心脏扩散张量成像中的异常值检测:射击拒绝还是稳健拟合?|文献速递-视觉大模型医疗图像应用
Title
题目
Outlier detection in cardiac diffusion tensor imaging: Shot rejection or robust fitting?
心脏扩散张量成像中的异常值检测:射击拒绝还是稳健拟合?
01
文献速递介绍
心脏扩散张量成像(Cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imaging, cDTI)是一种非侵入性、无需造影剂且无电离辐射的成像方法,通过检测水分子(各向异性)随机运动来表征心肌微观结构(Reese et al., 1995; Scollan et al., 1998)。扩散模型可用于拟合在不同方向和幅度扩散敏感条件下获取的图像。通常对每个体素拟合扩散张量模型(Basser et al., 1994),从中可提取平均扩散率(MD)、分数各向异性(FA)以及组织方向和组织排列的生物标记(如“片层”角E2A)等参数(Basser and Pierpaoli, 1996; Kung et al., 2011; Ferreira et al., 2014; Nielles-Vallespin et al., 2017)。这些指标已被证明在病理与健康状态之间存在差异,可为心肌疾病对组织结构和排列的影响提供深入见解。
与其他器官的扩散张量成像相比,cDTI面临更多挑战,主要源于心脏和呼吸运动,其幅度远大于水分子的扩散运动。尽管序列设计和运动补偿方案已取得显著进展(Stoeck et al., 2016),但通常需要重复成像以提供数据冗余并补偿较低的信噪比(SNR)。呼吸运动通常通过后期图像配准进行校正,但除了热噪声外,图像间仍可能存在结构化差异,这种“生理噪声”包括心脏相位、成像平面相对心脏位置的变化等。异常值处理方法 在cDTI中,受伪影影响的图像是常见问题,如信号丢失、配准失败或过强的生理噪声。目前,受损图像通常通过人工检查识别并移除,而自动化方法的研究较少(Ferreira et al., 2020; Coveney et al., 2023)。尽管脑扩散MRI领域中已有丰富的异常值处理方法,如稳健拟合,但这些方法在cDTI中的应用仍然有限。单体素异常值检测(SVOD):此方法通过迭代拟合结合稳健估计器来检测异常值(如RESTORE算法),对每个体素独立处理(Chang et al., 2005, 2012)。然而,SVOD可能无法检测图像中明显的伪影。
多体素异常值检测(MVOD):此方法利用多个体素的信息来检测异常值,例如通过图像间的相似性或模型预测与观测值之间的均方误差(Coveney et al., 2023)。MVOD可克服SVOD的局限,尤其在处理复杂伪影区域时表现更优。研究目标与结果 本研究提出了结合稳健M估计器的迭代加权最小二乘(IRLS)方法,并将SVOD和MVOD应用于健康志愿者和肥厚型心肌病(HCM)患者的cDTI数据。结果表明:稳健拟合优于射击拒绝(SR):稳健拟合在MD、FA和E2A指标上生成了更大的组间差异,并具有更高的统计显著性。MVOD优于SVOD:在MD和FA的组间差异上,MVOD表现更优,并在合成实验中更有效地从受损数据中恢复扩散指标。SVOD的不足影响有限:尽管SVOD未能识别所有伪影信号,但对扩散张量模型参数的稳健估计并无显著影响。结论 本研究表明,稳健拟合结合SVOD或MVOD可以完全取代射击拒绝用于cDTI异常值处理,从而提高数据质量并增强疾病相关指标的敏感性。
Aastract
摘要
Cardiac diffusion tensor imaging (cDTI) is highly prone to image corruption, yet robust-fitting methods arerarely used. Single voxel outlier detection (SVOD) can overlook corruptions that are visually obvious, perhapscausing reluctance to replace whole-image shot-rejection (SR) despite its own deficiencies. SVOD’s deficienciesmay be relatively unimportant: corrupted signals that are not statistical outliers ay not be detrimental.Multiple voxel outlier detection (MVOD), using a local myocardial neighbourhood, may overcome the shareddeficiencies of SR and SVOD for cDTI while keeping the benefits of both. Here, robust fitting methods usingM-estimators are derived for both non-linear least squares and weighted least squares fitting, and outlierdetection is applied using (i) SVOD; and (ii) SVOD and MVOD. These methods, along with non-robust fittingwith/without SR, are applied to cDTI datasets from healthy volunteers and hypertrophic cardiomyopathypatients. Robust fitting methods produce larger group differences with more statistical significance for MD,FA, and E2A, versus non-robust methods, with MVOD giving the largest group differences for MD and FA.Visual analysis demonstrates the superiority of robust-fitting methods over SR, especially when it is difficultto partition the images into good and bad sets. Synthetic experiments confirm that MVOD gives lowerroot-mean-square-error than SVOD.
心脏扩散张量成像(cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imaging, cDTI)非常容易受到图像损坏的影响,但稳健拟合方法很少被使用。单体素异常值检测(Single Voxel Outlier Detection, SVOD)可能会忽略一些肉眼明显的损坏,这可能导致尽管存在不足,仍倾向于使用全图像射击拒绝(Shot Rejection, SR)。然而,SVOD的不足可能并不重要:并非统计学上的异常信号未必对结果有显著影响。多体素异常值检测(Multiple Voxel Outlier Detection, MVOD),通过利用局部心肌邻域,可能克服SR和SVOD在cDTI中的共同缺陷,同时保留两者的优势。本研究中,为非线性最小二乘法和加权最小二乘法拟合推导了使用M估计器的稳健拟合方法,并将异常值检测应用于以下两种情况:(i) 仅使用SVOD;(ii) 同时使用SVOD和MVOD。这些方法以及非稳健拟合(有/无SR)被应用于来自健康志愿者和肥厚型心肌病患者的cDTI数据集。
结果表明,稳健拟合方法在MD(平均扩散率)、FA(分数各向异性)和E2A(扩展轴比)方面,与非稳健方法相比,能够产生更大的组间差异,并具有更显著的统计学意义。MVOD在MD和FA的组间差异中表现出最大优势。视觉分析显示,当难以将图像明确划分为“良好”或“损坏”时,稳健拟合方法明显优于SR。合成实验进一步证实,MVOD比SVOD具有更低的均方根误差(Root Mean Square Error, RMSE)。
Method
方法
DTI data are a series of 𝑛 images 𝑖 = 1 …𝑛 obtained with diffusionweightings 𝑏𝑖 and directions (unit vectors) 𝐠𝐢 = (𝑔𝑖,𝑥, 𝑔𝑖,𝑦, 𝑔𝑖,𝑧). Considering a single voxel, the noisy signal 𝑦𝑖 observed in image 𝑖 can be relatedto the signal model 𝑓(𝜽*, 𝑏𝑖 , 𝐠𝐢 ), with parameters 𝜽 and the error 𝜖𝑖 as:𝑦𝑖 = 𝑓(𝜽, 𝑏𝑖 , 𝐠𝐢 ) + 𝜖𝑖(1)We focus on the diffusion tensor model of the signal:𝑓(𝜽, 𝑏𝑖 , 𝐠𝐢) = 𝑆0 exp ( −𝑏𝑖 𝐠𝐢 𝐃 𝐠 𝑇 𝐢 ) = exp ( 𝐱𝑖𝜽 𝑇 )(2)where 𝐱𝑖 = ( 1,−𝑏𝑖 𝑔𝑖,𝑥 2 ,−2𝑏**𝑖 𝑔𝑖,𝑥𝑔𝑖,𝑦,−2𝑏𝑖 𝑔𝑖,𝑥𝑔𝑖,𝑧,−𝑏𝑖 𝑔𝑖,𝑦 2 ,−2𝑏𝑖 𝑔𝑖,𝑦𝑔𝑖,𝑧,−𝑏𝑖 𝑔𝑖,𝑧 2 ) , and model parameters 𝜃 = ( log(𝑆0 ), 𝐷𝑥𝑥, 𝐷𝑥𝑦, 𝐷𝑥𝑧, 𝐷𝑦𝑦,𝐷𝑦𝑧, 𝐷*𝑧𝑧 ) . The methods presented here can apply to other models, suchas the diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) model. We denote the standarddeviation of the Gaussian noise in the original complex images as 𝜎.We consider magnitude images, for which the noise distribution can becomplicated (St-Jean et al., 2020); we assume Rician distributed errorfor simplicity (Cárdenas-Blanco et al., 2008), and note that 𝜖**𝑖 resultsfrom both the Gaussian noise in the complex images and the magnitudeoperation.
DTI数据是一系列包含n张图像(𝑖 = 1 …𝑛)的集合,这些图像具有不同的扩散加权系数 𝑏 和方向(单位向量)𝐠𝐢 = (𝑔𝑖,𝑥, 𝑔𝑖,𝑦, 𝑔𝑖,𝑧)。考虑单个体素,在图像𝑖中观测到的带噪信号 𝑦𝑖 与信号模型 𝑓(𝜽*, 𝑏𝑖* , 𝐠𝐢 ) 的关系可以表示为:𝑦𝑖 = 𝑓(𝜽, 𝑏𝑖, 𝐠𝑖) + 𝜖𝑖 \tag{1}其中,参数为 𝜽,误差为 𝜖**𝑖。我们重点研究信号的扩散张量模型,其形式为:𝑓(𝜽, 𝑏𝑖, 𝐠𝑖) = 𝑆0 \exp( -𝑏𝑖 \𝐠𝑖 \𝐃 \𝐠𝑖^𝑇 ) = \exp( \𝐱_𝑖 \𝜽^𝑇 ) \tag{2}其中,𝐱𝑖=(1,−𝑏𝑖𝑔𝑖,𝑥2,−2𝑏𝑖𝑔𝑖,𝑥𝑔𝑖,𝑦,−2𝑏𝑖𝑔𝑖,𝑥𝑔𝑖,𝑧,−𝑏𝑖𝑔𝑖,𝑦2,−2𝑏𝑖𝑔𝑖,𝑦𝑔𝑖,𝑧,−𝑏𝑖𝑔𝑖,𝑧2)𝐱𝑖 = \big( 1, -𝑏𝑖 𝑔{𝑖,𝑥}^2, -2𝑏𝑖 𝑔{𝑖,𝑥}𝑔{𝑖,𝑦}, -2𝑏𝑖 𝑔{𝑖,𝑥}𝑔{𝑖,𝑧}, -𝑏𝑖 𝑔{𝑖,𝑦}^2, -2𝑏𝑖 𝑔{𝑖,𝑦}𝑔{𝑖,𝑧}, -𝑏𝑖 𝑔{𝑖,𝑧}^2 \big)
模型参数为 \𝜃 = \big( \log(𝑆0), 𝐷{𝑥𝑥}, 𝐷{𝑥𝑦}, 𝐷{𝑥𝑧}, 𝐷{𝑦𝑦}, 𝐷{𝑦𝑧}, 𝐷_{𝑧𝑧} \big)。本文所述方法同样适用于其他模型,例如扩散峰度成像(Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging, DKI)模型。我们将原始复图像中高斯噪声的标准差记为 𝜎。对于幅度图像,其噪声分布可能较为复杂(St-Jean et al., 2020);为了简化,假设误差服从Rician分布(Cárdenas-Blanco et al., 2008)。需要注意的是,𝜖**𝑖 既来自复图像中的高斯噪声,也来自幅度运算的影响。
Conclusion
结论
In this work, we have attempted to answer the question of whetherrobust-estimation can replace shot-rejection in cardiac diffusion tensorimaging, and whether the deficiencies of single voxel outlier detection are important for recovering correct diffusion tensor metrics. Wehave presented robust fitting with M-estimators followed by singlevoxel-outlier-detection and multiple-voxel-outlier-detection. Our results demonstrate that MVOD is more robust than SVOD, particularlyfor large numbers of corrupted images and low SNR. Nonetheless, theimprovement of MVOD over SVOD seems relatively minor for cardiacDTI, even as SVOD gives large improvements over shot-rejection,suggesting that researchers need not worry that SVOD misses signalsthat would be identified by shot-rejection, even if MVOD could identifythese signals. We recommend cDTI to start using robust-estimation inplace of shot-rejection.
在本研究中,我们探讨了稳健估计是否可以替代射击拒绝(shot-rejection)用于心脏扩散张量成像(cardiac DTI),以及单体素异常值检测(SVOD)的不足是否对恢复正确的扩散张量指标有重要影响。我们提出了结合M估计器的稳健拟合方法,并辅以单体素异常值检测和多体素异常值检测(MVOD)。
研究结果表明,MVOD比SVOD更稳健,特别是在损坏图像数量较多和信噪比(SNR)较低的情况下。然而,对于心脏DTI而言,MVOD相较于SVOD的改进相对较小,而SVOD相较于射击拒绝则表现出显著改进。这表明研究者无需担心SVOD会遗漏射击拒绝能够识别的信号,即使这些信号可以被MVOD检测到。
