CompletableFuture使用详解(IT枫斗者)
CompletableFuture使用详解
简介
概述
-
CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力,可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。从某种程度上说,这项能力是它的核心能力。而在以往,虽然通过CountDownLatch等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理,不仅耗费精力且难以维护。
-
CompletableFuture的继承结构如下: -
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-a61HTSe5-1680694141534)(C:%5CUsers%5Cquyanliang%5CAppData%5CRoaming%5CTypora%5Ctypora-user-images%5C1680692539301.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d35668d1665f47a5a7ac12a6a6e3b392.png)
-
CompletionStage接口定义了任务编排的方法,执行某一阶段,可以向下执行后续阶段。异步执行的,默认线程池是ForkJoinPool.commonPool(),但为了业务之间互不影响,且便于定位问题,强烈推荐使用自定义线程池。 -
CompletableFuture中默认线程池如下: -
// 根据commonPool的并行度来选择,而并行度的计算是在ForkJoinPool的静态代码段完成的 private static final boolean useCommonPool =(ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism() > 1);private static final Executor asyncPool = useCommonPool ?ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(); -
ForkJoinPool中初始化commonPool的参数 \ -
static {// initialize field offsets for CAS etctry {U = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();Class<?> k = ForkJoinPool.class;CTL = U.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("ctl"));RUNSTATE = U.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("runState"));STEALCOUNTER = U.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("stealCounter"));Class<?> tk = Thread.class;……} catch (Exception e) {throw new Error(e);}commonMaxSpares = DEFAULT_COMMON_MAX_SPARES;defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory =new DefaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory();modifyThreadPermission = new RuntimePermission("modifyThread");// 调用makeCommonPool方法创建commonPool,其中并行度为逻辑核数-1common = java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(new java.security.PrivilegedAction<ForkJoinPool>() {public ForkJoinPool run() { return makeCommonPool(); }});int par = common.config & SMASK; // report 1 even if threads disabledcommonParallelism = par > 0 ? par : 1; }
功能
常用方法
-
依赖关系
- thenApply():把前面任务的执行结果,交给后面的Function
- thenCompose():用来连接两个有依赖关系的任务,结果由第二个任务返回
-
and集合关系
thenCombine():合并任务,有返回值thenAccepetBoth():两个任务执行完成后,将结果交给thenAccepetBoth处理,无返回值runAfterBoth():两个任务都执行完成后,执行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
or聚合关系
applyToEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就使用哪一个结果,有返回值acceptEither():两个任务哪个执行的快,就消费哪一个结果,无返回值runAfterEither():任意一个任务执行完成,进行下一步操作(Runnable类型任务)
-
并行执行
allOf():当所有给定的 CompletableFuture 完成时,返回一个新的 CompletableFutureanyOf():当任何一个给定的CompletablFuture完成时,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
-
结果处理
- whenComplete:当任务完成时,将使用结果(或 null)和此阶段的异常(或 null如果没有)执行给定操作
- exceptionally:返回一个新的CompletableFuture,当前面的CompletableFuture完成时,它也完成,当它异常完成时,给定函数的异常触发这个CompletableFuture的完成
异步操作
-
CompletableFuture提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作: -
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor) -
这四个方法的区别:
-
runAsync() 以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数,没有返回结果,supplyAsync() 以Supplier函数式接口类型为参数,返回结果类型为U;Supplier接口的 get()是有返回值的(会阻塞)
-
使用没有指定Executor的方法时,内部使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行。
-
默认情况下CompletableFuture会使用公共的ForkJoinPool线程池,这个线程池默认创建的线程数是 CPU 的核数(也可以通过 JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism 来设置ForkJoinPool线程池的线程数)。如果所有CompletableFuture共享一个线程池,那么一旦有任务执行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,就会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,进而影响整个系统的性能。所以,强烈建议你要根据不同的业务类型创建不同的线程池,以避免互相干扰
-
异步操作
-
Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("无返回结果异步任务"); CompletableFuture.runAsync(runnable);CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("有返回值的异步任务");try {Thread.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "Hello World"; }); String result = future.get(); -
获取结果(join&get)
-
join()和get()方法都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值。join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException 需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch)
-
结果处理
-
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,我们可以执行特定的 Action。主要是下面的方法:
-
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action) public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor) -
Action的类型是BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>,它可以处理正常的计算结果,或者异常情况。
-
方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
-
这几个方法都会返回CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常
-
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if (new Random().nextInt(10) % 2 == 0) {int i = 12 / 0;}System.out.println("执行结束!");return "test"; }); // 任务完成或异常方法完成时执行该方法 // 如果出现了异常,任务结果为null future.whenComplete(new BiConsumer<String, Throwable>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String t, Throwable action) {System.out.println(t+" 执行完成!");} }); // 出现异常时先执行该方法 future.exceptionally(new Function<Throwable, String>() {@Overridepublic String apply(Throwable t) {System.out.println("执行失败:" + t.getMessage());return "异常xxxx";} });future.get(); -
上面的代码当出现异常时,输出结果如下
-
执行失败:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero null 执行完成!
