Connectionist Logic Systems and Hybrid Systems by Translation
Connectionist Logic Systems
Definition:
Connectionist Logic Systems (CLS) are computational models that combine elements of connectionism (neural networks) with symbolic logic. These systems aim to leverage the strengths of both paradigms—connectionism’s ability to process information in a distributed, parallel manner and symbolic logic’s capacity for clear, rule-based reasoning. Essentially, CLS integrates neural networks’ learning and pattern recognition capabilities with the structured reasoning of logical systems.
History:
The concept of combining neural networks with logic has been explored since the 1980s, coinciding with the resurgence of neural network research. Early work in this area attempted to address the limitations of pure neural networks, such as their lack of transparency and difficulties in performing symbolic reasoning tasks. Researchers began developing models that could perform logical inference using the distributed representations characteristic of neural networks.
Examples:
-
Neural-Symbolic Integration Models: These models represent logical formulas within a neural network, enabling the network to learn and reason about logical structures. For instance, the Neural-Symbolic Learning and Reasoning (NSLR) framework combines neural learning with logical deduction.
-
Hopfield Networks: While not a direct example of CLS, Hopfield networks have been used in connectionist logic systems to perform associative memory tasks that resemble logical operations.
In Connectionist Logic Systems, the basic structure integrates neural networks with symbolic logic. The neural network learns to represent and process logical formulas and can perform logical inference. Here’s a simplified diagram:
+-----------------------------------+
| |
| Logical Representation |
| (e.g., logical formulas, rules) |
| |
+------------------+----------------+|v
+-----------------------------------+
| |
| Neural Network (Connectionist) |
| |
| +---------------------------+ |
| | Logical Inference Layer | |
| | (encodes logical rules) | |
| +---------------------------+ |
| |
| +---------------------------+ |
| | Learning and Reasoning | |
| | (trains on data) | |
| +---------------------------+ |
| |
+-----------------------------------+|v
+-----------------------------------+
| |
| Output (Logical Reasoning) |
| |
+-----------------------------------+
Structure Overview:
- Logical Representation: Symbolic logical formulas or rules are represented in a way that can be processed by a neural network.
- Neural Network: The network consists of layers where one or more layers are specifically designed to encode and perform logical inference.
- Output: The system outputs reasoning results, which could be logical deductions or decisions made by integrating both symbolic and neural processing.
Hybrid Systems by Translation
Definition:
Hybrid Systems by Translation involve translating symbolic logic systems into connectionist models, allowing for the integration of symbolic reasoning into neural network frameworks. This approach focuses on transforming logical rules or expressions into a form that can be processed by a neural network, thereby enabling a hybrid system that benefits from both symbolic and connectionist methodologies.
History:
The development of hybrid systems by translation emerged from the need to create models that could perform complex reasoning tasks while still benefiting from the learning and generalization abilities of neural networks. Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, researchers worked on various methods to encode symbolic knowledge into neural networks, resulting in several hybrid approaches that bridged the gap between symbolic AI and connectionism.
Examples:
-
Knowledge-Based Artificial Neural Networks (KBANNs): These systems start with a symbolic knowledge base (such as a set of logical rules) and translate this into a neural network structure. The network can then be trained with data to refine the initial knowledge base, combining symbolic reasoning with data-driven learning.
-
Logic Tensor Networks (LTNs): LTNs integrate first-order logic with deep learning by translating logical formulas into differentiable constraints that can be used to train neural networks. This allows for the simultaneous processing of symbolic rules and raw data.
Conclusion
Both Connectionist Logic Systems and Hybrid Systems by Translation represent approaches to neural-symbolic integration, aiming to combine the best of both connectionist and symbolic paradigms. CLS focuses on embedding logic directly within neural network architectures, while Hybrid Systems by Translation involve converting symbolic logic into a form that neural networks can process, creating models that are both powerful and flexible.
Certainly! Let’s visualize the basic structures of Connectionist Logic Systems (CLS) and Hybrid Systems by Translation (HST).
Hybrid Systems by Translation work by converting symbolic logic into a format that can be used within a neural network. The structure involves translating logical rules into neural network configurations, enabling the network to perform symbolic reasoning tasks. Here’s a simplified diagram:
+-----------------------------------+
| |
| Symbolic Logic (Input) |
| (e.g., logical rules, knowledge)|
| |
+------------------+----------------+|v
+-----------------------------------+
| |
| Translation Module |
| (Translates symbolic logic |
| into a neural network format) |
| |
+------------------+----------------+|v
+-----------------------------------+
| |
| Neural Network (Hybrid Model) |
| |
| +---------------------------+ |
| | Symbolic Logic Layer | |
| | (encoded into the network) | |
| +---------------------------+ |
| |
| +---------------------------+ |
| | Data-Driven Layers | |
| | (train on data and refine) | |
| +---------------------------+ |
| |
+-----------------------------------+|v
+-----------------------------------+
| |
| Output (Reasoning/Decision) |
| |
+-----------------------------------+
Structure Overview:
- Symbolic Logic (Input): Symbolic logical rules or knowledge bases are the starting point.
- Translation Module: This component translates the symbolic logic into a neural network-compatible format.
- Neural Network: The hybrid model consists of a combination of layers, where symbolic logic is encoded alongside data-driven learning layers.
- Output: The final output is a reasoning or decision that incorporates both the translated symbolic logic and the learned data.
Summary
- CLS: Directly integrates symbolic logic into the neural network, allowing for logical inference within the connectionist framework.
- HST: Translates symbolic logic into a form that can be processed by a neural network, combining logical reasoning with neural learning.
These structures provide a simplified view of how these systems integrate neural networks with symbolic reasoning, leveraging the strengths of both paradigms.
相关文章:

Connectionist Logic Systems and Hybrid Systems by Translation
Connectionist Logic Systems Definition: Connectionist Logic Systems (CLS) are computational models that combine elements of connectionism (neural networks) with symbolic logic. These systems aim to leverage the strengths of both paradigms—connectionism’…...

盘点数据摆渡的8种常用方式 最推荐哪一种?
跨网数据摆渡是很多企业面临的一种传输场景,因为大部分企业为了保护核心数据,都会做不同级别的网络隔离,所以数据摆渡会涉及不同网络之间的数据传输和整合。这种情况下,数据需要从一个组织或地理位置传输到另一个组织或地理位置&a…...

仿照ContentLoadingProgressBar 的特点在Android项目中自定义Loading对话框
ContentLoadingProgressBar 是 Android 中的一个控件,继承自 ProgressBar。它在 ProgressBar 的基础上添加了一些特殊功能,主要用于在加载内容时显示进度。它的一些主要特点如下: 自动隐藏和显示:ContentLoadingProgressBar 会在…...

基于数据复杂度的数据库选型
数据模型的选择对于 IT 系统的开发至关重要,它不仅决定了数据存储和处理的方式,影响系统的性能、扩展性以及维护性等。本质上来说,不同的数据模型反映了我们对业务问题的不同思考和抽象程度。 今天我们从不同数据模型对于复杂数据和关系的支…...

QT基础知识5
思维导图 client.cpp #include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget), socket(new QTcpSocket(this))//给客户端实例化分配空间 {ui->setupUi(this);//初始化界面ui->msgEdit-&…...

C++中vector存放内置数据类型
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<vector> #include<algorithm>//迭代器先理解为指针 void MyPrint(int val) {cout << val << endl; } void test01() {vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);vector<int>:…...

shell编程:安装部署前常见环境检查
脚本任务 监测主机是否联通正常 检查安装操作系统版本是否和需求一致 检查CPU是否满足规格要求 检查内存是否满足规格要求 检查数据磁盘是否满足规格要求 检查操作系统分区目录大小是否满足需求 检查集群主机时间是否一致 0.配置文件准备及脚本变量初始化 编写config.i…...

思特科技:国家宝藏数字体验馆展现东方美学 让“文物活起来”
01 思特科技为“国家宝藏数字体验展”提供“数字技术”支持,带来国宝的数字化演绎。以《国家宝藏》顶级IP为基础,打造的全新沉浸文化项目“国宝数字体验展“,借由文物的视角、站在历史的星河中,探寻时间长河中不变的智慧…...