因此,我们建议在心脏DTI中使用稳健估计以替代射击拒绝。
Results
结果
3.1. Application to datasets
Fig. 2 shows global MD, FA, and absolute E2A, as fit to the originaldatasets, for the methods explained in Section 2.4. Table 1 showsthe group differences of the mean and median, and the 𝑝-value, forthe methods in Fig. 2. Table 1 shows that the group differences between Volunteers and HCM Patients was largest for MVOD methodsfor both MD and FA, and the significance was also higher (the 𝑝-valuewas lower). The SVOD methods showed the second largest differencebetween the groups for MD and FA, except for RWLS where shotrejection (WLS_SR) showed a slightly larger difference for mean MD(although the values are nearly identical) — note that difference ofmedians was nontheless much bigger for RWLS MD than for WLS_SRMD, and RWLS had nearly 6 times decrease in 𝑝-value compared toWLS_SR. It is visually clear that robust-fitting methods seem to reducethe spread of metric values in the healthy volunteers, especially for WLSmethods. Importantly for WLS, the 𝑝-value for MD does not pass thestandard significance test of 𝑝 < 0.05 at least without shot rejection,and the robust-fitting methods are much more significant still. For E2A,either SVOD or MVOD gave the largest group differences — there areseveral ties in the 𝑝-value due to the nature of the Wilcoxon signedrank test. Care should be taken to interpret the box-plots (dependingon whether points are classed as ‘fliers’, the box and whiskers will bedrawn differently, which can lead to discontinuous changes in the boxsizes). For WLS and WLS_SR methods, the box plot for volunteer E2Aseems narrower than for the robust methods, but in fact this is becausethe robust methods do not produce as many flier (out-lying) values ofE2A, so in this respect the ‘spread’ is reduced for robust methods.Figs. 3 and 4 show MD, FA, E2A and HA (helix angle) maps foran example volunteer and HCM patient respectively. These exampleswere the subjects with the largest MD values for the non-robust WLSmethods. Furthermore, even attempts at manual shot-rejection wereextremely difficult in these cases, since it was difficult to separate goodfrom bad images: even the better images appeared to contain large shotto-shot variations and corruptions at the sub-image level. Note that,we have shown all the myocardium in Figs. 3 and 4, although regionsof distortion and isolated artefacts were excluded from global metriccalculations, as explained in Appendix B.Fig. 3 shows a marked decrease in MD across the myocardium forrobust fitting compared to non-robust fitting (with or without shotrejection), especially around the septum. This decrease is slightly largerfor MVOD than SVOD, especially in the basal slice. The effects on FA areequivalent but in the opposite direction (an increase). The transmuralvariation of HA from right-handed (red) to left-handed (blue) is alsosuperior in MVOD, with the blue fibres in the bottom left of the midslice only convincingly recovered with MVOD. Additionally, SVOD andMVOD both show significantly more convincing transmural variationfrom red (right-handed) to green (circumferential) to blue (left-handed)in the septum of the basal slice, where the non-robust (with or withoutSR) methods show an extended region of red in the same area.Fig. 4 shows a strong increase in (magnitude of) E2A in the septumfor robust methods, particularly in the apical and basal slices. Thesechanges are also accompanied by a complete recovery of HA by robustfitting methods, whereas there are obvious corruptions of HA in bothnon-robust methods (including shot-rejection). Especially important isthe recovery of right-handed (red) HA in the septum of the basal slice,for both robust methods, whereas these right-handed fibres appearto be missing for not-robust methods. SVOD and MVOD appear todecrease MD substantially, moreso for MVOD than for SVOD.We reviewed differences in fitting methods for every subject byeye. Overall, the visual differences in diffusion measure maps betweenSVOD and MVOD seemed quite minor for most subjects. This seemsconsistent with Fig. 2 and Table 1: while MVOD modifies the results further in the ‘same direction’ in which SVOD improves uponshot-rejection, the improvement upon SVOD would appear relativelyminor in comparison to the improvement that SVOD makes over shotrejection.The RMSE of the predicted versus observed signals, correspondingto Figs. 3 and 4, are shown in Fig. 5. What is especially clear isthat while shot-rejection can reduce the RMSE of the fit to somedegree, the robust-estimation with SVOD and MVOD do substantiallybetter, leaving a nearly uniform (and lower) RMSE except in regions ofisolated artefact. Note that, after robust-fitting, these artefact regionsare extremely easy to identify from RMSE, suggesting that robust-fittingis able to turn RMSE into a useful metric for determining the qualityof the fit in a way that becomes independant of outliers and corruptionin some images, therefore leaving only the effects of artefacts thatpermeate the entire image series. Even after robust fitting, there aresome regions of elevated MD in Figs. 3 and 4 that remain, but these correspond to significantly higher RMSE than the rest of the myocardium,suggesting that these are likely to be artefacts not real features. Notethat MVOD has lower and more uniform RMSE than SVOD
3.1. 数据集的应用
图2展示了基于第2.4节中方法的原始数据集的全局MD(平均扩散率)、FA(分数各向异性)和E2A(片层角)的结果。表1则展示了不同方法在健康志愿者和肥厚型心肌病(HCM)患者之间的组间差异,包括均值、中位数和p值。
表1显示,对于MD和FA,MVOD方法的组间差异最大且显著性更高(p值更低)。SVOD在MD和FA方面的组间差异次于MVOD,但对于RWLS方法,射击拒绝(WLS_SR)在MD均值上的差异略大(尽管差异几乎相同)。然而,RWLS在MD中位数的差异显著更大,其p值相较于WLS_SR减少了近6倍。在健康志愿者的测量值中,稳健拟合方法明显减少了指标值的离散程度,尤其是WLS方法中。对于E2A,SVOD或MVOD通常表现出最大的组间差异,但由于Wilcoxon符号秩检验的性质,部分p值存在相同情况。箱线图的解释需要注意:基于是否将点分类为异常值,箱线图的箱体和须状线的绘制方式可能不同,从而导致箱体尺寸的非连续变化。在WLS和WLS_SR方法中,志愿者E2A的箱线图看起来比稳健方法更窄,但这是因为稳健方法减少了异常值的数量,从而降低了“离散性”。图3和图4分别展示了健康志愿者和HCM患者的MD、FA、E2A和HA(螺旋角)图。这些案例是非稳健WLS方法中MD值最大的个体。对于这些案例,即使进行人工射击拒绝,仍然很难区分“好图像”和“坏图像”,因为即使较好的图像也在子图像级别表现出显著的伪影和变化。
图3 相比非稳健拟合方法(无论是否使用射击拒绝),稳健拟合方法显著降低了心肌中的MD,尤其是在室间隔区域;MVOD在降低MD方面略优于SVOD,尤其是在基底切片。FA的影响相反(显著增加)。MVOD在螺旋角的跨壁变化中表现更优,从右旋(红色)到左旋(蓝色)的过渡更清晰,尤其是中切片的左下角区域仅通过MVOD才能明显恢复。此外,在基底切片的室间隔中,SVOD和MVOD显示了更明显的跨壁变化,而非稳健方法显示的红色区域更广。图4 稳健方法在室间隔中显著增加了E2A的幅值,特别是在心尖和基底切片。这些变化伴随着稳健拟合方法对HA的完全恢复,而非稳健方法(包括射击拒绝)在HA中存在明显的伪影。尤其重要的是,基底切片中室间隔区域的右旋HA(红色)通过稳健方法得以恢复,而非稳健方法未能表现出这些右旋纤维。此外,SVOD和MVOD显著降低了MD,且MVOD的效果优于SVOD。
RMSE分析 图5展示了预测信号与观测信号之间的均方根误差(RMSE)。射击拒绝能够在一定程度上降低RMSE,但稳健拟合结合SVOD和MVOD显著降低了RMSE,除孤立伪影区域外,其余区域RMSE接近均匀。稳健拟合后的伪影区域在RMSE中易于识别,表明稳健拟合方法可以将RMSE转化为一种有效的拟合质量评估指标,能够独立于异常值和图像伪影的影响,仅反映贯穿整个图像序列的伪影效应。
尽管稳健拟合后仍存在MD升高的区域,但这些区域的RMSE明显高于其他心肌区域,表明它们可能是伪影而非真实特征。MVOD的RMSE比SVOD更低且更均匀,进一步证明了其优越性。
Figure
图

