vst 算法R语言手工实现 | Seurat4 筛选高变基因的算法
1. vst算法描述
(1)为什么需要矫正

image source: https://ouyanglab.com/singlecell/basic.html
In this panel, we observe that there is a very strong positive relationship between a gene’s average expression and its observed variance. In other words, highly expressed genes have high variances associated with them and vice versa. This phenomenon is often referred to as heteroskedasticity within the data and must be corrected before proceeding with any downstream analysis steps.
高表达的基因其变异也高。这被叫做数据内的 异方差性,必须矫正后才能进一步下游分析。
In short, the dependance of a gene’s expression with its observed variance is what needs to be corrected prior to HVG selection [1].
简而言之,基因表达与其观察到的变异的依赖性是在HVG选择之前需要纠正的。
The Solution:
A very common way to correct this problem is by applying a Variance Stabilizing Transformation (VST) to the data, and we see in the right panel of the above figure that once VST is applied, the relationship of observed variance at any given level of average expression for a gene has been removed/standardized.
(2)Seurat4 R文档
> ?FindVariableFeatures
vst:
- First, fits a line to the relationship of log(variance) and log(mean) using local polynomial regression (loess).
- Then standardizes the feature values using the observed mean and expected variance (given by the fitted line).
- Feature variance is then calculated on the standardized values after clipping to a maximum (see clip.max parameter).
vst steps: 目的是在var~mean曲线中,不同mean值区域都能挑选var较大的基因
- 使用局部多项式拟合(loess) log(variance) 和log(mean) 平滑曲线模型
- 获取模型计算的值作为y=var.exp值
- 截取最大之后,var.standarlized = get variance after feature standardization:
(每个基因 - mean)/sd 后 取var(). 注意sd=sqrt(var.exp) - 按照 var.standarlized 降序排列,取前n(比如2000)个基因作为高变基因。
2. 加载数据及Seurat vst 结果
使用pbmc 3k数据,走标准Seurat4,选取top 2000 HVG [2]。
library(Seurat)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)pbmc=readRDS("d:\\code_R\\filtered_gene_bc_matrices\\pbmc3k.final.Rds")
DimPlot(pbmc, label=T)# pbmc <- FindVariableFeatures(pbmc, selection.method = "vst", nfeatures = 2000)# 0. 获取Seurat包计算的HVG ----
top10 <- head(VariableFeatures(pbmc), 10)
p1=VariableFeaturePlot(pbmc); p1
LabelPoints(plot = p1, points = top10, repel = TRUE)genelist1=VariableFeatures(pbmc)
length(genelist1)
head(genelist1)head( pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features )
3. 手工 HVG
(1) LOESS fit y~x
log(variance) ~ log(mean)
# use raw data: vst 的直接输入的是 counts,所以直接算的 行平均数,作为基因表达值
counts = pbmc@assays$RNA@counts# 计算每行均值
hvf.info <- data.frame(mean = rowMeans(x = counts, na.rm = T))# 计算每行方差
hvf.info$variance = apply(counts, 1, function(x){var(x, na.rm = T)
})head(hvf.info)
dim(hvf.info)if(0){#pdf( paste0(outputRoot, keyword, "_01_4B.HVG.pdf"), width=5.5, height =4.8)plot(hvf.info$mean, hvf.info$variance, pch=19, cex=0.3)plot(log10(hvf.info$mean), hvf.info$variance, pch=19, cex=0.3)plot(log10(hvf.info$mean), log10(hvf.info$variance), pch=19, cex=0.3) #looks good#dev.off()
}# 通过loess拟合,计算期望方差和标准化的方差
hvf.info$variance.expected <- 0
hvf.info$variance.standardized <- 0not.const <- (hvf.info$variance >0) & (!is.na(hvf.info$variance)) & (!is.na(hvf.info$mean))
table(not.const)
#TRUE
#13714# 拟合 y~x
loess.span=0.3 #default in Seurat4
fit <- loess(formula = log10(x = variance) ~ log10(x = mean),data = hvf.info[not.const, ],span = loess.span
)dim(hvf.info[not.const, ]) #13714 4
#str(fit)
(2). 获取模型给出的期望y值
# 期望y值:使用模型计算的值
hvf.info$variance.expected[not.const] <- 10 ^ fit$fitted
(3). 截取极端值后,计算标准化后的方差
#clip.max == 'auto',则自动设置为 列数(细胞数)的开方
clip.max <- sqrt(x = ncol(x = counts))
clip.max #51.9# 计算feature标准化( (counts - mean)/sd )后的方差,注意sd=sqrt(var)
# 求方差前截取极大值
hvf.info$variance.standardized[not.const]=(function(){result=c()for(i in 1:nrow(counts)){row.var=NAif(not.const[i]){# clip to a maximumrow.counts.std = (counts[i, ] - hvf.info$mean[i]) / sqrt(hvf.info$variance.expected[i])row.counts.std[row.counts.std>clip.max]=clip.max# 计算方差row.var=var( row.counts.std, na.rm = T )}# 返回结果result=c(result, row.var)}return(result)
