/lib/lsb/init-functions文件解析
零、背景
在玩AppArmor的时候涉及到了/etc/init.d/apparmor(无论是sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor start还是sudo systemctl start apparmor.service),而这个文件又涉及到了另一个文件、也就是本文的主角:/lib/lsb/init-functions。
执行sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor start命令时结果如下:
$ sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor start
/etc/init.d/apparmor:行43: /lib/lsb/init-functions: 没有那个文件或目录
而执行sudo systemctl start apparmor.services时结果如下:
$ sudo systemctl start apparmor
Job for apparmor.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
See "systemctl status apparmor.service" and "journalctl -xeu apparmor.service" for details.
通过systemctl status apparmor.service查看状态,结果如下:
$ systemctl status apparmor.service
× apparmor.service - LSB: AppArmor initializationLoaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apparmor; generated)Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Thu 2023-04-20 16:29:35 CST; 1min 29s agoDocs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)Process: 2489718 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/apparmor start (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)CPU: 8ms$ sudo systemctl status apparmor.service
× apparmor.service - LSB: AppArmor initializationLoaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apparmor; generated)Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Thu 2023-04-20 16:29:35 CST; 1min 39s agoDocs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)Process: 2489718 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/apparmor start (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)CPU: 8ms4月 20 16:29:35 Ding-Perlis-MP260S48 systemd[1]: Starting LSB: AppArmor initialization...
4月 20 16:29:35 Ding-Perlis-MP260S48 apparmor[2489718]: /etc/init.d/apparmor:行43: /lib/lsb/init-functions: 没有那个文件或目录4月 20 16:29:35 Ding-Perlis-MP260S48 systemd[1]: apparmor.service: Control process exited, code=exited, status=1/FAILURE
4月 20 16:29:35 Ding-Perlis-MP260S48 systemd[1]: apparmor.service: Failed with result 'exit-code'.
4月 20 16:29:35 Ding-Perlis-MP260S48 systemd[1]: Failed to start LSB: AppArmor initialization.
可以看到,失败的根本原因就是没有/lib/lsb/init-functions文件。
先来看一下/etc/init.d/apparmor文件中是怎样与/lib/lsb/init-functions文件联系的。/etc/init.d/apparmor文件片段如下:
APPARMOR_FUNCTIONS=/lib/apparmor/rc.apparmor.functions# Functions needed by rc.apparmor.functions. /lib/lsb/init-functions
……# Source AppArmor function library
if [ -f "${APPARMOR_FUNCTIONS}" ]; then. ${APPARMOR_FUNCTIONS}
elseaa_log_failure_msg "Unable to find AppArmor initscript functions"exit 1
fi
通过以上代码片段就可以看出,如果/lib/lsb/init-functions文件,则/etc/init.d/apparmor的第43行代码. /lib/lsb/init-functions就会导致以上错误。
那么这个/lib/lsb/init-fiunctions到底是何方神圣?其作用和内容又是怎样的?接下来就进行完全解析。
一、简介
根据ChatGPT的搜索结果(poe.com/ChatGPT),/lib/lsb/init-functions文件的介绍如下:
/lib/lsb/init-functions文件是一个Linux系统上的脚本文件,它包含了一些常用的函数,用于在系统启动时执行各种任务。这个文件通常被用来编写启动脚本,比如在系统启动时自动启动某个服务。
这个文件提供了许多函数,比如:
log_success_msg:用于记录启动成功的消息;
log_failure_msg:用于记录启动失败的消息;
log_warning_msg:用于记录启动警告的消息;
log_progress_msg:用于记录启动进度的消息;
pidofproc:用于获取某个进程的PID;
killproc:用于杀死某个进程;
start_daemon:用于启动一个后台进程。
这些函数可以让脚本编写者更加方便地编写启动脚本,同时也提高了启动脚本的可读性和可维护性。
再来看看/lib/lsb文件夹是干什么的:
/lib/lsb是一个目录,它通常包含了一些用于支持Linux Standard Base(LSB)规范的文件和脚本。LSB是一种标准,旨在使不同的Linux发行版之间更加兼容,从而提高应用程序在各种Linux发行版上的可移植性。
在/lib/lsb目录中,常见的文件和目录包括:
- init-functions:包含了一些常用的函数,用于在系统启动时执行各种任务,如启动服务等;
- lsb_release:用于显示当前系统的LSB版本和发行版信息;
- lsb_log_message:用于在系统日志中记录LSB兼容的日志信息;
- /etc/lsb-release:包含了当前系统的LSB版本和发行版信息,可以被其他脚本和程序引用。
这些文件和脚本可以帮助系统管理员编写LSB兼容的启动脚本和管理工具,从而提高系统的可移植性和可维护性。
笔者的Ubuntu系统(Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS)电脑中的/lib/lsb/目录下倒是没有那么多文件和文件夹,如下:
$ ls /lib/lsb/
init-functions init-functions.d$ tree /lib/lsb
/lib/lsb
├── init-functions
└── init-functions.d├── 00-verbose├── 40-systemd├── 50-ubuntu-logging└── 99-plymouth1 directory, 5 files
二、代码分析
通过上边介绍,已经对/lib/lsb/init-functions文件有了大致的了解。趁热打铁,结合概述看一下其源码:
# /lib/lsb/init-functions for Debian -*- shell-script -*-
#
#Copyright (c) 2002-08 Chris Lawrence
#All rights reserved.
#
#Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
#modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
#are met:
#1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
#2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
# documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
#3. Neither the name of the author nor the names of other contributors
# may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software
# without specific prior written permission.
#
#THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR
#IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
#WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
#ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE REGENTS OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
#LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
#CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
#SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR
#BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY,
#WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE
#OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE,
#EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.start_daemon () {local force nice pidfile exec args OPTINDforce=""nice=0pidfile=/dev/nullOPTIND=1while getopts fn:p: opt ; docase "$opt" inf) force="force";;n) nice="$OPTARG";;p) pidfile="$OPTARG";;esacdoneshift $(($OPTIND - 1))if [ "$1" = '--' ]; thenshiftfiexec="$1"; shiftargs="--start --nicelevel $nice --quiet --oknodo"if [ "$force" ]; then/sbin/start-stop-daemon $args \--chdir "$PWD" --startas $exec --pidfile /dev/null -- "$@"elif [ $pidfile ]; then/sbin/start-stop-daemon $args \--chdir "$PWD" --exec $exec --oknodo --pidfile "$pidfile" -- "$@"else/sbin/start-stop-daemon $args --chdir "$PWD" --exec $exec -- "$@"fi