Fig. 1. Examples from 6 datasets (1 per row in each sub-figure): (a) examples where shot-rejection has (correctly) identified a corrupted image, but SVOD has not identified allmyocardial voxels in the corrupted image; (b) examples where shot-rejection has not identified a corrupted image. The ‘reference’ image shows a typical ‘good image’, while the‘accepted’ or ‘rejected’ image columns show a different image with the same diffusion weighting for the same subject. The myocardial segmentation is also shown. For SVOD andMVOD columns, black/white voxels indicate outlier/non-outlier signals respectively
图1. 来自6个数据集的示例(每个子图中的每行对应一个数据集): (a) 射击拒绝(shot-rejection)方法正确识别了损坏图像,但单体素异常值检测(SVOD)未能识别损坏图像中所有的心肌体素; (b) 射击拒绝未能识别损坏图像的示例。“参考图像”(reference)展示了一个典型的“良好图像”,而“接受”(accepted)或“拒绝”(rejected)列显示了对同一受试者在相同扩散加权下获取的另一幅图像。图中同时显示了心肌分割结果。对于SVOD和MVOD列,黑色/白色体素分别表示异常值/非异常值信号。

Fig. 2. Diffusion measures MD (×10−3 mm2/s), FA, and absolute E2A (degrees) for volunteers and HCM patients for different fitting methods.
图2. 不同拟合方法下志愿者与HCM患者的扩散测量值:MD(×10⁻³ mm²/s)、FA和绝对E2A(单位:度)。

