JAVA高性能缓存项目
版本一
代码实现
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class CacheExample01 {private final static HashMap<String, Integer> cache = new HashMap<>();public static Integer check(String userId) throws InterruptedException {Integer result = cache.get(userId);//未查到结果则保存到缓存中,缓存中有则直接返回if (result == null) {result = computer(userId);cache.put(userId, result);}return result;}private static Integer computer(String userId) throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);//模拟查询数据库耗时return new Integer(userId);}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//模拟实际查询System.out.println("第一次查询:" + check("1314"));System.out.println("第二次查询:" + check("1314"));//结果为://第一次查询:1314//第二次查询:1314//其中第一次查询耗时>5s, 第二次查询耗时<1s;}
}特点
- 代码复用性差,缓存计算与业务耦合
- 线程不安全,并发情况下会导致意外错误
版本二 用装饰者模式解耦
计算接口
Computable.java文件
package computable;/*有一个计算函数computer, 用来代表耗时计算,每个计算器
都要实现这个接口,这样就可以无入侵实现缓存功能
*/
public interface Computable<A, V> {V compute(A arg) throws Exception;
}
具体耗时查询实现
ExpensiveFunciton.java文件
package computable;public class ExpensiveFunciton implements Computable<String, Integer>{@Overridepublic Integer compute(String arg) throws Exception {System.out.println("进入耗时缓存");Thread.sleep(5000);return Integer.valueOf(arg);}
}
缓存
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;public class CacheExample02<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, V> cache = new HashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample02(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}@Overridepublic synchronized V compute(A args) throws Exception {V result = cache.get(args);if (result == null) {result = c.compute(args);cache.put(args, result);}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CacheExample02<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample02<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第一次结算结果:" + result);result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);/*结果为:进入耗时缓存第一次查询结果:1314第二次查询结果:1314 */}
}特点
- 解决了缓存计算与业务耦合的问题,实现了无侵入式的计算接口
- 无法并行计算,效率低
版本三 ConcurrentHashMap保证线程安全
代码实现
用ConcurrentHashMap替代版本二的HashMap即可
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;public class CacheExample02<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, V> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample02(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}@Overridepublic V compute(A args) throws Exception {V result = cache.get(args);if (result == null) {result = c.compute(args);cache.put(args, result);}return result;}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CacheExample02<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample02<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第一次结算结果:" + result);result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);}
}
特点
- 用ConcurrentHashMap替代了HashMap,实现了线程安全
- 在计算完成前,多个要求计算相同值的请求到来,会导致计算多遍,导致低性能

版本四 用Future解决重复计算问题
代码实现
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;public class CacheExample03<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample03(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}@Overridepublic V compute(A arg) throws Exception {Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);if (f == null) {Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {@Overridepublic V call() throws Exception {return c.compute(arg);}};FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);f = ft;cache.put(arg, ft);ft.run();}return f.get();}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CacheExample03<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample03<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("6666");System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}
}
代码结果为:

结果分析
需要注意的是,如果把计算值从"1314", “6666”, “1314”, "1314"全部改成"1314"的话,代码结果如下

或

但是当相同请求结果上升到六个甚至更多时,也只会有2-3个线程进入耗时缓存

证明了这个方法能解决大部分的重复计算问题,不能完全解决。因为在多个相同请求值同时进入时,在第一个请求还未达到 cache.put(arg, ft);这条代码时,其它线程仍会重复计算。
注意:
如果线程的创建用的是Lambda 表达式,会导致进入耗时缓存略多于使用匿名内部类 Runnable 来创建线程,因为Lambda表达式性能略优于使用匿名内部类 Runnable。
使用Lambda表达式结果如下:

特点
- 解决了大部分的重复计算问题,但仍然存在小概率的重复计算情况

版本五 用原子组合操作解决小部分重复操作问题
代码实现
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;public class CacheExample02<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample02(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}@Overridepublic V compute(A arg) throws Exception {Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);if (f == null) {Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {@Overridepublic V call() throws Exception {return c.compute(arg);}};FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);if (f == null) {f = ft;ft.run();}}return f.get();}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CacheExample02<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample02<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blockse.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blockse.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第五次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blockse.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第六次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blockse.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第七次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第八次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第九次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第十次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}).start();}
}结果分析
代码结果:

可以看到在多个线程同时请求相同值时,也只有一个线程进入了耗时计算(在多次重复实验后也是如此)
特点
- 完全解决了重复计算的问题,使得不同线程在执行的同时避免了重复计算的消耗,大大提升了性能
- 未考虑在业务中计算出错时的错误处理以及缓存污染问题
版本六 处理缓存污染以及错误处理
代码实现
MayfailFunction.java文件
主要用于模拟业务中可能出现的计算错误
package computable;import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class MayfailFunction implements Computable<String, Integer>{@Overridepublic Integer compute(String arg) throws Exception{double random = Math.random();if (random < 0.5) {throw new IOException("计算出错");}TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);return Integer.valueOf(arg);}
}主要实现文件
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
import computable.MayfailFunction;public class CacheExample04<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample04(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}@Overridepublic V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {//具体计算部分用while(true)包裹起来,是为了在计算出错后能自动重复计算直至计算成功while (true) {Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);if (f == null) {Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {@Overridepublic V call() throws Exception {return c.compute(arg);}};FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);if (f == null) {f = ft;ft.run();}}try {return f.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {cache.remove(arg);//在出现错误的时候将计算出错的值从缓存池中移除,避免缓存池的污染throw e;} catch (ExecutionException e) {cache.remove(arg);e.printStackTrace();} catch (CancellationException e) {cache.remove(arg);throw e;}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CacheExample04<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample04<>(new MayfailFunction());new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第五次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.compute("1314");System.out.println("第六次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}
}结果分析
代码结果:

成功地实现了在计算出错的情况下,仍然能自动重复计算直到计算成功,并且及时将计算出错的值从缓存中去除。
注意:
如果在捕获错误时缺少cache.remove(arg);(即不及时将计算错误的值从缓存池中去除)会导致缓存池污染,导致相同请求值返回错误的值(在该代码中体现为一直出现计算错误并且不会停止)。
错误结果如下:

出现无止境的“计算出错”的报错
版本七 ScheduledExecutorService实现缓存过期
代码实现
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;
import computable.MayfailFunction;public class CacheExample05<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample05(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}@Overridepublic V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {while (true) {Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);if (f == null) {Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {@Overridepublic V call() throws Exception {return c.compute(arg);}};FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);if (f == null) {f = ft;ft.run();}}try {return f.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {cache.remove(arg);throw e;} catch (ExecutionException e) {cache.remove(arg);e.printStackTrace();} catch (CancellationException e) {cache.remove(arg);throw e;}}}private final static ScheduledExecutorService executor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(6);public V compute(A arg, long expireTime) throws CancellationException, InterruptedException {if (expireTime > 0) {executor.schedule(() -> {expire(arg);}, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);};return compute(arg);}public synchronized void expire(A key) {Future<V> f = cache.get(key);if (f != null) {if (!f.isDone()) {f.cancel(true);System.out.println("任务被取消了");}System.out.println("过期时间到,缓存被清除");cache.remove(key);}}
//随机赋予缓存失效时间,避免同时失效导致线程长时间阻塞public V computeRandomExpire(A arg) throws CancellationException, InterruptedException {long randomExpireTime = (long) Math.random() * 1000;return compute(arg, randomExpireTime);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CacheExample05<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample05<>(new MayfailFunction());new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");System.out.println("第一次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();Thread.sleep(10000);new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");System.out.println("第二次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");System.out.println("第三次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");System.out.println("第四次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");System.out.println("第五次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Integer result = example.computeRandomExpire("1314");System.out.println("第六次计算结果:" + result);} catch (Exception e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}).start();}
}特点:
- 实现了随机缓存过期失效功能
缓存项目性能测试
线程池压力测试
部分工具类用法功能:
-
isShutdown():
这个方法用来检查线程池是否已经被关闭。如果线程池已经调用了 shutdown() 方法,那么 isShutdown() 会返回 true。
shutdown() 方法会启动线程池的关闭过程,它会停止接收新的任务,并且会等待所有已提交的任务完成执行后关闭线程池。 -
isTerminated():
这个方法用来检查所有任务是否都已完成执行。如果线程池已经调用了 shutdown() 方法,并且所有提交的任务都已经执行完毕,那么isTerminated() 会返回 true。
isTerminated() 通常与 awaitTermination()方法一起使用,awaitTermination() 会阻塞当前线程直到所有任务执行完成或者超时。
简而言之,isShutdown() 表示线程池是否已经开始关闭过程,而 isTerminated() 表示线程池是否已经完全关闭,即所有任务都已执行完毕。在使用线程池时,通常先调用 shutdown() 方法来开始关闭过程,然后通过 isTerminated() 或 awaitTermination() 来检查关闭过程是否完成。
代码实现
创建含大量线程的线程池执行缓存的过程
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;public class CacheExample06<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample06(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}@Overridepublic V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {while (true) {Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);if (f == null) {Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {@Overridepublic V call() throws Exception {return c.compute(arg);}};FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);if (f == null) {f = ft;ft.run();}}try {return f.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {cache.remove(arg);throw e;} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();cache.remove(arg);} catch (CancellationException e) {cache.remove(arg);throw e;}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {CacheExample06<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample06<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(6000);long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 6000; i ++ ) {executor.submit(() -> {Integer result = null;try {result = example.compute("1314");} catch (CancellationException | InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("result:" + result);});};executor.shutdown();while (!executor.isTerminated()) {}System.out.println("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));}
}结果分析
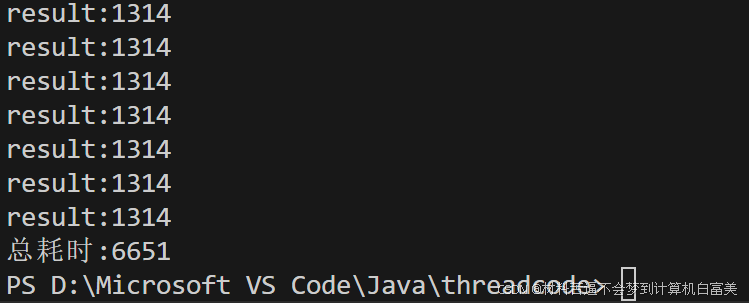
第一次缓存耗时5s + 后续从缓存中获取结果1.651s = 总耗时6651ms
存在问题
大量请求实际上不是同时到达,而是先后到达,导致给缓存池造成的压力较小,无法真正体现缓存池在多线程并发访问下的性能
CountDownLatch压力测试
使用CountDownLatch工具类来真正实现大量线程在同一时间下的并发访问,能给予缓存池更大的压力
工具类用法
- 计数器操作
countDown():每次调用这个方法,计数器的值就会减1。当计数器的值达到0时,CountDownLatch 就会“开启”,所有等待在 await() 方法上的线程将继续执行。
getCount():返回当前计数器的值。 - 等待
await():当前线程会在这里阻塞,直到 CountDownLatch 被“开启”(即计数器的值达到0)。如果 CountDownLatch 没有被开启,await() 方法会无限期地等待。
await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):与 await() 类似,但是它允许你设置一个超时时间。如果在指定的时间内计数器的值没有达到0,线程将不再阻塞,并返回一个布尔值,表示是否在超时前计数器已经达到0。
代码实现
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.CancellationException;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
import computable.Computable;
import computable.ExpensiveFunciton;public class CacheExample06<A, V> implements Computable<A, V> {private final Map<A, Future<V>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private final Computable<A, V> c;private CacheExample06(Computable<A, V> c) {this.c = c;}private final static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);private static CacheExample06<String, Integer> example = new CacheExample06<>(new ExpensiveFunciton());@Overridepublic V compute(A arg) throws InterruptedException, CancellationException {while (true) {Future<V> f = cache.get(arg);if (f == null) {Callable<V> callable = new Callable<V>() {@Overridepublic V call() throws Exception {return c.compute(arg);}};FutureTask<V> ft = new FutureTask<>(callable);f = cache.putIfAbsent(arg, ft);if (f == null) {f = ft;ft.run();}}try {return f.get();} catch (InterruptedException e) {cache.remove(arg);throw e;} catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();cache.remove(arg);} catch (CancellationException e) {cache.remove(arg);throw e;}}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i ++ ) {executor.submit(() -> {Integer result = null;try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "被阻塞");latch.await();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始运行");result = example.compute("1314");} catch (CancellationException | InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("result:" + result);});};executor.shutdown();Thread.sleep(5000);//保证所有线程都被阻塞后再统一放行latch.countDown();while (!executor.isTerminated()) {}System.out.println("总耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));}
}结果分析
部分截图,总的来说线程1 - 100先被阻塞,后统一被放行