应用场景
结果转换
- 将上一段任务的执行结果作为下一阶段任务的入参参与重新计算,产生新的结果。
thenApply
-
thenApply接收一个函数作为参数,使用该函数处理上一个CompletableFuture调用的结果,并返回一个具有处理结果的Future对象。 -
常用使用:
-
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int result = 100;System.out.println("第一次运算:" + result);return result; }).thenApply(number -> {int result = number * 3;System.out.println("第二次运算:" + result);return result; });
thenCompose
-
thenCompose的参数为一个返回CompletableFuture实例的函数,该函数的参数是先前计算步骤的结果。 -
常用方法:
-
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn); public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) ; -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(30);System.out.println("第一次运算:" + number);return number;}}).thenCompose(new Function<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>>() {@Overridepublic CompletionStage<Integer> apply(Integer param) {return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = param * 2;System.out.println("第二次运算:" + number);return number;}});}});
thenApply 和 thenCompose的区别:
- thenApply转换的是泛型中的类型,返回的是同一个CompletableFuture;
- thenCompose将内部的CompletableFuture调用展开来并使用上一个CompletableFutre调用的结果在下一步的CompletableFuture调用中进行运算,是生成一个新的CompletableFuture。
结果消费
- 与结果处理和结果转换系列函数返回一个新的
CompletableFuture不同,结果消费系列函数只对结果执行Action,而不返回新的计算值。 - 根据对结果的处理方式,结果消费函数又可以分为下面三大类:
thenAccept():对单个结果进行消费thenAcceptBoth():对两个结果进行消费thenRun():不关心结果,只对结果执行Action
thenAccept
-
观察该系列函数的参数类型可知,它们是函数式接口Consumer,这个接口只有输入,没有返回值。
-
常用方法:
-
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action); -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int number = new Random().nextInt(10);System.out.println("第一次运算:" + number);return number;}).thenAccept(number ->System.out.println("第二次运算:" + number * 5));
thenAcceptBoth
-
thenAcceptBoth函数的作用是,当两个CompletionStage都正常完成计算的时候,就会执行提供的action消费两个异步的结果。 -
常用方法:
-
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action); public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action); -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Integer> futrue1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(3) + 1;try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);return number;} });CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(3) + 1;try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);return number;} });futrue1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, new BiConsumer<Integer, Integer>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Integer x, Integer y) {System.out.println("最终结果:" + (x + y));} });
thenRun
-
thenRun也是对线程任务结果的一种消费函数,与thenAccept不同的是,thenRun会在上一阶段CompletableFuture计算完成的时候执行一个Runnable,而Runnable并不使用该CompletableFuture计算的结果。 -
常用方法:
-
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action); -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int number = new Random().nextInt(10);System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);return number; }).thenRun(() ->System.out.println("thenRun 执行"));
结果组合
thenCombine
-
合并两个线程任务的结果,并进一步处理。
-
常用方法:
-
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor); -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(10);System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);return number;}}); CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(10);System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);return number;}}); CompletableFuture<Integer> result = future1.thenCombine(future2, new BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer apply(Integer x, Integer y) {return x + y;}}); System.out.println("组合后结果:" + result.get());
任务交互
- 线程交互指将两个线程任务获取结果的速度相比较,按一定的规则进行下一步处理。
applyToEither
-
两个线程任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的转化操作。
-
常用方法:
-
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn); public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn); -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(10);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);return number;}}); CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(10);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);return number;} });future1.applyToEither(future2, new Function<Integer, Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer apply(Integer number) {System.out.println("最快结果:" + number);return number * 2;} });
acceptEither
-
两个线程任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的消费操作。
-
常用方法:
-
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action); -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(10) + 1;try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);return number;} });CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(10) + 1;try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number);return number;} });future1.acceptEither(future2, new Consumer<Integer>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Integer number) {System.out.println("最快结果:" + number);} });
runAfterEither
-
两个线程任务相比较,有任何一个执行完成,就进行下一步操作,不关心运行结果。
-
常用方法:
-
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action); -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(5);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("任务1结果:" + number);return number;} });CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer get() {int number = new Random().nextInt(5);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("任务2结果:" + number);return number;} });future1.runAfterEither(future2, new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("已经有一个任务完成了");} }).join();
