并发编程---阻塞队列(五)
阻塞队列
- 一 阻塞队列
- 1.1.阻塞队列概念
- 1.2.阻塞队列API案例
- 1.2.1. ArrayBlockingQueue
- 1.2.1.1.抛出异常
- 1.2.1.2.返回布尔
- 1.2.1.3.阻塞
- 1.2.1.4.超时
- 1.2.2.SynchronousQueue
- 二 阻塞队列应用---生产者消费者
- 2.1.传统模式
- 案例代码
- 结果
- 案例问题---防止虚假唤醒
- 2.2.⽣产者消费者防⽌虚假唤醒
- 2.2.1 新版⽣产者消费者写法 ReentrantLock.Condition
- 案例代码
- 2.2.2精准通知顺序访问
- 案例代码
- 2.3.Synchronized和Lock的区别
- 2.4. 阻塞队列模式⽣产者消费者
- 案例代码
一 阻塞队列
1.1.阻塞队列概念
概念:
- 在多线程领域:所谓阻塞,在某些情况下会挂起线程(即阻塞),⼀旦条件满⾜,被挂起的线程⼜ 会⾃动被唤醒。
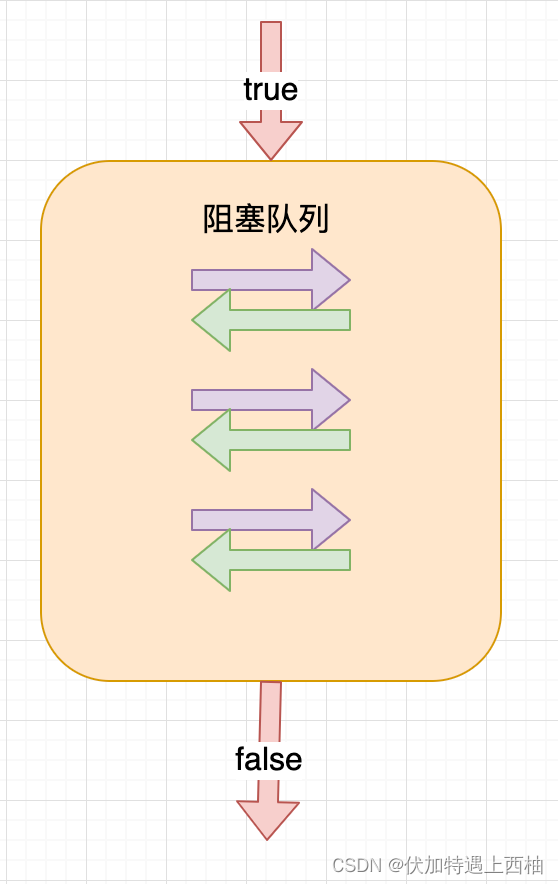
- 阻塞队列 是⼀个队列,在数据结构中起的作⽤如下图:
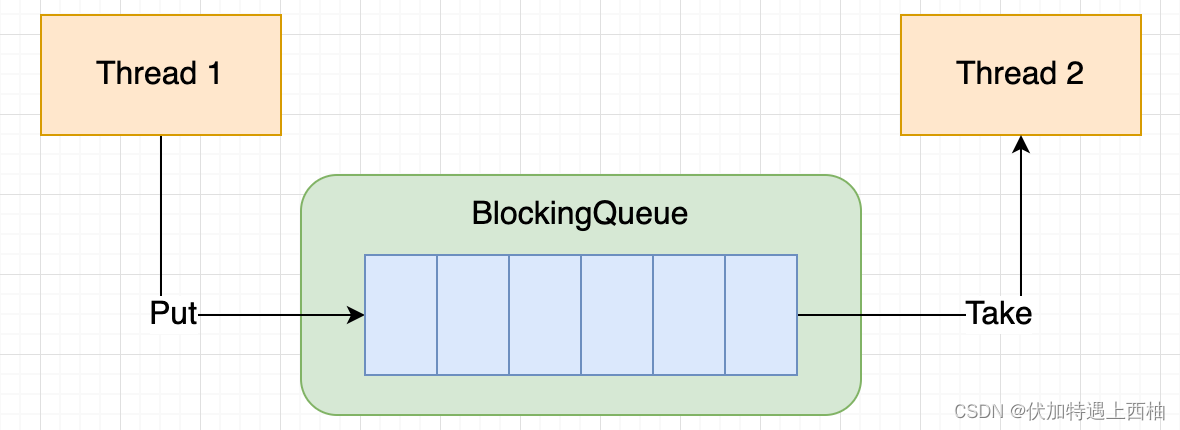
当队列是空的,从队列中获取(Take)元素的操作将会被阻塞
当队列是满的,从队列中添加(Put)元素的操作将会被阻塞
试图中空的队列中获取元素的线程将会被阻塞,直到其他线程往空的队列插⼊新的元素
试图向已满的队列中添加新元素的线程将会被阻塞,直到其他线程从队列中移除⼀个或多个元素 或者完全清空,使队列变得空闲起来后并后续新增
好处:阻塞队列不⽤⼿动控制什么时候该被阻塞,什么时候该被唤醒,简化了操作。
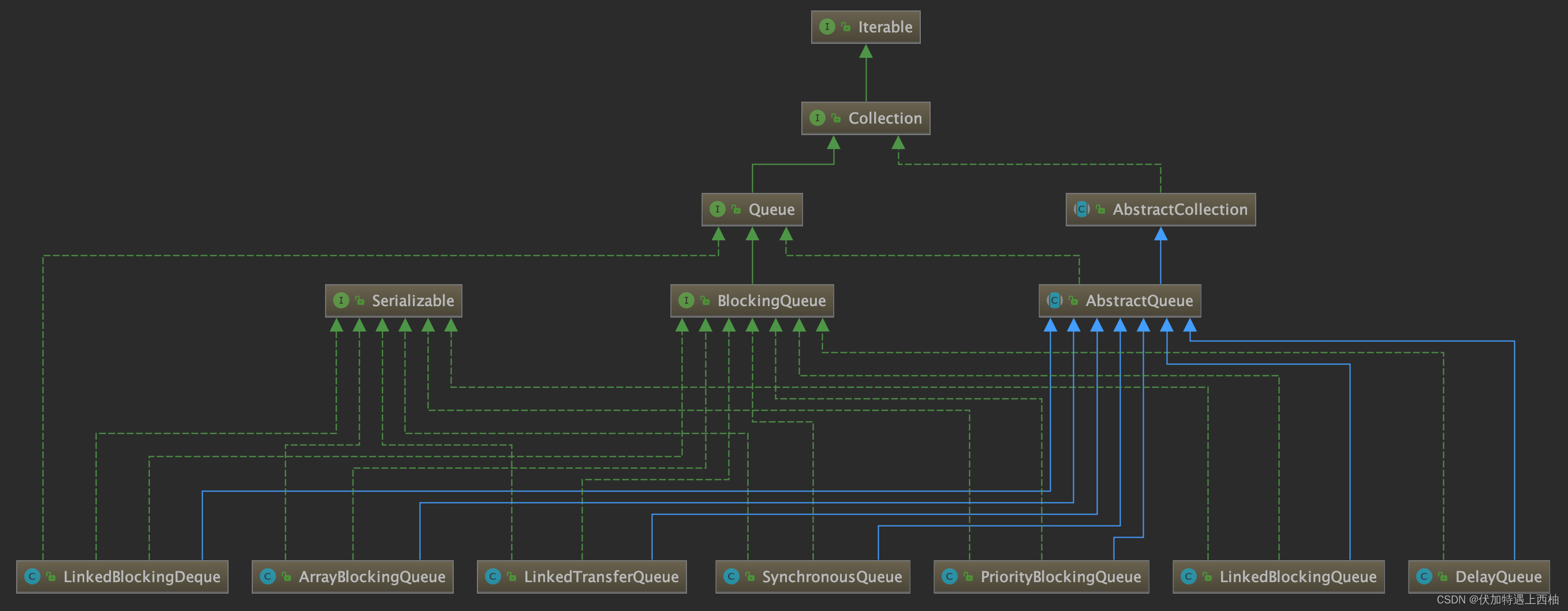
体系: Collection→ Queue→ BlockingQueue→七个阻塞队列实现类。
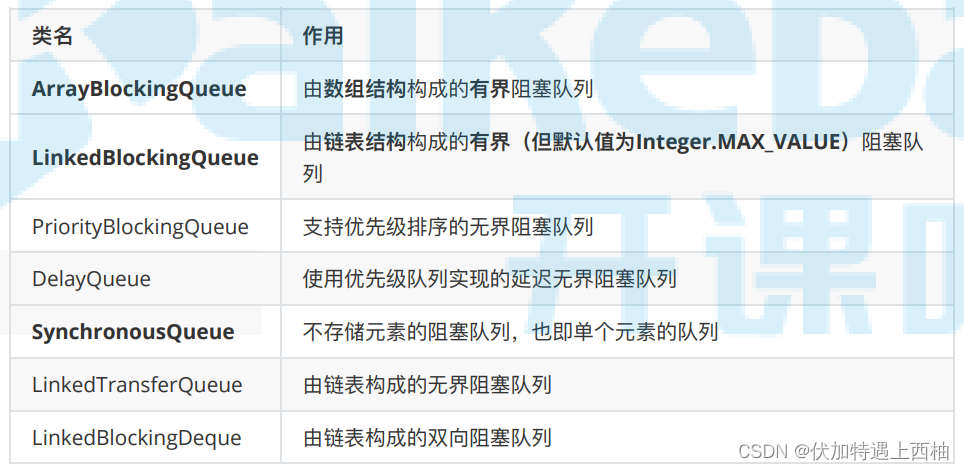
粗体标记的三个⽤得⽐较多,许多消息中间件底层就是⽤它们实现的。
需要注意的是 LinkedBlockingQueue 虽然是有界的,但有个巨坑,其默认⼤⼩是 Integer.MAX_VALUE ,⾼达21亿,⼀般情况下内存早爆了(在线程池的 ThreadPoolExecutor 有体现)。
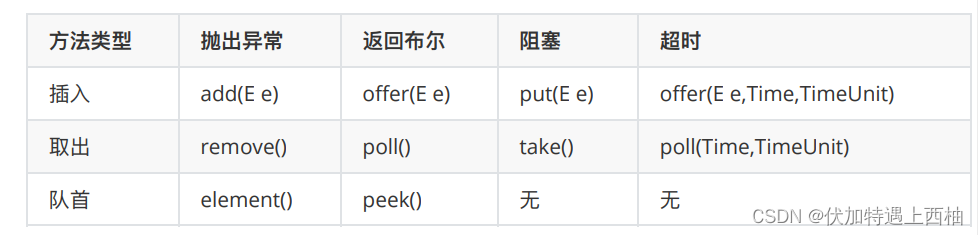
API:
抛出异常是指: 当队列满时,再次插⼊会抛出异常;
返回布尔是指:当队列满时,再次插⼊会返回false;
阻塞是指:当队列满时,再次插⼊会被阻塞,直到队列取出⼀个元素,才能插⼊。
超时是指:当⼀个时限过后,才会插⼊或者取出。
1.2.阻塞队列API案例
1.2.1. ArrayBlockingQueue
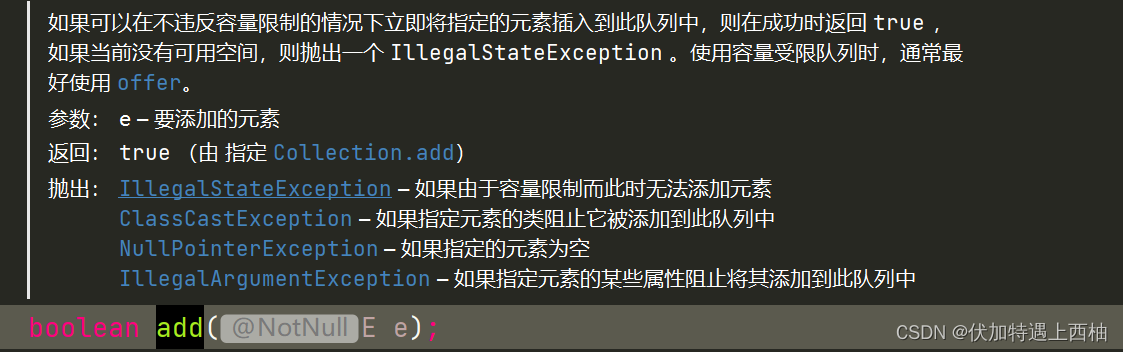
1.2.1.1.抛出异常

