从0开始使用面对对象C语言搭建一个基于OLED的图形显示框架(动态菜单组件实现)
目录
面对对象C的程序设计(范例)
面对对象C的程序设计(应用)
进一步谈论我上面给出的代码——继承
实现一个面对对象的文本编辑器
所以,什么是继承
重申我们对菜单的抽象
抽象菜单项目
抽象菜单动画
实现菜单功能
初始化我们的菜单
关于我们的图标设置,显示和隐藏
菜单本体功能
关于切换focus的菜单和进入父子菜单的函数
完整的测试文件
终于,我们来到了这个令人激动的部分了,现在,我们终于把所有的基础工作做好了,就差我们的动态组件了。
面对对象C的程序设计(范例)
我想,你可能使用过C++这门语言,他派生于C,但是最终的惯用编程范式又远远不同于C。尽管如此,C仍然可以按照一个相对变扭的方式完成面对对象的程序设计。这是因为在C语言本质上是过程化语言,没有直接的类和对象概念,因此面向对象设计需要通过结构体、函数指针等手段模拟实现。
面对对象,首先讲究的就是把所有的目标看成对象。举个例子,现在我们来看看动态多级菜单这个东西,按照面对对象的设计思路。我们说面对对象它通过抽象和封装将数据与功能结合,形成具有特定属性和行为的对象。
typedef struct {int x;int y;void (*move)(struct Point*, int, int);
} Point;
void movePoint(Point* p, int dx, int dy) {p->x += dx;p->y += dy;
}
int main() {Point p = {0, 0, movePoint};p.move(&p, 5, 3);return 0;
}
这个就是一个将点看作对象的例子。
我们设计对象的时候,要思考对象能干什么,进一步的,才需要知道他需要有什么。这种方式可以辅助一个习惯于面对过程的朋友设计一个对象。
面对对象C的程序设计(应用)
我们现在把上面谈到的用一下。
-
他能显示多级的文字菜单
-
他能将目前选中的文本区域进行反色
-
他能再切换选中文本的时候演示一个阻塞的动画(提示,笔者的框架没有做异步,这需要牵扯到中断,笔者不打算现在做)
-
如果一个子项存在子菜单,他能显示出来这个子菜单,然后还能返回去(怎么样触发进入和返回不是我们关心的,他能!)
-
他可以显示和隐藏我们的icon,为此,我们还需要注册接口。
为了做到上面的事情,我们要想他要拥有什么。
-
一个简略的文本编辑器,他能展示文字,我们菜单的文本绘制基本上依赖于这个文本编辑器
-
一个负责动画演示的结构体(对象),他能完成我们对“他能再切换选中文本的时候演示一个阻塞的动画”这个任务
-
一个菜单子项结构体数组,他维护了当前这个菜单子项的文本显示,是否有子菜单,甚至,还需要有callback行为的结构体数组(这个是额外任务,笔者没有做callback)
typedef void* CCgraphicWidgetBase;
/* update requist functions */
typedef void(*Update)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Hide)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Show)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef struct{Update update;Hide hide;Show show;
}CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation;
typedef struct
{CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation common;void (*switchToIndex)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t index);void (*enabled_showAnimations)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t enabled);void (*setIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*, CCGraphic_Image* image, uint8_t size);void (*showIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);void (*hideIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);CCGraphic_Menu* (*enterSub)(CCGraphic_Menu*);CCGraphic_Menu* (*backParent)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
}CCGraphic_MenuOperations;
typedef struct __CCGraphic_Menu{// 菜单项数组CCGraphic_MenuItem* menuItemArrays;// 菜单项数组个数uint8_t menuArraySize;// 内部主控件CCGraphicTextEdit* internelTextEdit;// 动画负责的结构体CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animation_holder;// 操作CCGraphic_MenuOperations operations;// 当前维护的其他信息uint8_t current_offset;uint8_t enabled_animations;CCGraphic_Image* icons_sources;uint8_t icon_size;uint8_t icon_state;
}CCGraphic_Menu;
任务:你可以改进这个抽象!你可以看到零碎一地的变量成员不太美观!
进一步谈论我上面给出的代码——继承
让我们进一步讨论更多的概念,上面的代码出现了一个很有意思的片段
typedef void* CCgraphicWidgetBase;
/* update requist functions */
typedef void(*Update)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Hide)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef void(*Show)(CCgraphicWidgetBase);
typedef struct{Update update;Hide hide;Show show;
}CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation;
typedef struct
{CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation common;void (*switchToIndex)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t index);void (*enabled_showAnimations)(CCGraphic_Menu*, uint8_t enabled);void (*setIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*, CCGraphic_Image* image, uint8_t size);void (*showIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);void (*hideIcon)(CCGraphic_Menu*);CCGraphic_Menu* (*enterSub)(CCGraphic_Menu*);CCGraphic_Menu* (*backParent)(CCGraphic_Menu*);
}CCGraphic_MenuOperations;
仔细研究一下,你会发现,我们似乎复用了一个结构体:CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation,也就是组件Widget的通用操作。为了理解这个特征,我们先不着急,实现一个完全面对对象的,一个简单的文本编辑器
实现一个面对对象的文本编辑器
#ifndef CCGraphic_TextEdit_H
#define CCGraphic_TextEdit_H
#include "Graphic/widgets/common/CCGraphic_WidgetBase.h"
#include "Graphic/base/CCGraphic_Point/CCGraphic_Point.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/common/CCGraphic_Size/CCGraphic_Size.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/common/CCGraphic_WidgetBase.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/base/CCGraphic_TextItem/CCGraphic_TextItem.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/base/CCGraphic_TextItem/CCGraphic_TextConfig.h"
typedef struct __CCGraphicTextEdit CCGraphicTextEdit;
// 前向声明:定义一个名为 `CCGraphicTextEdit` 的结构体类型。
typedef struct { CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation operation; // 控件通用操作,提供基本控件功能。
void (*appendText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* appendee); // 函数指针:向文本控件追加文本。
void (*setText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text); // 函数指针:设置控件内的完整文本内容。
void (*newLineText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text); // 函数指针:在控件中新起一行并写入文本。
void (*clear)(CCGraphicTextEdit*); // 函数指针:清空控件中的文本。
void (*relocate)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, CCGraphic_Point p, CCGraphic_Size size); // 函数指针:重新定位控件位置并调整控件尺寸。
} CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations;
// 结构体 `CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations`:定义文本控件支持的操作集合。
typedef struct __CCGraphicTextEdit { uint8_t acquired_stepped_update; // 标记是否启用分步更新机制的标志变量。
CCDeviceHandler* borrowed_device; // 设备处理器指针,用于管理外部设备资源。
CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations operations; // 文本控件支持操作的集合。
CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* handle; // 控件中的具体文本项句柄,用于操作字符显示内容。
} CCGraphicTextEdit;
// 结构体 `CCGraphicTextEdit`:定义文本控件的属性与操作。
void CCGraphic_init_CCGraphicTextEdit( CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, CCDeviceHandler* handler, CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* inited
