Linux 中的特殊文件权限:SUID、GUID 和 Sticky
注: 机翻,未校。
Special File Permissions in Linux: SUID, GUID and Sticky Bit
You see an s instead of x in the file permissions? Linux has some special file permissions called SUID, GUID and Sticky Bit. Know more about them.
在文件权限中看到 s 而不是 x?Linux 有一些特殊的文件权限,称为 SUID、GUID 和 Sticky Bit。
File permissions and ownership are the basic and yet essential security concepts in Linux. You probably are already familiar with these terms already. It typically looks like this:
文件权限和所有权是 Linux 中基本但必不可少的安全概念。可能已经熟悉这些术语。它通常看起来像这样:

Regular file permissions
Apart from these regular permissions, there are a few special file permissions and not many Linux users are aware of it.
除了这些常规权限外,还有一些特殊的文件权限,并且没有多少 Linux 用户知道它。

Linux Special Permissions: SUID, GUID and Sticky Bit
To start talking about of special permissions, I am going to presume that you have some knowledge of the basic file permissions. If not, please read our excellent guide explaining Linux file permission.
在开始讨论特殊权限之前,假设对基本文件权限有一定的了解。
Now I’m gonna show you some special permissions with new letters on the Linux file system.
现在,将展示 Linux 文件系统上带有新字母的一些特殊权限。
In this example, the passwd command, responsible to change the password of a user, has the letter s on the same place we expect to see x or -, for user permissions. It’s important to notice that this file belongs to the root user and root group.
在此示例中,负责更改用户密码的 passwd 命令在期望看到的 x 或 - 的同一位置具有字母 s,用于用户权限。请务必注意,此文件属于 root 用户和 root 组。
With this permission, you don’t need to give sudo access to a specific user when you want him to run some root script.
通过这种权限设置,无需给予特定用户 sudo 访问权限,就可以让他运行一些以 root 身份执行的脚本。
What is SUID?
When the SUID bit is set on an executable file, this means that the file will be executed with the same permissions as the owner of the executable file.
当在可执行文件上设置 SUID 位时,这意味着将以与可执行文件所有者相同的权限执行该文件。

