Python 小型项目大全 61~65
六十一、ROT13 密码
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project61.html

ROT13 密码是最简单的加密算法之一,代表“旋转 13 个空格”密码将字母A到Z表示为数字 0 到 25,加密后的字母距离明文字母 13 个空格: A变成N,B变成O,以此类推。加密过程和解密过程是一样的,这使得编程变得很简单。然而,加密也很容易被破解。正因为如此,你会经常发现 ROT13 被用来隐藏非敏感信息,如剧透或琐事答案,所以它不会被无意中读取。更多关于 ROT13 密码的信息可以在en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ROT13找到。如果你想更一般地了解密码和密码破解,你可以阅读我的书《Python 密码破解指南》(NoStarch 出版社,2018)。
运行示例
当您运行rot13cipher.py时,输出将如下所示:
ROT13 Cipher, by Al Sweigart email@protectedEnter a message to encrypt/decrypt (or QUIT):
> Meet me by the rose bushes tonight.
The translated message is:
Zrrg zr ol gur ebfr ohfurf gbavtug.(Copied to clipboard.)
Enter a message to encrypt/decrypt (or QUIT):
`--snip--`
工作原理
ROT13 与项目 6“凯撒密码”共享大量代码,尽管它要简单得多,因为它总是使用密钥 13。因为相同的代码执行加密和解密(第 27 到 39 行),所以没有必要询问玩家他们想要使用哪种模式。
一个不同之处是,这个程序保持原始消息的大小写,而不是自动将消息转换为大写。例如,HELLO加密为URYYB,而Hello加密为Uryyb。
"""ROT13 Cipher, by Al Sweigart email@protected
The simplest shift cipher for encrypting and decrypting text.
More info at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ROT13
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: tiny, cryptography"""try:import pyperclip # pyperclip copies text to the clipboard.
except ImportError:pass # If pyperclip is not installed, do nothing. It's no big deal.# Set up the constants:
UPPER_LETTERS = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
LOWER_LETTERS = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'print('ROT13 Cipher, by Al Sweigart email@protected')
print()while True: # Main program loop.print('Enter a message to encrypt/decrypt (or QUIT):')message = input('> ')if message.upper() == 'QUIT':break # Break out of the main program loop.# Rotate the letters in message by 13 characters.translated = ''for character in message:if character.isupper():# Concatenate uppercase translated character.transCharIndex = (UPPER_LETTERS.find(character) + 13) % 26translated += UPPER_LETTERS[transCharIndex]elif character.islower():# Concatenate lowercase translated character.transCharIndex = (LOWER_LETTERS.find(character) + 13) % 26translated += LOWER_LETTERS[transCharIndex]else:# Concatenate the character untranslated.translated += character# Display the translation:print('The translated message is:')print(translated)print()try:# Copy the translation to the clipboard:pyperclip.copy(translated)print('(Copied to clipboard.)')except:pass
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果把第 29 行的
character.isupper()改成character.islower()会怎么样? - 如果把第 43 行的
print(translated)改成print(message)会怎么样?
六十二、旋转立方体
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project62.html

这个项目的特点是使用三角函数的 3D 立方体旋转动画。您可以在自己的动画程序中修改 3D 点旋转数学和line()函数。
虽然我们将用来绘制立方体的块文本字符看起来不像细而直的线,但这种绘制被称为线框模型,因为它只渲染物体表面的边缘。图 62-1 显示了立方体和 icosphere 的线框模型,icosphere 是一个由三角形组成的粗糙球体。
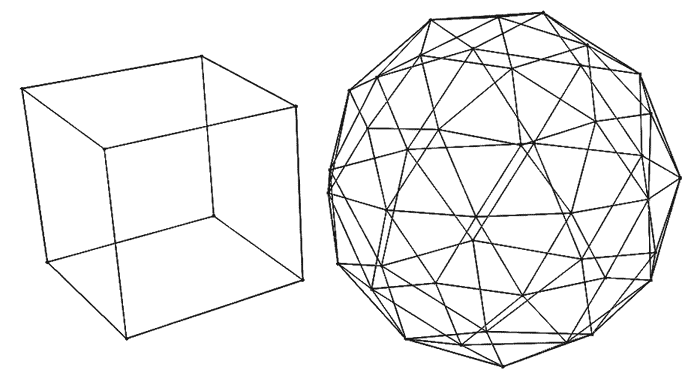
立方体(左)和 icosphere(右)的线框模型
运行示例
图 62-2 显示了运行rotatingcube.py时的输出。