anyOf
-
anyOf()的参数是多个给定的CompletableFuture,当其中的任何一个完成时,方法返回这个CompletableFuture。 -
常用方法:
-
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) -
具体使用:
-
Random random = new Random(); CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(5));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello"; });CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1));} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "world"; }); CompletableFuture<Object> result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
allOf
-
allOf方法用来实现多 CompletableFuture 的同时返回。
-
常用方法:
-
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) -
具体使用:
-
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("future1完成!");return "future1完成!"; });CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("future2完成!");return "future2完成!"; });CompletableFuture<Void> combindFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2);try {combindFuture.get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace(); } -
CompletableFuture常用方法总结:
-
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1mWmBu8C-1680694141535)(C:%5CUsers%5Cquyanliang%5CAppData%5CRoaming%5CTypora%5Ctypora-user-images%5C1680693984873.png)]
-
注:
CompletableFuture中还有很多功能丰富的方法,这里就不一一列举。
使用案例
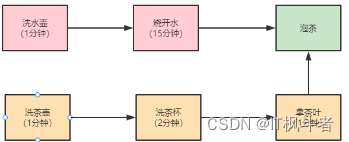
实现最优的“烧水泡茶”程序
-
著名数学家华罗庚先生在《统筹方法》这篇文章里介绍了一个烧水泡茶的例子,文中提到最优的工序应该是下面这样:
-
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-VW2F4P5T-1680694141536)(C:%5CUsers%5Cquyanliang%5CAppData%5CRoaming%5CTypora%5Ctypora-user-images%5C1680694045463.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0b31e5f063004f1c92fb979de7b1645e.png)
-
对于烧水泡茶这个程序,一种最优的分工方案:用两个线程 T1 和 T2 来完成烧水泡茶程序,T1 负责洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶这三道工序,T2 负责洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶三道工序,其中 T1 在执行泡茶这道工序时需要等待 T2 完成拿茶叶的工序。
基于Future实现
-
public class FutureTaskTest{public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 创建任务T2的FutureTaskFutureTask<String> ft2 = new FutureTask<>(new T2Task());// 创建任务T1的FutureTaskFutureTask<String> ft1 = new FutureTask<>(new T1Task(ft2));// 线程T1执行任务ft2Thread T1 = new Thread(ft2);T1.start();// 线程T2执行任务ft1Thread T2 = new Thread(ft1);T2.start();// 等待线程T1执行结果System.out.println(ft1.get());} }// T1Task需要执行的任务: // 洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶 class T1Task implements Callable<String> {FutureTask<String> ft2;// T1任务需要T2任务的FutureTaskT1Task(FutureTask<String> ft2){this.ft2 = ft2;}@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15);// 获取T2线程的茶叶String tf = ft2.get();System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:"+tf);System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");return "上茶:" + tf;} } // T2Task需要执行的任务: // 洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶 class T2Task implements Callable<String> {@Overridepublic String call() throws Exception {System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);return "龙井";} }
基于CompletableFuture实现
-
public class CompletableFutureTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//任务1:洗水壶->烧开水CompletableFuture<Void> f1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");sleep(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);});//任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");sleep(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);return "龙井";});//任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶CompletableFuture<String> f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, (__, tf) -> {System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:" + tf);System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");return "上茶:" + tf;});//等待任务3执行结果System.out.println(f3.join());}static void sleep(int t, TimeUnit u){try {u.sleep(t);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}} }
相关文章:
CompletableFuture使用详解(IT枫斗者)
CompletableFuture使用详解 简介 概述 CompletableFuture是对Future的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富的扩展,完美弥补了Future的局限性,同时CompletableFuture实现了对任务编排的能力。借助这项能力…...
4.15--设计模式之创建型之责任链模式(总复习版本)---脚踏实地,一步一个脚印
一、什么是责任链模式: 责任链模式属于行为型模式,是为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链,将链中每一个节点看作是一个对象,每个节点处理的请求均不同,且内部自动维护一个下一节点对象。 当一个请求从链式的首端发出时&a…...
STM32+W5500实现以太网通信
STM32系列32位微控制器基于Arm Cortex-M处理器,旨在为MCU用户提供新的开发自由度。它包括一系列产品,集高性能、实时功能、数字信号处理、低功耗/低电压操作、连接性等特性于一身,同时还保持了集成度高和易于开发的特点。本例采用STM32作为MC…...
全网最详细,Jmeter性能测试-性能基础详解,终成测试卷王(一)
目录:导读前言一、Python编程入门到精通二、接口自动化项目实战三、Web自动化项目实战四、App自动化项目实战五、一线大厂简历六、测试开发DevOps体系七、常用自动化测试工具八、JMeter性能测试九、总结(尾部小惊喜)前言 发起请求 发起HTTP…...

人工智能概述
一、人工智能发展必备三要素 算法 数据 算力 CPU、GPU、TPU 计算力之CPU、GPU对比: CPU主要适合I\O密集型任务GPU主要适合计算密集型任务 什么样的程序适合在GPU上运行? 计算密集型的程序 所谓计算密集型(Compute-intensive)的程序,就是…...

API接口安全—webservice、Swagger、WEBpack
API接口安全—webservice、Swagger、WEBpack1. API接口介绍1.1. 常用的API接口类1.1.1. API接口分类1.1.1.1. 类库型API1.1.1.2. 操作系统型API1.1.1.3. 远程应用型API1.1.1.4. WEB应用型API1.1.1.5. 总结1.1.2. API接口类型1.1.2.1. HTTP类接口1.1.2.2. RPC类接口1.1.2.3. web…...

从前M个字母中取N个的无重复排列 [2*+]
目录 从前M个字母中取N个的无重复排列 [2*+] 程序设计 程序分析 从前M个字母中取N个的无重复排列 [2*+] 输出从前M个字母中取N个的无重复字母排列 Input 输入M N 1<=M=10, N<=M Output 按字典序输出排列 Sample Input 4 2 Sample Output A B A C A D B A B C B …...