Fig. 3. Example healthy volunteer (highest MD from non-robust WLS fitting in the HV group of Fig. 2). First row: non-robust NLLS; Second row: non-robust NLLS after shot-rejection;Third row: robust NLLS with SVOD; Fourth row: robust NLLS with SVOD and MVOD (10 voxel neighbourhood).
图3. 健康志愿者示例(来自图2中HV组非稳健WLS拟合的最高MD值)。 第一行:非稳健NLLS(非线性最小二乘法)。 第二行:射击拒绝后的非稳健NLLS。 第三行:结合SVOD的稳健NLLS。 第四行:结合SVOD和MVOD(10体素邻域)的稳健NLLS。

Fig. 4. Example HCM patient (highest MD from non-robust WLS fitting in the HCM group of Fig. 2). First row: non-robust NLLS; Second row: non-robust NLLS after shot-rejection;
Third row: robust NLLS with SVOD; Fourth row: robust NLLS with SVOD and MVOD (10 voxel neighbourhood).
图4. HCM患者示例(来自图2中HCM组非稳健WLS拟合的最高MD值)。 第一行:非稳健NLLS(非线性最小二乘法)。 第二行:射击拒绝后的非稳健NLLS。 第三行:结合SVOD的稳健NLLS。 第四行:结合SVOD和MVOD(10体素邻域)的稳健NLLS。

Fig. 5. RMSE of fitting residuals, excluding identified outliers or excluded images (asapplied). RMSE is lower and more uniform for robust fitting methods, being lower forMVOD than SVOD, with remaining high RMSE regions seeming to indicate patches ofpersistent artefact across the image series.
图5. 拟合残差的均方根误差(RMSE),不包括已识别的异常值或被排除的图像(如适用)。 稳健拟合方法的RMSE更低且更均匀,其中MVOD的RMSE低于SVOD。残留的高RMSE区域似乎表明图像序列中存在持续性伪影的区域。

Fig. 6. Global diffusion measures MD (×10−3 mm2/s), FA, and absolute E2A (degrees) for synthetically corrupted data. Each sub-plot corresponds to a different corruption type.Different percentages of images have been corrupted, and different SNRs have been used to generate Rician error. The dotted line extending across each plot is the ‘‘syntheticground truth’’ from which synthetic data (with noise and corruptions) was generated, whereas the darker solid lines are the mean of non-robust fits excluding the images thatwere artificially corrupted. The box-and-whisker plots represent 10 synthetic datasets per corruption configuration (for narrow box-plots, the median line has been removed forclarity). Different colours correspond to different fitting methods, shown in the legend. For each corruption configuration, NLLS and WLS methods are shown to the left and rightagainst a differently shaded background
图6. 合成损坏数据的全局扩散测量结果:MD(×10⁻³ mm²/s)、FA和绝对E2A(单位:度)。每个子图对应一种不同的损坏类型。
图中显示了不同比例的图像被损坏,以及使用不同信噪比(SNR)生成的Rician误差。虚线表示“合成真值”,即用于生成带噪声和损坏的合成数据的参考值;深色实线表示排除人为损坏图像后的非稳健拟合均值。
箱线图展示了每种损坏配置下的10个合成数据集(对于较窄的箱线图,为了更清晰移除了中位线)。不同颜色表示图例中标注的不同拟合方法。对于每种损坏配置,NLLS方法和WLS方法分别显示在左侧和右侧,并用不同的阴影背景加以区分。

Fig. 7. RMSE of global diffusion measures of MD (×10−3 mm2/s), FA, and absolute E2A (degrees) for synthetically corrupted data. Each sub-plot corresponds to a different corruptiontype. Different percentages of images have been corrupted, and different SNRs have been used to generate Rician error. The RMSE is calculated against the mean of non-robustfits excluding the images that were artificially corrupted. The box-and-whisker plots represent the RMSE scores of all subjects (for narrow box-plots, the median line has beenremoved for clarity). Different colours correspond to different fitting methods, shown in the legend. For each corruption configuration, NLLS and WLS methods are shown to theleft and right against a differently shaded background.
图7. 合成损坏数据中全局扩散测量(MD ×10⁻³ mm²/s,FA和绝对E2A,以度为单位)的RMSE(均方根误差)。每个子图对应一种不同的损坏类型。
不同百分比的图像被损坏,并使用不同信噪比(SNR)生成Rician误差。RMSE是针对排除人为损坏图像后的非稳健拟合均值计算的。箱线图表示所有受试者的RMSE得分(对于较窄的箱线图,为了清晰性移除了中位线)。不同颜色表示图例中标注的不同拟合方法。对于每种损坏配置,NLLS方法和WLS方法分别显示在左侧和右侧,并用不同的阴影背景加以区分。
Table
表

Table 1Table of difference of group means, medians, and p-values, for MD, FA, absolute E2A, for several tested methods. Within each methodcategory (either NLLS or WLS) the largest difference of means and medians are shown in red, and the lowest 𝑝-value is shown in blue.
表1 MD(平均扩散率)、FA(分数各向异性)和绝对E2A的组均值差异、中位数差异及p值的表格比较。 在每种方法类别(NLLS或WLS)中,均值和中位数差异最大的结果用红色标注,p值最低的结果用蓝色标注。
相关文章:

心脏扩散张量成像中的异常值检测:射击拒绝还是稳健拟合?|文献速递-视觉大模型医疗图像应用
Title 题目 Outlier detection in cardiac diffusion tensor imaging: Shot rejection or robust fitting? 心脏扩散张量成像中的异常值检测:射击拒绝还是稳健拟合? 01 文献速递介绍 心脏扩散张量成像(Cardiac Diffusion Tensor Imagin…...