:程序绘制到屏幕上的线框立方体
工作原理
这个算法有两个主要部分:函数line()和函数rotatePoint()。立方体有八个点,每个角一个。程序将这些角存储为CUBE_CORNERS列表中的(x, y, z)元组。这些点也定义了立方体边缘线的连接。当所有的点都向同一个方向旋转相同的量时,它们会产生立方体旋转的错觉。
"""Rotating Cube, by Al Sweigart email@protected
A rotating cube animation. Press Ctrl-C to stop.
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: large, artistic, math"""# This program MUST be run in a Terminal/Command Prompt window.import math, time, sys, os# Set up the constants:
PAUSE_AMOUNT = 0.1 # Pause length of one-tenth of a second.
WIDTH, HEIGHT = 80, 24
SCALEX = (WIDTH - 4) // 8
SCALEY = (HEIGHT - 4) // 8
# Text cells are twice as tall as they are wide, so set scaley:
SCALEY *= 2
TRANSLATEX = (WIDTH - 4) // 2
TRANSLATEY = (HEIGHT - 4) // 2# (!) Try changing this to '#' or '*' or some other character:
LINE_CHAR = chr(9608) # Character 9608 is a solid block.# (!) Try setting two of these values to zero to rotate the cube only
# along a single axis:
X_ROTATE_SPEED = 0.03
Y_ROTATE_SPEED = 0.08
Z_ROTATE_SPEED = 0.13# This program stores XYZ coordinates in lists, with the X coordinate
# at index 0, Y at 1, and Z at 2\. These constants make our code more
# readable when accessing the coordinates in these lists.
X = 0
Y = 1
Z = 2def line(x1, y1, x2, y2):"""Returns a list of points in a line between the given points.Uses the Bresenham line algorithm. More info at:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bresenham%27s_line_algorithm"""points = [] # Contains the points of the line.# "Steep" means the slope of the line is greater than 45 degrees or# less than -45 degrees:# Check for the special case where the start and end points are# certain neighbors, which this function doesn't handle correctly,# and return a hard coded list instead:if (x1 == x2 and y1 == y2 + 1) or (y1 == y2 and x1 == x2 + 1):return [(x1, y1), (x2, y2)]isSteep = abs(y2 - y1) > abs(x2 - x1)if isSteep:# This algorithm only handles non-steep lines, so let's change# the slope to non-steep and change it back later.x1, y1 = y1, x1 # Swap x1 and y1x2, y2 = y2, x2 # Swap x2 and y2isReversed = x1 > x2 # True if the line goes right-to-left.if isReversed: # Get the points on the line going right-to-left.x1, x2 = x2, x1 # Swap x1 and x2y1, y2 = y2, y1 # Swap y1 and y2deltax = x2 - x1deltay = abs(y2 - y1)extray = int(deltax / 2)currenty = y2if y1 < y2:ydirection = 1else:ydirection = -1# Calculate the y for every x in this line:for currentx in range(x2, x1 - 1, -1):if isSteep:points.append((currenty, currentx))else:points.append((currentx, currenty))extray -= deltayif extray <= 0: # Only change y once extray <= 0.currenty -= ydirectionextray += deltaxelse: # Get the points on the line going left to right.deltax = x2 - x1deltay = abs(y2 - y1)extray = int(deltax / 2)currenty = y1if y1 < y2:ydirection = 1else:ydirection = -1# Calculate the y for every x in this line:for currentx in range(x1, x2 + 1):if isSteep:points.append((currenty, currentx))else:points.append((currentx, currenty))extray -= deltayif extray < 0: # Only change y once extray < 0.currenty += ydirectionextray += deltaxreturn pointsdef rotatePoint(x, y, z, ax, ay, az):"""Returns an (x, y, z) tuple of the x, y, z arguments rotated.The rotation happens around the 0, 0, 0 origin by anglesax, ay, az (in radians).Directions of each axis:-y|+-- +x/+z"""# Rotate around x axis:rotatedX = xrotatedY = (y * math.cos(ax)) - (z * math.sin(ax))rotatedZ = (y * math.sin(ax)) + (z * math.cos(ax))x, y, z = rotatedX, rotatedY, rotatedZ# Rotate around y axis:rotatedX = (z * math.sin(ay)) + (x * math.cos(ay))rotatedY = yrotatedZ = (z * math.cos(ay)) - (x * math.sin(ay))x, y, z = rotatedX, rotatedY, rotatedZ# Rotate around z axis:rotatedX = (x * math.cos(az)) - (y * math.sin(az))rotatedY = (x * math.sin(az)) + (y * math.cos(az))rotatedZ = zreturn (rotatedX, rotatedY, rotatedZ)def adjustPoint(point):"""Adjusts the 3D XYZ point to a 2D XY point fit for displaying onthe screen. This resizes this 2D point by a scale of SCALEX andSCALEY, then moves the point by TRANSLATEX and TRANSLATEY."""return (int(point[X] * SCALEX + TRANSLATEX),int(point[Y] * SCALEY + TRANSLATEY))"""CUBE_CORNERS stores the XYZ coordinates of the corners of a cube.
The indexes for each corner in CUBE_CORNERS are marked in this diagram:0---1/| /|2---3 || 4-|-5|/ |/6---7"""
CUBE_CORNERS = [[-1, -1, -1], # Point 0[ 1, -1, -1], # Point 1[-1, -1, 1], # Point 2[ 1, -1, 1], # Point 3[-1, 1, -1], # Point 4[ 1, 1, -1], # Point 5[-1, 1, 1], # Point 6[ 1, 1, 1]] # Point 7
# rotatedCorners stores the XYZ coordinates from CUBE_CORNERS after
# they've been rotated by rx, ry, and rz amounts:
rotatedCorners = [None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None]
# Rotation amounts for each axis:
xRotation = 0.0
yRotation = 0.0
zRotation = 0.0try:while True: # Main program loop.# Rotate the cube along different axes by different amounts:xRotation += X_ROTATE_SPEEDyRotation += Y_ROTATE_SPEEDzRotation += Z_ROTATE_SPEEDfor i in range(len(CUBE_CORNERS)):x = CUBE_CORNERS[i][X]y = CUBE_CORNERS[i][Y]z = CUBE_CORNERS[i][Z]rotatedCorners[i] = rotatePoint(x, y, z, xRotation,yRotation, zRotation)# Get the points of the cube lines:cubePoints = []for fromCornerIndex, toCornerIndex in ((0, 1), (1, 3), (3, 2), (2, 0), (0, 4), (1, 5), (2, 6), (3, 7), (4, 5), (5, 7), (7, 6), (6, 4)):fromX, fromY = adjustPoint(rotatedCorners[fromCornerIndex])toX, toY = adjustPoint(rotatedCorners[toCornerIndex])pointsOnLine = line(fromX, fromY, toX, toY)cubePoints.extend(pointsOnLine)# Get rid of duplicate points:cubePoints = tuple(frozenset(cubePoints))# Display the cube on the screen:for y in range(HEIGHT):for x in range(WIDTH):if (x, y) in cubePoints:# Display full block:print(LINE_CHAR, end='', flush=False)else:# Display empty space:print(' ', end='', flush=False)print(flush=False)print('Press Ctrl-C to quit.', end='', flush=True)time.sleep(PAUSE_AMOUNT) # Pause for a bit.# Clear the screen:if sys.platform == 'win32':os.system('cls') # Windows uses the cls command.else:os.system('clear') # macOS and Linux use the clear command.except KeyboardInterrupt:print('Rotating Cube, by Al Sweigart email@protected')sys.exit() # When Ctrl-C is pressed, end the program.
在输入源代码并运行几次之后,尝试对其进行实验性的修改。标有(!)的注释对你可以做的小改变有建议。你也可以自己想办法做到以下几点:
- 修改
CUBE_CORNERS和第 184 行的元组,创建不同的线框模型,如金字塔和扁平六边形。 - 将
CUBE_CORNERS的坐标增加1.5,使立方体围绕屏幕中心旋转,而不是围绕自己的中心旋转。
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果删除或注释掉第 208 到 211 行会发生什么?
- 如果把 184 行的元组改成
<((0, 1), (1, 3), (3, 2), (2, 0), (0,4), (4, 5), (5, 1))>会怎么样?
六十三、乌尔皇家游戏
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project63.html

乌尔的皇家游戏是一个来自美索不达米亚的有 5000 年历史的游戏。考古学家在 1922 年至 1934 年间的挖掘过程中,在现代伊拉克南部的乌尔皇家墓地重新发现了这款游戏。这些规则是根据游戏棋盘(如图 63-1 所示)和一块巴比伦泥板重建的,它们类似于 Parcheesi。你需要运气和技巧才能赢。

图 63-1 :在乌尔皇家墓地发现的五块游戏板之一
两名玩家每人从家中的七个代币开始,第一个将所有七个代币移动到目标位置的玩家获胜。玩家轮流掷出四个骰子。这些骰子是称为四面体的四角金字塔形状。每个骰子都有两个标记点,这使得骰子有标记或无标记的机会均等。我们的游戏用硬币代替骰子,硬币的头部作为标记点。玩家可以为出现的每一个标记点移动一格代币。这意味着他们可以在 0 到 4 个空格之间移动一个代币,尽管他们最有可能掷出两个空格。
代币沿着图 63-2 中所示的路径行进。一个空间上一次只能存在一个代币。如果一个代币在共享中间路径上落在对手的代币上,对手的代币会被送回家。如果一个代币落在中间的花方格上,它就不会被落在上面。如果一个代币落在其他四个花牌中的任何一个上,玩家可以再掷一次。我们的游戏将用字母X和O来代表代币。