代码
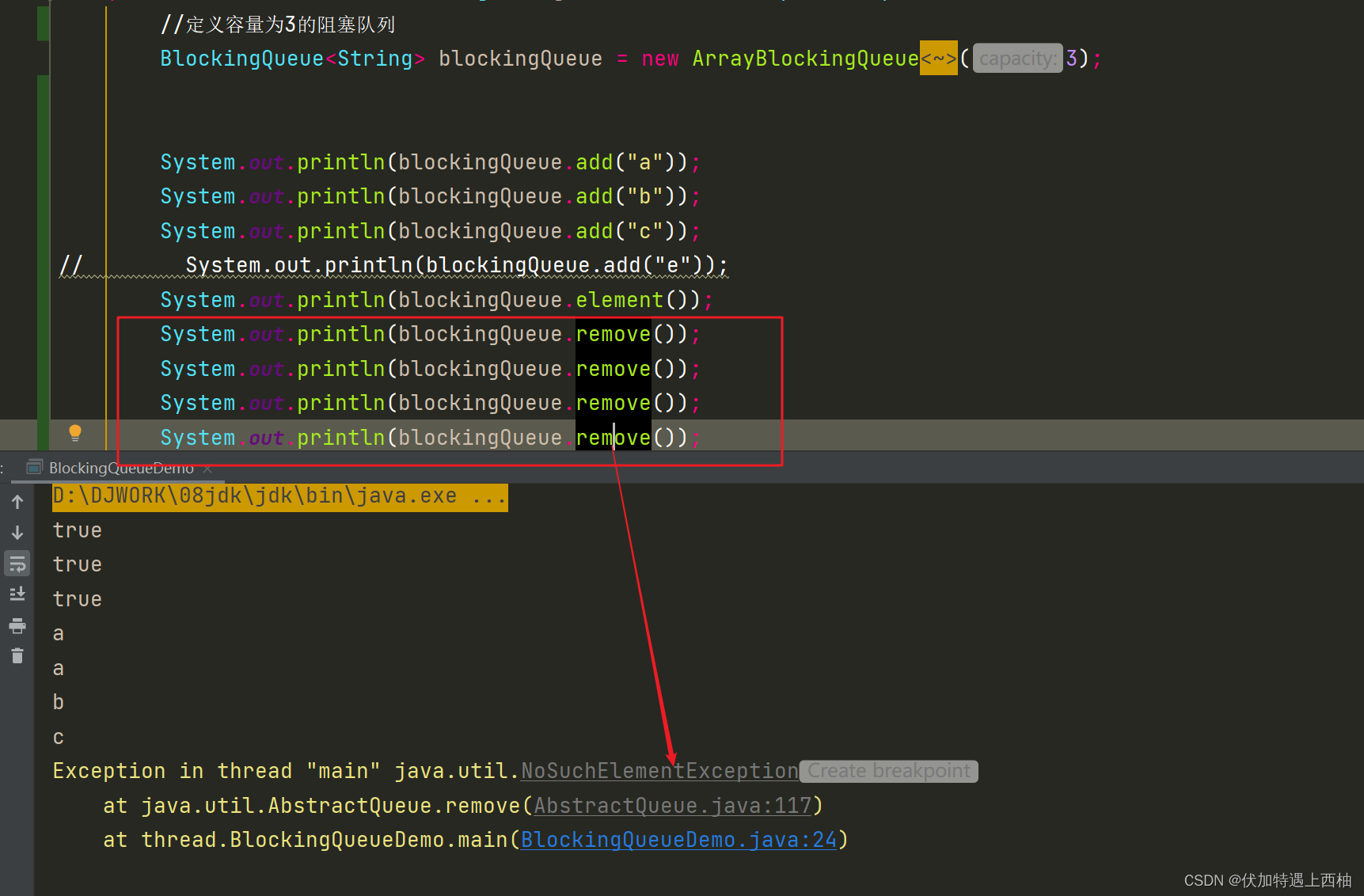
public class BlockingQueueDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//定义容量为3的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3);System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("e"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.element());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());}
结果分析
- 当添加四个元素时抛出
IllegalStateException: Queue full

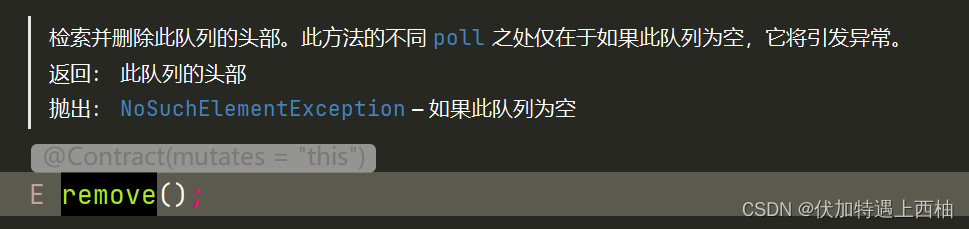
- 当取出四个元素时抛出
NoSuchElementException
1.2.1.2.返回布尔
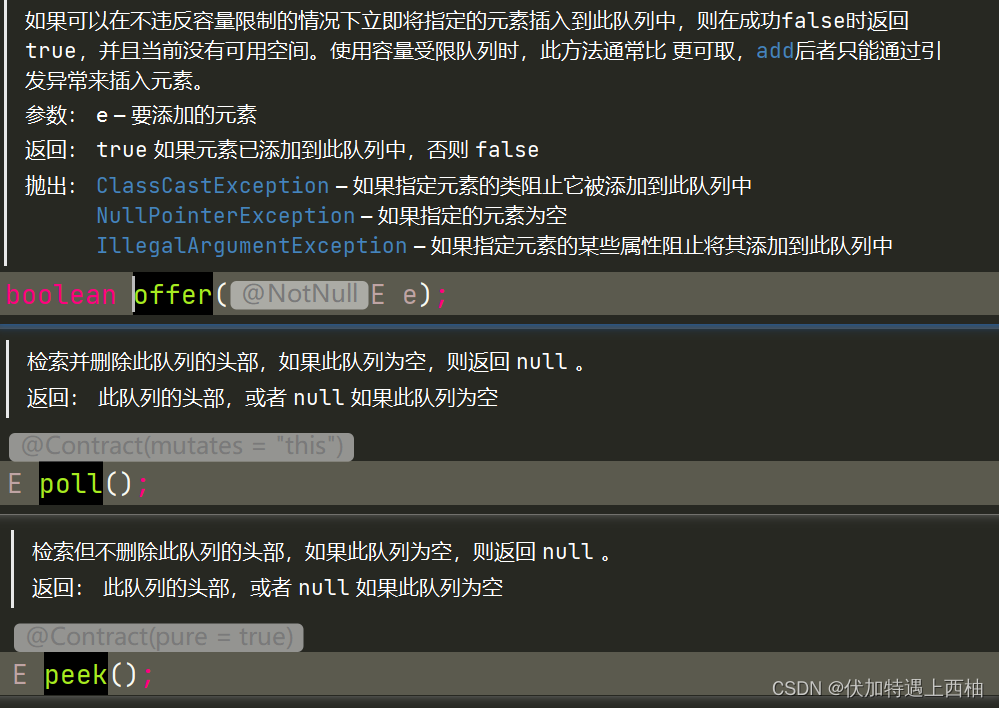
代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//定义容量为3的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3);System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("e"));System.out.println(blockingQueue.peek());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());}结果

