基于深度学习的太阳暗条检测(2020年以来)
A universal method for solar filament detection from Hα observations using semi-supervised deep learning
A&A, 686, A213 (2024)
A universal method for solar filament detection from Hα observations using semi-supervised deep learning (aanda.org)
ABSTRACT
Filaments are omnipresent features in the solar atmosphere. Their location, properties, and time evolution can provide important information about changes in solar activity and assist in the operational space weather forecast. Therefore, filaments have to be identified in full-disk images and their properties extracted from these images, but manual extraction is tedious and too time-consuming, and extraction with morphological image processing tools produces a large number of false positive detections. Automatic object detection, segmentation, and extraction in a reliable manner would allow for the processing of more data in a shorter time frame. The Chromospheric Telescope (ChroTel; Tenerife, Spain), the Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG), and the Kanzelhöhe Observatory for Solar and Environmental Research (KSO; Austria) provide regular full-disk observations of the Sun in the core of the chromospheric Hα absorption line. In this paper, we present a deep learning method that provides reliable extractions of solar filaments from Hα filtergrams. First, we trained the object detection algorithm YOLOv5 with labeled filament data of ChroTel Hα filtergrams. We used the trained model to obtain bounding boxes from the full GONG archive. In a second step, we applied a semi-supervised training approach where we used the bounding boxes of filaments to train the algorithm on a pixel-wise classification of solar filaments with u-net. We made use of the increased data set size, which avoids overfitting of spurious artifacts from the generated training masks. Filaments were predicted with an accuracy of 92%. With the resulting filament segmentations, physical parameters such as the area or tilt angle could be easily determined and studied. We demonstrated this in an example where we determined the rush-to-the pole for Solar Cycle 24 from the segmented GONG images. In a last step, we applied the filament detection to Hα observations from KSO and demonstrated the general applicability of our method to Hα filtergrams.

Developing an Automated Detection, Tracking, and Analysis Method for Solar Filaments Observed by CHASE via Machine Learning
The Astrophysical Journal, 965:150 (11pp), 2024 April 20
Developing an Automated Detection, Tracking, and Analysis Method for Solar Filaments Observed by CHASE via Machine Learning (iop.org)
Abstract
Studies on the dynamics of solar filaments have significant implications for understanding their formation, evolution, and eruption, which are of great importance for space weather warning and forecasting. The Hα Imaging Spectrograph (HIS) on board the recently launched Chinese Hα Solar Explorer (CHASE) can provide full-disk solar Hα spectroscopic observations, which bring us an opportunity to systematically explore and analyze the plasma dynamics of filaments. The dramatically increased observation data require automated processing and analysis, which are impossible if dealt with manually. In this paper, we utilize the U-Net model to identify filaments and implement the Channel and Spatial Reliability Tracking algorithm for automated filament tracking. In addition, we use the cloud model to invert the line-of-sight velocity of filaments and employ the graph theory algorithm to extract the filament spine, which can advance our understanding of the dynamics of filaments. The favorable test performance confirms the validity of our method, which will be implemented in the following statistical analyses of filament features and dynamics of CHASE/HIS observations.

Solar Filament Detection Based on an Improved Deep Learning Model
Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3745.
applsci-14-03745-v3.pdf
Abstract
Solar filaments are good tracers of space weather and magnetic flux ropes in the corona. Identifying and detecting filaments helps to forecast space weather and explore the solar magnetic field. Many automatic detection methods have been proposed to process the large number of observed images. Current methods face issues of unreliable dataset annotations and poor anti-interference capability. First, to address the issue of unreliable dataset annotations, we built a solar filament dataset using a manual annotation method. Second, we introduced Transformer into Convolutional Neural Networks. Transformer, with the ability to extract more global features, can help counter interference. In addition, there is large disparity in the size of solar filaments. Therefore, a multi-scale residual block is designed to extract features across various scales. Deformable large kernel attention and a res path are used to better integrate encoder and decoder information. Results show that this method outperforms the existing solar filament detection methods (improved U-Net and improved V-Net), achieving an F1 score of 91.19%. In particular, our results show lower interference by sunspots and background noise than existing methods. The ability to counter interference is improved.


