rman compress
级别 初始 备完 耗时
low 1804 3572 0:10
High 1812 3176 2:00
MEDIUM 1820 3288 0:13
BASIC 1828 3444 0:56 ---不如MEDIUM,时间还长
NO COMPRESS 1820 5924 0:5
RMAN> CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'MEDIUM';
RMAN> BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE include current controlfile plus archivelog;
SYMPTOMS
1> Rman COMPRESSION ALGORITHM is set to 'BASIC' ---> Default value
SET COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'BASIC' AS OF RELEASE 'DEFAULT' OPTIMIZE FOR LOAD TRUE;
两个命令都可以
RMAN> CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'basic';
old RMAN configuration parameters:
CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'MEDIUM' AS OF RELEASE 'DEFAULT' OPTIMIZE FOR LOAD TRUE;
new RMAN configuration parameters:
CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM 'basic' AS OF RELEASE 'DEFAULT' OPTIMIZE FOR LOAD TRUE;
2> Compressed backup takes more time then Uncompressed backup.
BACKUP AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET DATABASE include current controlfile plus archivelog;
BACKUP DATABASE include current controlfile plus archivelog;
COMPRESS:
=========
DBGIO: Type %Comp Blocks Tot Blocks Blksize ElpTime(s) IO Rt(b/s) Name [17:42:22.326] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: ---- ----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----- [17:42:22.326] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: IN 100.0 4192894 4194302 8192 808 42510133 <path>/<db_filename> [17:42:22.326] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: OUT 472348 8192 808 4788953 <path>/<backup_piece_name> [17:42:22.326] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: AGG 4192894 8192 808 42510133 [17:42:22.326] (krmkqio)
DBGMISC: ENTERED krmzlog [17:42:22.326]
NO COMPRESS:
============
DBGIO: Type %Comp Blocks Tot Blocks Blksize ElpTime(s) IO Rt(b/s) Name [17:49:38.004] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: ---- ----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----- [17:49:38.004] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: IN 100.0 4192894 4194302 8192 116 296105065 <path>/<db_filename> [17:49:38.004] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: OUT 4192900 8192 116 296105489 <path>/<backup_piece_name> [17:49:38.004] (krmkqio)
DBGIO: AGG 4192894 8192 116 296105065 [17:49:38.004] (krmkqio)
CHANGES
CAUSE
Bug 14157581 was created on this issue
Bug 14157581 - EXADATA: RMAN COMPRESS BASIC BACKUP EXTREMELY SLOW Bug 14157581 - EXADATA: RMAN COMPRESS BASIC BACKUP EXTREMELY SLOWBug 14157581 - EXADATA: RMAN COMPRESS BASIC BACKUP EXTREMELY SLOW> ----> Closed as duplicate of Bug 13784430 .
This was closed as not a Bug and expected behavior.
13784430Bug 13784430Bug 13784430Bug 13784430Thi
SOLUTION
This is an expected behavior as confirmed by development.Performance slowness can be a part of basic compression.
Moreover, the default compression algorithm is optimized for best compression (not best performance).
You can try using other other type of Compression((like LOW, MEDIUM and HIGH) ,However please note you need to have License for Advanced Compression to use them.
-----
GOAL
How does RMAN compression works ?
Goal of this document is to give you a Complete Understanding of
1. Null compression
2. Unused block compression
3. Binary compression
SOLUTION
A Complete Understanding of RMAN Compression
By default RMAN has three types of compression :
1. Null compression
2. Unused block compression
3. Binary compression
Untill Oracle Version 10.1 only 'Null' compression is done by default. In Oracle Version 10.2, and forward, 'Null' and 'unused block' compression is done by default. The types of compression are done automatically, no special command is required.
'Null' and 'unused block' compression are filtering which blocks are send to the backups. 'Binary' compression is an additional compression on the blocks send to the backup.
1. Null Compression
When backing up datafiles into backup sets, RMAN does not back up the contents of data blocks that have never contained data. This behavior is referred to as 'NULL block compression'. This means RMAN will not backup blocks that have never been used. RMAN, through Oracle version 9i and forward has performed null compression.
Example : You have a tablespace having one datafile of size 100MB and out of 100MB only 50 MB is used. Then RMAN will backup only 50MB.
NOTE: Null Compression also applies to Standard Edition and SE ONE
2. Unused Block
From Oracle version 10.2 forward, RMAN skips reading, and backing up, any database blocks that are not currently allocated to a database object. This is regardless of whether those blocks had previously been allocated. This behavior is reffered to as 'Unused Block Compression'. RMAN now creates more compact backups of datafiles, by skipping datafile blocks that are not currently allocated to a database object. Skipping these unallocated data blocks, i.e., for a dropped table, where possible enables RMAN to back up datafiles using less space, and can make I/O more efficient. No extra action is required on the part of the DBA to use this feature.
