【pytest框架源码分析二】pluggy源码分析之add_hookspecs和register
这里我们看一下_manager.py里的类和方法,最主要的是PluginManager类,类的初始化函数如下:
class PluginManager:"""Core class which manages registration of plugin objects and 1:N hookcalling.You can register new hooks by calling :meth:`add_hookspecs(module_or_class)<PluginManager.add_hookspecs>`.You can register plugin objects (which contain hook implementations) bycalling :meth:`register(plugin) <PluginManager.register>`.For debugging purposes you can call :meth:`PluginManager.enable_tracing`which will subsequently send debug information to the trace helper.:param project_name:The short project name. Prefer snake case. Make sure it's unique!"""def __init__(self, project_name: str) -> None:#: The project name.self.project_name: Final = project_nameself._name2plugin: Final[dict[str, _Plugin]] = {}self._plugin_distinfo: Final[list[tuple[_Plugin, DistFacade]]] = []#: The "hook relay", used to call a hook on all registered plugins.#: See :ref:`calling`.self.hook: Final = HookRelay()#: The tracing entry point. See :ref:`tracing`.self.trace: Final[_tracing.TagTracerSub] = _tracing.TagTracer().get("pluginmanage")self._inner_hookexec = _multicall
简单介绍下几个参数:
project_name: 项目名,同一个项目使用一个project name即可
_name2plugin:字典类型,用于存放插件名和插件的对应关系
_plugin_distinfo:存放了plugin及其distributions
hook:hook_relay实例,用于调用plugin
trace:与主流程无关,暂时用不上
_inner_hookexec :调用的_multicall函数,其在_call.py里,被注册的插件执行及结果返回逻辑都在这里面,我们后面具体看下。
接下来我们看下add_hookspecs和register方法,这两个是添加plugin的主要方法。前面我们介绍了hook中的HookspecMarker和HookimplMarker这两个装饰器,其实对hook来说,spec可以看作接口,impl是接口的实现,对应到add_hookspecs是添加hook的接口,register是添加实现的方法。这里我们简单举个例子:
import pluggyspec_test = pluggy.HookspecMarker('test11')
impl_test = pluggy.HookimplMarker('test11')# 定义spec类,相当于接口类,无具体内容
class Spec:@spec_testdef pluggy_test(self, arg1):print(f'this is spec test and arg is {arg1}')pass# 定义impl类,相当于实现类,具体内容在这里定义
class Impl1:@impl_testdef pluggy_test(self, arg1):print(f'this is test1 and arg is {arg1}')return arg1class Impl2:@impl_testdef pluggy_test(self, arg1):print(f'this is test2 and arg is {arg1}')return -1 * arg1pm = pluggy.PluginManager('test11')
pm.add_hookspecs(Spec)
pm.register(Impl1())
pm.register(Impl2())