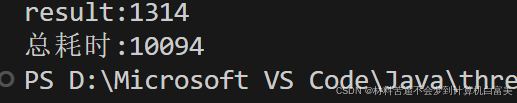
主线程sleep(5000) + 缓存计算5s + 剩余线程读取缓存94ms = 总耗时10094ms
相关文章:

JAVA高性能缓存项目
版本一 代码实现 import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class CacheExample01 {private final static HashMap<String, Integer> cache new HashMap<>();public static Integer check(String userId) throws InterruptedExce…...

智慧农业大数据平台:智汇田园,数驭未来
智慧农业大数据平台 计讯物联智慧农业大数据平台是一个集管理数字化、作业自动化、生产智能化、产品绿色化、环境信息化、服务现代化于一体的多功能监管系统。它通过与硬件产品的搭配使用,实现对农业生产全过程的实时监测、精准控制和科学管理。该平台集成了多个数…...
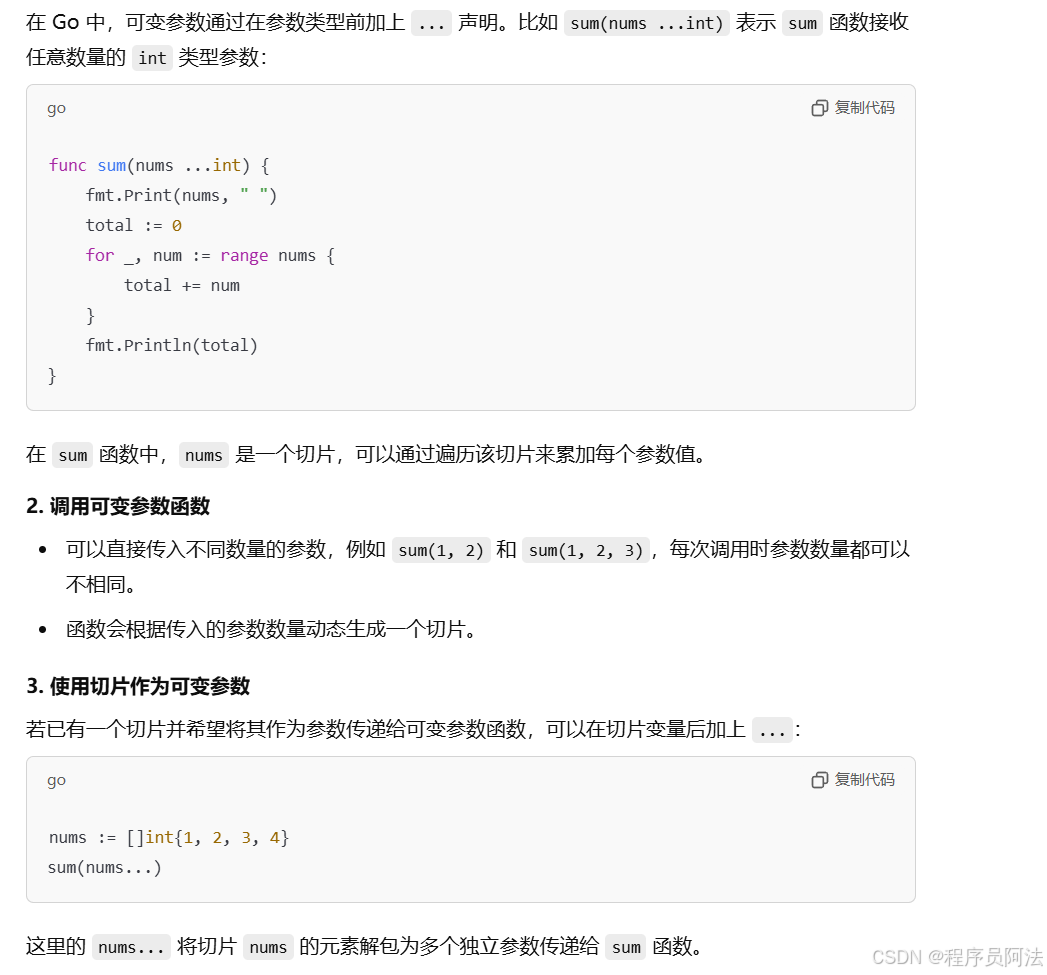
Go语言基础教程:可变参数函数
Go 语言允许函数接收可变数量的参数,这种特性对于处理数量不确定的参数特别有用。在本教程中,我们将通过示例代码讲解如何定义和使用 Go 的可变参数函数。 package mainimport "fmt"// 定义一个可变参数函数 sum,接收任意数量的整…...

