前端测试框架 jasmine 的使用
最近的项目在使用AngulaJs,对JS代码的测试问题就摆在了面前。通过对比我们选择了 Karma + jasmine ,使用 Jasmine做单元测试 ,Karma 自动化完成,当然了如果使用 Karma + jasmine 前提是必须安装 Nodejs。
安装好 Nodejs ,使用 npm 安装好必要的包,写了一个测试用例,测试通过,很好很强大。 没有 Nodejs 环境可以使用 Jasmine 做单元测试吗?当然可以,我们可以到 官网下一个示例看一看,比较简单。今天先讲一下如果直接使用
jasmine 做单元测试
简单示例
jasmine 示例下载地址 https://github.com/jasmine/jasmine/releases 选择最新版本下载下来示例代码结构如图

lib 文件夹下面: boot.js 启动文件 ,
console.js 输出辅助文件,
jasmine-html.js 测试页面 Dom 操作文件,
jasmine.js jasmine核心文件
spec 文件夹 : PlayerSpec.js 单元测试文件
SpecHelper.js jasmine 断言扩展文件(自定义 Matcher)
src 文件夹 ,下面是被测试的 js 文件。 SpecRunner.html 为测试结果页面。
SpecRunner.html 代码,注意js文件加载顺序
+ View Code
我们直接运行 SpecRunner.html 测试结果如下:

5个 specs,0个失败,全部通过。在 PlayerSpec.js 里添加一个Suite,看看报错是什么样的。
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
|

哈哈,测试未通过,看到没,这里显示了详细的错误信息。
jasmine 语法详解
首先了解几个概念: Suite 指一个测试集, describe方法标志着一个测试集。
Spec 表示测试用例,jasmine中用方法it来开始 specs。
一个 Suite可以包含多个 Spec,一个 spec 可以包含多个 expections 断言
示例1
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
示例2 包含多个断言
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
示例3 常用语法,describe嵌套
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 |
|
示例4 beforeEach,afterEach,beforeAll和afterAll函数
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
|
示例5 this关键字共享变量,嵌套describe
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 |
|
示例6 Pending 待定规则
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
|
示例7 Spies 对象监控
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 |
|
在上面这段代码里 ,要注意 Spies :and.callThrough 的用法 注意代码 spyOn(foo, 'getBar').and.callThrough(); 跟 spyOn(foo, 'getBar'); 的区别 spyOn(foo, 'getBar').and.callThrough() 会调用实例方法
产生实际的影响,而 spyOn(foo, 'getBar'); 只是调用了 Jasmine 保存的这个函数的 存根,不会影响到实际的值 ,如果没看明白请仔细看代码上我添加的注释。
示例8 其他属性
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 |
|
示例 9 Jasmine 时钟
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 |
|
示例 10 异步支持
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 |
|
示例11 自定义matcher
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 |
|
看完上面的示例应该在项目中应用没有什么问题了。
相关文章:

前端测试框架 jasmine 的使用
最近的项目在使用AngulaJs,对JS代码的测试问题就摆在了面前。通过对比我们选择了 Karma jasmine ,使用 Jasmine做单元测试 ,Karma 自动化完成,当然了如果使用 Karma jasmine 前提是必须安装 Nodejs。 安装好 Nodejs ,使用 npm 安装好必要…...

Qwen2-VL视觉大模型微调实战:LaTex公式OCR识别任务(完整代码)
《SwanLab机器学习实战教程》是一个主打「开箱即用」的AI训练系列教程,我们致力于提供完善的数据集、源代码、实验记录以及环境安装方式,手把手帮助你跑起训练,解决问题。 Qwen2-VL是通义千问团队最近开源的大语言模型,由阿里云通…...

「Mac玩转仓颉内测版42」小学奥数篇5 - 圆和矩形的面积计算
本篇将通过 Python 和 Cangjie 双语解决简单的几何问题:计算圆的面积和矩形的面积。通过这道题,学生将掌握如何使用公式解决几何问题,并学会用编程实现数学公式。 关键词 小学奥数Python Cangjie几何计算 一、题目描述 编写一个程序&#…...

Groom Blender to UE5
Groom Blender to UE5 - Character & Animation - Epic Developer Community Forums Hello, 你好, While exporting my “groom” from blender to UE5, I notice that the curves have a minimal resolution in Unreal. However I would like to get the same …...

开发一套ERP 第十弹 图片作为配置文件,本地读取图片,定时更新图片类型
echo Hello World在同一数据库中在建一个图床数据表,产品一,一对应,图片命名 最优的方案,使用 rust 在构建一个 http server 用于管理非数据库资源,也可以将来对接不同的图床,部署方便 考虑到数据库资源和图片资源,都可以被远程访问这种方法最佳...

第七十六条:努力保持故障的原子性
当对象抛出异常之后,通常我们期望这个对象仍然保持在一种定义良好的可用状态之中,即使失败是发生在执行某个操作的过程中间。对于受检的异常而言,这尤为重要,因为调用者期望能从这种异常中进行恢复。一般而言,失败的方…...