ES forceMerge 强制段合并为什么会提升检索性能?
根据以前的测试,forceMerge段合并,将段的个数合并成一个。带来了将近一倍的性能提升,测试过程文档(请参考我的另外一篇文章):ES优化实战- forceMerge搜索提升测试报告_es forcemerge_水的精神的博客-CSDN博…...

macOS Ventura 13.3.1 (22E261) Boot ISO 原版可引导镜像
本站下载的 macOS 软件包,既可以拖拽到 Applications(应用程序)下直接安装,也可以制作启动 U 盘安装,或者在虚拟机中启动安装。另外也支持在 Windows 和 Linux 中创建可引导介质。 macOS Ventura 13.3.1 为 Mac 提供下…...
html+css+JavaScript+json+servlet的社区系统(手把手教学)
目录 课前导读: 一、系统前期准备 二、前端代码的编写 三、登陆页面简介 四、注册页面 五、社区列表页 六、社区详情页 七、社区发帖页 八、注销 九、访问链接 登陆页面http://175.178.20.77:8080/java106_blog_system/login.html 总结: 课前…...
UI Toolkit(1)
UI ToolkitUI Toolkit界面画布设置背景制作UI布局UI Toolkit界面 在Unity 2021LTS版本之后UI Toolkit也被内置在Unity中,Unity有意的想让UI Toolkit 成为UI的主要搭建方式,当然与UGUI相比还是有一定的差别。他们各有有点,这次我们就开始介绍…...
vLive带你走进虚拟直播世界
虚拟直播是什么? 虚拟直播是基于5G实时渲染技术,在绿幕环境下拍摄画面,通过实时抠像、渲染与合成,再推流到直播平台的一种直播技术。尽管这种技术早已被影视工业所采用,但在全民化进程中却是困难重重,面临…...

初谈 ChatGPT
引子 最近,小编发现互联网中的大 V 突然都在用 ChatGPT 做宣传:“ChatGPT不会淘汰你,能驾驭ChatGPT的人会淘汰你”、“带领一小部分人先驾驭ChatGPT”。 确实,ChatGPT这个新生事物,如今被视为蒸汽机、电脑、iPhone 般的…...

JAVA练习103-螺旋矩阵
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 前言 提示:这里可以添加本文要记录的大概内容: 4月9日练习内容 提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考 一、题目-螺…...
RecvByteBufAllocator内存分配计算
虽然了解了整个内存池管理的细节,包括它的内存分配的具体逻辑,但是每次从NioSocketChannel中读取数据时,应该分配多少内存去读呢? 例如,客户端发送的数据为1KB , 应该分配多少内存去读呢? 例如:…...
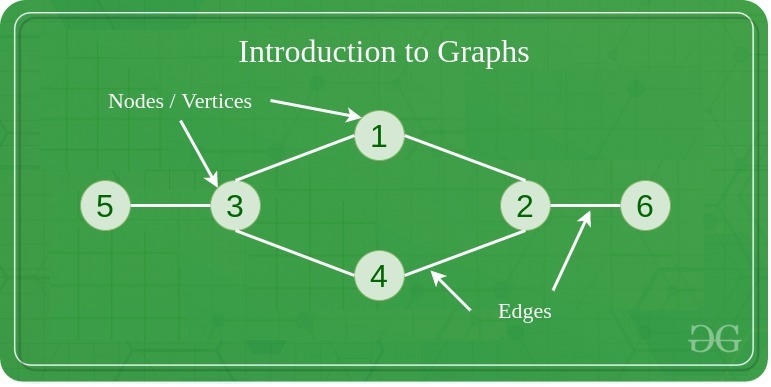
图数据结构与算法
什么是图数据的结构 图是由顶点和边组成的非线性数据结构。顶点有时也称为节点,边是连接图中任意两个节点的线或弧。更正式地说,图由一组顶点 ( V ) 和一组边 ( E ) 组成。该图由 G(E, V) 表示。 图的组成部分 顶点:顶点是图的基本单位。有时,顶点也称为顶点或节点。每个节…...

科普:c语言与C++的区别
C语言和C语言是两种广泛使用的编程语言,尽管它们非常相似,但它们在某些方面也存在不同之处。本文将详细介绍C语言和C语言的区别。 1. 编程范式 C语言是一种过程式编程语言,它的设计目标是为了编写操作系统和其他系统级编程。C语言是一种面向…...