}pidofproc () {local pidfile base status specified pid OPTINDpidfile=specified=OPTIND=1while getopts p: opt ; docase "$opt" inp) pidfile="$OPTARG"specified="specified";;esacdoneshift $(($OPTIND - 1))if [ $# -ne 1 ]; thenecho "$0: invalid arguments" >&2return 4fibase=${1##*/}if [ ! "$specified" ]; thenpidfile="/var/run/$base.pid"fiif [ -n "${pidfile:-}" ]; thenif [ -e "$pidfile" ]; thenif [ -r "$pidfile" ]; thenread pid < "$pidfile"if [ -n "${pid:-}" ]; thenif $(kill -0 "${pid:-}" 2> /dev/null); thenecho "$pid" || truereturn 0elif ps "${pid:-}" >/dev/null 2>&1; thenecho "$pid" || truereturn 0 # program is running, but not owned by this userelsereturn 1 # program is dead and /var/run pid file existsfifielsereturn 4 # pid file not readable, hence status is unknown.fielse# pid file doesn't exist, try to find the pid neverthelessif [ -x /bin/pidof ] && [ ! "$specified" ]; thenstatus="0"/bin/pidof -c -o %PPID -x $1 || status="$?"if [ "$status" = 1 ]; thenreturn 3 # program is not runningfireturn 0fireturn 3 # specified pid file doesn't exist, program probably stoppedfifiif [ "$specified" ]; thenreturn 3 # almost certain it's not runningfireturn 4 # Unable to determine status
}# start-stop-daemon uses the same algorithm as "pidofproc" above.
killproc () {local pidfile sig status base name_param is_term_sig OPTINDpidfile=name_param=is_term_sig=OPTIND=1while getopts p: opt ; docase "$opt" inp) pidfile="$OPTARG";;esacdoneshift $(($OPTIND - 1))base=${1##*/}if [ ! $pidfile ]; thenname_param="--name $base --pidfile /var/run/$base.pid"elsename_param="--name $base --pidfile $pidfile"fisig=$(echo ${2:-} | sed -e 's/^-\(.*\)/\1/')sig=$(echo $sig | sed -e 's/^SIG\(.*\)/\1/')if [ "$sig" = 15 ] || [ "$sig" = TERM ]; thenis_term_sig="terminate_signal"fistatus=0if [ ! "$is_term_sig" ]; thenif [ -n "$sig" ]; then/sbin/start-stop-daemon --stop --signal "$sig" \--quiet $name_param || status="$?"else/sbin/start-stop-daemon --stop \--retry 5 \--quiet $name_param || status="$?"fielse/sbin/start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet \--oknodo $name_param || status="$?"fiif [ "$status" = 1 ]; thenif [ -z "$sig" ]; thenreturn 0fireturn 3 # program is not runningfiif [ "$status" = 0 ] && [ "$is_term_sig" ] && [ "$pidfile" ]; thenpidofproc -p "$pidfile" "$1" >/dev/null || rm -f "$pidfile"fireturn 0
}# Return LSB status
status_of_proc () {local pidfile daemon name status OPTINDpidfile=OPTIND=1while getopts p: opt ; docase "$opt" inp) pidfile="$OPTARG";;esacdoneshift $(($OPTIND - 1))if [ -n "$pidfile" ]; thenpidfile="-p $pidfile"fidaemon="$1"name="$2"status="0"pidofproc $pidfile $daemon >/dev/null || status="$?"if [ "$status" = 0 ]; thenlog_success_msg "$name is running"return 0elif [ "$status" = 4 ]; thenlog_failure_msg "could not access PID file for $name"return $statuselselog_failure_msg "$name is not running"return $statusfi
}log_use_fancy_output () {TPUT=/usr/bin/tputEXPR=/usr/bin/exprif [ -t 1 ] &&[ "x${TERM:-}" != "x" ] &&[ "x${TERM:-}" != "xdumb" ] &&[ -x $TPUT ] && [ -x $EXPR ] &&$TPUT hpa 60 >/dev/null 2>&1 &&$TPUT setaf 1 >/dev/null 2>&1then[ -z $FANCYTTY ] && FANCYTTY=1 || trueelseFANCYTTY=0ficase "$FANCYTTY" in1|Y|yes|true) true;;*) false;;esac
}log_success_msg () {if [ -n "${1:-}" ]; thenlog_begin_msg $@filog_end_msg 0
}log_failure_msg () {if [ -n "${1:-}" ]; thenlog_begin_msg $@ "..."filog_end_msg 1 || true
}log_warning_msg () {if [ -n "${1:-}" ]; thenlog_begin_msg $@ "..."filog_end_msg 255 || true
}#
# NON-LSB HELPER FUNCTIONS
#
# int get_lsb_header_val (char *scriptpathname, char *key)
get_lsb_header_val () {if [ ! -f "$1" ] || [ -z "${2:-}" ]; thenreturn 1fiLSB_S="### BEGIN INIT INFO"LSB_E="### END INIT INFO"sed -n "/$LSB_S/,/$LSB_E/ s/# $2: \+\(.*\)/\1/p" "$1"
}# If the currently running init daemon is upstart, return zero; if the
# calling init script belongs to a package which also provides a native
# upstart job, it should generally exit non-zero in this case.
init_is_upstart()
{if [ -x /sbin/initctl ] && /sbin/initctl version 2>/dev/null | /bin/grep -q upstart; thenreturn 0fireturn 1
}# int log_begin_message (char *message)
log_begin_msg () {log_begin_msg_pre "$@"if [ -z "${1:-}" ]; thenreturn 1fiecho -n "$@" || truelog_begin_msg_post "$@"
}# Sample usage:
# log_daemon_msg "Starting GNOME Login Manager" "gdm"
#
# On Debian, would output "Starting GNOME Login Manager: gdm"
# On Ubuntu, would output " * Starting GNOME Login Manager..."
#
# If the second argument is omitted, logging suitable for use with
# log_progress_msg() is used:
#
# log_daemon_msg "Starting remote filesystem services"
#
# On Debian, would output "Starting remote filesystem services:"
# On Ubuntu, would output " * Starting remote filesystem services..."log_daemon_msg () {if [ -z "${1:-}" ]; thenreturn 1filog_daemon_msg_pre "$@"if [ -z "${2:-}" ]; thenecho -n "$1:" || truereturnfiecho -n "$1: $2" || truelog_daemon_msg_post "$@"
}# #319739
#
# Per policy docs:
#
# log_daemon_msg "Starting remote file system services"
# log_progress_msg "nfsd"; start-stop-daemon --start --quiet nfsd
# log_progress_msg "mountd"; start-stop-daemon --start --quiet mountd
# log_progress_msg "ugidd"; start-stop-daemon --start --quiet ugidd
# log_end_msg 0
#
# You could also do something fancy with log_end_msg here based on the
# return values of start-stop-daemon; this is left as an exercise for
# the reader...
#
# On Ubuntu, one would expect log_progress_msg to be a no-op.
log_progress_msg () {if [ -z "${1:-}" ]; thenreturn 1fiecho -n " $@" || true
}# int log_end_message (int exitstatus)
log_end_msg () {# If no arguments were passed, returnif [ -z "${1:-}" ]; thenreturn 1filocal retvalretval=$1log_end_msg_pre "$@"# Only do the fancy stuff if we have an appropriate terminal# and if /usr is already mountedif log_use_fancy_output; thenRED=$( $TPUT setaf 1)YELLOW=$( $TPUT setaf 3)NORMAL=$( $TPUT op)elseRED=''YELLOW=''NORMAL=''fiif [ $1 -eq 0 ]; thenecho "." || trueelif [ $1 -eq 255 ]; then/bin/echo -e " ${YELLOW}(warning).${NORMAL}" || trueelse/bin/echo -e " ${RED}failed!${NORMAL}" || truefilog_end_msg_post "$@"return $retval
}log_action_msg () {log_action_msg_pre "$@"echo "$@." || truelog_action_msg_post "$@"