高并发场景下解决并发数据不一致
简单的场景: 全量数据更新的情况下, 不在乎同一秒的请求都必须要成功, 只留下最新的更新请求数据 方案常用的是 1、数据库增加时间戳标识实现的乐观锁, 请求参数从源头带上微秒或者毫秒时间戳数据库存储, 然后在更新SQL语句上比较 (数据库的时间 < 参数传递的时间) 例如: A…...
OpenAI GPT-o1实现方案记录与梳理
本篇文章用于记录从各处收集到的o1复现方案的推测以及介绍 目录 Journey Learning - 上海交通大学NYUMBZUAIGAIRCore IdeaKey QuestionsKey TechnologiesTrainingInference A Tutorial on LLM Reasoning: Relevant methods behind ChatGPT o1 - UCL汪军教授Core Idea先导自回归…...
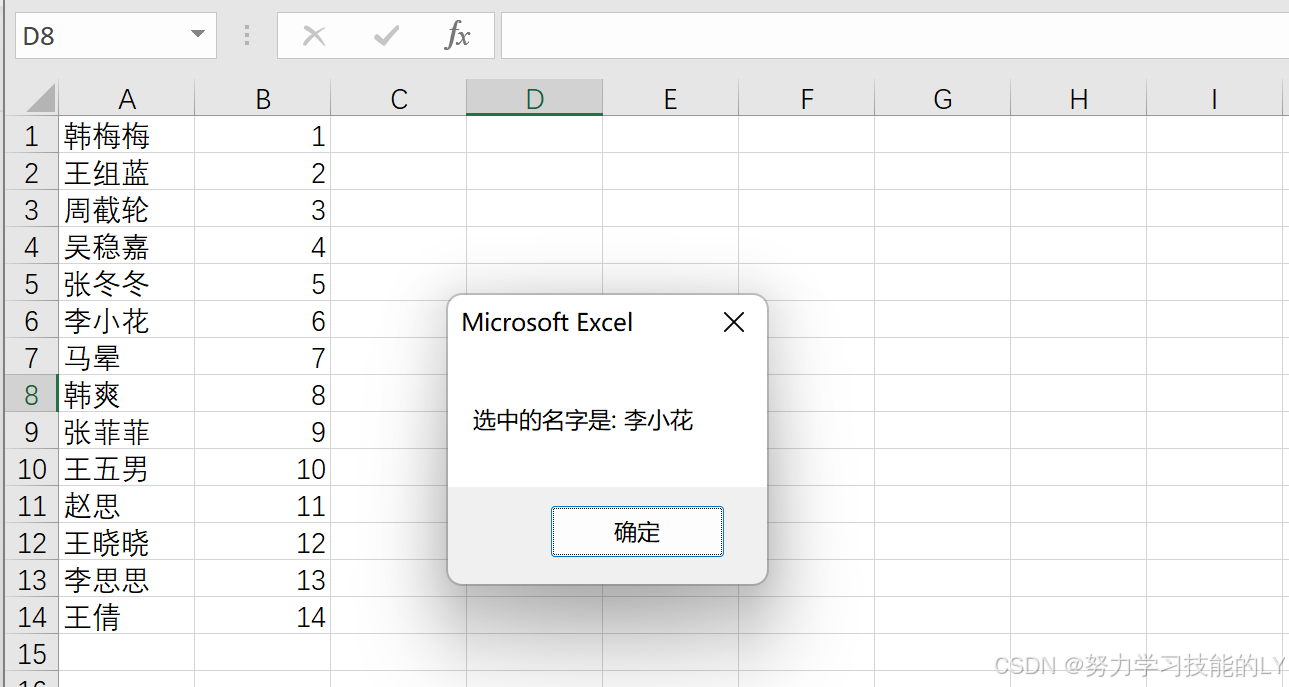
Excel:vba实现生成随机数
Sub 生成随机数字()Dim randomNumber As IntegerDim minValue As IntegerDim maxValue As Integer 设置随机数的范围(假入班级里面有43个学生,学号是从1→43)minValue 1maxValue 43 生成随机数(在1到43之间生成随机数)randomNumber Application.WorksheetFunctio…...

