Lesson10---list
Lesson10—list
第10章 c++的list的使用和实现
文章目录
- Lesson10---list
- 前言
- 一、list的初始化
- 二、list的遍历
- 1.迭代器
- 2.范围for
- 三、list常用的内置函数
- 1.sort(慎用)
- 2.unique
- 3.reverse
- 4.merge
- 5.splice
- 四、模拟实现
- 1.基本框架
- 2.构造函数
- 3.push_back
- 4. 遍历
- 5.const迭代器
- 6.代码
- 7.const迭代器改进
- 8.insert
- 9.erase
- 10. pop_back
- 11. push_front
- 12.pop_front
- 13.clear
- 14.析构函数
- 15.拷贝构造
- 16.赋值
- 17.initializer
- 五.完整代码
- 总结
前言
这篇博客写了怎么使用list和怎么实现
list和前面的string 和vector 的有很多重复的就不过多赘述
一、list的初始化
vector的底层是数组,list的底层是结构体,所以list不能用下标的方式去访问,因为这样会让效率变的特别低
可以直接用花括号去初始化这样就不要一个个尾插,vector和list都可以

二、list的遍历
1.迭代器

vector的底层是数组,在内存上是连续的但是链表不是,但这里链表依旧可以使用迭代器来遍历,非常的强大
既然可以用迭代器去访问一个在内存上不连续的list那能不能给这个链表用sort排序呢?
答案是不能,因为这样排序效率特别低,如果想要去排序链表,list提供了sort函数

2.范围for

有很多和vector重复了就不重复写了感兴趣的可以看我的vector篇
三、list常用的内置函数
1.sort(慎用)


默认是升序加上仿函数是降序
list的排序底层用的不是快排用的是归并排序,如果数据很多又要排序就不要用list用vector

list排序时间是vector的三倍左右,而且特别稳定基本都是三倍左右,虽然归并排序和快排都是nlogn但是list排序还是罗逊vector
甚至把list里面的数据拷贝给vector让vector用快排排序,把排序好的数据在拷贝回来这样会都比list的sort的归并排序快简直拉跨


2.unique
unique的作用是去重但数据必须是排序以后或者连续的

不排序或者不连续就会这样去不干净

3.reverse
逆置这个链表,比较简单

4.merge
合并链表,这里必须是要有序的


5.splice
这个函数差不多就是剪切的意思,第一个参数要迭代器,第二个参数是链表
从迭代器的位置插入一整个链表

还可以这样用

四、模拟实现
模板不建议声明和定义分开会有各种问题,建议直接把定义写在.h文件里面
1.基本框架
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prve;T _data;
};template<class T>
class my_list
{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;
private:Node* _head;
};
先把基本的框架写好来
2.构造函数

3.push_back

这里可以画个草图理解,要尾插就要先找尾巴
void push_back(const T& x)
{Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prve;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prve = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prve = newnode;
}

运行以后会这个错误

编译器给的是这个错误,这是因为,new Node 会去调用 node默认构造函数但是这里没有写


struct ListNode
{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prve;T _data;ListNode(const T& data = T()):_next(nullptr),_prve(nullptr),_data(data){}
};

4. 遍历
链表在逻辑上是连在一起的但是它在物理上就不一定是连续的了是所用它不能想vector一样的用++去遍历vector底层是数组
这里我采用迭代器的方式去遍历,因为指针++需要像数组那样在物理上连续才可以所以这里采用封装然后运算符重载去实现
class ListIterator
{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T> self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}self& operator++( ){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}
};



这样就可以遍历了,也支持范围for

5.const迭代器
如果有人这样去访问迭代器就会把回来的值改变不安全,有时候还会在不经意间改变原来的值


这里还需要重载一个const迭代器,只能去访问但是不能修改里面的值
template<class T>
class ListConstIterator{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListConstIterator<T> self;ListConstIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Node* _node;self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prve;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prve;return tmp;}const T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator ==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}
};这里只需要复制一份原来的迭代器改下名字就行,然后重载一下