1.2.1.3.阻塞
代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//定义容量为3的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3);blockingQueue.put("a");blockingQueue.put("b");blockingQueue.put("c");blockingQueue.put("d");System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());}结果
- 存储是容量已满
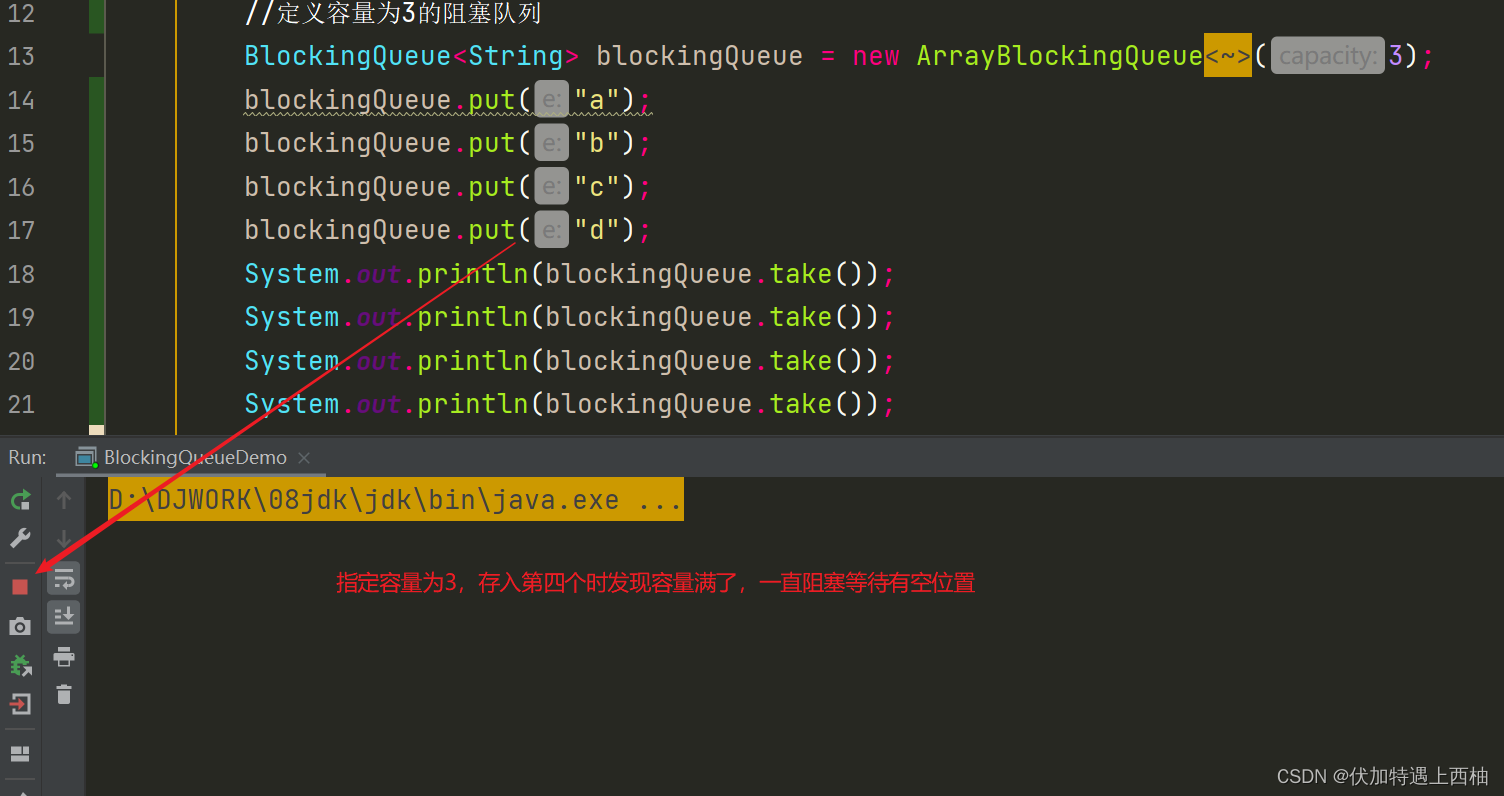
- 取得时候队列为空也会阻塞