Detection of Solar Filaments Using Suncharts from Kodaikanal Solar Observatory Archive Employing a Clustering Approach
The Astrophysical Journal, 943:140 (10pp), 2023 February 1
Detection of Solar Filaments Using Suncharts from Kodaikanal Solar Observatory Archive Employing a Clustering Approach (iop.org)
Abstract
With over 100 yr of solar observations, the Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO) is a one-of-a-kind solar data repository in the world. Among its many data catalogs, the “suncharts” at KoSO are of particular interest. These suncharts (1904–2020) are colored drawings of different solar features, such as sunspots, plages, filaments, and prominences, made on papers with a Stonyhurst latitude–longitude grid etched on them. In this paper, we analyze this unique data by first digitizing each sunchart using an industry-standard scanner and saving those digital images in a high-resolution “.tif” format. We then examine cycle 19 and cycle 20 data (two of the strongest cycles of the last century) with the aim of detecting filaments. To this end, we employed the “K-means clustering” method, and obtained different filament parameters such as position, tilt angle, length, and area. Our results show that filament length (and area) increases with latitude and the poleward migration is clearly dominated by a particular tilt sign. Lastly, we cross verified our findings with results from KoSO digitized photographic plate database for the overlapping time period and obtained a good agreement between them. This work, acting as a proof-of-theconcept, will kickstart new efforts to effectively use the entire hand-drawn series of multifeature, full-disk solar data and enable researchers to extract new sciences, such as the generation of pseudomagnetograms for the last 100 yr
Solar Filament Detection Using Deep Learning
<p><span>Solar Filament Detection Using Deep Learning</span><b></b></p> by Blessing Winifred Odume :: SSRN
Abstract
The paper presents a reliable approach for automatically detecting solar filaments in H-alpha full-disk solar images using a deep learning approach. This method minimizes the impact of noise on the solar images and accurately identifies solar filaments. A lack of datasets was addressed by using data argumentation to reduce overfitting. During deep learning, the initial dataset was augmented with new training data, which resulted in thousands of images being produced for training and validation. Consequently, 24,400 training samples were generated for SegNet and 20,000 for U-Net after the argumentation process.
Solar-Filament Detection and Classification Based on Deep Learning
Sol Phys 297, 104 (2022)
Solar-Filament Detection and Classification Based on Deep Learning | Solar Physics (springer.com)
Abstract
Solar filaments are distinct strip-like structures observed in chromospheric \text{H}\alpha images. Filament eruptions, flares, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) can be regarded as the same physical process of releasing magnetic energy at different times and solar atmosphere heights. It is very important to detect filaments for forecasting flares and CMEs. This article proposes a new solar-filament detection and classification method based on CondInst; a deep-learning model. A data set of solar filaments is built, including ten thousand filaments. To distinguish filaments that consist of only a single connected dark region and filaments that are broken into several fragments, the filaments are classified into isolated filaments and non-isolated filaments. The mean precision, recall, AP, and F1 obtained using the proposed method are 90.83\%, 83.88\%, 82.86\%, and 87.22\%, respectively. The results show that the method performs well in detecting and classifying isolated and non-isolated filaments, especially in solving the fragments problem of how to detect a filament that is broken into several fragments. The method also has good performance in handling various images, even with existing uneven brightness or low contrast. The precision of filament masks still needs to be improved in the future.
Solar Filament Segmentation Based on Improved U-Nets
Sol Phys 296, 176 (2021).
Solar Filament Segmentation Based on Improved U-Nets | Solar Physics (springer.com)
Abstract
To detect, track and characterize solar filaments more accurately, novel filament segmentation methods based on improved U-Nets are proposed. The full-disk H images from the Huairou Solar Observing Station of the National Astronomical Observatory and the Big Bear Solar Observatory were used for training and verifying the effectiveness of different improved networks’ filament segmentation performance. Comparative experiments with different solar dataset sizes and input image quality were performed. The impact of each improvement method on the segmentation effect was analyzed and compared based on experimental results. In order to further explore the influence of network depth on filament-segmentation accuracy, the segmentation results produced by Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (CGAN) were obtained and compared with improved U-nets. Experiments verified that U-Net with an Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling Module performs better for high-quality input solar images regardless of dataset sizes. CGAN performs better for low-quality input solar images with large dataset size. The algorithm may provide guidance for filament segmentation and more accurate segmentation results with less noise were acquired.
Solar Event Detection Using Deep-Learning-Based Object Detection Methods
Sol Phys 296, 160 (2021).
Solar Event Detection Using Deep-Learning-Based Object Detection Methods | Solar Physics (springer.com)
Abstract
Research on the detection of solar events has been conducted over many years. Recently, deep learning and data-driven approaches have been applied to solar event recognition. In this study, we present solar event detection using deep-learning-based object detection methods for real-time space weather monitoring. First, we construct a new object detection dataset using imaging data obtained by the Solar Dynamics Observatory with bounding boxes as labels for three representative features: coronal holes, sunspots, and prominences. Second, we train two representative object detection models: the Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) and the Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN) using the new dataset. The results show that both models perform similarly well for coronal hole and sunspot detection. For prominence detection, the SSD and Faster R-CNN exhibited relatively low performance. This study demonstrates that deep-learning-based object detection can successfully detect multiple types of solar events, and it may be extended to detect other solar events. In addition, we provide the dataset for further achievements of object detection studies in solar physics.
基于改进VNet太阳暗条检测方法
Vol.19 No.1 Jan., 2022 天 文 研 究 与 技 术
标题 (ati.ac.cn)
摘要
太阳暗条作为太阳大气磁场的示踪,对研究太阳磁场有极其重要的意义。针对现 有的暗条检测方法存在检测精度不高,弱小暗条错检、 漏检等问题,提出一种基于改进VNet网络的太阳暗条检测方法。首先,使用大熊湖天文台Hα全日面图像并结合磁图制作 了太阳暗条数据集。其次,在VNet网络下采样部分采用Inception模块融合不同尺度特征图 的特征,同时加入注意力机制增强特征图中暗条部分的语义信息。最后在上采样部分引入深 度监督模块,更多地保留太阳暗条的细节特征。为验证算法性能,采用191幅Hα全日面图 像数据集,其中包含暗条共3372条。算法在测试数据集上平均准确率达到0.9883,F1值 达到0.8385。实验结果证明,该方法可以有效识别Hα全日面图中的暗条。
相关文章:
基于深度学习的太阳暗条检测(2020年以来)
A universal method for solar filament detection from Hα observations using semi-supervised deep learning A&A, 686, A213 (2024) A universal method for solar filament detection from Hα observations using semi-supervised deep learning (aanda.org) ABS…...