然后加上const就可以了然后再去my_list里面加上就行

加上const迭代器的begin和end


这里就不让改了
6.代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prve;T _data;ListNode(const T& data = T()):_next(nullptr),_prve(nullptr),_data(data){}
};
template<class T>
class ListIterator{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T> self;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Node* _node;self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prve;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prve;return tmp;}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator ==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}
};
template<class T>
class ListConstIterator{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListConstIterator<T> self;ListConstIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Node* _node;self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prve;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prve;return tmp;}const T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator ==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}
};template<class T>
class my_list
{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const {return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const {return const_iterator(_head);}my_list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prve = _head;}void push_back(const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prve;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prve = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prve = newnode;}private:Node* _head;
};7.const迭代器改进
上面const迭代器有一个问题,就是只要解引用那一点点不一样甚至只是返回值加了const代码就边长了那么多这里还可以在优化一下
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prve;T _data;ListNode(const T& data = T()):_next(nullptr), _prve(nullptr), _data(data){}
};
template<class T,class Ref>
class ListIterator{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T,Ref> self;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Node* _node;self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prve;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prve;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator ==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}
};
//template<class T>
//class ListConstIterator
//
//{
//public:
//
// typedef ListNode<T> Node;
// typedef ListConstIterator<T> self;
// ListConstIterator(Node* node)
// :_node(node)
// {
//
// }
// Node* _node;
// self& operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// self& operator--()
// {
// _node = _node->_prve;
// return *this;
// }
// self operator++(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return tmp;
// }
// self operator--(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_prve;
// return tmp;
// }
// const T& operator*()
// {
// return _node->_data;
// }
// bool operator !=(const self& it)
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
// bool operator ==(const self& it)
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//};template<class T>
class my_list
{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T,T&> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T,const T&> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}my_list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prve = _head;}void push_back(const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prve;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prve = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prve = newnode;}private:Node* _head;
};
8.insert
可以画个草图方便理解
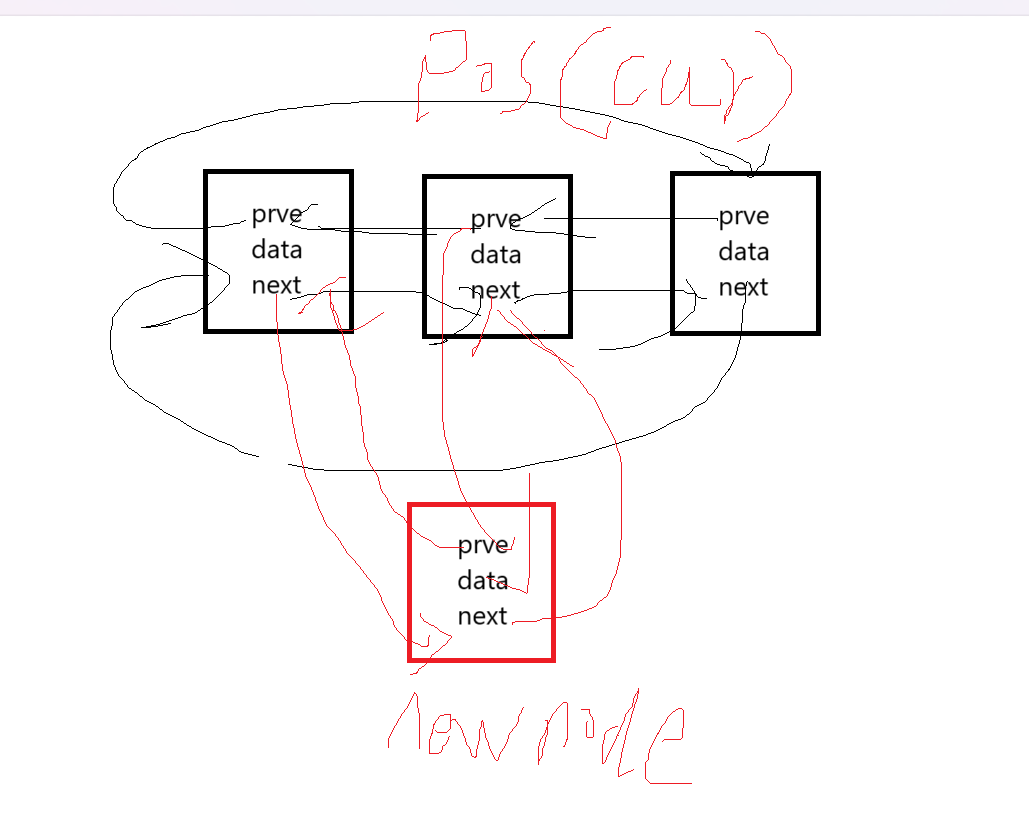
iterator insert(iterator pos ,const T& x)
{Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* cur = pos._node;newnode->_prve = cur->_prve;cur->_prve->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prve = newnode;return iterator(newnode);
}
9.erase
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prve = cur->_prve;Node* next = cur->_next;prve->_next = next;next->_prve = prve;delete cur;return iterator(next);
}
10. pop_back
void pop_back()
{erase(--end());
}
11. push_front
void push_front(const T& x)
{insert(begin(), x);
}
12.pop_front
void pop_front()
{erase(begin());
}
13.clear
void clear()
{auto it = begin();while (it !=end()){it=erase(it);}
}
14.析构函数
~my_list()
{clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;
}
15.拷贝构造
my_list(const my_list<T>& lt)
{_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prve = _head;for (const auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}
}
16.赋值
my_list<T>& operator = (my_list<T> lt)
{swap(lt._head, _head);return *this;
}
17.initializer
my_list(initializer_list<T> il)
{_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prve = _head;for (auto e : il){push_back(e);}
}
五.完整代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prve;T _data;ListNode(const T& data = T()):_next(nullptr), _prve(nullptr), _data(data){}
};
template<class T, class Ref>
class ListIterator{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref> self;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Node* _node;self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prve;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prve;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}bool operator !=(const self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator ==(const self& it){return _node == it._node;}
};
//template<class T>
//class ListConstIterator
//
//{
//public:
//
// typedef ListNode<T> Node;
// typedef ListConstIterator<T> self;
// ListConstIterator(Node* node)
// :_node(node)
// {
//
// }
// Node* _node;
// self& operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// self& operator--()
// {
// _node = _node->_prve;
// return *this;
// }
// self operator++(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_next;
// return tmp;
// }
// self operator--(int)
// {
// self tmp(*this);
// _node = _node->_prve;
// return tmp;
// }
// const T& operator*()
// {
// return _node->_data;
// }
// bool operator !=(const self& it)
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
// bool operator ==(const self& it)
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//};template<class T>
class my_list
{
public:typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, T&> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator begin()const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end()const{return const_iterator(_head);}void empty(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prve = _head;}my_list(){empty();}//lt2(lt1)my_list(initializer_list<T> il){empty();for (auto e : il){push_back(e);}}my_list(const my_list<T>& lt){empty();for (const auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}~my_list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}//lt3 = lt1my_list<T>& operator = (my_list<T> lt){swap(lt._head, _head);return *this;}void push_back(const T& x){/*Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prve;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prve = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prve = newnode;*/insert(end(), x);}iterator insert(iterator pos ,const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* cur = pos._node;newnode->_prve = cur->_prve;cur->_prve->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prve = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prve = cur->_prve;Node* next = cur->_next;prve->_next = next;next->_prve = prve;delete cur;return iterator(next);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it !=end()){it=erase(it);}}
private:Node* _head;
};
总结
例如:以上就是要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了list的使用和简单的模拟实现
相关文章:

Lesson10---list
Lesson10—list 第10章 c的list的使用和实现 文章目录 Lesson10---list前言一、list的初始化二、list的遍历1.迭代器2.范围for 三、list常用的内置函数1.sort(慎用)2.unique3.reverse4.merge5.splice 四、模拟实现1.基本框架2.构造函数3.push_back4. 遍…...
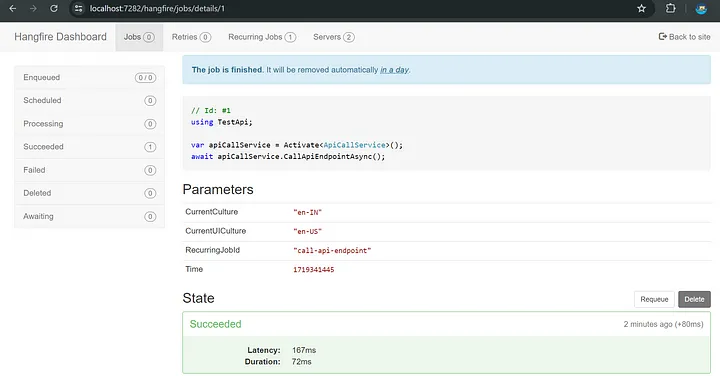
ASP.NET Core 8.0 中使用 Hangfire 调度 API
在这篇博文中,我们将引导您完成将 Hangfire 集成到 ASP.NET Core NET Core 项目中以安排 API 每天运行的步骤。Hangfire 是一个功能强大的库,可简化 .NET 应用程序中的后台作业处理,使其成为调度任务的绝佳选择。继续阅读以了解如何设置 Hang…...

