Android Retrofit 框架注解定义与解析模块深度剖析(一)
一、引言
在现代 Android 和 Java 开发中,网络请求是不可或缺的一部分。Retrofit 作为 Square 公司开源的一款强大的类型安全的 HTTP 客户端,凭借其简洁易用的 API 和高效的性能,在开发者社区中广受欢迎。Retrofit 的核心特性之一便是通过注解来定义 HTTP 请求,这种方式使得代码更加清晰、易读且易于维护。本文将深入 Retrofit 框架的源码,对其注解定义与解析模块进行全面且细致的分析,揭示其背后的实现原理。
二、Retrofit 框架概述
2.1 Retrofit 的基本工作流程
Retrofit 的主要工作流程可以概括为以下几个步骤:
- 定义服务接口:开发者使用注解定义一个接口,该接口包含了各种 HTTP 请求方法。
- 创建 Retrofit 实例:通过
Retrofit.Builder构建 Retrofit 实例,配置请求的基础 URL、转换器工厂、调用适配器工厂等。 - 创建服务代理对象:使用 Retrofit 实例创建服务接口的代理对象。
- 发起请求:调用服务代理对象的方法发起 HTTP 请求,并处理响应结果。
2.2 注解在 Retrofit 中的作用
注解在 Retrofit 中扮演着至关重要的角色,它们用于描述 HTTP 请求的各个方面,包括请求方法(如 GET、POST 等)、请求路径、请求参数、请求头、请求体等。通过注解,开发者可以以一种声明式的方式定义请求,而无需编写繁琐的网络请求代码。
三、Retrofit 注解的定义
3.1 HTTP 请求方法注解
3.1.1 @GET 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 表示 HTTP GET 请求的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留,以便通过反射获取
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface GET {/*** 指定请求的相对路径* @return 请求的相对路径,默认为空字符串*/String value() default "";
}
@GET 注解用于标记一个方法为 HTTP GET 请求,value 属性用于指定请求的相对路径。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("users/{id}")Call<User> getUser(@Path("id") int userId);
}
3.1.2 其他 HTTP 请求方法注解
除了 @GET 注解,Retrofit 还提供了 @POST、@PUT、@DELETE、@HEAD、@OPTIONS 和 @PATCH 等注解,它们的定义方式与 @GET 注解类似,只是用于不同的 HTTP 请求方法。
3.2 请求路径与参数注解
3.2.1 @Path 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于替换 URL 中占位符的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Path {/*** 指定 URL 中的占位符名称* @return 占位符名称*/String value();/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}
@Path 注解用于替换 URL 中的占位符,例如在上面的 getUser 方法中,@Path("id") 表示将 userId 参数的值替换到 URL 中的 {id} 占位符处。
3.2.2 @Query 和 @QueryMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加查询参数到 URL 中的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Query {/*** 指定查询参数的名称* @return 查询参数的名称*/String value();/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个查询参数到 URL 中的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface QueryMap {/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}
@Query 注解用于添加单个查询参数到 URL 中,@QueryMap 注解用于添加多个查询参数。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("search")Call<List<Item>> search(@Query("keyword") String keyword, @Query("page") int page);@GET("search")Call<List<Item>> searchWithMap(@QueryMap Map<String, String> queryParams);
}
3.2.3 @Header 和 @HeaderMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加请求头的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Header {/*** 指定请求头的名称* @return 请求头的名称*/String value();
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个请求头的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface HeaderMap {
}
@Header 注解用于添加单个请求头,@HeaderMap 注解用于添加多个请求头。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("data")Call<Data> getData(@Header("Authorization") String token);@GET("data")Call<Data> getDataWithMap(@HeaderMap Map<String, String> headers);
}
3.2.4 @Body 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于指定请求体的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Body {
}
@Body 注解用于指定请求体,通常用于 POST、PUT 等请求。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@POST("users")Call<User> createUser(@Body User user);
}
3.2.5 @FormUrlEncoded、@Field 和 @FieldMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于标记表单编码请求的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FormUrlEncoded {
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加表单字段的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Field {/*** 指定表单字段的名称* @return 表单字段的名称*/String value();/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个表单字段的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface FieldMap {/*** 指定是否对参数进行 URL 编码,默认为 false* @return 是否进行 URL 编码*/boolean encoded() default false;
}
@FormUrlEncoded 注解用于标记一个方法为表单编码请求,@Field 注解用于添加单个表单字段,@FieldMap 注解用于添加多个表单字段。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@FormUrlEncoded@POST("login")Call<LoginResponse> login(@Field("username") String username, @Field("password") String password);@FormUrlEncoded@POST("login")Call<LoginResponse> loginWithMap(@FieldMap Map<String, String> fields);
}
3.2.6 @Multipart、@Part 和 @PartMap 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于标记多部分请求的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Multipart {
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多部分请求中的一个部分的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Part {/*** 指定部分的名称* @return 部分的名称*/String value() default "";
}import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多部分请求中的多个部分的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法的参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface PartMap {
}
@Multipart 注解用于标记一个方法为多部分请求,@Part 注解用于添加多部分请求中的一个部分,@PartMap 注解用于添加多部分请求中的多个部分。多部分请求常用于文件上传等场景。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@Multipart@POST("upload")Call<UploadResponse> uploadFile(@Part("file"; filename="image.jpg"") RequestBody file);@Multipart@POST("upload")Call<UploadResponse> uploadFiles(@PartMap Map<String, RequestBody> files);
}
3.3 其他注解
3.3.1 @Headers 注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;/*** 用于添加多个请求头的注解*/
@Documented
// 该注解只能应用于方法上
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
// 该注解在运行时保留
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Headers {/*** 指定请求头的数组* @return 请求头的数组*/String[] value();
}
@Headers 注解用于在方法上添加多个请求头。例如:
java