图 63-2 :每个玩家的代币从他们的家到他们的目标的路径
在www.youtube.com/watch?v=WZskjLq040I可以找到优图伯·汤姆·斯科特和大英博物馆馆长欧文·芬克尔讨论乌尔王族游戏的视频。
运行示例
当您运行royalgameofur.py时,输出将如下所示:
The Royal Game of Ur, by Al Sweigart
`--snip--`XXXXXXX .......Home Goalv ^
+-----+-----+-----+--v--+ +--^--+-----+
|*****| | | | |*****| |
|* *< < < | |* *< |
|****h| g| f| e| |****t| s|
+--v--+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+--^--+
| | | |*****| | | | |
| > > >* *> > > > |
| i| j| k|****l| m| n| o| p|
+--^--+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+--v--+
|*****| | | | |*****| |
|* *< < < | |* *< |
|****d| c| b| a| |****r| q|
+-----+-----+-----+--^--+ +--v--+-----+^ vHome GoalOOOOOOO .......It is O's turn. Press Enter to flip...
Flips: H-H-H-H Select token to move 4 spaces: home quit
> home
O landed on a flower space and gets to go again.
Press Enter to continue...
`--snip--`
工作原理
就像项目 43“曼卡拉”一样,ASCII 艺术画游戏棋盘上的空格用字母a到t标注。掷骰子后,玩家可以选择一个包含其代币的空间来移动代币,或者他们可以选择home开始将代币从家中移到棋盘上。该程序将棋盘表示为一个字典,其中键为'a'到't',值为'X'和'O'用于标记(或' '用于空格)。
此外,这个字典有关键字'x_home'、'o_home'、'x_goal'和'o_goal',这些关键字的值是七个字符的字符串,表示家庭和目标有多满。这些字符串中的'X'或'O'字符代表主场或球门的代币,'.'代表空位置。displayBoard()函数在屏幕上显示这七个字符串。
"""The Royal Game of Ur, by Al Sweigart email@protected
A 5,000 year old board game from Mesopotamia. Two players knock each
other back as they race for the goal.
More info https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Game_of_Ur
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: large, board game, game, two-player
"""import random, sysX_PLAYER = 'X'
O_PLAYER = 'O'
EMPTY = ' '# Set up constants for the space labels:
X_HOME = 'x_home'
O_HOME = 'o_home'
X_GOAL = 'x_goal'
O_GOAL = 'o_goal'# The spaces in left to right, top to bottom order:
ALL_SPACES = 'hgfetsijklmnopdcbarq'
X_TRACK = 'HefghijklmnopstG' # (H stands for Home, G stands for Goal.)
O_TRACK = 'HabcdijklmnopqrG'FLOWER_SPACES = ('h', 't', 'l', 'd', 'r')BOARD_TEMPLATE = """
{} {} 30\. Home Goalv ^
+-----+-----+-----+--v--+ +--^--+-----+
|*****| | | | |*****| |
|* {} *< {} < {} < {} | |* {} *< {} |
|****h| g| f| e| |****t| s|
+--v--+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+--^--+
| | | |*****| | | | |
| {} > {} > {} >* {} *> {} > {} > {} > {} |
| i| j| k|****l| m| n| o| p|
+--^--+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+--v--+
|*****| | | | |*****| |
|* {} *< {} < {} < {} | |* {} *< {} |
|****d| c| b| a| |****r| q|
+-----+-----+-----+--^--+ +--v--+-----+^ vHome Goal
{} {} 48\. """def main():print('''The Royal Game of Ur, by Al SweigartThis is a 5,000 year old game. Two players must move their tokens
from their home to their goal. On your turn you flip four coins and can
move one token a number of spaces equal to the heads you got.Ur is a racing game; the first player to move all seven of their tokens
to their goal wins. To do this, tokens must travel from their home to
their goal:X Home X Goalv ^
+---+---+---+-v-+ +-^-+---+
|v<<<<<<<<<<<<< | | ^<|<< |
|v | | | | | | ^ |
+v--+---+---+---+---+---+---+-^-+
|>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>^ |
|>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>v |
+^--+---+---+---+---+---+---+-v-+
|^ | | | | | | v |
|^<<<<<<<<<<<<< | | v<<<< |
+---+---+---+-^-+ +-v-+---+^ vO Home O GoalIf you land on an opponent's token in the middle track, it gets sent
back home. The **flower** spaces let you take another turn. Tokens in
the middle flower space are safe and cannot be landed on.''')input('Press Enter to begin...')gameBoard = getNewBoard()turn = O_PLAYERwhile True: # Main game loop.# Set up some variables for this turn:if turn == X_PLAYER:opponent = O_PLAYERhome = X_HOMEtrack = X_TRACKgoal = X_GOALopponentHome = O_HOMEelif turn == O_PLAYER:opponent = X_PLAYERhome = O_HOMEtrack = O_TRACKgoal = O_GOALopponentHome = X_HOMEdisplayBoard(gameBoard)input('It is ' + turn + '\'s turn. Press Enter to flip...')flipTally = 0print('Flips: ', end='')for i in range(4): # Flip 4 coins.result = random.randint(0, 1)if result == 0:print('T', end='') # Tails.else:print('H', end='') # Heads.if i != 3:print('-', end='') # Print separator.flipTally += resultprint(' ', end='')if flipTally == 0:input('You lose a turn. Press Enter to continue...')turn = opponent # Swap turns to the other player.continue# Ask the player for their move:validMoves = getValidMoves(gameBoard, turn, flipTally)if validMoves == []:print('There are no possible moves, so you lose a turn.')input('Press Enter to continue...')turn = opponent # Swap turns to the other player.continuewhile True:print('Select move', flipTally, 'spaces: ', end='')print(' '.join(validMoves) + ' quit')move = input('> ').lower()if move == 'quit':print('Thanks for playing!')sys.exit()if move in validMoves:break # Exit the loop when a valid move is selected.print('That is not a valid move.')# Perform the selected move on the board:if move == 'home':# Subtract tokens at home if moving from home:gameBoard[home] -= 1nextTrackSpaceIndex = flipTallyelse:gameBoard[move] = EMPTY # Set the "from" space to empty.nextTrackSpaceIndex = track.index(move) + flipTallymovingOntoGoal = nextTrackSpaceIndex == len(track) - 1if movingOntoGoal:gameBoard[goal] += 1# Check if the player has won:if gameBoard[goal] == 7:displayBoard(gameBoard)print(turn, 'has won the game!')print('Thanks for playing!')sys.exit()else:nextBoardSpace = track[nextTrackSpaceIndex]# Check if the opponent has a tile there:if gameBoard[nextBoardSpace] == opponent:gameBoard[opponentHome] += 1# Set the "to" space to the player's token:gameBoard[nextBoardSpace] = turn# Check if the player landed on a flower space and can go again:if nextBoardSpace in FLOWER_SPACES:print(turn, 'landed on a flower space and goes again.')input('Press Enter to continue...')else:turn = opponent # Swap turns to the other player.def getNewBoard():"""Returns a dictionary that represents the state of the board. Thekeys are strings of the space labels, the values are X_PLAYER,O_PLAYER, or EMPTY. There are also counters for how many tokens areat the home and goal of both players."""board = {X_HOME: 7, X_GOAL: 0, O_HOME: 7, O_GOAL: 0}# Set each space as empty to start:for spaceLabel in ALL_SPACES:board[spaceLabel] = EMPTYreturn boarddef displayBoard(board):"""Display the board on the screen."""# "Clear" the screen by printing many newlines, so the old# board isn't visible anymore.print('\n' * 60)xHomeTokens = ('X' * board[X_HOME]).ljust(7, '.')xGoalTokens = ('X' * board[X_GOAL]).ljust(7, '.')oHomeTokens = ('O' * board[O_HOME]).ljust(7, '.')oGoalTokens = ('O' * board[O_GOAL]).ljust(7, '.')# Add the strings that should populate BOARD_TEMPLATE in order,# going from left to right, top to bottom.spaces = []spaces.append(xHomeTokens)spaces.append(xGoalTokens)for spaceLabel in ALL_SPACES:spaces.append(board[spaceLabel])spaces.append(oHomeTokens)spaces.append(oGoalTokens)print(BOARD_TEMPLATE.format(*spaces))def getValidMoves(board, player, flipTally):validMoves = [] # Contains the spaces with tokens that can move.if player == X_PLAYER:opponent = O_PLAYERtrack = X_TRACKhome = X_HOMEelif player == O_PLAYER:opponent = X_PLAYERtrack = O_TRACKhome = O_HOME# Check if the player can move a token from home:if board[home] > 0 and board[track[flipTally]] == EMPTY:validMoves.append('home')# Check which spaces have a token the player can move:for trackSpaceIndex, space in enumerate(track):if space == 'H' or space == 'G' or board[space] != player:continuenextTrackSpaceIndex = trackSpaceIndex + flipTallyif nextTrackSpaceIndex >= len(track):# You must flip an exact number of moves onto the goal,# otherwise you can't move on the goal.continueelse:nextBoardSpaceKey = track[nextTrackSpaceIndex]if nextBoardSpaceKey == 'G':# This token can move off the board:validMoves.append(space)continueif board[nextBoardSpaceKey] in (EMPTY, opponent):# If the next space is the protected middle space, you# can only move there if it is empty:if nextBoardSpaceKey == 'l' and board['l'] == opponent:continue # Skip this move, the space is protected.validMoves.append(space)return validMovesif __name__ == '__main__':main()
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果把 152 行的
nextTrackSpaceIndex == len(track) - 1改成nextTrackSpaceIndex == 1会怎么样? - 如果把 106 行的
result = random.randint(0, 1)改成result = 1会怎么样? - 如果把 184 行的
board = {X_HOME: 7, X_GOAL: 0, O_HOME: 7, O_GOAL: 0}改成board = {}会导致什么错误?
六十四、七段显示模块
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project64.html