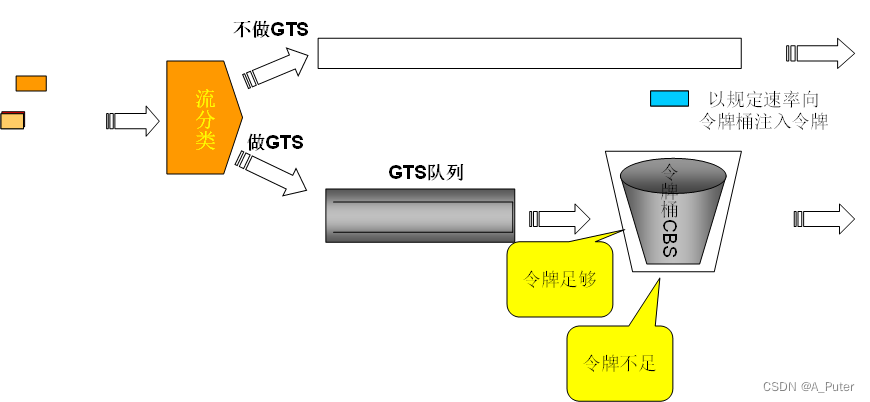
流量整形(GTS和LR)
Generic Traffic Shaping通用流量整形 通用流量整形(简称GTS)可以对不规则或不符合预定流量特性的流量进行整形,以保证网络上下游之间的带宽匹配,避免拥塞发生。 GTS与CAR一样,都采用了令牌桶技术来控制流量。GTS与CAR的主要区别在于:利用CAR进行报文流量控制时,…...

Java接口详细讲解
目录 Java接口概念 Java接口主要有以下特点 Java接口的具体作用 定义接口 实现接口 接口继承 默认方法 静态方法 Java接口概念 Java编程语言中是一个抽象类型,是抽象方法的集合,接口通常以interface来声明。一个类通过继承接口的方式,从而来继承接口的抽象方法。 …...

元宇宙地产暴跌,林俊杰亏麻了
文/章鱼哥出品/陀螺财经随着元宇宙的兴起,元宇宙地产曾一度被寄予厚望,成为各大投资者追捧的对象。然而,最近的一次元宇宙地产价值暴跌再次提醒我们,高收益背后可能伴随着高风险。根据元宇宙分析平台WeMeta的数据显示,…...
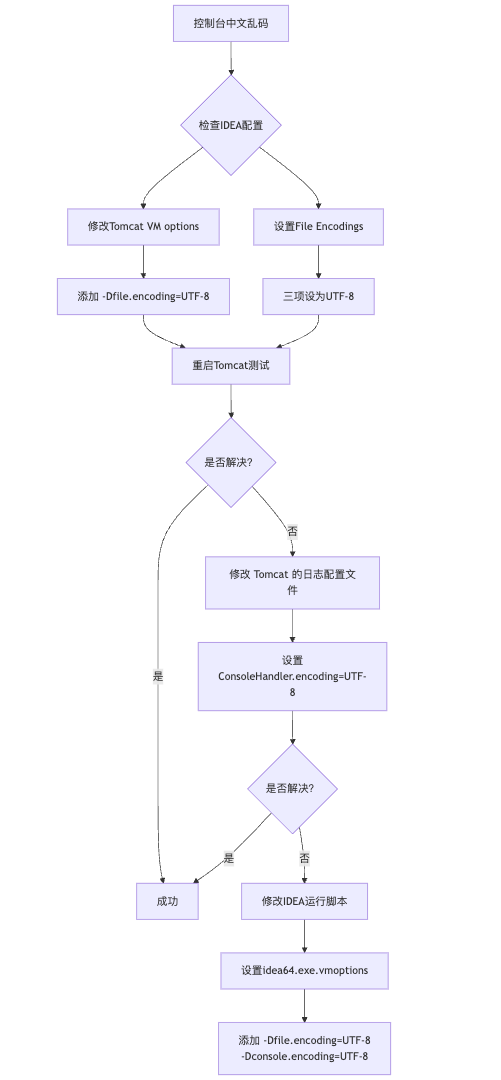
IDEA运行Tomcat出现乱码问题解决汇总
最近正值期末周,有很多同学在写期末Java web作业时,运行tomcat出现乱码问题,经过多次解决与研究,我做了如下整理: 原因: IDEA本身编码与tomcat的编码与Windows编码不同导致,Windows 系统控制台…...
