Android SharedPreference详解
Android SharedPreference详解
SharedPreferences作为一种数据持久化的方式,是处理简单的key-value类型数据时的首选。
一般用法:
//demo是该sharedpreference对应文件名,对应的是一个xml文件,里面存放key-value格式的数据.
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences = context.getSharedPreferences("demo", MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE);
//提供了getXXX的读取数据方法
boolean xxx = sharedPreferences.getBoolean("xxx", false);
//通过Editor提供了putXXX系列的存储方法,调用完需要使用apply()或commit()使之生效,不同点后面介绍
SharedPreferences.Editor edit = sharedPreferences.edit();
edit.putBoolean("xxx", true);
edit.apply();//使存储生效
//edit.commit();//使存储生效
每个SharedPreferences都对应了当前package的data/data/package_name/share_prefs/目录下的一个文件
源码解析
Context.java中getSharedPreferences接口说明:
/*** Retrieve and hold the contents of the preferences file 'name', returning* a SharedPreferences through which you can retrieve and modify its* values. Only one instance of the SharedPreferences object is returned* to any callers for the same name, meaning they will see each other's* edits as soon as they are made.** @param name Desired preferences file. If a preferences file by this name* does not exist, it will be created when you retrieve an* editor (SharedPreferences.edit()) and then commit changes (Editor.commit()).* @param mode Operating mode. Use 0 or {@link #MODE_PRIVATE} for the* default operation, {@link #MODE_WORLD_READABLE}* and {@link #MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE} to control permissions.** @return The single {@link SharedPreferences} instance that can be used* to retrieve and modify the preference values.** @see #MODE_PRIVATE* @see #MODE_WORLD_READABLE* @see #MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE*/public abstract SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name,int mode);
ContextImpl中getSharedPreferences实现:
@Overridepublic SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode) {SharedPreferencesImpl sp;synchronized (ContextImpl.class) {if (sSharedPrefs == null) {sSharedPrefs = new ArrayMap<String, ArrayMap<String, SharedPreferencesImpl>>();}final String packageName = getPackageName();ArrayMap<String, SharedPreferencesImpl> packagePrefs = sSharedPrefs.get(packageName);if (packagePrefs == null) {packagePrefs = new ArrayMap<String, SharedPreferencesImpl>();sSharedPrefs.put(packageName, packagePrefs);}// At least one application in the world actually passes in a null// name. This happened to work because when we generated the file name// we would stringify it to "null.xml". Nice.if (mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion <Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {if (name == null) {name = "null";}}sp = packagePrefs.get(name);if (sp == null) {File prefsFile = getSharedPrefsFile(name);sp = new SharedPreferencesImpl(prefsFile, mode);packagePrefs.put(name, sp);return sp;}}if ((mode & Context.MODE_MULTI_PROCESS) != 0 ||getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {// If somebody else (some other process) changed the prefs// file behind our back, we reload it. This has been the// historical (if undocumented) behavior.sp.startReloadIfChangedUnexpectedly();}return sp;}
这段代码里,我们可以看出,
- SharedPreferencesImpl是保存在全局个map cache里的,只会创建一次。
- MODE_MULTI_PROCESS模式下,每次获取都会尝试去读取文件reload。当然会有一些逻辑尽量减少读取次数,比如当前是否有正在进行的读取操作,文件的修改时间和大小与上次有没有变化等。
Context.java中提供了以下四种mode:
//这是默认模式,仅caller uid的进程可访问
/*** File creation mode: the default mode, where the created file can only* be accessed by the calling application (or all applications sharing the* same user ID).* @see #MODE_WORLD_READABLE* @see #MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE*/
int MODE_PRIVATE = 0x0000;//所有人可写,也就是任何应用都可修改它,这是极其危险的,因此改选项已被Deprected
/*** @deprecated Creating world-readable files is very dangerous, and likely* to cause security holes in applications. It is strongly discouraged;* instead, applications should use more formal mechanism for interactions* such as {@link ContentProvider}, {@link BroadcastReceiver}, and* {@link android.app.Service}. There are no guarantees that this* access mode will remain on a file, such as when it goes through a* backup and restore.* File creation mode: allow all other applications to have read access* to the created file.* @see #MODE_PRIVATE* @see #MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE*/
int MODE_WORLD_READABLE = 0x0001; //所有人可读,这个参数同样非常危险,可能导致隐私数据泄漏
/*** @deprecated Creating world-writable files is very dangerous, and likely* to cause security holes in applications. It is strongly discouraged;* instead, applications should use more formal mechanism for interactions* such as {@link ContentProvider}, {@link BroadcastReceiver}, and* {@link android.app.Service}. There are no guarantees that this* access mode will remain on a file, such as when it goes through a* backup and restore.* File creation mode: allow all other applications to have write access* to the created file.* @see #MODE_PRIVATE* @see #MODE_WORLD_READABLE*/