res = pm.hook.pluggy_test(arg1=1)
print(res)
返回为
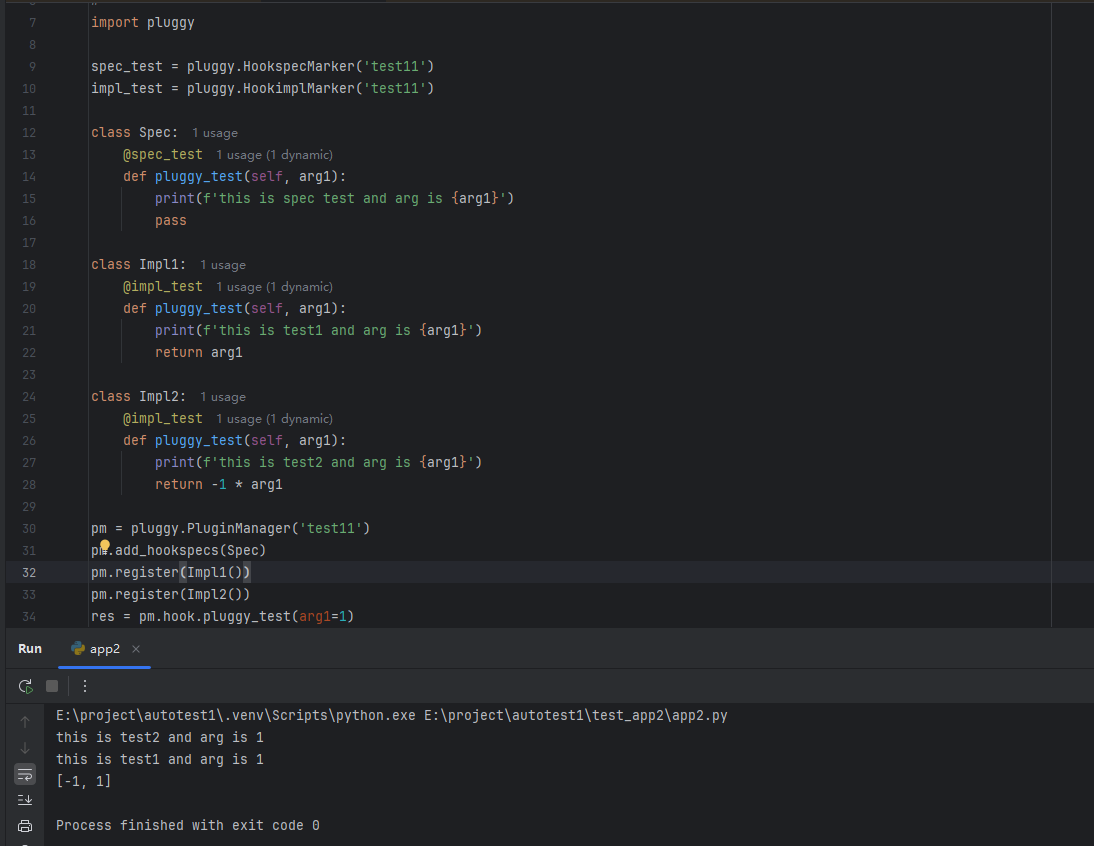
这里可以看出初始化pm后,先add_hookspecs,再register具体的实现,调用时,未打印sepc类中的内容,只打印了impl类中的内容,并且后注册的先执行。这就是pluggin的注册执行的大概流程,接下来看下具体的代码。
def add_hookspecs(self, module_or_class: _Namespace) -> None:"""Add new hook specifications defined in the given ``module_or_class``.Functions are recognized as hook specifications if they have beendecorated with a matching :class:`HookspecMarker`."""names = []for name in dir(module_or_class):spec_opts = self.parse_hookspec_opts(module_or_class, name)if spec_opts is not None:hc: HookCaller | None = getattr(self.hook, name, None)if hc is None:hc = HookCaller(name, self._hookexec, module_or_class, spec_opts)setattr(self.hook, name, hc)else:# Plugins registered this hook without knowing the spec.hc.set_specification(module_or_class, spec_opts)for hookfunction in hc.get_hookimpls():self._verify_hook(hc, hookfunction)names.append(name)if not names:raise ValueError(f"did not find any {self.project_name!r} hooks in {module_or_class!r}")
add_hookspecs方法输入参数为module_or_class,即为module或者class,上面我举的例子是一个class,也可以是一个模块,如pytest就是入参了一个_pytest.hookspec,hookspec为pytest的一个py文件,用于添加spec。
接下来是具体的方法,定义了一个names的list,然后dir(module_or_class) 查看我们入参模块或者类的所有属性和方法(dir()内置函数,可查看所有属性和方法,注意这里是属性名和方法名,是str类型的,不是直接的方法),然后进入parse_hookspec_opts(module_or_class, name)方法
def parse_hookspec_opts(self, module_or_class: _Namespace, name: str) -> HookspecOpts | None:"""Try to obtain a hook specification from an item with the given namein the given module or class which is being searched for hook specs.:returns:The parsed hookspec options for defining a hook, or None to skip thegiven item.This method can be overridden by ``PluginManager`` subclasses tocustomize how hook specifications are picked up. By default, returns theoptions for items decorated with :class:`HookspecMarker`."""method = getattr(module_or_class, name)opts: HookspecOpts | None = getattr(method, self.project_name + "_spec", None)return opts
这个方法首先根据name名获取了对应的方法,然后根据获取了方法的project_name + "_spec"的属性,HookspecOpts在_hook中有定义,这里我们前面讲过在HookspecMarker的__call__方法中有设置这个属性,所有加了HookspecMarker注解的方法都自动加了这个属性。

