NS3学习——tcpVegas算法代码详解(1)
目录
一、源码
二、详解
1.定义日志和命名空间
2.注册Typeld类:TcpVegas和GetTypeId方法的实现
3.构造函数和析构函数
4.TcpVegas类中成员函数
(1) Fork函数
(2) PktsAcked函数
(3) EnableVegas函数
(4) DisableVegas函数
一、源码
/* -*- Mode:C++; c-file-style:"gnu"; indent-tabs-mode:nil; -*- */
/** Copyright (c) 2016 ResiliNets, ITTC, University of Kansas** This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as* published by the Free Software Foundation;** This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the* GNU General Public License for more details.** You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software* Foundation, Inc., 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA** Author: Truc Anh N. Nguyen <annguyen@ittc.ku.edu>** James P.G. Sterbenz <jpgs@ittc.ku.edu>, director* ResiliNets Research Group http://wiki.ittc.ku.edu/resilinets* Information and Telecommunication Technology Center (ITTC)* and Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science* The University of Kansas Lawrence, KS USA.*/#include "tcp-vegas.h"
#include "tcp-socket-state.h"#include "ns3/log.h"namespace ns3 {NS_LOG_COMPONENT_DEFINE ("TcpVegas");
NS_OBJECT_ENSURE_REGISTERED (TcpVegas);TypeId
TcpVegas::GetTypeId (void)
{static TypeId tid = TypeId ("ns3::TcpVegas").SetParent<TcpNewReno> ().AddConstructor<TcpVegas> ().SetGroupName ("Internet").AddAttribute ("Alpha", "Lower bound of packets in network",UintegerValue (2),MakeUintegerAccessor (&TcpVegas::m_alpha),MakeUintegerChecker<uint32_t> ()).AddAttribute ("Beta", "Upper bound of packets in network",UintegerValue (4),MakeUintegerAccessor (&TcpVegas::m_beta),MakeUintegerChecker<uint32_t> ()).AddAttribute ("Gamma", "Limit on increase",UintegerValue (1),MakeUintegerAccessor (&TcpVegas::m_gamma),MakeUintegerChecker<uint32_t> ());return tid;
}TcpVegas::TcpVegas (void): TcpNewReno (),m_alpha (2),m_beta (4),m_gamma (1),m_baseRtt (Time::Max ()),m_minRtt (Time::Max ()),m_cntRtt (0),m_doingVegasNow (true),m_begSndNxt (0)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
}TcpVegas::TcpVegas (const TcpVegas& sock): TcpNewReno (sock),m_alpha (sock.m_alpha),m_beta (sock.m_beta),m_gamma (sock.m_gamma),m_baseRtt (sock.m_baseRtt),m_minRtt (sock.m_minRtt),m_cntRtt (sock.m_cntRtt),m_doingVegasNow (true),m_begSndNxt (0)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
}TcpVegas::~TcpVegas (void)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
}Ptr<TcpCongestionOps>
TcpVegas::Fork (void)
{return CopyObject<TcpVegas> (this);
}void
TcpVegas::PktsAcked (Ptr<TcpSocketState> tcb, uint32_t segmentsAcked,const Time& rtt)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << tcb << segmentsAcked << rtt);if (rtt.IsZero ()){return;}m_minRtt = std::min (m_minRtt, rtt);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated m_minRtt = " << m_minRtt);m_baseRtt = std::min (m_baseRtt, rtt);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated m_baseRtt = " << m_baseRtt);// Update RTT counterm_cntRtt++;NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated m_cntRtt = " << m_cntRtt);
}void
TcpVegas::EnableVegas (Ptr<TcpSocketState> tcb)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << tcb);m_doingVegasNow = true;m_begSndNxt = tcb->m_nextTxSequence;m_cntRtt = 0;m_minRtt = Time::Max ();
}void
TcpVegas::DisableVegas ()
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);m_doingVegasNow = false;
}void
