YOLOv7+单目测距(python)
YOLOv7+单目测距(python)
- 1. 相关配置
- 2. 测距原理
- 3. 相机标定
- 3.1:标定方法1
- 3.2:标定方法2
- 4. 相机测距
- 4.1 测距添加
- 4.2 主代码
- 5. 实验效果
相关链接
1. YOLOV5 + 单目测距(python)
2. YOLOV5 + 单目跟踪(python)
3. YOLOV7 + 单目跟踪(python)
4. YOLOV5 + 双目测距(python)
5. YOLOV7 + 双目测距(python)
6. 具体实现效果已在Bilibili发布,点击跳转
本篇博文工程源码下载
链接1:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_45077760/87708470
链接2:https://github.com/up-up-up-up/yolov7_Monocular_ranging
文章结构前三章节和 YOLOV5 + 单目测距 这篇博文一样,如看过该博文,直接跳转第四章节
1. 相关配置
系统:win 10
YOLO版本:yolov7
拍摄视频设备:安卓手机
电脑显卡:NVIDIA 2080Ti(CPU也可以跑,GPU只是起到加速推理效果)
2. 测距原理
单目测距原理相较于双目十分简单,无需进行立体匹配,仅需利用下边公式线性转换即可:
D = (F*W)/P
其中D是目标到摄像机的距离, F是摄像机焦距(焦距需要自己进行标定获取), W是目标的宽度或者高度(行人检测一般以人的身高为基准), P是指目标在图像中所占据的像素

了解基本原理后,下边就进行实操阶段
3. 相机标定
3.1:标定方法1
可以参考张学友标定法获取相机的焦距
3.2:标定方法2
直接使用代码获得焦距,需要提前拍摄一个矩形物体,拍摄时候相机固定,距离被拍摄物体自行设定,并一直保持此距离,背景为纯色,不要出现杂物;最后将拍摄的视频用以下代码检测:
import cv2win_width = 1920
win_height = 1080
mid_width = int(win_width / 2)
mid_height = int(win_height / 2)foc = 1990.0 # 根据教程调试相机焦距
real_wid = 9.05 # A4纸横着的时候的宽度,视频拍摄A4纸要横拍,镜头横,A4纸也横
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
w_ok = 1capture = cv2.VideoCapture('5.mp4')
capture.set(3, win_width)
capture.set(4, win_height)while (True):ret, frame = capture.read()# frame = cv2.flip(frame, 1)if ret == False:breakgray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)gray = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 140, 200, 60) # 扫描不到纸张轮廓时,要更改阈值,直到方框紧密框住纸张kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3, 3))binary = cv2.dilate(binary, kernel, iterations=2)contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)# cv2.drawContours(frame, contours, -1, (0, 255, 0), 2) # 查看所检测到的轮框for c in contours:if cv2.contourArea(c) < 1000: # 对于矩形区域,只显示大于给定阈值的轮廓,所以一些微小的变化不会显示。对于光照不变和噪声低的摄像头可不设定轮廓最小尺寸的阈值continuex, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c) # 该函数计算矩形的边界框if x > mid_width or y > mid_height:continueif (x + w) < mid_width or (y + h) < mid_height:continueif h > w:continueif x == 0 or y == 0:continueif x == win_width or y == win_height:continuew_ok = wcv2.rectangle(frame, (x + 1, y + 1), (x + w_ok - 1, y + h - 1), (0, 255, 0), 2)dis_inch = (real_wid * foc) / (w_ok - 2)dis_cm = dis_inch * 2.54# os.system("cls")# print("Distance : ", dis_cm, "cm")frame = cv2.putText(frame, "%.2fcm" % (dis_cm), (5, 25), font, 0.8, (0, 255, 0), 2)frame = cv2.putText(frame, "+", (mid_width, mid_height), font, 1.0, (0, 255, 0), 2)cv2.namedWindow('res', 0)cv2.namedWindow('gray', 0)cv2.resizeWindow('res', win_width, win_height)cv2.resizeWindow('gray', win_width, win_height)cv2.imshow('res', frame)cv2.imshow('gray', binary)c = cv2.waitKey(40)if c == 27: # 按退出键esc关闭窗口breakcv2.destroyAllWindows()
