跟着 Lua 5.1 官方参考文档学习 Lua (10)
文章目录
- 5.2 – Coroutine Manipulation
- `coroutine.create (f)`
- `coroutine.resume (co [, val1, ···])`
- `coroutine.running ()`
- `coroutine.status (co)`
- 例子:**协程的状态**
- `coroutine.wrap (f)`
- `coroutine.yield (···)`
- 5.3 – Modules
- `module (name [, ···])`
- `require (modname)`
- `package.loaded`
- `package.loaders`
- `package.preload`
- `package.path`
- `package.cpath`
- `package.loadlib (libname, funcname)`
- 例子:package.loadlib 的使用
- `package.seeall (module)`
- 5.4 – String Manipulation
- `string.byte (s [, i [, j]])`
- `string.char (···)`
- 例子:string.byte 和 string.char 的使用
- `string.format (formatstring, ···)`
- 例子:string.format 的使用
- `string.len (s)`
- `string.lower (s)`
- `string.upper (s)`
- `string.rep (s, n)`
- `string.reverse (s)`
- `string.sub (s, i [, j])`
- `string.dump (function)`
5.2 – Coroutine Manipulation
The operations related to coroutines comprise a sub-library of the basic library and come inside the table coroutine. See §2.11 for a general description of coroutines.
coroutine.create (f)
Creates a new coroutine, with body f. f must be a Lua function. Returns this new coroutine, an object with type "thread".
coroutine.resume (co [, val1, ···])
Starts or continues the execution of coroutine co. The first time you resume a coroutine, it starts running its body. The values val1, ··· are passed as the arguments to the body function. If the coroutine has yielded, resume restarts it; the values val1, ··· are passed as the results from the yield.
If the coroutine runs without any errors, resume returns true plus any values passed to yield (if the coroutine yields) or any values returned by the body function (if the coroutine terminates). If there is any error, resume returns false plus the error message.
coroutine.running ()
Returns the running coroutine, or nil when called by the main thread.
coroutine.status (co)
Returns the status of coroutine co, as a string:
"running", if the coroutine is running (that is, it called status);
"suspended", if the coroutine is suspended in a call to yield, or if it has not started running yet;
"normal" if the coroutine is active but not running (that is, it has resumed another coroutine);
and "dead" if the coroutine has finished its body function, or if it has stopped with an error.
例子:协程的状态
-- 创建一个协程
local co
co = coroutine.create(function()print("协程1开始执行")-- 检查协程状态,应该是runningprint("协程1状态: " .. coroutine.status(co)) -- "running"local co2 = coroutine.create(function()print("协程2开始执行")print("协程2里的协程1状态: " .. coroutine.status(co)) -- "normal"print("协程2执行结束")end)-- 启动协程2coroutine.resume(co2)coroutine.yield() -- 暂停协程print("协程1恢复执行")
end)-- 初始状态:协程被创建但未执行,所以状态是"suspended"
print("协程1初始状态: " .. coroutine.status(co)) -- "suspended"-- 启动协程
coroutine.resume(co)-- 在协程内部调用status,应该输出"running"
-- 输出会在协程内部看到,表明此时协程正在执行
print("协程1执行后,状态: " .. coroutine.status(co)) -- "suspended"(外部查看状态,仍然是suspended)-- 恢复协程
coroutine.resume(co)-- 最后,协程结束,状态变为"dead"
print("协程1结束后的状态: " .. coroutine.status(co)) -- "dead"输出
协程1初始状态: suspended
协程1开始执行
协程1状态: running
协程2开始执行
协程2里的协程1状态: normal
协程2执行结束
协程1执行后,状态: suspended
协程1恢复执行
协程1结束后的状态: dead
coroutine.wrap (f)
Creates a new coroutine, with body f. f must be a Lua function. Returns a function that resumes the coroutine each time it is called. Any arguments passed to the function behave as the extra arguments to resume. Returns the same values returned by resume, except the first boolean. In case of error, propagates the error.
coroutine.yield (···)
Suspends the execution of the calling coroutine. The coroutine cannot be running a C function, a metamethod, or an iterator. Any arguments to yield are passed as extra results to resume.
协程的例子见这篇文章
5.3 – Modules
The package library provides basic facilities for loading and building modules in Lua. It exports two of its functions directly in the global environment: require and module. Everything else is exported in a table package.
