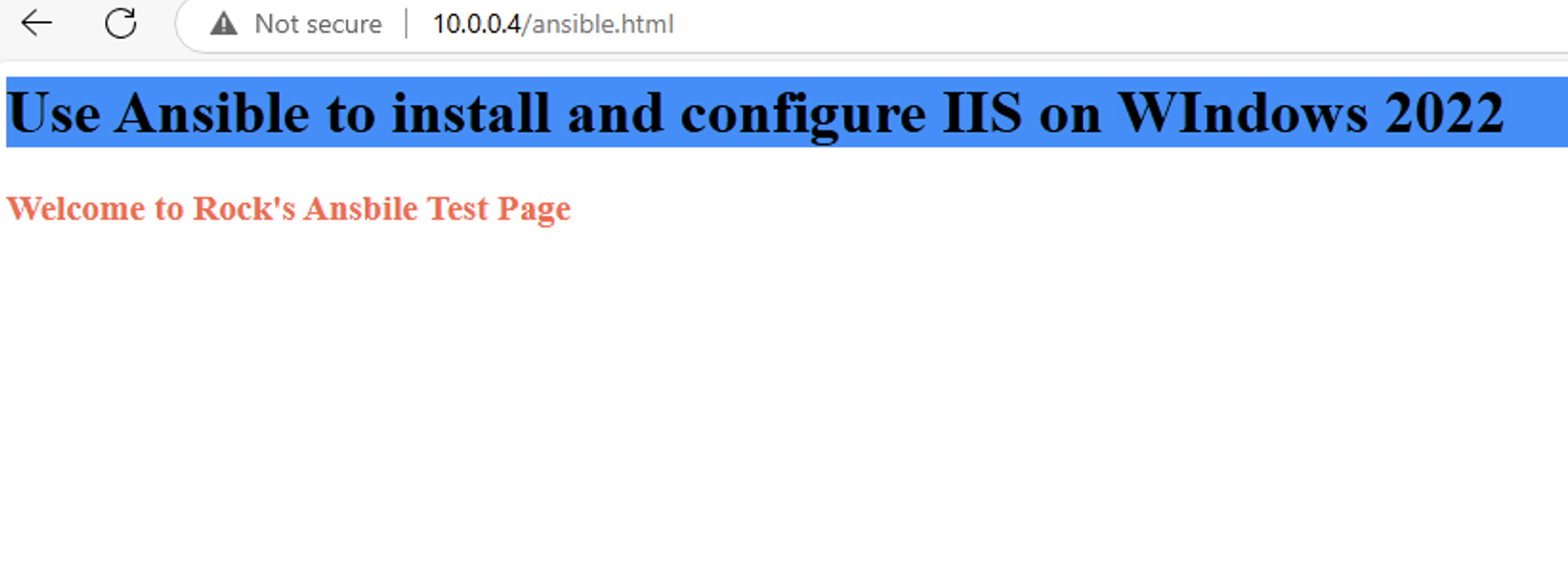
通过 Ansible 在 Windows 2022 上安装 IIS Web 服务器
拓扑结构 这是一个用于通过 Ansible 部署 IIS Web 服务器的实验室拓扑。 前提条件: 在被管理的节点上安装WinRm 准备一张自签名的证书 开放防火墙入站tcp 5985 5986端口 准备自签名证书 PS C:\Users\azureuser> $cert New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName &…...
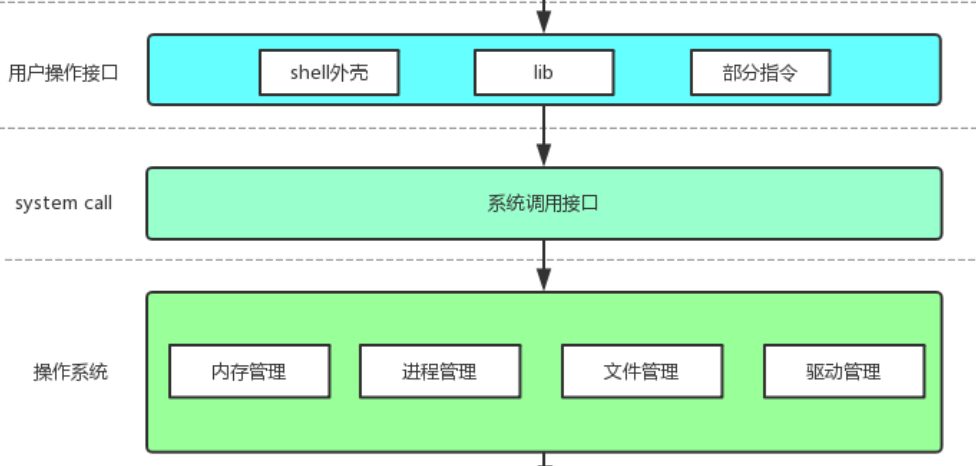
【Linux手册】探秘系统世界:从用户交互到硬件底层的全链路工作之旅
目录 前言 操作系统与驱动程序 是什么,为什么 怎么做 system call 用户操作接口 总结 前言 日常生活中,我们在使用电子设备时,我们所输入执行的每一条指令最终大多都会作用到硬件上,比如下载一款软件最终会下载到硬盘上&am…...