TcpVegas::CongestionStateSet (Ptr<TcpSocketState> tcb,const TcpSocketState::TcpCongState_t newState)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << tcb << newState);if (newState == TcpSocketState::CA_OPEN){EnableVegas (tcb);}else{DisableVegas ();}
}void
TcpVegas::IncreaseWindow (Ptr<TcpSocketState> tcb, uint32_t segmentsAcked)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << tcb << segmentsAcked);if (!m_doingVegasNow){// If Vegas is not on, we follow NewReno algorithmNS_LOG_LOGIC ("Vegas is not turned on, we follow NewReno algorithm.");TcpNewReno::IncreaseWindow (tcb, segmentsAcked);return;}if (tcb->m_lastAckedSeq >= m_begSndNxt){ // A Vegas cycle has finished, we do Vegas cwnd adjustment every RTT.NS_LOG_LOGIC ("A Vegas cycle has finished, we adjust cwnd once per RTT.");// Save the current right edge for next Vegas cyclem_begSndNxt = tcb->m_nextTxSequence;/** We perform Vegas calculations only if we got enough RTT samples to* insure that at least 1 of those samples wasn't from a delayed ACK.*/if (m_cntRtt <= 2){ // We do not have enough RTT samples, so we should behave like RenoNS_LOG_LOGIC ("We do not have enough RTT samples to do Vegas, so we behave like NewReno.");TcpNewReno::IncreaseWindow (tcb, segmentsAcked);}else{NS_LOG_LOGIC ("We have enough RTT samples to perform Vegas calculations");/** We have enough RTT samples to perform Vegas algorithm.* Now we need to determine if cwnd should be increased or decreased* based on the calculated difference between the expected rate and actual sending* rate and the predefined thresholds (alpha, beta, and gamma).*/uint32_t diff;uint32_t targetCwnd;uint32_t segCwnd = tcb->GetCwndInSegments ();/** Calculate the cwnd we should have. baseRtt is the minimum RTT* per-connection, minRtt is the minimum RTT in this window** little trick:* desidered throughput is currentCwnd * baseRtt* target cwnd is throughput / minRtt*/double tmp = m_baseRtt.GetSeconds () / m_minRtt.GetSeconds ();targetCwnd = static_cast<uint32_t> (segCwnd * tmp);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Calculated targetCwnd = " << targetCwnd);NS_ASSERT (segCwnd >= targetCwnd); // implies baseRtt <= minRtt/** Calculate the difference between the expected cWnd and* the actual cWnd*/diff = segCwnd - targetCwnd;NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Calculated diff = " << diff);if (diff > m_gamma && (tcb->m_cWnd < tcb->m_ssThresh)){/** We are going too fast. We need to slow down and change from* slow-start to linear increase/decrease mode by setting cwnd* to target cwnd. We add 1 because of the integer truncation.*/NS_LOG_LOGIC ("We are going too fast. We need to slow down and ""change to linear increase/decrease mode.");segCwnd = std::min (segCwnd, targetCwnd + 1);tcb->m_cWnd = segCwnd * tcb->m_segmentSize;tcb->m_ssThresh = GetSsThresh (tcb, 0);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated cwnd = " << tcb->m_cWnd <<" ssthresh=" << tcb->m_ssThresh);}else if (tcb->m_cWnd < tcb->m_ssThresh){ // Slow start modeNS_LOG_LOGIC ("We are in slow start and diff < m_gamma, so we ""follow NewReno slow start");TcpNewReno::SlowStart (tcb, segmentsAcked);}else{ // Linear increase/decrease modeNS_LOG_LOGIC ("We are in linear increase/decrease mode");if (diff > m_beta){// We are going too fast, so we slow downNS_LOG_LOGIC ("We are going too fast, so we slow down by