module (name [, ···])
忽略,基本不使用
require (modname)
Loads the given module. The function starts by looking into the package.loaded table to determine whether modname is already loaded. If it is, then require returns the value stored at package.loaded[modname]. Otherwise, it tries to find a loader for the module.
To find a loader, require is guided by the package.loaders array. By changing this array, we can change how require looks for a module. The following explanation is based on the default configuration for package.loaders.【见package.loaders中的说明】
First require queries package.preload[modname]. If it has a value, this value (which should be a function) is the loader. Otherwise require searches for a Lua loader using the path stored in package.path. If that also fails, it searches for a C loader using the path stored in package.cpath. If that also fails, it tries an all-in-one loader (see package.loaders).
Once a loader is found, require calls the loader with a single argument, modname. If the loader returns any value, require assigns the returned value to package.loaded[modname]. If the loader returns no value and has not assigned any value to package.loaded[modname], then require assigns true to this entry. In any case, require returns the final value of package.loaded[modname].
If there is any error loading or running the module, or if it cannot find any loader for the module, then require signals an error.
package.loaded
A table used by require to control which modules are already loaded. When you require a module modname and package.loaded[modname] is not false, require simply returns the value stored there.
package.loaders
A table used by require to control how to load modules.
Each entry in this table is a searcher function. When looking for a module, require calls each of these searchers in ascending order, with the module name (the argument given to require) as its sole parameter. The function can return another function (the module loader) or a string explaining why it did not find that module (or nil if it has nothing to say). Lua initializes this table with four functions.
The first searcher simply looks for a loader in the package.preload table.
The second searcher looks for a loader as a Lua library, using the path stored at package.path. A path is a sequence of templates separated by semicolons. For each template, the searcher will change each interrogation mark in the template by filename, which is the module name with each dot replaced by a “directory separator” (such as “/” in Unix); then it will try to open the resulting file name. So, for instance, if the Lua path is the string
"./?.lua;./?.lc;/usr/local/?/init.lua"
the search for a Lua file for module foo will try to open the files ./foo.lua, ./foo.lc, and /usr/local/foo/init.lua, in that order.
The third searcher looks for a loader as a C library, using the path given by the variable package.cpath. For instance, if the C path is the string
"./?.so;./?.dll;/usr/local/?/init.so"
the searcher for module foo will try to open the files ./foo.so, ./foo.dll, and /usr/local/foo/init.so, in that order. Once it finds a C library, this searcher first uses a dynamic link facility to link the application with the library. Then it tries to find a C function inside the library to be used as the loader. The name of this C function is the string “luaopen_” concatenated with a copy of the module name where each dot is replaced by an underscore. Moreover, if the module name has a hyphen, its prefix up to (and including) the first hyphen is removed. For instance, if the module name is a.v1-b.c, the function name will be luaopen_b_c.
The fourth searcher tries an all-in-one loader. It searches the C path for a library for the root name of the given module. For instance, when requiring a.b.c, it will search for a C library for a. If found, it looks into it for an open function for the submodule; in our example, that would be luaopen_a_b_c. With this facility, a package can pack several C submodules into one single library, with each submodule keeping its original open function.