int MODE_WORLD_READABLE = 0x0002//设置该参数后,每次获取对应的SharedPreferences时都会尝试从磁盘中读取修改过的文件
/*** SharedPreference loading flag: when set, the file on disk will* be checked for modification even if the shared preferences* instance is already loaded in this process. This behavior is* sometimes desired in cases where the application has multiple* processes, all writing to the same SharedPreferences file.* Generally there are better forms of communication between* processes, though.** <p>This was the legacy (but undocumented) behavior in and* before Gingerbread (Android 2.3) and this flag is implied when* targetting such releases. For applications targetting SDK* versions <em>greater than</em> Android 2.3, this flag must be* explicitly set if desired.** @see #getSharedPreferences** @deprecated MODE_MULTI_PROCESS does not work reliably in* some versions of Android, and furthermore does not provide any* mechanism for reconciling concurrent modifications across* processes. Applications should not attempt to use it. Instead,* they should use an explicit cross-process data management* approach such as {@link android.content.ContentProvider ContentProvider}.*/
int MODE_MULTI_PROCESS = 0x0004;
MODE_MULTI_PROCESS
当设置MODE_MULTI_PROCESS这个参数的时候,即使当前进程内已经创建了该SharedPreferences,仍然在每次获取的时候都会尝试从本地文件中刷新。在同一个进程中,同一个文件只有一个实例。MODE_MULTI_PROCESS的作用如上getSharedPreferences实现.这个方法先判断是否已创建SharedPreferences实例,若未创建,则先创建。之后判断mode如果为MODE_MULTI_PROCESS, 则调用startReloadIfChangeUnexpectedly(),看下其实现:
SharedPreferencesImpl.java
void startReloadIfChangedUnexpectedly() {synchronized (this) {// TODO: wait for any pending writes to disk?if (!hasFileChangedUnexpectedly()) {return;}startLoadFromDisk();}}private void startLoadFromDisk() {synchronized (this) {mLoaded = false;}new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load") {public void run() {synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {loadFromDiskLocked();}}}.start();}
可以看出MODE_MULTI_PROCESS的作用就是在每次获取SharedPreferences实例的时候尝试从磁盘中加载修改过的数据,并且读取是在异步线程中,因此一个线程的修改最终会反映到另一个线程,但不能立即反映到另一个进程,所以通过SharedPreferences无法实现多进程同步。
综合: 如果仅仅让多进程可访问同一个SharedPref文件,不需要设置MODE_MULTI_PROCESS, 如果需要实现多进程同步,必须设置这个参数,但也只能实现最终一致,无法即时同步。
由于SharedPreference内容都会在内存里存一份,所以不要使用SharedPreference保存较大的内容,避免不必要的内存浪费。
注意有一个锁mLoaded ,在对SharedPreference做其他操作时,都必须等待该锁释放:
@Nullablepublic String getString(String key, @Nullable String defValue) {synchronized (this) {awaitLoadedLocked();String v = (String)mMap.get(key);return v != null ? v : defValue;}}
写操作有两个commit apply 。 commit 是同步的,写入内存的同时会等待写入文件完成,apply是异步的,先写入内存,在异步线程里再写入文件。apply肯定要快一些,优先推荐使用apply:
/*** Commit your preferences changes back from this Editor to the* {@link SharedPreferences} object it is editing. This atomically* performs the requested modifications, replacing whatever is currently* in the SharedPreferences.** <p>Note that when two editors are modifying preferences at the same* time, the last one to call commit wins.** <p>If you don't care about the return value and you're* using this from your application's main thread, consider* using {@link #apply} instead.** @return Returns true if the new values were successfully written* to persistent storage.*/boolean commit();/*** Commit your preferences changes back from this Editor to the* {@link SharedPreferences} object it is editing. This atomically* performs the requested modifications, replacing whatever is currently* in the SharedPreferences.** <p>Note that when two editors are modifying preferences at the same* time, the last one to call apply wins.** <p>Unlike {@link #commit}, which writes its preferences out* to persistent storage synchronously, {@link #apply}* commits its changes to the in-memory* {@link SharedPreferences} immediately but starts an* asynchronous commit to disk and you won't be notified of* any failures. If another editor on this* {@link SharedPreferences} does a regular {@link #commit}* while a {@link #apply} is still outstanding, the* {@link #commit} will block until all async commits are* completed as well as the commit itself.** <p>As {@link SharedPreferences} instances are singletons within* a process, it's safe to replace any instance of {@link #commit} with* {@link #apply} if you were already ignoring the return value.** <p>You don't need to worry about Android component* lifecycles and their interaction with <code>apply()</code>* writing to disk. The framework makes sure in-flight disk* writes from <code>apply()</code> complete before switching* states.** <p class='note'>The SharedPreferences.Editor interface* isn't expected to be implemented directly. However, if you* previously did implement it and are now getting errors* about missing <code>apply()</code>, you can simply call* {@link #commit} from <code>apply()</code>.*/void apply();