1.2.1.4.超时
代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//定义容量为3的阻塞队列BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<String>(3);System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a",2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));}
结果
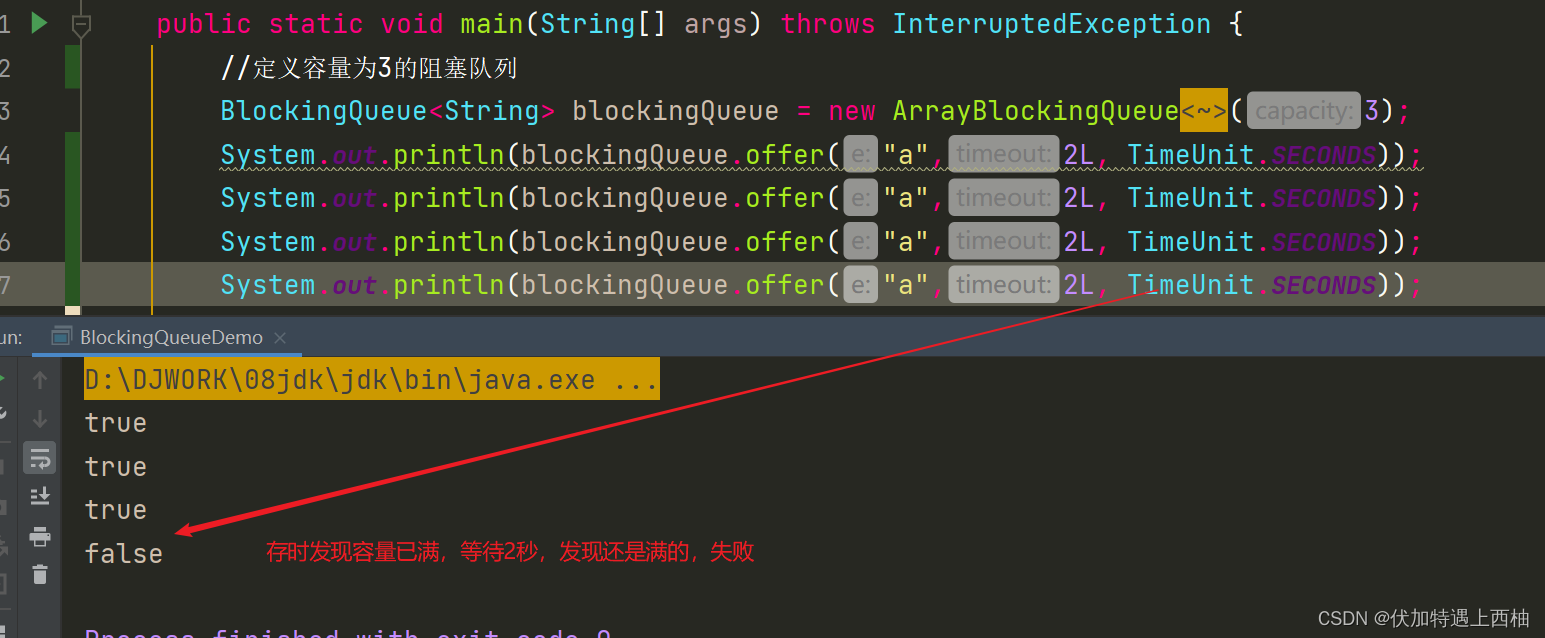
1.2.2.SynchronousQueue
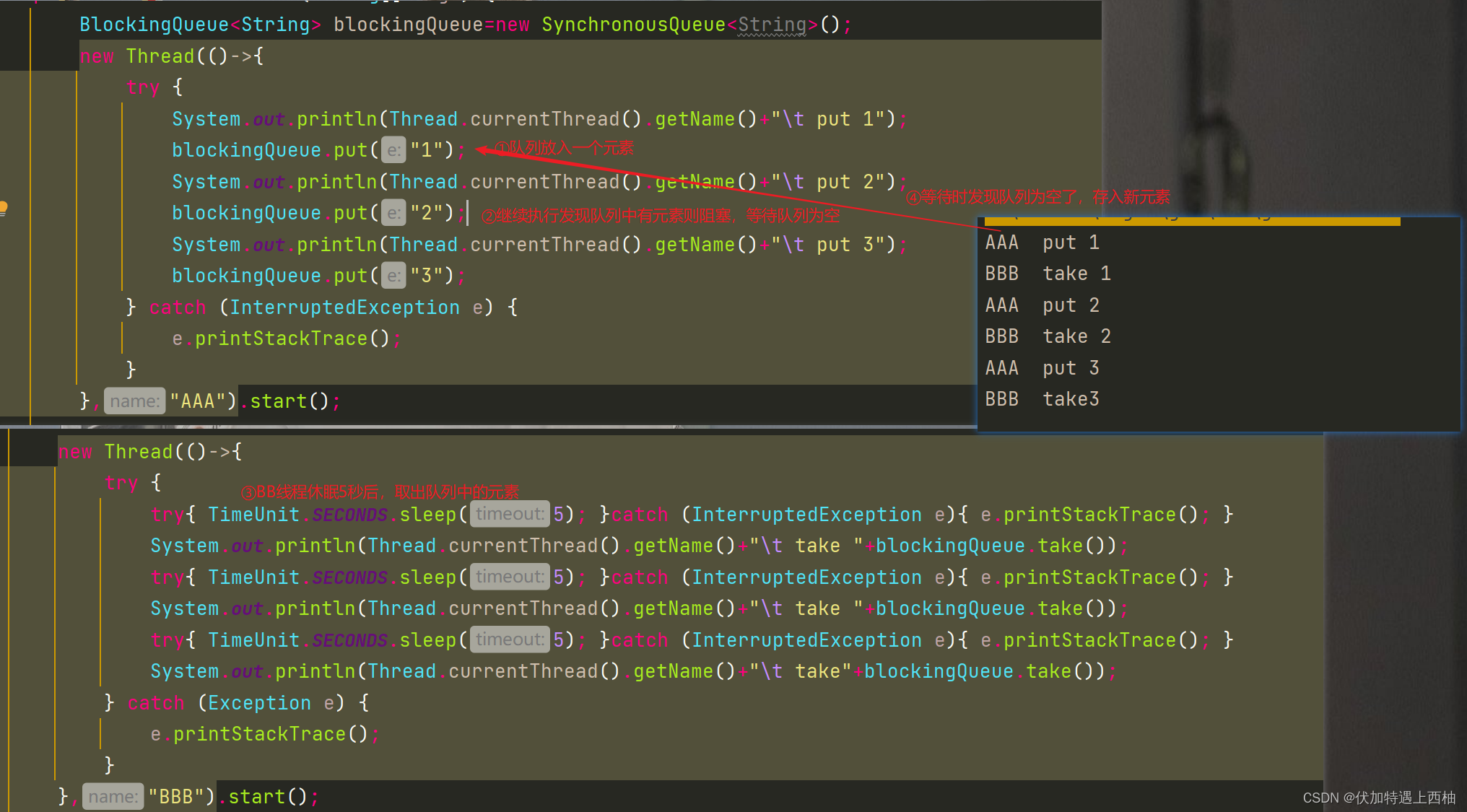
队列只有⼀个元素,如果想插⼊多个,阻塞到队列元素取出后,才能插⼊,只能有⼀个“坑位”,⽤⼀个
插⼀个,详⻅SynchronousQueueDemo。
代码
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue=new SynchronousQueue<String>();new Thread(()->{try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 1");blockingQueue.put("1");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 2");blockingQueue.put("2");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t put 3");blockingQueue.put("3");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}},"AAA").start();new Thread(()->{try {try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t take "+blockingQueue.take());try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t take "+blockingQueue.take());try{ TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t take"+blockingQueue.take());} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}},"BBB").start();}
}结果
二 阻塞队列应用—生产者消费者
2.1.传统模式
传统模式使⽤ Synchronized来进⾏操作。
案例代码
/*** 题目:现在两个线程,可以操作初始值为零的一个变量,* 实现一个线程对该变量加1,一个线程对该变量-1,* 实现交替,来10轮,变量初始值为0.* 1.高内聚低耦合前提下,线程操作资源类* 2.判断/干活/通知* 3.防止虚假唤醒(判断只能用while,不能用if)* 知识小总结:多线程编程套路+while判断+新版写法*/
public class ProdConsumerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Aircondition aircondition = new Aircondition();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {aircondition.increment();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {try {aircondition.decrement();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "B").start();}
}
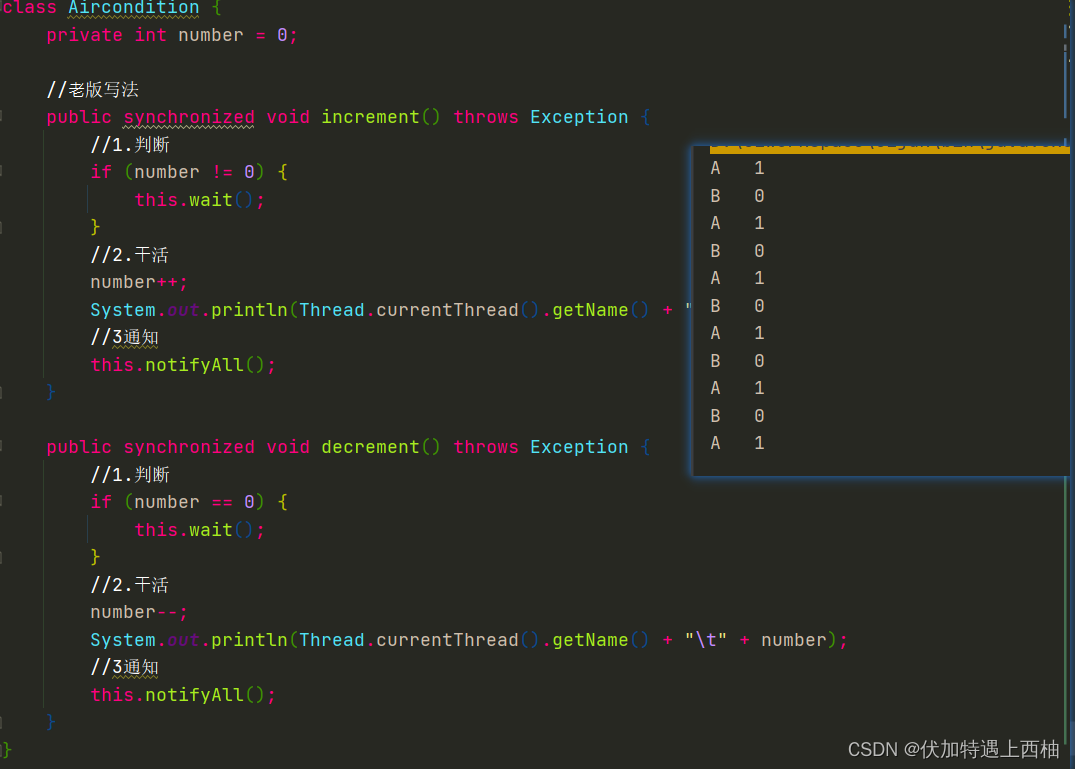
class Aircondition {private int number = 0;//⽼版写法public synchronized void increment() throws Exception {//1.判断if (number != 0) {this.wait();}//2.⼲活number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);//3通知this.notifyAll();}public synchronized void decrement() throws Exception {//1.判断if (number == 0) {this.wait();}//2.⼲活number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);//3通知this.notifyAll();}
}
结果
案例问题—防止虚假唤醒
上述我们只用了一个线程作为生产者,一个线程作为消费者,我们用多个来进行测试。防止虚假唤醒(判断只能用while,不能用if)
while循环与if判断
while是循环语句,当满足条件时执行语句,执行完循环以后再回来判断是否满足,满足继续执行,然后继续判断,不满足直接执行下面的语句
if是判断语句,满足条件就行,执行完以后继续执行下面的语句,不会再回来判断执行。
A线程生产包子,B线程消费包子,C线程生产包子,D线程消费包子

public class ProdConsumerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Aircondition aircondition = new Aircondition();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {aircondition.increment();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {try {aircondition.decrement();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "B").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {aircondition.increment();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "C").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {aircondition.decrement();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "D").start();}
}
Aircondition
class Aircondition {private int number = 0;//⽼版写法public synchronized void increment() throws Exception {//1.判断while (number != 0) {this.wait();}//2.⼲活number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);//3通知this.notifyAll();}public synchronized void decrement() throws Exception {//1.判断while (number == 0) {this.wait();}//2.⼲活number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + number);//3通知this.notifyAll();}
}
2.2.⽣产者消费者防⽌虚假唤醒
2.2.1 新版⽣产者消费者写法 ReentrantLock.Condition
Synchronized用在多线程中太重了,在高并发场景使用lock方式更加合适。所以我们使用lock来加锁和解锁。对应的等待和唤醒线程方法也换成java.util.concurrent.locks下面的newCondition方法。