有这个属性的方法会返回对应的HookspecOpts,没的则返回None。add_hookspecs方法接着判断spec_opts如果不是None,去hook中根据名称获取对应的HookCaller,如果没有就返回None,一般我们添加时都是没有的,会返回None,这是再判断hc也是None,我们就给hook里添加一个。
hc = HookCaller(name, self._hookexec, module_or_class, spec_opts)
setattr(self.hook, name, hc)
如果hc不是None,这里其实就是plugin已经注册了,但是spec不是我们当前添加的这个spec。则进一步处理,进入set_specification(module_or_class, spec_opts)方法。
def set_specification(self,specmodule_or_class: _Namespace,spec_opts: HookspecOpts,) -> None:if self.spec is not None:raise ValueError(f"Hook {self.spec.name!r} is already registered "f"within namespace {self.spec.namespace}")self.spec = HookSpec(specmodule_or_class, self.name, spec_opts)if spec_opts.get("historic"):self._call_history = []
如果spec不是None,则抛错(刚初始化的HookCaller其spec都是None,一般设置过才不是None),如果是None,则设置对应的spec。这边还涉及到historic参数,我们后面再捋捋。回到add_hookspecs方法,下一步就是校验_verify_hook,这个方法register时再一起看。最后把所有符合要求的name放到names里(即加了spec装饰器的方法),最后判断下names是不是为空,为空则抛错。
接下来看下register方法
def register(self, plugin: _Plugin, name: str | None = None) -> str | None:"""Register a plugin and return its name.:param name:The name under which to register the plugin. If not specified, aname is generated using :func:`get_canonical_name`.:returns:The plugin name. If the name is blocked from registering, returns``None``.If the plugin is already registered, raises a :exc:`ValueError`."""plugin_name = name or self.get_canonical_name(plugin)if plugin_name in self._name2plugin:if self._name2plugin.get(plugin_name, -1) is None:return None # blocked plugin, return None to indicate no registrationraise ValueError("Plugin name already registered: %s=%s\n%s"% (plugin_name, plugin, self._name2plugin))if plugin in self._name2plugin.values():raise ValueError("Plugin already registered under a different name: %s=%s\n%s"% (plugin_name, plugin, self._name2plugin))# XXX if an error happens we should make sure no state has been# changed at point of returnself._name2plugin[plugin_name] = plugin# register matching hook implementations of the pluginfor name in dir(plugin):hookimpl_opts = self.parse_hookimpl_opts(plugin, name)if hookimpl_opts is not None:normalize_hookimpl_opts(hookimpl_opts)method: _HookImplFunction[object] = getattr(plugin, name)hookimpl = HookImpl(plugin, plugin_name, method, hookimpl_opts)name = hookimpl_opts.get("specname") or namehook: HookCaller | None = getattr(self.hook, name, None)if hook is None:hook = HookCaller(name, self._hookexec)setattr(self.hook, name, hook)elif hook.has_spec():self._verify_hook(hook, hookimpl)hook._maybe_apply_history(hookimpl)hook._add_hookimpl(hookimpl)return plugin_name
方法入参为一个plugin对象和name,如果有name传入,则plugin_name取name,否则根据plugin取name
def get_canonical_name(self, plugin: _Plugin) -> str:"""Return a canonical name for a plugin object.Note that a plugin may be registered under a different namespecified by the caller of :meth:`register(plugin, name) <register>`.To obtain the name of a registered plugin use :meth:`get_name(plugin)<get_name>` instead."""name: str | None = getattr(plugin, "__name__", None)return name or str(id(plugin))
get_canonical_name中直接取了plugin的__name__,如果这个__name__不存在则取其对象的id(id是python中判断身份的唯一标识,任何对象都会有自己的id,判断两个对象是否为同一个就是通过id这个内置函数判断的)。接下来判断plugin_name是否在_name2plugin中,如果在且其值为None时,说明被block了,直接返回,不为None时则抛错:插件已注册。
第二个判断plugin是否在_name2plugin中,由于上面已经判断过其name是否在_name2plugin这个dict中,走到这里说明其name这个key不在,如果plugin这个value在,说明plugin使用其他name注册了,抛出报错。
接下来self._name2plugin[plugin_name] = plugin往_name2plugin存ket-value。
最后遍历plugin中的所有方法,根据方法名在 self.parse_hookimpl_opts(plugin, name)获取对应的opts参数,
def parse_hookimpl_opts(self, plugin: _Plugin, name: str) -> HookimplOpts | None:"""Try to obtain a hook implementation from an item with the given namein the given plugin which is being searched for hook impls.:returns:The parsed hookimpl options, or None to skip the given item.This method can be overridden by ``PluginManager`` subclasses tocustomize how hook implementation are picked up. By default, returns theoptions for items decorated with :class:`HookimplMarker`."""method: object = getattr(plugin, name)if not inspect.isroutine(method):return Nonetry:res: HookimplOpts | None = getattr(method, self.project_name + "_impl", None)except Exception:res = {} # type: ignore[assignment]if res is not None and not isinstance(res, dict):# false positiveres = None # type:ignore[unreachable]return res