七段显示器是一种 LCD 组件,用于在袖珍计算器、微波炉和其他小型电子设备中显示数字。通过 LCD 中七个线段的不同组合,七段显示器可以表示数字 0 到 9。它们看起来像这样:
__ __ __ __ __ __ __ __| | | __| __| |__| |__ |__ | |__| |__||__| | |__ __| | __| |__| | |__| __|
这个程序的好处是其他程序可以把它作为一个模块导入。项目 14,“倒计时”和项目 19,“数字钟”,导入sevseg.py文件,这样他们就可以使用它的getSevSegStr()函数。你可以在en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seven-segment_display找到更多关于七段显示器和其他变化的信息。
运行示例
尽管它是一个模块,当你直接运行程序时,sevseg.py输出一个它产生的数字的示例演示。输出将如下所示:
This module is meant to be imported rather than run.
For example, this code:import sevsegmyNumber = sevseg.getSevSegStr(42, 3)print(myNumber)Will print 42, zero-padded to three digits:__ __
| | |__| __|
|__| | |__
工作原理
getSevSegStr()函数首先创建一个包含三个字符串的列表。这些字符串表示数字的顶行、中间行和底行。第 27 行到第 75 行有一长串针对每个数字(以及小数点和减号)的if - elif语句,这些语句将每个数字的行连接到这些字符串。这三个字符串在第 84 行用换行符连接在一起,因此函数返回一个适合传递给print()的多行字符串。
"""Sevseg, by Al Sweigart email@protected
A seven-segment number display module, used by the Countdown and Digital
Clock programs.
More info at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Seven-segment_display
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: short, module""""""A labeled seven-segment display, with each segment labeled A to G:
__A__
| | Each digit in a seven-segment display:
F B __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
|__G__| | | | __| __| |__| |__ |__ | |__| |__|
| | |__| | |__ __| | __| |__| | |__| __|
E C
|__D__|"""def getSevSegStr(number, minWidth=0):"""Return a seven-segment display string of number. The returnedstring will be padded with zeros if it is smaller than minWidth."""# Convert number to string in case it's an int or float:number = str(number).zfill(minWidth)rows = ['', '', '']for i, numeral in enumerate(number):if numeral == '.': # Render the decimal point.rows[0] += ' 'rows[1] += ' 'rows[2] += '.'continue # Skip the space in between digits.elif numeral == '-': # Render the negative sign:rows[0] += ' 'rows[1] += ' __ 'rows[2] += ' 'elif numeral == '0': # Render the 0.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += '| |'rows[2] += '|__|'elif numeral == '1': # Render the 1.rows[0] += ' 'rows[1] += ' |'rows[2] += ' |'elif numeral == '2': # Render the 2.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += ' __|'rows[2] += '|__ 'elif numeral == '3': # Render the 3.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += ' __|'rows[2] += ' __|'elif numeral == '4': # Render the 4.rows[0] += ' 'rows[1] += '|__|'rows[2] += ' |'elif numeral == '5': # Render the 5.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += '|__ 'rows[2] += ' __|'elif numeral == '6': # Render the 6.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += '|__ 'rows[2] += '|__|'elif numeral == '7': # Render the 7.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += ' |'rows[2] += ' |'elif numeral == '8': # Render the 8.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += '|__|'rows[2] += '|__|'elif numeral == '9': # Render the 9.rows[0] += ' __ 'rows[1] += '|__|'rows[2] += ' __|'# Add a space (for the space in between numerals) if this# isn't the last numeral and the decimal point isn't next:if i != len(number) - 1 and number[i + 1] != '.':rows[0] += ' 'rows[1] += ' 'rows[2] += ' 'return '\n'.join(rows)# If this program isn't being imported, display the numbers 00 to 99.
if __name__ == '__main__':print('This module is meant to be imported rather than run.')print('For example, this code:')print(' import sevseg')print(' myNumber = sevseg.getSevSegStr(42, 3)')print(' print(myNumber)')print()print('...will print 42, zero-padded to three digits:')print(' __ __ ')print('| | |__| __|')print('|__| | |__ ')
在输入源代码并运行几次之后,尝试对其进行实验性的修改。你也可以自己想办法做到以下几点:
- 为数字创建新的字体,比如使用五行和
chr(9608)返回的块字符串。 - 查看维基百科关于七段显示的文章,了解如何显示字母,然后将它们添加到
sevseg.py。 - 从
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sixteen-segment_display学习十六段显示,并创建一个十六段显示模块来生成该样式的数字。
探索程序
试着找出下列问题的答案。尝试对代码进行一些修改,然后重新运行程序,看看这些修改有什么影响。
- 如果将第 80、81 和 82 行的单空格字符串改为空字符串会发生什么?
- 如果将第 18 行的默认参数
minWidth=0改为minWidth=8,会发生什么?
六十五、闪光地毯
原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project65.html