);
// 函数声明:初始化 `CCGraphicTextEdit` 控件,传入控件对象、设备处理器和已初始化的文本项。
#endif
你可能会问,怎么看起来这么奇怪,我们应该如何调用功能呢?你看,这就是思维没有转变过来,笔者想要说的是,现在功能被集成进入了结构体,意味着,我们想要调用的不叫函数了,是一个结构体的方法。
static void __helper_on_set_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* edit, char* sources, uint32_t shown_time)
{edit->operations.setText(edit, sources);HAL_Delay(shown_time * 1000);edit->operations.clear(edit);
}
看到了吗?当我们想要设置文本的时候,不是
CCGraphicTextEdit_setText(edit, sources);
而是
edit->operations.setText(edit, sources);
看起来好像没什么区别,我想说的是,你现在不知道,也没法去引用一个函数,叫“给一个是CCGraphicTextEdit的结构体设置文本”的函数,你找不到,我藏起来了(笑),而是,一个属于CCGraphicTextEdit这个类的对象可以被设置文本,文本是sources,这就是面对对象的设计思考范式。换而言之,一个CCGraphicTextEdit的对象可以设置文本,他能设置文本而且优先的投射到绘图设备上,而你完全不知道底下发生了什么,只知道这样做一定没有问题!
在源文件中,我们才将如何实现暴露出来
#include "Graphic/widgets/components/CCGraphic_TextEdit/CCGraphic_TextEdit.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/base/CCGraphic_TextItem/CCGraphic_TextItem.h"
#include "Graphic/CCGraphic_device_adapter.h"
static void __pvt_update_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:更新控件所依赖的设备内容。
{text_self->borrowed_device->operations.update_device_function(text_self->borrowed_device // 调用设备的更新函数,使文本控件的内容刷新显示。 );
}
static void __pvt_show(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:绘制并显示文本控件内容。
{CCGraphicWidget_drawAsciiTextItem(text_self->borrowed_device, text_self->handle // 绘制文本控件的内容。 );if(text_self->acquired_stepped_update) // 如果启用了分步更新,则执行设备更新。 __pvt_update_text(text_self);
}
static void __pvt_hide(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:隐藏控件,即清除其显示区域。
{text_self->borrowed_device->operations.clearArea_function(text_self->borrowed_device, text_self->handle->tl_point.x, text_self->handle->tl_point.y, text_self->handle->TexthandleSize.width, text_self->handle->TexthandleSize.height // 清除控件所在区域的内容。 );__pvt_update_text(text_self);
}
static void __pvt_clear_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self)
// 静态函数:清除控件中的文本内容。
{CCGraphic_Point tl = text_self->handle->tl_point; CCGraphic_Size size = text_self->handle->TexthandleSize; // 获取控件左上角坐标和尺寸,用于清除操作。
text_self->borrowed_device->operations.clearArea_function(text_self->borrowed_device, tl.x, tl.y, size.width, size.height // 执行清除操作。 );__pvt_update_text(text_self);
}
static void __pvt_append_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, char* text)
// 静态函数:向控件追加文本。
{CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setAsciiText(text_self->handle, text); // 设置追加的文本内容。 __pvt_show(text_self); // 显示控件内容。
}
static void __pvt_newLine_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, char* text)
// 静态函数:在控件中新建一行并写入文本。
{CCGraphic_Point new_begin = CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_on_newLine_point(text_self->handle); // 获取新行起始点坐标。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setAsciiText(text_self->handle, text); // 设置文本内容。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setIndexedPoint(text_self->handle, &new_begin); // 更新文本项的绘制位置。
__pvt_show(text_self); // 显示控件内容。
}
static void __pvt_setText(CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, char* text)
// 静态函数:设置控件的完整文本内容。
{__pvt_clear_text(text_self); // 清除原有内容。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setIndexedPoint(text_self->handle, &(text_self->handle->tl_point) // 重置文本绘制位置为控件起点。 );
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_setAsciiText(text_self->handle, text); // 设置新的文本内容。
__pvt_show(text_self); // 显示控件内容。
}
static void __pvt_relocate(CCGraphicTextEdit* edit, CCGraphic_Point p, CCGraphic_Size size)
// 静态函数:重新定位控件位置并调整尺寸。
{__pvt_hide(edit); // 隐藏控件内容。
CCGraphicWidget_AsciiTextItem_relocate(edit->handle, p, size); // 重新设置控件位置和尺寸。
}
void CCGraphic_init_CCGraphicTextEdit( CCGraphicTextEdit* text_self, CCDeviceHandler* handler, CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* inited
)
// 初始化函数:设置文本编辑控件的初始状态。
{text_self->acquired_stepped_update = 0; // 初始化为未启用分步更新。
text_self->borrowed_device = handler; // 绑定设备处理器。
text_self->handle = inited; // 设置文本项句柄。
text_self->operations.appendText = __pvt_append_text; text_self->operations.clear = __pvt_clear_text; text_self->operations.newLineText = __pvt_newLine_text; text_self->operations.setText = __pvt_setText; text_self->operations.relocate = __pvt_relocate; // 绑定控件的各类操作函数。
text_self->operations.operation.hide = (Hide)__pvt_hide; text_self->operations.operation.show = (Show)__pvt_show; text_self->operations.operation.update = (Update)__pvt_update_text; // 绑定通用控件操作。
}
可以看到,代码被分成了一层一层的,关心哪一个方法,只需要进入对应的方法查看即可。
所以,什么是继承
继承允许一个类从另一个类中获取属性和方法,从而实现代码复用和逻辑扩展。也就是说,我们认为继承表达了“一个对象是另一个对象”的陈述。比如说。
typedef struct { CCGraphicWidgetCommonOperation operation; // 控件通用操作,提供基本控件功能。
void (*appendText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* appendee); // 函数指针:向文本控件追加文本。
void (*setText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text); // 函数指针:设置控件内的完整文本内容。
void (*newLineText)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, char* text); // 函数指针:在控件中新起一行并写入文本。
void (*clear)(CCGraphicTextEdit*); // 函数指针:清空控件中的文本。
void (*relocate)(CCGraphicTextEdit*, CCGraphic_Point p, CCGraphic_Size size); // 函数指针:重新定位控件位置并调整控件尺寸。
} CCGraphicTextEdit_SupportiveOperations;
表达了CCGraphicTextEdit的功能集合是CCGraphicWidget的一个超集,他不光拥有一个Widget该有的操作,而且,还有自己跟Widget独有的操作,这就是继承的力量——复用接口,甚至可以是实现!
重申我们对菜单的抽象
根据最之前的描述,菜单本身应该是一个树状的结构,你可以看到:
抽象菜单项目
#ifndef CCGraphic_MenuItem_H
#define CCGraphic_MenuItem_H
#include "Graphic/CCGraphic_common.h"
/* This version we use simple menu Item */
/* announced the menu type for the further usage */
// 预声明 `CCGraphic_Menu` 类型,用于菜单关联。
typedef struct __CCGraphic_Menu CCGraphic_Menu;
// 结构体 `CCGraphic_Menu` 的前向声明,以便在结构中使用指针引用该类型。