Linux Kernel 之十 详解 PREEMPT_RT、Xenomai 的架构、源码、构建及使用
概述 现在的 RTOS 基本可以分为 Linux 阵营和非 Linux 阵营这两大阵营。非 Linux 阵营的各大 RTOS 都是独立发展,使用上也相对独立;而 Linux 阵营则有多种不同的实现方法来改造 Linux 以实现实时性要求。本文我们重点关注 Linux 阵营的实时内核实现方法! 本文我们重点关注 …...

RabbitMQ-消息消费确认
我们一般使用的是消费者作为被动方接收 RabbitMQ 推送消息,另一种是消费者作为主动方可以主动拉取消息。 RabbitMq 服务器推送消息分为隐式(自动)确认和显示确认。 1 消费者拉取消息 消费者作为主动方拉取消息,每次只能获取一条。 using (var channel c…...

E10.【C语言】练习:编写一个猜数字游戏
目录 1.规则 2.准备 3.游戏代码 1.规则 1.程序生成1-100间的随机数 2.用户猜数字 猜对了:游戏结束 猜错了:程序会告知猜大了或猜小了,继续进行游戏,直到猜对 3.游戏可以一直玩除非退出游戏 2.准备 1.框架:循…...

RK3568-rk809rtc休眠唤醒
参考链接 https://www.360doc.cn/article/71858349_1119199262.html修改驱动drivers/mfd/rk808.c static void rk817_shutdown_prepare(void) { int ret; …...

【Uniapp-Vue3】pages.json页面路由globalStyle的属性
项目的全局配置在pages.json中。 一、导航栏设置 二、下拉刷新设置 下拉就可以看到设置的样式 三、上拉触底 这个页面中,向下滑动页面到底部就会输出“到底了” 现在将触底距离设置为500 走到半路就会输出“到底了”...

NHANES数据挖掘|特征变量对死亡率预测的研究设计与分析
书接上回,应各位临床或在科室的小伙伴们需求,除了多组学和算法开发外,插播关于临床护理方向的数据挖掘,今天分享两篇NHANES的分析文献。 1、时依中介分析 DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02191-5 整体思路 基于 NHANES 数据…...

【Sharding-JDBC学习】概述_shardingsphere-jdbc 和sharding-jdbc
1.概述 1.1.分库分表是什么 小明是一家初创电商平台的开发人员,他负责卖家模块的功能开发,其中涉及了店铺、商品的相关业务,设计如下 数据库: 通过以下SQL能够获取到商品相关的店铺信息、地理区域信息: SELECT p.*…...

用户登录/登出功能,当登录页面在另一域名下
需求: 要求为某网址增加用户登录功能。登录页面是现成的,但是位于另一个域名。当request 没带token ,要求跳转此登录页面,用户登录后会返回token. 此时再跳回原网址。这个过程如何避免发生跨域问题? 最简单的方案 登…...

自动化解决方案:修复devicedisplaystatusmanager.dll丢失
在Windows操作系统中,DLL(动态链接库)文件扮演着至关重要的角色。它们为应用程序提供必要的函数和数据,以确保系统的平稳运行。然而,有时我们可能会遇到DLL文件丢失或损坏的问题,比如DeviceDisplayStatusMa…...

.Net8 Avalonia跨平台UI框架——<vlc:VideoView>控件播放海康监控、摄像机视频(Windows / Linux)
一、UI效果 二、新建用户控件:VideoViewControl.axaml 需引用:VideoLAN.LibVLC.Windows包 Linux平台需安装:VLC 和 LibVLC (sudo apt-get update、sudo apt-get install vlc libvlccore-dev libvlc-dev) .axaml 代码 注…...

网络协议(八):IP 协议
目录 1. IP 协议简介 2. 首部属性 2.1 版本号 2.2 首部长度 2.3 服务类型 2.4 总长度 2.5 > 16位标识 & 3位标志 & 13位片偏移 2.5.1 > 16 位标识 2.5.2 > 3 位标志 2.5.3 > 13 位片偏移 2.6 生存时间(TTL) 2.7 > 8 位协议 2.8 首部校验和…...

深度解析 pytest 参数化与 --count 执行顺序的奥秘
有这样一个业务场景,登录不同地区的账号,重复500遍,以验证登录功能是否正常。 登录的代码如下,其中login_data是一个fixture,用来组织数据: pytest.mark.parametrize("login_data", [cn_test, …...

【traefik】forwadAuth中间件跨namespace请求的问题
前情提要 - fowardAuth鉴权中间件的使用: 【traefik】使用forwardAuth中间件做网关层的全局鉴权 1. 问题 我的 traefik-ingress-controller 所在 namespace: traefik 业务服务所在 namespace: apps 路由与 forwardAuth 中间件配置如下: # 路由 apiV…...

java学习记录16
并发基础 进程与线程 进程 进程(Process)是计算机中正在运行的程序。程序是一种静态的概念,而进程是程序在执行过程中创建的动态实体。每个进程都有自己的内存空间、代码、数据和资源,它也是操作系统进行任务调度和资源分配的基…...

【Lua学习之旅】之单行/多行注释
Lua的注释 单行注释多行注释 单行注释 lua中的单行注释采用两个短横线"--" --这是lua单行注释多行注释 写法一: --[[ 这个lua的多行注释, 很多资料说多行注释不可以嵌套, 根据我的测试,这种写法的多行注释在lua54版…...

[Effective C++]条款45 运用成员函数模板接受所有兼容类型
本文初发于 “天目中云的小站”,同步转载于此。 条款45 : 运用成员函数模板接受所有兼容类型 本条款中我们将会以智能指针为例, 介绍如何通过成员函数模板使一个模板类可以接受所有兼容类型. 我们先来构建一个简单的继承体系 : class Top { ... }; class Middle: p…...