斯坦利·库布里克执导的 1980 年心理恐怖片《闪光》发生在闹鬼的远眺酒店。酒店地毯的六边形设计成为这部著名电影的标志性部分。地毯的特点是交替和连锁的六边形,其催眠效果非常适合这样一部令人紧张的电影。这个项目中的短程序,类似于项目 35,“六边形网格”,在屏幕上打印这个重复的图案。
注意,这个程序使用原始字符串,它在开始的引号前面加上小写的r,这样字符串中的反斜杠就不会被解释为转义字符。
运行示例
当您运行shiningcarpet.py时,输出将如下所示:
_ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ __\ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _
\ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/
/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_
_/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \__
__/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \___
_ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ __\ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _
\ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/
/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_
_/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \__
__/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \___
_ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ ___ \ \ \_/ __\ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _ \ \ \___/ _
\ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/ \ \ \_____/
/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_/ / / ___ \_
_/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \___/ / / _ \__
__/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \_____/ / / \___
工作原理
创建这样的程序(或类似的第三十五个项目)并不是从编码开始,而是在文本编辑器中绘制镶嵌形状。一旦你写出了图案,你就可以把它切割成需要平铺的最小单元:
_ \ \ \_/ __\ \ \___/ _
\ \ \_____/
/ / / ___ \_
_/ / / _ \__
__/ / / \___
将这段文本复制并粘贴到源代码中后,您可以围绕它编写程序的其余部分。软件不仅仅是坐下来从头到尾写代码。每个专业软件开发人员都要经历几次反复的修补、实验和调试。最终的结果可能只有九行代码,但是一个小程序并不一定意味着花了很少的精力来完成它。
"""Shining Carpet, by Al Sweigart email@protected
Displays a tessellation of the carpet pattern from The Shining.
This code is available at https://nostarch.com/big-book-small-python-programming
Tags: tiny, beginner, artistic"""# Set up the constants:
X_REPEAT = 6 # How many times to tessellate horizontally.
Y_REPEAT = 4 # How many times to tessellate vertically.for i in range(Y_REPEAT):print(r'_ \ \ \_/ __' * X_REPEAT)print(r' \ \ \___/ _' * X_REPEAT)print(r'\ \ \_____/ ' * X_REPEAT)print(r'/ / / ___ \_' * X_REPEAT)print(r'_/ / / _ \__' * X_REPEAT)print(r'__/ / / \___' * X_REPEAT)
探索程序
在实践中,尝试创建如下模式:
___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|
_|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|__
___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|
_|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|__
___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|
_|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|__(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))(
(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))(
(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )(( )))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))( ))(/ __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/
/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____
\ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __\____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \/ __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/
/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____
\ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __ \ \__/ / __\____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \ \____/ / \\__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__
__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \
__/ __/ __/ __/ __/ __/ __/ __/ __/ __/\__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/
__/ / / / / / / / / /\__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__ \__
__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \__/ \/ ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^/ \ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV
|() ()| |() ()| |() ()| |() ()| |() ()| |() ()|\ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___ \ ^ / ___
\ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV / \ VVV /
)| |() ()| |() ()| |() ()| |() ()| |() ()| |() (
相关文章:

Python 小型项目大全 61~65
六十一、ROT13 密码 原文:http://inventwithpython.com/bigbookpython/project61.html ROT13 密码是最简单的加密算法之一,代表“旋转 13 个空格”密码将字母A到Z表示为数字 0 到 25,加密后的字母距离明文字母 13 个空格: A变成N&…...
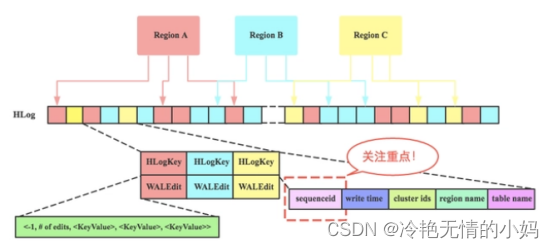
Hlog
Hlog 简介 Hlog是Hbase实现WAL(Write ahead log )方式产生的日志信息 , 内部是一个简单的顺序日志。每个RegionServer对应1个Hlog(备注:1.X版本的可以开启MultiWAL功能,允许对应多个Hlog),所有对于该RegionServer的写入都会被记录到Hlog中。H…...

学编程应该选择什么操作系统?
今天来聊一个老生常谈的问题,学编程时到底选择什么操作系统?Mac、Windows,还是别的什么。。 作为一个每种操作系统都用过很多年的程序员,我会结合我自己的经历来给大家一些参考和建议。 接下来先分别聊聊每种操作系统的优点和不…...
Oracle基础部分二(伪列/表、单个函数、空值处理、行列转换、分析函数、集合运算)
Oracle基础部分二(伪列/表、单个函数、空值处理、行列转换、分析函数、集合运算)1 伪列、伪表1.1 伪列1.2 伪表2 单个函数2.1 常用字符串函数2.1.1 length() 询指定字符的长度2.1.2 substr() 用于截取字符串2.1.3 concat() 用于字符串拼接2.2 常用数值函…...

c/c++:原码,反码,补码和常见的数据类型取值范围,溢出
c/c:原码,反码,补码和常见的数据类型取值范围,溢出 2022找工作是学历、能力和运气的超强结合体,遇到寒冬,大厂不招人,此时学会c的话, 我所知道的周边的会c的同学,可手握…...

Java题目训练——年终奖和迷宫问题
目录 一、年终奖 二、迷宫问题 一、年终奖 题目描述: 小东所在公司要发年终奖,而小东恰好获得了最高福利,他要在公司年会上参与一个抽奖游戏,游戏在一个6*6的棋盘上进行,上面放着36个价值不等的礼物, 每…...
ORACLE EBS系统应用基础概述(1)
一、前言 有网友在论坛发帖惊呼:好不容易把EBS系统安装好了,进去一看傻眼了,不知道从哪儿下手?发出惊叹的这位网友所遇到的问题,实际上也是很多人曾经遇到或正在遇到的问题。长期以来,国内的非专业人士&am…...

电子科技大学信息与通信工程学院2023考研复试总结
一、笔试 笔试主要考察数字逻辑(数电)的相关知识,满分200分,需要复习的内容不多且知识点比较集中。根据考场上实际感受,题目难度不大但是题量稍大,2h完成试卷几乎没有多少剩余时间。笔试的体型分为填空题、…...
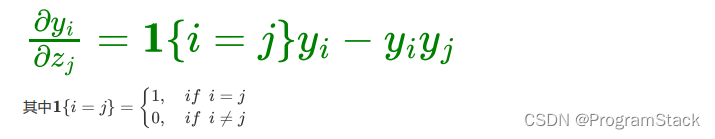
神经网络激活函数
神经网络激活函数神经网络激活函数的定义为什么神经网络要用激活函数神经网络激活函数的求导Sigmoid激活函数Tanh激活函数Softmax激活函数神经网络激活函数的定义 所谓激活函数(Activation Function),就是在人工神经网络的神经元上运行的函数…...