})() #2min
(4) 第(3)步主要参考
来源是Seurat4 函数FindVariableFeatures.default 中:
hvf.info$variance.standardized <- SparseRowVarStd(mat = object,mu = hvf.info$mean,sd = sqrt(hvf.info$variance.expected),vmax = clip.max,display_progress = verbose)
查找SparseRowVarStd的定义:
$ find .| xargs grep -in "SparseRowVarStd" --color=auto
grep: .: Is a directory
./data_manipulation.cpp:305:NumericVector SparseRowVarStd(Eigen::SparseMatrix<double> mat,
./data_manipulation.h:40:NumericVector SparseRowVarStd(Eigen::SparseMatrix<double> mat,
./RcppExports.cpp:185:// SparseRowVarStd
./RcppExports.cpp:186:NumericVector SparseRowVarStd(Eigen::SparseMatrix<double> mat, NumericVector mu, NumericVector sd, double vmax, bool display_progress);
./RcppExports.cpp:187:RcppExport SEXP _Seurat_SparseRowVarStd(SEXP matSEXP, SEXP muSEXP, SEXP sdSEXP, SEXP vmaxSEXP, SEXP display_progressSEXP) {
./RcppExports.cpp:195: rcpp_result_gen = Rcpp::wrap(SparseRowVarStd(mat, mu, sd, vmax, display_progress));
./RcppExports.cpp:421: {"_Seurat_SparseRowVarStd", (DL_FUNC) &_Seurat_SparseRowVarStd, 5},
发现是Seurat4 的 c++函数,定义在 seurat-4.1.0/src/data_manipulation.cpp:301
/* standardize matrix rows using given mean and standard deviation,clip values larger than vmax to vmax,then return variance for each row */
// [[Rcpp::export(rng = false)]]
NumericVector SparseRowVarStd(Eigen::SparseMatrix<double> mat,NumericVector mu,NumericVector sd,double vmax,bool display_progress){if(display_progress == true){Rcpp::Rcerr << "Calculating feature variances of standardized and clipped values" << std::endl;}mat = mat.transpose();NumericVector allVars(mat.cols());Progress p(mat.outerSize(), display_progress);for (int k=0; k<mat.outerSize(); ++k){p.increment();if (sd[k] == 0) continue;double colSum = 0;int nZero = mat.rows();for (Eigen::SparseMatrix<double>::InnerIterator it(mat,k); it; ++it){nZero -= 1;colSum += pow(std::min(vmax, (it.value() - mu[k]) / sd[k]), 2);}colSum += pow((0 - mu[k]) / sd[k], 2) * nZero;allVars[k] = colSum / (mat.rows() - 1);}return(allVars);
}
结合R的上下文,大致能猜出来c++代码啥意思。
想看懂细节,则需要更多c++知识储备:
- cpp最顶部的头文件:
#include <RcppEigen.h>
#include <progress.hpp>
#include <cmath>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <Rinternals.h>using namespace Rcpp;
Eigen::SparseMatrix<double> mat:泛型;矩阵::系数矩阵- 稀疏矩阵的方法:
mat.transpose(),mat.cols(),mat.outerSize(), for (Eigen::SparseMatrix<double>::InnerIterator it(mat,k); it; ++it): 集合的迭代器- Rcpp 数据类型:
NumericVector,
4. 结果比较
(1) 结果检查1:基因列表一致
手工计算的和Seurat4的HVG gene list结果完全一致。
# Check 1: HVG gene list
hvf.info=hvf.info[order(-hvf.info$variance.standardized),]
head(hvf.info)
tail(hvf.info)
#top.features=head( rownames(hvf.info), n=250)
top.features_2=head( rownames(hvf.info), n=2000)
length(top.features_2)
head(top.features_2)
setdiff(top.features_2, genelist1)
setdiff(genelist1, top.features_2)
#
if(0){# Check: gene and their parampbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[c(setdiff(genelist1, top.features_2)),]hvf.info[c(setdiff(genelist1, top.features_2)),]#pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[c(setdiff(top.features_2, genelist1)),]hvf.info[c(setdiff(top.features_2, genelist1)),]
}
(2) 结果检查2:基因参数一致
手工计算的和Seurat4的HVG gene 参数完全一致。
# check2: HVG and its params
# 1.
dim(pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features)
head( pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features )
# vst.mean vst.variance vst.variance.expected vst.variance.standardized vst.variable
#AL627309.1 0.003333333 0.003323453 0.003575582 0.9294859 FALSE
#AP006222.2 0.001111111 0.001110288 0.001112798 0.9977442 FALSE
#RP11-206L10.2 0.001851852 0.001849107 0.001921811 0.9621691 FALSE
#RP11-206L10.9 0.001111111 0.001110288 0.001112798 0.9977442 FALSE
#LINC00115 0.006666667 0.006624676 0.007342308 0.9022607 FALSE
#NOC2L 0.106666667 0.158310485 0.203482316 0.7780061 FALSE# 2.
dim(hvf.info)
hvf.info=hvf.info[rownames(pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features),]