#define NO_SUB_MENU (NULL)
// 定义宏 `NO_SUB_MENU` 表示没有子菜单,为空指针。
typedef struct __CCGraphic_MenuItem { char* text; // 菜单项显示的文本内容。
CCGraphic_Menu* subMenu; // 指向子菜单的指针,若无子菜单则为 `NO_SUB_MENU`。
CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu; // 指向父菜单的指针,用于返回或层级控制。
} CCGraphic_MenuItem;
// 定义菜单项结构体 `CCGraphic_MenuItem`,包含菜单文字、子菜单及父菜单指针。
void CCGraphic_MenuItem_register_menuItem( CCGraphic_MenuItem* item, // 菜单项指针,用于注册菜单项。
CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu, // 父菜单指针,将菜单项附加到此菜单下。
char* text, // 菜单项文本内容。
CCGraphic_Menu* subMenu // 子菜单指针,可为 `NO_SUB_MENU`。
);
// 函数声明:将菜单项注册到指定父菜单下,同时设置菜单项文本和子菜单。
#endif
提示:需要做callback?(用户明确选择了这个菜单项目)试一下在CCGraphic_MenuItem中添加抽象!完成你的代码!
抽象菜单动画
typedef struct __CCGraphic_MenuAnimations CCGraphic_MenuAnimations;
// 前向声明 `CCGraphic_MenuAnimations` 结构体,表示菜单动画的管理结构。
typedef void (*DoByStep)(CCGraphic_MenuAnimations*);
// 定义一个函数指针类型 `DoByStep`,指向以 `CCGraphic_MenuAnimations*` 为参数的函数,
// 该函数用于执行逐步动画操作。
typedef struct { DoByStep doByStep; // 操作结构体,包含逐步执行动画的函数指针。
} CCGraphic_MenuAnimationsOperations;
// 定义 `CCGraphic_MenuAnimationsOperations` 结构体,封装了逐步动画执行的操作。
/*this struct shouldn't be registered by programmersit shoule be registered by program, so no interface ispubliced!
*/
// 该结构体不应由程序员手动注册,而是由程序自动注册,因此没有提供公开接口。
typedef struct __CCGraphic_MenuAnimations { /* animating rectangle */ // 定义菜单动画的结构体。
CCDeviceHandler* handler; // 设备处理器,用于控制设备的操作。
CCGraphic_Point tl_point; // 动画的起始点(左上角坐标)。
CCGraphic_Size animationOffsetSize; // 动画的偏移尺寸,用于表示动画区域的大小。
int16_t x_step; // x轴每步移动的像素值,用于控制动画的水平位移。
int16_t y_step; // y轴每步移动的像素值,用于控制动画的垂直位移。
CCGraphic_MenuAnimationsOperations op; // 操作对象,包含执行逐步动画的函数指针。
uint8_t is_doing; // 标志位,表示动画是否正在进行中。
} CCGraphic_MenuAnimations;
// 定义菜单动画结构体,封装了动画的状态、操作及设备控制。
初始化一个动画的办法是:
static void __pvt_init_animations( CCGraphic_Menu* menu, CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations
) { /* no animations are registered */ // 如果没有提供动画对象,直接返回。 if (animations == NULL) { return; }
// 获取菜单中的文本编辑项句柄,进行后续动画初始化。 CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem* internelTextEdit = menu->internelTextEdit->handle;
/* calculate the animations holding size */ // 计算动画的大小,首先设置动画起始点为文本编辑项的起始点。 animations->tl_point = internelTextEdit->tl_point;
// 设置动画的高度为字体的大小(通过 `__fetch_font_size` 获取字体的高度)。 animations->animationOffsetSize.height = __fetch_font_size(internelTextEdit->font_size).height;
// 设置动画的宽度为文本处理器的宽度。 animations->animationOffsetSize.width = internelTextEdit->TexthandleSize.width;
// 设置设备处理器,使用菜单中的文本编辑项借用的设备。 animations->handler = menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device;
// 设置每步的水平和垂直步长(默认值)。 animations->x_step = _DEFAULT_X_STEP; animations->y_step = _DEFAULT_Y_STEP;
// 设置执行逐步动画操作的函数指针,指向 `__pvt_doByStep` 函数。 animations->op.doByStep = __pvt_doByStep;
/* set state */ // 设置动画状态为未开始。 animations->is_doing = 0;
}
对于逐步开始动画的办法是
/* do by steps */
static void __pvt_doByStep(CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations)
{ // 如果动画尚未开始(is_doing 为 0),则直接返回,避免不必要的操作。 if (!animations->is_doing) return;
// 使用设备的操作对象反转(擦除)动画区域,传入当前动画的起始位置(tl_point)和尺寸。 animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function( animations->handler, animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y, animations->animationOffsetSize.width, animations->animationOffsetSize.height );
// 更新动画的起始点(左上角坐标),按水平步长(x_step)和垂直步长(y_step)更新。 animations->tl_point.x += animations->x_step; animations->tl_point.y += animations->y_step;
// 再次调用反转(擦除)区域,传入更新后的动画位置和尺寸。 animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function( animations->handler, animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y, animations->animationOffsetSize.width, animations->animationOffsetSize.height );
// 调用更新设备函数,刷新屏幕以显示动画效果。 animations->handler->operations.update_device_function( animations->handler );
}
看到了吗,非必要不调用刷新设备的操作就在这里体现了。当然,当我们配置不需要动画的时候
static void __pvt_do_as_immediate(CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations, CCGraphic_Point* end_tpl)
{if(!animations->is_doing) return;animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(animations->handler, animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,animations->animationOffsetSize.width, animations->animationOffsetSize.height);animations->tl_point = *end_tpl;animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(animations->handler, animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,animations->animationOffsetSize.width, animations->animationOffsetSize.height);animations->handler->operations.update_device_function(animations->handler);
}
直接拉到最后就好了。
实现菜单功能
到了真正实现的时候,一切反而水到渠成。
初始化我们的菜单
void CCGraphic_init_Menu(CCGraphic_Menu* blank_menu,CCGraphic_MenuItem* menuItemArrays,uint8_t menuArraySize,CCGraphicTextEdit* configured_menu,CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* blank_animations,uint8_t enabled_animations
)
{blank_menu->internelTextEdit = configured_menu;blank_menu->menuItemArrays = menuItemArrays;blank_menu->menuArraySize = menuArraySize;blank_menu->animation_holder = blank_animations;blank_menu->current_offset = 0;blank_menu->icon_state = 0;blank_menu->enabled_animations = enabled_animations;
// map the functionsblank_menu->operations.common.hide = (Hide)__pvt_hide_CCGraphic_Menu;blank_menu->operations.common.show = (Show)__pvt_show_CCGraphic_Menu;blank_menu->operations.common.update = (Update)__pvt_update;blank_menu->operations.switchToIndex = __pvt_switchIndex;blank_menu->operations.enabled_showAnimations = __pvt_setAnimationShowState_wrapper;// iconsblank_menu->operations.setIcon = __pvt_setIcon;blank_menu->operations.hideIcon = __pvt_hideIcon;blank_menu->operations.showIcon = __pvt_showIcon;blank_menu->operations.enterSub = __pvt_enterSub;blank_menu->operations.backParent = __pvt_backParent;__pvt_init_animations(blank_menu, blank_animations);