2.C 语言基本语法
文章目录二、C 语言基本语法1.语句2.表达式3.语句块4.空格5.注释6.printf()函数基本用法7.占位符8.输出格式10.标准库,头文件提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考 二、C 语言基本语法 1.语句 C语言的代码由一行行语句࿰…...

Qt 6.5 LTS 正式发布
Qt 6.5 LTS 已正式发布。此版本为图形和 UI 开发者以及应用程序后端引入了许多新功能,还包含许多修复和通用的改进。Qt 6.5 将成为商业许可证持有者的长期支持 (LTS) 版本。 部分更新亮点: 改进主题和样式 使用 Qt 6.5,应用程序能够便捷地支持…...

Linux权限提升—定时任务、环境变量、权限配置不当、数据库等提权
Linux权限提升—定时任务、环境变量、权限配置不当、数据库等提权1. 前言1.1. 如何找编译好的EXP2. 定时任务提权2.1. 查看定时任务2.2. 通配符注入提权2.2.1. 创建执行脚本2.2.2. 创建定时任务2.2.3. 查看效果2.2.4. 提权操作2.2.4.1. 切换普通用户2.2.4.2. 执行命令2.2.4.3. …...

Python爬虫——使用requests和beautifulsoup4库来爬取指定网页的信息
以下是一个简单的Python代码,使用requests和beautifulsoup4库来爬取指定网页的信息: import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoupurl "https://example.com"# 发送GET请求,获取网页内容 response requests.get(url)# 将网页内…...
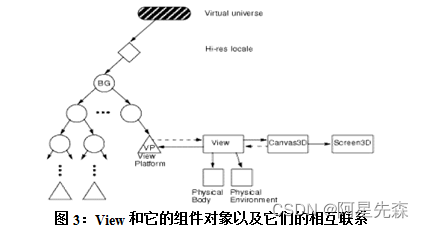
基于Java3D的网络三维技术的设计与实现
3D图形技术并不是一个新话题,在图形工作站以至于PC机上早已日臻成熟,并已应用到各个领域。然而互联网的出现,却使3D图形技术发生了和正在发生着微妙而深刻的变化。Web3D协会(前身是VRML协会)最先使用Web3D术语…...
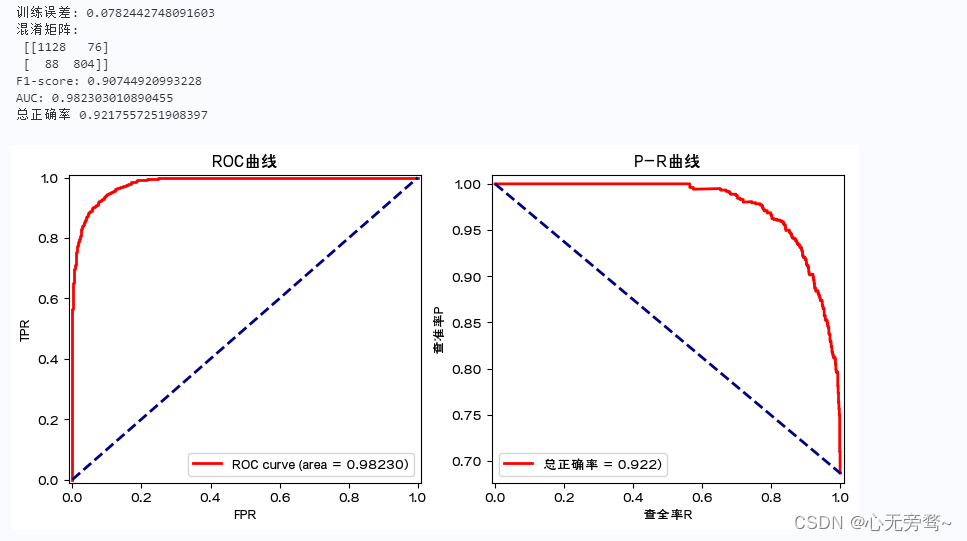
python机器学习数据建模与分析——数据预测与预测建模
文章目录前言一、预测建模1.1 预测建模涉及的方面:1.2 预测建模的几何理解1.3 预测模型参数估计的基本策略1.4 有监督学习算法与损失函数:1.5 参数解空间和搜索策略1.6 预测模型的评价1.6.1 模型误差的评价指标1.6.2 模型的图形化评价工具1.6.3 训练误差…...

Flink系列-6、Flink DataSet的Transformation
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。 大数据系列文章目录 官方网址:https://flink.apache.org/ 学习资料:https://flink-learning.org.cn/ 目录Flink 算子Ma…...

Java-类的知识进阶
Java类的知识进阶 类的继承(扩张类) Java类的继承是指一个类可以继承另一个类的属性和方法,从而使得子类可以重用父类的代码。继承是面向对象编程中的重要概念,它可以帮助我们避免重复编写代码,提高代码的复用性和可…...
摘要算法)
C# | 上位机开发新手指南(六)摘要算法
C# | 上位机开发新手指南(六)摘要算法 文章目录C# | 上位机开发新手指南(六)摘要算法前言常见摘要算法源码MD5算法SHA-1算法SHA-256算法SHA-512算法BLAKE2算法RIPEMD算法Whirlpool算法前言 你知道摘要算法么?它在保障…...
测试工程师:“ 这锅我不背 ” ,面对灵魂三问,如何回怼?
前言 在一个周末的早餐我被同事小周叫出去跑步,本想睡个懒觉,但是看他情绪不太稳定的样子,无奈艰难爬起陪他去跑步。 只见她气冲冲的对着河边大喊:真是冤枉啊!!! 原来是在工作中被莫名其妙背锅࿰…...
【Java闭关修炼】SpringBoot-SpringMVC概述和入门
SpringMVC概述和入门 MVC概述 实体类Bean:专门 存储业务数据 Student User业务处理Bean:指的是Service或者Dao 专门用来处理业务逻辑或者数据访问 用户通过视图层发送请求到服务器,在服务器中请求被Controller接受,Controller调用相应的MOdel层处理请求…...