Let’s take a practical example. If you look at the binary executable file of the passwd command, it has the SUID bit set.
让举一个实际的例子。如果查看 passwd 命令的二进制可执行文件,它会设置了 SUID 位。
linux:~$ ls -l /usr/bin/passwd
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 59640 Mar 22 2019 /usr/bin/passwd
This means that any user running the passwd command will be running it with the same permission as root.
这意味着任何运行 passwd 命令的用户都将以与 root 相同的权限运行它。
What’s the benefit? The passwd command needs to edit files like /etc/passwd, /etc/shadow to change the password. These files are owned by root and can only be modified by root. But thanks to the setuid flag (SUID bit), a regular user will also be able to modify these files (that are owned by root) and change his/her password.
有什么好处?passwd 命令需要编辑 /etc/passwd、/etc/shadow 等文件以更改密码。这些文件归 root 所有,只能由 root 修改。但是多亏了 setuid 标志(SUID 位),普通用户也将能够修改这些文件(由 root 拥有)并更改他/她的密码。
This is the reason why you can use the passwd command to change your own password despite of the fact that the files this command modifies are owned by root.
这就是为什么可以使用 passwd 命令更改自己的密码的原因,尽管此命令修改的文件归 root 所有。
Why can a normal user not change the password of other users?
Note that a normal user can’t change passwords for other users, only for himself/herself. But why? If you can run the passwd command as a regular user with the same permissions as root and modify the files like /etc/passwd, why can you not change the password of other users?
请注意,普通用户不能为其他用户更改密码,只能为自己更改密码。但是为什么?如果可以以与root相同权限的普通用户身份运行passwd命令并修改/etc/passwd之类的文件,为什么不能更改其他用户的密码?
If you check the code for the passwd command, you’ll find that it checks the UID of the user whose password is being modified with the UID of the user that ran the command. If it doesn’t match and if the command wasn’t run by root, it throws an error.
如果检查 passwd 命令的代码,会发现它会检查密码正在修改的用户的 UID 与运行命令的用户的 UID 一起检查。如果它不匹配,并且如果命令不是由 root 运行的,则会引发错误。
The setuid/SUID concept is tricky and should be used with utmost cautious otherwise you’ll leave security gaps in your system. It’s an essential security concept and many commands (like ping command and programs (like sudo) utilize it.
setuid/SUID 概念很棘手,应非常谨慎地使用,否则会在系统中留下安全漏洞。这是一个基本的安全概念,许多命令(如 ping 命令)和程序(如 sudo)都使用它。
Now that you understand the concept SUID, let’s see how to set the SUID bit.
现在已经了解了 SUID 的概念,让看看如何设置 SUID 位。
How to set SUID bit?
I find the symbolic way easier while setting SUID bit. You can use the chmod command in this way:
发现在设置 SUID 位时,符号方式更容易。可以通过以下方式使用 chmod 命令:
chmod u+s file_name
Here’s an example: 下面是一个示例:
linux:~$ ls -l test.txt
-rwxrw-rw- 1 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 0 Apr 12 17:51 test.txt
linux:~$ chmod u+s test.txt
linux:~$ ls -l test.txt
-rwsrw-rw- 1 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 0 Apr 12 17:52 test.txt
You can also use the numeric way. You just need to add a fourth digit to the normal permissions. The octal number used to set SUID is always 4.
也可以使用数字方式。只需要在正常权限中添加第四位数字即可。用于设置 SUID 的八进制数始终为 4。
linux:~$ ls -l test2.txt
-rwxrw-rw- 1 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 0 Apr 12 17:53 test2.txt
linux:~$ chmod 4766 test2.txt
linux:~$ ls -l test2.txt
-rwsrw-rw- 1 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 0 Apr 12 17:54 test2.txt
How to remove SUID?
You can use either the symbolic mode in chmod command like this:
可以在 chmod 命令中使用符号模式,如下所示:
chmod u-s test.txt
Or, use the numeric way with 0 instead of 4 with the permissions you want to set:
或者,使用带有 0 而不是 4 的数字方式来设置要设置的权限:
chmod 0766 test2.txt
Difference between small s and capital S as SUID bit
Remember the definition of SUID? It allows a file to be executed with the same permissions as the owner of the file.
还记得SUID的定义吗?它允许使用与文件所有者相同的权限执行文件。
But what if the file doesn’t have execute bit set in the first place? Like this:
但是,如果文件一开始就没有设置执行位怎么办?喜欢这个:
linux:~$ ls -l test.txt
-rw-rw-rw- 1 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 0 Apr 12 17:51 test.txt
If you set the SUID bit, it will show a capital S, not small s:
如果设置 SUID 位,它将显示大写字母 S,而不是小 s:
linux:~$ chmod u+s test.txt
linux:~$ ls -l test.txt
-rwSrw-rw- 1 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 0 Apr 12 17:52 test.txt
The S as SUID flag means there is an error that you should look into. You want the file to be executed with the same permission as the owner but there is no executable permission on the file. Which means that not even the owner is allowed to execute the file and if file cannot be executed, you won’t get the permission as the owner. This fails the entire point of setting the SUID bit.
S as SUID 标志表示存在应调查的错误。希望以与所有者相同的权限执行文件,但该文件没有可执行权限。这意味着甚至连所有者都不允许执行该文件,如果文件无法执行,将无法获得作为所有者的权限。这无法满足设置 SUID 位的全部意义。
How to find all files with SUID set?
If you want to search files with this permission, use find command in the terminal with option -perm.
如果要使用此权限搜索文件,请在终端中使用带有 -perm 选项的 find 命令。
find / -perm /4000
What is SGID?
SGID is similar to SUID. With the SGID bit set, any user executing the file will have same permissions as the group owner of the file.
SGID类似于SUID。设置了 SGID 位后,执行文件的任何用户都将具有与文件组所有者相同的权限。
It’s benefit is in handling the directory. When SGID permission is applied to a directory, all sub directories and files created inside this directory will get the same group ownership as main directory (not the group ownership of the user that created the files and directories).
它的好处是处理目录。当将 SGID 权限应用于目录时,在此目录中创建的所有子目录和文件将获得与主目录相同的组所有权(而不是创建文件和目录的用户的组所有权)。