Word分栏后出现空白页解决方法
Word分栏后出现空白页解决方法 只需要在后面的空白页设置相同的页面布局(分栏格式),然后按Ctrl backspace即可删除该空白页。 参考文章:Word分栏出现空白怎么解决。...

基于HTML和CSS的校园网页设计与实现
摘要 随着计算机、互联网与通信技术的进步,Internet在人们的学习、工作和生活中的地位也变得越来越高,校园网站已经成为学校与学生,学生与学生之间交流沟通的重要平台,对同学了解学校内发生的各种事情起到了重要的作用。学校网站…...

【算法day7】字符串:反转与替换
题目引用 反转字符串反转字符串II替换数字 1.反转字符串 编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。输入字符串以字符数组 s 的形式给出。 不要给另外的数组分配额外的空间,你必须原地修改输入数组、使用 O(1) 的额外空间解决这一问题。 示例 1&am…...

分布式存储厂商
分布式存储 以下是对分布式存储厂商XSKY星辰天合、IOMesh(SmartX)、SmartX的深度对比: 1. XSKY星辰天合 产品与服务:XSKY星辰天合提供统一存储平台,支持块、文件和对象存储服务。已为近2400家大型政企机构实施部署&…...

合合信息扫描全能王线下体验活动:科技与人文的完美交融
文章目录 前言签到欢迎仪式产品体验智能高清滤镜去除透字效果照片高清修复 破冰行动会议感受 前言 作为合合信息旗下扫描全能王的忠实粉丝,上周,我很荣幸参与了扫描全能王“扫出你的能量buff”快闪活动及技术交流会。这次活动的不仅让我对这款强大的文档…...

单链表在Go语言中的实现与操作
简介 单链表是一种基本的线性数据结构,由节点组成,每个节点存储数据和指向下一个节点的指针。今天,我们将深入探讨如何在Go语言中实现和操作单链表。 单链表的优缺点 优点: 动态内存分配,灵活性高。插入和删除节点操…...

网关整合sentinel无法读取nacos配置问题分析
sentinel无法读取nacos配置问题分析 1.spring-cloud-gateway整合sentinel2.问题现象3.原因猜测4.源码分析4. 结语 最近公司需要上线一个集约项目,虽然为内网项目,但曾经有过内网被攻破,导致内部系统被攻击的案例,且集约系统同时在…...

简化XPath表达式的方法与实践
XPath表达式用于在XML或HTML文档中定位元素。有时候,XPath表达式可能会变得非常冗长和复杂,这不仅难以阅读和维护,而且也可能影响性能。因此,学会如何简化XPath表达式是非常重要的。本文将介绍几种简化XPath表达式的方法ÿ…...

【文件下载】接口传递文件成功和失败时,前端的处理方式
问题 使用bold类型从后端接口获取文件流,获取成功的时候通过a标签下载;失败的时候,后端返回的是json,这个时候就无法向用户展示后端返回的错误提示信息。 思路 根据返回类型是否为 application/json 区分是否返回成功ÿ…...

html+css网页设计马林旅行社移动端4个页面
htmlcss网页设计马林旅行社移动端4个页面 网页作品代码简单,可使用任意HTML辑软件(如:Dreamweaver、HBuilder、Vscode 、Sublime 、Webstorm、Text 、Notepad 等任意html编辑软件进行运行及修改编辑等操作)。 获取源码 1&#…...

视频 的 音频通道提取 以及 视频转URL 的在线工具!
视频 的 音频通道提取 以及 视频转URL 的在线工具! 工具地址: https://www.lingyuzhao.top/toolsPage/VideoTo.html 它提供了便捷的方法来处理视频文件,具体来说是帮助用户从视频中提取音频轨道,并将视频转换为可以通过网络访问的URL链接。无…...

容易被遗忘的测试用例
网络服务器启动了吗?应用程序服务器启动了吗?数据库上线了吗?测试数据是否预先加载到数据库中?每当我们准备开始测试应用程序时,一切都应该已经准备妥当。 然而,当测试开始后,我们可能会漏掉一些…...
)
uni-app写的微信小程序如何实现账号密码登录后获取token,并且每天的第一次登录后都会直接获取参数而不是耀重新登录(2)
接uni-app写的微信小程序如何实现账号密码登录后获取token,并且每天的第一次登录后都会直接获取参数而不是耀重新登录(1), 在main.js中 import App from ./App// #ifndef VUE3 import Vue from vue import ./uni.promisify.adap…...

统计中间件稳定性指标
目前订单业务域涉及中间件:MySQL、Redis、TiDB、MQ、ES。(遗漏项请补充) 一、RDS 资源使用率 实例ID实例名称规格maxCPUavgCPUmaxDISKmaxIOPSavgIOPS活跃会话maxTPSavgTPSmaxQPSavgQPS实例风险 慢查询 慢查询会消耗大量的系统资源&#x…...