案例代码
class Aircondition{private int number = 0;private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition condition = lock.newCondition();//新版写法public void increment() throws Exception{lock.lock();try{//1.判断while (number != 0){condition.await();}//2.干活number++;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+number);//3通知condition.signalAll();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void decrement() throws Exception{lock.lock();try{//1.判断while (number == 0){condition.await();}//2.干活number--;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+number);//3通知condition.signalAll();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}
}public class ProdConsumerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Aircondition aircondition = new Aircondition();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {aircondition.increment();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "A").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {try {aircondition.decrement();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "B").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {aircondition.increment();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "C").start();new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {try {aircondition.decrement();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}, "D").start();}
}
2.2.2精准通知顺序访问
现在有这样一个需求:
备注:多线程之间按顺序调用,实现A->B->C
三个线程启动,要求如下:
A打印5次,B打印10次,C打印15次
接着
A打印5次,B打印10次,C打印15次
来10轮
1.高内聚低耦合前提下,线程操作资源类
2.判断/干活/通知
3.多线程交互中,防止虚假唤醒(判断只能用while,不能用if)
4.标志位
案例代码
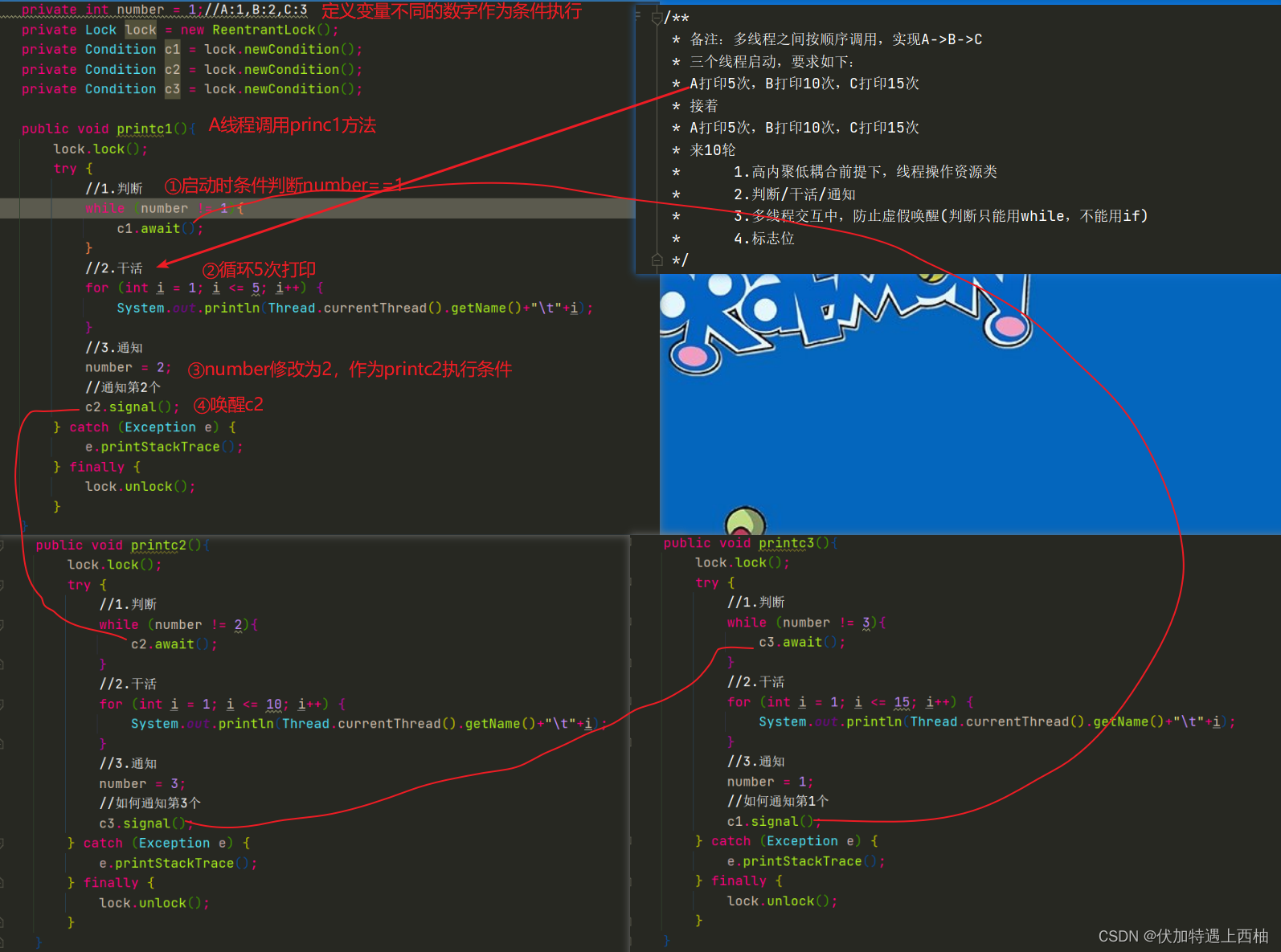
class ShareData{private int number = 1;//A:1,B:2,C:3private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();private Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();private Condition c3 = lock.newCondition();public void printc1(){lock.lock();try {//1.判断while (number != 1){c1.await();}//2.干活for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+i);}//3.通知number = 2;//通知第2个c2.signal();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void printc2(){lock.lock();try {//1.判断while (number != 2){c2.await();}//2.干活for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+i);}//3.通知number = 3;//如何通知第3个c3.signal();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void printc3(){lock.lock();try {//1.判断while (number != 3){c3.await();}//2.干活for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+i);}//3.通知number = 1;//如何通知第1个c1.signal();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}
}/*** 备注:多线程之间按顺序调用,实现A->B->C* 三个线程启动,要求如下:* A打印5次,B打印10次,C打印15次* 接着* A打印5次,B打印10次,C打印15次* 来10轮* 1.高内聚低耦合前提下,线程操作资源类* 2.判断/干活/通知* 3.多线程交互中,防止虚假唤醒(判断只能用while,不能用if)* 4.标志位*/
public class ConditionDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {ShareData shareData = new ShareData();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {shareData.printc1();}},"A").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {shareData.printc2();}},"B").start();new Thread(()->{for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {shareData.printc3();}},"C").start();}
}结果
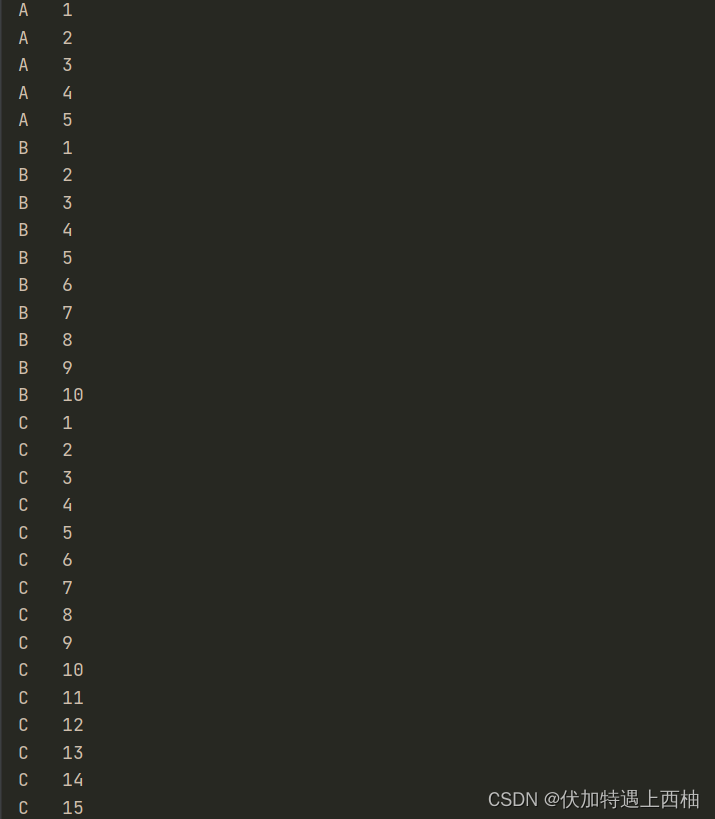
结果分析
2.3.Synchronized和Lock的区别
synchronized关键字和 java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock都能加锁,两者有什么区别呢?
- 原始构成: sync是JVM层⾯的,底层通过monitorenter和monitorexit来实现的。 Lock是
JDK API层⾯的。( sync⼀个enter会有两个exit,⼀个是正常退出,⼀个是异常退出) - 使⽤⽅法: sync不需要⼿动释放锁,⽽ Lock需要⼿动释放。
- 是否可中断: sync不可中断,除⾮抛出异常或者正常运⾏完成。 Lock是可中断的,通过调
⽤ interrupt()⽅法。 - 是否为公平锁: sync只能是⾮公平锁,⽽ Lock既能是公平锁,⼜能是⾮公平锁。
- 绑定多个条件: sync不能,只能随机唤醒。⽽ Lock可以通过 Condition来绑定多个条件,精确唤醒。
2.4. 阻塞队列模式⽣产者消费者
为什么需要BlockingQueue?
好处是我们不需要关⼼什么时候需要阻塞线程,什么时候需要唤醒线程,因为这⼀切BlockingQueue都
给你⼀⼿包办好了,使⽤阻塞队列 后就不需要⼿动加锁了。
在Concurrent包发布以前,在多线程环境下,我们每个程序员都必须去⾃⼰控制这些细节,尤其还要兼
顾效率和线程安全,⽽这会给我们的程序带来不⼩的复杂度。
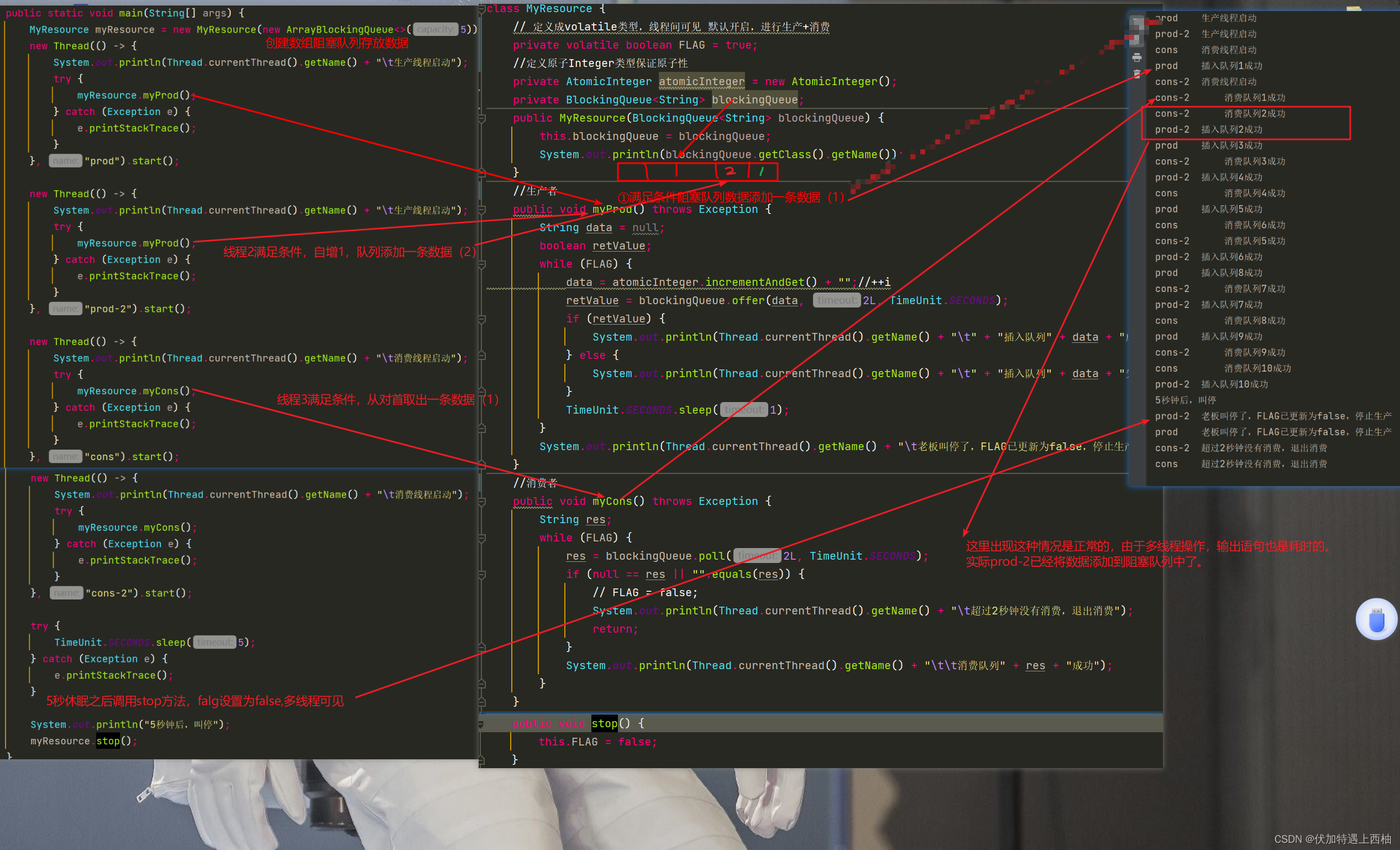
案例代码
public class ProdConsBlockQueueDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {MyResource myResource = new MyResource(new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5));new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t生产线程启动");try {myResource.myProd();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "prod").start();new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t生产线程启动");try {myResource.myProd();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "prod-2").start();new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t消费线程启动");try {myResource.myCons();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "cons").start();new Thread(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t消费线程启动");try {myResource.myCons();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "cons-2").start();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("5秒钟后,叫停");myResource.stop();}
}class MyResource {// 定义成volatile类型,线程间可见 默认开启,进行生产+消费private volatile boolean FLAG = true;//定义原子Integer类型保证原子性private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue;public MyResource(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;System.out.println(blockingQueue.getClass().getName());}public void myProd() throws Exception {String data = null;boolean retValue;while (FLAG) {data = atomicInteger.incrementAndGet() + "";//++iretValue = blockingQueue.offer(data, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);if (retValue) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "插入队列" + data + "成功");} else {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "插入队列" + data + "失败");}TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t老板叫停了,FLAG已更新为false,停止生产");}public void myCons() throws Exception {String res;while (FLAG) {res = blockingQueue.poll(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);if (null == res || "".equals(res)) {// FLAG = false;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t超过2秒钟没有消费,退出消费");return;}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t\t消费队列" + res + "成功");}}public void stop() {this.FLAG = false;}
}结果分析
相关文章:

并发编程---阻塞队列(五)
阻塞队列一 阻塞队列1.1.阻塞队列概念1.2.阻塞队列API案例1.2.1. ArrayBlockingQueue1.2.1.1.抛出异常1.2.1.2.返回布尔1.2.1.3.阻塞1.2.1.4.超时1.2.2.SynchronousQueue二 阻塞队列应用---生产者消费者2.1.传统模式案例代码结果案例问题---防止虚假唤醒2.2.⽣产者消费者防⽌虚…...

本科课程【计算机组成原理】实验1 - 输出ABCD程序的生成
大家好,我是【1+1=王】, 热爱java的计算机(人工智能)渣硕研究生在读。 如果你也对java、人工智能等技术感兴趣,欢迎关注,抱团交流进大厂!!! Good better best, never let it rest, until good is better, and better best. 近期会把自己本科阶段的一些课程设计、实验报…...
Java并发编程(2) —— 线程创建的方式与原理
一、Java线程创建的三种方式 1. 继承Thread类并重写run()方法 ///方法一:使用匿名内部类重写Thread的run()方法Thread t1 new Thread() {Overridepublic void run() {try {sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}log.debug("…...

你写的js性能有多差你知道吗 | js性能优化
性能的计算⽅式 确认⾃⼰需要关注的指标 常⻅的指标有: ⻚⾯总加载时间 load⾸屏时间⽩屏时间 代码 尝试⽤⼀个指令, 挂载在重要元素上, 当此元素inserted就上报 各个属性所代表的含义 connectStart, connectEnd 分别代表TCP建⽴连接和连接成功的时间节点。如果浏…...
线程的状态、状态之间的相互转换
目录 一、线程的状态 1. NEW 2. TERMINATED 3. RUNNABLE 4. TIMED_WAITING 5. BLOCKED 6. WAITING 二、线程状态转换 1. 线程状态转换简图 一、线程的状态 线程的状态一共有 6 种: NEW:安排了工作,还未开始行动(调用 st…...

Java8使用Lambda表达式(流式)快速实现List转map 、分组、过滤等操作
利用java8新特性,可以用简洁高效的代码来实现一些数据处理。1 数据准备1.1 定义1个Fruit对象package com.wkf.workrecord.work;import org.junit.Test;import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List;/*** author wuKeFan* date …...
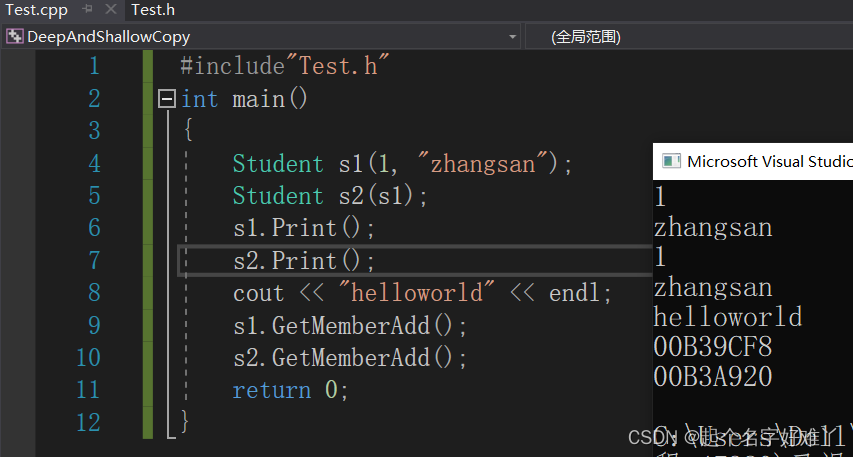
C++之深浅拷贝
一、浅拷贝 我们看下以下代码 Test.h 文件 #pragma once #include<iostream> using namespace std; class Student { public:Student(){}~Student(){if (m_Id ! nullptr){delete m_Id;m_Id nullptr;}}Student(int id, string strName){m_Id new int[id];m_strName s…...