public interface ApiService {@Headers({"Content-Type: application/json","Authorization: Bearer token123"})@GET("data")Call<Data> getData();
}
四、Retrofit 注解的解析
4.1 解析入口:ServiceMethod 类
ServiceMethod 是 Retrofit 中解析注解的核心类,它负责将接口方法上的注解信息解析为实际的 HTTP 请求信息。以下是 ServiceMethod 类的部分源码:
java
abstract class ServiceMethod<T> {/*** 解析接口方法上的注解,创建 ServiceMethod 实例* @param retrofit Retrofit 实例* @param method 接口方法* @param <T> 响应类型* @return ServiceMethod 实例*/static <T> ServiceMethod<T> parseAnnotations(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {// 创建 RequestFactory.Builder 实例,用于构建 RequestFactoryRequestFactory.Builder requestFactoryBuilder = new RequestFactory.Builder(retrofit, method);// 解析请求方法和路径相关的注解requestFactoryBuilder.parseMethodAnnotation(method.getAnnotations());// 获取方法的参数类型Type[] parameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();// 获取方法的参数注解Annotation[][] parameterAnnotationsArray = method.getParameterAnnotations();// 遍历方法的每个参数for (int p = 0; p < parameterTypes.length; p++) {// 解析参数的注解requestFactoryBuilder.parseParameter(p, parameterTypes[p], parameterAnnotationsArray[p]);}// 构建 RequestFactory 实例RequestFactory requestFactory = requestFactoryBuilder.build();// 获取方法的返回类型Type returnType = method.getGenericReturnType();if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(returnType)) {throw methodError(method,"Method return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);}if (returnType == void.class) {throw methodError(method, "Service methods cannot return void.");}// 创建 CallAdapter 实例,用于将 Call 对象转换为其他类型CallAdapter<T, ?> callAdapter = createCallAdapter(retrofit, method, returnType, requestFactory);// 获取响应类型Type responseType = callAdapter.responseType();if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(responseType)) {throw methodError(method, "Call return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);}// 创建 Converter 实例,用于将响应数据转换为指定类型Converter<ResponseBody, T> responseConverter =createResponseConverter(retrofit, method, responseType);// 获取 OkHttpClient 实例okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory = retrofit.callFactory();// 创建 ServiceMethod 实例return new HttpServiceMethod<>(callFactory, requestFactory, callAdapter, responseConverter);}/*** 创建 CallAdapter 实例* @param retrofit Retrofit 实例* @param method 接口方法* @param returnType 方法的返回类型* @param requestFactory 请求工厂* @param <T> 响应类型* @return CallAdapter 实例*/private static <T> CallAdapter<T, ?> createCallAdapter(Retrofit retrofit, Method method, Type returnType, RequestFactory requestFactory) {try {// 通过 Retrofit 实例获取 CallAdapter.Factory 列表,并调用其 get 方法创建 CallAdapter 实例return (CallAdapter<T, ?>) retrofit.callAdapter(returnType, method.getAnnotations());} catch (RuntimeException e) {throw methodError(method, e, "Unable to create call adapter for %s", returnType);}}/*** 创建响应转换器实例* @param retrofit Retrofit 实例* @param method 接口方法* @param responseType 响应类型* @param <T> 响应类型* @return 响应转换器实例*/private static <T> Converter<ResponseBody, T> createResponseConverter(Retrofit retrofit, Method method, Type responseType) {try {// 通过 Retrofit 实例获取 Converter.Factory 列表,并调用其 responseBodyConverter 方法创建响应转换器实例return retrofit.responseBodyConverter(responseType, method.getAnnotations());} catch (RuntimeException e) {throw methodError(method, e, "Unable to create converter for %s", responseType);}}/*** 抽象方法,用于执行请求* @param args 方法参数* @return 响应结果*/abstract @Nullable T invoke(Object[] args);
}
parseAnnotations 方法是解析的入口,它接收 Retrofit 实例和 Method 实例作为参数,通过以下步骤完成注解解析:
- 创建
RequestFactory.Builder实例,用于构建RequestFactory。 - 调用
requestFactoryBuilder.parseMethodAnnotation方法解析请求方法和路径相关的注解。 - 遍历方法的每个参数,调用
requestFactoryBuilder.parseParameter方法解析参数的注解。 - 构建
RequestFactory实例。 - 获取方法的返回类型,并创建
CallAdapter实例,用于将Call对象转换为其他类型。 - 获取响应类型,并创建
Converter实例,用于将响应数据转换为指定类型。 - 获取
OkHttpClient实例,并创建ServiceMethod实例。
4.2 解析请求方法和路径注解:RequestFactory.Builder.parseMethodAnnotation 方法
java
static final class Builder {// 存储请求方法(如 GET、POST 等)private String httpMethod;// 存储请求是否需要请求体private boolean hasBody;// 存储请求的相对路径private String relativeUrl;// 存储请求的请求头private okhttp3.Headers headers;// 存储路径中的占位符名称private List<String> relativeUrlParamNames;// 标记是否为多部分请求private boolean isMultipart;// 标记是否为表单编码请求private boolean isFormEncoded;/*** 解析请求方法和路径相关的注解* @param annotations 方法上的注解数组*/void parseMethodAnnotation(Annotation[] annotations) {for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {if (annotation instanceof HttpMethod) {// 如果注解是 HttpMethod 类型(如 @GET、@POST 等)HttpMethod httpMethodAnnotation = (HttpMethod) annotation;// 获取请求方法this.httpMethod = httpMethodAnnotation.value();// 判断是否需要请求体this.hasBody = httpMethodAnnotation.hasBody();String path = httpMethodAnnotation.path();if (!path.isEmpty()) {// 检查路径是否以 / 开头if (path.startsWith("/")) {throw methodError(method, "@%s path must not start with /: %s",httpMethodAnnotation.annotationType().getSimpleName(), path);}this.relativeUrl = path;// 解析路径中的占位符this.relativeUrlParamNames = parsePathParameters(path);}} else if (annotation instanceof Headers) {// 如果注解是 Headers 类型String[] headersToParse = ((Headers) annotation).value();if (headersToParse.length == 0) {throw methodError(method, "@Headers annotation is empty.");}// 解析请求头this.headers = parseHeaders(headersToParse);} else if (annotation instanceof Multipart) {// 如果注解是 Multipart 类型if (this.hasBody) {throw methodError(method, "Only one encoding annotation is allowed.");}this.isMultipart = true;this.hasBody = true;} else if (annotation instanceof FormUrlEncoded) {// 如果注解是 FormUrlEncoded 类型if (this.hasBody) {throw methodError(method, "Only one encoding annotation is allowed.");}this.isFormEncoded = true;this.hasBody = true;}}if (httpMethod == null) {throw methodError(method, "HTTP method annotation is required (e.g., @GET, @POST, etc.).");}}/*** 解析路径中的占位符* @param path 请求路径* @return 占位符名称列表*/private static List<String> parsePathParameters(String path) {// 定义正则表达式,用于匹配路径中的占位符Matcher m = PARAM_URL_REGEX.matcher(path);List<String> patterns = new ArrayList<>();while (m.find()) {String name = m.group(1);if (name == null) {continue;}if (patterns.contains(name)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("URL path "" + path + "" has duplicate param "" + name + "".");}patterns.add(name);}return patterns;}/*** 解析请求头* @param headers 请求头数组* @return OkHttp 的 Headers 实例*/private static okhttp3.Headers parseHeaders(String[] headers) {okhttp3.Headers.Builder builder = new okhttp3.Headers.Builder();for (String header : headers) {int colon = header.indexOf(':');if (colon == -1 || colon == 0 || colon == header.length() - 1) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Headers value must be in the form "Name: Value". Found: "" + header + """);}String name = header.substring(0, colon).trim();String value = header.substring(colon + 1).trim();builder.add(name, value);}return builder.build();}
}
parseMethodAnnotation 方法遍历方法上的所有注解,根据注解的类型进行不同的处理:
- 如果注解是
HttpMethod类型(如@GET、@POST等),获取请求方法、判断是否需要请求体,并解析路径中的占位符。 - 如果注解是
Headers类型,解析请求头。 - 如果注解是
Multipart类型,标记为多部分请求。 - 如果注解是
FormUrlEncoded类型,标记为表单编码请求。
4.3 解析参数注解:RequestFactory.Builder.parseParameter 方法
java
static final class Builder {// 存储参数处理器数组private ParameterHandler<?>[] parameterHandlers;/*** 解析方法参数的注解* @param p 参数索引* @param parameterType 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组*/void parseParameter(int p, Type parameterType, @Nullable Annotation[] annotations) {if (annotations == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}ParameterHandler<?> result = null;for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {// 创建参数处理器ParameterHandler<?> annotationAction = parseParameterAnnotation(p, parameterType, annotations, annotation);if (annotationAction == null) {continue;}if (result != null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "Multiple Retrofit annotations found, only one allowed.");}result = annotationAction;}if (result == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}// 将参数处理器添加到参数处理器数组中parameterHandlers[p] = result;}/*** 解析单个参数注解* @param p 参数索引* @param type 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组* @param annotation 当前要解析的注解* @return 参数处理器*/private @Nullable ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(int p, Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Annotation annotation) {if (annotation instanceof Path) {// 如果注解
4.3 解析参数注解:RequestFactory.Builder.parseParameter 方法(续)
java
static final class Builder {// 存储参数处理器数组private ParameterHandler<?>[] parameterHandlers;/*** 解析方法参数的注解* @param p 参数索引* @param parameterType 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组*/void parseParameter(int p, Type parameterType, @Nullable Annotation[] annotations) {if (annotations == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}ParameterHandler<?> result = null;for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {// 创建参数处理器ParameterHandler<?> annotationAction = parseParameterAnnotation(p, parameterType, annotations, annotation);if (annotationAction == null) {continue;}if (result != null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "Multiple Retrofit annotations found, only one allowed.");}result = annotationAction;}if (result == null) {throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");}// 将参数处理器添加到参数处理器数组中parameterHandlers[p] = result;}/*** 解析单个参数注解* @param p 参数索引* @param type 参数类型* @param annotations 参数上的注解数组* @param annotation 当前要解析的注解* @return 参数处理器*/private @Nullable ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(int p, Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Annotation annotation) {if (annotation instanceof Path) {// 如果注解是 Path 类型Path path = (Path) annotation;// 检查路径中是否包含该占位符if (!relativeUrlParamNames.contains(path.value())) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@Path parameter "" + path.value()+ "" not found in relative URL "" + relativeUrl + """);}// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Path parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 PathParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Path<>(path.value(), path.encoded(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Query) {// 如果注解是 Query 类型Query query = (Query) annotation;// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Query parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 QueryParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Query<>(query.value(), query.encoded(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof QueryMap) {// 如果注解是 QueryMap 类型if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@QueryMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@QueryMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 QueryMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.QueryMap<>(converterFactory.stringConverter(valueType, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Header) {// 如果注解是 Header 类型Header header = (Header) annotation;// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Header parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 HeaderParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Header<>(header.value(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof HeaderMap) {// 如果注解是 HeaderMap 类型if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@HeaderMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@HeaderMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 HeaderMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.HeaderMap<>(converterFactory.stringConverter(valueType, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Body) {// 如果注解是 Body 类型if (isFormEncoded || isMultipart) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Body parameters cannot be used with form or multi - part encoding.");}// 创建 BodyParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Body<>(converterFactory.requestBodyConverter(type, annotations, methodAnnotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Field) {// 如果注解是 Field 类型if (!isFormEncoded) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@Field parameters can only be used with form encoding.");}Field field = (Field) annotation;// 检查参数类型是否为基本类型或字符串if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(type)) {throw parameterError(method, p,"@Field parameter type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", type);}// 创建 FieldParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Field<>(field.value(), field.encoded(),converterFactory.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof FieldMap) {// 如果注解是 FieldMap 类型if (!isFormEncoded) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@FieldMap parameters can only be used with form encoding.");}if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@FieldMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@FieldMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 FieldMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.FieldMap<>(converterFactory.stringConverter(valueType, annotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof Part) {// 如果注解是 Part 类型if (!isMultipart) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@Part parameters can only be used with multipart encoding.");}Part part = (Part) annotation;String partName = part.value();if (!"".equals(partName) && !partName.endsWith(";")) {partName = partName + ";";}// 创建 PartParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.Part<>(partName,converterFactory.requestBodyConverter(type, annotations, methodAnnotations, retrofit));} else if (annotation instanceof PartMap) {// 如果注解是 PartMap 类型if (!isMultipart) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap parameters can only be used with multipart encoding.");}if (!Map.class.isAssignableFrom(Utils.getRawType(type))) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap parameter type must be Map.");}Type keyType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, String.class);if (keyType != String.class) {throw parameterError(method, p, "@PartMap keys must be of type String: %s", type);}Type valueType = Utils.getSupertype(type, Map.class, Object.class);// 创建 PartMapParameterHandler 实例return new ParameterHandler.PartMap<>(converterFactory.requestBodyConverter(valueType, annotations, methodAnnotations, retrofit));}return null;}
}
4.3.1 详细解析逻辑
-
@Path注解解析:- 首先,从
Path注解中获取占位符名称,检查该占位符是否存在于之前解析得到的relativeUrlParamNames列表中。如果不存在,会抛出异常,确保路径占位符的正确性。 - 接着,检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。如果存在,也会抛出异常,因为
@Path参数类型应该是基本类型或字符串。 - 最后,创建
ParameterHandler.Path实例,该实例负责处理路径占位符的替换。converterFactory.stringConverter方法用于创建一个将参数类型转换为字符串的转换器,以便将参数值正确地替换到路径中。
- 首先,从
-
@Query注解解析:- 对于
Query注解,同样会检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。 - 然后创建
ParameterHandler.Query实例,该实例会将参数值作为查询参数添加到 URL 中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将参数值转换为字符串形式。
- 对于
-
@QueryMap注解解析:- 先检查参数类型是否为
Map类型,如果不是会抛出异常。 - 接着检查
Map的键类型是否为String类型,若不是也会抛出异常。 - 最后创建
ParameterHandler.QueryMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为查询参数添加到 URL 中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将Map的值转换为字符串。
- 先检查参数类型是否为
-
@Header注解解析:- 检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。
- 创建
ParameterHandler.Header实例,该实例会将参数值作为请求头添加到请求中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将参数值转换为字符串形式的请求头值。
-
@HeaderMap注解解析:- 检查参数类型是否为
Map类型,以及Map的键类型是否为String类型。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.HeaderMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为请求头添加到请求中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将Map的值转换为字符串形式的请求头值。
- 检查参数类型是否为
-
@Body注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码或多部分请求,如果是则抛出异常,因为
@Body参数不能与表单或多部分编码同时使用。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.Body实例,该实例会将参数作为请求体发送。converterFactory.requestBodyConverter用于将参数类型转换为RequestBody类型,以便进行网络传输。
- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码或多部分请求,如果是则抛出异常,因为
-
@Field注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
@Field参数只能用于表单编码请求。 - 检查参数类型是否包含不可解析的类型变量或通配符。
- 创建