Python | Leetcode Python题解之第506题相对名次
题目: 题解: class Solution:desc ("Gold Medal", "Silver Medal", "Bronze Medal")def findRelativeRanks(self, score: List[int]) -> List[str]:ans [""] * len(score)arr sorted(enumerate(score), …...
)
安全见闻(6)
声明:学习视频来自b站up主 泷羽sec,如涉及侵权马上删除文章 感谢泷羽sec 团队的教学 视频地址:安全见闻(6)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 学无止境,开拓自己的眼界才能走的更远 本文主要讲解通讯协议涉及的安全问题。…...

Promise、async、await 、异步生成器的错误处理方案
1、Promise.all 的错误处理 Promise.all 方法接受一个 Promise 数组,并返回所有解析 Promise 的结果数组: const promise1 Promise.resolve("one"); const promise2 Promise.resolve("two");Promise.all([promise1, promise2]).…...

腾讯云:数智教育专场-学习笔记
15点13分2024年10月21日(短短5天的时间,自己的成长速度更加惊人)-开始进行“降本增效”学习模式,根据小米手环对于自己的行为模式分析(不断地寻找数据之间的关联性),每天高效记忆时间࿰…...

Ovis: 多模态大语言模型的结构化嵌入对齐
论文题目:Ovis: Structural Embedding Alignment for Multimodal Large Language Model 论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.20797 github地址:https://github.com/AIDC-AI/Ovis/?tabreadme-ov-file 今天,我将分享一项重要的研…...

python的Django的render_to_string函数和render函数模板的使用
一、render_to_string render_to_string 是 Django 框架中的一个便捷函数,用于将模板渲染为字符串。 render_to_string(template_name.html, context, requestNone, usingNone) template_name.html:要渲染的模板文件的名称。context:传递给…...
基于Python大数据的王者荣耀战队数据分析及可视化系统
作者:计算机学姐 开发技术:SpringBoot、SSM、Vue、MySQL、JSP、ElementUI、Python、小程序等,“文末源码”。 专栏推荐:前后端分离项目源码、SpringBoot项目源码、Vue项目源码、SSM项目源码、微信小程序源码 精品专栏:…...

【Linux学习】(3)Linux的基本指令操作
前言 配置Xshell登录远程服务器Linux的基本指令——man、cp、mv、alias&which、cat&more&less、head&tail、date、cal、find、grep、zip&tar、bc、unameLinux常用热键 一、配置Xshell登录远程服务器 以前我们登录使用指令: ssh 用户名你的公网…...

Mac 使用脚本批量导入 Apple 歌曲
最近呢,买了一个 iPad,虽然家里笔记本台式都有,显示器都是 2个,比较方便看代码(边打游戏边追剧)。 但是在床上拿笔记本始终还是不方便,手机在家看还是小了点,自从有 iPad 之后&…...

全桥PFC电路及MATLAB仿真
一、PFC电路原理概述 PFC全称“Power Factor Correction”(功率因数校正),PFC电路即能对功率因数进行校正,或者说是能提高功率因数的电路。是开关电源中很常见的电路。功率因数是用来描述电力系统中有功功率(实际使用…...
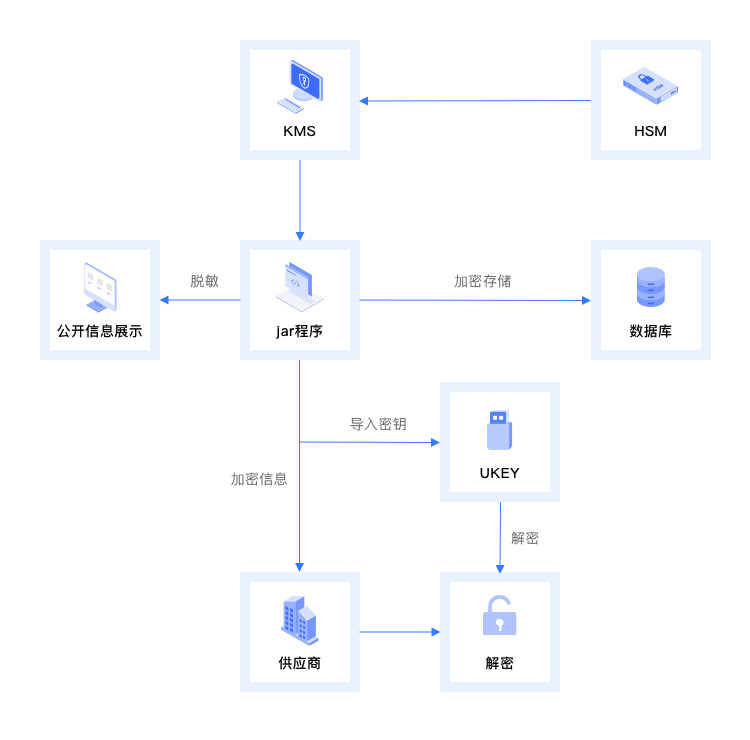
【安当产品应用案例100集】025-确保数据安全传输——基于KMS与HSM的定期分发加密解决方案
引言: 在当今快速发展的数字化时代,企业面临着前所未有的信息安全挑战。尤其是在需要向供应商定期分发敏感数据的情况下,如何保证这些数据在传输过程中的安全性变得至关重要。为此,我们推出了结合安当KMS密钥管理平台与HSM密码机…...

十 缺陷检测解决策略之三:频域+空域
十 缺陷检测解决策略之三:频域空域 read_image (Image, 矩形) * 中间低频,四周高频 fft_image (Image, ImageFFT) * 中间低频,四周高频 fft_generic (Image, ImageFFT1, to_freq, -1, sqrt, dc_center, complex) * 中间高频,四周低频 rft_ge…...

