C++编程:无锁环形队列 (LockFreeRingQueue)的简单实现、测试和分析
文章目录
- 0. 概述
- 1. 无锁环形队列概述
- 1.1 无锁环形队列的特点
- 1.2 无锁环形队列的优势与局限
- 2. `LockFreeRingQueue` 实现
- 2.1 `Enqueue` 操作流程图
- 2.2 `Dequeue` 操作流程图
- 3. 核心实现细节
- 3.1 环形队列的大小调整
- 3.2 索引计算
- 3.3 原子操作与CAS
- 3.4 线程让步
- 4. 测试示例程序
- 4.1 实现代码
- 4.2 代码解释:
- 4.3 运行程序:
- 4.4 执行结果:
- 5. 单元测试
- 5.1 测试代码解释:
- 5.2 测试运行:
- 6. 总结
0. 概述
在现代多线程编程中,高效的并发数据结构对于提升系统性能至关重要,尤其是在处理高并发场景时。本文将详细介绍一种无锁环形队列 (LockFreeRingQueue) 的实现,并探讨其在实际应用中的优势与局限。
本文详细测试代码 lock_free_ring_queue
1. 无锁环形队列概述
无锁环形队列是一种高效的并发数据结构,适用于多线程环境下的生产者-消费者模型。它通过使用原子操作(如CAS操作)来避免锁的使用,从而消除了锁竞争带来的性能开销和潜在的死锁风险。
1.1 无锁环形队列的特点
- 线程安全:通过原子操作保证数据的正确性。
- 高效性:避免了锁竞争,减少了线程上下文切换的开销。
- 避免ABA问题:设计时特别考虑了ABA问题的影响,通过合理的索引管理避免了这一问题。
1.2 无锁环形队列的优势与局限
优势:
- 高并发性:无锁结构通过避免锁的使用,使多个线程可以并发执行,提高了吞吐量。
- 低延迟:在高并发场景下,无锁结构减少了线程竞争带来的上下文切换,降低了系统延迟。
- 避免死锁:由于没有锁的存在,自然避免了死锁问题。
局限:
- 复杂性:无锁结构通常比锁机制实现更复杂,容易引入难以调试的并发错误。
- 硬件依赖性:原子操作(如CAS)通常依赖于底层硬件支持,在不同平台上表现可能有所不同。
- 有限应用场景:无锁队列并不适合所有场景,在某些情况下(如低并发或非实时系统),传统的锁机制可能更为适合。
2. LockFreeRingQueue 实现
下面是一个基于C++实现的无锁环形队列的实现,该队列支持多生产者和多消费者线程的并发访问。
#ifndef RING_QUEUE_HPP
#define RING_QUEUE_HPP#include <atomic>
#include <memory>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <thread>template <typename T>
class LockFreeRingQueue {public:// Constructor that initializes the ring queue with the specified sizeexplicit LockFreeRingQueue(uint32_t size);// Default destructor~LockFreeRingQueue() = default;// Disable copy constructor and assignment operatorLockFreeRingQueue(const LockFreeRingQueue&) = delete;LockFreeRingQueue& operator=(const LockFreeRingQueue&) = delete;// Enqueue operation to add an element to the queuebool Enqueue(const T& data);// Dequeue operation to remove an element from the queuebool Dequeue(T* data);// Check if the queue is emptybool IsEmpty() const noexcept;// Check if the queue is fullbool IsFull() const noexcept;// Get the current size of the queueuint32_t Size() const noexcept;private:// Check if the given number is a power of twostatic bool IsPowerOfTwo(uint32_t num) noexcept;// Calculate the ceiling power of two greater than or equal to the given numberstatic uint32_t CeilPowerOfTwo(uint32_t num) noexcept;// Round up the given number to the nearest power of twostatic uint32_t RoundupPowerOfTwo(uint32_t num) noexcept;// Get the index within the queueuint32_t IndexOfQueue(uint32_t index) const noexcept;private:const uint32_t size_; // Size of the queue, must be a power of twostd::atomic<uint32_t> length_; // Current length of the queuestd::atomic<uint32_t> read_index_; // Index for the consumer to readstd::atomic<uint32_t> write_index_; // Index for the producer to writestd::atomic<uint32_t> last_write_index_; // Last confirmed write indexstd::unique_ptr<T[]> queue_; // Array to store the queue elements
};template <typename T>
LockFreeRingQueue<T>::LockFreeRingQueue(uint32_t size): size_(size <= 1U ? 2U: IsPowerOfTwo(size) ? size: RoundupPowerOfTwo(size)),length_(0U),read_index_(0U),write_index_(0U),last_write_index_(0U),queue_(std::make_unique<T[]>(size_)) {if (size == 0U) {throw std::out_of_range("Queue size must be greater than 0");}
}template <typename T>
bool LockFreeRingQueue<T>::Enqueue(const T& data) {uint32_t current_read_index;uint32_t current_write_index;do {current_read_index = read_index_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);current_write_index = write_index_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);// Check if the queue is fullif (IndexOfQueue(current_write_index + 1U) == IndexOfQueue(current_read_index)) {return false; // Queue is full}} while (!write_index_.compare_exchange_weak(current_write_index, current_write_index + 1U, std::memory_order_release,std::memory_order_relaxed));queue_[IndexOfQueue(current_write_index)] = data;// Confirm the write operationwhile (!last_write_index_.compare_exchange_weak(current_write_index, current_write_index + 1U,std::memory_order_release, std::memory_order_relaxed)) {std::this_thread::yield(); // Yield CPU to avoid busy-waiting}length_.fetch_add(1U, std::memory_order_relaxed);return true;