ParameterHandler.Field实例,该实例会将参数值作为表单字段添加到请求体中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将参数值转换为字符串形式的表单字段值。
- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
-
@FieldMap注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,以及参数类型是否为
Map类型,Map的键类型是否为String类型。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.FieldMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为表单字段添加到请求体中。converterFactory.stringConverter用于将Map的值转换为字符串形式的表单字段值。
- 检查当前请求是否为表单编码请求,以及参数类型是否为
-
@Part注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
@Part参数只能用于多部分请求。 - 处理
Part注解的value属性,确保其格式正确。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.Part实例,该实例会将参数作为多部分请求的一部分添加到请求体中。converterFactory.requestBodyConverter用于将参数类型转换为RequestBody类型。
- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,如果不是则抛出异常,因为
-
@PartMap注解解析:- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,以及参数类型是否为
Map类型,Map的键类型是否为String类型。 - 创建
ParameterHandler.PartMap实例,该实例会将Map中的键值对作为多部分请求的多个部分添加到请求体中。converterFactory.requestBodyConverter用于将Map的值转换为RequestBody类型。
- 检查当前请求是否为多部分请求,以及参数类型是否为
4.4 创建 RequestFactory 实例
在完成所有参数注解的解析后,会调用 RequestFactory.Builder 的 build 方法来构建 RequestFactory 实例:
java
RequestFactory build() {return new RequestFactory(this);
}
RequestFactory 类封装了所有解析得到的请求信息,包括请求方法、请求路径、请求头、请求体等,后续会根据这些信息创建实际的 Request 对象。
4.5 创建 CallAdapter 和 Converter 实例
在 ServiceMethod.parseAnnotations 方法中,还会创建 CallAdapter 和 Converter 实例:
java
// 创建 CallAdapter 实例,用于将 Call 对象转换为其他类型
CallAdapter<T, ?> callAdapter = createCallAdapter(retrofit, method, returnType, requestFactory);
// 获取响应类型
Type responseType = callAdapter.responseType();
if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(responseType)) {throw methodError(method, "Call return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);
}// 创建 Converter 实例,用于将响应数据转换为指定类型
Converter<ResponseBody, T> responseConverter =createResponseConverter(retrofit, method, responseType);
4.5.1 CallAdapter 实例创建
createCallAdapter 方法通过 Retrofit 实例的 callAdapter 方法从 CallAdapter.Factory 列表中查找合适的 CallAdapter.Factory,并调用其 get 方法创建 CallAdapter 实例。CallAdapter 的作用是将 Call 对象转换为其他类型,例如将 Call<Response> 转换为 Observable<Response> 等,以支持不同的异步编程模型。
4.5.2 Converter 实例创建
createResponseConverter 方法通过 Retrofit 实例的 responseBodyConverter 方法从 Converter.Factory 列表中查找合适的 Converter.Factory,并调用其 responseBodyConverter 方法创建 Converter 实例。Converter 的作用是将 ResponseBody 转换为指定的响应类型,例如将 JSON 数据转换为 Java 对象。
4.6 创建 ServiceMethod 实例
最后,根据前面解析得到的信息,创建 ServiceMethod 实例:
java
// 获取 OkHttpClient 实例
okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory = retrofit.callFactory();
// 创建 ServiceMethod 实例
return new HttpServiceMethod<>(callFactory, requestFactory, callAdapter, responseConverter);
HttpServiceMethod 是 ServiceMethod 的具体实现类,它负责执行实际的 HTTP 请求,并处理响应结果。在 invoke 方法中,会根据 RequestFactory 创建 Request 对象,使用 OkHttpClient 发送请求,然后通过 CallAdapter 和 Converter 处理响应。
java
final class HttpServiceMethod<ResponseT, ReturnT> extends ServiceMethod<ReturnT> {private final okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory;private final RequestFactory requestFactory;private final CallAdapter<ResponseT, ReturnT> callAdapter;private final Converter<ResponseBody, ResponseT> responseConverter;HttpServiceMethod(okhttp3.Call.Factory callFactory, RequestFactory requestFactory,CallAdapter<ResponseT, ReturnT> callAdapter,Converter<ResponseBody, ResponseT> responseConverter) {this.callFactory = callFactory;this.requestFactory = requestFactory;this.callAdapter = callAdapter;this.responseConverter = responseConverter;}@Override@Nullable ReturnT invoke(Object[] args) {// 创建 OkHttp 的 Request 对象Request request = requestFactory.create(args);// 创建 OkHttp 的 Call 对象okhttp3.Call call = callFactory.newCall(request);// 调用 CallAdapter 的 adapt 方法将 Call 对象转换为指定类型return callAdapter.adapt(new OkHttpCall<>(request, callFactory, responseConverter));}
}
五、注解解析后的使用
当 ServiceMethod 实例创建完成后,就可以使用它来发起 HTTP 请求了。在调用服务接口的方法时,实际上是调用 ServiceMethod 的 invoke 方法:
java
public interface ApiService {@GET("users/{id}")Call<User> getUser(@Path("id") int userId);
}// 创建 Retrofit 实例
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl("https://api.example.com/").addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create()).build();// 创建服务代理对象
ApiService apiService = retrofit.create(ApiService.class);// 发起请求
Call<User> call = apiService.getUser(1);
call.enqueue(new Callback<User>() {@Overridepublic void onResponse(Call<User> call, Response<User> response) {if (response.isSuccessful()) {User user = response.body();// 处理响应数据} else {// 处理请求失败}}@Overridepublic void onFailure(Call<User> call, Throwable t) {// 处理请求异常}
});
在上述代码中,apiService.getUser(1) 实际上调用了 ServiceMethod 的 invoke 方法,该方法会根据之前解析得到的注解信息创建 Request 对象,使用 OkHttpClient 发送请求,并通过 CallAdapter 和 Converter 处理响应结果。
六、总结
Retrofit 的注解定义与解析模块是其核心功能之一,通过使用注解,开发者可以以一种简洁、声明式的方式定义 HTTP 请求。在解析过程中,Retrofit 利用 Java 的反射机制,在运行时获取方法和参数上的注解信息,并根据注解类型进行相应的处理。具体步骤包括解析请求方法和路径注解、解析参数注解、创建 RequestFactory、CallAdapter 和 Converter 实例,最终创建 ServiceMethod 实例来执行实际的 HTTP 请求。这种设计使得 Retrofit 具有高度的灵活性和可扩展性,开发者可以通过自定义 CallAdapter.Factory 和 Converter.Factory 来满足不同的需求。同时,注解的使用也使得代码更加清晰、易读和易于维护,提高了开发效率。
相关文章:
)
Android Retrofit 框架注解定义与解析模块深度剖析(一)
一、引言 在现代 Android 和 Java 开发中,网络请求是不可或缺的一部分。Retrofit 作为 Square 公司开源的一款强大的类型安全的 HTTP 客户端,凭借其简洁易用的 API 和高效的性能,在开发者社区中广受欢迎。Retrofit 的核心特性之一便是通过注…...