Open your terminal and check the permission on the file /var/local:
打开终端并检查文件 /var/local 的权限:
linux:~$ ls -ld /var/local
drwxrwsr-x 1 root staff 512 Apr 24 2018 /var/local
This folder /var/local has the letter s on the same place you expect to see x or - for group permissions.
此文件夹 /var/local 的同一位置包含字母“s”,希望看到组权限的“x”或“-”。
A practical example of SGID is with Samba server for sharing files on your local network. It’s guaranteed that all new files will not lose the permissions desired, no matter who created it.
SGID的一个实际例子是与Samba服务器一起使用,用于在本地网络上共享文件。可以保证所有新文件都不会丢失所需的权限,无论它是由谁创建的。
How to set SGID?
You can set the SGID bit in symbolic mode like this:
可以像这样在符号模式下设置 SGID 位:
chmod g+s directory_name
Here’s an example: 下面是一个示例:
linux:~$ ls -ld folder/
drwxrwxr-x 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:32 folder/
linux:~$ chmod g+s folder
linux:~$ ls -ld folder/
drwxrwsr-x 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:32 folder/
You may also use the numeric way. You just need to add a fourth digit to the normal permissions. The octal number used to SGID is always 2.
也可以使用数字方式。只需要在正常权限中添加第四位数字即可。用于 SGID 的八进制数始终为 2。
linux:~$ ls -ld folder2/
drwxrwxr-x 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:33 folder2/
linux:~$ chmod 2775 folder2
linux:~$ ls -ld folder2/
drwxrwsr-x 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:33 folder2/
How to remove SGID bit?
Just use the -s instead of +s like this:
只需使用 -s 而不是 +s,如下所示:
chmod g-s folder
Removing SGID is the same as removing SGID. Use the additional 0 before the permissions you want to set:
删除 SGID 与删除 SGID 相同。在要设置的权限之前使用额外的 0:
chmod 0755 folder
How to find files with SGID set in Linux
To find all the files with SGID bit set, use this command:
要查找设置了 SGID 位的所有文件,请使用以下命令:
find . -perm /2000
What is a Sticky Bit?
The sticky bit works on the directory. With sticky bit set on a directory, all the files in the directory can only be deleted or renamed by the file owners only or the root.
粘滞位在目录上工作。在目录上设置粘滞位时,目录中的所有文件只能由文件所有者或根用户删除或重命名。

This is typically used in the /tmp directory that works as the trash can of temporary files.
这通常在 /tmp 目录中使用,该目录充当临时文件的垃圾桶。
linux:~$ ls -ld /tmp
drwxrwxrwt 1 root root 512 Apr 12 13:24 /tmp
As you can see, the folder /tmp, has the letter t on the same place we expect to see x or – for others permissions. This means that a user (except root) cannot delete the temporary files created by other users in the /tmp directory.
如所见,文件夹 /tmp 在希望看到 x 或 – 的同一位置上有字母 t,用于其他权限。这意味着用户(root 除外)无法删除其他用户在 /tmp 目录中创建的临时文件。
How to set the sticky bit? 如何设置粘滞位?
As always, you can use both symbolic and numeric mode to set the sticky bit in Linux.
与往常一样,可以在 Linux 中使用符号和数字模式来设置粘滞位。
chmod +t my_dir
Here’s an example: 下面是一个示例:
linux:~$ ls -ld my_dir/
drwxrwxr-x 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:54 my_dir/
linux:~$ chmod +t my_dir/
linux:~$ ls -ld my_dir/
drwxrwxr-t 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:54 my_dir/
The numeric way is to add a fourth digit to the normal permissions. The octal number used for sticky bit is always 1.
数字方式是在正常权限上添加第四位数字。用于粘滞位的八进制数始终为 1。
linux:~$ ls -ld my_dir/
drwxrwxr-x 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:55 my_dir/
linux:~$ chmod 1775 tmp2/
linux:~$ ls -ld tmp2/
drwxrwxr-t 2 linuxhandbook linuxhandbook 4096 Apr 12 19:55 my_dir/
How to remove the sticky bit: 如何去除粘性钻头:
You can use the symbolic mode:
可以使用符号模式:
chmod -t my_dir
Or the numeric mode with 0 before the regular permissions:
或者常规权限前加 0 的数字模式:
chmod 0775 tmp2
How to find files with sticky bit set in Linux 如何在 Linux 中查找设置了粘滞位的文件
This command will return all files/directories in with sticky bit set:
此命令将返回设置了粘滞位的所有文件/目录:
linux:~$ find . -perm /1000
If the directory doesn’t have the execute permission set for all, setting a sticky bit will result in showing T instead of t. An indication that things are not entirely correct with the sticky bit.
如果目录没有为所有目录设置执行权限,则设置粘滞位将导致显示 T 而不是 t。表明粘性位的情况并不完全正确。
Conclusion 结论
I’ll put this picture here to recall what you have just learned:
把这张图片放在这里,是为了回忆你刚刚学到的东西:

This flexibility to manage folders, files and all their permissions are so important in the daily work of a sysadmin. You could see that all those special permissions are not so difficult to understand but they must be used with utmost caution.
这种管理文件夹、文件及其所有权限的灵活性在系统管理员的日常工作中非常重要。可以看到,所有这些特殊权限并不难理解,但必须非常谨慎地使用它们。
via:
-
What is SUID, GUID and Sticky Bit in Linux? How to Use Them? Sep 15, 2022 — Abhishek Prakash
https://linuxhandbook.com/suid-sgid-sticky-bit/
相关文章:

Linux 中的特殊文件权限:SUID、GUID 和 Sticky
注: 机翻,未校。 Special File Permissions in Linux: SUID, GUID and Sticky Bit You see an s instead of x in the file permissions? Linux has some special file permissions called SUID, GUID and Sticky Bit. Know more about them. 在文件权…...

2024 某公司python 面试真题
Q: Can the type of options or labels of switch-case be floating? 在C语言中,switch-case语句的标签必须是整数类型,不能是浮点型。而在Python中,没有switch-case语句,但是可以使用字典来实现类似的功能,而字典的键…...
jwt伪造身份组组组合拳艰难通关
前言 现在的攻防演练不再像以往那样一个漏洞直捣黄龙,而是需要各种组合拳才能信手沾来,但是有时候使尽浑身解数也不能诚心如意。 前期信息收集 首先是拿到靶标的清单 访问系统的界面,没有什么能利用的功能点 首先进行目录扫描,…...

leetcode日记(64)最小覆盖子串
很复杂的题目,无论是思路还是实践都很难… 思路还是看了答案(?)设定两个指针“框”出一串字符串,初始两个指针都指在s的零位,先移动下指针,直到使框出的字符串中包含t中所有字符串,…...

C语言——编译与链接
目录 引言 翻译环境与运行环境 翻译环境 1.翻译环境的简述 2.编译过程 2.1 预处理(预编译) 2.2 编译 2.2.1 词法分析 2.2.2 语法分析 2.2.3 语义分析 2.3 汇编 3.链接 运行环境 结束语 引言 C语言编译与链接过程是理解程序如何从代码转化…...
你一定想看的LVS详细介绍及常见模式(NAT,DR,防火墙标记)实验详解
目录 一、什么是LVS 二、LVS的核心思想 三、 LVS的优势 四、LVS的调度算法 4.1. LVS的调度算法类型 4.2. LVS静态调度算法 4.3. LVS动态调度算法 4.4.在4.15版本内核以后新增调度算法 五、LVS软件相关信息 六、ipvsadm命令 七、 LVS的NAT模式实验详解 7.1实验环境 7.…...

嵌入式初学-C语言-十七
#接嵌入式初学-C语言-十六# 函数的递归调用 含义: 在一个函数中直接或者间接调用了函数本身,称之为函数的递归调用 // 直接调用a()->a(); // 间接调用a()->b()->a();a()->b()->..->a();递归调用的本质: 本是是一种循环…...

leetcode数论(2280. 表示一个折线图的最少线段数)-几何
前言 经过前期的基础训练以及部分实战练习,粗略掌握了各种题型的解题思路。现阶段开始专项练习。 数论包含最大公约数(>2个数)、最大公约数性质、最小公倍数、区间范围质因素计数(最下间隔)、质因素分解、判断质数、平方根、立方根、互质、同余等等。 描述 给…...