TDengine 快速体验(Docker 镜像方式)
简介 TDengine 可以通过安装包、Docker 镜像 及云服务快速体验 TDengine 的功能,本节首先介绍如何通过 Docker 快速体验 TDengine,然后介绍如何在 Docker 环境下体验 TDengine 的写入和查询功能。如果你不熟悉 Docker,请使用 安装包的方式快…...
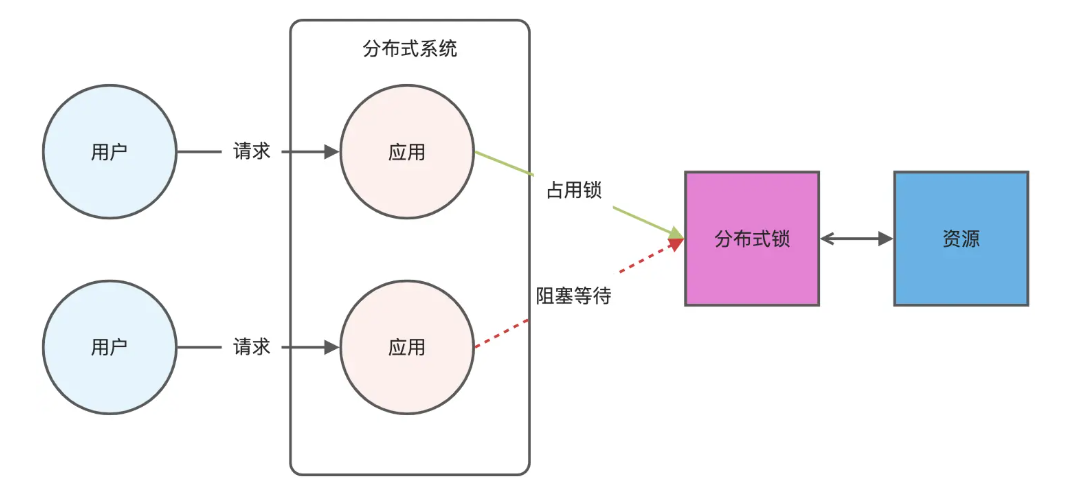
Redis相关知识总结(缓存雪崩,缓存穿透,缓存击穿,Redis实现分布式锁,如何保持数据库和缓存一致)
文章目录 1.什么是Redis?2.为什么要使用redis作为mysql的缓存?3.什么是缓存雪崩、缓存穿透、缓存击穿?3.1缓存雪崩3.1.1 大量缓存同时过期3.1.2 Redis宕机 3.2 缓存击穿3.3 缓存穿透3.4 总结 4. 数据库和缓存如何保持一致性5. Redis实现分布式…...
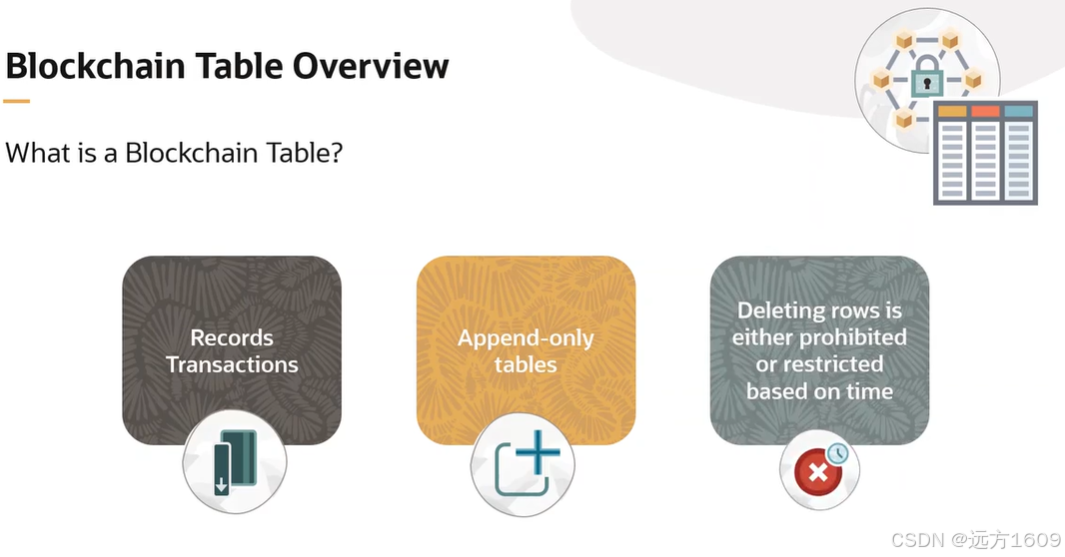
23-Oracle 23 ai 区块链表(Blockchain Table)
小伙伴有没有在金融强合规的领域中遇见,必须要保持数据不可变,管理员都无法修改和留痕的要求。比如医疗的电子病历中,影像检查检验结果不可篡改行的,药品追溯过程中数据只可插入无法删除的特性需求;登录日志、修改日志…...
` 方法)
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 `window.crypto.getRandomValues()` 方法
深入浅出:JavaScript 中的 window.crypto.getRandomValues() 方法 在现代 Web 开发中,随机数的生成看似简单,却隐藏着许多玄机。无论是生成密码、加密密钥,还是创建安全令牌,随机数的质量直接关系到系统的安全性。Jav…...
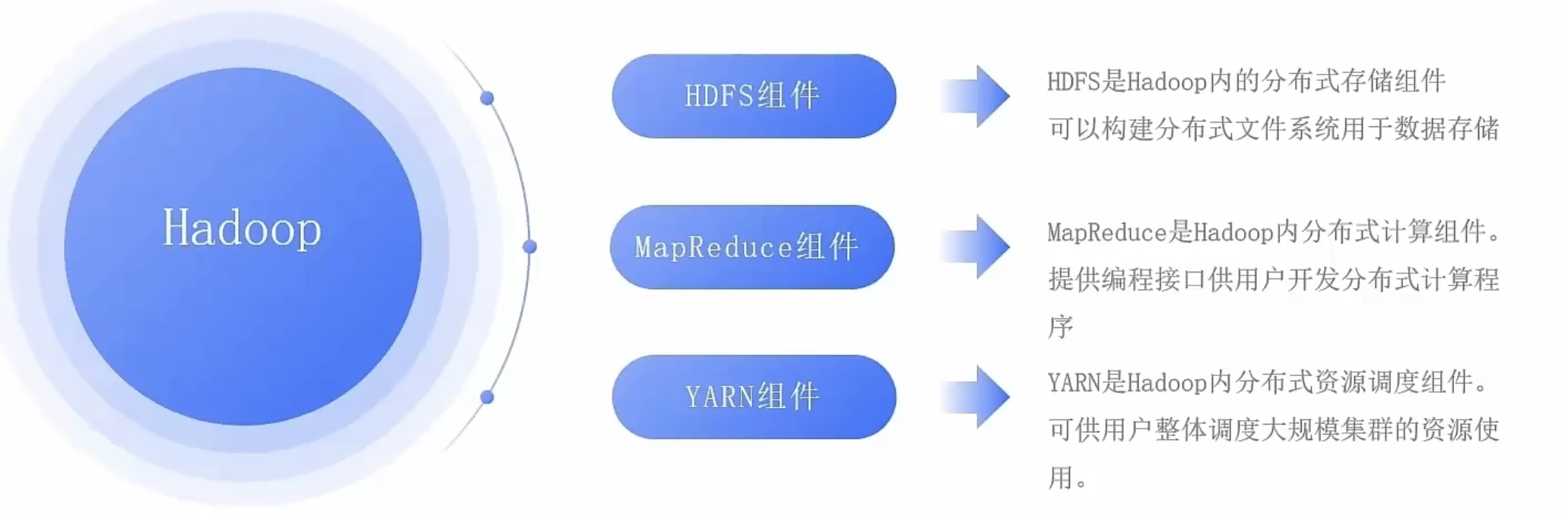
大数据零基础学习day1之环境准备和大数据初步理解
学习大数据会使用到多台Linux服务器。 一、环境准备 1、VMware 基于VMware构建Linux虚拟机 是大数据从业者或者IT从业者的必备技能之一也是成本低廉的方案 所以VMware虚拟机方案是必须要学习的。 (1)设置网关 打开VMware虚拟机,点击编辑…...