反复调节 ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 140, 200, 60)这一行里边的三个参数,直到线条紧紧包裹住你所拍摄视频的物体,然后调整相机焦距直到左上角距离和你拍摄视频时相机到物体的距离接近为止
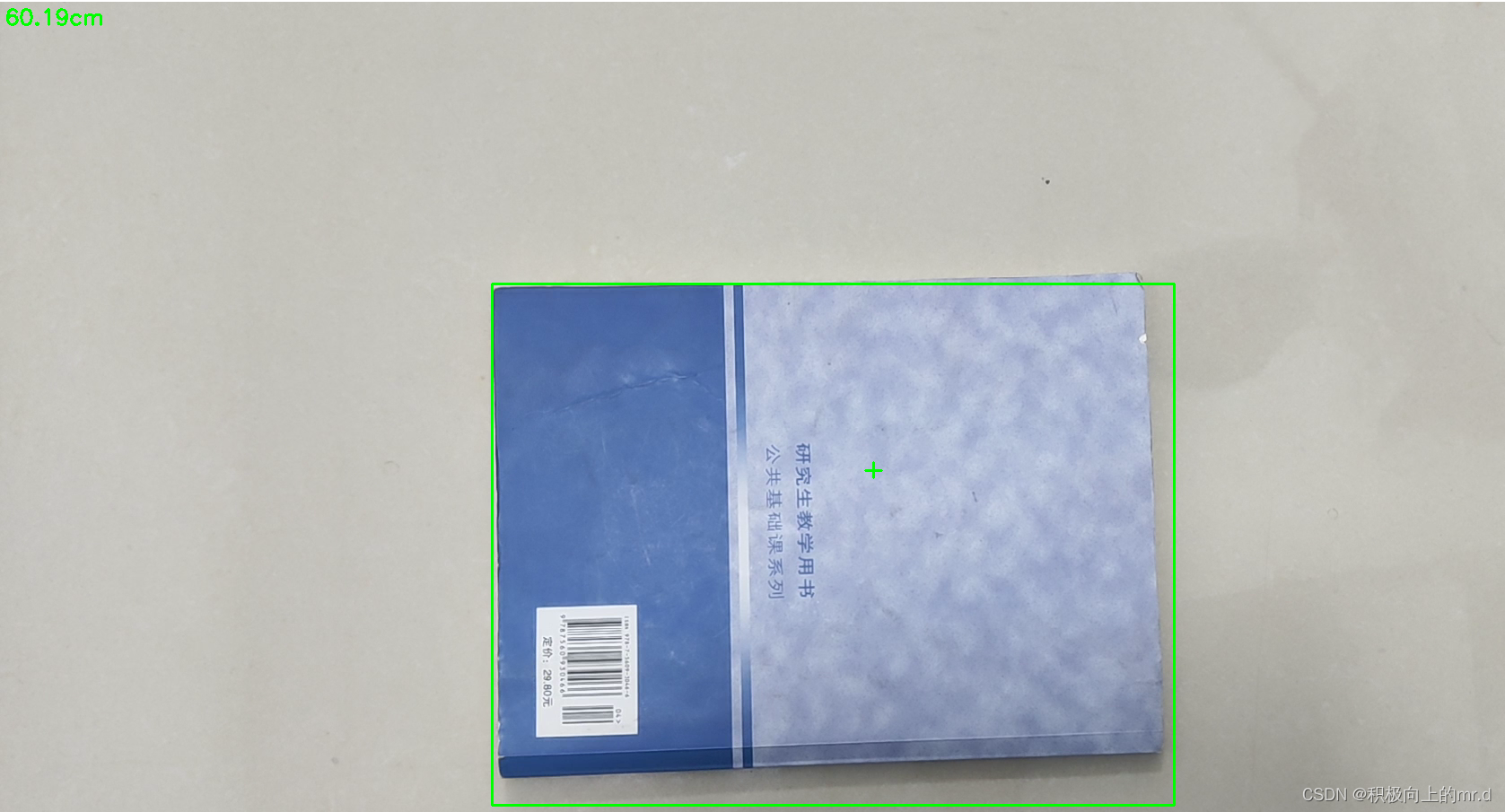

然后将相机焦距写进测距代码distance.py文件里,这里行人用高度表示,根据公式 D = (F*W)/P,知道相机焦距F、行人的高度66.9(单位英寸→170cm/2.54)、像素点距离 h,即可求出相机到物体距离D。 这里用到h-2是因为框的上下边界像素点不接触物体
foc = 1990.0 # 镜头焦距
real_hight_person = 66.9 # 行人高度
real_hight_car = 57.08 # 轿车高度# 自定义函数,单目测距
def person_distance(h):dis_inch = (real_hight_person * foc) / (h - 2)dis_cm = dis_inch * 2.54dis_cm = int(dis_cm)dis_m = dis_cm/100return dis_mdef car_distance(h):dis_inch = (real_hight_car * foc) / (h - 2)dis_cm = dis_inch * 2.54dis_cm = int(dis_cm)dis_m = dis_cm/100return dis_m
4. 相机测距
4.1 测距添加
主要是把测距部分加在了画框附近,首先提取边框的像素点坐标,然后计算边框像素点高度,在根据 公式 D = (F*W)/P 计算目标距离
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):if save_txt: # Write to filexywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywhline = (cls, *xywh, conf) if opt.save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label formatwith open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')if save_img or view_img: # Add bbox to imagex1 = int(xyxy[0]) # 获取四个边框坐标y1 = int(xyxy[1])x2 = int(xyxy[2])y2 = int(xyxy[3])h = y2 - y1label = f'{names[int(cls)]} {conf:.2f}'if label is not None:if (label.split())[0] == 'person':dis_m = person_distance(h) # 调用函数,计算行人实际距离label += f' {dis_m}m' # 将行人距离显示写在标签后plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=1)if (label.split())[0] == 'car' or (label.split())[0] == 'truck':dis_m = car_distance(h) # 调用函数,计算行人实际高度label += f' {dis_m}m' # 将行人距离显示写在标签后plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=1)
4.2 主代码
import argparse
import time
from pathlib import Pathimport cv2
import torch
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
from numpy import randomfrom models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.datasets import LoadStreams, LoadImages
from utils.general import check_img_size, check_requirements, check_imshow, non_max_suppression, apply_classifier, \scale_coords, xyxy2xywh, strip_optimizer, set_logging, increment_path
from utils.plots import plot_one_box
from utils.torch_utils import select_device, load_classifier, time_synchronized, TracedModel