如何利用 LNMP 搭建 WordPress 站点
作者 乐维社区(forum.lwops.cn) 许远 在这个信息爆炸的时代,拥有一个能够迅速传达信息、展示个性、并能够与世界互动的在线平台,已成为企业和个人的基本需求。WordPress,以其无与伦比的易用性和强大的扩展性࿰…...
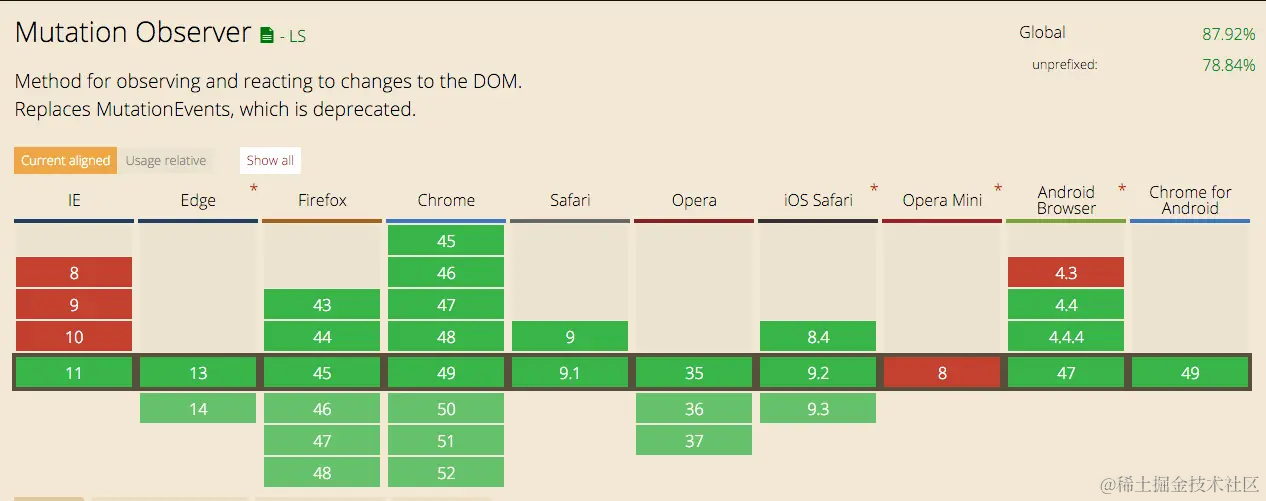
“Mutation Observer:让DOM变化尽在掌握
Mutation Observer(变动观察者) 定义 Mutation Observer是一种JavaScript API,用于异步监测DOM树的变动,包括元素的添加、删除、属性变化等。当DOM发生变动时,它可以触发回调函数,允许你对变动作出响应。 …...