学校招生小程序源码介绍
基于ThinkPHPFastAdminUniApp开发的学校招生小程序源码,专为学校招生场景量身打造,功能实用且操作便捷。 从技术架构来看,ThinkPHP提供稳定可靠的后台服务,FastAdmin加速开发流程,UniApp则保障小程序在多端有良好的兼…...
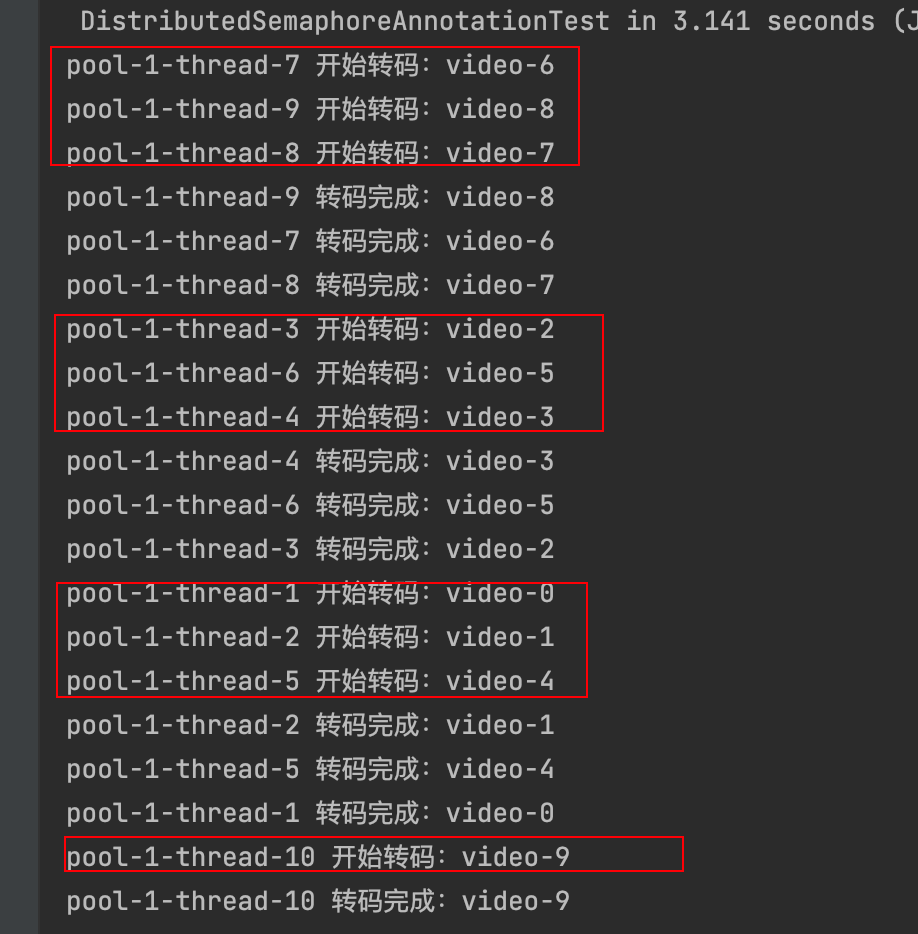
令牌桶 滑动窗口->限流 分布式信号量->限并发的原理 lua脚本分析介绍
文章目录 前言限流限制并发的实际理解限流令牌桶代码实现结果分析令牌桶lua的模拟实现原理总结: 滑动窗口代码实现结果分析lua脚本原理解析 限并发分布式信号量代码实现结果分析lua脚本实现原理 双注解去实现限流 并发结果分析: 实际业务去理解体会统一注…...

Java多线程实现之Thread类深度解析
Java多线程实现之Thread类深度解析 一、多线程基础概念1.1 什么是线程1.2 多线程的优势1.3 Java多线程模型 二、Thread类的基本结构与构造函数2.1 Thread类的继承关系2.2 构造函数 三、创建和启动线程3.1 继承Thread类创建线程3.2 实现Runnable接口创建线程 四、Thread类的核心…...

在web-view 加载的本地及远程HTML中调用uniapp的API及网页和vue页面是如何通讯的?
uni-app 中 Web-view 与 Vue 页面的通讯机制详解 一、Web-view 简介 Web-view 是 uni-app 提供的一个重要组件,用于在原生应用中加载 HTML 页面: 支持加载本地 HTML 文件支持加载远程 HTML 页面实现 Web 与原生的双向通讯可用于嵌入第三方网页或 H5 应…...
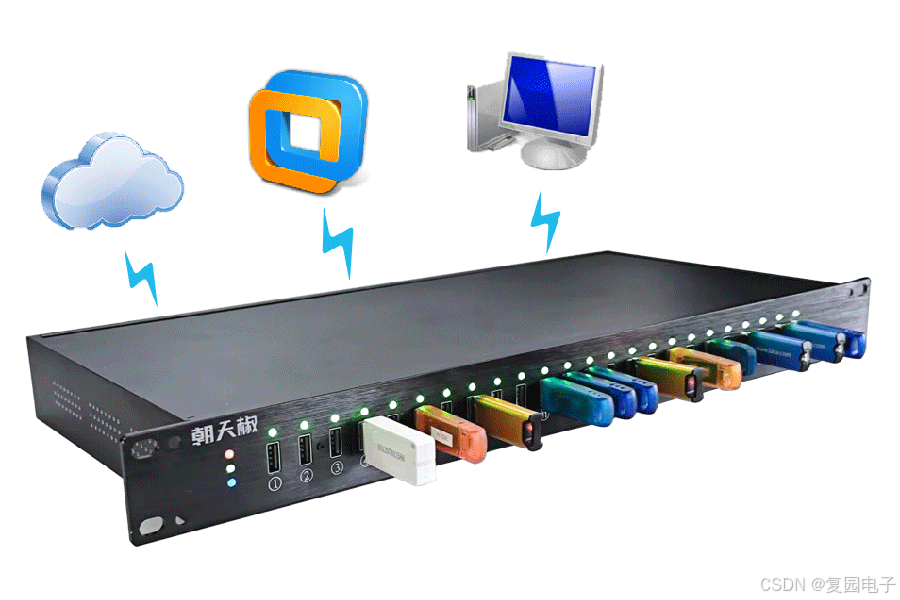
USB Over IP专用硬件的5个特点
USB over IP技术通过将USB协议数据封装在标准TCP/IP网络数据包中,从根本上改变了USB连接。这允许客户端通过局域网或广域网远程访问和控制物理连接到服务器的USB设备(如专用硬件设备),从而消除了直接物理连接的需要。USB over IP的…...