decrementing cwnd");segCwnd--;tcb->m_cWnd = segCwnd * tcb->m_segmentSize;tcb->m_ssThresh = GetSsThresh (tcb, 0);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated cwnd = " << tcb->m_cWnd <<" ssthresh=" << tcb->m_ssThresh);}else if (diff < m_alpha){// We are going too slow (having too little data in the network),// so we speed up.NS_LOG_LOGIC ("We are going too slow, so we speed up by incrementing cwnd");segCwnd++;tcb->m_cWnd = segCwnd * tcb->m_segmentSize;NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated cwnd = " << tcb->m_cWnd <<" ssthresh=" << tcb->m_ssThresh);}else{// We are going at the right speedNS_LOG_LOGIC ("We are sending at the right speed");}}tcb->m_ssThresh = std::max (tcb->m_ssThresh, 3 * tcb->m_cWnd / 4);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated ssThresh = " << tcb->m_ssThresh);}// Reset cntRtt & minRtt every RTTm_cntRtt = 0;m_minRtt = Time::Max ();}else if (tcb->m_cWnd < tcb->m_ssThresh){TcpNewReno::SlowStart (tcb, segmentsAcked);}
}std::string
TcpVegas::GetName () const
{return "TcpVegas";
}uint32_t
TcpVegas::GetSsThresh (Ptr<const TcpSocketState> tcb,uint32_t bytesInFlight)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << tcb << bytesInFlight);return std::max (std::min (tcb->m_ssThresh.Get (), tcb->m_cWnd.Get () - tcb->m_segmentSize), 2 * tcb->m_segmentSize);
}} // namespace ns3二、详解
1.定义日志和命名空间
#include "tcp-vegas.h" //包含TCP Vegas算法的头文件。
#include "tcp-socket-state.h" //包含TCP套接字状态的头文件#include "ns3/log.h" //包含NS-3日志功能的头文件namespace ns3 {NS_LOG_COMPONENT_DEFINE ("TcpVegas"); //定义了一个日志组件,用于记录日志信息。
NS_OBJECT_ENSURE_REGISTERED (TcpVegas);2.注册Typeld类:TcpVegas和GetTypeId方法的实现
TypeId
TcpVegas::GetTypeId (void)
{static TypeId tid = TypeId ("ns3::TcpVegas") //设置类的名称为TcpVegas 位于ns3命名空间下.SetParent<TcpNewReno> () //设置TcpVegas的父类为TcpNewReno.AddConstructor<TcpVegas> () //添加TcpVegas类的构造函数 创建相关对象.SetGroupName ("Internet") //将TcpVegas分类到"Internet"组下.AddAttribute ("Alpha", "Lower bound of packets in network",UintegerValue (2),MakeUintegerAccessor (&TcpVegas::m_alpha),MakeUintegerChecker<uint32_t> ()).AddAttribute ("Beta", "Upper bound of packets in network",UintegerValue (4),MakeUintegerAccessor (&TcpVegas::m_beta),MakeUintegerChecker<uint32_t> ()).AddAttribute ("Gamma", "Limit on increase",UintegerValue (1),MakeUintegerAccessor (&TcpVegas::m_gamma),MakeUintegerChecker<uint32_t> ());return tid; //返回TcpVegas的TypeId对象
}AddAttribute方法用于添加类的属性,这些属性可以在NS-3的配置系统中设置和获取。
- "Alpha"、"Beta"和"Gamma"是TcpVegas算法的三个参数,它们分别控制算法的行为:
- "Alpha":网络中数据包的下界,初始值为2。
- "Beta":网络中数据包的上界,初始值为4。
- "Gamma":增加的极限,初始值为1。
- UintegerValue:设置属性的初始值。
- MakeUintegerAccessor:创建一个访问器,用于访问和修改属性值。
- MakeUintegerChecker<uint32_t>():创建一个检查器,确保属性值是有效的无符号整数。
该段代码在NS-3中注册TcpVegas类,并设置其属性和行为,使得TcpVegas可以在NS-3的模拟中被创建和配置。
3.构造函数和析构函数
TcpVegas::TcpVegas (void) //默认构造函数: TcpNewReno (), //TcpVegas通过调用其父类TcpNewReno的默认构造函数来进行初始化m_alpha (2),m_beta (4), m_gamma (1), m_baseRtt (Time::Max ()),m_minRtt (Time::Max ()),m_cntRtt (0),m_doingVegasNow (true),m_begSndNxt (0)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this); //日志记录构造函数的调用,this指向当前对象的指针
}TcpVegas::TcpVegas (const TcpVegas& sock) //复制构造函数: TcpNewReno (sock),m_alpha (sock.m_alpha),m_beta (sock.m_beta),m_gamma (sock.m_gamma),m_baseRtt (sock.m_baseRtt),m_minRtt (sock.m_minRtt),m_cntRtt (sock.m_cntRtt),m_doingVegasNow (true),m_begSndNxt (0)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