}template <typename T>
bool LockFreeRingQueue<T>::Dequeue(T* data) {if (data == nullptr) {throw std::invalid_argument("Null pointer passed to Dequeue");}uint32_t current_read_index;uint32_t current_last_write_index;do {current_read_index = read_index_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);current_last_write_index = last_write_index_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);// Check if the queue is emptyif (IndexOfQueue(current_last_write_index) == IndexOfQueue(current_read_index)) {return false; // Queue is empty}*data = queue_[IndexOfQueue(current_read_index)];if (read_index_.compare_exchange_weak(current_read_index, current_read_index + 1U, std::memory_order_release,std::memory_order_relaxed)) {length_.fetch_sub(1U, std::memory_order_relaxed);return true;}} while (true);
}template <typename T>
bool LockFreeRingQueue<T>::IsEmpty() const noexcept {return length_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) == 0U;
}template <typename T>
bool LockFreeRingQueue<T>::IsFull() const noexcept {uint32_t next_write_index = IndexOfQueue(write_index_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed) + 1U);return next_write_index == read_index_.load(std::memory_order_acquire);
}template <typename T>
uint32_t LockFreeRingQueue<T>::Size() const noexcept {return length_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);
}template <typename T>
bool LockFreeRingQueue<T>::IsPowerOfTwo(uint32_t num) noexcept {return (num != 0U) && ((num & (num - 1U)) == 0U);
}template <typename T>
uint32_t LockFreeRingQueue<T>::CeilPowerOfTwo(uint32_t num) noexcept {num |= (num >> 1U);num |= (num >> 2U);num |= (num >> 4U);num |= (num >> 8U);num |= (num >> 16U);return num - (num >> 1U);
}template <typename T>
uint32_t LockFreeRingQueue<T>::RoundupPowerOfTwo(uint32_t num) noexcept {return CeilPowerOfTwo((num - 1U) << 1U);
}template <typename T>
uint32_t LockFreeRingQueue<T>::IndexOfQueue(uint32_t index) const noexcept {return index & (size_ - 1U);
}#endif // RING_QUEUE_HPP
2.1 Enqueue 操作流程图
2.2 Dequeue 操作流程图
3. 核心实现细节
3.1 环形队列的大小调整
环形队列的大小通常为2的幂次,以便可以通过位运算快速计算索引。RoundUpPowerOfTwo 函数将任意正整数向上调整为最接近的2的幂次。
确保环形队列的大小是 2 的幂次方主要有以下几个原因:
-
简化索引计算:
- 在环形队列中,元素的位置通过取模运算来计算。
- 如果队列的大小是 2 的幂次方,那么取模运算可以被位运算 & 替代,这个操作更加高效。
-
避免对齐问题:
- 对于某些硬件架构来说,内存访问的效率会受到内存对齐的影响。
- 如果队列大小是 2 的幂次方,那么它就能很好地符合内存对齐要求,从而提高访问效率。
-
位操作优化:
- 很多处理器都针对 2 的幂次方大小的数据提供了优化的指令集。
- 比如,判断一个数是否是 2 的幂次方可以用位操作 (num & (num - 1)) == 0 来实现,这比普通的除法要高效得多。
-
缓存友好性:
- 当队列大小是 2 的幂次方时,元素在内存中的分布更加规则有序。
- 这有利于利用缓存,减少缓存未命中的情况,提高整体性能。
3.2 索引计算
通过IndexOfQueue 函数,索引计算可以使用位与操作(&)而不是取模运算(%),从而提升计算速度。
3.3 原子操作与CAS
通过 std::atomic_compare_exchange_weak 原子操作实现无锁队列的核心逻辑。CAS(Compare-And-Swap)是无锁数据结构的基础,用于确保多个线程在修改共享数据时不会引发数据竞争。
3.4 线程让步
在 Enqueue 操作中,当多个线程尝试修改相同的共享变量时,失败的线程可以选择让出CPU时间片,以减少竞争和等待时间。
4. 测试示例程序
下面是一个简单的C++示例程序,演示了如何使用 LockFreeRingQueue 类。该程序将进行一些基本的入队和出队操作,然后在多线程环境下测试队列的使用。
4.1 实现代码
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>#include "lock_free_ring_queue.h" // 假设你的类定义在这个文件中void SingleProducerSingleConsumerExample() {LockFreeRingQueue<int> queue(4);// 单生产者线程入队std::thread producer([&queue]() {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {if (queue.Enqueue(i)) {std::cout << "Producer enqueued: " << i << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "Queue is full, cannot enqueue: " << i << std::endl;}}});// 单消费者线程出队std::thread consumer([&queue]() {int value = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {while (!queue.Dequeue(&value)) {std::this_thread::yield(); // 等待队列中有数据}std::cout << "Consumer dequeued: " << value << std::endl;}});producer.join();consumer.join();