Harry技术添加存储(minio、aliyun oss)、短信sms(aliyun、模拟)、邮件发送等功能
Harry技术添加存储(minio、aliyun oss)、短信sms(aliyun、模拟)、邮件发送等功能 基于SpringBoot3Vue3前后端分离的Java快速开发框架 项目简介:基于 JDK 17、Spring Boot 3、Spring Security 6、JWT、Redis、Mybatis-P…...

【python基础——异常BUG】
什么是异常(BUG) 检测到错误,py编译器无法继续执行,反而出现错误提示 如果遇到错误能继续执行,那么就捕获(try) 1.得到异常:try的执行,try内只可以捕获一个异常 2.预案执行:except后面的语句 3.传入异常:except … as uestcprint(uestc) 4.没有异常:else… 5.鉴定完毕,收尾的语…...

解决Qt打印中文字符出现乱码
在 Windows 平台上,默认的控制台编码可能不是 UTF-8,这可能会导致中文字符的显示问题。 下面是在 Qt 应用程序中设置中文字体,并确保控制台输出为 UTF-8 编码: 1. Qt 应用程序代码 在 Qt 中,我们可以使用 QApplic…...

KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南
Linux_k8s篇 欢迎来到Linux的世界,看笔记好好学多敲多打,每个人都是大神! 题目:KubeSphere 容器平台高可用:环境搭建与可视化操作指南 版本号: 1.0,0 作者: 老王要学习 日期: 2025.06.05 适用环境: Ubuntu22 文档说…...