}TcpVegas::~TcpVegas (void) //析构函数
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);
}默认构造函数:
m_alpha (2),m_beta (4),m_gamma (1):这些行初始化TcpVegas算法的参数alpha、beta和gamma,分别设置为2、4和1。m_baseRtt (Time::Max ()),m_minRtt (Time::Max ()):将基础往返时间(baseRtt)和最小往返时间(minRtt)初始化为最大时间值,表示它们尚未被设置。m_cntRtt (0):初始化往返时间计数器(cntRtt)为0。即用于计数自连接建立以来观测到的RTT样本数量。m_doingVegasNow (true):初始化标志doingVegasNow为true,表示Vegas算法默认是启用的。m_begSndNxt (0):初始化发送下一个序列号(begSndNxt)为0。- 日志系统记录构造函数的调用,
this指向当前对象的指针。
复制构造函数:用于创建一个与另一个TcpVegas对象sock相同的新对象。
: TcpNewReno (sock):表明TcpVegas复制构造函数首先调用其父类TcpNewReno的复制构造函数来复制父类成员。- 接下来,复制
sock对象中的alpha、beta、gamma、baseRtt、minRtt和cntRtt成员变量的值到新对象。 m_doingVegasNow (true)和m_begSndNxt (0):与默认构造函数类似,初始化doingVegasNow为true和begSndNxt为0。- const TcpVegas& sock:参数
sock是TcpVegas类型的对象引用,它指向一个已经存在的对象
4.TcpVegas类中成员函数
(1) Fork函数
Ptr<TcpCongestionOps>
TcpVegas::Fork (void)
{return CopyObject<TcpVegas> (this);
}
Fork函数用于创建当前TcpVegas对象的一个副本,并返回这个副本的智能指针;Ptr<TcpCongestionOps>是一个智能指针,指向TcpCongestionOps类型的对象。Ptr是NS-3中用于管理对象生命周期的智能指针模板类,而TcpCongestionOps是一个抽象基类,代表TCP拥塞控制操作。CopyObject<TcpVegas> (this):这是NS-3中用于复制对象的模板函数,它创建了当前对象的一个副本,并返回一个指向新对象的智能指针。这里的this指针指向当前的TcpVegas对象。
(2) PktsAcked函数
void
TcpVegas::PktsAcked (Ptr<TcpSocketState> tcb, uint32_t segmentsAcked,const Time& rtt)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << tcb << segmentsAcked << rtt);if (rtt.IsZero ()){return;}m_minRtt = std::min (m_minRtt, rtt);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated m_minRtt = " << m_minRtt);m_baseRtt = std::min (m_baseRtt, rtt);NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated m_baseRtt = " << m_baseRtt);// Update RTT counterm_cntRtt++;NS_LOG_DEBUG ("Updated m_cntRtt = " << m_cntRtt);
}- PktsAcked函数在收到ACK时被调用,用于更新最小 RTT(m_minRtt)和基础 RTT(m_baseRtt),并统计 RTT 样本的数量 (m_cntRtt)。
- 如果 rtt 为零,则直接返回,不进行任何操作。这通常是为了避免处理无效的数据(例如无效的 ACK 或零延迟的情况)。
std::min是 C++ 标准库中的一个函数模板,它返回两个参数中的较小值。- m_minRtt 表示当前连接或当前窗口内的最小 RTT。在每次收到 ACK 包时,如果新的 RTT 比当前记录的 m_minRtt 小,就会更新 m_minRtt。
std::min(m_minRtt, rtt) 会选择 m_minRtt 和当前 RTT 中较小的一个,并将其赋值给 m_minRtt。确保 m_minRtt 始终保持为最小的 RTT 值。 - m_baseRtt 用于记录连接过程中观察到的最小 RTT(通常是在连接的初期或网络的稳定阶段)。这代表了网络的基准延迟(即理想的延迟)。
- 与 m_minRtt 类似,m_baseRtt 会更新为当前 RTT 和已有的 m_baseRtt 中的最小值。这可以确保 m_baseRtt 始终为连接期间的最小延迟。
- m_cntRtt 是 RTT 样本的计数器。每次收到 ACK 包时,都会增加 m_cntRtt 的值,表示新的 RTT 样本被记录。
baseRtt 和 minRtt的区别见:
TCP Vegas拥塞控制算法——baseRtt 和 minRtt的区别-CSDN博客
(3) EnableVegas函数
void
TcpVegas::EnableVegas (Ptr<TcpSocketState> tcb)
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this << tcb);m_doingVegasNow = true;m_begSndNxt = tcb->m_nextTxSequence;m_cntRtt = 0;m_minRtt = Time::Max ();
}void
TcpVegas::DisableVegas ()
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);m_doingVegasNow = false;
}EnableVegas函数用于启用Vegas算法。m_doingVegasNow标志被设置为true,表示Vegas算法现在被激活。m_begSndNxt被设置为下一个传输序列号,用于跟踪Vegas周期的开始。- 将
m_cntRtt成员变量重置为0,在每个新的Vegas周期开始时重置这个计数器。 - 将
m_minRtt重置为Time::Max(),即最大可能的时间值;用于在新的Vegas周期中重新寻找最小的RTT值。
(4) DisableVegas函数
void TcpVegas::DisableVegas ()
{NS_LOG_FUNCTION (this);m_doingVegasNow = false;
}DisableVegas函数用于禁用Vegas算法。m_doingVegasNow标志被设置为false,表示Vegas算法现在被禁用。
相关文章:
)
NS3学习——tcpVegas算法代码详解(1)
目录 一、源码 二、详解 1.定义日志和命名空间 2.注册Typeld类:TcpVegas和GetTypeId方法的实现 3.构造函数和析构函数 4.TcpVegas类中成员函数 (1) Fork函数 (2) PktsAcked函数 (3) EnableVegas函数 (4) DisableVegas函数 一、源码 /* -*- Mode:C; c-file-style:&qu…...