from distance import person_distance,car_distancedef detect(save_img=False):source, weights, view_img, save_txt, imgsz, trace = opt.source, opt.weights, opt.view_img, opt.save_txt, opt.img_size, not opt.no_tracesave_img = not opt.nosave and not source.endswith('.txt') # save inference imageswebcam = source.isnumeric() or source.endswith('.txt') or source.lower().startswith(('rtsp://', 'rtmp://', 'http://', 'https://'))# Directoriessave_dir = Path(increment_path(Path(opt.project) / opt.name, exist_ok=opt.exist_ok)) # increment run(save_dir / 'labels' if save_txt else save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True) # make dir# Initializeset_logging()device = select_device(opt.device)half = device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA# Load modelmodel = attempt_load(weights, map_location=device) # load FP32 modelstride = int(model.stride.max()) # model strideimgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride) # check img_sizeif trace:model = TracedModel(model, device, opt.img_size)if half:model.half() # to FP16# Second-stage classifierclassify = Falseif classify:modelc = load_classifier(name='resnet101', n=2) # initializemodelc.load_state_dict(torch.load('weights/resnet101.pt', map_location=device)['model']).to(device).eval()# Set Dataloadervid_path, vid_writer = None, Noneif webcam:view_img = check_imshow()cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inferencedataset = LoadStreams(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride)else:dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride)# Get names and colorsnames = model.module.names if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.namescolors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in names]# Run inferenceif device.type != 'cpu':model(torch.zeros(1, 3, imgsz, imgsz).to(device).type_as(next(model.parameters()))) # run onceold_img_w = old_img_h = imgszold_img_b = 1t0 = time.time()for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0if img.ndimension() == 3:img = img.unsqueeze(0)# Warmupif device.type != 'cpu' and (old_img_b != img.shape[0] or old_img_h != img.shape[2] or old_img_w != img.shape[3]):old_img_b = img.shape[0]old_img_h = img.shape[2]old_img_w = img.shape[3]for i in range(3):model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0]# Inferencet1 = time_synchronized()with torch.no_grad(): # Calculating gradients would cause a GPU memory leakpred = model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0]t2 = time_synchronized()# Apply NMSpred = non_max_suppression(pred, opt.conf_thres, opt.iou_thres, classes=opt.classes, agnostic=opt.agnostic_nms)t3 = time_synchronized()# Apply Classifierif classify:pred = apply_classifier(pred, modelc, img, im0s)# Process detectionsfor i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per