}void MultiProducerMultiConsumerExample() {LockFreeRingQueue<int> queue(8);auto producer = [&queue](int id) {for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {int value = id * 10 + i;if (queue.Enqueue(value)) {std::cout << "Producer " << id << " enqueued: " << value << std::endl;} else {std::cout << "Queue is full, Producer " << id << " cannot enqueue: " << value << std::endl;}}};auto consumer = [&queue](int id) {int value = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {while (!queue.Dequeue(&value)) {std::this_thread::yield(); // 等待队列中有数据}std::cout << "Consumer " << id << " dequeued: " << value << std::endl;}};std::thread producers[2];std::thread consumers[2];// 启动两个生产者线程for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {producers[i] = std::thread(producer, i);}// 启动两个消费者线程for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {consumers[i] = std::thread(consumer, i);}for (auto &producer : producers) {producer.join();}for (auto &consumer : consumers) {consumer.join();}
}int main() {std::cout << "Single Producer, Single Consumer Example:" << std::endl;SingleProducerSingleConsumerExample();std::cout << "\nMulti Producer, Multi Consumer Example:" << std::endl;MultiProducerMultiConsumerExample();return 0;
}
4.2 代码解释:
-
SingleProducerSingleConsumerExample:-
创建了一个大小为 4 的队列。
-
使用一个生产者线程将数字
0-3入队。 -
使用一个消费者线程从队列中出队并打印结果。
-
-
MultiProducerMultiConsumerExample:-
创建了一个大小为 8 的队列。
-
启动两个生产者线程,每个线程将其线程 ID 和循环计数拼接成值并入队。
-
启动两个消费者线程,从队列中出队并打印结果。
-
4.3 运行程序:
将上面的代码保存为 main.cpp,并确保你已经编译和链接了 LockFreeRingQueue 类的实现。
编译示例:
g++ -std=c++14 main.cpp -pthread -o lock_free_ring_queue_example
./lock_free_ring_queue_example
4.4 执行结果:
$ ./lock_free_ring_queue_example
Single Producer, Single Consumer Example:
Producer enqueued: Consumer dequeued: 0
0
Producer enqueued: 1
Producer enqueued: 2
Producer enqueued: 3
Consumer dequeued: 1
Consumer dequeued: 2
Consumer dequeued: 3Multi Producer, Multi Consumer Example:
Producer 0 enqueued: 0
Producer 0 enqueued: 1
Producer 0 enqueued: 2
Producer 0 enqueued: 3
Consumer 1 dequeued: 0
Consumer 1 dequeued: 1
Consumer 1 dequeued: 2
Consumer 1 dequeued: 3
Producer 1 enqueued: 10
Producer 1 enqueued: 11
Producer 1 enqueued: 12
Producer 1 enqueued: 13
Consumer 0 dequeued: 10
Consumer 0 dequeued: 11
Consumer 0 dequeued: 12
Consumer 0 dequeued: 13
5. 单元测试
下面是使用gtest编写的LockFreeRingQueue类的完整单元测试。测试涵盖了基本功能,包括队列的初始化、入队、出队、边界条件,以及在多线程环境下的行为。
#include "lock_free_ring_queue.h" // 假设你的类定义在这个文件中
#include <gtest/gtest.h>#include <algorithm>
#include <memory>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>class LockFreeRingQueueTest : public ::testing::Test {protected:void SetUp() override {// 初始化队列大小queue_size_ = 64;queue_ = std::make_unique<LockFreeRingQueue<int>>(queue_size_);}std::unique_ptr<LockFreeRingQueue<int>> queue_;uint32_t queue_size_;
};// 测试队列初始化
TEST_F(LockFreeRingQueueTest, Initialization) {EXPECT_EQ(queue_->Size(), 0U);EXPECT_TRUE(queue_->IsEmpty());
}// 测试入队和出队单个元素
TEST_F(LockFreeRingQueueTest, SingleEnqueueDequeue) {int value_in = 42;int value_out = 0;EXPECT_TRUE(queue_->Enqueue(value_in));EXPECT_EQ(queue_->Size(), 1U);EXPECT_FALSE(queue_->IsEmpty());EXPECT_TRUE(queue_->Dequeue(&value_out));EXPECT_EQ(value_out, value_in);EXPECT_EQ(queue_->Size(), 0U);EXPECT_TRUE(queue_->IsEmpty());
}// 测试队列满时入队
TEST_F(LockFreeRingQueueTest, EnqueueFullQueue) {for (uint32_t i = 0; i < queue_size_ - 1; ++i) { // 注意减1EXPECT_TRUE(queue_->Enqueue(static_cast<int>(i)));}EXPECT_EQ(queue_->Size(), queue_size_ - 1);EXPECT_FALSE(queue_->Enqueue(100)); // 队列已满,入队失败
}// 测试空队列出队
TEST_F(LockFreeRingQueueTest, DequeueEmptyQueue) {int value_out = 0;EXPECT_FALSE(queue_->Dequeue(&value_out)); // 队列为空,出队失败
}// 多线程测试