相机雷达外参标定综述“Automatic targetless LiDAR–camera calibration: a survey“
相机雷达外参标定综述--Automatic targetless LiDAR–camera calibration: a survey 前言1 Introduction2 Background3 Automatic targetless LiDAR–camera calibration3.1 Information theory based method(信息论方法)3.1.1 Pairs of point cloud and image attributes(属性…...

【Java基础-27】Java中的访问修饰符:分类、作用及应用场景
在Java编程中,访问修饰符(Access Modifiers)是控制类、方法、变量和构造函数访问权限的关键工具。通过合理使用访问修饰符,可以有效地封装代码,保护数据,并确保代码的安全性和可维护性。本文将详细介绍Java…...

Redis+注解实现限流机制(IP、自定义等)
简介 在项目的使用过程中,限流的场景是很多的,尤其是要提供接口给外部使用的时候,但是自己去封装的话,相对比较耗时。 本方式可以使用默认(方法),ip、自定义参数进行限流,根据时间…...

SAP从入门到放弃系列之委外分包(Subcontracting)-Part1
以前写过一篇委外相关的文章,没有很详细的写。只是一个概念的概述ERP实施-委外业务-委外采购业务 最近看PA教材,遇到了这块内容,就再详细的整理一下SAP关于委外的理论知识。 文章目录 概述分包和物料需求计划 (MRP)委外分包订单分包委外业务…...

nlp新词发现——浅析 TF·IDF
传统nlp任务处理文本及其依赖已有的词表,只有在词表里出现的词才能被识别并加以处理。但这也带来了一些问题: 假设没有词表,如何从文本中发现新词? 随着时间推移,新词会不断出现,固有词表会过时࿰…...

WebGL2示例项目常见问题解决方案
WebGL2示例项目常见问题解决方案 webgl2examples Rendering algorithms implemented in raw WebGL 2. [这里是图片001] 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/we/webgl2examples 项目基础介绍 WebGL2示例项目(https://github.com/tsherif/webgl2examples.gi…...

鸿蒙元服务从0到上架【第三篇】(第二招有捷径)
第一招:开始发布元服务 AppGallery 上传通过IDE生成的图标,后面按照步骤填写 后台有隐私政策链接生成处,前往填写生成 第二招:用户协议 对于没有服务器或者是需要极速开发的开发者,可通过gitee生成用户协议&…...

Jimureport h2命令执行分析记录
首先找testConnection接口,前面进行了jimureport-spring-boot-starter-1.5.8.jar反编译查找,接口找到发现请求参数是json var1是JmreportDynamicDataSourceVo类型,也就是如上图的dbSource,根据打印的结果可以知道这里是local cac…...

vue 集成 webrtc-streamer 播放视频流 - 解决阿里云内外网访问视频流问题
资料: 史上最详细的webrtc-streamer访问摄像机视频流教程-CSDN博客 webrtc目录 前端集成 html文件夹里的webrtcstreamer.js,集成到前端,可以访问webrtc,转换rtsp为webrtc视频流,在前端video中播放 <videoref&quo…...