注册/解注册sharedpreference变动监听:
/*** Registers a callback to be invoked when a change happens to a preference.** <p class="caution"><strong>Caution:</strong> The preference manager does* not currently store a strong reference to the listener. You must store a* strong reference to the listener, or it will be susceptible to garbage* collection. We recommend you keep a reference to the listener in the* instance data of an object that will exist as long as you need the* listener.</p>** @param listener The callback that will run.* @see #unregisterOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener*/void registerOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener(OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener listener);/*** Unregisters a previous callback.* * @param listener The callback that should be unregistered.* @see #registerOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener*/void unregisterOnSharedPreferenceChangeListener(OnSharedPreferenceChangeListener listener);
为什么不推荐使用MODE_MULTI_PROCESS?
android文档已经Deprected了这个flag,并且说明不应该通过SharedPreference做进程间数据共享?这是为啥呢?从前面但分析可看到当设置这个flag后,每次获取(获取而不是初次创建)SharedPreferences实例的时候,会判断shared_pref文件是否修改过:
private boolean hasFileChangedUnexpectedly() {synchronized (this) {if (mDiskWritesInFlight > 0) {// If we know we caused it, it's not unexpected.if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "disk write in flight, not unexpected.");return false;}}final StructStat stat;try {/** Metadata operations don't usually count as a block guard* violation, but we explicitly want this one.*/BlockGuard.getThreadPolicy().onReadFromDisk();stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());} catch (ErrnoException e) {return true;}synchronized (this) {return mStatTimestamp != stat.st_mtime || mStatSize != stat.st_size;}}
这里先判断mDiskWritesInFlight>0,如果成立,说明是当前进程修改了文件,不需要重新读取。然后通过文件最后修改时间,判断文件是否修改过。如果修改了,则重新读取:
private void startLoadFromDisk() {synchronized (this) {mLoaded = false;}new Thread("SharedPreferencesImpl-load") {public void run() {synchronized (SharedPreferencesImpl.this) {loadFromDiskLocked();}}}.start();
}private void loadFromDiskLocked() {if (mLoaded) {return;}if (mBackupFile.exists()) {mFile.delete();mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile);}Map map = null;StructStat stat = null;try {stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());if (mFile.canRead()) {BufferedInputStream str = null;try {str = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(mFile), 16*1024);map = XmlUtils.readMapXml(str);} finally {IoUtils.closeQuietly(str);}}} catch (ErrnoException e) {}mLoaded = true;if (map != null) {mMap = map;mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtime;mStatSize = stat.st_size;} else {mMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();}notifyAll();
}
这里起码有3个坑!
- 使用MODE_MULTI_PROCESS时,不要保存SharedPreference变量,必须每次都从context.getSharedPreferences 获取。如果你图方便使用变量存了下来,那么无法触发reload,有可能两个进程数据不同步。
- 前面提到过,load数据是耗时的,并且其他操作会等待该锁。这意味着很多时候获取SharedPreference数据都不得不从文件再读一遍,大大降低了内存缓存的作用。文件读写耗时也影响了性能。
- 修改数据时得用commit,保证修改时写入了文件,这样其他进程才能通过文件大小或修改时间感知到。
重点是这段:
if (mBackupFile.exists()) {mFile.delete();mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile);
}
重新读取时,如果发现存在mBackupFile,则将原文件mFile删除,并将mBackupFile重命名为mFile。mBackupFile又是如何创建的呢?答案是在修改SharedPreferences时将内存中的数据写会磁盘时创建的:
private void writeToFile(MemoryCommitResult mcr) {// Rename the current file so it may be used as a backup during the next readif (mFile.exists()) {if (!mBackupFile.exists()) {if (!mFile.renameTo(mBackupFile)) {mcr.setDiskWriteResult(false);return;}} else {mFile.delete();}}FileOutputStream str = createFileOutputStream(mFile);XmlUtils.writeMapXml(mcr.mapToWriteToDisk, str);FileUtils.sync(str);str.close();ContextImpl.setFilePermissionsFromMode(mFile.getPath(), mMode, 0);final StructStat stat = Os.stat(mFile.getPath());synchronized (this) {mStatTimestamp = stat.st_mtime;mStatSize = stat.st_size;}// Writing was successful, delete the backup file if there is one.mBackupFile.delete();mcr.setDiskWriteResult(true);return;}
这段代码只保留了核心流程,忽略了错误处理流程。可以看到,写文件的步骤大致是:
- 将原文件重命名为mBackupFile
- 重新创建原文件mFile, 并将内容写入其中
- 删除mBackupFile
所以,只有当一个进程正处于写文件的过程中的时候,如果另一个进程读文件,才会看到mBackupFile, 这时候读进程会将mBackupFile重命名为mFile, 这样读结果是,读进程只能读到修改前的文件,同时,由于mBackupFile重命名为了mFile, 所以写进程写那个文件就没有文件名引用了,因此其写入的内容无法再被任何进程访问到。所以其内容丢失了,可认为写入失败了,而SharedPreferences对这种失败情况没有任何重试机制,所以就可能出现数据丢失的情况。
回到这段的重点:为什么不推荐用MODE_MULTI_PROCESS?从前面分析可知,这种模式下,每次获取SharedPreferences都会检测文件是否改变,只要读的时候另一进程在写,就会导致写丢失。这样失败概率就会大幅度提高。反之,若不设置这个模式,则只在第一次创建SharedPreferences的时候读取,导致写失败的概率就会大幅度降低,当然,仍然存在失败的可能。