【吊打面试官系列-Elasticsearch面试题】Elasticsearch 在部署时,对 Linux 的设置有哪些优化方法?
大家好,我是锋哥。今天分享关于 【Elasticsearch 在部署时,对 Linux 的设置有哪些优化方法?】面试题,希望对大家有帮助; Elasticsearch 在部署时,对 Linux 的设置有哪些优化方法? 面试官 :想了解对 ES 集…...

MySQL·C/C++访问数据库
目录 准备工作 测试是否安装成功 C/C语言访问 官方文档 接口介绍使用 mysql_init() mysql_close() 补充1:makefile编写 mysql_real_connect() 测试1:编译链接 mysql_query() 测试2:SQL语句测试 改 增 删 查 错误1&#x…...

python.tkinter设计标记语言(渲染2-渲染器)
TOC 前言 本文仅作为笔记记录。 在前文中,我们通过标记意义解释生成了带有明确渲染要求的参数组,以<title>为例,我们获取了title, level两个明确的渲染标记,这一部分由Tin标记解释器完成,不需要编写者花费过多…...

Cadence学习笔记 Day0 Cadence17.4环境安装
当然是选择“吴法安装” 直接跟着吴川斌博客的方法来就可以了,这里大致记录一下我的安装步骤: 安装许可证管理器破解许可证管理器安装软件以及补丁破解软件 获取 直接放出链接:吴川斌的博客 下载得到: 一、安装许可证管理器&am…...

k8s创建secret并在container中获取secret
k8s创建secret并在container中获取secret 本文使用的deployment和service与我的上一篇文章一样。link也放在下面了,如果不懂什么事deployment和service,可以先看我的上一篇文章。 k8s使用kustomize来部署应用 下面我们将通过创建secret开始。secret是我…...

Leetcode每日一题之仅仅反转字母(C++)
在学习之余对于知识的巩固也尤为重要,不论难度高低,都会对代码的理解有所加深,下面我们开始练习 思路解析 关于本题的核心思路就是如何判断字符串中元素是否为字母以及如何遍历字符串以达到仅反转的目的,这里用到的知识就是关于 s…...