项目上传到Gitee过程
在gitee上新建一个仓库 点击“克隆/下载”获取仓库地址 电脑上要装好git 在电脑本地文件夹右键“Git Bash Here” 依次执行如下命令 git init git remote add origin https://gitee.com/qlexcel/stm32-simple.git git pull origin master git add . git commit -m ‘init’…...

DeepSeek R1在医学领域的应用与技术分析(Discuss V1版)
DeepSeek R1作为一款高性能、低成本的国产开源大模型,正在深刻重塑医学软件工程的开发逻辑与应用场景。其技术特性,如混合专家架构(MoE)和参数高效微调(PEFT),与医疗行业的实际需求紧密结合,推动医疗AI从“技术驱动”向“场景驱动”转型。以下从具体业务领域需求出发,…...

数学之快速幂-数的幂次
题目描述 给定三个正整数 N,M,P,求 输入描述 第 1 行为一个整数 T,表示测试数据数量。 接下来的 T 行每行包含三个正整数 N,M,P。 输出描述 输出共 T 行,每行包含一个整数,表示答案。 输入输出样例 示例 1 输入 3 2 3 7 4…...

git subtree管理的仓库怎么删除子仓库
要删除通过 git subtree 管理的子仓库,可以按照以下步骤操作: 1. 确认子仓库路径 首先确认要删除的子仓库的路径,假设子仓库路径为 <subtree-path>。 2. 从主仓库中移除子仓库目录 使用 git rm 命令删除子仓库的目录: …...