查看linux的版本
在 Linux 系统中,有多种方法可以查看当前系统的版本信息。以下是一些常用的方法: 1. 使用 uname 命令 uname 命令可以显示系统的内核版本和其他相关信息。 uname -a这个命令会输出类似如下的信息: Linux hostname 5.4.0-88-generic #99-U…...

Mysql补充
单例 双重检查锁 class Singleton {private static volatile Singleton instance ;private Singleton() {}public static Singleton getInstance(){if(instance null) {synchronized (Singleto.class) {if(instance null){instance new Singleton() ;}} return instance;} …...

com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService用法详解及使用例子
IService 是 MyBatis-Plus 中的一个接口,提供了通用的 CRUD 操作,简化了数据库操作的代码。下面是 IService 的用法详解及示例代码。 1. 引入依赖 确保在你的 pom.xml 中添加了 MyBatis-Plus 的依赖: <dependency><groupId>co…...
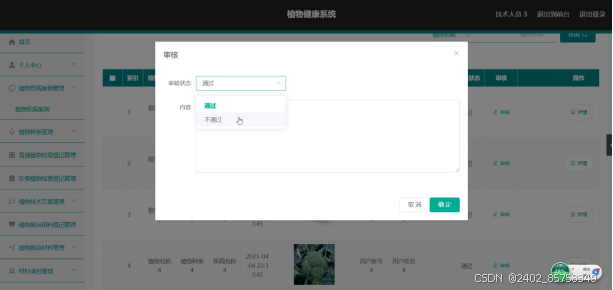
植物健康,Spring Boot来保障
5系统详细实现 5.1 系统首页 植物健康系统需要登录才可以看到首页。具体界面的展示如图5.1所示。 图5.1 系统首页界面 5.2 咨询专家 可以在咨询专家栏目发布消息。具体界面如图5.2所示。 图5.2 咨询专家界面 5.3 普通植物检查登记 普通员工可以对普通植物检查登记信息进行添…...