有望第一次走出慢牛
A股已走完30多年历程。 大约每十年,会经历一轮牛熊周期。特点是每一轮周期,大约九成的时间都是熊市主导。就是我们常说的 快牛慢熊。 这一次,会不会重复历史? 历史不会简单重复。已经感受到了盘面的变化。 有人说,股市爆涨爆…...
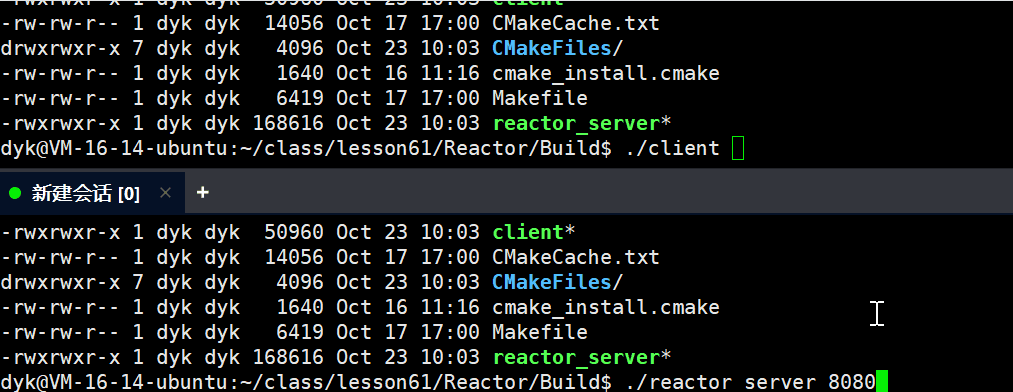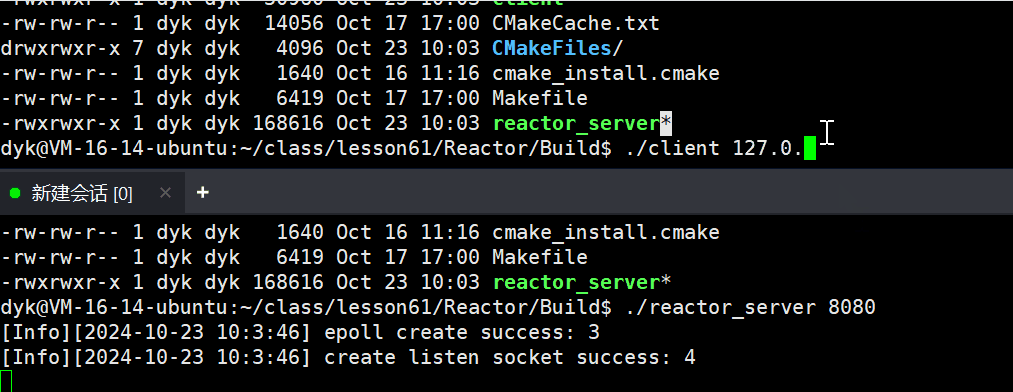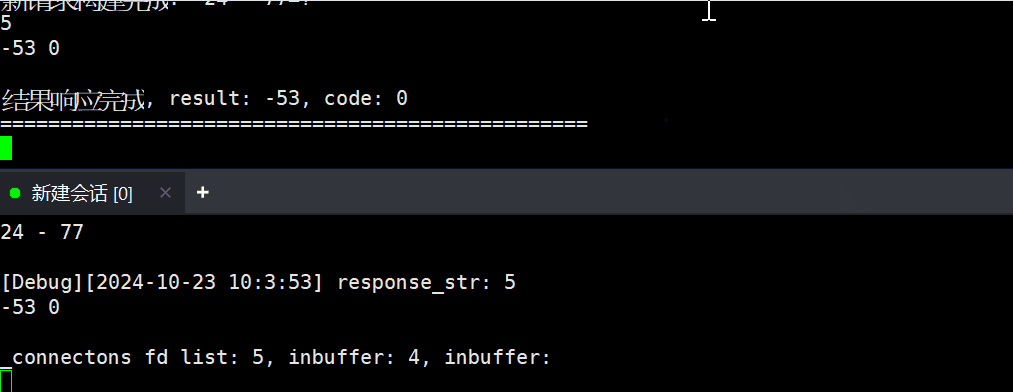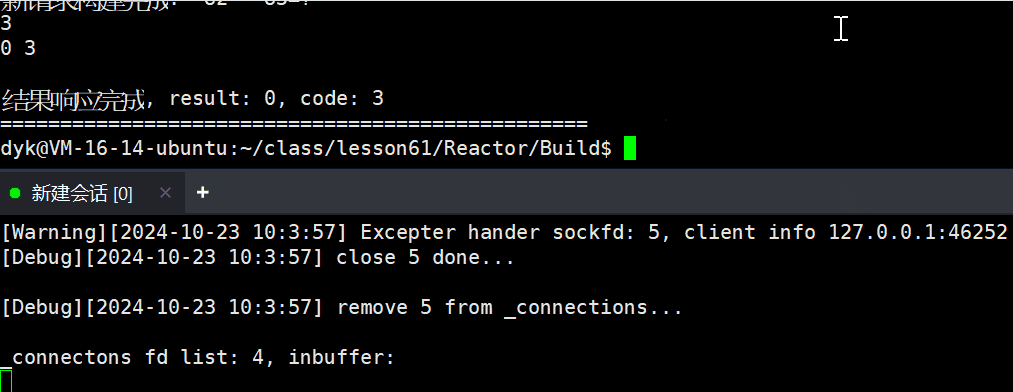
计算机网络(十二) —— 高级IO
#1024程序员节 | 征文# 目录 一,预备 1.1 重新理解IO 1.2 五种IO模型 1.3 非阻塞IO 二,select 2.1 关于select 2.2 select接口参数解释 2.3 timeval结构体和fd_set类型 2.4 socket就绪条件 2.5 select基本工作流程 2.6 简单select的服务器代…...

vscode里如何用git
打开vs终端执行如下: 1 初始化 Git 仓库(如果尚未初始化) git init 2 添加文件到 Git 仓库 git add . 3 使用 git commit 命令来提交你的更改。确保在提交时加上一个有用的消息。 git commit -m "备注信息" 4 …...