PDF预览:利用vue3-pdf-app实现前端PDF在线展示
目录 PDF预览:利用vue3-pdf-app实现前端PDF在线展示 一、vue3-pdf-app组件介绍及其优点 1、vue3-pdf-app是什么 2、作用与场景 3、类似的插件 二、项目初始化与依赖安装 1、初始化Vue3项目 2、安装依赖 三、集成vue3-pdf-app插件 1、引入插件 2、配置组件…...

【OpenCV C++20 学习笔记】拉普拉斯(Laplace)二阶求导-边缘检测
拉普拉斯二阶求导 原理拉普拉斯算子(Laplacian Operator) API实例 原理 在OpenCV中,Sobel算法可以对图片中的值求一阶导数,从而计算出图片中的边缘线。其原理如下面的示意图: 那么,如果再求一次导数的,即求二阶导数&…...
MySQL的下载和安装步骤
一、数据库概述 我们先来了解三个概念:数据库、数据库管理系统、SQL。 名称全称简称数据库存储数据的仓库,数据是有组织的进行存储DataBase(DB)数据库管理系统操纵和管理数据库的大型软件DataBase Management System (DBMS)SQL操…...

Java国际版同城服务美容美发到店服务上门服务系统
🌍全球美妆新风尚!国际版同城服务,美容美发一键享 🏙️【国际视野,同城便捷】🏙️ 在这个全球化的时代,美丽不再受地域限制!国际版同城服务系统,将全球顶尖的美容美发资…...

硬件模拟的基本原理
具体来说,这种设计方法减少了集成电路 (IC) 设计和开发的设计迭代次数,并且广泛适用于所有电力电子设计。我详细介绍了我在快速上市 IC 开发方面的经验,并将该方法与其他旨在缩短产品开发时间的技术进行了对比。 产品开发流程 图 1ÿ…...
WPF学习(8)- Button按钮
1. 用法解析 Button因为继承了ButtonBase,而ButtonBase又继承了ContentControl,所以,Button可以通过设置Content属性来设置要显示的内容。例如 <Button Content"确定"/>我们使用Button的时机,通常是鼠标点击事件…...