学习资料电子版 免费下载的网盘网站(非常全!)
我分享一个私人收藏的电子书免费下载的网盘网站(学习资料为主): link3.cc/sbook123 所有资料都保存在网盘了,直接转存即可,非常的便利! 包括了少儿,小学,初中,中职&am…...

SpringMVC-全局异常处理
文章目录 1. 全局异常处理2. 项目异常处理方案2.1 异常分类2.2 异常解决方案2.3 异常解决方案具体实现 1. 全局异常处理 问题:当我们在SpingMVC代码中没有对异常进行处理时,三层架构的默认处理异常方案是将异常抛给上级调用者。也就是说Mapper层报错会将…...

基于Spring Boot的宠物健康顾问系统的设计与实现(LW+源码+讲解)
专注于大学生项目实战开发,讲解,毕业答疑辅导,欢迎高校老师/同行前辈交流合作✌。 技术范围:SpringBoot、Vue、SSM、HLMT、小程序、Jsp、PHP、Nodejs、Python、爬虫、数据可视化、安卓app、大数据、物联网、机器学习等设计与开发。 主要内容:…...

【Linux内核系列】:深入理解缓冲区
🔥 本文专栏:Linux 🌸作者主页:努力努力再努力wz ★★★ 本文前置知识: 文件系统以及相关系统调用接口 输入以及输出重定向 那么在此前的学习中,我们了解了文件的概念以及相关的系统调用接口,并…...

Python开发Scikit-learn面试题及参考答案
目录 如何用 SimpleImputer 处理数据集中的缺失值? 使用 StandardScaler 对数据进行标准化的原理是什么?与 MinMaxScaler 有何区别? 如何用 OneHotEncoder 对类别型特征进行编码? 解释特征选择中 SelectKBest 与 VarianceThreshold 的应用场景。 如何通过 PolynomialFe…...
在算法竞赛中的常见用法和注意事项)
~(取反)在算法竞赛中的常见用法和注意事项
在算法竞赛中,取反符号 ~ 主要用于按位取反操作,其功能是对整数的二进制表示逐位取反(0 变 1,1 变 0)。以下是 ~ 在算法竞赛中的常见用法和注意事项: 1. 按位取反的基本用法 ~ 对整数的二进制表示进行取反…...
)
C++ MySQL 常用接口(基于 MySQL Connector/C++)
C MySQL 常用接口(基于 MySQL Connector/C) 1. 数据库连接 接口: sql::mysql::MySQL_Driver *driver; sql::Connection *con;作用: 用于创建 MySQL 连接对象。 示例: driver sql::mysql::get_mysql_driver_insta…...

本地部署 OpenManus 保姆级教程(Windows 版)
一、环境搭建 我的电脑是Windows 10版本,其他的没尝试,如果大家系统和我的不一致,请自行判断,基本上没什么大的出入啊。 openManus的Git地址:https://github.com/mannaandpoem/OpenManus 根据官网的两种安装推荐方式如…...

【Pandas】pandas Series compare
# Pandas2.2 Series ## Computations descriptive stats |方法|描述| |-|:-------| |Series.compare(other[, align_axis, ...])|用于比较两个 Series| ### pandas.Series.compare pandas.Series.compare 方法用于比较两个 Series,并返回一个包含差异的 DataFram…...

基于DeepSeek的智慧医药系统(源码+部署教程)
运行环境 智慧医药系统运行环境如下: 前端: HTMLCSS后端:Java AIGCDeepseekIDE工具:IDEA技术栈:Springboot HTMLCSS MySQL 主要角色 智慧医药系统主要分为两个角色。 游客 尚未进行注册和登录。具备登录注册、…...

如何为服务设置合理的线程数
1. 首先,要确定最大线程数的限制因素。通常,线程数量受限于内存、CPU和操作系统限制。比如,每个线程都需要一定的栈内存,默认情况下Java线程的栈大小是1MB(64位系统可能更大),所以如果内存不足&…...

Unity--Cubism Live2D模型使用
了解LIVE2D在unity的使用--前提记录 了解各个组件的作用 Live2D Manuals & Tutorials 这些文件都是重要的控制动画参数的 Cubism Editor是编辑Live2D的工具,而导出的数据的类型,需要满足以上的条件 SDK中包含的Cubism的Importer会自动生成一个Pref…...