TEST_F(LockFreeRingQueueTest, MultiThreadedEnqueueDequeue) {const int num_threads = 4;const int num_elements_per_thread = 10;auto enqueue_function = [&](int thread_id) {for (int i = 0; i < num_elements_per_thread; ++i) {queue_->Enqueue(thread_id * num_elements_per_thread + i);}};auto dequeue_function = [&](int thread_id, int* result_array) {for (int i = 0; i < num_elements_per_thread; ++i) {int value = 0;while (!queue_->Dequeue(&value)) {std::this_thread::yield();}result_array[thread_id * num_elements_per_thread + i] = value;}};std::vector<std::thread> threads;int results[num_threads * num_elements_per_thread] = {0};for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(enqueue_function, i);}for (auto& thread : threads) {thread.join();}threads.clear();for (int i = 0; i < num_threads; ++i) {threads.emplace_back(dequeue_function, i, results);}for (auto& thread : threads) {thread.join();}EXPECT_EQ(queue_->Size(), 0U);EXPECT_TRUE(queue_->IsEmpty());// 检查所有元素是否都已被成功出队std::sort(std::begin(results), std::end(results));for (int i = 0; i < num_threads * num_elements_per_thread; ++i) {EXPECT_EQ(results[i], i);}
}// 边界条件测试:初始化大小为1的队列
TEST(LockFreeRingQueueBoundaryTest, InitializationWithSizeOne) {LockFreeRingQueue<int> small_queue(1);EXPECT_EQ(small_queue.Size(), 0U);EXPECT_TRUE(small_queue.IsEmpty());int value_in = 99;EXPECT_TRUE(small_queue.Enqueue(value_in));EXPECT_FALSE(small_queue.Enqueue(value_in)); // 队列应该已经满了
}// 边界条件测试:入队和出队仅一个元素
TEST(LockFreeRingQueueBoundaryTest, SingleElementQueue) {LockFreeRingQueue<int> small_queue(1);int value_in = 123;int value_out = 0;EXPECT_TRUE(small_queue.Enqueue(value_in));EXPECT_FALSE(small_queue.Enqueue(value_in)); // 队列已满EXPECT_TRUE(small_queue.Dequeue(&value_out));EXPECT_EQ(value_out, value_in);EXPECT_FALSE(small_queue.Dequeue(&value_out)); // 队列为空
}int main(int argc, char** argv) {::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}
5.1 测试代码解释:
-
基本功能测试:
-
Initialization: 检查队列是否正确初始化。 -
SingleEnqueueDequeue: 测试单个元素的入队和出队操作。 -
EnqueueFullQueue: 测试在队列已满时的入队操作。 -
DequeueEmptyQueue: 测试在队列为空时的出队操作。
-
-
多线程测试:
MultiThreadedEnqueueDequeue: 使用多个线程测试队列的入队和出队操作。每个线程分别执行入队和出队操作,最后检查所有元素是否正确出队。
-
边界条件测试:
-
InitializationWithSizeOne: 测试初始化大小为1的队列。 -
SingleElementQueue: 测试大小为1的队列的入队和出队操作。
-
5.2 测试运行:
将上面的代码保存为一个测试文件(例如lock_free_ring_queue_test.cpp),并确保你已经安装了gtest库。然后编译并运行测试。
编译示例:
g++ -std=c++14 lock_free_ring_queue_test.cpp -lgtest -lgtest_main -pthread -o lock_free_ring_queue_test
./lock_free_ring_queue_test
测试结果:
$ ./lock_free_ring_queue_test
[==========] Running 7 tests from 2 test suites.
[----------] Global test environment set-up.
[----------] 5 tests from LockFreeRingQueueTest
[ RUN ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.Initialization
[ OK ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.Initialization (0 ms)
[ RUN ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.SingleEnqueueDequeue
[ OK ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.SingleEnqueueDequeue (0 ms)
[ RUN ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.EnqueueFullQueue
[ OK ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.EnqueueFullQueue(0 ms)
[ RUN ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.DequeueEmptyQueue
[ OK ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.DequeueEmptyQueue (0 ms)
[ RUN ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.MultiThreadedEnqueueDequeue
[ OK ] LockFreeRingQueueTest.MultiThreadedEnqueueDequeue (10 ms)
[----------] 5 tests from LockFreeRingQueueTest (10 ms total)[----------] Global test environment tear-down
[==========] 7 tests from 2 test suites ran. (10 ms total)
[ PASSED ] 7 tests.
6. 总结
无锁环形队列在高并发场景下具有显著的性能优势,其设计充分利用了现代硬件提供的原子操作和内存模型。然而,在实际应用中,开发者需要权衡无锁结构带来的复杂性和潜在的硬件依赖问题。
相关文章:
的简单实现、测试和分析)
C++编程:无锁环形队列 (LockFreeRingQueue)的简单实现、测试和分析
文章目录 0. 概述1. 无锁环形队列概述1.1 无锁环形队列的特点1.2 无锁环形队列的优势与局限 2. LockFreeRingQueue 实现2.1 Enqueue 操作流程图2.2 Dequeue 操作流程图 3. 核心实现细节3.1 环形队列的大小调整3.2 索引计算3.3 原子操作与CAS3.4 线程让步 4. 测试示例程序4.1 实…...