}
关于我们的图标设置,显示和隐藏
static void __pvt_setIcon(CCGraphic_Menu* menu, CCGraphic_Image* sources, uint8_t size)
{ // 设置菜单的图标源和图标数量 menu->icons_sources = sources; menu->icon_size = size;
// 初始化每个图标的尺寸和位置 for (uint8_t i = 0; i < menu->icon_size; i++) { // 设置图标的高度和宽度 sources[i].image_size.height = ICON_HEIGHT; sources[i].image_size.width = ICON_WIDTH;
// 设置每个图标的位置,`y` 方向依次排列 sources[i].point.x = 0; sources[i].point.y = i * ICON_HEIGHT; }
// 显示图标 __pvt_showIcon(menu);
}
static void __pvt_showIcon(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{ // 如果没有图标源,则不执行任何操作 if (!menu->icons_sources) return; // 设置图标的状态为显示(1) menu->icon_state = 1; CCGraphic_Point tlp; CCGraphic_Size _size; // 获取显示图标的位置和大小 __pvt_providePoint(menu, &tlp, 1); __pvt_provideSize(menu, &_size, 1); // 设置动画的显示状态为 0(关闭动画) __pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 0); // 将菜单项的文本编辑区域重新定位到指定的位置和大小 menu->internelTextEdit->operations.relocate(menu->internelTextEdit, tlp, _size); // 遍历图标源,逐一绘制每个图标 for (uint8_t i = 0; i < menu->icon_size; i++) { CCGraphicWidget_draw_image( menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device, &menu->icons_sources[i] ); } // 设置动画的显示状态为 1(启用动画) __pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 1); // 仅显示文本编辑器 __pvt_show_textEditOnly(menu);
}
static void __pvt_hideIcon(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{ // 如果没有图标源,则不执行任何操作 if (!menu->icons_sources) return; CCGraphic_Point tlp; CCGraphic_Size _size; // 设置图标的状态为隐藏(0) menu->icon_state = 0; // 获取隐藏图标的位置和大小 __pvt_providePoint(menu, &tlp, 0); __pvt_provideSize(menu, &_size, 0); // 设置动画的显示状态为 0(关闭动画) __pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 0); // 将菜单项的文本编辑区域重新定位到指定的位置和大小 menu->internelTextEdit->operations.relocate(menu->internelTextEdit, tlp, _size); // 清除图标区域 menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device->operations.clearArea_function( menu->internelTextEdit->borrowed_device, 0, 0, ICON_WIDTH, ICON_HEIGHT * menu->icon_size ); // 仅显示文本编辑器 __pvt_show_textEditOnly(menu);
}
图标的绘制就是让位子绘制,清除掉重新绘制这个思路。
菜单本体功能
static void __pvt_update(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{// 调用文本编辑器的更新操作,刷新菜单显示menu->internelTextEdit->operations.operation.update(menu->internelTextEdit);
}
// 更新动画状态
static void __pvt_setAnimationShowState(CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations, uint8_t is_doing)
{// 如果动画状态没有变化,直接返回if(is_doing == animations->is_doing){return;}// 如果动画正在进行,先逆向绘制区域,清除之前的显示animations->handler->operations.reverseArea_function(animations->handler, animations->tl_point.x, animations->tl_point.y,animations->animationOffsetSize.width, animations->animationOffsetSize.height);// 更新动画状态animations->is_doing = is_doing;// 更新设备,刷新显示animations->handler->operations.update_device_function(animations->handler);
}
/*以下是显示/隐藏图标时,提供布局计算的函数
*/
static void __pvt_providePoint(CCGraphic_Menu* menu, CCGraphic_Point* p, uint8_t icons_enabled)
{// 根据是否启用图标,设置图标显示的起始位置p->x = icons_enabled ? ICON_WIDTH : 0;p->y = 0;
}
static void __pvt_provideSize(CCGraphic_Menu* menu, CCGraphic_Size* size, uint8_t icons_enabled
){// 根据是否启用图标,调整文本区域的宽度和高度size->width = menu->internelTextEdit->handle->TexthandleSize.width - (icons_enabled ? ICON_HEIGHT : 0);size->height = menu->internelTextEdit->handle->TexthandleSize.height;
}
// 获取当前菜单项是否有子菜单
static inline CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_current_owns_subMenu(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{return menu->menuItemArrays[menu->current_offset].subMenu;
}
// 获取当前菜单项的父菜单
static inline CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_owns_parent_current(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{return menu->menuItemArrays[menu->current_offset].parentMenu;
}
// 仅显示文本编辑器的内容,更新菜单显示
void __pvt_show_textEditOnly(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{// 如果菜单没有项,则直接返回if(menu->menuArraySize == 0){return;}// 设置动画状态为不显示__pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 0);// 设置文本编辑器的内容,显示第一项菜单CCGraphicTextEdit* edit = menu->internelTextEdit;edit->operations.setText(edit, menu->menuItemArrays[0].text);// 显示后续菜单项for(uint8_t i = 1; i < menu->menuArraySize; i++){edit->operations.newLineText(edit, menu->menuItemArrays[i].text);}// 设置动画状态为显示__pvt_setAnimationShowState(menu->animation_holder, 1);
}
// 隐藏菜单和图标
void __pvt_hide_CCGraphic_Menu(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{// 隐藏图标__pvt_hideIcon(menu);// 隐藏文本编辑器menu->internelTextEdit->operations.operation.hide(menu->internelTextEdit);// 获取动画控制器CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animation = menu->animation_holder;// 如果没有动画控制器,则返回if(!animation) return;// 如果动画正在进行,则停止动画if(animation->is_doing){__pvt_setAnimationShowState(animation, 0);}
}
/* 绘制菜单显示 */
void __pvt_show_CCGraphic_Menu(CCGraphic_Menu* menu)
{// 仅显示文本编辑器内容__pvt_show_textEditOnly(menu);
}
// 执行动画,逐步更新菜单位置直到目标位置
void __pvt_do_stepped_animate(CCGraphic_MenuAnimations* animations, CCGraphic_Point* end_tl_p
)
{// 如果动画步长为负,表示需要向下移动if(animations->y_step < 0){// 逐步向下执行动画,直到达到目标位置while(animations->tl_point.y > end_tl_p->y){__pvt_doByStep(animations); // 执行单步动画
#ifdef REQ_ANIMATION_DELAY// 延时,模拟动画效果__device_delay(ANIMATION_DELAY_MS);
#endif}}// 如果动画步长为正,表示需要向上移动else{// 逐步向上执行动画,直到达到目标位置while(animations->tl_point.y < end_tl_p->y){__pvt_doByStep(animations); // 执行单步动画
#ifdef REQ_ANIMATION_DELAY// 延时,模拟动画效果__device_delay(ANIMATION_DELAY_MS);
#endif} }}
关于切换focus的菜单和进入父子菜单的函数
// 切换菜单项索引并执行动画
static void __pvt_switchIndex(CCGraphic_Menu* menu, uint8_t index)
{// 如果索引没有变化,不做任何操作if(index == menu->current_offset) return;