head(hvf.info)
# mean variance variance.expected variance.standardized
#AL627309.1 0.003333333 0.003323453 0.003575582 0.9294859
#AP006222.2 0.001111111 0.001110288 0.001112798 0.9977442
#RP11-206L10.2 0.001851852 0.001849107 0.001921811 0.9621691
#RP11-206L10.9 0.001111111 0.001110288 0.001112798 0.9977442
#LINC00115 0.006666667 0.006624676 0.007342308 0.9022607
#NOC2L 0.106666667 0.158310485 0.203482316 0.7780061
比较高变基因的参数:
> hvf.info[genelist1|> head(), ]mean variance variance.expected variance.standardized
PPBP 0.2451852 9.577506 0.5888573 11.171153
S100A9 6.0466667 278.681037 34.8969051 7.985838
IGLL5 0.2792593 8.894938 0.6929479 7.964379
LYZ 10.2466667 564.108825 70.8492711 7.962098
GNLY 1.5740741 45.239046 6.0378423 7.492585
FTL 27.6674074 2008.688897 278.9968379 7.199683
> pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[genelist1|> head(), ]vst.mean vst.variance vst.variance.expected vst.variance.standardized vst.variable
PPBP 0.2451852 9.577506 0.5888573 11.172765 TRUE
S100A9 6.0466667 278.681037 34.8969051 7.985838 TRUE
IGLL5 0.2792593 8.894938 0.6929479 7.965360 TRUE
LYZ 10.2466667 564.108825 70.8492711 7.962098 TRUE
GNLY 1.5740741 45.239046 6.0378423 7.492585 TRUE
FTL 27.6674074 2008.688897 278.9968379 7.199683 TRUE> table(abs(hvf.info[genelist1, 4] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[genelist1, 4])<0.005)
FALSE TRUE 3 1997# 差别不大,差异的绝对值大于0.005的共三个:
> keep2=abs(hvf.info[genelist1, 4] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[genelist1, 4])>0.005
> table(keep2)
keep2
FALSE TRUE 1997 3 > hvf.info[genelist1, ][keep2, ]mean variance variance.expected variance.standardized
IGJ 0.16777778 16.822896 0.36540081 3.481455
SLC48A1 0.03370370 0.871409 0.04618194 2.215032
NAPA-AS1 0.02962963 1.050622 0.03932270 1.274513
> pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[genelist1, ][keep2, ]vst.mean vst.variance vst.variance.expected vst.variance.standardized vst.variable
IGJ 0.16777778 16.822896 0.36540081 3.498952 TRUE
SLC48A1 0.03370370 0.871409 0.04618194 2.220942 TRUE
NAPA-AS1 0.02962963 1.050622 0.03932270 1.280866 TRUE
最后一列略有区别:
#
all( abs(hvf.info[,1] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[,1]) < 1e-6) #T
all( abs(hvf.info[,2] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[,2]) < 1e-6) #T
all( abs(hvf.info[,3] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[,3]) < 1e-6) #Ttable( abs(hvf.info[,4] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[,4]) < 1e-6) #not all T
table( abs(hvf.info[,4] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[,4]) < 0.01)
#FALSE TRUE
# 1 13713keep = abs(hvf.info[,4] - pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[,4]) > 1e-2> table(keep)
keep
FALSE TRUE
13713 1
> hvf.info[keep, ]mean variance variance.expected variance.standardized
IGJ 0.1677778 16.8229 0.3654008 3.481455
> pbmc@assays$RNA@meta.features[keep, ]vst.mean vst.variance vst.variance.expected vst.variance.standardized vst.variable
IGJ 0.1677778 16.8229 0.3654008 3.498952 TRUE
(3) 绘图比较
 (a) var~avg with top 2000 HVG selected by vst;
(a) var~avg with top 2000 HVG selected by vst;
(b) std.var ~ avg with top 2000 HVG selected by vst;
( c) same as (b), but draw by Seurat functions.
# plot1
plot(log10(hvf.info$mean), log10(hvf.info$variance), pch=19, cex=0.3, main="vst manully #1", mgp=c(2,1,0))
points(log10(hvf.info[top.features_2, ]$mean), log10(hvf.info[top.features_2, ]$variance), pch=19, cex=0.3, col="red")# plot2
plot(log10(hvf.info$mean), hvf.info$variance.standardized, pch=19, cex=0.3, main="vst manully #2", mgp=c(2,1,0))
points(log10(hvf.info[top.features_2,]$mean), (hvf.info[top.features_2,]$variance.standardized), pch=19, cex=0.3, col="red")# plot3: Seurat
LabelPoints(plot = p1, points = top10, repel = TRUE)
#
Ref:
- [1] https://medium.com/byte-sized-machine-learning/selection-of-highly-variable-genes-hvgs-in-scrna-seq-647c8eee3845
- [2] https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/479549742
相关文章:

vst 算法R语言手工实现 | Seurat4 筛选高变基因的算法
1. vst算法描述 (1)为什么需要矫正 image source: https://ouyanglab.com/singlecell/basic.html In this panel, we observe that there is a very strong positive relationship between a gene’s average expression and its observed variance. I…...

阿里通义千问大模型Qwen2-72B-Instruct通用能力登顶国内第一!
前言: 中国互联网协会副秘书长裴玮近日在2024中国互联网大会上发布《中国互联网发展报告(2024)》。《报告》指出, 在人工智能领域,2023年我国人工智能产业应用进程持续推进,核心产业规模达到5784亿元。 截至2024年3月ÿ…...

CH04_依赖项属性
第4章:依赖项属性 本章目标 理解依赖项属性理解属性验证 依赖项属性 属性与事件是.NET抽象模型的核心部分。WPF使用了更高级的依赖项属性(Dependency Property)功能来替换原来.NET的属性,实现了更高效率的保存机制…...

CentOS 7开启SSH连接
1. 安装openssh-server 1.1 检查是否安装openssh-server服务 yum list installed | grep openssh-server如果有显示内容,则已安装跳过安装步骤,否则进行第2步 1.2 安装openssh-server yum install openssh-server2. 开启SSH 22监听端口 2.1 打开ssh…...

代理伺服器分類詳解
代理伺服器的主要分類 代理伺服器可以根據不同的標準進行分類。以下是幾種常見的分類方式: 按協議分類按匿名性分類按使用場景分類 1. 按協議分類 根據支持的協議類型,代理伺服器可以分為以下幾類: HTTP代理:專門用於處理HTT…...

计数,桶与基数排序
目录 一. 计数排序 概念 步骤思路如下 实现代码如下 时间复杂度与空间复杂度 1. 时间复杂度 2. 空间复杂度 计数排序的特点 二. 桶排序 概念 步骤思路如下 实现代码如下 时间复杂度与空间复杂度 1. 时间复杂度 2. 空间复杂度 桶排序的特点 三. 基数排序 概念 步…...

unity渲染人物模型透明度问题
问题1:有独立的手和衣服的模型,但最终只渲染出来半透明衣服 问题2:透明度贴图是正确的但显示却不正确 这上面两个模型的问题都是因为人物模型是一个完整的,为啥有些地方可以正常显示,有些地方透明度却有问题。 其中…...

CH03_布局
第3章:布局 本章目标 理解布局的原则理解布局的过程理解布局的容器掌握各类布局容器的运用 理解 WPF 中的布局 WPF 布局原则 WPF 窗口只能包含单个元素。为在WPF 窗口中放置多个元素并创建更贴近实用的用户男面,需要在窗口上放置一个容器&#x…...