进网许可认证、交换路由设备检测项目更新25年1月起
实施时间 2025年1月1日起实施 涉及设备范围 核心路由器、边缘路由器、以太网交换机、三层交换机、宽带网络接入服务器(BNAS) 新增检测依据 GBT41266-2022网络关键设备安全检测方法交换机设备 GBT41267-2022网络关键设备安全技术要求交换机设备 GB/…...

Provides transitive vulnerable dependency maven 提示依赖存在漏洞问题的解决方法
问题描述 如下图所示,对于 java 项目某些依赖,IDEA 提示,引用了含有漏洞的依赖。如果是单个依赖,可以考虑直接升级版本即可。但是对于传递性依赖,比如 flink 项目中,依赖的部分模块,它们自己依…...

WebAuthn 项目常见问题解决方案
WebAuthn 项目常见问题解决方案 webauthn Webauthn / passkeys helper library to make your life easier. Client side, server side and demo included. [这里是图片001] 项目地址: https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/webaut/webauthn 项目基础介绍 WebAuthn 项目是一个开源…...
)
LeetCode 844. 比较含退格的字符串 (C++实现)
1. 题目描述 给定 s 和 t 两个字符串,当它们分别被输入到空白的文本编辑器后,如果两者相等,返回 true 。# 代表退格字符。 注意:如果对空文本输入退格字符,文本继续为空。 示例 1: 输入:s …...

Python8-写一些小作业
记录python学习,直到学会基本的爬虫,使用python搭建接口自动化测试就算学会了,在进阶webui自动化,app自动化 python基础8-灵活运用顺序、选择、循环结构 写一些小练习题目1、给一个半径,求圆的面积和周长,…...

C++ STL vector基本原理和用法
文章目录 基本原理1. 数据存储结构2. 内存管理机制3. 迭代器实现原理4. 元素访问原理5. 插入和删除元素原理 常见用法1. 概述2. 包含头文件3. 定义和初始化4. 常用成员函数5. 迭代器6. 内存管理与性能特点7. 应用场景 基本原理 以下是关于 std::vector 的基本原理讲解…...

【计算机视觉基础CV-图像分类】05 - 深入解析ResNet与GoogLeNet:从基础理论到实际应用
引言 在上一篇文章中,我们详细介绍了ResNet与GoogLeNet的网络结构、设计理念及其在图像分类中的应用。本文将继续深入探讨如何在实际项目中应用这些模型,特别是如何保存训练好的模型、加载模型以及使用模型进行新图像的预测。通过这些步骤,读…...

【人工智能-初级】基于用户的协同过滤推荐算法
文章目录 1. 数据集2. 实验代码3. 代码解释4. 实验结果5. 评估基于用户的协同过滤算法是一种常见的推荐算法,它的核心思想是根据用户之间的相似性来进行推荐。 实验案例: 使用的是电影推荐数据集 MovieLens,实验中我们会通过用户评分数据计算用户之间的相似性,并使用基于用户…...

如何识别钓鱼邮件和诈骗网站?(附网络安全意识培训PPT资料)
识别钓鱼邮件和诈骗网站是网络安全中的一个重要环节。以下是一些识别钓鱼邮件和诈骗网站的方法: 识别钓鱼邮件: 检查发件人地址: 仔细查看发件人的电子邮件地址,看是否与官方域名一致。 检查邮件内容: 留意邮件中是否…...

Rust 在前端基建中的使用
摘要 随着前端技术的不断发展,前端基础设施(前端基建)的建设已成为提升开发效率、保障产品质量的关键环节。然而,在应对复杂业务场景与高性能需求时,传统的前端技术栈逐渐暴露出诸多不足。近年来,Rust语言…...
)
云计算——弹性云计算器(ECS)
弹性云服务器:ECS 概述 云计算重构了ICT系统,云计算平台厂商推出使得厂家能够主要关注应用管理而非平台管理的云平台,包含如下主要概念。 ECS(Elastic Cloud Server):即弹性云服务器,是云计算…...
(二)TensorRT-LLM | 模型导出(v0.20.0rc3)
0. 概述 上一节 对安装和使用有个基本介绍。根据这个 issue 的描述,后续 TensorRT-LLM 团队可能更专注于更新和维护 pytorch backend。但 tensorrt backend 作为先前一直开发的工作,其中包含了大量可以学习的地方。本文主要看看它导出模型的部分&#x…...