// 如果新索引大于当前索引,表示需要向下移动if(index > menu->current_offset){// 如果当前动画步长为负,改为正值if(menu->animation_holder->y_step < 0){menu->animation_holder->y_step = -menu->animation_holder->y_step;}}// 如果新索引小于当前索引,表示需要向上移动else{// 如果当前动画步长为正,改为负值if(menu->animation_holder->y_step > 0){menu->animation_holder->y_step = -menu->animation_holder->y_step;}}// 更新当前菜单项的索引menu->current_offset = index;// 计算目标位置CCGraphic_Point end_tlp;end_tlp = menu->animation_holder->tl_point; end_tlp.y = index * menu->animation_holder->animationOffsetSize.height;// 如果启用了动画,执行逐步动画if(menu->enabled_animations)__pvt_do_stepped_animate(menu->animation_holder, &end_tlp);else// 否则,立即执行动画__pvt_do_as_immediate(menu->animation_holder, &end_tlp);
}
// 进入子菜单并显示子菜单的内容
static CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_enterSub(CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu)
{// 缓存父菜单的图标状态uint8_t cached_icon_state = parentMenu->icon_state;// 获取父菜单的子菜单CCGraphic_Menu* subone = __pvt_current_owns_subMenu(parentMenu);// 如果没有子菜单,返回NULLif(!subone) return NULL;// 隐藏当前菜单parentMenu->operations.common.hide(parentMenu);// 恢复父菜单的图标状态parentMenu->icon_state = cached_icon_state;// 如果子菜单有图标,显示图标,否则显示子菜单if(subone->icon_state){subone->operations.showIcon(subone);}else{subone->operations.common.show(subone);}// 返回子菜单return subone;
}
// 返回父菜单并显示父菜单的内容
static CCGraphic_Menu* __pvt_backParent(CCGraphic_Menu* subMenu)
{// 缓存子菜单的图标状态uint8_t cached_icon_state = subMenu->icon_state;// 获取子菜单的父菜单CCGraphic_Menu* parentMenu = __pvt_owns_parent_current(subMenu);// 如果没有父菜单,返回NULLif(!parentMenu) return NULL;// 隐藏当前子菜单subMenu->operations.common.hide(subMenu);// 恢复子菜单的图标状态subMenu->icon_state = cached_icon_state;// 如果父菜单有图标,显示图标,否则显示父菜单if(parentMenu->icon_state){parentMenu->operations.showIcon(parentMenu);}else{parentMenu->operations.common.show(parentMenu);}// 返回父菜单return parentMenu;
}
完整的测试文件
现在来看看完整的测试文件!
#include "Test/OLED_TEST/oled_test.h"
#include "Test/GraphicTest/graphic_test.h"
#include "Graphic/widgets/components/CCGraphic_TextEdit/CCGraphic_TextEdit.h"
void test_oled_iic_functionalities()
{OLED_Handle handle;user_init_hard_iic_oled_handle(&handle);test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 1, 2);HAL_Delay(1000);test_clear(&handle);test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 2, 1);HAL_Delay(1000);test_clear(&handle);
}
void test_oled_spi_functionalities()
{OLED_Handle handle;user_init_hard_spi_oled_handle(&handle);test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 1, 2);HAL_Delay(1000);test_clear(&handle);test_set_pixel_line(&handle, 2, 1);HAL_Delay(1000);test_clear(&handle);
}
static void __helper_on_set_text(CCGraphicTextEdit* edit, char* sources, uint32_t shown_time)
{edit->operations.setText(edit, sources);HAL_Delay(shown_time * 1000);edit->operations.clear(edit);
}
#define SET_TEXT_CONV(SRC, SECS) do{ sources = SRC;\__helper_on_set_text(&edit, sources, SECS);}while(0)
static void __test_common(CCDeviceHandler* handler)
{CCGraphicTextEdit edit;CCGraphic_AsciiTextItem item;CCGraphic_Point p;p.x = 0;p.y = 0;CCGraphic_Size acceptablesize = CCGraphicWidget_MaxAcceptable_Size(handler);CCGraphicWidget_init_AsciiTextItem(&item, p, acceptablesize, ASCII_6x8);CCGraphic_init_CCGraphicTextEdit(&edit, handler, &item);edit.acquired_stepped_update = 1;char* sources;SET_TEXT_CONV("Hello! Welcome CCGraphic SimpleTest!", 5);SET_TEXT_CONV("If you see this sentences, ""it means that you have passed the GraphicTest""and congratulations!", 7);
SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On Base begin", 4);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Points", 4);on_test_draw_points(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Lines", 4);on_test_draw_line(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Circles", 4);on_test_draw_circle(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Rectangle", 4);on_test_draw_rectangle(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Triangle", 4);on_test_draw_triangle(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Ellipse", 4);on_test_draw_ellipse(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Arc", 4);on_test_draw_arc(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On Base end", 4);SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On widget begin", 4);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Image Drawing", 4);
/* widget test */on_test_draw_image(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Ascii Draw", 4);on_test_draw_ascii(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On widget end", 4);SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On component begin", 4);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test TextEdit", 4);/* components test */on_test_component_textEdit_test(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Frame", 4);on_test_component_frame_test(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Test Menu", 4);on_test_component_menu(handler);HAL_Delay(1000);SET_TEXT_CONV("Graphic Test On component end", 4);SET_TEXT_CONV("Finish Testing, enjoy!", 4);
}
void test_graphic_hardiic_functionalities()
{CCDeviceHandler handler;on_test_init_hardiic_oled(&handler);
__test_common(&handler);
}
void test_graphic_soft_spi_functionalities()
{CCDeviceHandler handler;on_test_init_softspi_oled(&handler);
__test_common(&handler);
}
void test_graphic_hard_spi_functionalities()
{CCDeviceHandler handler;on_test_init_hardspi_oled(&handler);
__test_common(&handler);
}
效果就是这个完整的测试视频:
完整测试视频
目录导览
总览
协议层封装
OLED设备封装
绘图设备抽象
基础图形库封装
基础组件实现
动态菜单组件实现
相关文章:
)
从0开始使用面对对象C语言搭建一个基于OLED的图形显示框架(动态菜单组件实现)
目录 面对对象C的程序设计(范例) 面对对象C的程序设计(应用) 进一步谈论我上面给出的代码——继承 实现一个面对对象的文本编辑器 所以,什么是继承 重申我们对菜单的抽象 抽象菜单项目 抽象菜单动画 实现菜单功…...