植物生长时为什么会扭动?科学家解开令查尔斯·达尔文困惑的千古之谜
在一项新的研究中,来自美国和以色列的物理学家可能已经弄清了植物生长过程中的一种古怪行为–也是查尔斯-达尔文本人在其生命的最后几十年里所好奇的一个谜:对于许多人类来说,植物可能看起来静止不动,甚至有点无趣。但实际上&…...

SAP LE学习笔记02 - WM和库存管理(IM)之间的关系,保管Lot(Quant)
上一章学习了LE的基础知识。 1,LE的概述,LE里面包含下面3个大的模块 - LE-WM 仓库管理 / - LE-SHP 发货/ - LE-TRA 运输 2,仓库的结构 - 仓库番号 / -保管域Type(存储区域)/ - 保管区画(存储区)/ - 棚番(Storage Bin 仓位&…...

Span<T> 是 C# 7.2 引入的重要类型
Span<T> 是 C# 7.2 引入的一个非常重要的类型,它提供了一种低开销、类型安全的方式来操作连续的内存区域。Span<T> 本质上是一个结构体,它封装了一个内存段的引用(通过指针)以及该内存段的长度。由于它直接操作内存&a…...

Python办公自动化:初识 `openpyxl`
1.1 什么是 openpyxl? openpyxl 是一个用于读写 Excel 2010 xlsx/xlsm/xltx/xltm 文件的 Python 库。它允许我们通过 Python 脚本自动化处理 Excel 文件,包括创建新的工作簿、修改现有的工作簿、格式化单元格、处理公式和图表等功能。这对于办公自动化、…...

Pocketbase实战体验:内置数据库与实时功能如何超越传统MySQL
Pocketbase 是一个开源的实时后端服务器,内置了数据库、实时订阅、用户认证、RESTful API 等功能,而 MySQL 是一个广泛使用的关系数据库管理系统。以下是 Pocketbase 相对于 MySQL 的一些潜在优点: 完整的后端解决方案 一体化:P…...

ChatGPT 3.5/4.0 新手使用手册(详细版)
1. 什么是 ChatGPT? ChatGPT是由 OpenAI 开发的先进人工智能语言模型,能够理解并生成自然语言文本。它可以帮助你进行写作、回答问题、提供建议,甚至参与对话。ChatGPT 3.5 和 4.0 是两个不同版本,它们都拥有强大的语言处理能力&…...

【Java学习】Stream流详解
所属专栏:Java学习 Stream流是JDK 8引入的一个概念,它提供了一种高效且表达力强的方式来处理数据集合(如List、Set等)或数组。Stream API可以以声明性方式(指定做什么)来处理数据序列。流操作可以被分为两大…...
什么是表压缩(Table Compression)?)
Oracle(69)什么是表压缩(Table Compression)?
表压缩(Table Compression)是一种数据库优化技术,用于减少表数据的存储空间和提高I/O性能。通过压缩表数据,可以显著减少存储需求,并在某些情况下提高查询性能,特别是对于只读或主要是读取操作的表。表压缩…...

java JUC编程
Java并发工具包(JUC),全称Java Util Concurrent,是Java提供的一个用于构建多线程应用程序的工具包,位于java.util.concurrent包及其子包中。 并发编程主要解决以下三个经典问题: 1. **原子性问题…...

vue3+element-plus表格分页选中加默认回显选中
1.需求 某个表单需要选择多条数据,点击选择按钮,弹框出来一个分页列表,选择多条数据,外面表单中显示选中的数据,可以删除数据,再次点击按钮,回显当前选中的数据。 2.解决办法 1.el-table加ro…...

Erupt 项目搭建
创建Spring Boot项目 Maven依赖 Spring Boot版本为 2.7.10,erupt版本为 1.12.14 erupt版本要与Spring Boot版本适配,3.x.x版本Spring Boot暂不适用说是 <properties><erupt.version>1.12.14</erupt.version></properties> <…...

HarmonyOS Next 系列之列表下拉刷新和触底加载更多数据实现(十一)
系列文章目录 HarmonyOS Next 系列之省市区弹窗选择器实现(一) HarmonyOS Next 系列之验证码输入组件实现(二) HarmonyOS Next 系列之底部标签栏TabBar实现(三) HarmonyOS Next 系列之HTTP请求封装和Token…...

比特位的计算
给你一个整数 n ,对于 0 < i < n 中的每个 i ,计算其二进制表示中 1 的个数 ,返回一个长度为 n 1 的数组 ans 作为答案。 示例 1: 输入:n 2 输出:[0,1,1] 解释: 0 --> 0 1 --> …...

SQLAlchemy 学习笔记
通信类型:AF_INET 协议家族一般是表示TCP通信的SOC_STREAM和UDP通信的SOCK_DGRAM。对于TCP通信,建立socket连接,: s socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)连接socket, s.connect((host,port))socket通信…...