这个方法和上面parse_hookspec_opts方法类似,也是先获取方法,然后获取方法中的self.project_name + "_impl"属性,如果没有则返回None,加了HookimplMarker装饰器的都会有这个属性。所以hookspec_opts不是None时,进入下一步,normalize_hookimpl_opts设置hookspec_opts的默认值。
def normalize_hookimpl_opts(opts: HookimplOpts) -> None:opts.setdefault("tryfirst", False)opts.setdefault("trylast", False)opts.setdefault("wrapper", False)opts.setdefault("hookwrapper", False)opts.setdefault("optionalhook", False)opts.setdefault("specname", None)
接下来去plugin根据name获取对应的方法,找到方法后,实例化HookImpl对象,name取hookimpl_opts.get(“specname”) or name,使用装饰器时,我们可以添加这个specname参数(添加则取它,不添则不取),HookCaller则根据name到self.hook中取。
如果hook为空(即未根据name获取到HookCaller),则重新实例化一个HookCaller对象,并且添加到self.hook中去,如果hook存在,则进入_verify_hook方法
def _verify_hook(self, hook: HookCaller, hookimpl: HookImpl) -> None:if hook.is_historic() and (hookimpl.hookwrapper or hookimpl.wrapper):raise PluginValidationError(hookimpl.plugin,"Plugin %r\nhook %r\nhistoric incompatible with yield/wrapper/hookwrapper"% (hookimpl.plugin_name, hook.name),)assert hook.spec is not Noneif hook.spec.warn_on_impl:_warn_for_function(hook.spec.warn_on_impl, hookimpl.function)# positional arg checkingnotinspec = set(hookimpl.argnames) - set(hook.spec.argnames)if notinspec:raise PluginValidationError(hookimpl.plugin,"Plugin %r for hook %r\nhookimpl definition: %s\n""Argument(s) %s are declared in the hookimpl but ""can not be found in the hookspec"% (hookimpl.plugin_name,hook.name,_formatdef(hookimpl.function),notinspec,),)if hook.spec.warn_on_impl_args:for hookimpl_argname in hookimpl.argnames:argname_warning = hook.spec.warn_on_impl_args.get(hookimpl_argname)if argname_warning is not None:_warn_for_function(argname_warning, hookimpl.function)if (hookimpl.wrapper or hookimpl.hookwrapper) and not inspect.isgeneratorfunction(hookimpl.function):raise PluginValidationError(hookimpl.plugin,"Plugin %r for hook %r\nhookimpl definition: %s\n""Declared as wrapper=True or hookwrapper=True ""but function is not a generator function"% (hookimpl.plugin_name, hook.name, _formatdef(hookimpl.function)),)if hookimpl.wrapper and hookimpl.hookwrapper:raise PluginValidationError(hookimpl.plugin,"Plugin %r for hook %r\nhookimpl definition: %s\n""The wrapper=True and hookwrapper=True options are mutually exclusive"% (hookimpl.plugin_name, hook.name, _formatdef(hookimpl.function)),)
这个方法有如下几个判断:
1.首先判断了hook的is_historic和wrapper参数,这些参数不能同时为true。
2.然后判断了下hook.spec不能为None,这个在register方法中已经判断过,可能是担心其他地方又使用到,重新判断了下。
3.warn_on_impl如果为true,则warn一下。
4.接下来判断了下hookimpl中的参数是否比spec中的多,如果多会报错。
5.再下面还是关于warn的,这个和上面那个warn类似,只是这个是针对特定参数的。
6.判断hookwrapper参数为true的时候,其实现的方法是不是生成器方法,即方法中是不是yield返回的
7.最后判断了下hookwrapper和wrapper是不是同时为true,如果是,则报错。hookwrapper和wrapper是新旧版本的不同名称,只要用一个参数即可
然后进入_maybe_apply_history方法
def _maybe_apply_history(self, method: HookImpl) -> None:"""Apply call history to a new hookimpl if it is marked as historic."""if self.is_historic():assert self._call_history is not Nonefor kwargs, result_callback in self._call_history:res = self._hookexec(self.name, [method], kwargs, False)if res and result_callback is not None:# XXX: remember firstresult isn't compat with historicassert isinstance(res, list)result_callback(res[0])
开始判断了下is_historic是否为true,是的话确认下_call_history 是否为None(一般is_historic为true时,_call_history 会被初始为[]),然后遍历了下_call_history,在res and result_callback都不是None的情况下,result_callback(res[0])。historic这部分后面一起串起来看。
这时主方法到了_add_hookimpl这里。
def _add_hookimpl(self, hookimpl: HookImpl) -> None:"""Add an implementation to the callback chain."""for i, method in enumerate(self._hookimpls):if method.hookwrapper or method.wrapper:splitpoint = ibreakelse:splitpoint = len(self._hookimpls)if hookimpl.hookwrapper or hookimpl.wrapper:start, end = splitpoint, len(self._hookimpls)else:start, end = 0, splitpointif hookimpl.trylast:self._hookimpls.insert(start, hookimpl)elif hookimpl.tryfirst:self._hookimpls.insert(end, hookimpl)else:# find last non-tryfirst methodi = end - 1while i >= start and self._hookimpls[i].tryfirst:i -= 1self._hookimpls.insert(i + 1, hookimpl)
1.这个方法开始先是查询有多少wrapper为true的impl方法,在wrapper和非wrapper方法数组中找到分界点。这个数组中wrapper和非wrapper方法是分在前后两部分的,互不交叉。
2.然后判断新增的impl的wrapper是否为true,如果是true,则插入到分界点到数组末尾这段,如果不是true,则插到0到分界点这个位置。
3.在判断有无设置trylast或者tryfirst,如果有trylast则放到数组开头,如果是tryfirst,则放到数组末尾;如果都没有,则放到当前段tryfirst那一段的前一个。(越靠前的后执行,越靠后的先执行)
到这里就register完成了。
相关文章:

【pytest框架源码分析二】pluggy源码分析之add_hookspecs和register
这里我们看一下_manager.py里的类和方法,最主要的是PluginManager类,类的初始化函数如下: class PluginManager:"""Core class which manages registration of plugin objects and 1:N hookcalling.You can register new hoo…...

四、数据存储
在爬虫项目中,我们需要将目标站点数据进行持久化保存,一般数据保存的方式有两种: 文件保存数据库保存 在数据保存的过程中需要对数据完成去重操作,所有需要使用 redis 中的 set 数据类型完成去重。 1.CSV文件存储 1.1 什么是c…...

【原创】Ollama Test API For Linux/MacOS/Unix
安装Json解析工具 Linux/Unix sudo apt-get install jq -yMacOS brew install jq -y设置环境变量 export IP"192.168.250.229" export PORT"8080" export MODEL"deepseek-r1:7b"检查Ollama版本 curl http://"$IP":"$PORT&qu…...

LeetCode-Hot100-005盛最多水的容器
不懂的可以在评论区问我。 代码 双指针,开始的时候一个在最左边,一个在最右边。每次移动矮的那头,因为这是矮柱子作为容器能装的水的极限了。 class Solution { public:int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {int left 0; int rig…...

电源测试系统有哪些可以利用AI工具的科技??
AI技术的发展对电源模块测试系统的影响是深远的,不仅协助系统提升了测试效率和精度,还推动了测试方法的创新和智能化。那么在电源测试系统中哪些模块可以利用AI工具实现自动化测试? 1. 自动化测试与效率提升 智能测试流程优化 AI算法可以自动优化测试…...