EtherCAT主站IGH-- 23 -- IGH之fsm_slave.h/c文件解析
EtherCAT主站IGH-- 23 -- IGH之fsm_slave.h/c文件解析 0 预览一 该文件功能`fsm_slave.c` 文件功能函数预览二 函数功能介绍`fsm_slave.c` 中主要函数的作用1. `ec_fsm_slave_init`2. `ec_fsm_slave_clear`3. `ec_fsm_slave_exec`4. `ec_fsm_slave_set_ready`5. `ec_fsm_slave_…...

windows10 配置使用json server作为图片服务器
步骤1:在vs code中安装json server, npm i -g json-server 注意:需要安装对应版本的json server,不然可能会报错,比如: npm i -g json-server 0.16.3 步骤2:出现如下报错: json-server 不是…...

Linux——网络(tcp)
文章目录 目录 文章目录 前言 一、TCP逻辑 1. 面向连接 三次握手(建立连接) 四次挥手(关闭连接) 2. 可靠性 3. 流量控制 4. 拥塞控制 5. 基于字节流 6. 全双工通信 7. 状态机 8. TCP头部结构 9. TCP的应用场景 二、编写tcp代码函数…...

腾讯云开发提供免费GPU服务
https://ide.cloud.tencent.com/dashboard/web 适用于推理场景,每个月10000分钟免费时长 166 小时 40 分钟 自带学术加速,速度还是不错的 白嫖 Tesla T4 16G 算力 显存:16GB 算力:8 TFlops SP CPU:8 核 内存&#…...