为什么不做写失败重试?
为什么android不做写失败重试呢?原因是写进程并不能发现写失败的情况。难道写的过程中,目标文件被删不会抛异常吗?答案是不会。删除文件只是从文件系统中删除了一个节点信息而已,重命名也是新建了一个具有相同名称的节点信息,并把文件地址指向另一个磁盘地址而已,原来,之前的写过程仍然会成功写到原来的磁盘地址。所以目前的实现方案并不能检测到失败。
有没有办法解决写失败呢?
个人觉得是可以做到的,读里面读那段关键操作:
if (mBackupFile.exists()) {mFile.delete();mBackupFile.renameTo(mFile);
}
mBackupFile存在,意味着当前正处于写读过程中,这时候是不是可以考虑直接读mBackupFile文件,而不删除mFile呢?这样读话,读取效果一样,都是读的mBackupFile,同时写进程写的mFile也不会被mBacupFile覆盖,写也就能成功了。即使通过这段代码重命名,写进程写完后发现mBackupFile不存在了,其实也能认为发生了读重命名,大可以重试一次。
多进程使用SharedPreference方案
说简单也简单,就是依据google的建议使用ContentProvider了。我看过网上很多的例子,但总是觉得少了点什么
有的方案里将所有读取操作都写作静态方法,没有继承SharedPreference 。 这样做需要强制改变调用者的使用习惯,不怎么好。
大部分方案做成ContentProvider后,所有的调用都走的ContentProvider。但如果调用进程与SharedPreference 本身就是同一个进程,只用走原生的流程就行了,不用拐个弯去访问ContentProvider,减少不必要的性能损耗。
我这里也写了一个跨进程方案,简单介绍如下
SharedPreferenceProxy 继承SharedPreferences。其所有操作都是通过ContentProvider完成。简要代码:
public class SharedPreferenceProxy implements SharedPreferences {
@Nullable@Overridepublic String getString(String key, @Nullable String defValue) {OpEntry result = getResult(OpEntry.obtainGetOperation(key).setStringValue(defValue));return result == null ? defValue : result.getStringValue(defValue);}@Overridepublic Editor edit() {return new EditorImpl();}private OpEntry getResult(@NonNull OpEntry input) {try {Bundle res = ctx.getContentResolver().call(PreferenceUtil.URI, PreferenceUtil.METHOD_QUERY_VALUE, preferName, input.getBundle());return new OpEntry(res);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();return null;}
...public class EditorImpl implements Editor {private ArrayList<OpEntry> mModified = new ArrayList<>();@Overridepublic Editor putString(String key, @Nullable String value) {OpEntry entry = OpEntry.obtainPutOperation(key).setStringValue(value);return addOps(entry);}@Overridepublic void apply() {Bundle intput = new Bundle();intput.putParcelableArrayList(PreferenceUtil.KEY_VALUES, convertBundleList());intput.putInt(OpEntry.KEY_OP_TYPE, OpEntry.OP_TYPE_APPLY);try {ctx.getContentResolver().call(PreferenceUtil.URI, PreferenceUtil.METHOD_EIDIT_VALUE, preferName, intput);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
...}
...}
OpEntry只是一个对Bundle操作封装的类。
所有跨进程的操作都是通过SharedPreferenceProvider的call方法完成。SharedPreferenceProvider里会访问真正的SharedPreference
public class SharedPreferenceProvider extends ContentProvider{private Map<String, MethodProcess> processerMap = new ArrayMap<>();@Overridepublic boolean onCreate() {processerMap.put(PreferenceUtil.METHOD_QUERY_VALUE, methodQueryValues);processerMap.put(PreferenceUtil.METHOD_CONTAIN_KEY, methodContainKey);processerMap.put(PreferenceUtil.METHOD_EIDIT_VALUE, methodEditor);processerMap.put(PreferenceUtil.METHOD_QUERY_PID, methodQueryPid);return true;}@Nullable@Overridepublic Bundle call(@NonNull String method, @Nullable String arg, @Nullable Bundle extras) {MethodProcess processer = processerMap.get(method);return processer == null?null:processer.process(arg, extras);}
...
}
重要差别的地方在这里:在调用getSharedPreferences时,会先判断caller的进程pid是否与SharedPreferenceProvider相同。如果不同,则返回SharedPreferenceProxy。如果相同,则返回ctx.getSharedPreferences。只会在第一次调用时进行判断,结果会保存起来。
public static SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(@NonNull Context ctx, String preferName) {//First check if the same processif (processFlag.get() == 0) {Bundle bundle = ctx.getContentResolver().call(PreferenceUtil.URI, PreferenceUtil.METHOD_QUERY_PID, "", null);int pid = 0;if (bundle != null) {pid = bundle.getInt(PreferenceUtil.KEY_VALUES);}//Can not get the pid, something wrong!if (pid == 0) {return getFromLocalProcess(ctx, preferName);}processFlag.set(Process.myPid() == pid ? 1 : -1);return getSharedPreferences(ctx, preferName);} else if (processFlag.get() > 0) {return getFromLocalProcess(ctx, preferName);} else {return getFromRemoteProcess(ctx, preferName);}}private static SharedPreferences getFromRemoteProcess(@NonNull Context ctx, String preferName) {synchronized (SharedPreferenceProxy.class) {if (sharedPreferenceProxyMap == null) {sharedPreferenceProxyMap = new ArrayMap<>();}SharedPreferenceProxy preferenceProxy = sharedPreferenceProxyMap.get(preferName);if (preferenceProxy == null) {preferenceProxy = new SharedPreferenceProxy(ctx.getApplicationContext(), preferName);sharedPreferenceProxyMap.put(preferName, preferenceProxy);}return preferenceProxy;}}private static SharedPreferences getFromLocalProcess(@NonNull Context ctx, String preferName) {return ctx.getSharedPreferences(preferName, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);}
这样,只有当调用者是正真跨进程时才走的contentProvider。对于同进程的情况,就没有必要走contentProvider了。对调用者来说,这都是透明的,只需要获取SharedPreferences就行了,不用关心获得的是SharedPreferenceProxy,还是SharedPreferenceImpl。即使你当前没有涉及到多进程使用,将所有获取SharedPreference的地方封装并替换后,对当前逻辑也没有任何影响。
相关文章:

Android SharedPreference详解
Android SharedPreference详解 SharedPreferences作为一种数据持久化的方式,是处理简单的key-value类型数据时的首选。 一般用法: //demo是该sharedpreference对应文件名,对应的是一个xml文件,里面存放key-value格式的数据. SharedPreferences sharedPreferences…...
论文阅读 | 可证安全隐写(网络空间安全科学学报 2023)
可证安全隐写:理论、应用与展望 一、什么是可证安全隐写? 对于经验安全的隐写算法,即使其算法设计得相当周密,隐写分析者(攻击者)在观察了足够数量的载密(含有隐写信息的数据)和载体…...

Arthas jvm(查看当前JVM的信息)
文章目录 二、命令列表2.1 jvm相关命令2.1.3 jvm(查看当前JVM的信息) 二、命令列表 2.1 jvm相关命令 2.1.3 jvm(查看当前JVM的信息) 基础语法: jvm [arthas18139]$ jvmRUNTIME …...

【c++】介绍
C是一种强大而灵活的编程语言,广泛用于开发各种应用程序和系统软件。它结合了C语言的高效性和面向对象编程的特性,为程序员提供了丰富的工具和功能,以满足各种编程需求。 C的历史可以追溯到上世纪80年代,最初由丹尼斯里奇和贝尔实…...