}log_action_begin_msg () {log_action_begin_msg_pre "$@"echo -n "$@..." || truelog_action_begin_msg_post "$@"
}log_action_cont_msg () {echo -n "$@..." || true
}log_action_end_msg () {local endlog_action_end_msg_pre "$@"if [ -z "${2:-}" ]; thenend="."elseend=" ($2)."fiif [ $1 -eq 0 ]; thenecho "done${end}" || trueelseif log_use_fancy_output; thenRED=$( $TPUT setaf 1)NORMAL=$( $TPUT op)/bin/echo -e "${RED}failed${end}${NORMAL}" || trueelseecho "failed${end}" || truefifilog_action_end_msg_post "$@"
}# Pre&Post empty function declaration, to be overriden from /lib/lsb/init-functions.d/*
log_daemon_msg_pre () { :; }
log_daemon_msg_post () { :; }
log_begin_msg_pre () { :; }
log_begin_msg_post () { :; }
log_end_msg_pre () { :; }
log_end_msg_post () { :; }
log_action_msg_pre () { :; }
log_action_msg_post () { :; }
log_action_begin_msg_pre () { :; }
log_action_begin_msg_post () { :; }
log_action_end_msg_pre () { :; }
log_action_end_msg_post () { :; }# Include hooks from other packages in /lib/lsb/init-functions.d
for hook in $(run-parts --lsbsysinit --list /lib/lsb/init-functions.d 2>/dev/null); do[ -r $hook ] && . $hook || true
doneFANCYTTY=
[ -e /etc/lsb-base-logging.sh ] && . /etc/lsb-base-logging.sh || true本文只关注与/etc/init.d/apparmor相关的函数。下边逐一进行分析:
- log_daemon_msg函数
代码如下:
# Sample usage:
# log_daemon_msg "Starting GNOME Login Manager" "gdm"
#
# On Debian, would output "Starting GNOME Login Manager: gdm"
# On Ubuntu, would output " * Starting GNOME Login Manager..."
#
# If the second argument is omitted, logging suitable for use with
# log_progress_msg() is used:
#
# log_daemon_msg "Starting remote filesystem services"
#
# On Debian, would output "Starting remote filesystem services:"
# On Ubuntu, would output " * Starting remote filesystem services..."log_daemon_msg () {if [ -z "${1:-}" ]; thenreturn 1filog_daemon_msg_pre "$@"if [ -z "${2:-}" ]; thenecho -n "$1:" || truereturnfiecho -n "$1: $2" || truelog_daemon_msg_post "$@"
}- log_end_msg函数
代码如下:
# int log_end_message (int exitstatus)
log_end_msg () {# If no arguments were passed, returnif [ -z "${1:-}" ]; thenreturn 1filocal retvalretval=$1log_end_msg_pre "$@"# Only do the fancy stuff if we have an appropriate terminal# and if /usr is already mountedif log_use_fancy_output; thenRED=$( $TPUT setaf 1)YELLOW=$( $TPUT setaf 3)NORMAL=$( $TPUT op)elseRED=''YELLOW=''NORMAL=''fiif [ $1 -eq 0 ]; thenecho "." || trueelif [ $1 -eq 255 ]; then/bin/echo -e " ${YELLOW}(warning).${NORMAL}" || trueelse/bin/echo -e " ${RED}failed!${NORMAL}" || truefilog_end_msg_post "$@"return $retval
}- log_daemon_msg_pre、log_daemon_msg_post、log_end_msg_pre、log_end_msg_post
log_daemon_msg_pre、log_daemon_msg_post、log_end_msg_pre、log_end_msg_post等函数在同文件(/lib/lsb/init-functions)中,如下:
# Pre&Post empty function declaration, to be overriden from /lib/lsb/init-functions.d/*
log_daemon_msg_pre () { :; }
log_daemon_msg_post () { :; }
log_begin_msg_pre () { :; }
log_begin_msg_post () { :; }
log_end_msg_pre () { :; }
log_end_msg_post () { :; }
log_action_msg_pre () { :; }
log_action_msg_post () { :; }
log_action_begin_msg_pre () { :; }
log_action_begin_msg_post () { :; }
log_action_end_msg_pre () { :; }
log_action_end_msg_post () { :; }根据注释,这些函数在/lib/lsb/init-functions.d/下重载,没有重载的函数就是使用以上默认的空函数。笔者电脑上/lib/lsb/init-functions.d/下的内容如下(上边实际上已经列出了):
$ ls /lib/lsb/init-functions.d/
00-verbose 40-systemd 50-ubuntu-logging 99-plymouth
这里只列出50-ubuntu-logging文件的内容,如下:
# Default init script logging functions suitable for Ubuntu.
# See /lib/lsb/init-functions for usage help.
LOG_DAEMON_MSG=""log_use_plymouth () {if [ "${loop:-n}" = y ]; thenreturn 1fiplymouth --ping >/dev/null 2>&1
}log_success_msg () {echo " * $@" || true
}log_failure_msg () {if log_use_fancy_output; thenRED=`$TPUT setaf 1`NORMAL=`$TPUT op`echo " $RED*$NORMAL $@" || trueelseecho " * $@" || truefi
}log_warning_msg () {if log_use_fancy_output; thenYELLOW=`$TPUT setaf 3`NORMAL=`$TPUT op`echo " $YELLOW*$NORMAL $@" || trueelseecho " * $@" || truefi
}log_begin_msg () {log_daemon_msg "$1"
}log_daemon_msg () {if [ -z "$1" ]; thenreturn 1fiif log_use_fancy_output && $TPUT xenl >/dev/null 2>&1; thenCOLS=`$TPUT cols`if [ "$COLS" ] && [ "$COLS" -gt 6 ]; thenCOL=`$EXPR $COLS - 7`elseCOLS=80COL=73fiif log_use_plymouth; then# If plymouth is running, don't output anything at this time# to avoid buffering problems (LP: #752393)if [ -z "$LOG_DAEMON_MSG" ]; thenLOG_DAEMON_MSG=$*returnfifi# We leave the cursor `hanging' about-to-wrap (see terminfo(5)# xenl, which is approximately right). That way if the script# prints anything then we will be on the next line and not# overwrite part of the message.# Previous versions of this code attempted to colour-code the# asterisk but this can't be done reliably because in practice# init scripts sometimes print messages even when they succeed# and we won't be able to reliably know where the colourful# asterisk ought to go.printf " * $* " || true# Enough trailing spaces for ` [fail]' to fit in; if the message# is too long it wraps here rather than later, which is what we# want.$TPUT hpa `$EXPR $COLS - 1` || trueprintf ' ' || trueelseecho " * $@" || trueCOL=fi
}log_progress_msg () {:
}log_end_msg () {if [ -z "$1" ]; thenreturn 1fiif [ "$COL" ] && [ -x "$TPUT" ]; then# If plymouth is running, print previously stored output# to avoid buffering problems (LP: #752393)if log_use_plymouth; thenif [ -n "$LOG_DAEMON_MSG" ]; thenlog_daemon_msg $LOG_DAEMON_MSGLOG_DAEMON_MSG=""fifiprintf "\r" || true$TPUT hpa $COLif [ "$1" -eq 0 ]; thenecho "[ OK ]" || trueelseprintf '[' || true$TPUT setaf 1 || true # redprintf fail || true$TPUT op || true # normalecho ']' || truefielseif [ "$1" -eq 0 ]; thenecho " ...done." || trueelseecho " ...fail!" || truefifireturn $1
}log_action_msg () {echo " * $@" || true
}log_action_begin_msg () {log_daemon_msg "$@..." || true
}log_action_cont_msg () {log_daemon_msg "$@..." || true
}log_action_end_msg () {# In the future this may do something with $2 as well.log_end_msg "$1" || true
}就分析到这里吧,不再深入了。
相关文章:

/lib/lsb/init-functions文件解析
零、背景 在玩AppArmor的时候涉及到了/etc/init.d/apparmor(无论是sudo /etc/init.d/apparmor start还是sudo systemctl start apparmor.service),而这个文件又涉及到了另一个文件、也就是本文的主角:/lib/lsb/init-functions。 …...

【ChatGPT】ChatGPT-5 强到什么地步?
Yan-英杰的主页 悟已往之不谏 知来者之可追 C程序员,2024届电子信息研究生 目录 ChatGPT-5 强到什么地步? 技术 深度学习模型的升级 更好的预测能力 自适应学习能力 特点 语言理解能力更强 自我修正和优化 更广泛的应用领域 应用 对话系统 智能写作…...
[ARM+Linux] 基于全志h616外设开发笔记
修改用户密码 配置网络 nmcli dev wifi 命令扫描周围WIFI热点 nmcli dev wifi connect xxx password xxx 命令连接WiFi 查看ip地址的指令: ifconfig ip addr show wlan0 SSH登录 这是企业开发调试必用方式,比串口来说不用接线,前提是接入网络…...
如何实现24小时客户服务
许多企业都有着这样的愿望:在不增加客服人员的同时能实现24小时客户服务。 那么有没有什么方法可以实现这一想法呢?在想解决方案之前我们可以先来谈谈客服的作用。 客服的作用主要为以下2点: 帮助用户更快地了解产品(减轻产品的…...
)
查询数据库空间(mysql和oracle)
Mysql版 1、查看所有数据库容量大小 -- 查看所有数据库容量大小 SELECTtable_schema AS 数据库,sum( table_rows ) AS 记录数,sum(TRUNCATE ( data_length / 1024 / 1024, 2 )) AS 数据容量(MB),sum(TRUNCATE ( index_length / 1024 / 1024, 2 )) AS 索引容量(MB) FROMinfor…...