Example : You have a tablespace having one datafile of size 100MB and out of 100MB, 50MB is used by the user tables. Then user dropped a table belonging to that tablespace which was of 25MB, with the new unused block compression on 25MB of the files is backed up. In this example if null compression is used then it would have backed up 50MB because null compression will consider the blocks that are formatted/ever used.
Unused Block Compression is done, if all of the following conditions apply:
+ The COMPATIBLE initialization parameter is set to 10.2 or higher
+ There are currently no guaranteed restore points defined for the database
+ The datafile is locally managed
+ The datafile is being backed up to a backup set as part of a full backup or a level 0 incremental backup
+ The backup set is being created on DISK
+ The backup is done to TAPE using "OSB" (Oracle Secure Backup)
+ The backup is done with ZDLRA
Note:
Unused block compression is NOT used if backup done to tape using a THIRD PARTY BACKUP SOFTWARE !
Unused block compression is ONLY used in Enterprise Edition.
3. Binary Compression
Binary Compression can be done by specifying "AS COMPRESSED" clause in backup command, this compression is called as binary compression.
RMAN can apply a binary compression algorithm as it writes data to backup sets. This compression is similar to the compression provided by many tape vendors when backing up data to tape. But we cannot give exact percentage of compression. This binary compression algorithm can greatly reduce the space required for disk backup storage. It is typically 2x to 4x, and greater for text-intensive databases.
The command to take the compressed backup :
RMAN> backup as compressed backupset database;
+ There is some CPU overhead associated with compressing backup sets. If the database being backed up is running at or near its maximum load, you may find the overhead from using AS COMPRESSED BACKUPSET unacceptable. In most other circumstances, compressing backupsets saves enough disk space to be worth the CPU overhead. ---时间太慢
+ There is no special command to restore database from the compressed backupsets, the restore command will be the same as with uncompressed backups.
+ The restore from the compressed backpuset will take more time than uncompressed backupsets.
In addition to the existing binary compression of backup in oracle 10G, RMAN 11G executable offers a wider range of compression levels with the Advanced Compression Option (ACO). The default compression algorithm setting is BASIC and does not require the Advanced Compression Option.
If, however, you have enabled the Oracle Database 11g Release 2 Advanced Compression Option, you can choose from the following compression levels:
LOW - Least impact on backup throughput and suited for environments where CPU resources are the limiting factor.
MEDIUM - Recommended for most environments. Good combination of compression ratios and speed
HIGH - Best suited for backups over slower networks where the limiting factor is network speed
NOTE: Only BASIC compression is allowed in Standard Edition
Compression can be used for backupset of datafile, archive log and controlfiles. For example:
RMAN> backup as compressed backupset archivelog all;
RMAN> backup as compressed backupset database;
RMAN> backup as compressed backupset current controlfile;
RMAN compress the backupset contents before writing to disk. No extra decompression steps are required during recovery for rman compressed backup;
To configure the compression algorithm:
RMAN> CONFIGURE COMPRESSION ALGORITHM '<alg_name>';
4. Various Compression Types:
For various compression types you can refer to V$RMAN_COMPRESSION_ALGORITHM
SQL> select ALGORITHM_NAME, ALGORITHM_DESCRIPTION, ALGORITHM_COMPATIBILITY from V$RMAN_COMPRESSION_ALGORITHM ;
ALGORITHM_NAME ALGORITHM_DESCRIPTION ALGORITHM_COMPATIB
--------------- ------------------------------------------------------------ ------------------
BZIP2 good compression ratio 9.2.0.0.0
BASIC good compression ratio 9.2.0.0.0
LOW maximum possible compression speed 11.2.0.0.0
ZLIB balance between speed and compression ratio 11.0.0.0.0
MEDIUM balance between speed and compression ratio 11.0.0.0.0
HIGH maximum possible compression ratio 11.2.0.0.0
6 rows selected.
5. Undo Block Compression/Optimization
Starting 11g, RMAN performs undo block optimization. In backup undo optimization, RMAN excludes undo not needed for recovery of a backup, that is, for transactions that have been committed. Undo optimization is only possible if:
- This is a backup set backup
- Full or incremental level 0
- Not a validate
- Backup piece version is 11.0 or above
- User has not disabled undo optimization with:
_undo_block_compression = FALSE - Backup is going to DISK or OSB tape
- No Guaranteed Restore Point (This check is enabled from 11.2 onwards)
相关文章:

rman compress
级别 初始 备完 耗时 low 1804 3572 0:10 High 1812 3176 2:00 MEDIUM 1820 3288 0:13 BASIC 1828 3444 0:56 ---不如MEDIUM,时间还长 NO COMPRESS 1820 5924 0:5 R…...

创建一个Oracle版本的JDK的Docker镜像
背景说明 OpenJDK 和Oracle JDK 一般情况下我们选择OpenJDK,两者针对大部分场景都可以满足,有些地方例如反射技术获得某些包路径下的类对象等,有时候选择OpenJDK会导致空指针异常。 两者在底层实现方面有部分区别。 创建镜像 这里是Linux…...
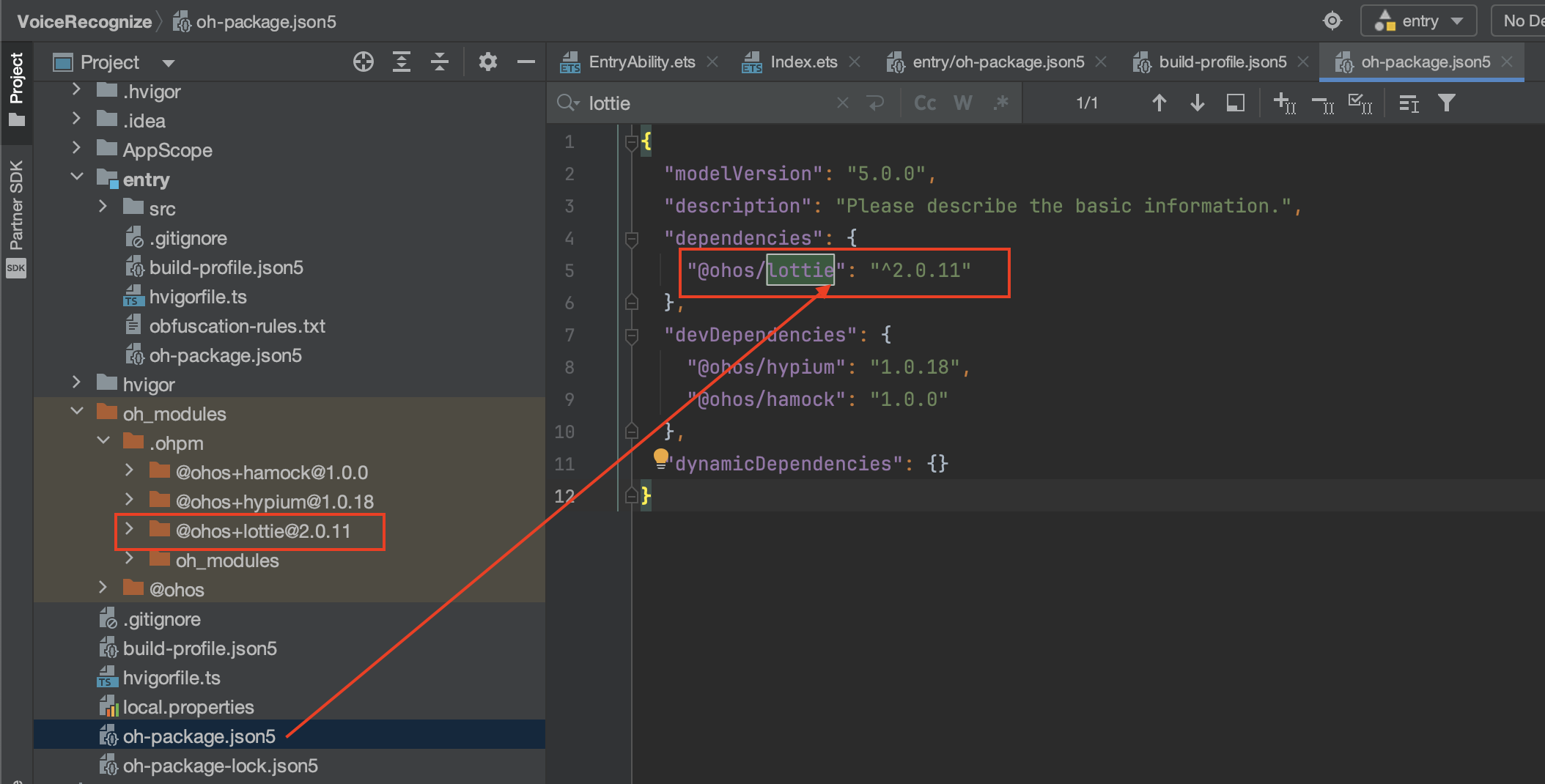
Harmony OS DevEco Studio 如何导入第三方库(以lottie为例)?-- HarmonyOS自学2
在做鸿蒙开发时,离不开第三方库的引入 一.有哪些支持的Harmony OS的 第三方库? 第三方库下载地址: 1 tpc_resource: 三方组件资源汇总 2 OpenHarmony三方库中心仓 二. 如何加入到DevEco Studio工程 以 lottie为例 OpenHarmony-TPC/lot…...