【3-3】springcloud
OpenFeign 启动OpenFeign 定义客户端接口 注入客户端并使用 OpenFeignhttp调用ribbon负载均衡 gateway 来自:https://mynamelancelot.github.io/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-gateway.html#cors https://blog.csdn.net/qingdao666666/article/details/119973771 …...

Goby 漏洞安全通告| Ollama /api/tags 未授权访问漏洞(CNVD-2025-04094)
漏洞名称:Ollama /api/tags 未授权访问漏洞(CNVD-2025-04094) English Name:Ollama /api/tags Unauthorized Access Vulnerability (CNVD-2025-04094) CVSS core: 6.5 风险等级: 中风险 漏洞描述: O…...

Debian 包版本号比较规则详解
1 版本号组成结构 Debian 版本号格式为:[epoch:]upstream_version[-debian_revision] 示例:2:1.18.3~betadfsg1-5b1 组件说明比较优先级Epoch冒号前的数字 (2:)最高Upstream主版本 (1.18.3~betadfsg1)中Debian修订号减号后的部分 (5)最…...

009---基于Verilog HDL的单比特信号边沿检测
文章目录 摘要一、边沿检测二、时序逻辑实现2.1 rtl2.2 tb 三、组合逻辑实现3.1 rtl3.2 tb 摘要 文章为学习记录。采用时序逻辑和组合逻辑实现边沿检测的核心逻辑。组合逻辑实现的上升沿和下降沿的脉冲比时序逻辑实现的上升沿和下降沿的脉冲提前一拍。 一、边沿检测 边沿检测…...

2025全开源Java多语言跨境电商外贸商城/Tk/FB内嵌商城I商家入驻I批量下单I完美运行
商城程序介绍: 2025全新版UI 新增全球多站点选择 PC端:vueelementui 用户端使用:uniapp 管理端使用:vueelementui 后台服务使用:springbootmybatisplusmysql 商城功能介绍: 商城含21种语言 代理…...

iOS实现一个强大的本地状态记录容器
我们开发中经常会遇到这样的场景,就是我们客户端用户进行了某个操作,这个操作影响了数据的状态,但是我们又不方便重新请求一次数据, 这个时候,就需要我们记录一下本地状态在内存中,随着业务越来越复杂&…...

【mysql】有索引和没有索引字段更新时锁的不同
结论 对于有索引的的字段作为更新条件,如果更加语句用上了索引,那么只会在对于的更新字段的索引和对于记录的主键索引上加上x锁 如果更新字段没有索引,由于需要全部扫描,那么就会给所有主键索引加上x,导致其他事务的更…...

机器学习的三个基本要素
机器学习的基本要素包括模型、学习准则(策略)和优化算法三个部分。机器学习方法之间的不同,主要来自其模型、学习准则(策略)、优化算法的不同。 模型 机器学习首要考虑的问题是学习什么样的模型(Model&am…...

神经机器翻译:联合学习对齐和翻译
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 摘要 神经机器翻译是最近提出的机器翻译方法。与传统的统计机器翻译不同,神经机器翻译旨在构建一个可以联合调整以最大化翻译性能的单一神经网络。最近为神经机器翻译提出的模型通常属于编码…...

[Web 安全] PHP 反序列化漏洞 —— PHP 魔术方法
关注这个专栏的其他相关笔记:[Web 安全] 反序列化漏洞 - 学习笔记-CSDN博客 PHP 魔术方法 - 简介 - PHP 魔术方法 - 简单教程,简单编程PHP 中,以两个下划线 ( __ ) 开头方法称之为 「 魔术方法 」 这些 「 魔术方法 」 在 [PHP](/l/yufei/php…...

聆听PostgreSQL数据库的使用
参考:(1)零基础入门PostgreSQL教程 (2)菜鸟教程 文章目录 一、PostgreSQL是什么?二、基本使用1.下载2.操作(1)数据库(2)表 一、PostgreSQL是什么?…...

2025嵌入式软件开发工程师--音频方向
一、选择题(每题3分,共30分) 1.以下哪个不是C语言中的关键字?( ) A. int B. Float C. Define D. Return 2.以下代码的输出是: ( ) inta 5, b 10; printf("%d“, a b); A. 15 B.16 …...