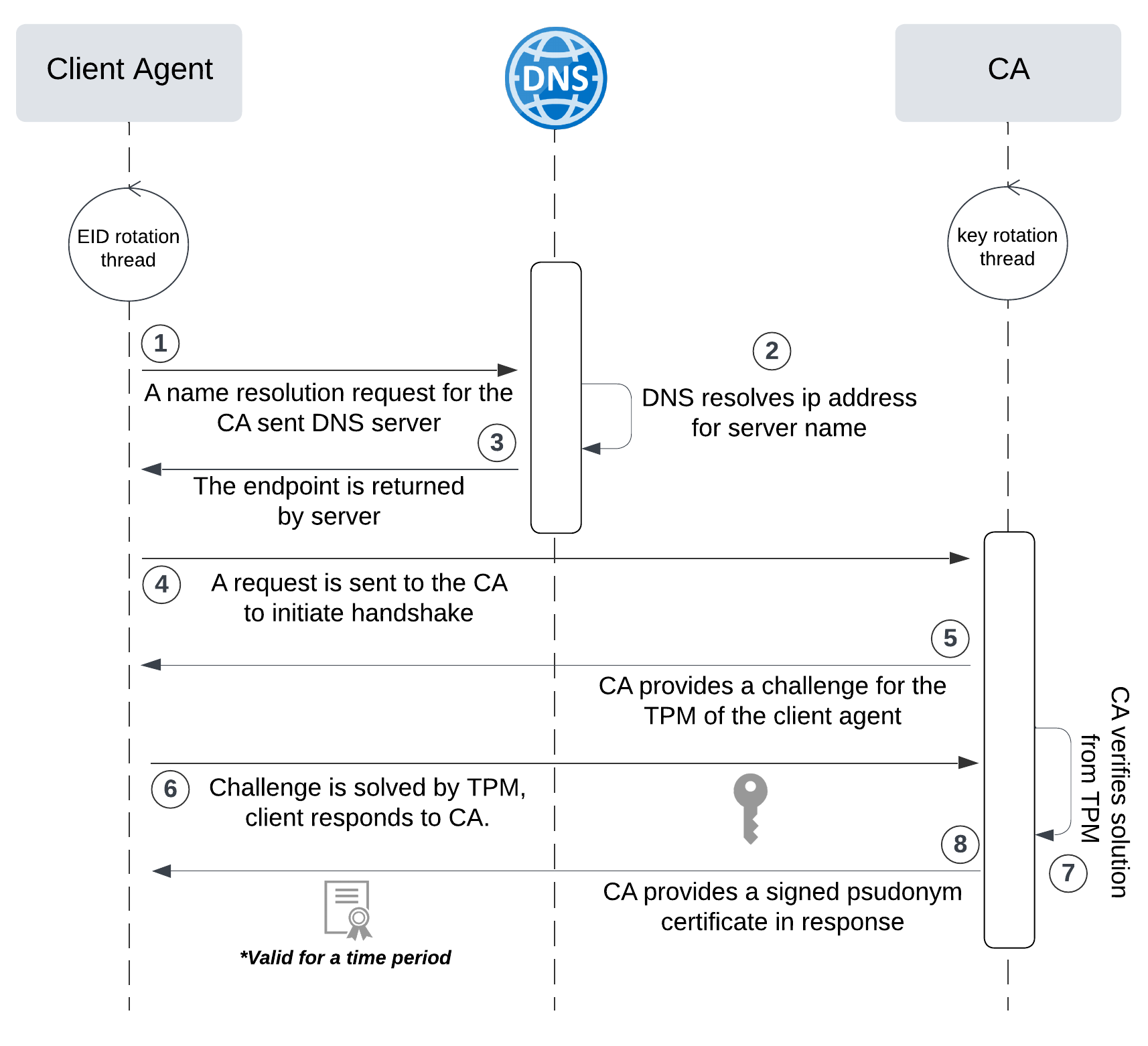
网络六边形受到攻击
大家读完觉得有帮助记得关注和点赞!!! 抽象 现代智能交通系统 (ITS) 的一个关键要求是能够以安全、可靠和匿名的方式从互联车辆和移动设备收集地理参考数据。Nexagon 协议建立在 IETF 定位器/ID 分离协议 (…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...

镜像里切换为普通用户
如果你登录远程虚拟机默认就是 root 用户,但你不希望用 root 权限运行 ns-3(这是对的,ns3 工具会拒绝 root),你可以按以下方法创建一个 非 root 用户账号 并切换到它运行 ns-3。 一次性解决方案:创建非 roo…...
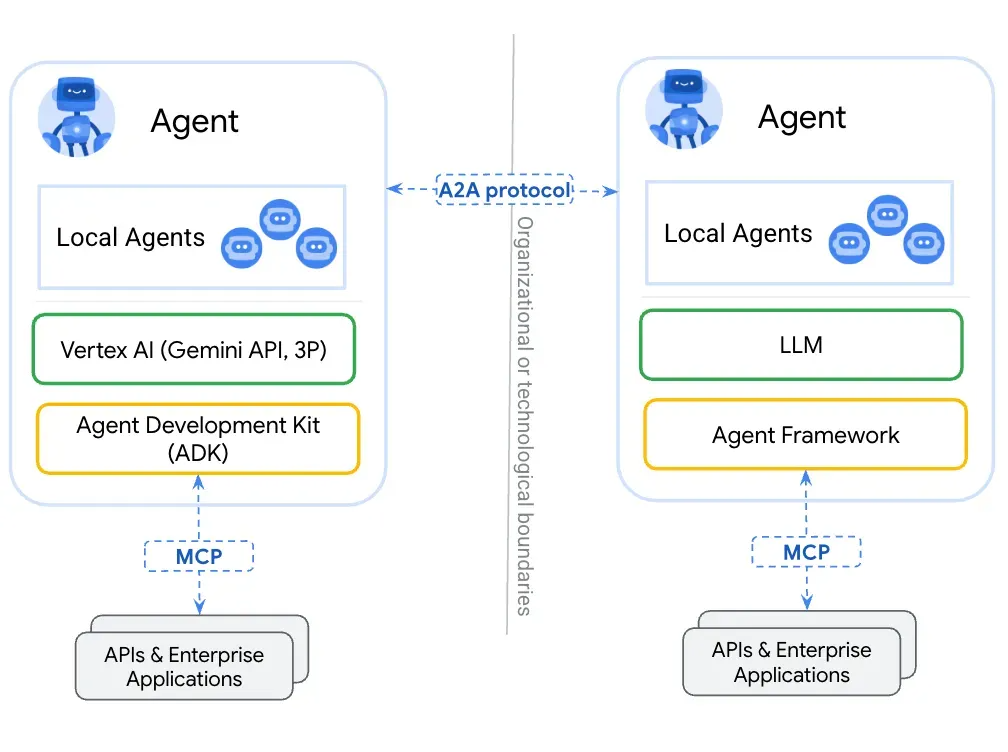
第一篇:Agent2Agent (A2A) 协议——协作式人工智能的黎明
AI 领域的快速发展正在催生一个新时代,智能代理(agents)不再是孤立的个体,而是能够像一个数字团队一样协作。然而,当前 AI 生态系统的碎片化阻碍了这一愿景的实现,导致了“AI 巴别塔问题”——不同代理之间…...