JAVA数据导出为Excel
目录 一、导入依赖 二、使用的相关类 1、XSSFWorkbook 构造方法 创建表 操作表 保存表 样式和格式 日期处理 密码保护 其他 2、XSSFSheet 获取属性和信息 行操作 列操作 表的属性 合并单元格 保护表 页眉和页脚 注释 其它 3、XSSFRow 获取属性和信息 单…...

【数据结构与算法 | 灵神题单 | 快慢指针(链表)篇】力扣876, 2095, 234
1. 力扣876:链表的中间节点 1.1 题目: 给你单链表的头结点 head ,请你找出并返回链表的中间结点。 如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。 示例 1: 输入:head [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[3,4,…...

第十五届蓝桥杯图形化省赛题目及解析
第十五届蓝桥杯图形化省赛题目及解析 一. 单选题 1. 运行以下程序,角色会说( )? A、29 B、31 C、33 D、35 正确答案:C 答案解析: 重复执行直到m>n不成立,即重复执行直到m<n。所有当m小于或者 等于n时&…...
)
linux下NTP服务器实战(chrony软件)
linux下NTP服务器实战(chrony软件) 记录linux下NTP服务器搭建及相关管理操作,使用chrony软件包安装部署。相比ntp服务,Chrony服务适用于更高精度、更高稳定性、自动化等场景。 1. 安装 chrony 在大多数Linux发行版上,chrony可以通过包管理…...