【Oracle】Oracle中的merge into
目录 解释使用场景语法示例案例一案例二 MERGE INTO的优缺点优点:缺点: 注意事项附:Oracle中的MERGE INTO实现的效果,如果改为用MySQL应该怎么实现注意 解释 在Oracle数据库中,MERGE INTO是一种用于对表进行合并&…...
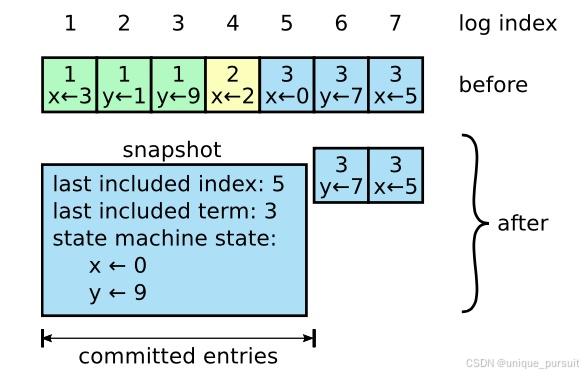
【论文阅读笔记】In Search of an Understandable Consensus Algorithm (Extended Version)
1 介绍 分布式一致性共识算法指的是在分布式系统中,使得所有节点对同一份数据的认知能够达成共识的算法。且算法允许所有节点像一个整体一样工作,即使其中一些节点出现故障也能够继续工作。之前的大部分一致性算法实现都是基于Paxos,但Paxos…...
CentOS 7 网络配置
如想了解请查看 虚拟机安装CentOS7 第一步:查看虚拟机网络编辑器、查看NAT设置 (子网ID,网关IP) 第二步:配置VMnet8 IP与DNS 注意事项:子网掩码与默认网关与 第一步 保持一致 第三步:网络配置…...
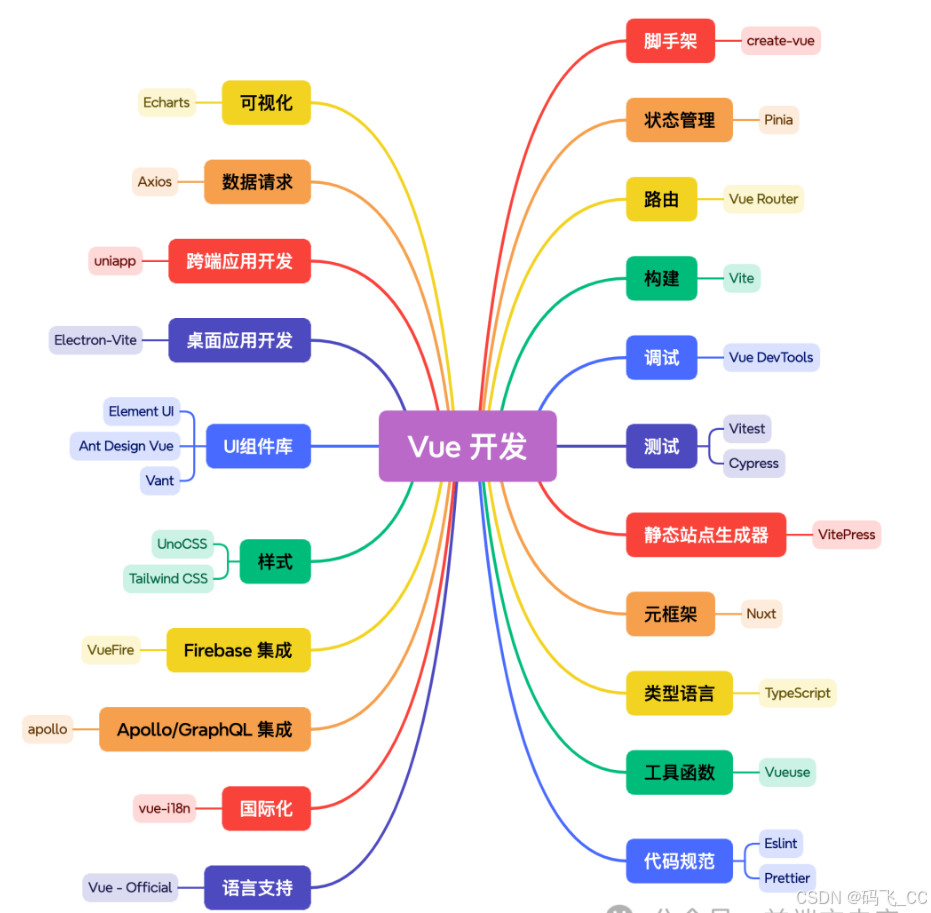
2024 React 和 Vue 的生态工具
react Vue...

AI学习指南机器学习篇-t-SNE模型应用与Python实践
AI学习指南机器学习篇-t-SNE模型应用与Python实践 在机器学习领域,数据的可视化是非常重要的,因为它可以帮助我们更好地理解数据的结构和特征。而t-SNE(t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding)是一种非常强大的降维和可视…...