ES6笔记总结(Xmind格式):第二天
Xmind鸟瞰图: 简单文字总结: ES6知识总结 Proxy(代理): 1.作用:实现数据的私有化处理 2.target 目标对象 handler处理函数 3.处理函数中有两个方法:get,set 4.读取数据会触发g…...

Kotlin 流flow、ShareFlow、StateFlow、Channel的解释与使用
一、介绍 随着Android接入kotlin开发,Android之前好多模式也渐渐被kotlin替代。开发模式也在做渐进的转型,从MVC到MVP在到MVVP以及现在的MVI等。 流IO在java中和kotlin中使用率都是比较高的,场景很多。如Java的IO和NIO,再到我们现…...
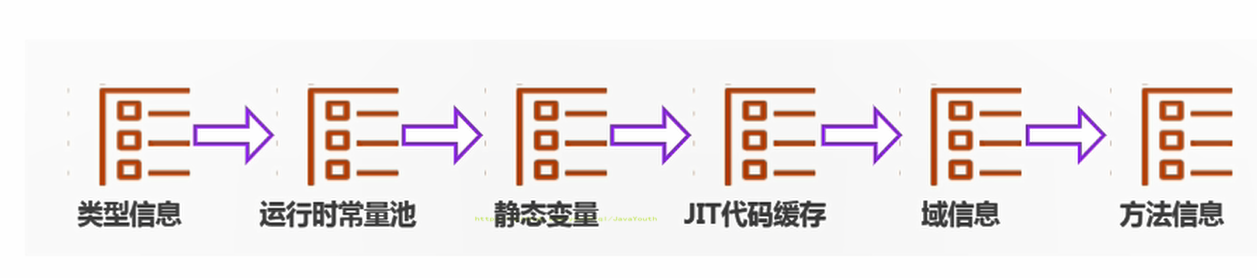
【个人学习】JVM(7):方法区概述、方法区内部结构、垃圾回收等
方法区 栈、堆、方法区的交互关系 从线程共享与否的角度来看 ThreadLocal:如何保证多个线程在并发环境下的安全性?典型场景就是数据库连接管理,以及会话管理。 栈、堆、方法区的交互关系 下面涉及了对象的访问定位 Person 类的 .class 信息存放在方法区中person 变量存放…...

@Scheduled 定时任务自定义
简介 Scheduled 定时任务自定义可以通过SchedulingConfigurer实现。 SchedulingConfigurer 是 Spring Framework 中的一个接口,用于配置定时任务。当你需要对定时任务进行更高级别的定制时,这个接口就显得非常有用。 可以通过SchedulingConfigurer 接口…...

一种新颖的面试方式
你好,我是 shengjk1,多年大厂经验,努力构建 通俗易懂的、好玩的编程语言教程。 欢迎关注!你会有如下收益: 了解大厂经验拥有和大厂相匹配的技术等 希望看什么,评论或者私信告诉我! 文章目录 一…...

【Linux】生产消费模型实践 --- 基于信号量的环形队列
你送出去的每颗糖都去了该去的地方, 其实地球是圆的, 你做的好事终会回到你身上。 --- 何炅 --- 基于信号量的环形队列 1 信号量2 框架构建3 代码实现4 测试运行 1 信号量 信号量本质是一个计数器,可以在初始化时对设置资源数量…...

Science Robotics 与蜜蜂群互动的蜂窝型机器人系统
蜜蜂,如黄蜂,蚂蚁和其他社会昆虫,建立大型自组织群体,通常被解释为自我调节的“超有机体”。这些超生物是生态系统的重要稳定剂,因此被认为是“关键物种”。例如,蜜蜂群落通过觅食授粉服务的生态效应对陆地…...

Vue 计算属性:优雅地处理数据逻辑
在 Vue.js 中,计算属性(Computed Properties)是一种非常实用的功能,它允许我们根据组件的响应式依赖进行缓存和派生状态。计算属性可以让我们以声明式的方式编写复杂的逻辑,而不必担心性能问题。 什么是计算属性&…...