大语言模型如何处理长文本?常用文本分割技术详解
为什么需要文本分割? 引言:为什么需要文本分割?一、基础文本分割方法1. 按段落分割(Paragraph Splitting)2. 按句子分割(Sentence Splitting)二、高级文本分割策略3. 重叠分割(Sliding Window)4. 递归分割(Recursive Splitting)三、生产级工具推荐5. 使用LangChain的…...

高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景
高危文件识别的常用算法:原理、应用与企业场景 高危文件识别旨在检测可能导致安全威胁的文件,如包含恶意代码、敏感数据或欺诈内容的文档,在企业协同办公环境中(如Teams、Google Workspace)尤为重要。结合大模型技术&…...

scikit-learn机器学习
# 同时添加如下代码, 这样每次环境(kernel)启动的时候只要运行下方代码即可: # Also add the following code, # so that every time the environment (kernel) starts, # just run the following code: import sys sys.path.append(/home/aistudio/external-libraries)机…...

深度学习之模型压缩三驾马车:模型剪枝、模型量化、知识蒸馏
一、引言 在深度学习中,我们训练出的神经网络往往非常庞大(比如像 ResNet、YOLOv8、Vision Transformer),虽然精度很高,但“太重”了,运行起来很慢,占用内存大,不适合部署到手机、摄…...

算术操作符与类型转换:从基础到精通
目录 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 算术操作符超级详解 算术操作符:、-、*、/、% 赋值操作符:和复合赋值 单⽬操作符:、--、、- 前言:从基础到实践——探索运算符与类型转换的奥秘 在先前的文…...

React从基础入门到高级实战:React 实战项目 - 项目五:微前端与模块化架构
React 实战项目:微前端与模块化架构 欢迎来到 React 开发教程专栏 的第 30 篇!在前 29 篇文章中,我们从 React 的基础概念逐步深入到高级技巧,涵盖了组件设计、状态管理、路由配置、性能优化和企业级应用等核心内容。这一次&…...

大数据治理的常见方式
大数据治理的常见方式 大数据治理是确保数据质量、安全性和可用性的系统性方法,以下是几种常见的治理方式: 1. 数据质量管理 核心方法: 数据校验:建立数据校验规则(格式、范围、一致性等)数据清洗&…...

跨平台商品数据接口的标准化与规范化发展路径:淘宝京东拼多多的最新实践
在电商行业蓬勃发展的当下,多平台运营已成为众多商家的必然选择。然而,不同电商平台在商品数据接口方面存在差异,导致商家在跨平台运营时面临诸多挑战,如数据对接困难、运营效率低下、用户体验不一致等。跨平台商品数据接口的标准…...
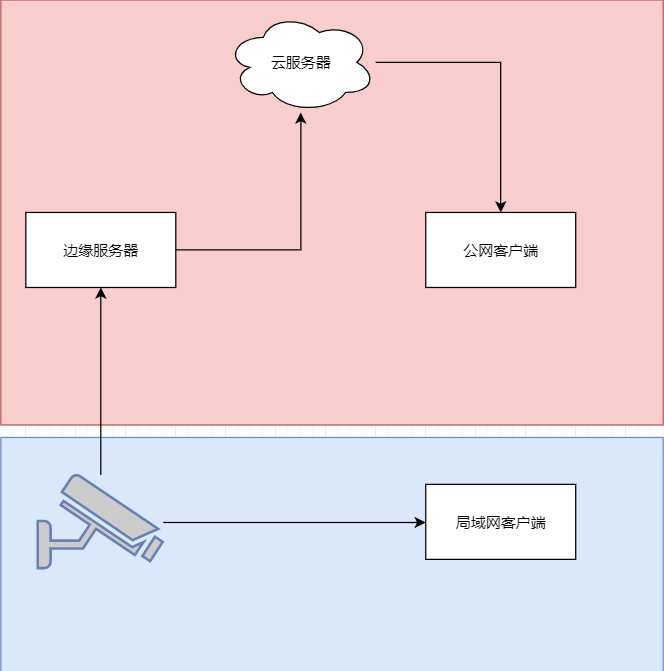
java 局域网 rtsp 取流 WebSocket 推送到前端显示 低延迟
众所周知 摄像头取流推流显示前端延迟大 传统方法是服务器取摄像头的rtsp流 然后客户端连服务器 中转多了,延迟一定不小。 假设相机没有专网 公网 1相机自带推流 直接推送到云服务器 然后客户端拉去 2相机只有rtsp ,边缘服务器拉流推送到云服务器 …...

如何优雅地绕过限制调用海外AI-API?反向代理与API中转技术详解
阅读时长 | 8分钟 适用读者 | 需要跨境调用OpenAI等AI服务的开发者/企业 一、问题背景:为什么需要代理? 最近在技术社区看到这样的求助: "公司服务器在国内,但业务需要调用OpenAI接口,直接访…...