Flutter GPU 是什么?为什么它对 Flutter 有跨时代的意义?
Flutter 3.24 版本引入了 Flutter GPU 概念的新底层图形 API flutter_gpu ,还有 flutter_scene 的 3D 渲染支持库,它们目前都是预览阶段,只能在 main channel 上体验,并且依赖 Impeller 的实现。 Flutter GPU 是 Flutter 内置的底…...
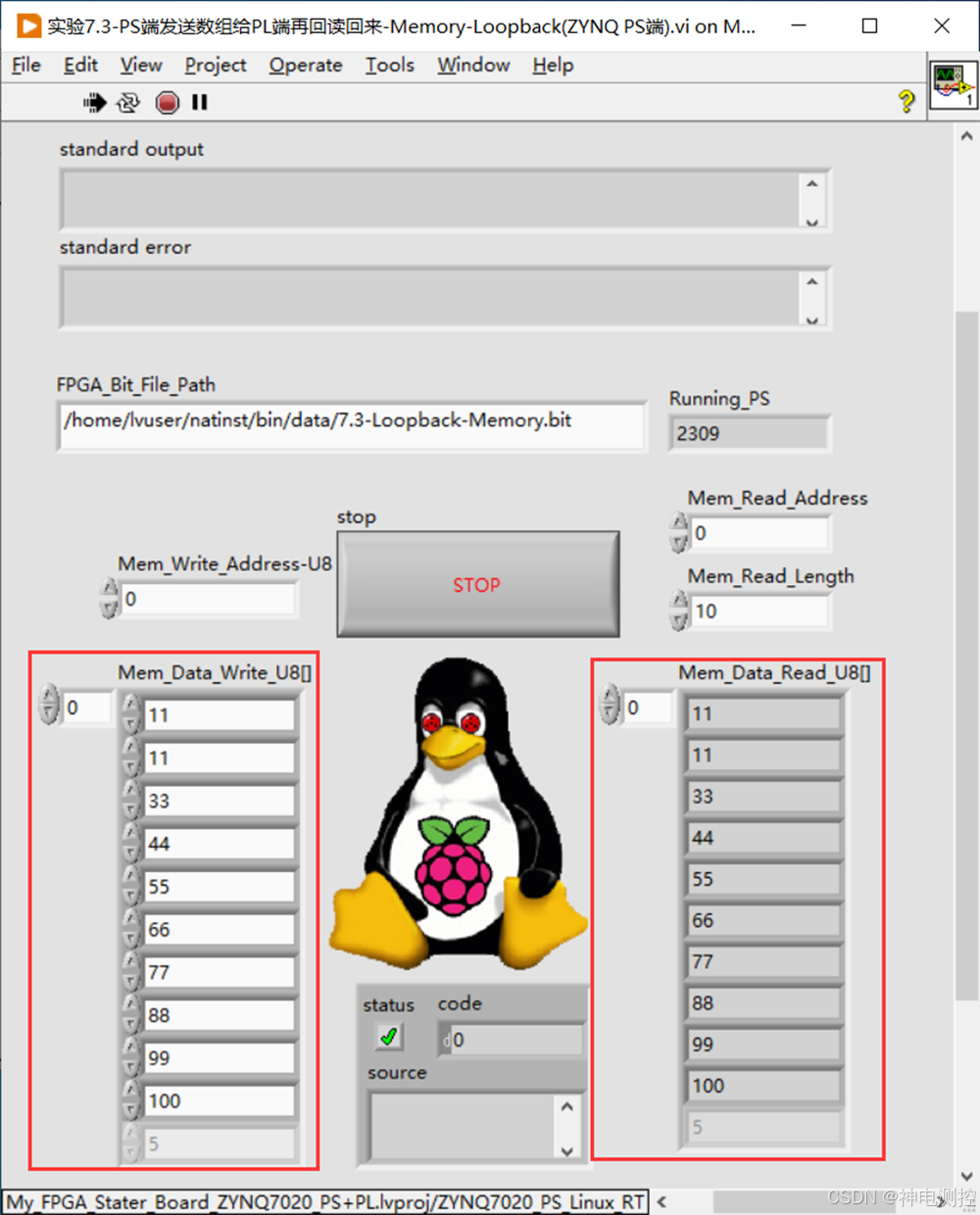
第6章>>实验7:PS(ARM)端Linux RT与PL端FPGA之间(通过Memory存储器进行通信和交互)《LabVIEW ZYNQ FPGA宝典》
1、实验内容 上一节实验里面介绍的Reg寄存器通道比较适合在PS端和PL端之间传递标量数据,也就是单个元素,如果要传递多个元素的数组或者连续数据流的话,Reg寄存器通道就不是很合适了。 本节实验我们向大家讲解如何借助Memory存储器通道在PS&am…...

通用前端的学习
通用前端的概念 通用前端的概念是我自创的,也是我多年开发全栈时的个人理解,结合自己对各种语言的比较,发现前端都具有几个特征,而这几个特征,很多人只能用具体的表象来描述,比如用安卓方式来说明…...

git本地仓库关联多个远程仓库时git pull失败问题
目录 问题描述 原因 解决办法 1.多个远程仓库需有继承关系 2.一句命令实现创建本地分支且与远程分支关联 问题描述 今天操作本地仓库时,关联了两个远程仓库,欲在本地仓库创建一个分支,与第二个远程仓库的某个分支关联,然后将…...
、Web 3.0和元宇宙三者联系、应用及未来发展趋势的详细分析)
人工智能(AI)、Web 3.0和元宇宙三者联系、应用及未来发展趋势的详细分析
人工智能(AI)、Web 3.0和元宇宙作为当前科技领域的热门话题,它们之间存在着紧密的联系,并在各自领域内展现出广泛的应用和未来的发展趋势。以下是对这三者联系、应用及未来发展趋势的详细分析: 一、人工智能ÿ…...

【IEEE出版 | 高校主办】第三届人工智能、物联网和云计算技术国际会议(AIoTC 2024)
第三届人工智能、物联网和云计算技术国际会议(AIoTC 2024) 2024 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things and Cloud Computing Technology 2024年9月13-15日 | 中国武汉 重要信息 大会官网:www.ic…...