CoreLocation的一切
Overview 概述 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-pgnvehxf-1678717852996)(./blog_cover.png)] Core Location 提供的服务可以确定设备的地理位置、高度和方向,或者它相对于附近 iBeacon 设备的位置。 该框架使用设备上的所…...

HashMap原理
初始化 从HashMap 源码中我们可以发现,HashMap的初始化有一下四种方式 //HashMap默认的初始容量大小 16,容量必须是2的幂 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 1 << 4; // HashMap最大容量 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY 1 <&…...
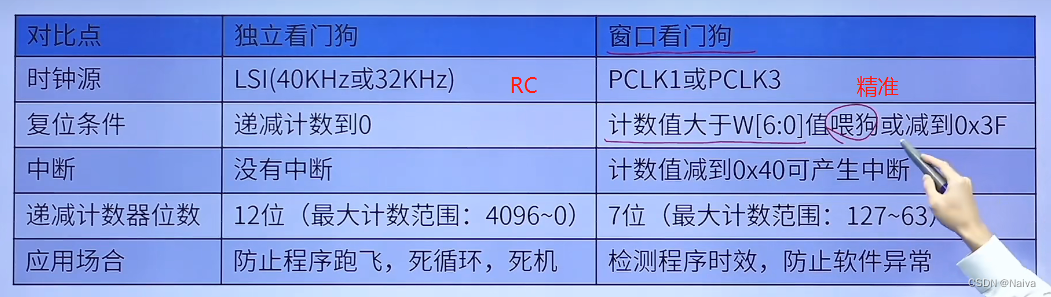
STM32入门笔记(02):独立看门狗(IWDG)和窗户看门狗(WWDG)(SPL库函数版)
1.IWDG狗简介 除了始终控制器的RCC_CSR寄存器的父为标志位和备份区域中的寄存器以外,系统复位 将复位所有寄存器至它们的复位状态。 当发生以下任一事件时,产生一个系统复位: 1.NRST引脚上的 低 电平,即 外部复位;2…...
javaSE系列之方法与数组的使用
[TOC] javaSE系列之方法与数组的使用 方法的定义 方法类似于C语言中的"函数"。 方法的种类 这里方法分为有参方法也分为无参方法, 形参和实参是两个实体(这里相当于函数的传值调用和传址调用) 1.非静态方法:普通方法/…...

常用命令总结
将常用命令汇集于此,以便在忘记的时候查询,持续更新…… Git Local changes 添加名字: git config --global user.name "<你的名字>"添加邮件: git config --globa user.email "<你的邮箱>"…...

【Linux:程序地址空间--原来操作系统也喜欢画大饼】
目录 1 代码感受 2 进程地址空间 3 扩展 1 代码感受 在正式讲程序地址空间前我们先来看一段简单的代码来分析分析: 1 #include<iostream>2 #include<unistd.h>3 using namespace std;4 5 int g_val100;6 7 int main()8 {9 pid_t idfork();10 if(i…...

Python实现简单信号滤波实战
在有些项目中需要对信号进行滤波处理,尤其是在医疗的设备中如心跳、脉搏等设备的采样后进行处理。滤波的目的就是除去某些频率的信号如噪声。常见的包括有低通滤波、高通滤波、带通滤波。 低通滤波指的是去除高于某一阈值频率的信号;高通滤波去除低于某…...

Java(110):非对称加密RSA的使用(KeyPair生成密钥)
Java(110):非对称加密RSA的使用(KeyPair生成密钥) RSA 算法是一种非对称加解密算法。服务方生成一对 RSA 密钥,即公钥 私钥,将公钥提供给调用方,调用方使用公钥对数据进行加密后,服务方根据私钥进行解密。 1、RSA生…...
整合 Mybatis 开发流程)
(Mybatis 学习【1】)整合 Mybatis 开发流程
Mybatis 整合流程 ① 添加MyBatis的依赖 ② 创建数据库表 ③ 编写pojo实体类 ④ 编写映射文件UserMapper.xml ⑤ 编写核心文件mybatis-config.xml ⑥ 编写测试类** 编写 pojo 实体类 (设计相应的数据库) Data AllArgsConstructor NoArgsConstructor public class…...

一文搞懂Kerberos
Kerberos一词来源于古希腊神话中的Cerberus——守护地狱之门的三头犬,Kerberos是为TCP/IP 网络设计的可信第三方鉴别协议,最初是在麻省理工学院(MIT)为Athena 项目而开发的。Kerberos服务起着可信仲裁者的作用,可提供安全的网络鉴别ÿ…...

Go爬虫学习笔记(三)
day3 04|敏捷之道:大型Go项目的开发流程是怎样的? 瀑布模式 流程: 市场调研需求分析产品设计研发实现集成与测试项目交付与维护 适用场景: 需求在规划和设计阶段就已经确定了,而且在项目开发周期内&…...
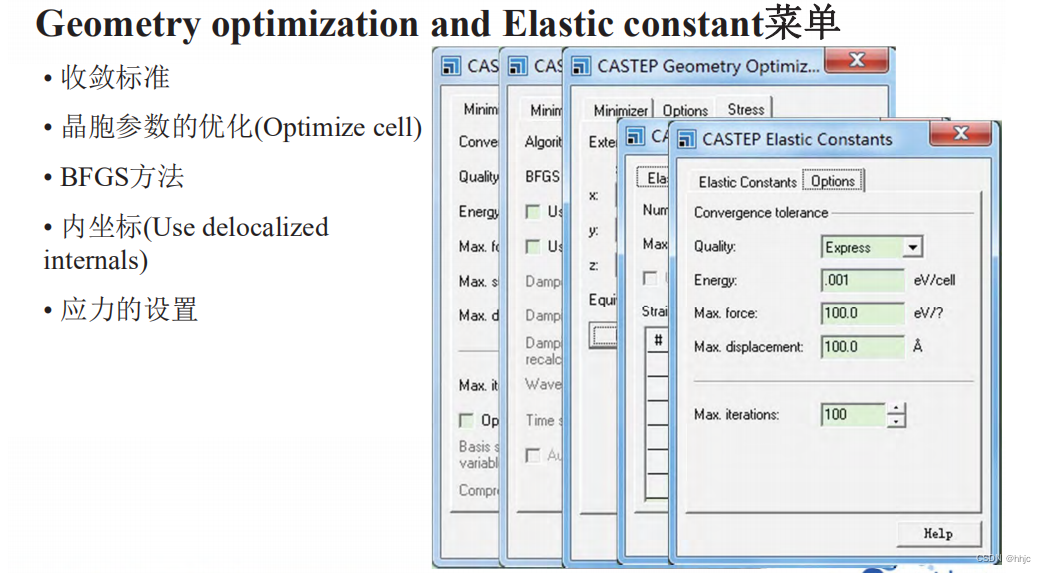
CASTEP参数设置(2)
虚拟试验(分子模拟) 在表征材料以及材料的相关性质时,只要是采用已有的理论加以解释 但是通常来说,需要采用已有的理论来进行设计和探索,伴随着工业软件的发展,应当选用仿真技术来缩小探索范围 传统试验V…...
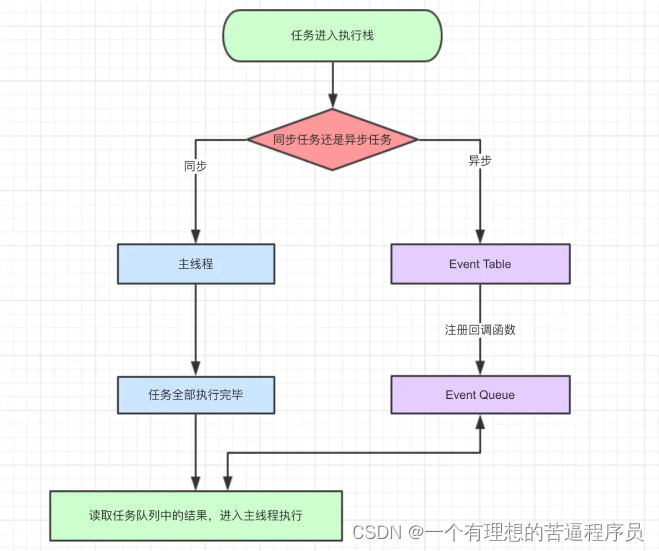
浅谈对Promise的理解以及在工作中的应用
浅谈对Promise的理解以及在工作中的应用Promise的概念背景知识JavaScript的同步和异步JavaScript事件循环回调函数进行异步操作解决方案:PromisePromise 在工作中的运用创建PromisePromise封装AJAXPromise链式操作Promise.all()Promise.race()async和await总结Promi…...
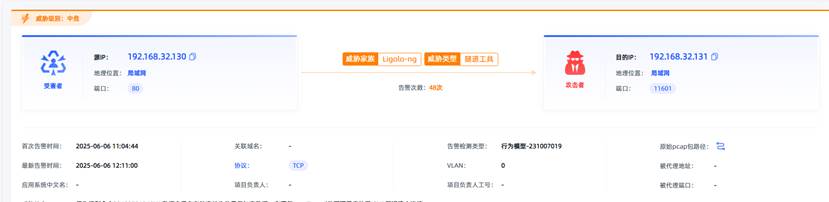
观成科技:隐蔽隧道工具Ligolo-ng加密流量分析
1.工具介绍 Ligolo-ng是一款由go编写的高效隧道工具,该工具基于TUN接口实现其功能,利用反向TCP/TLS连接建立一条隐蔽的通信信道,支持使用Let’s Encrypt自动生成证书。Ligolo-ng的通信隐蔽性体现在其支持多种连接方式,适应复杂网…...
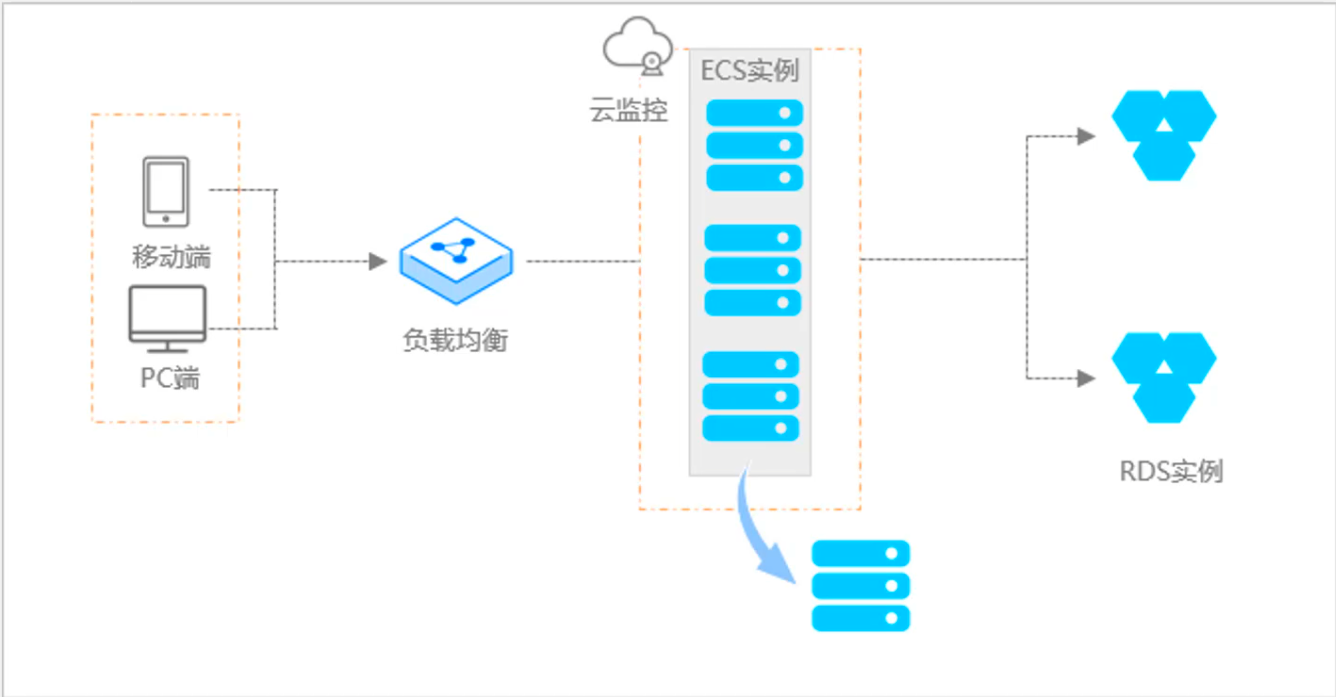
阿里云ACP云计算备考笔记 (5)——弹性伸缩
目录 第一章 概述 第二章 弹性伸缩简介 1、弹性伸缩 2、垂直伸缩 3、优势 4、应用场景 ① 无规律的业务量波动 ② 有规律的业务量波动 ③ 无明显业务量波动 ④ 混合型业务 ⑤ 消息通知 ⑥ 生命周期挂钩 ⑦ 自定义方式 ⑧ 滚的升级 5、使用限制 第三章 主要定义 …...