应用升级/灾备测试时使用guarantee 闪回点迅速回退
1.场景 应用要升级,当升级失败时,数据库回退到升级前. 要测试系统,测试完成后,数据库要回退到测试前。 相对于RMAN恢复需要很长时间, 数据库闪回只需要几分钟。 2.技术实现 数据库设置 2个db_recovery参数 创建guarantee闪回点,不需要开启数据库闪回。…...

Linux相关概念和易错知识点(42)(TCP的连接管理、可靠性、面临复杂网络的处理)
目录 1.TCP的连接管理机制(1)三次握手①握手过程②对握手过程的理解 (2)四次挥手(3)握手和挥手的触发(4)状态切换①挥手过程中状态的切换②握手过程中状态的切换 2.TCP的可靠性&…...

Linux简单的操作
ls ls 查看当前目录 ll 查看详细内容 ls -a 查看所有的内容 ls --help 查看方法文档 pwd pwd 查看当前路径 cd cd 转路径 cd .. 转上一级路径 cd 名 转换路径 …...
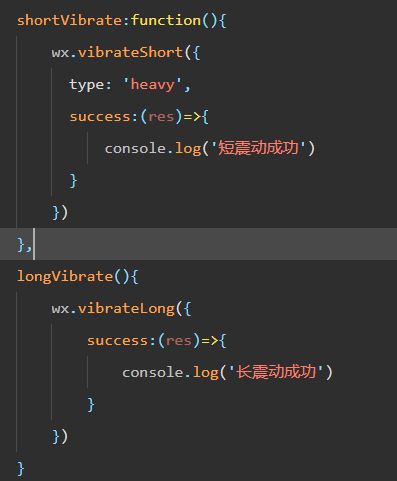
微信小程序 - 手机震动
一、界面 <button type"primary" bindtap"shortVibrate">短震动</button> <button type"primary" bindtap"longVibrate">长震动</button> 二、js逻辑代码 注:文档 https://developers.weixin.qq…...