谷歌浏览器插件
项目中有时候会用到插件 sync-cookie-extension1.0.0:开发环境同步测试 cookie 至 localhost,便于本地请求服务携带 cookie 参考地址:https://juejin.cn/post/7139354571712757767 里面有源码下载下来,加在到扩展即可使用FeHelp…...
)
Java 语言特性(面试系列2)
一、SQL 基础 1. 复杂查询 (1)连接查询(JOIN) 内连接(INNER JOIN):返回两表匹配的记录。 SELECT e.name, d.dept_name FROM employees e INNER JOIN departments d ON e.dept_id d.dept_id; 左…...
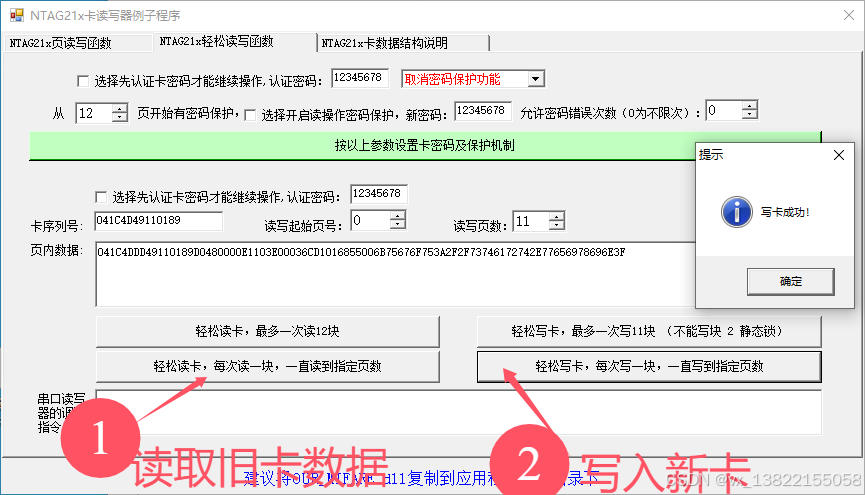
VB.net复制Ntag213卡写入UID
本示例使用的发卡器:https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?ftt&id615391857885 一、读取旧Ntag卡的UID和数据 Private Sub Button15_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button15.Click轻松读卡技术支持:网站:Dim i, j As IntegerDim cardidhex, …...
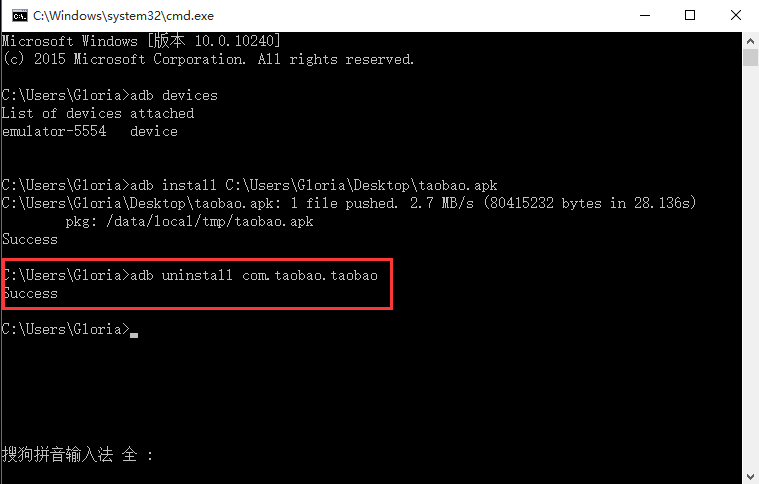
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...
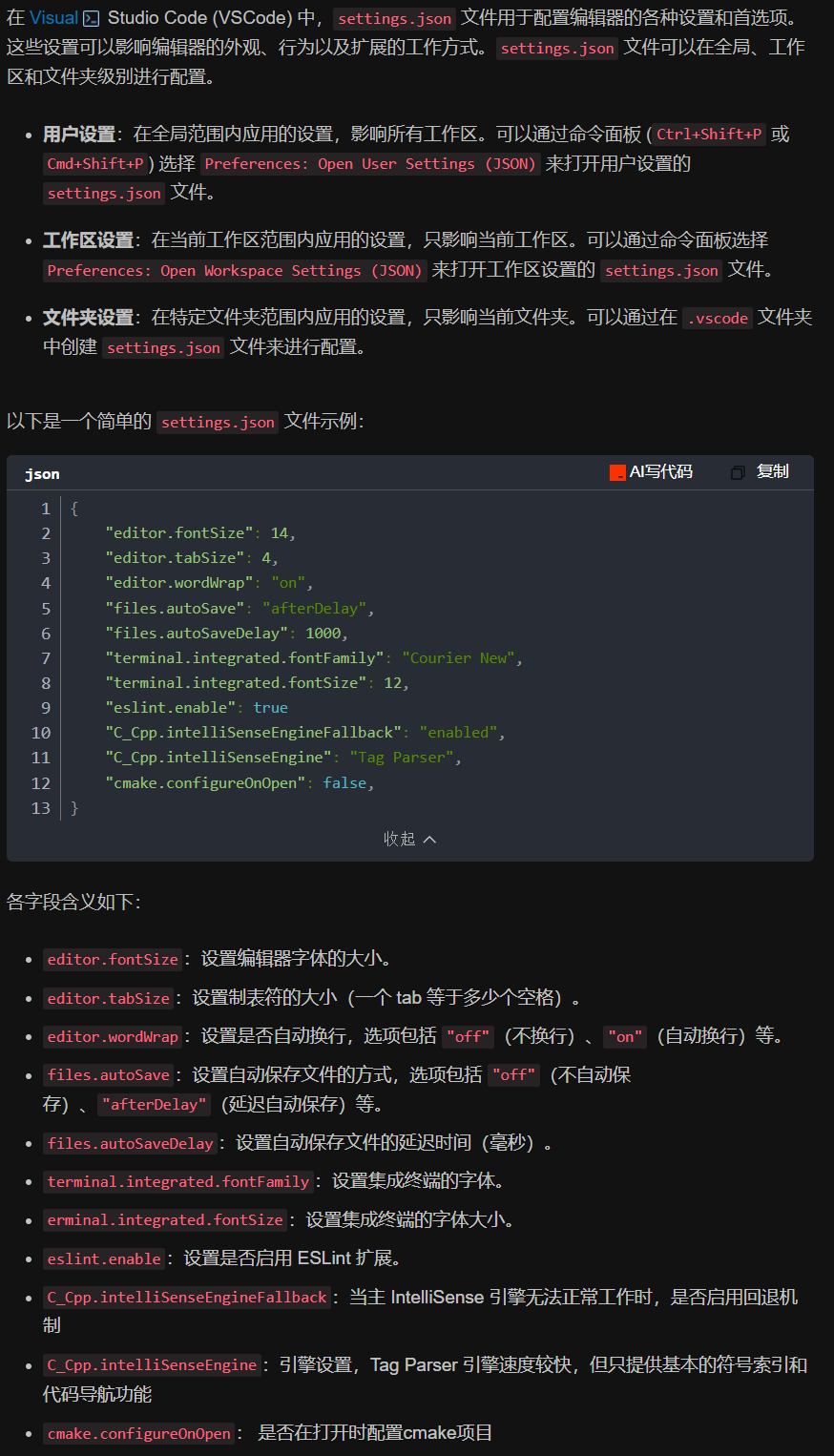
vscode(仍待补充)
写于2025 6.9 主包将加入vscode这个更权威的圈子 vscode的基本使用 侧边栏 vscode还能连接ssh? debug时使用的launch文件 1.task.json {"tasks": [{"type": "cppbuild","label": "C/C: gcc.exe 生成活动文件"…...
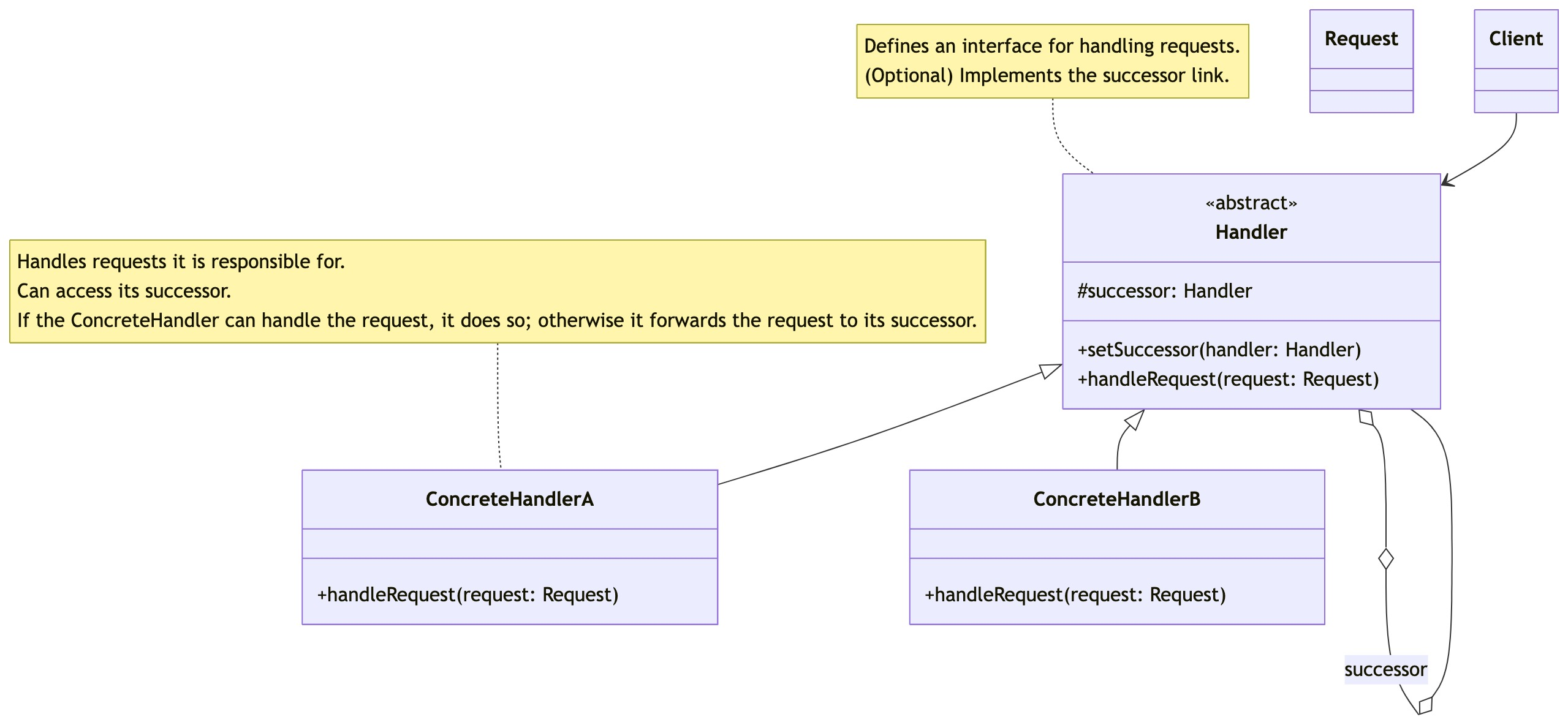
零基础设计模式——行为型模式 - 责任链模式
第四部分:行为型模式 - 责任链模式 (Chain of Responsibility Pattern) 欢迎来到行为型模式的学习!行为型模式关注对象之间的职责分配、算法封装和对象间的交互。我们将学习的第一个行为型模式是责任链模式。 核心思想:使多个对象都有机会处…...
Unity | AmplifyShaderEditor插件基础(第七集:平面波动shader)
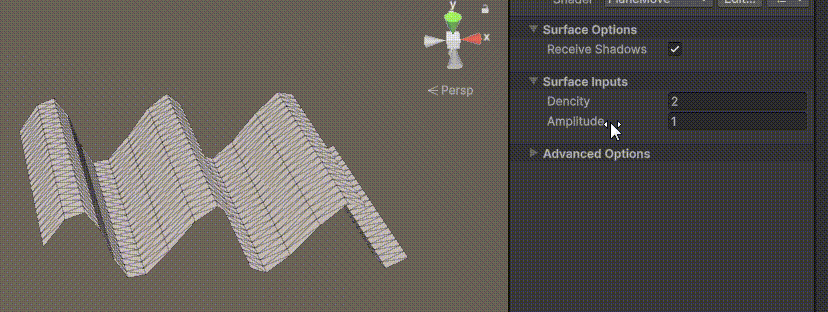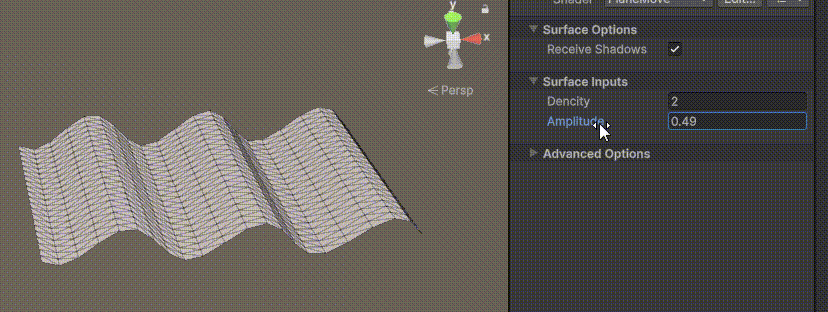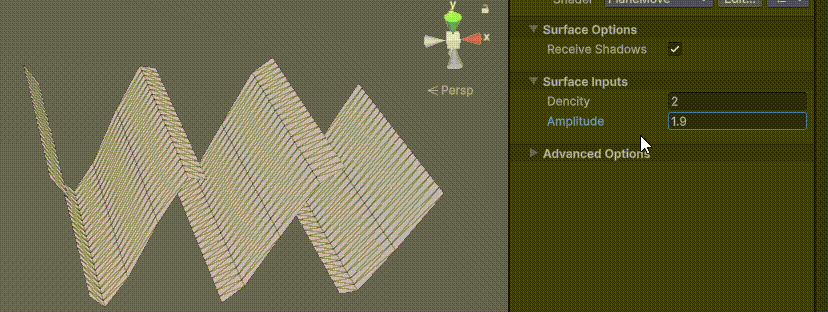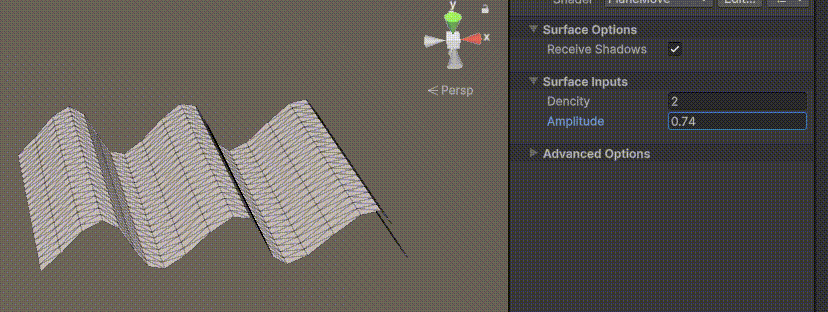
目录 一、👋🏻前言 二、😈sinx波动的基本原理 三、😈波动起来 1.sinx节点介绍 2.vertexPosition 3.集成Vector3 a.节点Append b.连起来 4.波动起来 a.波动的原理 b.时间节点 c.sinx的处理 四、🌊波动优化…...