为什么 SQLite 一定要用 C 语言来开发?
SQLite 是一种专门为在 Unix 和类 Unix 操作系统上运行的 Linux 服务器应用程序而设计的数据库管理系统,是一种轻量级的关系型数据库管理系统,它适用于许多嵌入式设备和物联网设备。它使用 C 语言编写,并且是一个开源项目。 简单易用&#x…...

TensorFlow Lite,ML Kit 和 Flutter 移动深度学习:6~11
原文:Mobile Deep Learning with TensorFlow Lite, ML Kit and Flutter 协议:CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 译者:飞龙 本文来自【ApacheCN 深度学习 译文集】,采用译后编辑(MTPE)流程来尽可能提升效率。 不要担心自己的…...

你的GPT跟ChatGPT可能只差了一个DPU
“人类永远不会嫌网络太快,就像永远不会嫌高铁太快,你只会嫌它慢,希望它更快些。” 一个月内,百度、阿里、腾讯、商汤、讯飞、360等国内大厂扎堆发布“中国版 GPT ”,这家的名字还没记清楚,另一家的又蹦了出…...
springboot服务端接口外网远程调试,并实现HTTP服务监听 - 内网穿透
文章目录 前言1. 本地环境搭建1.1 环境参数1.2 搭建springboot服务项目 2. 内网穿透2.1 安装配置cpolar内网穿透2.1.1 windows系统2.1.2 linux系统 2.2 创建隧道映射本地端口2.3 测试公网地址 3. 固定公网地址3.1 保留一个二级子域名3.2 配置二级子域名3.2 测试使用固定公网地址…...

NumPy的应用-1
准备工作 在Python中使用NumPy时,需要先安装NumPy。可以使用以下命令来安装NumPy: pip install numpy安装完成后,在Python中引入NumPy: import numpy as np安装完成并引入NumPy后,我们可以开始使用NumPy进行数据分析…...

k8s的yaml文件中kind类型详解
在Kubernetes(k8s)的YAML语法中,kind是一种重要的关键字,它用于指定Kubernetes资源的类型。根据Kubernetes官方文档,以下是kind可能的取值: Deployment:用于定义应用程序的声明式更新。Statefu…...