PTA 7-4 BCD解密
7-4 BCD解密(10分) BCD数是用一个字节来表达两位十进制的数,每四个比特表示一位。所以如果一个BCD数的十六进制是0x12,它表达的就是十进制的12。但是小明没学过BCD,把所有的BCD数都当作二进制数转换成十进制输出了。于…...
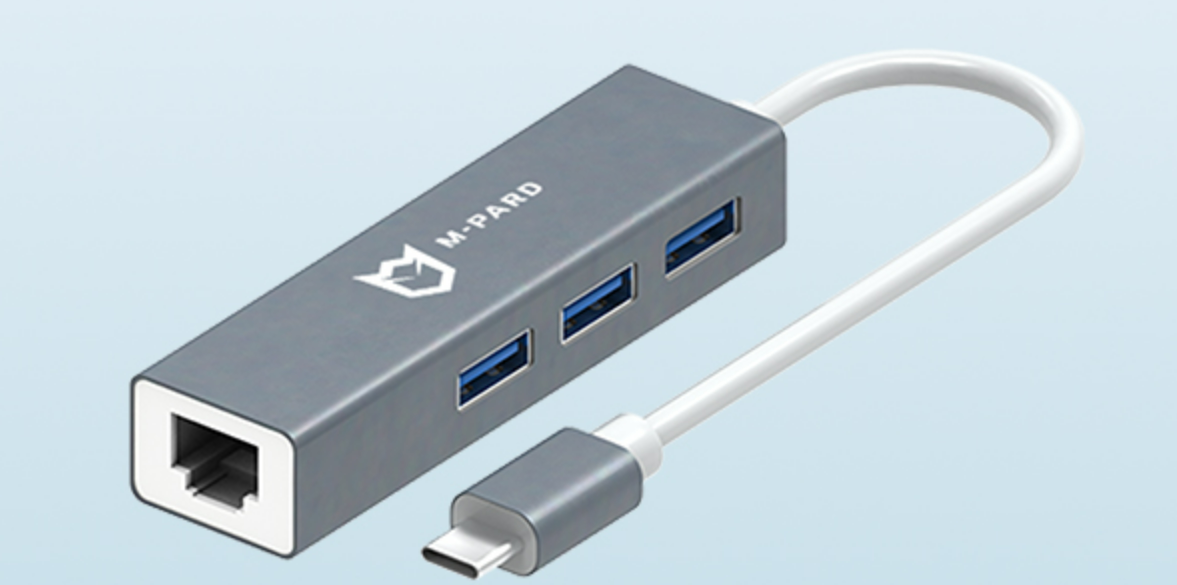

铭豹扩展坞 USB转网口 突然无法识别解决方法
当 USB 转网口扩展坞在一台笔记本上无法识别,但在其他电脑上正常工作时,问题通常出在笔记本自身或其与扩展坞的兼容性上。以下是系统化的定位思路和排查步骤,帮助你快速找到故障原因: 背景: 一个M-pard(铭豹)扩展坞的网卡突然无法识别了,扩展出来的三个USB接口正常。…...

智慧医疗能源事业线深度画像分析(上)
引言 医疗行业作为现代社会的关键基础设施,其能源消耗与环境影响正日益受到关注。随着全球"双碳"目标的推进和可持续发展理念的深入,智慧医疗能源事业线应运而生,致力于通过创新技术与管理方案,重构医疗领域的能源使用模式。这一事业线融合了能源管理、可持续发…...