基于Docker Compose部署Java微服务项目
一. 创建根项目 根项目(父项目)主要用于依赖管理 一些需要注意的点: 打包方式需要为 pom<modules>里需要注册子模块不要引入maven的打包插件,否则打包时会出问题 <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8…...
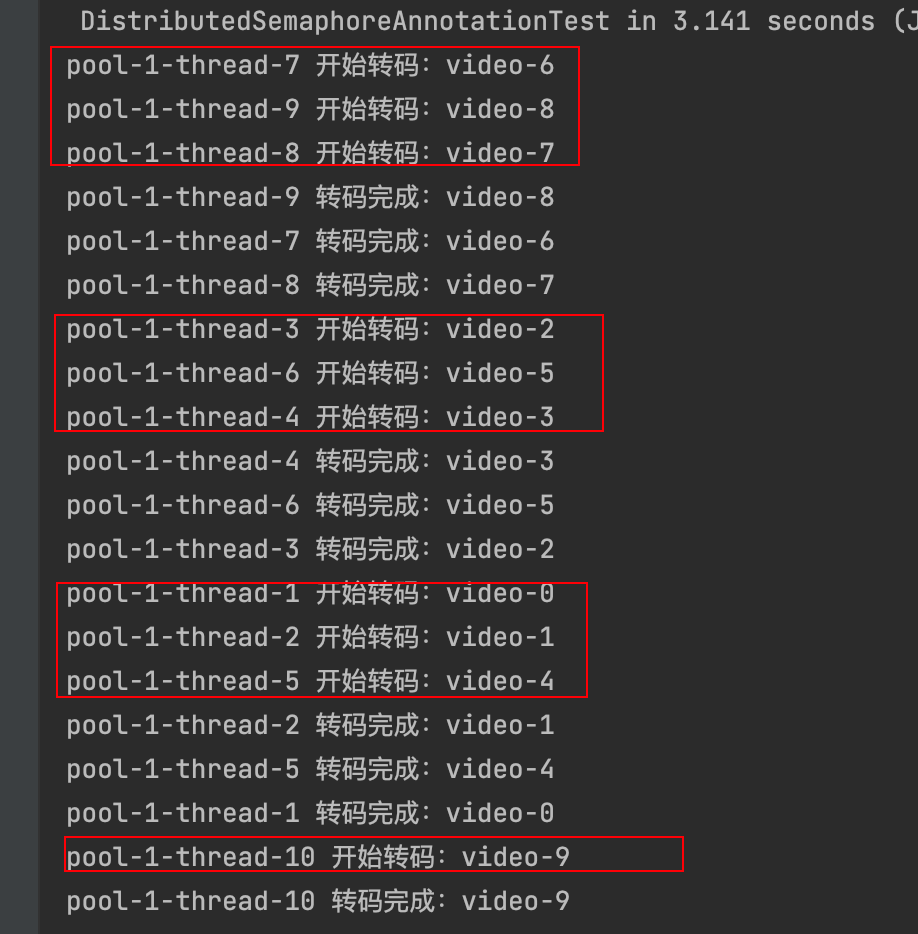
令牌桶 滑动窗口->限流 分布式信号量->限并发的原理 lua脚本分析介绍
文章目录 前言限流限制并发的实际理解限流令牌桶代码实现结果分析令牌桶lua的模拟实现原理总结: 滑动窗口代码实现结果分析lua脚本原理解析 限并发分布式信号量代码实现结果分析lua脚本实现原理 双注解去实现限流 并发结果分析: 实际业务去理解体会统一注…...
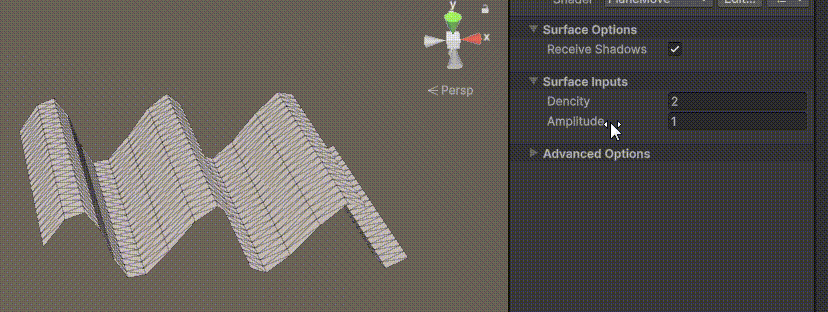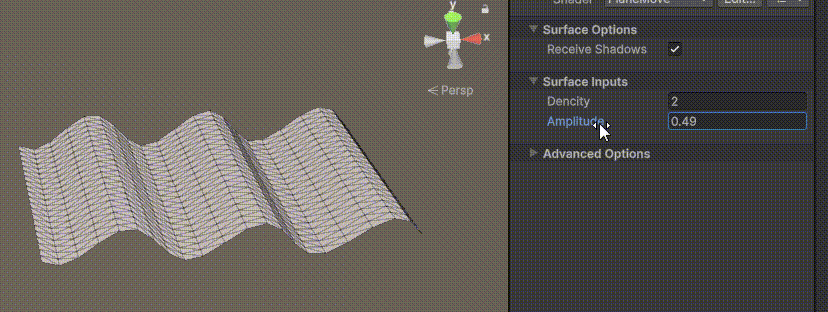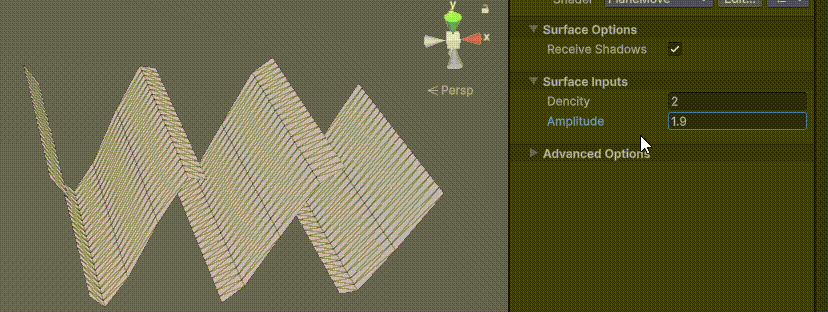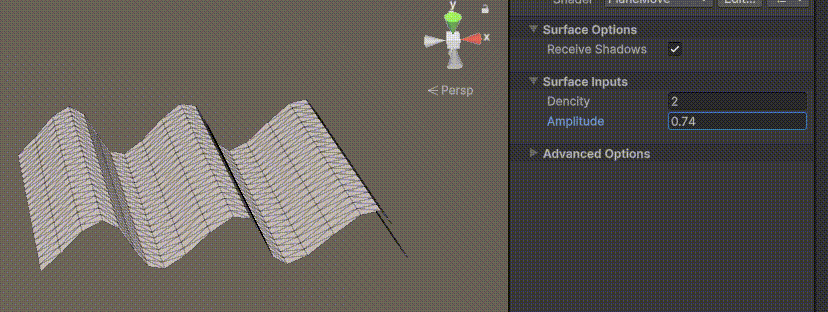
Unity | AmplifyShaderEditor插件基础(第七集:平面波动shader)
目录 一、👋🏻前言 二、😈sinx波动的基本原理 三、😈波动起来 1.sinx节点介绍 2.vertexPosition 3.集成Vector3 a.节点Append b.连起来 4.波动起来 a.波动的原理 b.时间节点 c.sinx的处理 四、🌊波动优化…...

中医有效性探讨
文章目录 西医是如何发展到以生物化学为药理基础的现代医学?传统医学奠基期(远古 - 17 世纪)近代医学转型期(17 世纪 - 19 世纪末)现代医学成熟期(20世纪至今) 中医的源远流长和一脉相承远古至…...

LangChain知识库管理后端接口:数据库操作详解—— 构建本地知识库系统的基础《二》
这段 Python 代码是一个完整的 知识库数据库操作模块,用于对本地知识库系统中的知识库进行增删改查(CRUD)操作。它基于 SQLAlchemy ORM 框架 和一个自定义的装饰器 with_session 实现数据库会话管理。 📘 一、整体功能概述 该模块…...