Objective-C常用命名规范总结
【OC】常用命名规范总结 文章目录 【OC】常用命名规范总结1.类名(Class Name)2.协议名(Protocol Name)3.方法名(Method Name)4.属性名(Property Name)5.局部变量/实例变量(Local / Instance Variables&…...

【解密LSTM、GRU如何解决传统RNN梯度消失问题】
解密LSTM与GRU:如何让RNN变得更聪明? 在深度学习的世界里,循环神经网络(RNN)以其卓越的序列数据处理能力广泛应用于自然语言处理、时间序列预测等领域。然而,传统RNN存在的一个严重问题——梯度消失&#…...
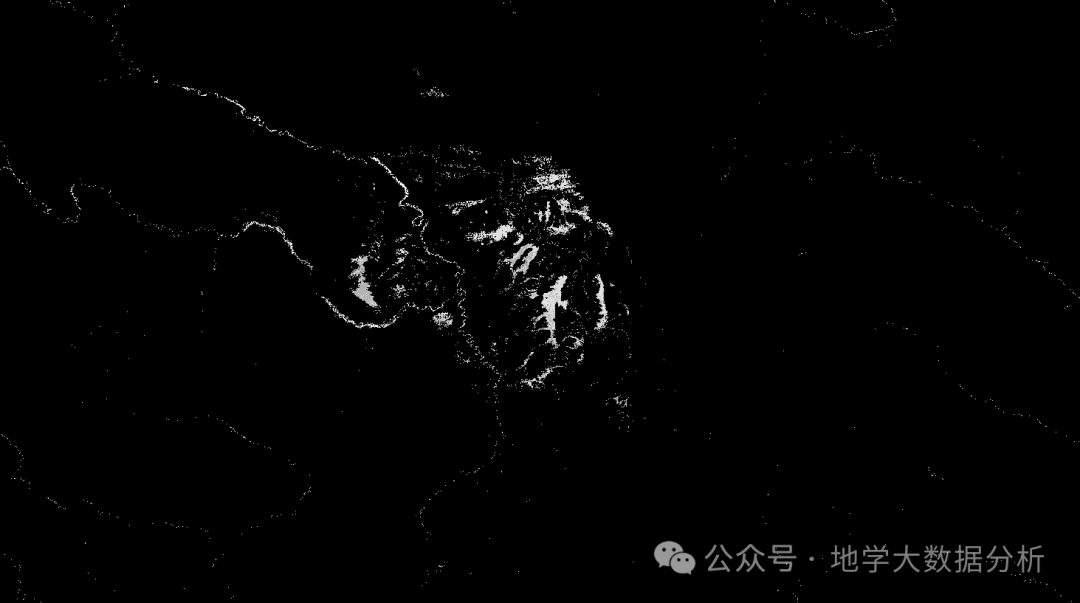

全球首个30米分辨率湿地数据集(2000—2022)
数据简介 今天我们分享的数据是全球30米分辨率湿地数据集,包含8种湿地亚类,该数据以0.5X0.5的瓦片存储,我们整理了所有属于中国的瓦片名称与其对应省份,方便大家研究使用。 该数据集作为全球首个30米分辨率、覆盖2000–2022年时间…...

第25节 Node.js 断言测试
Node.js的assert模块主要用于编写程序的单元测试时使用,通过断言可以提早发现和排查出错误。 稳定性: 5 - 锁定 这个模块可用于应用的单元测试,通过 require(assert) 可以使用这个模块。 assert.fail(actual, expected, message, operator) 使用参数…...