C++:std::is_convertible
C++标志库中提供is_convertible,可以测试一种类型是否可以转换为另一只类型: template <class From, class To> struct is_convertible; 使用举例: #include <iostream> #include <string>using namespace std;struct A { }; struct B : A { };int main…...
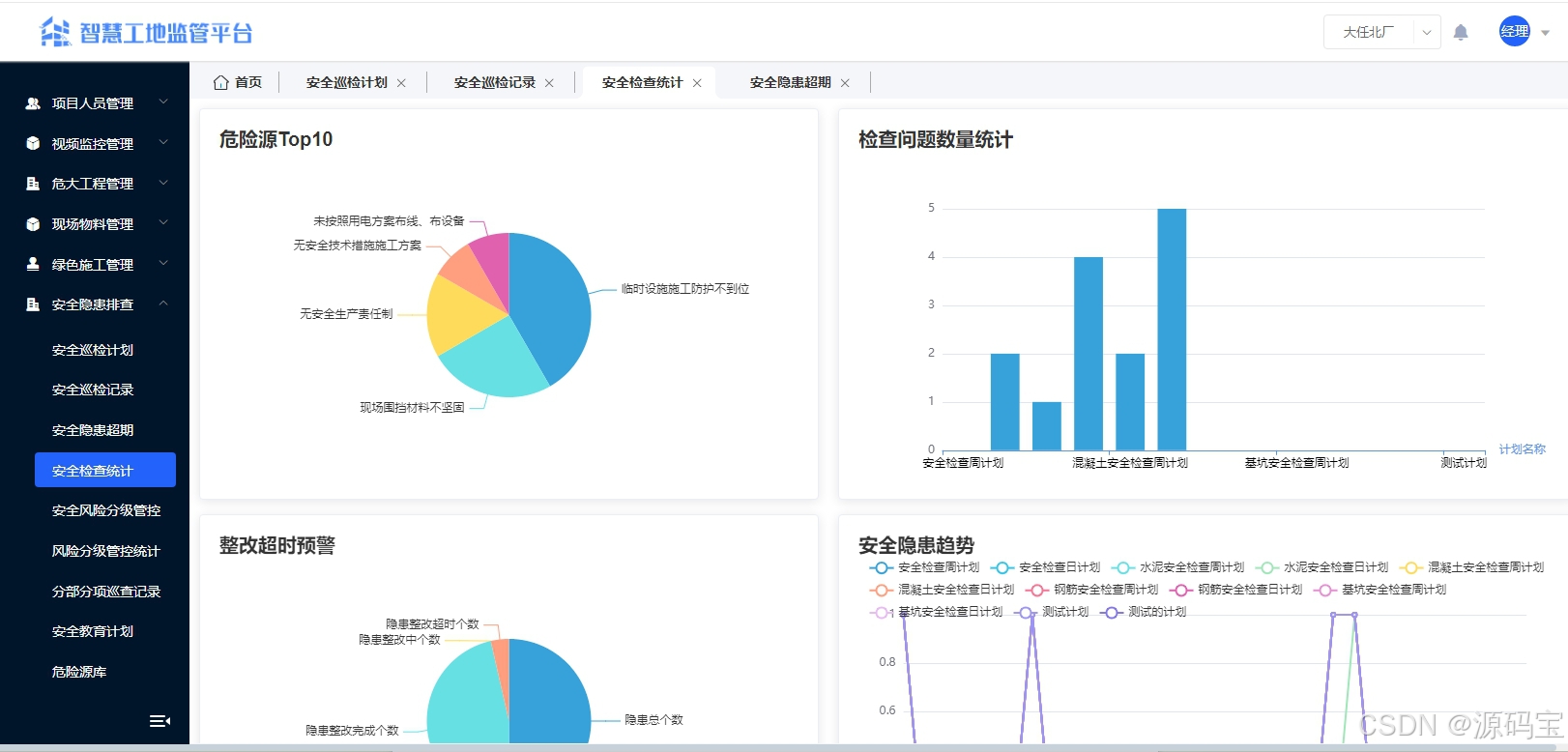
智慧工地云平台源码,基于微服务架构+Java+Spring Cloud +UniApp +MySql
智慧工地管理云平台系统,智慧工地全套源码,java版智慧工地源码,支持PC端、大屏端、移动端。 智慧工地聚焦建筑行业的市场需求,提供“平台网络终端”的整体解决方案,提供劳务管理、视频管理、智能监测、绿色施工、安全管…...
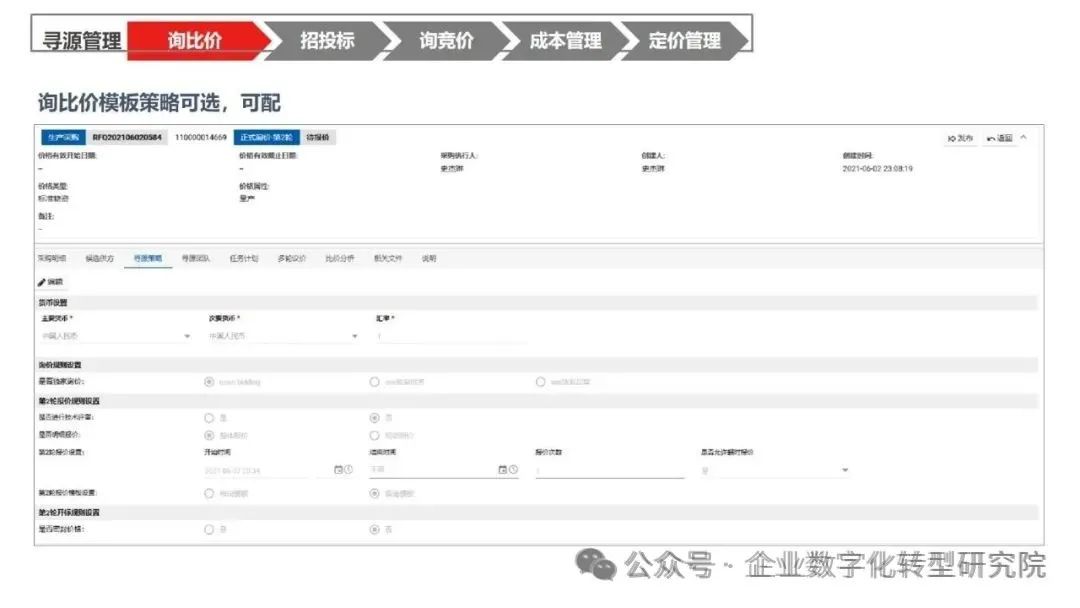
PPT|230页| 制造集团企业供应链端到端的数字化解决方案:从需求到结算的全链路业务闭环构建
制造业采购供应链管理是企业运营的核心环节,供应链协同管理在供应链上下游企业之间建立紧密的合作关系,通过信息共享、资源整合、业务协同等方式,实现供应链的全面管理和优化,提高供应链的效率和透明度,降低供应链的成…...