oracle(19c)用户管理
简介 本文介绍 Oracle 中的用户管理,包含以下内容: 概念介绍 系统用户 解锁 hr 用户 创建用户 用户相关案例 使用 Profile 管理用户口令 Oracle 的认证方式 重置管理员(sys)密码 1. 概念介绍 使用前可以自行安装oracle数据库 oracle19c安装&a…...
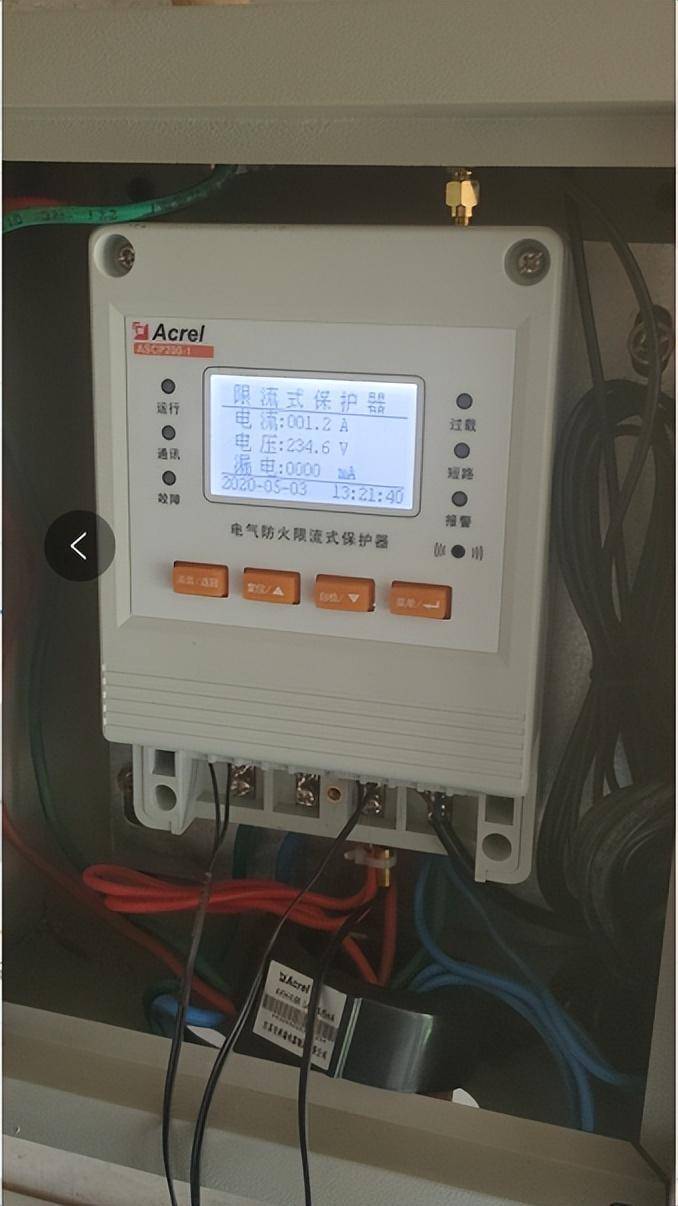

浅谈安科瑞智慧用电系统在电气火灾中的应用
摘要:为了对电气火灾事故进行预测和预警,同时为了对电气火灾事故的应急救援提供 支持,将智慧用电监控系统应用于电气火灾中。该系统利用物联网、移动互联网、云平台、大数据技术,实现对电气线路电流、漏电、温度、谐波等参数进行…...

【Material-UI】Button 组件中的尺寸设置(Sizes)详解
文章目录 一、基础尺寸选项1. 小尺寸(Small)2. 中等尺寸(Medium)3. 大尺寸(Large) 二、尺寸的应用场景三、高级用法和最佳实践1. 使用主题调整默认尺寸2. 确保一致性3. 考虑无障碍设计 四、总结 在用户界面…...

Java学习Day20
Vue学习 nodejs的安装与环境配置 1.直接去官网下载合适版本的nodejs( https://nodejs.org/zh-cn/download/prebuilt-installer) 2.解压下载的安装包,将文件路径配置到系统变量的path中,然后确认后退出。可以使用终端来查看安装的nodejs版本。使用winR…...

代理IP怎么弄,如何在电脑中设置IPXProxy代理IP?
随着互联网的不断普及,人们可以利用网络在不同的领域实现更多的可能性。在这个过程中,许多新型网络技术受到人们的关注,代理IP就是其中之一。使用代理IP可以隐藏真实的IP地址,帮助我们突破网络限制、保护隐私、进行网页抓取等一系…...

MacOS 查看端口命令
netstat 命令 查看所有监听的端口 netstat -nat | grep LISTEN 查看9000端口 netstat -nat | grep 9000 # 示例输出 tcp4 0 0 127.0.0.1.9000 *.* LISTEN lsof 命令 查看所有TCP监听的端口 lsof -n -P -i TCP -s TCP:LISTEN 参…...

【python】序列化与反序列化
序列化与反序列化 JSON、CSV和YAML都是常见的数据序列化和反序列化格式。它们都可以用于将数据从一种表示形式转换为另一种表示形式。 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,它使用键值对的形式来表示数据ÿ…...

补充:关于GRU的详细运作原理以及特殊的优化思路
1. GRU的基本结构和运作原理 1.1 GRU的基本概念 Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) 是一种简化版的循环神经网络 (RNN),它通过引入门控机制来解决长期依赖问题,同时减少参数数量以降低计算复杂度。 1.2 GRU的结构详解 GRU 包含两个门控机制:更新门 (update gate) 和重置门 (re…...

xxl-job 源码梳理(2)-服务端
目录 1. 控制面的接口2.手动触发任务2. 定时任务的实现 1. 控制面的接口 服务端包含xxl-job的管理端,页面上的接口后端一系列的controller接口 appName是一个核心概念,它是指执行器应用的名称,appName是执行器的唯一标识 页面上的接口&#…...