package.preload
A table to store loaders for specific modules (see require).
package.path
The path used by require to search for a Lua loader.
At start-up, Lua initializes this variable with the value of the environment variable LUA_PATH or with a default path defined in luaconf.h, if the environment variable is not defined. Any “;;” in the value of the environment variable is replaced by the default path
package.cpath
The path used by require to search for a C loader.
Lua initializes the C path package.cpath in the same way it initializes the Lua path package.path, using the environment variable LUA_CPATH or a default path defined in luaconf.h.
package.loadlib (libname, funcname)
Dynamically links the host program with the C library libname. Inside this library, looks for a function funcname and returns this function as a C function. (So, funcname must follow the protocol (see lua_CFunction)).
This is a low-level function. It completely bypasses the package and module system. Unlike require, it does not perform any path searching and does not automatically adds extensions. libname must be the complete file name of the C library, including if necessary a path and extension. funcname must be the exact name exported by the C library (which may depend on the C compiler and linker used).
This function is not supported by ANSI C. As such, it is only available on some platforms (Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris, BSD, plus other Unix systems that support the dlfcn standard).
例子:package.loadlib 的使用
mylib.c
#include <lua.h>
#include <lauxlib.h>
#include <lualib.h>// C 函数:加法
int add(lua_State *L) {// 从栈中获取两个参数double a = luaL_checknumber(L, 1);double b = luaL_checknumber(L, 2);// 将结果推送到 Lua 栈上lua_pushnumber(L, a + b);return 1; // 返回一个结果
}// 导出函数
int luaopen_mylib(lua_State *L) {lua_register(L, "add", add); // 注册 add 函数return 0;
}编译
gcc -o mylib.so -shared mylib.c -fPIC -I/usr/local/include/luajit-2.1 -lluajit-5.1
lua代码
-- 使用 package.loadlib 加载共享库
local lib = package.loadlib("./mylib.so", "luaopen_mylib")-- 加载库后,调用返回的函数
lib() -- 这会注册 C 库中的 "add" 函数到 Lua 环境-- 调用 "add" 函数,传递两个数字
local result = add(10, 20)
print("结果:", result) -- 输出: 结果: 30package.seeall (module)
忽略,基本不使用
5.4 – String Manipulation
This library provides generic functions for string manipulation, such as finding and extracting substrings, and pattern matching. When indexing a string in Lua, the first character is at position 1 (not at 0, as in C). Indices are allowed to be negative and are interpreted as indexing backwards, from the end of the string. Thus, the last character is at position -1, and so on.
The string library provides all its functions inside the table string. It also sets a metatable for strings where the __index field points to the string table. Therefore, you can use the string functions in object-oriented style. For instance, string.byte(s, i) can be written as s:byte(i).
The string library assumes one-byte character encodings.
string.byte (s [, i [, j]])
Returns the internal numerical codes of the characters s[i], s[i+1], ···, s[j]. The default value for i is 1; the default value for j is i.
Note that numerical codes are not necessarily portable across platforms.
string.char (···)
Receives zero or more integers. Returns a string with length equal to the number of arguments, in which each character has the internal numerical code equal to its corresponding argument.
Note that numerical codes are not necessarily portable across platforms.
例子:string.byte 和 string.char 的使用
local bytes = { string.byte("hello", 1, #("hello")) }
for i, b in ipairs(bytes) doprint(b) -- 输出 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' 的字节值 104 101 108 108 111
endprint(string.char(104, 101, 108, 108, 111)) -- 输出 hello