详解python的修饰符
Python 中的修饰符(Decorator)是一种用于修改或扩展函数或类行为的工具。它们本质上是一个函数,接受另一个函数或类作为参数,并返回一个新的函数或类。修饰符通常用于在不修改原函数或类代码的情况下,添加额外的功能。…...

《攻克语言密码:教AI理解隐喻与象征》
在自然语言处理(NLP)领域,让计算机理解人类语言中的隐喻和象征,是迈向更高语言理解水平的关键一步。从“时间就是金钱”这样的概念隐喻,到文学作品里象征着坚韧的“寒梅”,这些非字面意义的表达方式承载着丰…...

如何解除TikTok地区限制:实用方法解析
随着社交媒体的不断发展,TikTok作为一款短视频平台,已经在全球范围内吸引了数以亿计的用户。然而,不同地区对TikTok的使用权限存在一定的限制,这使得一些用户无法享受平台提供的完整内容和功能。 一、了解TikTok地区限制的原因 在…...
概率论基础知识-贝叶斯公式)
神经网络|(七)概率论基础知识-贝叶斯公式
【1】引言 前序我们已经了解了一些基础知识。 古典概型:有限个元素参与抽样,每个元素被抽样的概率相等。 条件概率:在某条件已经达成的前提下,新事件发生的概率。实际计算的时候,应注意区分,如果是计算综…...

《DeepSeek 网页/API 性能异常(DeepSeek Web/API Degraded Performance):网络安全日志》
DeepSeek 网页/API 性能异常(DeepSeek Web/API Degraded Performance)订阅 已识别 - 已识别问题,并且正在实施修复。 1月 29, 2025 - 20:57 CST 更新 - 我们将继续监控任何其他问题。 1月 28, 2025 - 22&am…...

使用Edu邮箱申请一年免费的.me域名
所需材料:公立Edu教育邮箱一枚(P.S:该服务不支持所有的Edu教育邮箱,仅支持比较知名的院校) 说到域名,.me这个后缀可谓是个性十足,适合个人网站、博客等。.me是黑山的国家顶级域名(c…...

【MCU】DFU、IAP、OTA
我发现很多人把几个概念都学混了,只记得一个升级了 DFU DFU (device firmware update)是指的 USB DFU,这个是 USB 的一个机制,可以升级设备的固件,可以去 USB-IF 查看规范文件。 OTA 全称为 Over-the-air update,利…...

2025.1.21——六、BUU XSS COURSE 1 XSS漏洞|XSS平台搭建
题目来源:buuctf BUU XSS COURSE 1 目录 一、打开靶机,整理信息 二、解题思路 step 1:输入框尝试一下 step 2:开始xss注入 step 3:搭建平台 step 4:利用管理员cookie访问地址 三、小结 二编&#…...

跟李沐学AI:视频生成类论文精读(Movie Gen、HunyuanVideo)
Movie Gen:A Cast of Media Foundation Models 简介 Movie Gen是Meta公司提出的一系列内容生成模型,包含了 3.2.1 预训练数据 Movie Gen采用大约 100M 的视频-文本对和 1B 的图片-文本对进行预训练。 图片-文本对的预训练流程与Meta提出的 Emu: Enh…...

7.抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)
抽象工厂与工厂方法极其类似,都是绕开new的,但是有些许不同。 动机 在软件系统中,经常面临着“一系列相互依赖的对象”的创建工作;同时,由于需求的变化,往往存在更多系列对象的创建工作。 假设案例 假设…...

python-leetcode-路径总和
112. 路径总和 - 力扣(LeetCode) # Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode: # def __init__(self, val0, leftNone, rightNone): # self.val val # self.left left # self.right right class Solution:de…...

WGCLOUD使用介绍 - 如何监控ActiveMQ和RabbitMQ
根据WGCLOUD官网的信息,目前没有针对ActiveMQ和RabbitMQ这两个组件专门做适配 不过可以使用WGCLOUD已经具备的通用监测模块:进程监测、端口监测或者日志监测、接口监测 来对这两个组件进行监控...

智能汽车网络安全威胁报告
近年来随着智能汽车技术的快速发展,针对智能汽车的攻击也逐渐从传统的针对单一车辆控制器的攻击转变为针对整车智能化服务的攻击,包括但不限于对远程控制应用程序的操控、云服务的渗透、智能座舱系统的破解以及对第三方应用和智能服务的攻击。随着WP.29 …...

WPS怎么使用latex公式?
1、下载并安装mathtype https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43135178/article/details/125143654?sharetypeblogdetail&sharerId125143654&sharereferPC&sharesourceweixin_43135178&spm1011.2480.3001.8118 2、将mathtype嵌入在WPS MathType面板嵌入器,免费工具…...

Cyber Security 101-Build Your Cyber Security Career-Security Principles(安全原则)
了解安全三元组以及常见的安全模型和原则。 任务1:介绍 安全已成为一个流行词;每家公司都想声称其产品或服务是安全的。但事实真的如此吗? 在我们开始讨论不同的安全原则之前,了解我们正在保护资产的对手至关重要。您是否试图阻止蹒跚学步…...

java_网络服务相关_gateway_nacos_feign区别联系
1. spring-cloud-starter-gateway 作用:作为微服务架构的网关,统一入口,处理所有外部请求。 核心能力: 路由转发(基于路径、服务名等)过滤器(鉴权、限流、日志、Header 处理)支持负…...

【OSG学习笔记】Day 18: 碰撞检测与物理交互
物理引擎(Physics Engine) 物理引擎 是一种通过计算机模拟物理规律(如力学、碰撞、重力、流体动力学等)的软件工具或库。 它的核心目标是在虚拟环境中逼真地模拟物体的运动和交互,广泛应用于 游戏开发、动画制作、虚…...

AI Agent与Agentic AI:原理、应用、挑战与未来展望
文章目录 一、引言二、AI Agent与Agentic AI的兴起2.1 技术契机与生态成熟2.2 Agent的定义与特征2.3 Agent的发展历程 三、AI Agent的核心技术栈解密3.1 感知模块代码示例:使用Python和OpenCV进行图像识别 3.2 认知与决策模块代码示例:使用OpenAI GPT-3进…...