JavaScript typeof与instanceof的区别
typeof 和 instanceof 都是 JavaScript 中的运算符,用于检查数据类型或对象的类型。它们有不同的用途和适用场景: 1. typeof 作用:返回变量的数据类型,适用于原始数据类型(如 number、string、boolean 等)…...

C++11 可变的模板参数
前言 本期我们接着继续介绍C11的新特性,本期我们介绍的这个新特性是很多人都感觉抽象的语法!它就是可变的模板参数! 目录 前言 一、可变的模板参数 1.1可变的参数列表 1.2可变的参数包 1.3可变参数包的解析 • 递归展开解析 • 逗号…...

手机在网状态查询接口如何用PHP进行调用?
一、什么是手机在网状态查询接口? 手机在网状态查询接口,即输入手机号码查询手机号在网状态,返回有正常使用、停机、在网但不可用、不在网(销号/未启用/异常)、预销户等多种状态。 二、手机在网状态查询适用哪些场景…...

MATLAB中多张fig图合并为一个图
将下列两个图和为一个图 打开查看-----绘图浏览器 点击第一幅图中曲线右键复制,到第二幅图中粘贴即可完成...

Java启动Tomcat: Can‘t load IA 32-bit .dll on a AMD 64-bit platform报错问题解决
🎬 鸽芷咕:个人主页 🔥 个人专栏: 《C干货基地》《粉丝福利》 ⛺️生活的理想,就是为了理想的生活! 专栏介绍 在软件开发和日常使用中,BUG是不可避免的。本专栏致力于为广大开发者和技术爱好者提供一个关于BUG解决的经…...

基于微信小程序的家教信息管理系统的设计与实现(论文+源码)_kaic
摘 要 随着互联网时代的来临,使得传统的家教模式已不复存在,亟需一种方便、快捷的在线教学平台。因此,利用Java语言作为支撑和MySQL数据库存储数据,结合微信小程序的便利性,为用户开发出了一个更加人性化、方便的家庭…...

【Android】BottomSheet基本用法总结(BottomSheetDialog,BottomSheetDialogFragment)
BottomSheet BottomSheet 是一种位于屏幕底部的面板,用于显示附加内容或选项。提供了从屏幕底部向上滑动显示内容的交互方式。这种设计模式在 Material Design 中被广泛推荐,因为它可以提供一种优雅且不干扰主屏幕内容的方式来展示额外信息或操作。 具体…...

Linux下实现ls命令的功能
教材:<Linux编程技术详解> 杜华 编著 人民邮电出版社 参考页码:P136 书中源代码: //p4.10.c 实现类似ls命令的功能 #include<stdio.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<dirent.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include&l…...

【中国留学网-注册_登录安全分析报告】
前言 由于网站注册入口容易被黑客攻击,存在如下安全问题: 暴力破解密码,造成用户信息泄露短信盗刷的安全问题,影响业务及导致用户投诉带来经济损失,尤其是后付费客户,风险巨大,造成亏损无底洞…...

jvm中的程序计数器、虚拟机栈和本地方法栈
引言 本文主要介绍一下jvm虚拟机中的程序计数器、虚拟机栈和本地方法栈。 程序计数器 作用 作用:记录下一条jvm指令的执行地址。 下面具体描述一下程序计数器的作用。 这里有两个代码,右边的为源代码,左边为编译之后的字节码。 当我们…...

安卓数据存储——SharedPreferences
共享参数 SharedPreferences 1、sharedPreferences是Android的一个轻量级存储工具,采用的存储结构是key - value的键值对方式 2、共享参数的存储介质是符合XML规范的配置文件。保存路径是:/data/data/应用包名/shared_prefs/文件名.xml 使用场景&…...