C++中`union`
文章目录 C中的union什么是union?定义union示例一输出结果: 示例二修正后的代码解释输出结果结论 union的特性匿名union示例 union和struct的区别1. 内存布局2. 同时访问3. 用途 union和class的区别1. 数据成员2. 功能性3. 适用场景 在C编程中࿰…...

Linux——网络(1)
一、IPC(进程间通信方式) IPC:Inter Process Communication 共享内存(最高效的进程间通信方式) 虚拟地址 mmu(memory management unit ) 共享内存: 1.是一块,内核预留的空间 2.最高效的…...

【五】阿伟开始学Kafka
阿伟开始学Kafka 概述 人生若只如初见,阿伟心里回想起了第一次和Kafka见面的场景,记忆虽然已经有些模糊,但是感觉初次见面是美好的。积累了一些实战经验之后,阿伟感觉不能再是面对百度开发了,于是决心系统的学习一下Ka…...

Java—Arrays api
public static String toString(数组) //把数组拼接成一个字符串 public static int binarySearch(数组,查找的元素) //二分查找法查找元素 public static int[] copyOf(原数组,新数组长度) //拷贝数组 public st…...
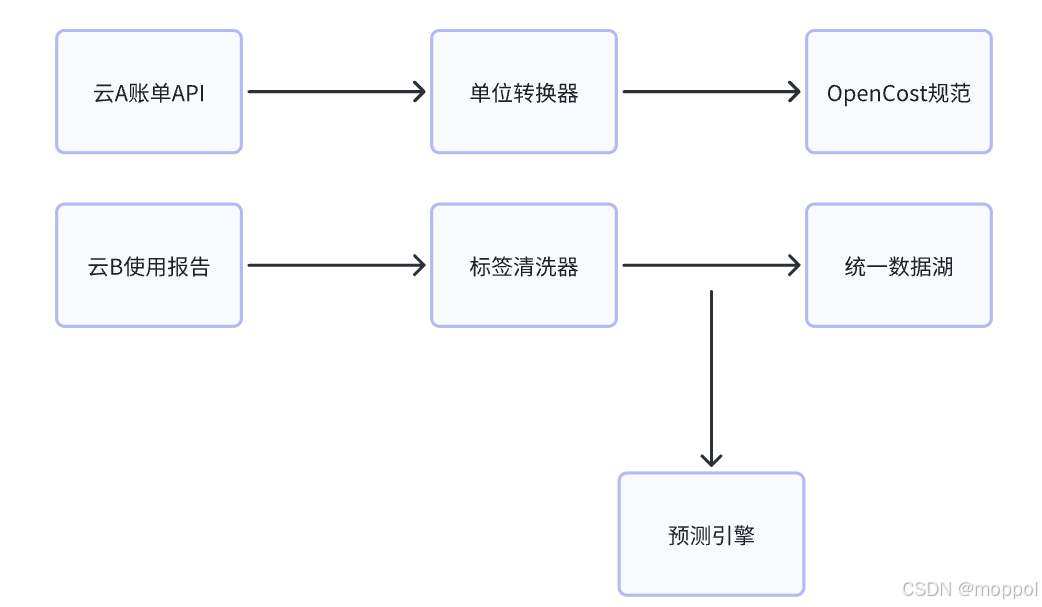
多云管理“拦路虎”:深入解析网络互联、身份同步与成本可视化的技术复杂度
一、引言:多云环境的技术复杂性本质 企业采用多云策略已从技术选型升维至生存刚需。当业务系统分散部署在多个云平台时,基础设施的技术债呈现指数级积累。网络连接、身份认证、成本管理这三大核心挑战相互嵌套:跨云网络构建数据…...