string.format (formatstring, ···)
Returns a formatted version of its variable number of arguments following the description given in its first argument (which must be a string). The format string follows the same rules as the printf family of standard C functions. The only differences are that the options/modifiers *, l, L, n, p, and h are not supported and that there is an extra option, q. The q option formats a string in a form suitable to be safely read back by the Lua interpreter: the string is written between double quotes, and all double quotes, newlines, embedded zeros, and backslashes in the string are correctly escaped when written. For instance, the call
string.format('%q', 'a string with "quotes" and \n new line')
will produce the string:
"a string with \"quotes\" and \new line"
The options c, d, E, e, f, g, G, i, o, u, X, and x all expect a number as argument, whereas q and s expect a string.
This function does not accept string values containing embedded zeros, except as arguments to the q option.
%c - 接受一个数字,并将其转化为ASCII码表中对应的字符
%d, %i - 接受一个数字并将其转化为有符号的整数格式
%o - 接受一个数字并将其转化为八进制数格式
%u - 接受一个数字并将其转化为无符号整数格式
%x - 接受一个数字并将其转化为十六进制数格式,使用小写字母
%X - 接受一个数字并将其转化为十六进制数格式,使用大写字母
%e - 接受一个数字并将其转化为科学记数法格式,使用小写字母e
%E - 接受一个数字并将其转化为科学记数法格式,使用大写字母E
%f - 接受一个数字并将其转化为浮点数格式
%g(%G) - 接受一个数字并将其转化为%e(%E,对应%G)及%f中较短的一种格式
%q - 接受一个字符串并将其转化为可安全被Lua编译器读入的格式
%s - 接受一个字符串并按照给定的参数格式化该字符串
为进一步细化格式, 可以在%号后添加参数.参数将以如下的顺序读入:
(1) 符号:一个+号表示其后的数字转义符将让正数显示正号.默认情况下只有负数显示符号.
(2) 占位符: 一个0,在后面指定了字串宽度时占位用.不填时的默认占位符是空格.
(3) 对齐标识: 在指定了字串宽度时,默认为右对齐,增加-号可以改为左对齐.
(4) 宽度数值
(5) 小数位数/字串裁切:在宽度数值后增加的小数部分n,若后接f(浮点数转义符,如%6.3f)则设定该浮点数的小数只保留n位,若后接s(字符串转义符,如%5.3s)则设定该字符串只显示前n位.
在这些参数的后面则是上述所列的转义码类型(c, d, i, f, …).
例子:string.format 的使用
print(string.format("%%c: %c", 83)) -- %c: S
print(string.format("%+d", 17.0)) -- +17
print(string.format("%05d", 17)) -- 00017
print(string.format("%o", 17)) -- 21
print(string.format("%u", 3.14)) -- 3
print(string.format("%x", 13)) -- d
print(string.format("%X", 13)) -- D
print(string.format("%e", 1000)) -- 1.000000e+03
print(string.format("%E", 1000)) -- 1.000000E+03
print(string.format("%6.3f", 13)) -- 13.000
print(string.format("%s", "monkey")) -- monkey
print(string.format("%10s", "monkey")) -- monkey
print(string.format("%5.3s", "monkey")) -- mon
string.len (s)
Receives a string and returns its length. The empty string "" has length 0. Embedded zeros are counted, so "a\000bc\000" has length 5.
string.lower (s)
Receives a string and returns a copy of this string with all uppercase letters changed to lowercase. All other characters are left unchanged. The definition of what an uppercase letter is depends on the current locale.
string.upper (s)
Receives a string and returns a copy of this string with all lowercase letters changed to uppercase. All other characters are left unchanged. The definition of what a lowercase letter is depends on the current locale.
string.rep (s, n)
Returns a string that is the concatenation of n copies of the string s.
string.reverse (s)
Returns a string that is the string s reversed.
string.sub (s, i [, j])
Returns the substring of s that starts at i and continues until j; i and j can be negative. If j is absent, then it is assumed to be equal to -1 (which is the same as the string length). In particular, the call string.sub(s,1,j) returns a prefix of s with length j, and string.sub(s, -i) returns a suffix of s with length i.
string.dump (function)
Returns a string containing a binary representation of the given function, so that a later loadstring on this string returns a copy of the function. function must be a Lua function without upvalues.
相关文章:
)
跟着 Lua 5.1 官方参考文档学习 Lua (10)
文章目录 5.2 – Coroutine Manipulationcoroutine.create (f)coroutine.resume (co [, val1, ])coroutine.running ()coroutine.status (co)例子:**协程的状态** coroutine.wrap (f)coroutine.yield () 5.3 – Modulesmodule (name [, ])require (modname)package.…...