Linux内核分析(调度类和调度实体)
文章目录 前言一、调度类1. stop_sched_class2. dl_sched_class3. rt_sched_class4. fair_sched_class5. idle_sched_class总结 二、调度类中的操作函数三、调度实体 前言 调度是操作系统内核的一个关键职责,它涉及到如何合理分配CPU时间给不同的进程或线程。在Lin…...
流,递归复制和删除多级文件)
用输入输出流(I/O)流,递归复制和删除多级文件
一、(I/O)流递归复制一个文件 第一种: else if语句过多,看起来冗余,优点:多级文件一次性复制完整 import java.io.*;//数据源:src/main/java/day15_8_13/haha //目标;src/main/java/LaJi pub…...

kafka监控工具EFAK
kafka监控工具(EFAK) 1、下载2、解压3、配置3.1、安装数据库,需要mysql是,并创建ke数据库3.2、修改配置文件 4、启动4.1、启动zookeeper4.2、启动kafka4.3、启动EFAK 5、访问http://ip:8048 github地址:https://github…...

Page与自定义Components生命周期
自定义组件 自定义组件一般可以用component,装饰,在结构体里面用build方法定义UI,或者用builder装饰一个方法,来作为自定义组件的构造方法 而页面page一般用Entry,和component结合起来使用 页面生命周期方法: onPageShow:页面每次显示时触发 onPageHid…...

Chain of Thought (CoT) 系列论文:大模型思维链,提升 LLM 的推理能力
文章目录 1. COT:Chain of Thought1. 研究背景2. CoT的原理3. CoT Prompt 1. COT:Chain of Thought COT 是 2022.01 由 google 提出的针对提升 LLM 的推理能力的 Prompt Engineering 方法。 paper: Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Re…...

MVC 数据库
MVC 数据库 引言 在软件开发领域,Model-View-Controller(MVC)是一种流行的软件架构模式,它将应用程序分为三个核心组件:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。这种模式有助于提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将深入探讨MVC架构与数据库之间的关系,以…...