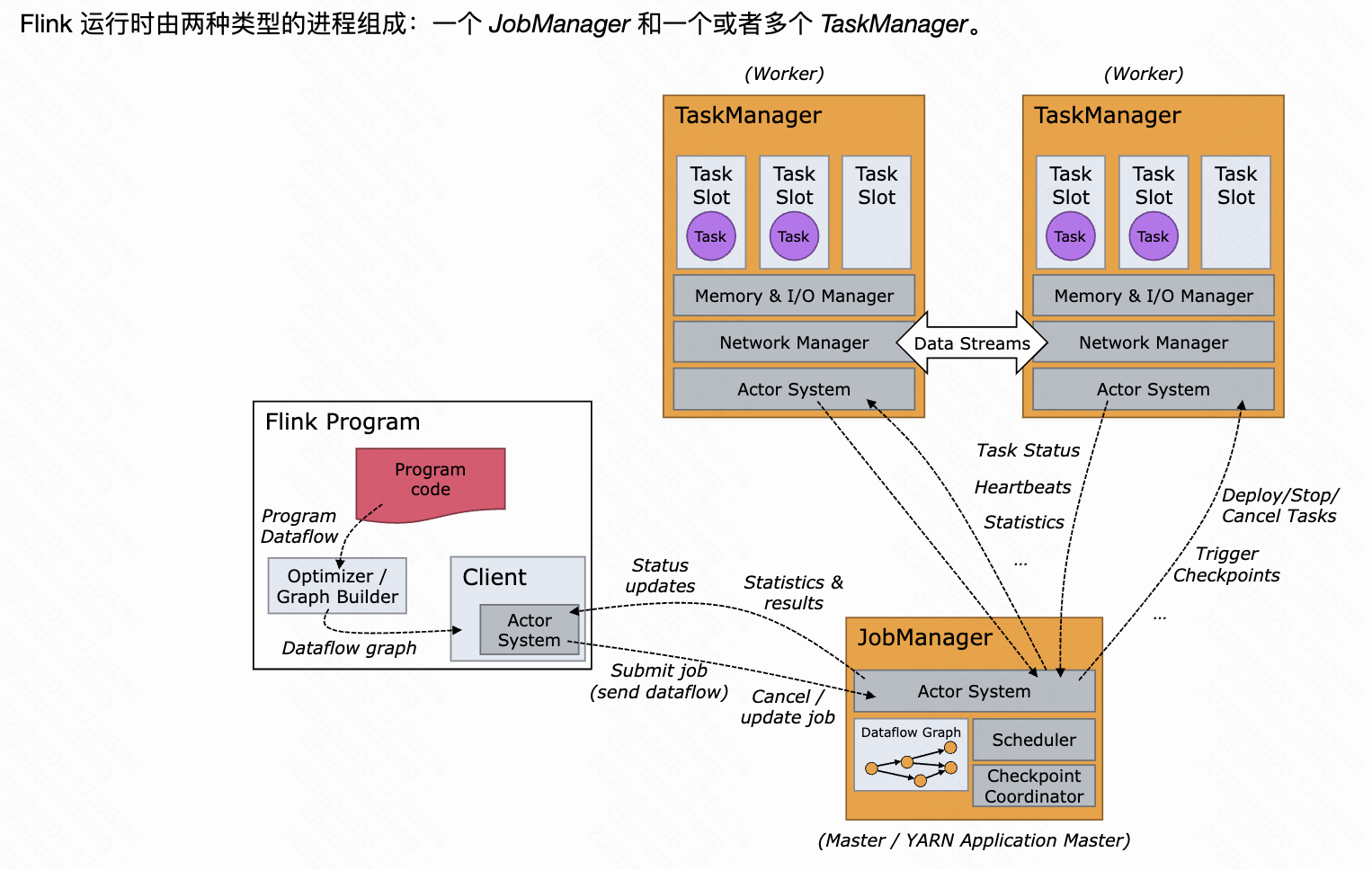
《基于Apache Flink的流处理》笔记
思维导图 1-3 章 4-7章 8-11 章 参考资料 源码: https://github.com/streaming-with-flink 博客 https://flink.apache.org/bloghttps://www.ververica.com/blog 聚会及会议 https://flink-forward.orghttps://www.meetup.com/topics/apache-flink https://n…...