mac-chrome提示您的连接不是私密连接
一、现象介绍 关闭代理之后就ok打开代理,就会提示您的连接不是私密连接 二、原因 由于代理部分的问题,无法找到正确的网站ip地址 三、解决方法 1、键盘直接输入thisisunsafe,可以继续访问网站,如果还是不对的话,那…...
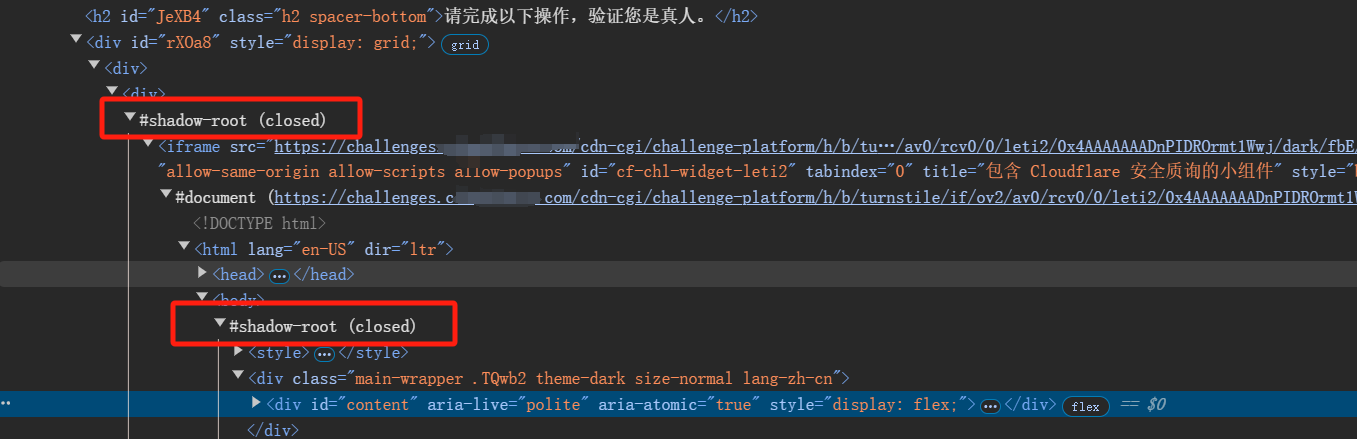
028.爬虫专用浏览器-抓取#shadowRoot(closed)下的内容
一、什么是Shadow DOM Shadow DOM是一种在web开发中用于封装HTML标记、样式和行为的技术,以避免组件间的样式和脚本冲突。它允许开发者将网页的一部分隐藏在一个独立的作用域内,从而实现更加模块化和可维护的代码结构 二、js操作Shadow DOM // 获取宿…...
Serv00 免费虚拟主机 零成本搭建 PHP / Node.js 网站
本文首发于只抄博客,欢迎点击原文链接了解更多内容。 前言 Serv00 是一个提供免费虚拟主机的平台,包含了 3GB 的存储空间和 512MB 的内存空间,足够我们搭建一个 1IP 的小网站了。同时他还不限制每月的流量,并提供了 16 个数据库&…...

C#里使用ORM访问mariadb数据库
数据库,对于开发人员来说,是必须掌握的内容。 曾经我的老板对我说,只要会数据库的增删查改,就不会没有饭吃。 经过了20年多的工作经历,说明这个是铁的事实,毕竟计算机就是加工数据处理的而设计的。 数据就是信息,信息就是金钱,有了钱就可以有饭吃。 管理数据,就是…...

电商揭秘:商城积分体系简析
引言 商城积分体系划分是一个复杂而细致的过程,它旨在通过积分这一虚拟货币来激励用户行为、提升用户粘性,并促进商城的销售和用户活跃度。以下是对商城积分体系划分的详细解析: 一、积分获取方式 消费积分: 基础积分:…...
 暂停执行线程(Suspend Executing Thread))
[OS] 终端控制(Terminal Control) 暂停执行线程(Suspend Executing Thread)
7. 终端控制(Terminal Control) 在终端中打印信息时,我们可以使用 ANSI 转义序列来控制光标的位置、清除屏幕等操作。\033 是转义字符,用于引导 ANSI 控制码来控制终端显示。可以将它理解为“命令前缀”,后面跟着具体…...

水陆两栖车应对应急事件发挥的作用_鼎跃安全
随着气候变化,城市内涝等问题日益严重。为了应对可能出现的洪水灾害,许多城市开始将水陆两栖车纳入应急救援装备体系。在暴雨引发城市积水时,水陆两栖车可以作为一种高效的救援和运输工具,及时疏散被困群众,运送应急物…...