【计算机网络篇】数据链路层 功能|组帧|流量控制与可靠传输机制
🧸安清h:个人主页 🎥个人专栏:【计算机网络】 🚦作者简介:一个有趣爱睡觉的intp,期待和更多人分享自己所学知识的真诚大学生。 系列文章目录 【计算机网络篇】计算机网络概述 【计算机网络篇…...

Apache CVE-2021-41773漏洞复现
1、环境搭建 docker pull blueteamsteve/cve-2021-41773:no-cgid docker run -d -p 8080:80 97308de4753d 2、使⽤poc curl http://47.121.212.195:8080/cgi-bin/.%2e/.%2e/.%2e/.%2e/etc/passwd 3、工具验证...
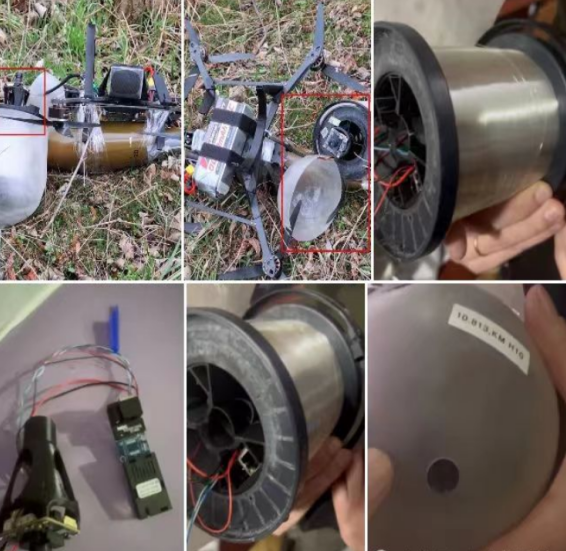

带线无人机现身俄罗斯抗干扰技术详解
带线无人机在俄罗斯的出现,特别是其光纤制导技术的应用,标志着无人机抗干扰技术的一大进步。以下是对俄罗斯带线无人机抗干扰技术的详细解析: 一、带线无人机抗干扰技术背景 技术突破:俄军成功研发了光纤制导无人机,…...

ArcGIS10.2/10.6安装包下载与安装(附详细安装步骤)
相信从事地理专业的小伙伴来说,应该对今天的标题不会陌生。Arcgis是一款很常用的地理信息系统软件,主要用于地理数据的采集、管理、分析和展示。目前比较常见的版本有ArcGIS 10.2和ArcGIS 10.6。 不可否认,Arcgis具有强大的地图制作、空间分…...

生信服务器 | 组蛋白甲基化修饰、DNA亲和纯化测序、优青博导团队指导设计、解读实验结果。
查看原文>>>生信服务器 | 组蛋白甲基化修饰、DNA亲和纯化测序、优青博导团队免费指导设计、解读实验结果、一台服务器解决您所有的分析困扰!...
)
浏览器访问 AWS ECS 上部署的 Docker 容器(监听 80 端口)
✅ 一、ECS 服务配置 Dockerfile 确保监听 80 端口 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]或 EXPOSE 80 CMD ["python3", "-m", "http.server", "80"]任务定义(Task Definition&…...

【git】把本地更改提交远程新分支feature_g
创建并切换新分支 git checkout -b feature_g 添加并提交更改 git add . git commit -m “实现图片上传功能” 推送到远程 git push -u origin feature_g...

涂鸦T5AI手搓语音、emoji、otto机器人从入门到实战
“🤖手搓TuyaAI语音指令 😍秒变表情包大师,让萌系Otto机器人🔥玩出智能新花样!开整!” 🤖 Otto机器人 → 直接点明主体 手搓TuyaAI语音 → 强调 自主编程/自定义 语音控制(TuyaAI…...

汇编常见指令
汇编常见指令 一、数据传送指令 指令功能示例说明MOV数据传送MOV EAX, 10将立即数 10 送入 EAXMOV [EBX], EAX将 EAX 值存入 EBX 指向的内存LEA加载有效地址LEA EAX, [EBX4]将 EBX4 的地址存入 EAX(不访问内存)XCHG交换数据XCHG EAX, EBX交换 EAX 和 EB…...