Java设计模式之命令模式介绍和案例示范
一、命令模式简介 命令模式(Command Pattern)是一种行为型设计模式,它将请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可以用不同的请求对客户端进行参数化、对请求排队或记录日志,以及支持可撤销的操作。命令模式的核心思想是将发出请…...

Leetcode面试经典150题-74.搜索二维矩阵
解法都在代码里,不懂就留言或者私信 二分查找,比较简单 class Solution {/**解题思路:每一行有序、每一列也有序,只是整体不是严格有序的,那我们需要找一个点,只能往两个方向走,往一个方向走是…...

【数字集成电路与系统设计】基本的组合逻辑电路
目录 一、简单例子引入 1.1 端口声明 1.1.2 Verilog实现 1.1.3 Chisel实现 逐行解释 1.2 内部逻辑实现 1.2.1 Verilog实现 1.2.2 Chisel实现 Chisel 关键点解释 1.3 常用的硬件原语 二、Chisel主要数据类型介绍 2.1 数据类型 2.2 数据宽度 2.3 数据转换 2.4 运算…...

11. 建立你的第一个Web3项目
11. 建立你的第一个Web3项目 在这一部分,我们将带你一步步地建立一个简单的Web3项目,从环境搭建到智能合约的创建与部署,再到开发一个去中心化应用(dApp)并与智能合约交互。这是你迈向Web3开发的第一步。 1. 环境搭建…...

衡石分析平台使用手册-容器部署
容器部署 本文介绍如何在容器上部署 HENGSHI SENSE,以及部署后如何进行版本升级和数据备份。 部署前准备工作 单机部署前,请完成如下准备工作。 1.检查 docker 的环境。需要满足 Docker 版本 > 17.09安装 docker-compose。 2.获取并导入离线…...

静态库,动态库以及makefile基础
一.静态(链接)库 libfun.a 静态链接进可执行程序 可执行程序偏大 运行时只需要可执行程序即可 生成静态库步骤 gcc -c fun.c -o fun.o ar rcv libfun.a fun.o //需要用.o文件生成数据库 运行 gcc main.c libfun.a 二.动态库 libfun.so 动…...

Python基础语法(1)上
常量和表达式 我们可以把 Python 当成一个计算器,来进行一些算术运算。 print(1 2 - 3) print(1 2 * 3) print(1 2 / 3) 这里我们可能会有疑问,为什么不是1.6666666666666667呢? 其实在编程中,一般没有“四舍五入”这样的规则…...

使用 Python/java/go做一个微信机器人
E云是一套完整的的第三方服务平台,包含微信API服务、企微API服务、SCRM系统定制、企微系统定制、服务类软件定制等模块,本文档主要讲述个微API服务相关,以下简称API,它能处理用户微信中的各种事件,提供了开发者与个微对…...

【北京迅为】iTOP-i.MX6开发板使用手册第四部分固件编译第十四章非设备树Android4.4系统编译
可根据用户需求更换,百变定制,高端产品无忧! 迅为IMX6Q兼容四核商业级 、双核商业级、四核工业级 、更可提供i.MX6Q家族PLUS版本核心板。 核心板采用十层PCB沉金盲埋设计,更能保证电磁兼容与系统稳定。 公众号:迅为电…...
测评造假?Mistral首个多模态模型Pixtral 12B发布
测评造假?Mistral首个多模态模型Pixtral 12B发布! 近日,法国人工智能(AI)初创公司Mistral于9月11日宣布推出其首款多模态AI大模型——Pixtral 12B,成功吸引了全球科技界的广泛关注。这款集图像与文本处理能…...

【Java-简单练习题】
1.”AABBBCCC“>>"A2B3C3" public class Test6 {public static void main(String[] args) {String ns "AABBBCCCC";String retcompress(ns);System.out.println(ret);}public static String compress(String str) {StringBuilder ret new StringB…...