C++ GDl+ 多张图片合并生成GIF动画格式图片
使用ImageMagick多张图合成GIF。 1、工具下载安装 下载地址:ImageMagick – Download,windows下载版本如下: 下载后,安装,安装时选择为C/C安装动态库和头文件。 2、代码实现 附加包含目录:ImageMagick-7.…...

国防科技大学计算机基础课程笔记02信息编码
1.机内码和国标码 国标码就是我们非常熟悉的这个GB2312,但是因为都是16进制,因此这个了16进制的数据既可以翻译成为这个机器码,也可以翻译成为这个国标码,所以这个时候很容易会出现这个歧义的情况; 因此,我们的这个国…...

云启出海,智联未来|阿里云网络「企业出海」系列客户沙龙上海站圆满落地
借阿里云中企出海大会的东风,以**「云启出海,智联未来|打造安全可靠的出海云网络引擎」为主题的阿里云企业出海客户沙龙云网络&安全专场于5.28日下午在上海顺利举办,现场吸引了来自携程、小红书、米哈游、哔哩哔哩、波克城市、…...
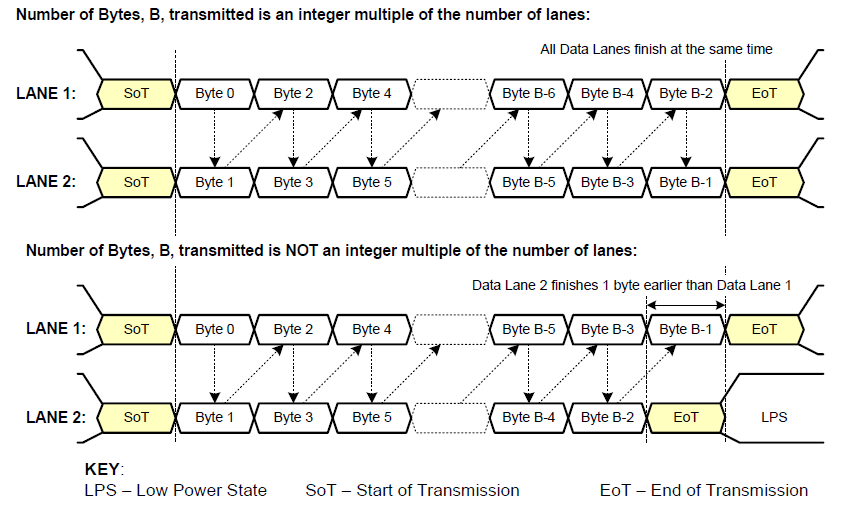
《从零掌握MIPI CSI-2: 协议精解与FPGA摄像头开发实战》-- CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一)
CSI-2 协议详细解析 (一) 1. CSI-2层定义(CSI-2 Layer Definitions) 分层结构 :CSI-2协议分为6层: 物理层(PHY Layer) : 定义电气特性、时钟机制和传输介质(导线&#…...
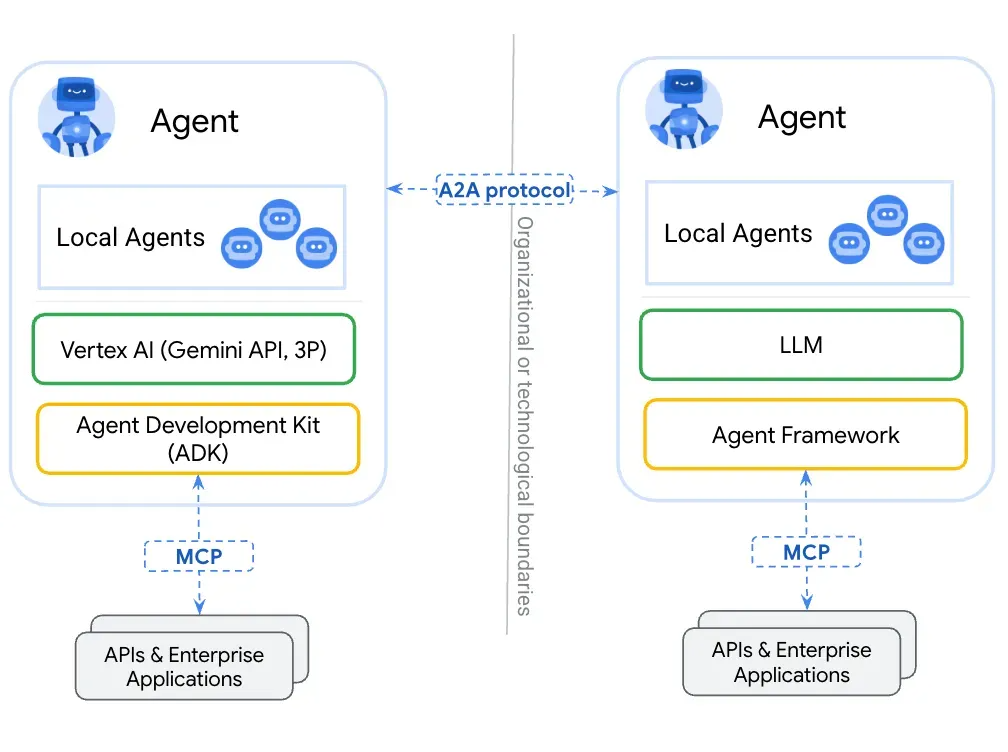
第一篇:Agent2Agent (A2A) 协议——协作式人工智能的黎明
AI 领域的快速发展正在催生一个新时代,智能代理(agents)不再是孤立的个体,而是能够像一个数字团队一样协作。然而,当前 AI 生态系统的碎片化阻碍了这一愿景的实现,导致了“AI 巴别塔问题”——不同代理之间…...
Python爬虫(一):爬虫伪装
一、网站防爬机制概述 在当今互联网环境中,具有一定规模或盈利性质的网站几乎都实施了各种防爬措施。这些措施主要分为两大类: 身份验证机制:直接将未经授权的爬虫阻挡在外反爬技术体系:通过各种技术手段增加爬虫获取数据的难度…...
详解:相对定位 绝对定位 固定定位)
css的定位(position)详解:相对定位 绝对定位 固定定位
在 CSS 中,元素的定位通过 position 属性控制,共有 5 种定位模式:static(静态定位)、relative(相对定位)、absolute(绝对定位)、fixed(固定定位)和…...