第三天:C语言控制结构
目录 1. 条件语句 2. 循环语句 3. 实例:计算阶乘 在前两天的学习中,您已经掌握了C语言的基本知识。今天,我们将学习C语言的控制结构,包括条件语句和循环语句。通过控制结构,您可以实现程序的分支和循环,…...
访问若依vue版后端api接口
访问若依vue版后端api接口 如何使用Talend API Tester进行访问若依vue-前后端分离版的后端api接口? 方法一: 写好一个后台api接口,启动项目 直接使用Talend API Tester进行访问后台api出现如下错误,原因是因为若依系统有jwt认证…...
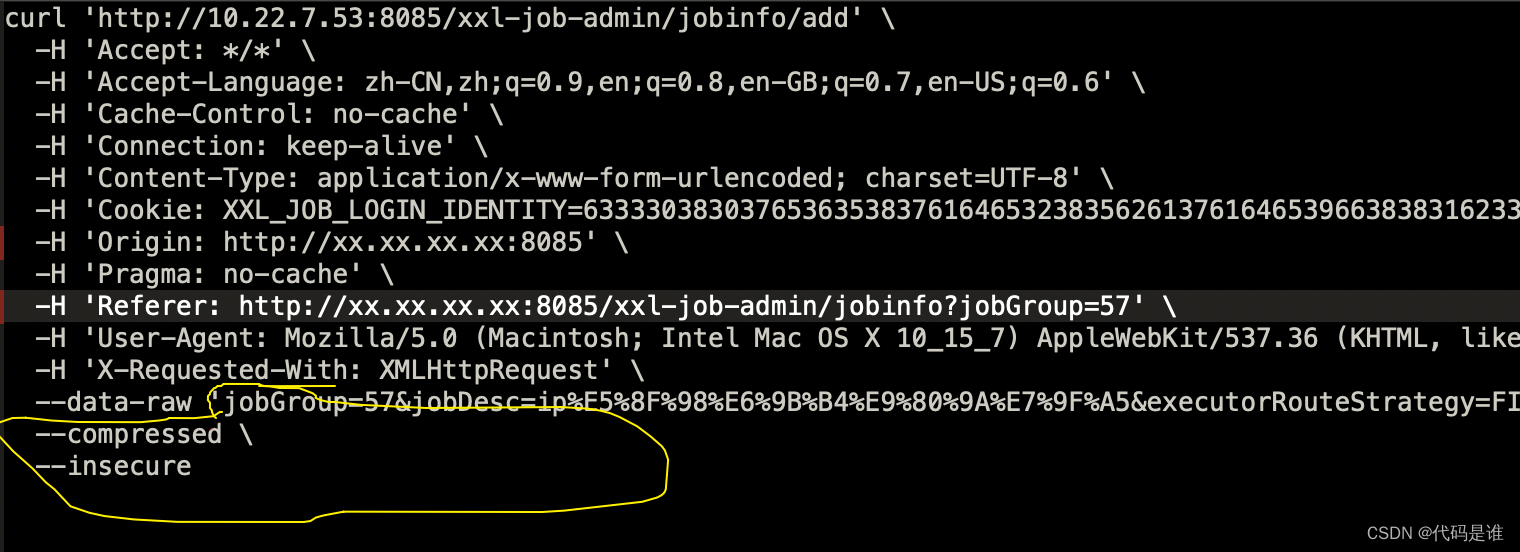
另一种迁移xxl-job任务的方法,适合不满足数据迁移条件
以为多个项目组同时使用一个xxl-job,同时涉及到版本提升,由此不太满足数据库数据迁移,所以这里提供另一种解决办法 使用工具:postman,json转excel,excel 核心:excel拼接: 1.使用f12抓取xxl任务访…...
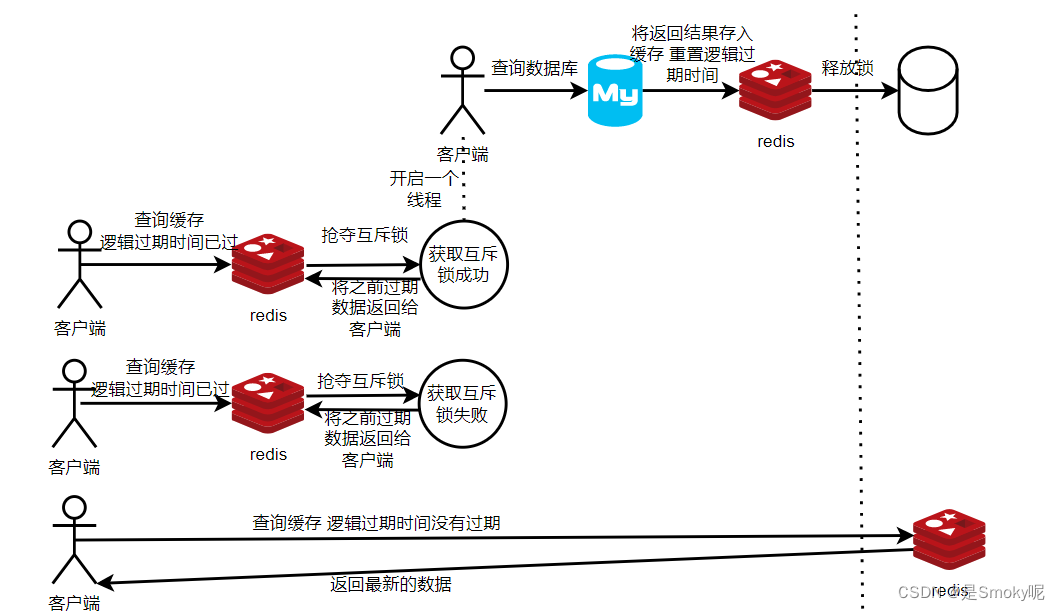
Redis缓存穿透、击穿、雪崩面试题详解
缓存穿透 问题: 指的是客户端请求的数据在缓存中找不到,数据库中也没有存储,客户端还不断的发起请求。这样每次都无法在数据库查询到,缓存中永远没有这个数据。 这样的话,客户端一直去访问,会给后端数据…...
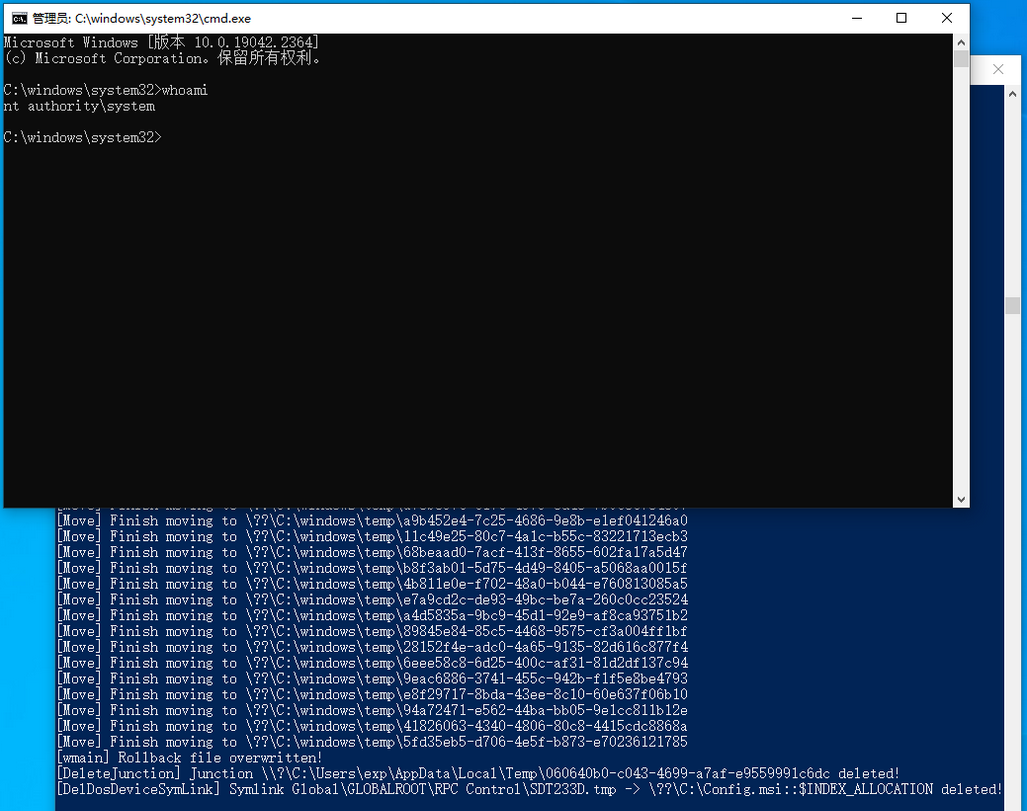
【网络安全】本地提权漏洞分析
0. 前言 CVE-2023-21752 是 2023 年开年微软第一个有 exploit 的漏洞,原本以为有利用代码会很好分析,但是结果花费了很长时间,难点主要了两个:漏洞点定位和漏洞利用代码分析,欢迎指正。 1. 漏洞简介 根据官方信息&a…...

电脑端(PC)按键精灵——3.其他命令
电脑端(PC)按键精灵——3.其他命令 前两节说了安装、键盘和鼠标命令,这一章说下其他命令 按键精灵小白入门详细教程: 电脑端(PC)按键精灵—小白入门 详细教程 命令介绍 1. Delay 延时 简介 //1秒=1000毫秒, 1分钟=60000毫秒,…...