CI/CD 流水线系统-开源框架Tekton
文章目录 CI/CD 流水线系统-开源框架Tekton什么是TektonTekton优点Tekton 组件介绍Tekton 概念术语 CI/CD 流水线系统-开源框架Tekton 什么是Tekton 官网:https://tekton.dev/ Tekton 是一个强大、灵活的构建 CI/CD 流水线系统的开源框架,允许开发者构建、测试和…...
Spring MVC(下)
博主主页: 码农派大星. 数据结构专栏:Java数据结构 数据库专栏:MySQL数据库 JavaEE专栏:JavaEE 关注博主带你了解更多JavaEE知识 目录 1.响应 1.1 返回静态页面 1.2 返回数据ResponseBody 1.3 返回HTML代码⽚段 1.4 返回JSON 1.5 设置状态码 1.6 设置Header 2 . …...

开发涉及的安全规范整理
#1024程序员节|征文# 文章目录 前言安全场景与措施API调用方式鉴权参数校验日志打印数据保存加密 总结 前言 这篇文章我们来整理下写代码和方案设计中的安全规范问题,内容偏服务端,即使是入门的新人,如果你对安全有所了解会让成熟…...
)
驱动开发系列26 - Linux Graphics 调试 mesa 的 glDrawArrays (二)
目录 一:概述 二:Gallium3D 的工作流程 三:tc_draw_vbo 与 tc_call_draw_single 的关系: 四:tc_draw_vbo 与 tc_call_draw_single 的具体执行流程: 五:mesa中线程池设计介绍: 六:总结: 一:概述 众所周知,Mesa 的 Gallium3D 是一个图形驱动框架,它将图形管线…...
laya-spine动画的使用
laya2和laya3的spine动画在使用过程中并无太大区别,这里以laya3为例。 转换 首先将做好的spine动画按jison格式导出,导出完之后的文件应包括图集、图片和json类型的3个文件。然后再用laya的骨骼动画转换工具转换成laya内置的模式,转换后的文…...
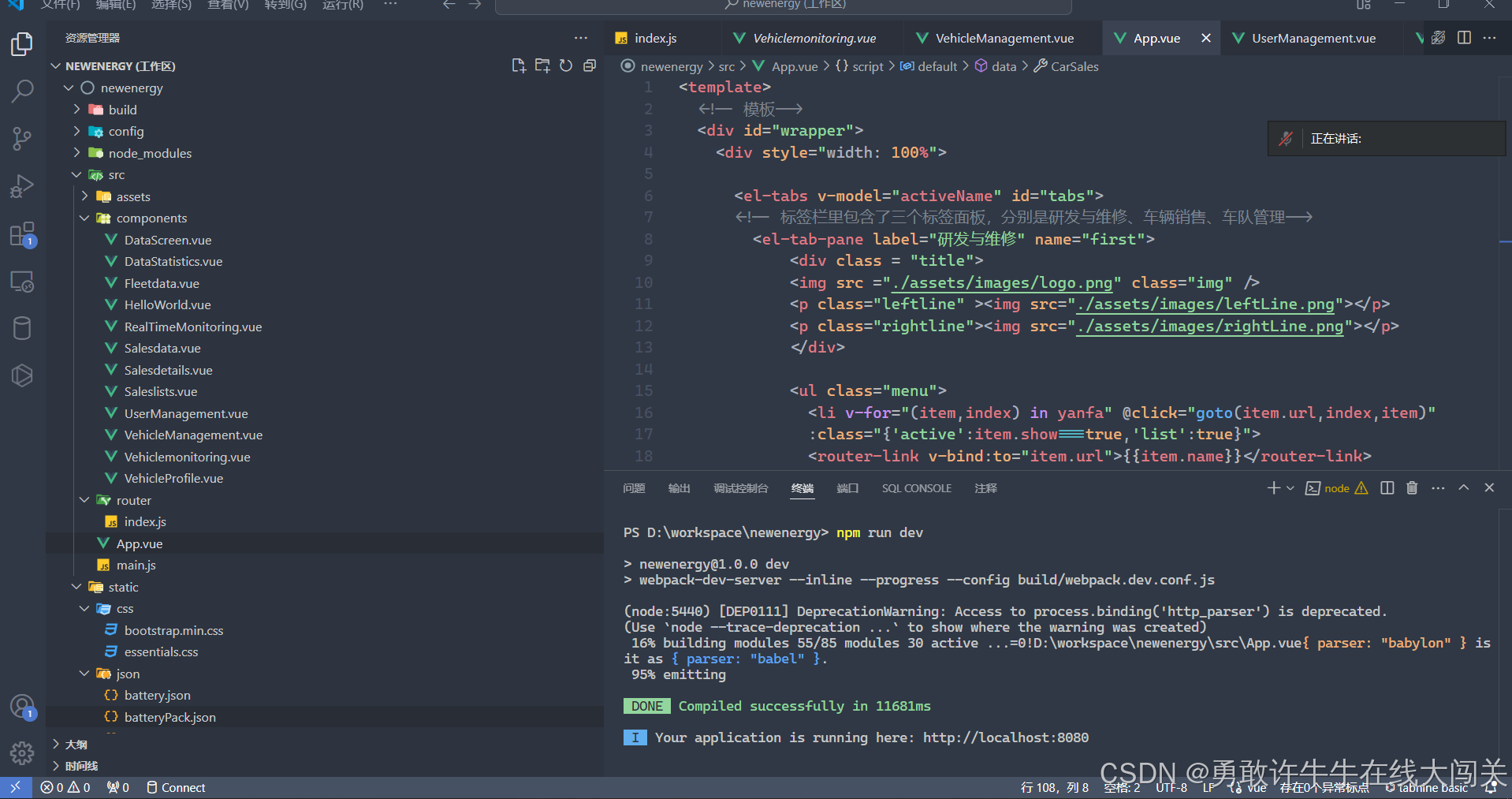
Vue项目实战-新能源汽车可视化(一)(持续更新中)
一.项目代码 1.App.vue <template><!-- 模板--><div id"wrapper"><div style"width: 100%"><el-tabs v-model"activeName" id"tabs"> <!-- 标签栏里包含了三个标签面板,分别是研发与维…...