Notepad++ 下载安装教程
目录 1.下教程 2.安装教程 1.下教程 Downloads | Notepad (notepad-plus-plus.org) 进入下载地址后选择最新版点击连接 点击链接后,向下滑动,下载适合自己电脑版本的安装包 这里大家没有梯子可能打不开页面,可以直接从本文开头下载。 2.安…...

shader 案例学习笔记之smoothstep函数
参考:smoothstep 用来生成0-1的平滑过渡值 smoothstep函数源码实现: float smoothstep(float t1, float t2, float x) {// Scale, bias and saturate x to 0..1 rangex clamp((x - t1) / (t2 - t1), 0.0, 1.0); // Evaluate polynomialreturn x * x *…...
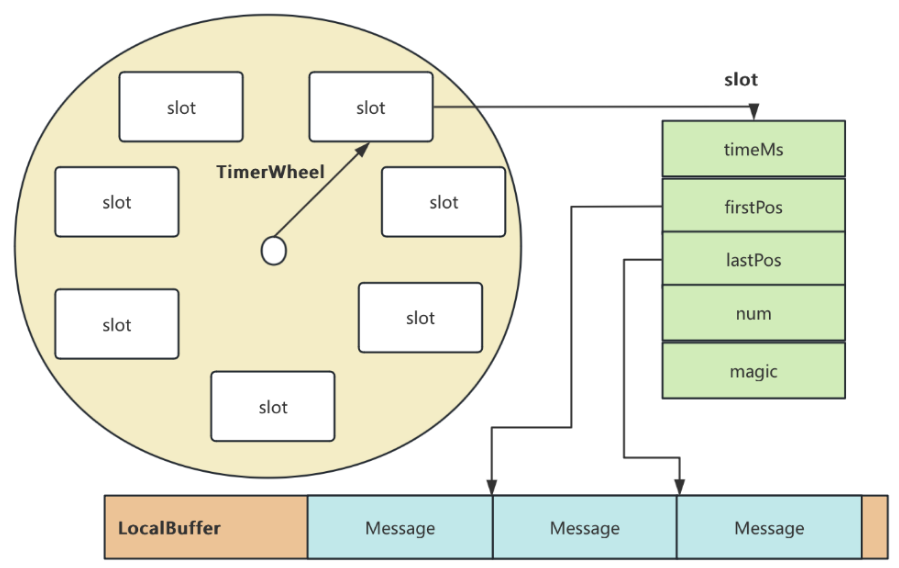
RocketMQ延迟消息机制
两种延迟消息 RocketMQ中提供了两种延迟消息机制 指定固定的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个MessageDelayLevel参数,对应18个预设的延迟级别指定时间点的延迟级别 通过在Message中设定一个DeliverTimeMS指定一个Long类型表示的具体时间点。到了时间点后…...

SCAU期末笔记 - 数据分析与数据挖掘题库解析
这门怎么题库答案不全啊日 来简单学一下子来 一、选择题(可多选) 将原始数据进行集成、变换、维度规约、数值规约是在以下哪个步骤的任务?(C) A. 频繁模式挖掘 B.分类和预测 C.数据预处理 D.数据流挖掘 A. 频繁模式挖掘:专注于发现数据中…...
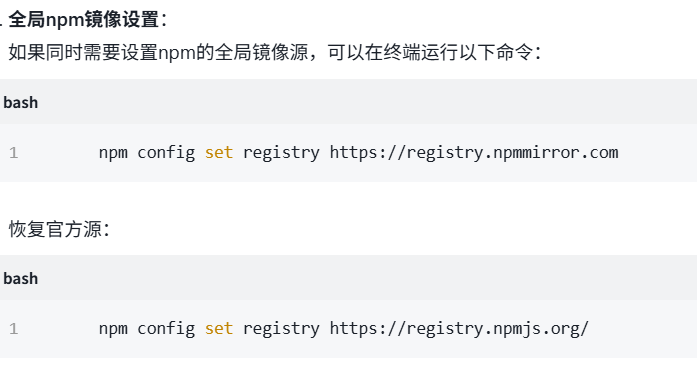
关于nvm与node.js
1 安装nvm 安装过程中手动修改 nvm的安装路径, 以及修改 通过nvm安装node后正在使用的node的存放目录【这句话可能难以理解,但接着往下看你就了然了】 2 修改nvm中settings.txt文件配置 nvm安装成功后,通常在该文件中会出现以下配置&…...