工业安全零事故的智能守护者:一体化AI智能安防平台
前言: 通过AI视觉技术,为船厂提供全面的安全监控解决方案,涵盖交通违规检测、起重机轨道安全、非法入侵检测、盗窃防范、安全规范执行监控等多个方面,能够实现对应负责人反馈机制,并最终实现数据的统计报表。提升船厂…...
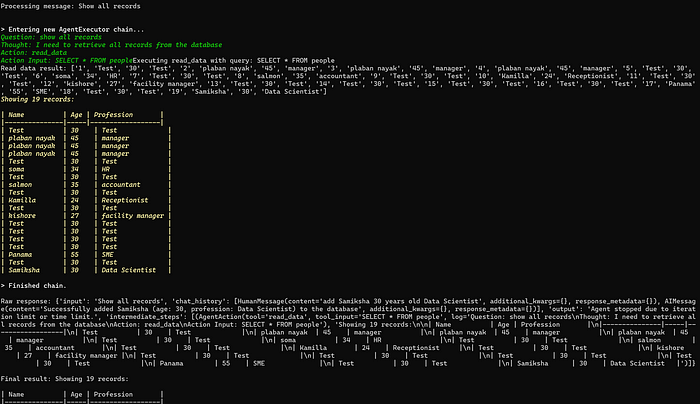
理解 MCP 工作流:使用 Ollama 和 LangChain 构建本地 MCP 客户端
🌟 什么是 MCP? 模型控制协议 (MCP) 是一种创新的协议,旨在无缝连接 AI 模型与应用程序。 MCP 是一个开源协议,它标准化了我们的 LLM 应用程序连接所需工具和数据源并与之协作的方式。 可以把它想象成你的 AI 模型 和想要使用它…...
《通信之道——从微积分到 5G》读书总结
第1章 绪 论 1.1 这是一本什么样的书 通信技术,说到底就是数学。 那些最基础、最本质的部分。 1.2 什么是通信 通信 发送方 接收方 承载信息的信号 解调出其中承载的信息 信息在发送方那里被加工成信号(调制) 把信息从信号中抽取出来&am…...
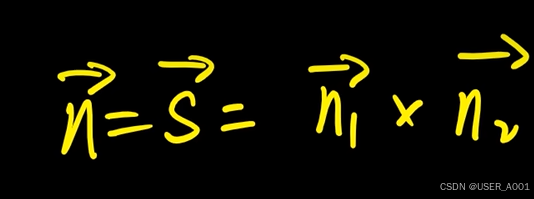
高等数学(下)题型笔记(八)空间解析几何与向量代数
目录 0 前言 1 向量的点乘 1.1 基本公式 1.2 例题 2 向量的叉乘 2.1 基础知识 2.2 例题 3 空间平面方程 3.1 基础知识 3.2 例题 4 空间直线方程 4.1 基础知识 4.2 例题 5 旋转曲面及其方程 5.1 基础知识 5.2 例题 6 空间曲面的法线与切平面 6.1 基础知识 6.2…...
初学 pytest 记录
安装 pip install pytest用例可以是函数也可以是类中的方法 def test_func():print()class TestAdd: # def __init__(self): 在 pytest 中不可以使用__init__方法 # self.cc 12345 pytest.mark.api def test_str(self):res add(1, 2)assert res 12def test_int(self):r…...

08. C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险
C#入门系列【类的基本概念】:开启编程世界的奇妙冒险 嘿,各位编程小白探险家!欢迎来到 C# 的奇幻大陆!今天咱们要深入探索这片大陆上至关重要的 “建筑”—— 类!别害怕,跟着我,保准让你轻松搞…...

Web中间件--tomcat学习
Web中间件–tomcat Java虚拟机详解 什么是JAVA虚拟机 Java虚拟机是一个抽象的计算机,它可以执行Java字节码。Java虚拟机是Java平台的一部分,Java平台由Java语言、Java API和Java虚拟机组成。Java虚拟机的主要作用是将Java字节码转换为机器代码&#x…...
基础)
6个月Python学习计划 Day 16 - 面向对象编程(OOP)基础
第三周 Day 3 🎯 今日目标 理解类(class)和对象(object)的关系学会定义类的属性、方法和构造函数(init)掌握对象的创建与使用初识封装、继承和多态的基本概念(预告) &a…...
QT开发技术【ffmpeg + QAudioOutput】音乐播放器
一、 介绍 使用ffmpeg 4.2.2 在数字化浪潮席卷全球的当下,音视频内容犹如璀璨繁星,点亮了人们的生活与工作。从短视频平台上令人捧腹的搞笑视频,到在线课堂中知识渊博的专家授课,再到影视平台上扣人心弦的高清大片,音…...