Java线上CPU飙高问题排查全指南
一、引言 在Java应用的线上运行环境中,CPU飙高是一个常见且棘手的性能问题。当系统出现CPU飙高时,通常会导致应用响应缓慢,甚至服务不可用,严重影响用户体验和业务运行。因此,掌握一套科学有效的CPU飙高问题排查方法&…...
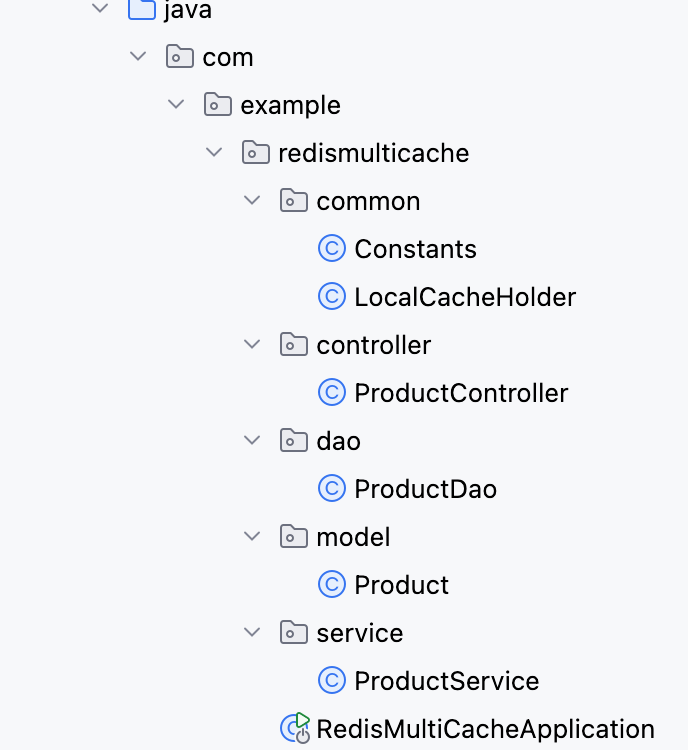
【Redis】笔记|第8节|大厂高并发缓存架构实战与优化
缓存架构 代码结构 代码详情 功能点: 多级缓存,先查本地缓存,再查Redis,最后才查数据库热点数据重建逻辑使用分布式锁,二次查询更新缓存采用读写锁提升性能采用Redis的发布订阅机制通知所有实例更新本地缓存适用读多…...
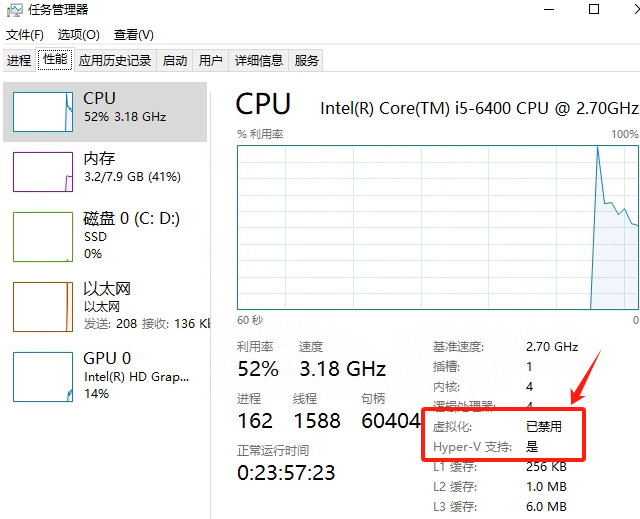
Windows电脑能装鸿蒙吗_Windows电脑体验鸿蒙电脑操作系统教程
鸿蒙电脑版操作系统来了,很多小伙伴想体验鸿蒙电脑版操作系统,可惜,鸿蒙系统并不支持你正在使用的传统的电脑来安装。不过可以通过可以使用华为官方提供的虚拟机,来体验大家心心念念的鸿蒙系统啦!注意:虚拟…...

CppCon 2015 学习:REFLECTION TECHNIQUES IN C++
关于 Reflection(反射) 这个概念,总结一下: Reflection(反射)是什么? 反射是对类型的自我检查能力(Introspection) 可以查看类的成员变量、成员函数等信息。反射允许枚…...

数据源指的是哪里的数据,磁盘中还是内存中
在 MyDB 项目中,特别是这段缓存框架代码: T obj getForCache(key);以及它的上下文: AbstractCache 是一个抽象类,内部有两个抽象方法,留给实现类去实现具体的操作: protected abstract T getForCache(lon…...

如何计算1920*1080分辨率的YUV或RGB图像数据占用大小?
好多开发者在对接大牛直播SDK的时候,经常问到的问题是,1920*1080分辨率的YUV或RGB图像数据,到底多少字节?在音视频图像开发中,19201080(即 Full HD)是一种极其常见的分辨率。但很多开发者在处理…...