小试牛刀-Telebot区块链游戏机器人
目录 1.编写目的 2.实现功能 2.1 Wallet功能 2.2 游戏功能 2.3 提出功能 2.4 辅助功能 3.功能实现详解 3.1 wallet功能 3.2 游戏功能 3.3 提出功能 3.4 辅助功能 4.测试视频 Welcome to Code Blocks blog 本篇文章主要介绍了 [Telebot区块链游戏机器人] ❤博主…...
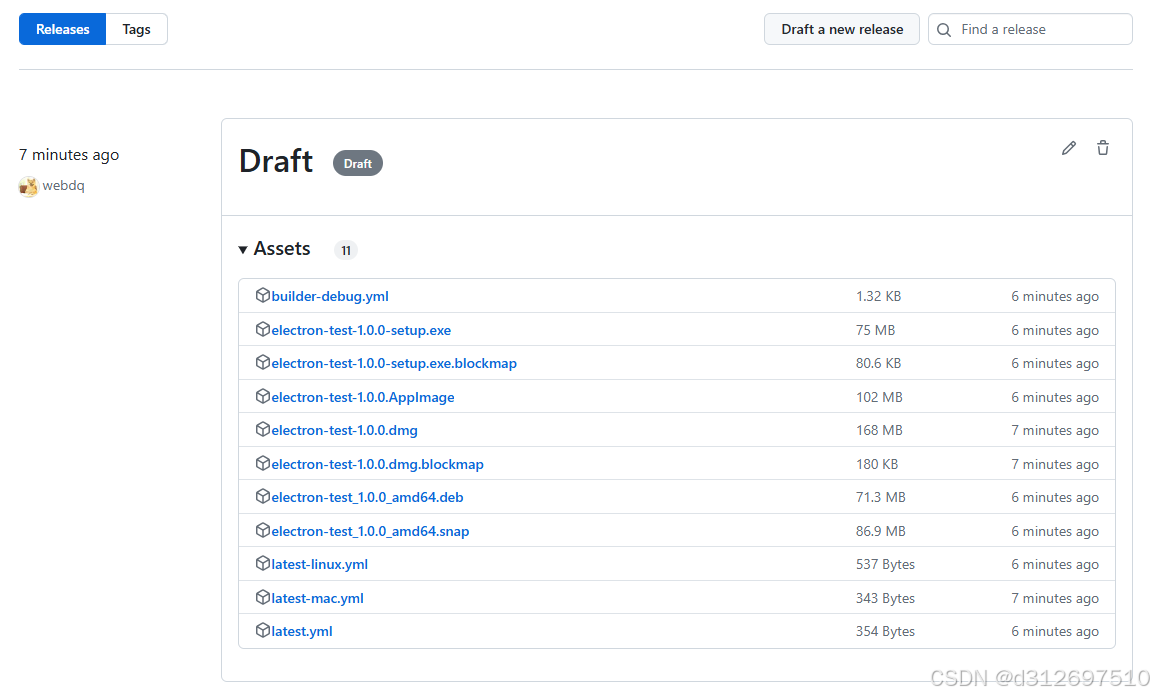
使用github actions构建多平台electron应用
1. 创建electron项目 使用pnpm创建项目 pnpm create quick-start/electron 2. 修改electron-builder.yml文件 修改mac的target mac:target:- target: dmgarch: universal 3. 添加workflow 创建 .github/workflows/main.yml 文件 name: Build/release Electron appon:work…...

java通过pdf-box插件完成对pdf文件中图片/文字的替换
需要引入的Maven依赖: <!-- pdf替换图片 --><dependency><groupId>e-iceblue</groupId><artifactId>spire.pdf.free</artifactId><version>5.1.0</version></dependency> java代码: public AjaxResult replacepd…...
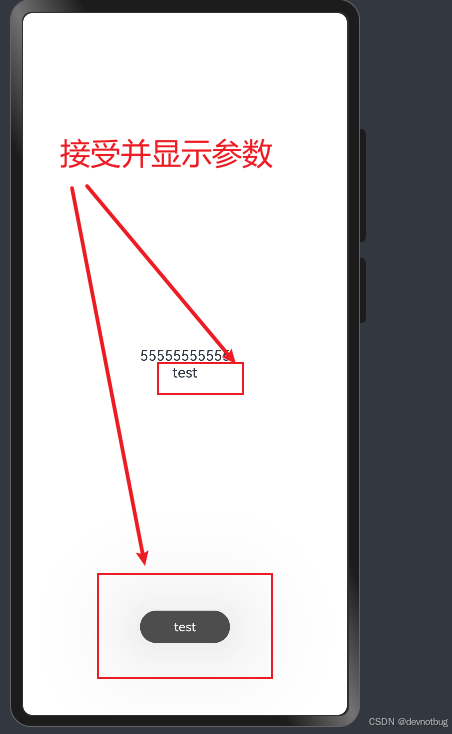
鸿蒙 next 5.0 版本页面跳转传参 接受参数 ,,接受的时候 要先定义接受参数的类型, 代码可以直接CV使用 [教程]
1, 先看效果 2, 先准备好两个页面 index 页面 传递参数 import router from ohos.routerEntry Component struct Index {Statelist: string[] [星期一, 星期二,星期三, 星期四,星期五]StateactiveIndex: number 0build() {Row() {Column({ space: 10 }) {ForEach(this.list,…...