C++文档识别接口如何实现 高效办公
数字化信息爆炸时代,办公效率的提升成为企业和个人的迫切需求。人工智能技术的飞速发展,为我们带来了前所未有的便利,文档识别接口便是其中之一。 与传统的人工手动录入相比,文档识别接口优势显著。人工手动录入,不仅耗…...

【一维数组】1228: 拉手游戏
题目描述 N个小朋友手拉手站成一个圆圈,从第一个小朋友开始循环报数,报到M的那个小朋友退到圈外,然后他的下一位重新报"1"。这样继续下去,直到最后只剩下一个小朋友,他原来站在什么位置上呢? 输…...

准确--Centos最小化安装通过命令去修改ip和dns
在 CentOS 7 中,最小化安装后没有图形界面,你需要手动配置网络。可以按照以下步骤进行配置: 1. 查看网络接口名称 首先,查看当前的网络接口名称。你可以通过以下命令查看: ip addr在你提供的截图中,网络…...

FreeRTOS 任务间通信机制:队列、信号量、事件标志组详解与实验
1. FreeRTOS 消息队列 1.1 简介 队列是 任务间通信的主要形式,可用于在任务之间以及中断与任务之间传递消息。队列在 FreeRTOS 中具有以下关键特点: 队列默认采用 先进先出 FIFO 方式,也可以使用 xQueueSendToFront()实现 LIFO。FreeRT…...

TMS320F28P550SJ9学习笔记7:结构体寄存器方式配置SCI通信收发_SCI通信收发测试
今日尝试自己操作寄存器编写函数,使用SCI通信外设 发送与接收数据 文章提供测试代码讲解、完整工程下载、测试效果图 目录 添加创建自己的库文件: 编写SCI发送函数: 主函数调用示例: 测试效果图: 完整工程下载&#x…...

ubuntu22.04机器人开发环境配置
1. ros2环境配置(humble) #配置源 # https://docs.ros.org/en/humble/Installation/Ubuntu-Install-Debs.html sudo apt install software-properties-common sudo add-apt-repository universe sudo apt update && sudo apt install curl -y# …...

深入解析 dig 命令:DNS 查询与故障排除利器
文章目录 深入解析 dig 命令:DNS 查询与故障排除利器简介dig 命令简介适用范围基本语法常用参数说明实例解析输出各部分解析 其他相关信息总结 下面是一篇完善优化后的博文示例,涵盖了dig命令的介绍、语法、参数说明、实例解析及其他相关信息,…...

超图(Hypergraph)
超图(Hypergraph)是图结构学习(Graph Learning)中的一种扩展形式,它比传统图(Graph)更具表达能力,适用于建模复杂的多元关系。 超图是一种由 超节点(Hypernodesÿ…...

管理 SELinux 安全性
SELinux是如何保护资源的? SELinux(Security-Enhanced Linux)通过强制访问控制(MAC)机制来保护系统资源。 SELinux 依据预定义的安全策略来管理进程对资源的访问。这些策略详细规定了哪些进程能够访问哪些资源&#…...

nodejs关于后端服务开发的探究
前提 在当前的环境中关于web server的主流开发基本上都是java、php之类的,其中java spring系列基本上占了大头,而python之流也在奋起直追,但别忘了nodejs也是可以做这个服务的,只是位置有点尴尬,现在就来探究下nodejs…...

如何在语言模型的参数中封装知识?——以T5模型为例
【摘要】 这篇论文探讨了大型语言模型在无需外部知识的情况下,能否通过预训练来存储和检索知识以回答开放领域的问题。作者通过微调预训练模型来回答问题,而这些模型在训练时并未提供任何额外的知识或上下文。这种方法随着模型规模的增加而表现出良好的…...

面试java做了一道逻辑题,人麻了
题目:给你一个5升水壶,一个6升水壶,去池塘中取水,如何保证最后取出的水是3升? 思考了很久终于想出来了,这里用X5代表5升的桶,X6代表6升的桶: ① 6升桶装满,X50ÿ…...

数据仓库为什么要分层
数据仓库分层架构是数据仓库设计中的一个重要概念,其主要目的是为了更好地组织和管理数据,提高数据仓库的可维护性、可扩展性和性能。分层架构将数据仓库划分为多个层次,每个层次都有其特定的职责和功能。以下是数据仓库分层的主要原因和好处…...

【Python运维】实现高效的自动化备份与恢复:Python脚本从入门到实践
《Python OpenCV从菜鸟到高手》带你进入图像处理与计算机视觉的大门! 解锁Python编程的无限可能:《奇妙的Python》带你漫游代码世界 在信息化时代,数据备份和恢复的有效性对企业和个人来说至关重要。本文将带领读者深入了解如何使用Python编写自动化备份与恢复脚本,确保重…...

RLock类详细介绍、应用场景和示例代码
概述 org.redisson.api.RLock 是 Redisson 提供的 分布式可重入锁(类似 ReentrantLock),基于 Redis 实现,常用于 分布式环境 下的 并发控制。 1. RLock 详解 🔹 特点 基于 Redis 实现,支持 集群环境。可…...

bash: uwsgi: 未找到命令
针对你提出的“bash: uwsgi: command not found”问题,以下是一些可能的解决方案,请按照步骤逐一排查: 1、检查uwsgi命令是否正确: 确保你输入的命令是uwsgi,而不是uWSGI或其他变体。 2、确认uwsgi是否已安装&…...