Hudi集成Flink-写入方式
文章目录 一、CDC 入湖1.1、[开启binlog](https://blog.csdn.net/wuxintdrh/article/details/130142601)1.2、创建测试表1.2.1、创建mysql表1.2.2、将 binlog 日志 写入 kafka1、使用 mysql-cdc 监听 binlog2、kafka 作为 sink表3、写入sink 表 1.2.3、将 kakfa 数据写入hudi1、…...

深度探索list
1.list的基本组成 list是一个双向链表,它的基本组成就是 成员作用prev指针指向上一个元素next指针指向下一个元素data用来保存数据 2.list的迭代器 由于人们一般习惯于:迭代器是找到下一个元素,迭代器–是找到上一个元素。在双向链表list中…...

QQuick-自绘
QQuick提供了丰富的控件,搭配qml很容易就可以搭配出一套丝滑的UI界面。但是在有些场景下无论是出于效率还是现有控件的局限都需要进行自绘才能实现自身的需求。QQuick支持多种自绘: 可以使用的方案: 1. 继承QQuickPaintedItem ,重写 paint …...
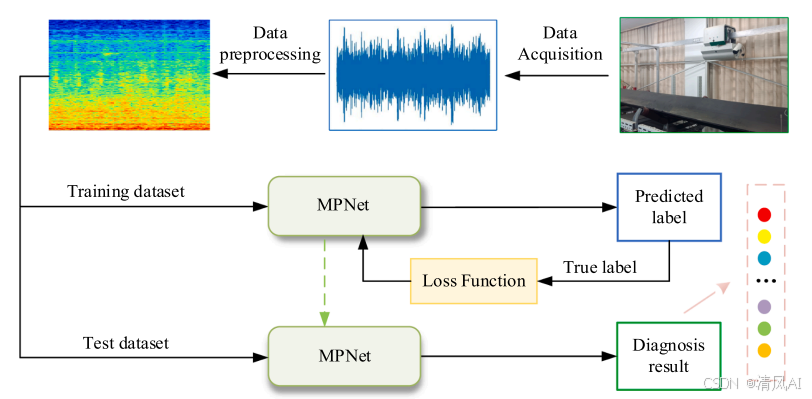
MPNet:旋转机械轻量化故障诊断模型详解python代码复现
目录 一、问题背景与挑战 二、MPNet核心架构 2.1 多分支特征融合模块(MBFM) 2.2 残差注意力金字塔模块(RAPM) 2.2.1 空间金字塔注意力(SPA) 2.2.2 金字塔残差块(PRBlock) 2.3 分类器设计 三、关键技术突破 3.1 多尺度特征融合 3.2 轻量化设计策略 3.3 抗噪声…...

零门槛NAS搭建:WinNAS如何让普通电脑秒变私有云?
一、核心优势:专为Windows用户设计的极简NAS WinNAS由深圳耘想存储科技开发,是一款收费低廉但功能全面的Windows NAS工具,主打“无学习成本部署” 。与其他NAS软件相比,其优势在于: 无需硬件改造:将任意W…...
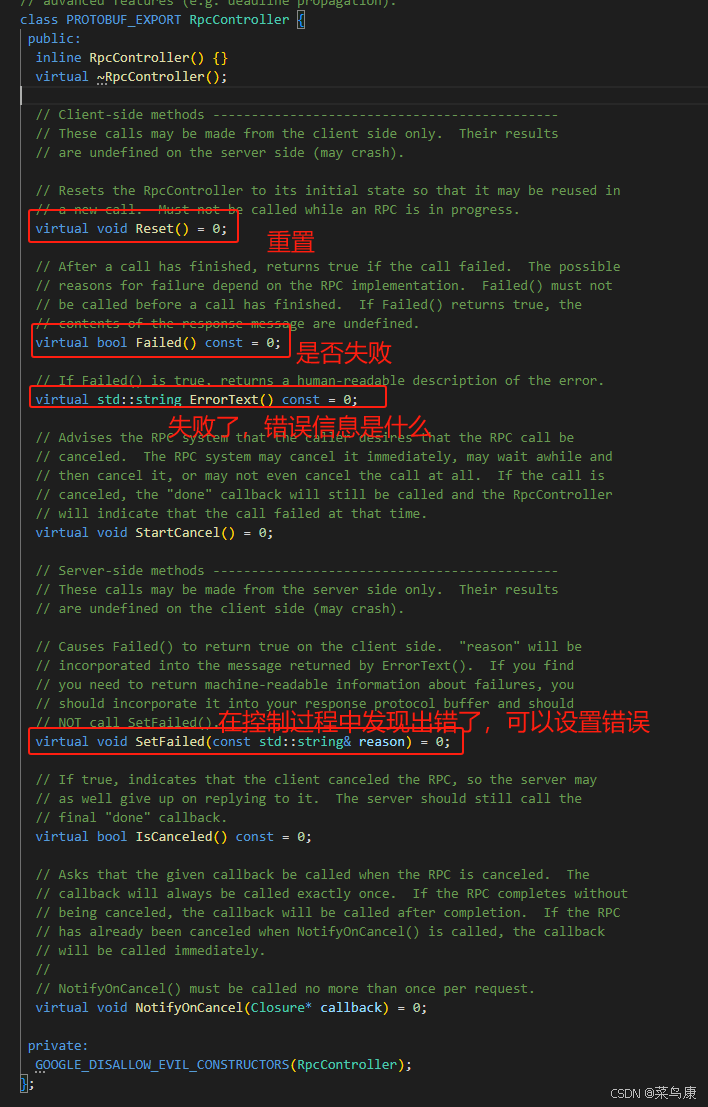
C++实现分布式网络通信框架RPC(3)--rpc调用端
目录 一、前言 二、UserServiceRpc_Stub 三、 CallMethod方法的重写 头文件 实现 四、rpc调用端的调用 实现 五、 google::protobuf::RpcController *controller 头文件 实现 六、总结 一、前言 在前边的文章中,我们已经大致实现了rpc服务端的各项功能代…...
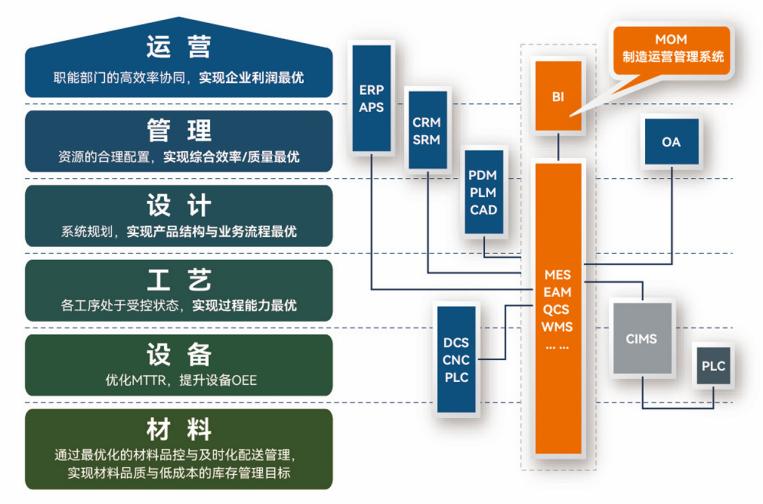
盘古信息PCB行业解决方案:以全域场景重构,激活智造新未来
一、破局:PCB行业的时代之问 在数字经济蓬勃发展的浪潮中,PCB(印制电路板)作为 “电子产品之母”,其重要性愈发凸显。随着 5G、人工智能等新兴技术的加速渗透,PCB行业面临着前所未有的挑战与机遇。产品迭代…...