docker 部署发现spring.profiles.active 问题
报错: org.springframework.boot.context.config.InvalidConfigDataPropertyException: Property spring.profiles.active imported from location class path resource [application-test.yml] is invalid in a profile specific resource [origin: class path re…...
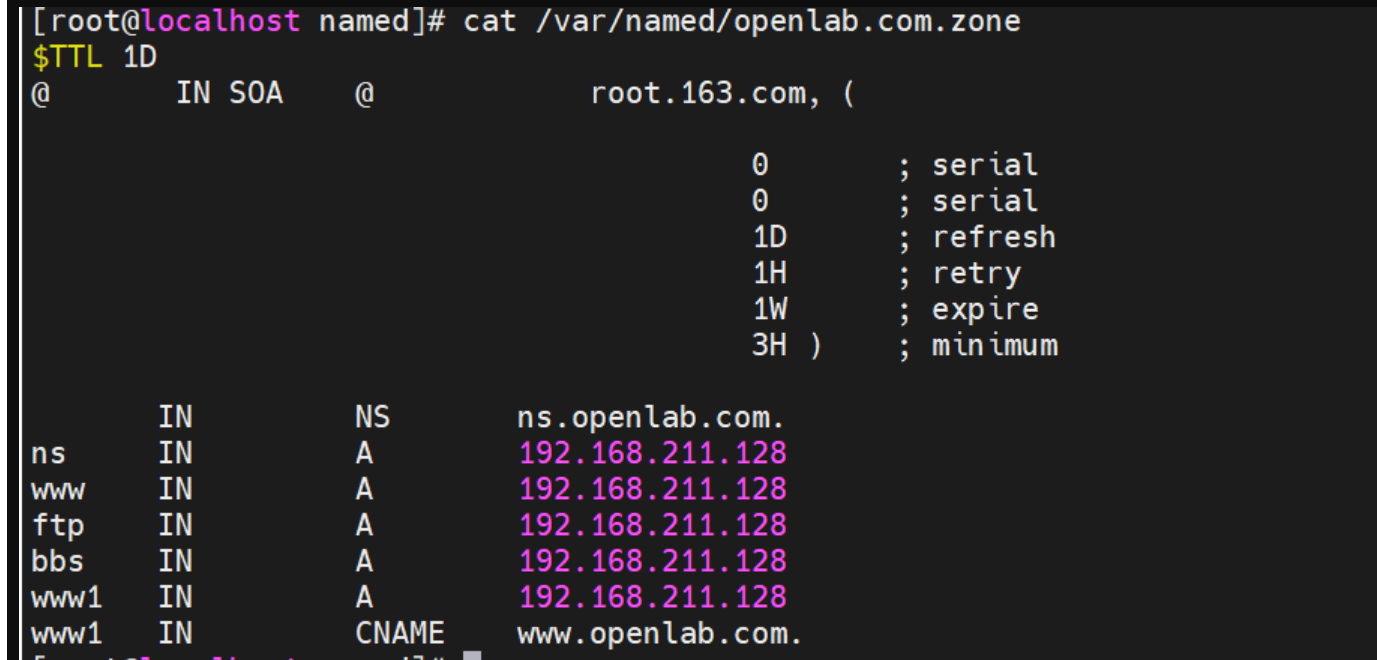
搭建DNS域名解析服务器(正向解析资源文件)
正向解析资源文件 1)准备工作 服务端及客户端都关闭安全软件 [rootlocalhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld [rootlocalhost ~]# setenforce 0 2)服务端安装软件:bind 1.配置yum源 [rootlocalhost ~]# cat /etc/yum.repos.d/base.repo [Base…...