基于数据挖掘的疾病数据可视化分析与预测系统
【大数据】基于数据挖掘的疾病数据可视化分析与预测系统(完整系统源码开发笔记详细部署教程)✅ 目录 一、项目简介二、项目界面展示三、项目视频展示 一、项目简介 📌 技术核爆点:✔️ Python全栈开发Flask高能框架 ✔️ 爬虫技术…...

rv1106g2摄像头wlan0固定mac地址
wq9001无线网卡的mac地址是一个随机地址,在每次启动后,都会变更,使得dhcp分配的地址不同。要想有固定的mac地址,要做以下操作。 在文件uckfox-pico/sysdrv/drv_ko/wifi/insmod_wifi.sh添加函数wlan0_init wlan0_init() {wlan0add…...

企业日常工作中常用的 Linux 操作系统命令整理
Linux 操作系统命令整理 在企业级运维、开发和日常工作中,Linux 命令是绕不开的核心技能。不论是日志排查、进程管理,还是高效运维优化,掌握这些命令都能让你事半功倍!本篇文章整理了自己在日常工作中积累最常用的 Linux 命令&am…...
docker详细操作--未完待续
docker介绍 docker官网: Docker:加速容器应用程序开发 harbor官网:Harbor - Harbor 中文 使用docker加速器: Docker镜像极速下载服务 - 毫秒镜像 是什么 Docker 是一种开源的容器化平台,用于将应用程序及其依赖项(如库、运行时环…...
【机器视觉】单目测距——运动结构恢复
ps:图是随便找的,为了凑个封面 前言 在前面对光流法进行进一步改进,希望将2D光流推广至3D场景流时,发现2D转3D过程中存在尺度歧义问题,需要补全摄像头拍摄图像中缺失的深度信息,否则解空间不收敛…...

对WWDC 2025 Keynote 内容的预测
借助我们以往对苹果公司发展路径的深入研究经验,以及大语言模型的分析能力,我们系统梳理了多年来苹果 WWDC 主题演讲的规律。在 WWDC 2025 即将揭幕之际,我们让 ChatGPT 对今年的 Keynote 内容进行了一个初步预测,聊作存档。等到明…...

解决本地部署 SmolVLM2 大语言模型运行 flash-attn 报错
出现的问题 安装 flash-attn 会一直卡在 build 那一步或者运行报错 解决办法 是因为你安装的 flash-attn 版本没有对应上,所以报错,到 https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases 下载对应版本,cu、torch、cp 的版本一定要对…...
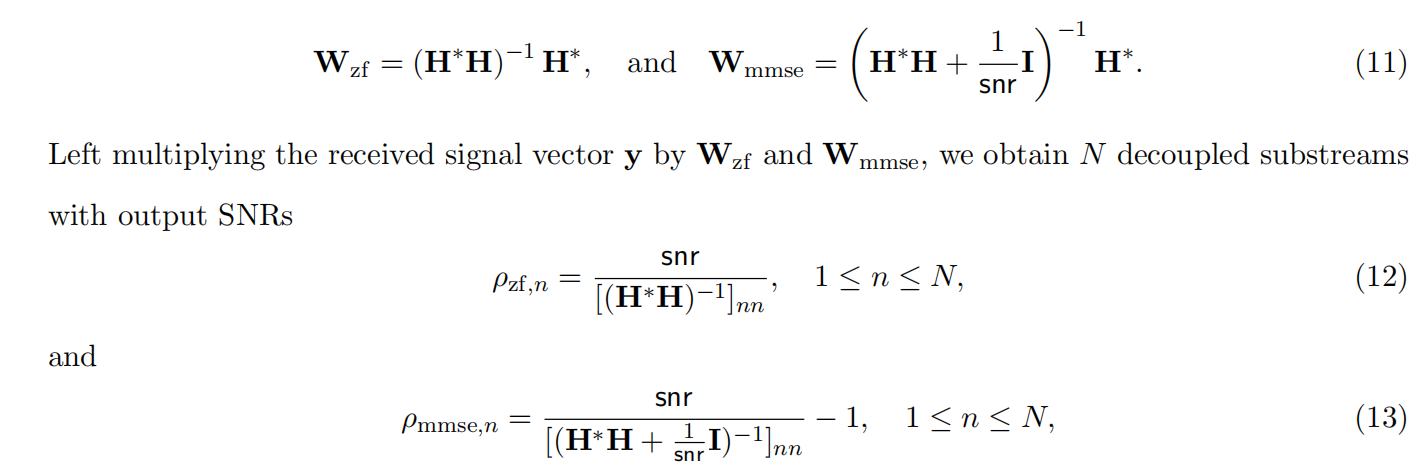
均衡后的SNRSINR
本文主要摘自参考文献中的前两篇,相关文献中经常会出现MIMO检测后的SINR不过一直没有找到相关数学推到过程,其中文献[1]中给出了相关原理在此仅做记录。 1. 系统模型 复信道模型 n t n_t nt 根发送天线, n r n_r nr 根接收天线的 MIMO 系…...