百度SEO前10关键词排名波动跟用户行为反馈有很大关系
大家好,我是林汉文(谷歌SEO专家),在百度SEO优化中,网站的排名并非一成不变,尤其是前10名的位置,更是动态变化。很多站长可能会发现,有时明明内容质量不错,外链也稳定&…...
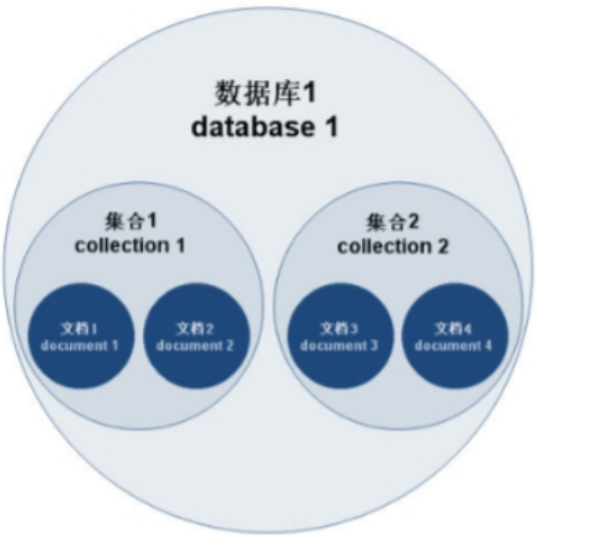
MongoDB学习和应用(高效的非关系型数据库)
一丶 MongoDB简介 对于社交类软件的功能,我们需要对它的功能特点进行分析: 数据量会随着用户数增大而增大读多写少价值较低非好友看不到其动态信息地理位置的查询… 针对以上特点进行分析各大存储工具: mysql:关系型数据库&am…...
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...
2025盘古石杯决赛【手机取证】
前言 第三届盘古石杯国际电子数据取证大赛决赛 最后一题没有解出来,实在找不到,希望有大佬教一下我。 还有就会议时间,我感觉不是图片时间,因为在电脑看到是其他时间用老会议系统开的会。 手机取证 1、分析鸿蒙手机检材&#x…...
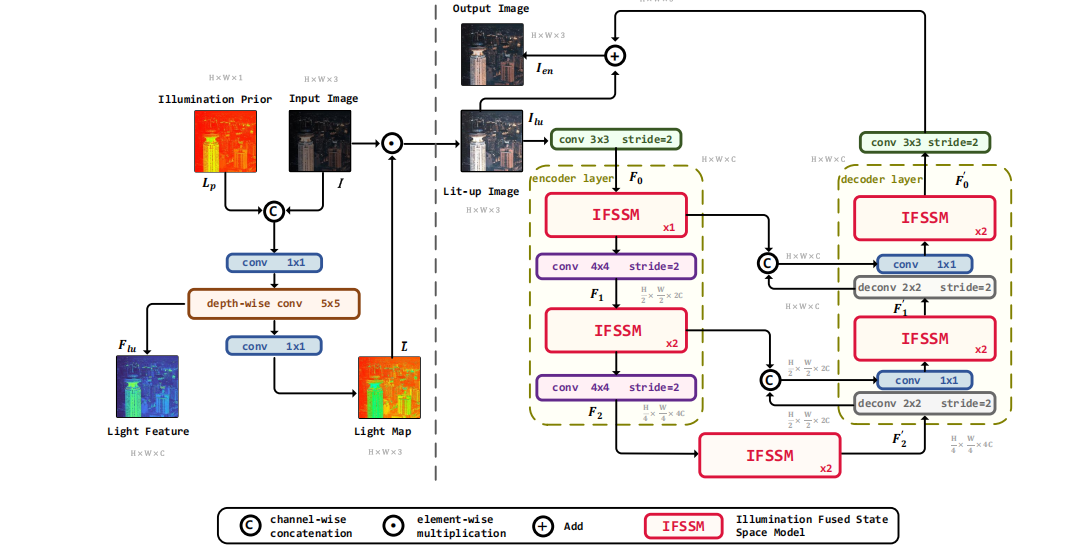
深度学习水论文:mamba+图像增强
🧀当前视觉领域对高效长序列建模需求激增,对Mamba图像增强这方向的研究自然也逐渐火热。原因在于其高效长程建模,以及动态计算优势,在图像质量提升和细节恢复方面有难以替代的作用。 🧀因此短时间内,就有不…...