Oracle查询表空间大小
1 查询数据库中所有的表空间以及表空间所占空间的大小 SELECTtablespace_name,sum( bytes ) / 1024 / 1024 FROMdba_data_files GROUP BYtablespace_name; 2 Oracle查询表空间大小及每个表所占空间的大小 SELECTtablespace_name,file_id,file_name,round( bytes / ( 1024 …...
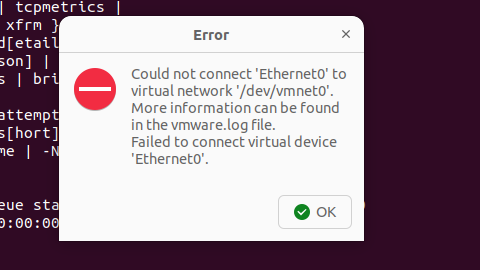
解决Ubuntu22.04 VMware失败的问题 ubuntu入门之二十八
现象1 打开VMware失败 Ubuntu升级之后打开VMware上报需要安装vmmon和vmnet,点击确认后如下提示 最终上报fail 解决方法 内核升级导致,需要在新内核下重新下载编译安装 查看版本 $ vmware -v VMware Workstation 17.5.1 build-23298084$ lsb_release…...

Linux相关概念和易错知识点(42)(TCP的连接管理、可靠性、面临复杂网络的处理)
目录 1.TCP的连接管理机制(1)三次握手①握手过程②对握手过程的理解 (2)四次挥手(3)握手和挥手的触发(4)状态切换①挥手过程中状态的切换②握手过程中状态的切换 2.TCP的可靠性&…...
dedecms 织梦自定义表单留言增加ajax验证码功能
增加ajax功能模块,用户不点击提交按钮,只要输入框失去焦点,就会提前提示验证码是否正确。 一,模板上增加验证码 <input name"vdcode"id"vdcode" placeholder"请输入验证码" type"text&quo…...
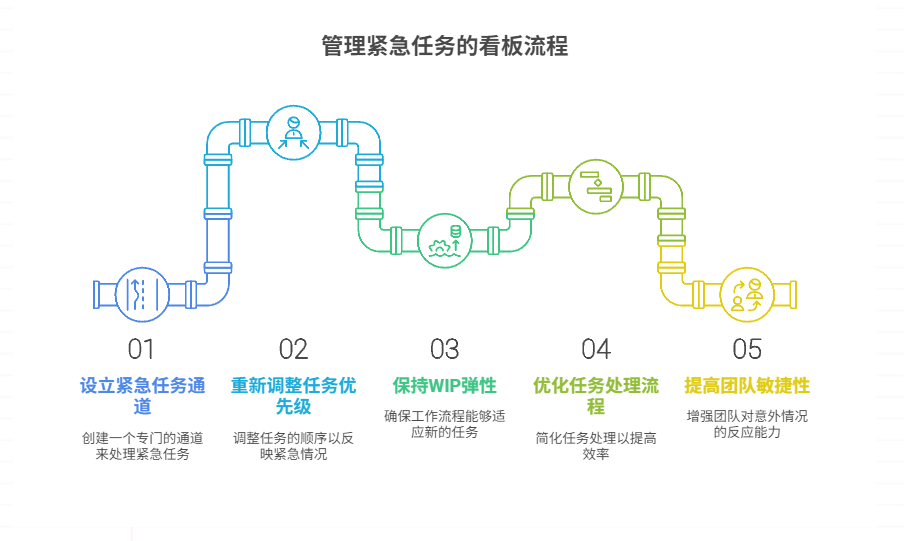
如何在看板中有效管理突发紧急任务
在看板中有效管理突发紧急任务需要:设立专门的紧急任务通道、重新调整任务优先级、保持适度的WIP(Work-in-Progress)弹性、优化任务处理流程、提高团队应对突发情况的敏捷性。其中,设立专门的紧急任务通道尤为重要,这能…...
WordPress插件:AI多语言写作与智能配图、免费AI模型、SEO文章生成
厌倦手动写WordPress文章?AI自动生成,效率提升10倍! 支持多语言、自动配图、定时发布,让内容创作更轻松! AI内容生成 → 不想每天写文章?AI一键生成高质量内容!多语言支持 → 跨境电商必备&am…...

汇编常见指令
汇编常见指令 一、数据传送指令 指令功能示例说明MOV数据传送MOV EAX, 10将立即数 10 送入 EAXMOV [EBX], EAX将 EAX 值存入 EBX 指向的内存LEA加载有效地址LEA EAX, [EBX4]将 EBX4 的地址存入 EAX(不访问内存)XCHG交换数据XCHG EAX, EBX交换 EAX 和 EB…...
 自用)
css3笔记 (1) 自用
outline: none 用于移除元素获得焦点时默认的轮廓线 broder:0 用于移除边框 font-size:0 用于设置字体不显示 list-style: none 消除<li> 标签默认样式 margin: xx auto 版心居中 width:100% 通栏 vertical-align 作用于行内元素 / 表格单元格ÿ…...