jmeter聚合报告中参数详解
sample、average、min、max、90%line、95%line,99%line、Error错误率、吞吐量Thoughput、KB/sec每秒传输的数据量 sample(样本数) 表示测试中发送的请求数量,即测试执行了多少次请求。 单位,以个或者次数表示。 示例:…...

MySQL 部分重点知识篇
一、数据库对象 1. 主键 定义 :主键是用于唯一标识表中每一行记录的字段或字段组合。它具有唯一性和非空性特点。 作用 :确保数据的完整性,便于数据的查询和管理。 示例 :在学生信息表中,学号可以作为主键ÿ…...

苹果AI眼镜:从“工具”到“社交姿态”的范式革命——重新定义AI交互入口的未来机会
在2025年的AI硬件浪潮中,苹果AI眼镜(Apple Glasses)正在引发一场关于“人机交互形态”的深度思考。它并非简单地替代AirPods或Apple Watch,而是开辟了一个全新的、日常可接受的AI入口。其核心价值不在于功能的堆叠,而在于如何通过形态设计打破社交壁垒,成为用户“全天佩戴…...

Ubuntu系统复制(U盘-电脑硬盘)
所需环境 电脑自带硬盘:1块 (1T) U盘1:Ubuntu系统引导盘(用于“U盘2”复制到“电脑自带硬盘”) U盘2:Ubuntu系统盘(1T,用于被复制) !!!建议“电脑…...
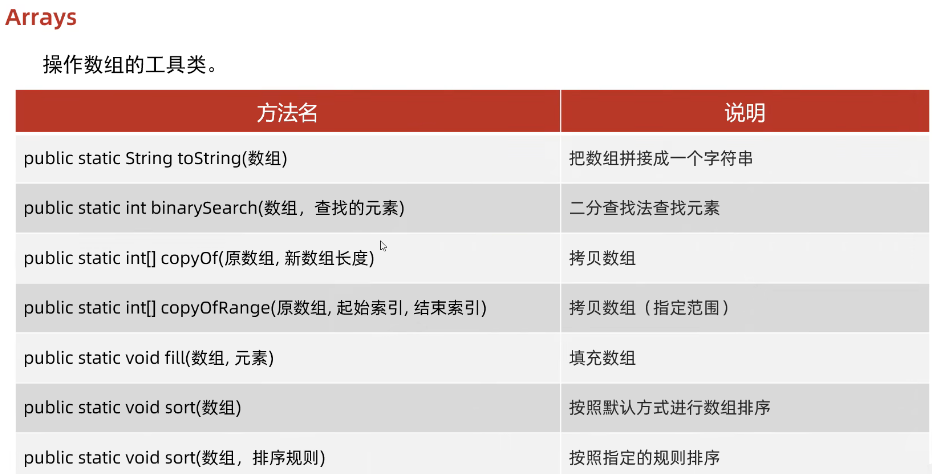
Java数组Arrays操作全攻略
Arrays类的概述 Java中的Arrays类位于java.util包中,提供了一系列静态方法用于操作数组(如排序、搜索、填充、比较等)。这些方法适用于基本类型数组和对象数组。 常用成员方法及代码示例 排序(sort) 对数组进行升序…...