【Zephyr 系列 10】实战项目:打造一个蓝牙传感器终端 + 网关系统(完整架构与全栈实现)
🧠关键词:Zephyr、BLE、终端、网关、广播、连接、传感器、数据采集、低功耗、系统集成 📌目标读者:希望基于 Zephyr 构建 BLE 系统架构、实现终端与网关协作、具备产品交付能力的开发者 📊篇幅字数:约 5200 字 ✨ 项目总览 在物联网实际项目中,**“终端 + 网关”**是…...

rnn判断string中第一次出现a的下标
# coding:utf8 import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import random import json""" 基于pytorch的网络编写 实现一个RNN网络完成多分类任务 判断字符 a 第一次出现在字符串中的位置 """class TorchModel(nn.Module):def __in…...
消息队列系统设计与实践全解析
文章目录 🚀 消息队列系统设计与实践全解析🔍 一、消息队列选型1.1 业务场景匹配矩阵1.2 吞吐量/延迟/可靠性权衡💡 权衡决策框架 1.3 运维复杂度评估🔧 运维成本降低策略 🏗️ 二、典型架构设计2.1 分布式事务最终一致…...
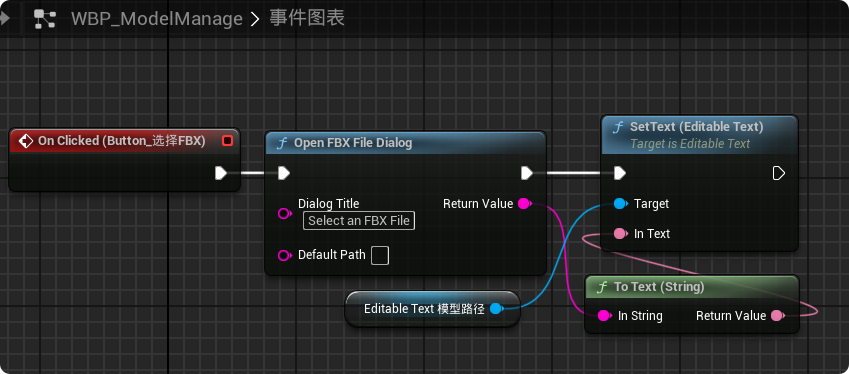
【UE5 C++】通过文件对话框获取选择文件的路径
目录 效果 步骤 源码 效果 步骤 1. 在“xxx.Build.cs”中添加需要使用的模块 ,这里主要使用“DesktopPlatform”模块 2. 添加后闭UE编辑器,右键点击 .uproject 文件,选择 "Generate Visual Studio project files",重…...

JS红宝书笔记 - 3.3 变量
要定义变量,可以使用var操作符,后跟变量名 ES实现变量初始化,因此可以同时定义变量并设置它的值 使用var操作符定义的变量会成为包含它的函数的局部变量。 在函数内定义变量时省略var操作符,可以创建一个全局变量 如果需要定义…...