涂鸦T5AI手搓语音、emoji、otto机器人从入门到实战
“🤖手搓TuyaAI语音指令 😍秒变表情包大师,让萌系Otto机器人🔥玩出智能新花样!开整!” 🤖 Otto机器人 → 直接点明主体 手搓TuyaAI语音 → 强调 自主编程/自定义 语音控制(TuyaAI…...
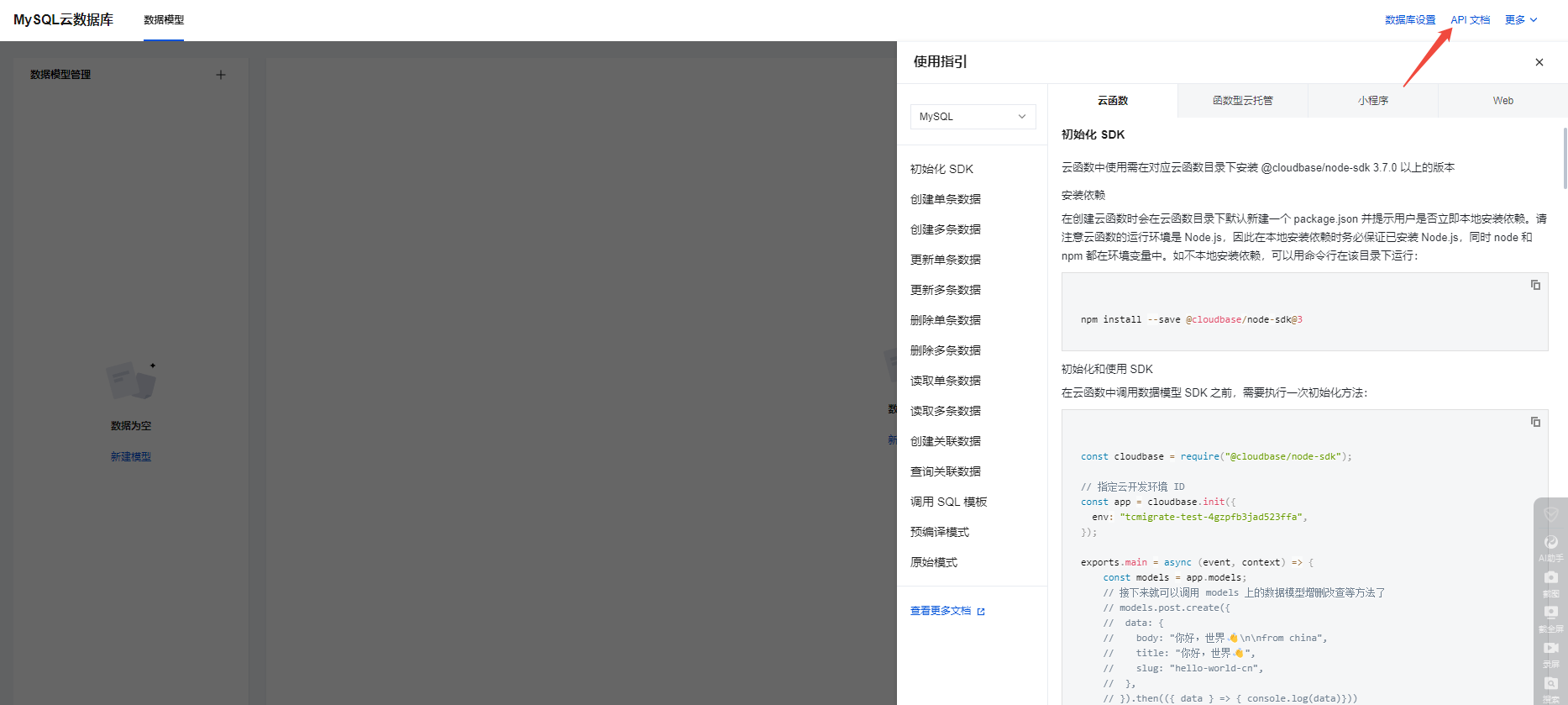
微信小程序云开发平台MySQL的连接方式
注:微信小程序云开发平台指的是腾讯云开发 先给结论:微信小程序云开发平台的MySQL,无法通过获取数据库连接信息的方式进行连接,连接只能通过云开发的SDK连接,具体要参考官方文档: 为什么? 因为…...
SpringCloudGateway 自定义局部过滤器
场景: 将所有请求转化为同一路径请求(方便穿网配置)在请求头内标识原来路径,然后在将请求分发给不同服务 AllToOneGatewayFilterFactory import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; impor…...

高防服务器能够抵御哪些网络攻击呢?
高防服务器作为一种有着高度防御能力的服务器,可以帮助网站应对分布式拒绝服务攻击,有效识别和清理一些恶意的网络流量,为用户提供安全且稳定的网络环境,那么,高防服务器一般都可以抵御哪些网络攻击呢?下面…...