Python爬虫实战:研究feedparser库相关技术
1. 引言 1.1 研究背景与意义 在当今信息爆炸的时代,互联网上存在着海量的信息资源。RSS(Really Simple Syndication)作为一种标准化的信息聚合技术,被广泛用于网站内容的发布和订阅。通过 RSS,用户可以方便地获取网站更新的内容,而无需频繁访问各个网站。 然而,互联网…...

Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析
Java求职者面试指南:Spring、Spring Boot、MyBatis框架与计算机基础问题解析 一、第一轮提问(基础概念问题) 1. 请解释Spring框架的核心容器是什么?它在Spring中起到什么作用? Spring框架的核心容器是IoC容器&#…...

代码随想录刷题day30
1、零钱兑换II 给你一个整数数组 coins 表示不同面额的硬币,另给一个整数 amount 表示总金额。 请你计算并返回可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。如果任何硬币组合都无法凑出总金额,返回 0 。 假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。 题目数据保证结果符合 32 位带…...

vulnyx Blogger writeup
信息收集 arp-scan nmap 获取userFlag 上web看看 一个默认的页面,gobuster扫一下目录 可以看到扫出的目录中得到了一个有价值的目录/wordpress,说明目标所使用的cms是wordpress,访问http://192.168.43.213/wordpress/然后查看源码能看到 这…...

python爬虫——气象数据爬取
一、导入库与全局配置 python 运行 import json import datetime import time import requests from sqlalchemy import create_engine import csv import pandas as pd作用: 引入数据解析、网络请求、时间处理、数据库操作等所需库。requests:发送 …...
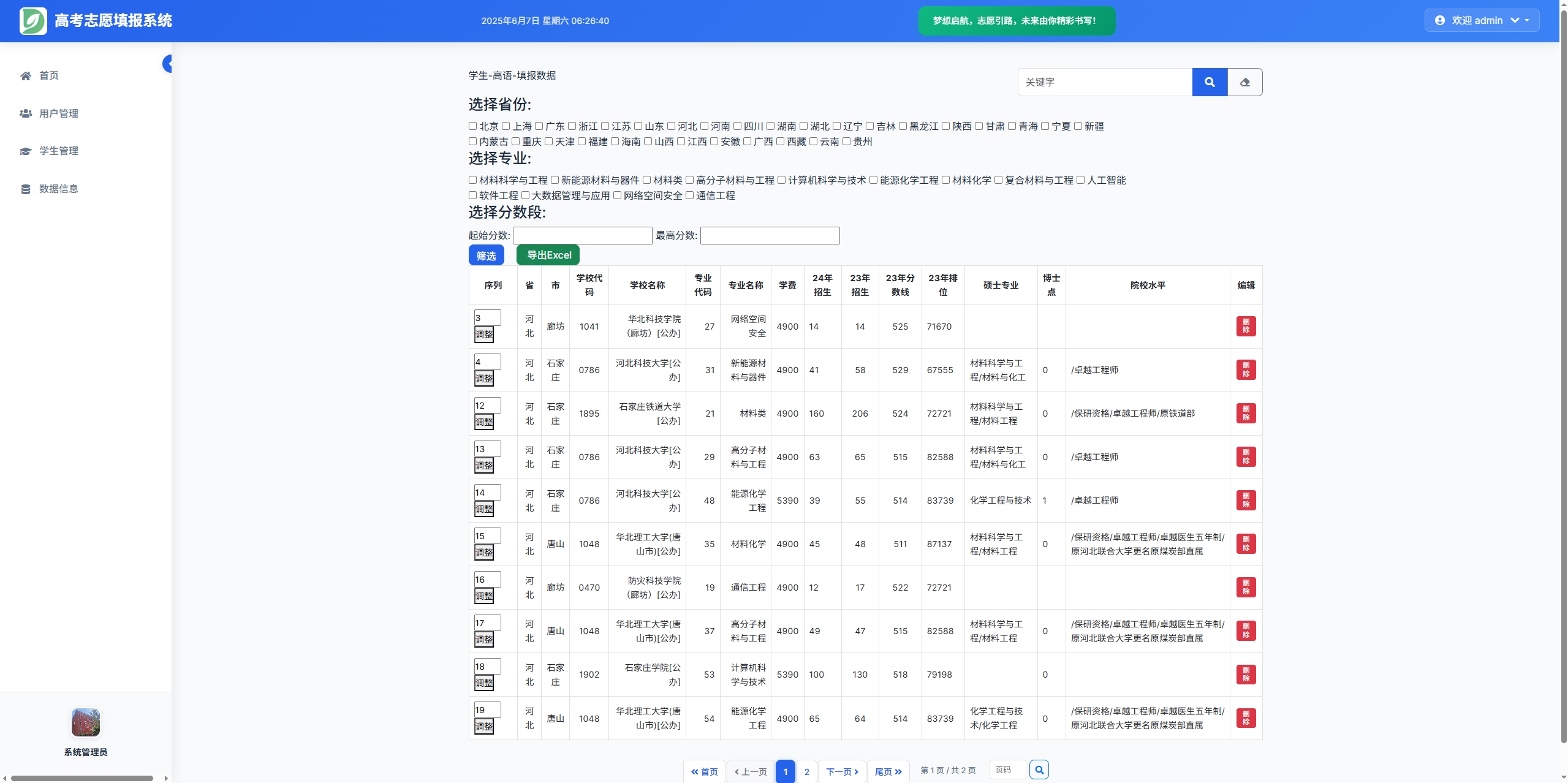
高考志愿填报管理系统---开发介绍
高考志愿填报管理系统是一款专为教育机构、学校和教师设计的学生信息管理和志愿填报辅助平台。系统基于Django框架开发,采用现代化的Web技术,为教育工作者提供高效、安全、便捷的学生管理解决方案。 ## 📋 系统概述 ### 🎯 系统定…...

【WebSocket】SpringBoot项目中使用WebSocket
1. 导入坐标 如果springboot父工程没有加入websocket的起步依赖,添加它的坐标的时候需要带上版本号。 <dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId> </dep…...