Android Framework预装traceroute执行文件到system/bin下
文章目录 Android SDK中寻找traceroute代码内置traceroute到SDK中traceroute参数说明-I 参数(使用 ICMP Echo 请求)-T 参数(使用 TCP SYN 包) 相关文章 Android SDK中寻找traceroute代码 设备使用的是Android 11,在/s…...
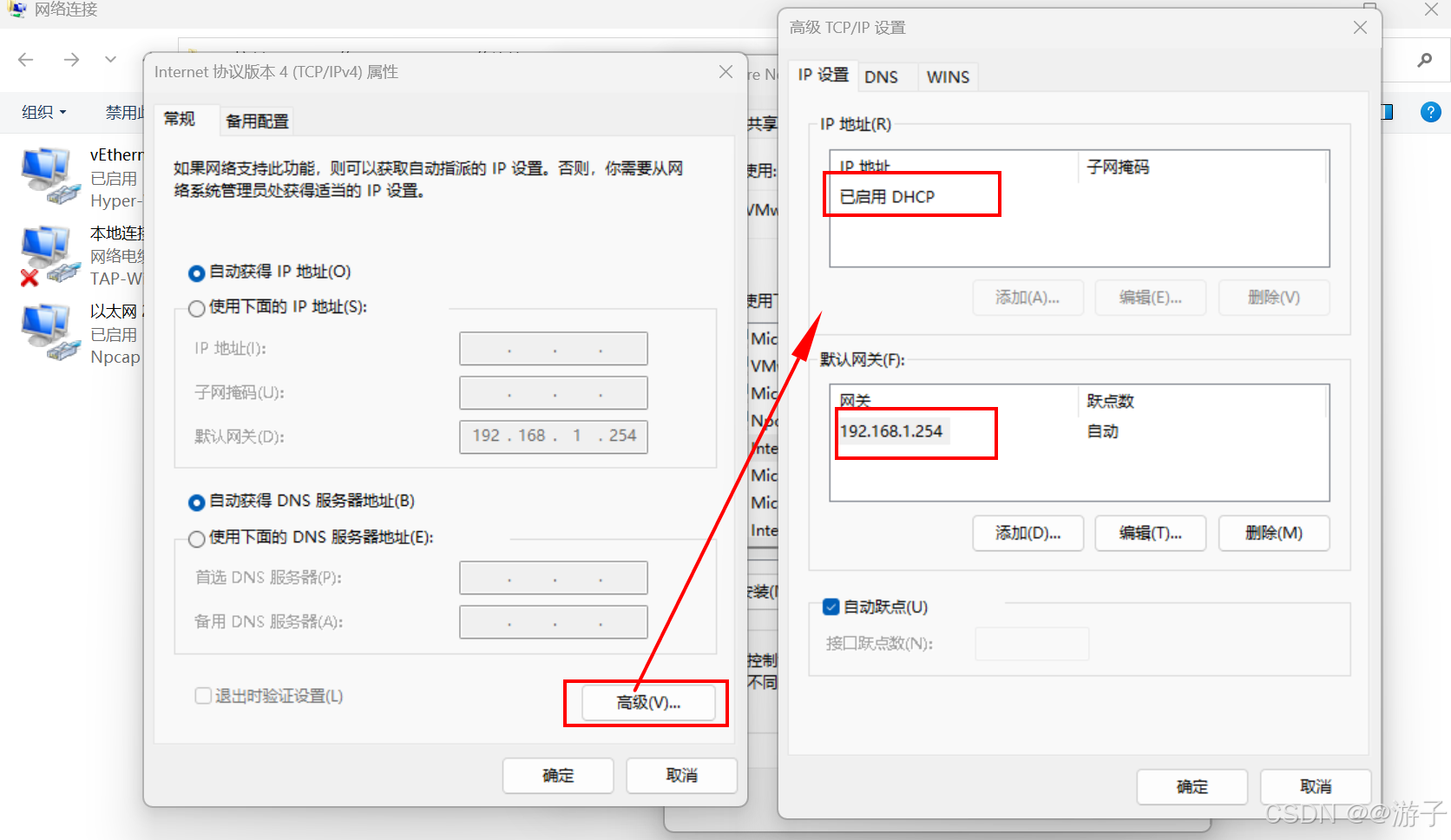
虚拟机网络不通的问题(这里以win10的问题为主,模式NAT)
当我们网关配置好了,DNS也配置好了,最后在虚拟机里还是无法访问百度的网址。 第一种情况: 我们先考虑一下,网关的IP是否和虚拟机编辑器里的IP一样不,如果不一样需要更改一下,因为我们访问百度需要从物理机…...