【electron6】浏览器实时播放PCM数据
pcm介绍:PCM(Puls Code Modulation)全称脉码调制录音,PCM录音就是将声音的模拟信号表示成0,1标识的数字信号,未经任何编码和压缩处理,所以可以认为PCM是未经压缩的音频原始格式。PCM格式文件中不包含头部信…...
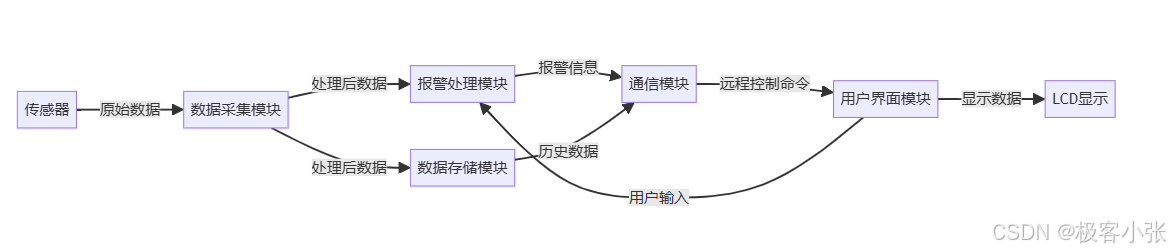
嵌入式C/C++、FreeRTOS、STM32F407VGT6和TCP:智能家居安防系统的全流程介绍(代码示例)
1. 项目概述 随着物联网技术的快速发展,智能家居安防系统越来越受到人们的重视。本文介绍了一种基于STM32单片机的嵌入式安防中控系统的设计与实现方案。该系统集成了多种传感器,实现了实时监控、报警和远程控制等功能,为用户提供了一个安全、可靠的家居安防解决方案。 1.1 系…...
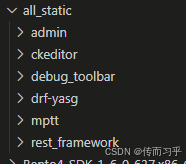
【Django】django自带后台管理系统样式错乱,uwsgi启动css格式消失的问题
正常情况: ERROR:(css、js文件加载失败) 问题:CSS加载的样式没有了,原因:使用了django自带的admin,在使用 python manage.py runserver启动 的时候,可以加载到admin的文…...
:手搓截屏和帧率控制)
Python|GIF 解析与构建(5):手搓截屏和帧率控制
目录 Python|GIF 解析与构建(5):手搓截屏和帧率控制 一、引言 二、技术实现:手搓截屏模块 2.1 核心原理 2.2 代码解析:ScreenshotData类 2.2.1 截图函数:capture_screen 三、技术实现&…...