将对透视变换后的图像使用Otsu进行阈值化,来分离黑色和白色像素。这句话中的Otsu是什么意思?
Otsu 是一种自动阈值化方法,用于将图像分割为前景和背景。它通过最小化图像的类内方差或等价地最大化类间方差来选择最佳阈值。这种方法特别适用于图像的二值化处理,能够自动确定一个阈值,将图像中的像素分为黑色和白色两类。 Otsu 方法的原…...
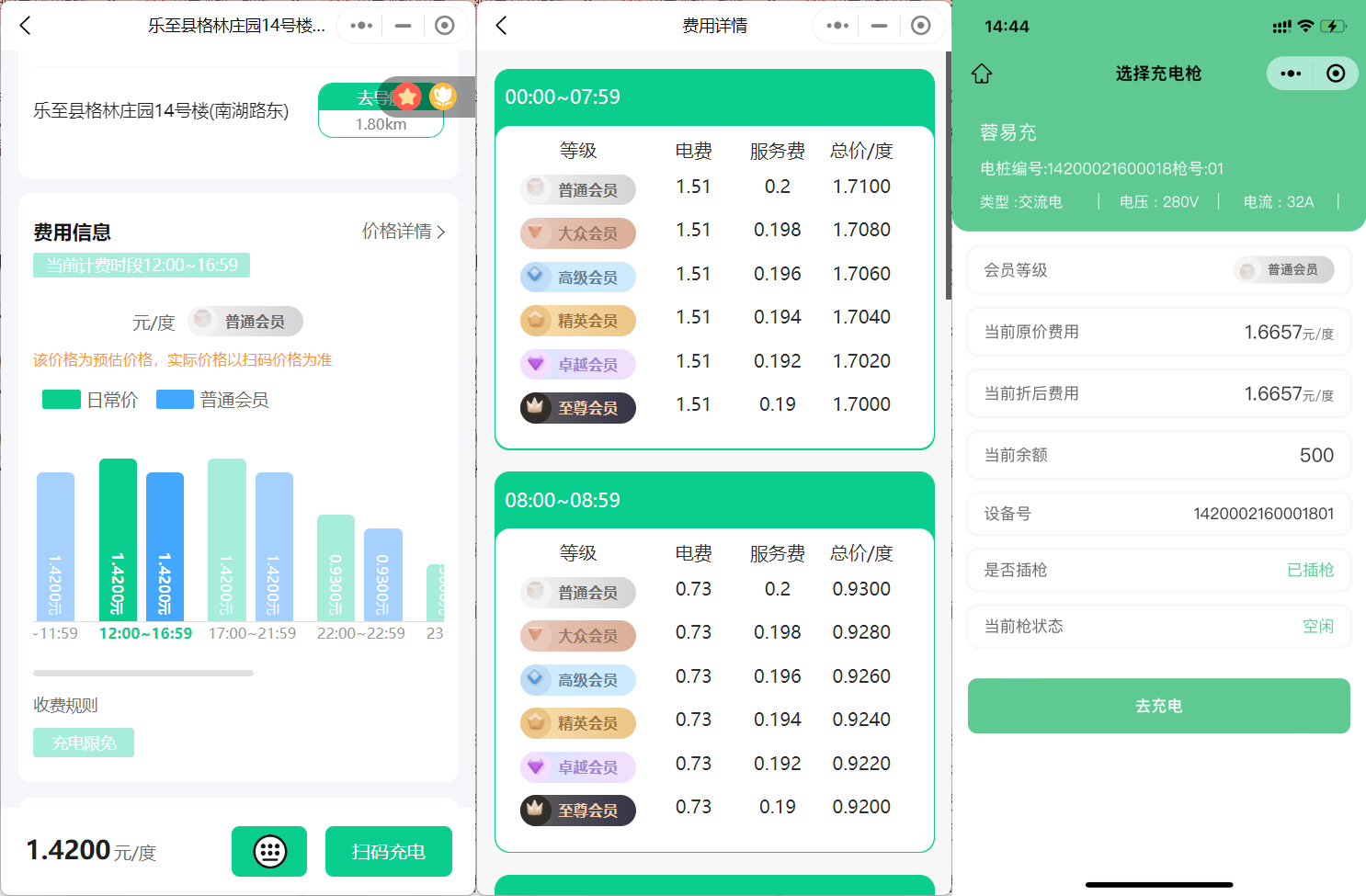
新能源汽车智慧充电桩管理方案:新能源充电桩散热问题及消防安全监管方案
随着新能源汽车的快速普及,充电桩作为核心配套设施,其安全性与可靠性备受关注。然而,在高温、高负荷运行环境下,充电桩的散热问题与消防安全隐患日益凸显,成为制约行业发展的关键瓶颈。 如何通过智慧化管理手段优化散…...
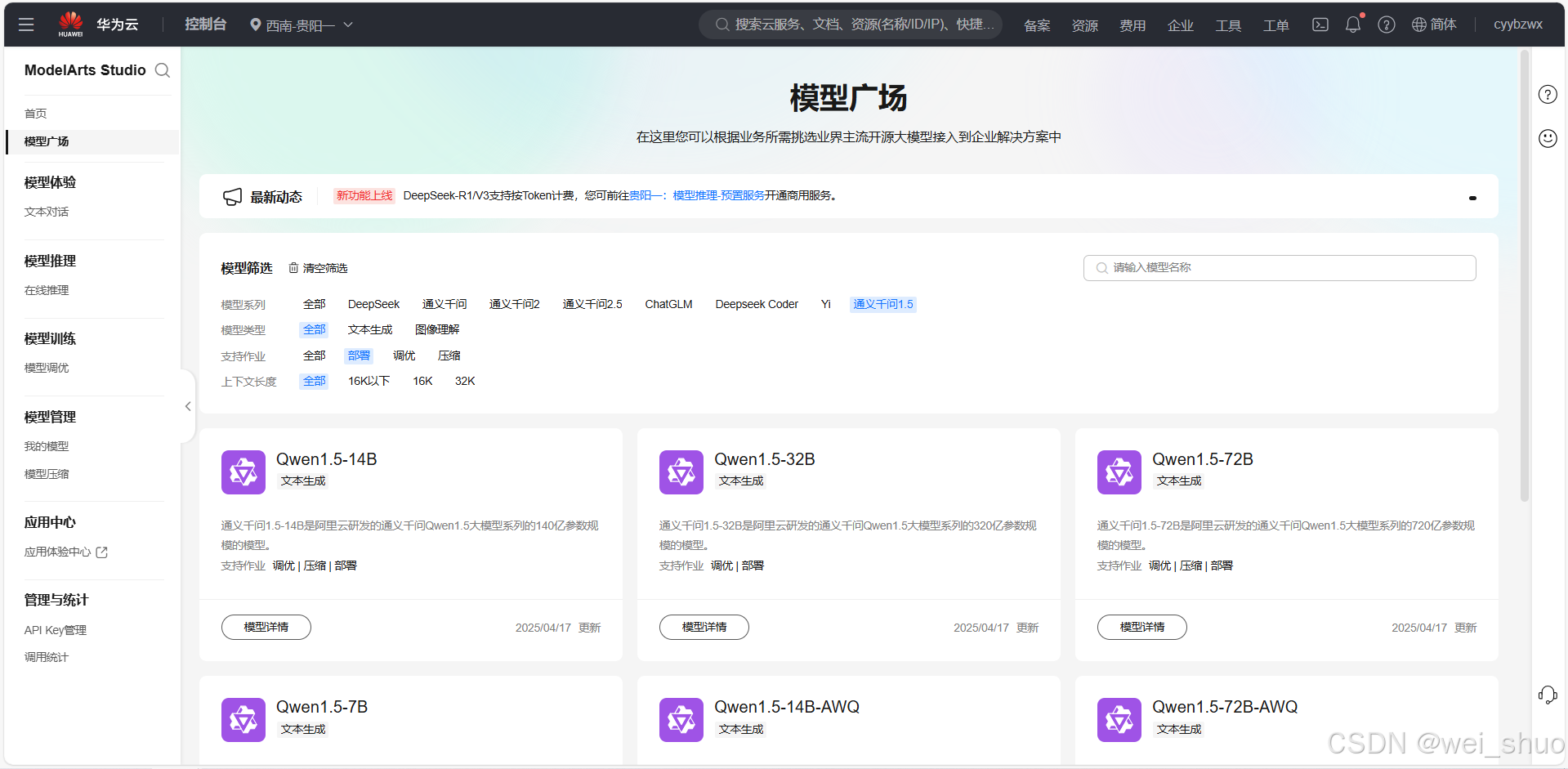
华为云Flexus+DeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建
华为云FlexusDeepSeek征文|DeepSeek-V3/R1 商用服务开通全流程与本地部署搭建 前言 如今大模型其性能出色,华为云 ModelArts Studio_MaaS大模型即服务平台华为云内置了大模型,能助力我们轻松驾驭 DeepSeek-V3/R1,本文中将分享如何…...