iview框架主题色的应用
1.下载 less要使用3.0.0以下的版本 npm install less2.7.3 npm install less-loader4.0.52./src/config/theme.js文件 module.exports {yellow: {theme-color: #FDCE04},blue: {theme-color: #547CE7} }在sass中使用theme配置的颜色主题,无需引入,直接可…...

多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现
多模态图像修复系统:基于深度学习的图片修复实现 1. 系统概述 本系统使用多模态大模型(Stable Diffusion Inpainting)实现图像修复功能,结合文本描述和图片输入,对指定区域进行内容修复。系统包含完整的数据处理、模型训练、推理部署流程。 import torch import numpy …...

关于uniapp展示PDF的解决方案
在 UniApp 的 H5 环境中使用 pdf-vue3 组件可以实现完整的 PDF 预览功能。以下是详细实现步骤和注意事项: 一、安装依赖 安装 pdf-vue3 和 PDF.js 核心库: npm install pdf-vue3 pdfjs-dist二、基本使用示例 <template><view class"con…...

es6+和css3新增的特性有哪些
一:ECMAScript 新特性(ES6) ES6 (2015) - 革命性更新 1,记住的方法,从一个方法里面用到了哪些技术 1,let /const块级作用域声明2,**默认参数**:函数参数可以设置默认值。3&#x…...
阿里云Ubuntu 22.04 64位搭建Flask流程(亲测)
cd /home 进入home盘 安装虚拟环境: 1、安装virtualenv pip install virtualenv 2.创建新的虚拟环境: virtualenv myenv 3、激活虚拟环境(激活环境可以在当前环境下安装包) source myenv/bin/activate 此时,终端…...

【WebSocket】SpringBoot项目中使用WebSocket
1. 导入坐标 如果springboot父工程没有加入websocket的起步依赖,添加它的坐标的时候需要带上版本号。 <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId> </dep…...