Android Wi-Fi 连接失败日志分析
1. Android wifi 关键日志总结 (1) Wi-Fi 断开 (CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED reason3) 日志相关部分: 06-05 10:48:40.987 943 943 I wpa_supplicant: wlan0: CTRL-EVENT-DISCONNECTED bssid44:9b:c1:57:a8:90 reason3 locally_generated1解析: CTR…...
)
椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)
一、ECC算法概述 椭圆曲线密码学(Elliptic Curve Cryptography)是基于椭圆曲线数学理论的公钥密码系统,由Neal Koblitz和Victor Miller在1985年独立提出。相比RSA,ECC在相同安全强度下密钥更短(256位ECC ≈ 3072位RSA…...
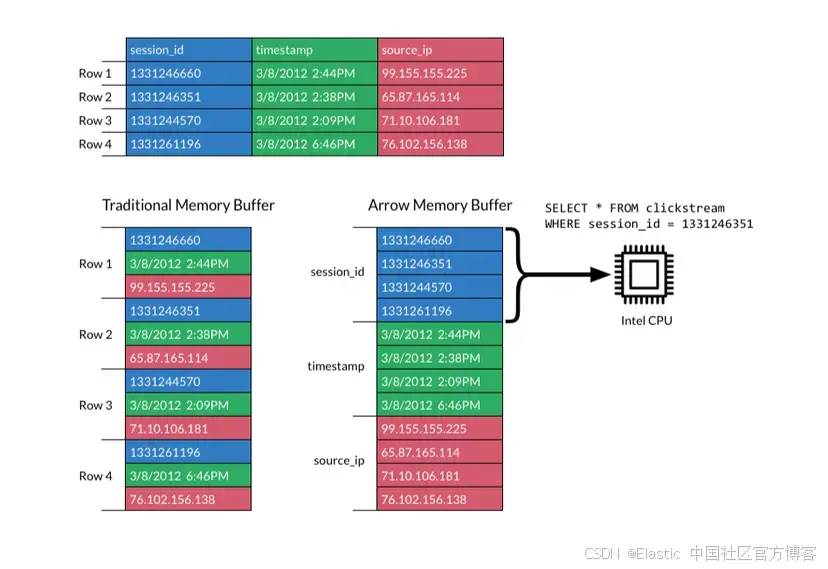
JavaScript 中的 ES|QL:利用 Apache Arrow 工具
作者:来自 Elastic Jeffrey Rengifo 学习如何将 ES|QL 与 JavaScript 的 Apache Arrow 客户端工具一起使用。 想获得 Elastic 认证吗?了解下一期 Elasticsearch Engineer 培训的时间吧! Elasticsearch 拥有众多新功能,助你为自己…...
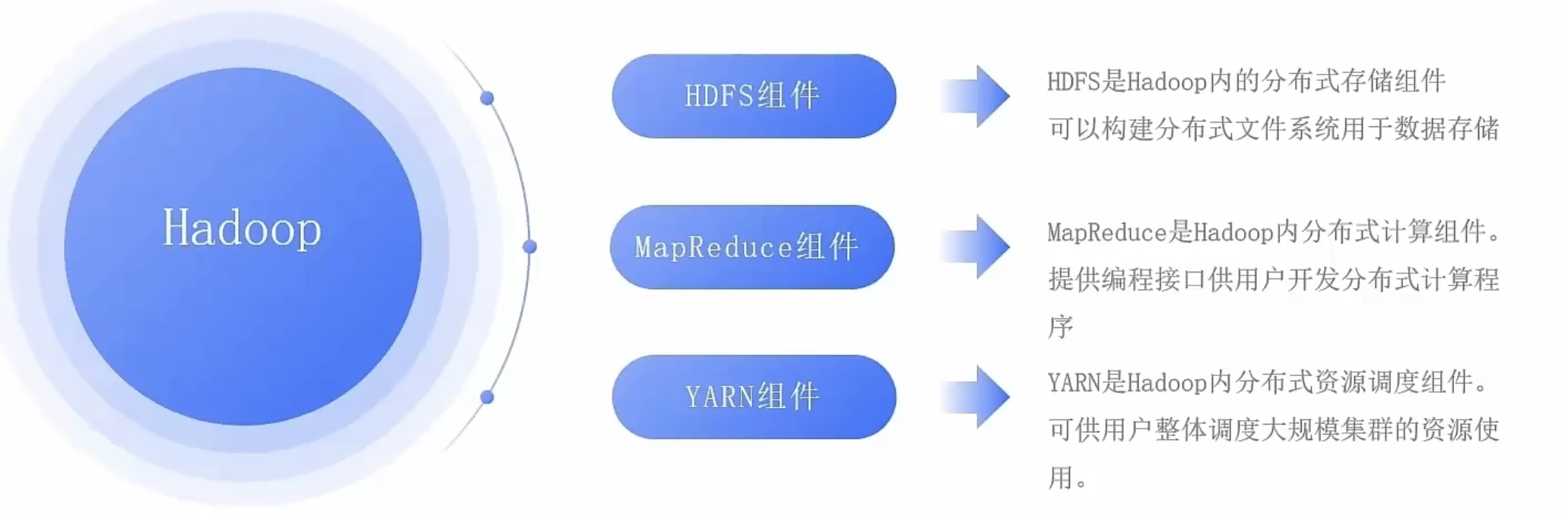
大数据零基础学习day1之环境准备和大数据初步理解
学习大数据会使用到多台Linux服务器。 一、环境准备 1、VMware 基于VMware构建Linux虚拟机 是大数据从业者或者IT从业者的必备技能之一也是成本低廉的方案 所以VMware虚拟机方案是必须要学习的。 (1)设置网关 打开VMware虚拟机,点击编辑…...

基于Docker Compose部署Java微服务项目
一. 创建根项目 根项目(父项目)主要用于依赖管理 一些需要注意的点: 打包方式需要为 pom<modules>里需要注册子模块不要引入maven的打包插件,否则打包时会出问题 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8…...

linux 下常用变更-8
1、删除普通用户 查询用户初始UID和GIDls -l /home/ ###家目录中查看UID cat /etc/group ###此文件查看GID删除用户1.编辑文件 /etc/passwd 找到对应的行,YW343:x:0:0::/home/YW343:/bin/bash 2.将标红的位置修改为用户对应初始UID和GID: YW3…...

数据库分批入库
今天在工作中,遇到一个问题,就是分批查询的时候,由于批次过大导致出现了一些问题,一下是问题描述和解决方案: 示例: // 假设已有数据列表 dataList 和 PreparedStatement pstmt int batchSize 1000; // …...
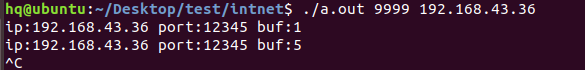
网络编程(UDP编程)
思维导图 UDP基础编程(单播) 1.流程图 服务器:短信的接收方 创建套接字 (socket)-----------------------------------------》有手机指定网络信息-----------------------------------------------》有号码绑定套接字 (bind)--------------…...

蓝桥杯3498 01串的熵
问题描述 对于一个长度为 23333333的 01 串, 如果其信息熵为 11625907.5798, 且 0 出现次数比 1 少, 那么这个 01 串中 0 出现了多少次? #include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std;int n 23333333;int main() {//枚举 0 出现的次数//因…...