Vue.js 3 的设计思路:从声明式UI到高效渲染机制
目录 一、声明式UI与虚拟DOM的灵活性 二、渲染器:虚拟DOM到真实DOM的桥梁 三、组件的本质与实现 四、编译与运行时的协同优化 五、性能与可维护性的权衡 总结 Vue.js 3 作为新一代前端框架,其设计理念在声明式UI描述、虚拟DOM优化、组件化架构…...

部署前后端项目
部署项目 liunx 软件安装 软件安装方式 在Linux系统中,安装软件的方式主要有四种,这四种安装方式的特点如下: 建议nginx、MySQL、Redis等等使用docker安装,会很便捷,这里只演示JDK、ngxin手动的安装 安装JDK 上述我…...

Vue Diff算法原理深度解析:如何高效更新虚拟DOM?
文章目录 1. 为什么需要Diff算法?2. Diff算法核心原则3. 核心流程图解4. 核心代码实现(简化版)5. Key的重要性示例6. 算法优化策略7. 时间复杂度优化8. 与其他框架的对比9. 总结 1. 为什么需要Diff算法? 在Vue的响应式系统中&…...
UE5 学习系列(二)用户操作界面及介绍
这篇博客是 UE5 学习系列博客的第二篇,在第一篇的基础上展开这篇内容。博客参考的 B 站视频资料和第一篇的链接如下: 【Note】:如果你已经完成安装等操作,可以只执行第一篇博客中 2. 新建一个空白游戏项目 章节操作,重…...

java_网络服务相关_gateway_nacos_feign区别联系
1. spring-cloud-starter-gateway 作用:作为微服务架构的网关,统一入口,处理所有外部请求。 核心能力: 路由转发(基于路径、服务名等)过滤器(鉴权、限流、日志、Header 处理)支持负…...

R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解
R语言AI模型部署方案:精准离线运行详解 一、项目概述 本文将构建一个完整的R语言AI部署解决方案,实现鸢尾花分类模型的训练、保存、离线部署和预测功能。核心特点: 100%离线运行能力自包含环境依赖生产级错误处理跨平台兼容性模型版本管理# 文件结构说明 Iris_AI_Deployme…...
)
Spring Boot 实现流式响应(兼容 2.7.x)
在实际开发中,我们可能会遇到一些流式数据处理的场景,比如接收来自上游接口的 Server-Sent Events(SSE) 或 流式 JSON 内容,并将其原样中转给前端页面或客户端。这种情况下,传统的 RestTemplate 缓存机制会…...

浅谈不同二分算法的查找情况
二分算法原理比较简单,但是实际的算法模板却有很多,这一切都源于二分查找问题中的复杂情况和二分算法的边界处理,以下是博主对一些二分算法查找的情况分析。 需要说明的是,以下二分算法都是基于有序序列为升序有序的情况…...
企业如何增强终端安全?
在数字化转型加速的今天,企业的业务运行越来越依赖于终端设备。从员工的笔记本电脑、智能手机,到工厂里的物联网设备、智能传感器,这些终端构成了企业与外部世界连接的 “神经末梢”。然而,随着远程办公的常态化和设备接入的爆炸式…...

中医有效性探讨
文章目录 西医是如何发展到以生物化学为药理基础的现代医学?传统医学奠基期(远古 - 17 世纪)近代医学转型期(17 世纪 - 19 世纪末)现代医学成熟期(20世纪至今) 中医的源远流长和一脉相承远古至…...

QT3D学习笔记——圆台、圆锥
类名作用Qt3DWindow3D渲染窗口容器QEntity场景中的实体(对象或容器)QCamera控制观察视角QPointLight点光源QConeMesh圆锥几何网格QTransform控制实体的位置/旋转/缩放QPhongMaterialPhong光照材质(定义颜色、反光等)QFirstPersonC…...

vulnyx Blogger writeup
信息收集 arp-scan nmap 获取userFlag 上web看看 一个默认的页面,gobuster扫一下目录 可以看到扫出的目录中得到了一个有价值的目录/wordpress,说明目标所使用的cms是wordpress,访问http://192.168.43.213/wordpress/然后查看源码能看到 这…...
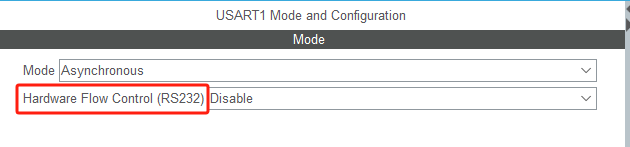
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析及应用
STM32HAL库USART源代码解析 前言STM32CubeIDE配置串口USART和UART的选择使用模式参数设置GPIO配置DMA配置中断配置硬件流控制使能生成代码解析和使用方法串口初始化__UART_HandleTypeDef结构体浅析HAL库代码实际使用方法使用轮询方式发送使用轮询方式接收使用中断方式发送使用中…...