从WWDC看苹果产品发展的规律
WWDC 是苹果公司一年一度面向全球开发者的盛会,其主题演讲展现了苹果在产品设计、技术路线、用户体验和生态系统构建上的核心理念与演进脉络。我们借助 ChatGPT Deep Research 工具,对过去十年 WWDC 主题演讲内容进行了系统化分析,形成了这份…...

关于iview组件中使用 table , 绑定序号分页后序号从1开始的解决方案
问题描述:iview使用table 中type: "index",分页之后 ,索引还是从1开始,试过绑定后台返回数据的id, 这种方法可行,就是后台返回数据的每个页面id都不完全是按照从1开始的升序,因此百度了下,找到了…...
【机器视觉】单目测距——运动结构恢复
ps:图是随便找的,为了凑个封面 前言 在前面对光流法进行进一步改进,希望将2D光流推广至3D场景流时,发现2D转3D过程中存在尺度歧义问题,需要补全摄像头拍摄图像中缺失的深度信息,否则解空间不收敛…...

Ascend NPU上适配Step-Audio模型
1 概述 1.1 简述 Step-Audio 是业界首个集语音理解与生成控制一体化的产品级开源实时语音对话系统,支持多语言对话(如 中文,英文,日语),语音情感(如 开心,悲伤)&#x…...

Python如何给视频添加音频和字幕
在Python中,给视频添加音频和字幕可以使用电影文件处理库MoviePy和字幕处理库Subtitles。下面将详细介绍如何使用这些库来实现视频的音频和字幕添加,包括必要的代码示例和详细解释。 环境准备 在开始之前,需要安装以下Python库:…...
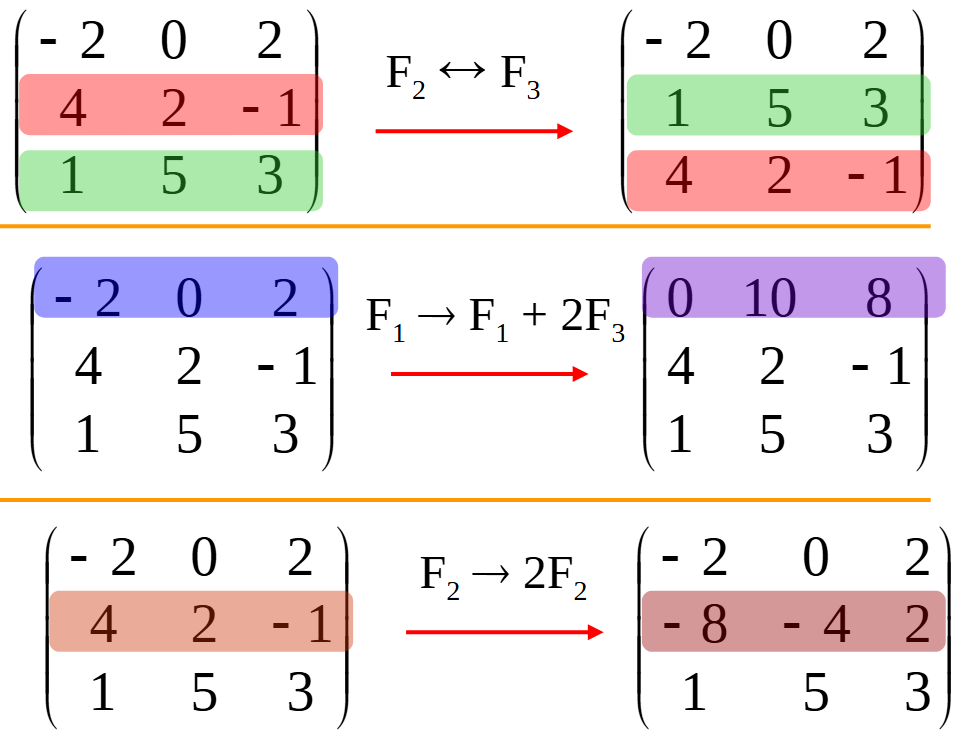
使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的高级操作
在科学计算和工程领域,向量和矩阵操作是解决问题的核心技能之一。Python 的 SymPy 库提供了强大的符号计算功能,能够高效地处理向量和矩阵的各种操作。本文将深入探讨如何使用 SymPy 进行向量和矩阵的创建、合并以及维度拓展等操作,并通过具体…...