Java 二维码
Java 二维码 **技术:**谷歌 ZXing 实现 首先添加依赖 <!-- 二维码依赖 --><dependency><groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId><artifactId>core</artifactId><version>3.5.1</version></dependency><de…...

高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数
高效线程安全的单例模式:Python 中的懒加载与自定义初始化参数 在软件开发中,单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种常见的设计模式,确保一个类仅有一个实例,并提供一个全局访问点。在多线程环境下,实现单例模式时需要注意线程安全问题,以防止多个线程同时创建实例,导致…...
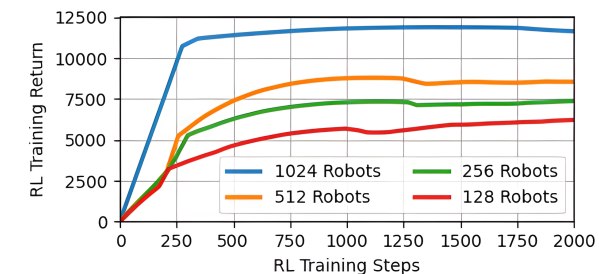
【VLNs篇】07:NavRL—在动态环境中学习安全飞行
项目内容论文标题NavRL: 在动态环境中学习安全飞行 (NavRL: Learning Safe Flight in Dynamic Environments)核心问题解决无人机在包含静态和动态障碍物的复杂环境中进行安全、高效自主导航的挑战,克服传统方法和现有强化学习方法的局限性。核心算法基于近端策略优化…...
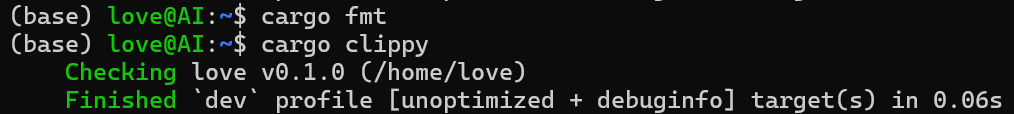
【笔记】WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录
#工作记录 WSL 中 Rust 安装与测试完整记录 1. 运行环境 系统:Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (WSL2)架构:x86_64 (GNU/Linux)Rust 版本:rustc 1.87.0 (2025-05-09)Cargo 版本:cargo 1.87.0 (2025-05-06) 2. 安装 Rust 2.1 使用 Rust 官方安…...
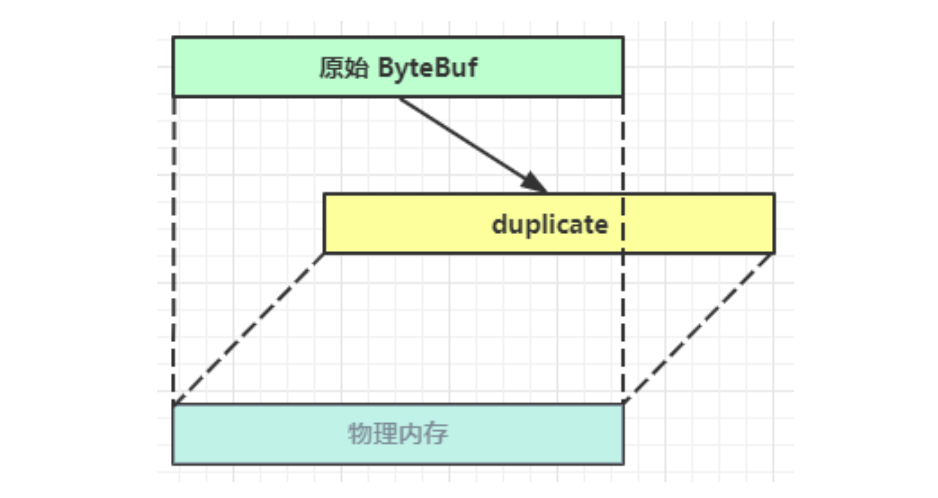
Netty从入门到进阶(二)
二、Netty入门 1. 概述 1.1 Netty是什么 Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients. Netty是一个异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用框架,用于…...

【SpringBoot自动化部署】
SpringBoot自动化部署方法 使用Jenkins进行持续集成与部署 Jenkins是最常用的自动化部署工具之一,能够实现代码拉取、构建、测试和部署的全流程自动化。 配置Jenkins任务时,需要添加Git仓库地址和凭证,设置构建触发器(如GitHub…...