使用van-uploader 的UI组件,结合vue2如何实现图片上传组件的封装
以下是基于 vant-ui(适配 Vue2 版本 )实现截图中照片上传预览、删除功能,并封装成可复用组件的完整代码,包含样式和逻辑实现,可直接在 Vue2 项目中使用: 1. 封装的图片上传组件 ImageUploader.vue <te…...
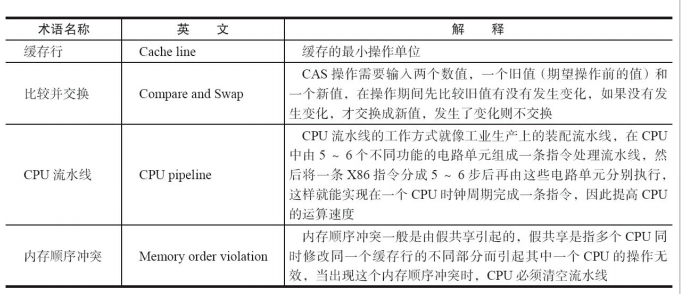
JUC笔记(上)-复习 涉及死锁 volatile synchronized CAS 原子操作
一、上下文切换 即使单核CPU也可以进行多线程执行代码,CPU会给每个线程分配CPU时间片来实现这个机制。时间片非常短,所以CPU会不断地切换线程执行,从而让我们感觉多个线程是同时执行的。时间片一般是十几毫秒(ms)。通过时间片分配算法执行。…...

Fabric V2.5 通用溯源系统——增加图片上传与下载功能
fabric-trace项目在发布一年后,部署量已突破1000次,为支持更多场景,现新增支持图片信息上链,本文对图片上传、下载功能代码进行梳理,包含智能合约、后端、前端部分。 一、智能合约修改 为了增加图片信息上链溯源,需要对底层数据结构进行修改,在此对智能合约中的农产品数…...

AGain DB和倍数增益的关系
我在设置一款索尼CMOS芯片时,Again增益0db变化为6DB,画面的变化只有2倍DN的增益,比如10变为20。 这与dB和线性增益的关系以及传感器处理流程有关。以下是具体原因分析: 1. dB与线性增益的换算关系 6dB对应的理论线性增益应为&…...

JavaScript基础-API 和 Web API
在学习JavaScript的过程中,理解API(应用程序接口)和Web API的概念及其应用是非常重要的。这些工具极大地扩展了JavaScript的功能,使得开发者能够创建出功能丰富、交互性强的Web应用程序。本文将深入探讨JavaScript中的API与Web AP…...