unix/linux,sudo,其发展历程详细时间线、由来、历史背景
sudo 的诞生和演化,本身就是一部 Unix/Linux 系统管理哲学变迁的微缩史。来,让我们拨开时间的迷雾,一同探寻 sudo 那波澜壮阔(也颇为实用主义)的发展历程。 历史背景:su的时代与困境 ( 20 世纪 70 年代 - 80 年代初) 在 sudo 出现之前,Unix 系统管理员和需要特权操作的…...

土地利用/土地覆盖遥感解译与基于CLUE模型未来变化情景预测;从基础到高级,涵盖ArcGIS数据处理、ENVI遥感解译与CLUE模型情景模拟等
🔍 土地利用/土地覆盖数据是生态、环境和气象等诸多领域模型的关键输入参数。通过遥感影像解译技术,可以精准获取历史或当前任何一个区域的土地利用/土地覆盖情况。这些数据不仅能够用于评估区域生态环境的变化趋势,还能有效评价重大生态工程…...

【学习笔记】深入理解Java虚拟机学习笔记——第4章 虚拟机性能监控,故障处理工具
第2章 虚拟机性能监控,故障处理工具 4.1 概述 略 4.2 基础故障处理工具 4.2.1 jps:虚拟机进程状况工具 命令:jps [options] [hostid] 功能:本地虚拟机进程显示进程ID(与ps相同),可同时显示主类&#x…...
初学 pytest 记录
安装 pip install pytest用例可以是函数也可以是类中的方法 def test_func():print()class TestAdd: # def __init__(self): 在 pytest 中不可以使用__init__方法 # self.cc 12345 pytest.mark.api def test_str(self):res add(1, 2)assert res 12def test_int(self):r…...