C#释放内存空间的方法
目录 前言释放 C# 对象内存的六种方法1、手动释放内存空间2、使用 Using 语句3、使用 垃圾回收器4、GC.Collect() 方法5、GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers() 方法6、WeakReference 类 注意 前言 当不再需要对象时释放内存空间对于防止内存泄漏和提高应用程序性能至关重要。C# 提供…...

《鸢尾花数学大系:从加减乘除到机器学习》开源资源
《鸢尾花数学大系:从加减乘除到机器学习》开源资源 Gitee:https://gitee.com/higkoo/ bilibili:https://space.bilibili.com/513194466 GitHub:https://github.com/Visualize-ML...

如何将一台服务器的pip环境迁移到另一个机器?
在没有网络的情况下,将一台服务器的 pip 环境迁移到另一台机器,可按以下步骤进行操作: 步骤一:在源服务器上导出已安装的包列表 在有网络且已安装所需 Python 包的源服务器上,使用以下命令导出已安装的 Python 包列表: pip freeze > requirements.txt该命令会将当前…...

在软件开发中正确使用MySQL日期时间类型的深度解析
在日常软件开发场景中,时间信息的存储是底层且核心的需求。从金融交易的精确记账时间、用户操作的行为日志,到供应链系统的物流节点时间戳,时间数据的准确性直接决定业务逻辑的可靠性。MySQL作为主流关系型数据库,其日期时间类型的…...

Linux链表操作全解析
Linux C语言链表深度解析与实战技巧 一、链表基础概念与内核链表优势1.1 为什么使用链表?1.2 Linux 内核链表与用户态链表的区别 二、内核链表结构与宏解析常用宏/函数 三、内核链表的优点四、用户态链表示例五、双向循环链表在内核中的实现优势5.1 插入效率5.2 安全…...

.Net框架,除了EF还有很多很多......
文章目录 1. 引言2. Dapper2.1 概述与设计原理2.2 核心功能与代码示例基本查询多映射查询存储过程调用 2.3 性能优化原理2.4 适用场景 3. NHibernate3.1 概述与架构设计3.2 映射配置示例Fluent映射XML映射 3.3 查询示例HQL查询Criteria APILINQ提供程序 3.4 高级特性3.5 适用场…...

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...

STM32+rt-thread判断是否联网
一、根据NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP位判断 static bool is_conncected(void) {struct netdev *dev RT_NULL;dev netdev_get_first_by_flags(NETDEV_FLAG_INTERNET_UP);if (dev RT_NULL){printf("wait netdev internet up...");return false;}else{printf("loc…...

oracle与MySQL数据库之间数据同步的技术要点
Oracle与MySQL数据库之间的数据同步是一个涉及多个技术要点的复杂任务。由于Oracle和MySQL的架构差异,它们的数据同步要求既要保持数据的准确性和一致性,又要处理好性能问题。以下是一些主要的技术要点: 数据结构差异 数据类型差异ÿ…...

拉力测试cuda pytorch 把 4070显卡拉满
import torch import timedef stress_test_gpu(matrix_size16384, duration300):"""对GPU进行压力测试,通过持续的矩阵乘法来最大化GPU利用率参数:matrix_size: 矩阵维度大小,增大可提高计算复杂度duration: 测试持续时间(秒&…...
)
Typeerror: cannot read properties of undefined (reading ‘XXX‘)
最近需要在离线机器上运行软件,所以得把软件用docker打包起来,大部分功能都没问题,出了一个奇怪的事情。同样的代码,在本机上用vscode可以运行起来,但是打包之后在docker里出现了问题。使用的是dialog组件,…...
)
Angular微前端架构:Module Federation + ngx-build-plus (Webpack)
以下是一个完整的 Angular 微前端示例,其中使用的是 Module Federation 和 npx-build-plus 实现了主应用(Shell)与子应用(Remote)的集成。 🛠️ 项目结构 angular-mf/ ├── shell-app/ # 主应用&…...

Hive 存储格式深度解析:从 TextFile 到 ORC,如何选对数据存储方案?
在大数据处理领域,Hive 作为 Hadoop 生态中重要的数据仓库工具,其存储格式的选择直接影响数据存储成本、查询效率和计算资源消耗。面对 TextFile、SequenceFile、Parquet、RCFile、ORC 等多种存储格式,很多开发者常常陷入选择困境。本文将从底…...