Java 二维码
Java 二维码 **技术:**谷歌 ZXing 实现 首先添加依赖 <!-- 二维码依赖 --><dependency><groupId>com.google.zxing</groupId><artifactId>core</artifactId><version>3.5.1</version></dependency><de…...

蓝桥杯 冶炼金属
原题目链接 🔧 冶炼金属转换率推测题解 📜 原题描述 小蓝有一个神奇的炉子用于将普通金属 O O O 冶炼成为一种特殊金属 X X X。这个炉子有一个属性叫转换率 V V V,是一个正整数,表示每 V V V 个普通金属 O O O 可以冶炼出 …...
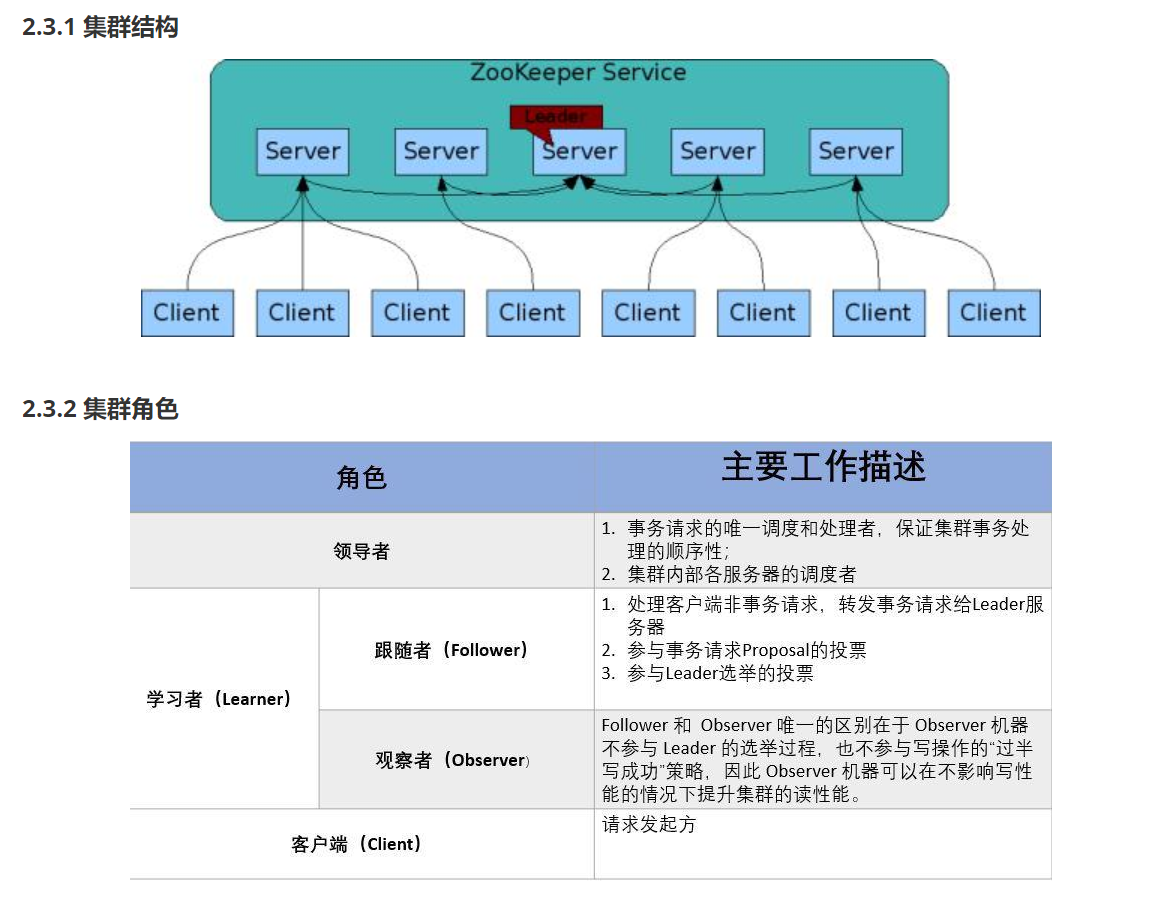
HDFS分布式存储 zookeeper
hadoop介绍 狭义上hadoop是指apache的一款开源软件 用java语言实现开源框架,允许使用简单的变成模型跨计算机对大型集群进行分布式处理(1.海量的数据存储 2.海量数据的计算)Hadoop核心组件 hdfs(分布式文件存储系统)&a…...

【无标题】路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论
路径问题的革命性重构:基于二维拓扑收缩色动力学模型的零点隧穿理论 一、传统路径模型的根本缺陷 在经典正方形路径问题中(图1): mermaid graph LR A((A)) --- B((B)) B --- C((C)) C --- D((D)) D --- A A -.- C[无直接路径] B -…...