imageif webcam: # batch_size >= 1p, s, im0, frame = path[i], '%g: ' % i, im0s[i].copy(), dataset.countelse:p, s, im0, frame = path, '', im0s, getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)p = Path(p) # to Pathsave_path = str(save_dir / p.name) # img.jpgtxt_path = str(save_dir / 'labels' / p.stem) + ('' if dataset.mode == 'image' else f'_{frame}') # img.txtgn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwhif len(det):# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 sizedet[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()# Print resultsfor c in det[:, -1].unique():n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per classs += f"{n} {names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string# Write resultsfor *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):if save_txt: # Write to filexywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist() # normalized xywhline = (cls, *xywh, conf) if opt.save_conf else (cls, *xywh) # label formatwith open(txt_path + '.txt', 'a') as f:f.write(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line + '\n')if save_img or view_img: # Add bbox to imagex1 = int(xyxy[0]) # 获取四个边框坐标y1 = int(xyxy[1])x2 = int(xyxy[2])y2 = int(xyxy[3])h = y2 - y1label = f'{names[int(cls)]} {conf:.2f}'if label is not None:if (label.split())[0] == 'person':dis_m = person_distance(h) # 调用函数,计算行人实际高度label += f' {dis_m}m' # 将行人距离显示写在标签后plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=1)if (label.split())[0] == 'car' or (label.split())[0] == 'truck':dis_m = car_distance(h) # 调用函数,计算行人实际高度label += f' {dis_m}m' # 将行人距离显示写在标签后plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors[int(cls)], line_thickness=1)# Print time (inference + NMS)print(f'{s}Done. ({(1E3 * (t2 - t1)):.1f}ms) Inference, ({(1E3 * (t3 - t2)):.1f}ms) NMS')# Stream resultsif view_img:cv2.imshow(str(p), im0)cv2.waitKey(1) # 1 millisecond# Save results (image with detections)if save_img:if dataset.mode == 'image':cv2.imwrite(save_path, im0)print(f" The image with the result is saved in: {save_path}")else: # 'video' or 'stream'if vid_path != save_path: # new videovid_path = save_pathif isinstance(vid_writer, cv2.VideoWriter):vid_writer.release() # release previous video writerif vid_cap: # videofps = vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)w = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))else: # streamfps, w, h = 30, im0.shape[1], im0.shape[0]save_path += '.mp4'vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v'), fps, (w, h))vid_writer.write(im0)if save_txt or save_img:s = f"\n{len(list(save_dir.glob('labels/*.txt')))} labels saved to {save_dir / 'labels'}" if save_txt else ''#print(f"Results saved to {save_dir}{s}")print(f'Done. ({time.time() - t0:.3f}s)')if __name__ == '__main__':parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()parser.add_argument('--weights', nargs='+', type=str, default='yolov7.pt', help='model.pt path(s)')parser.add_argument('--source', type=str, default='inference/images/2.mp4', help='source') # file/folder, 0 for webcamparser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=640, help='inference size (pixels)')parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.25, help='object confidence threshold')parser.add_argument('--iou-thres', type=float, default=0.45, help='IOU threshold for NMS')parser.add_argument('--device', default='', help='cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu')parser.add_argument('--view-img', action='store_true', help='display results')parser.add_argument('--save-txt', action='store_true', help='save results to *.txt')parser.add_argument('--save-conf', action='store_true', help='save confidences in --save-txt labels')parser.add_argument('--nosave', action='store_true', help='do not save images/videos')parser.add_argument('--classes', nargs='+', type=int, help='filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3')parser.add_argument('--agnostic-nms', action='store_true', help='class-agnostic NMS')parser.add_argument('--augment', action='store_true', help='augmented inference')parser.add_argument('--update', action='store_true', help='update all models')parser.add_argument('--project', default='runs/detect', help='save results to project/name')parser.add_argument('--name', default='exp', help='save results to project/name')parser.add_argument('--exist-ok', action='store_true', help='existing project/name ok, do not increment')parser.add_argument('--no-trace', action='store_true', help='don`t trace model')opt = parser.parse_args()print(opt)#check_requirements(exclude=('pycocotools', 'thop'))with torch.no_grad():if opt.update: # update all models (to fix SourceChangeWarning)for opt.weights in ['yolov7.pt']:detect()strip_optimizer(opt.weights)else:detect()
5. 实验效果
由于yolov7和yolov5机制问题,yolov7推理时间相较于yolov5较长,实验效果如下
更多有关测距的代码见我博客主页
相关文章:

YOLOv7+单目测距(python)
YOLOv7单目测距(python) 1. 相关配置2. 测距原理3. 相机标定3.1:标定方法13.2:标定方法2 4. 相机测距4.1 测距添加4.2 主代码 5. 实验效果 相关链接 1. YOLOV5 单目测距(python) 2. YOLOV5 单目跟踪&…...
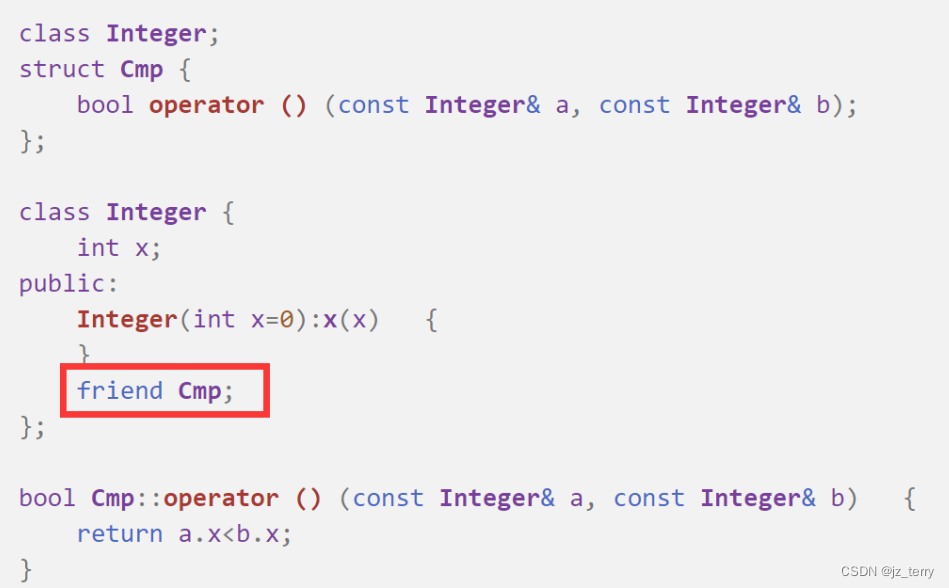
SYSU程设c++(第九周)函数对象、友元函数、友元类
函数对象: 如果一个类定义了operator()运算符函数,则可以使用该类的对象名为函数名调用这个函数. 函数对象是一个对象,但调用形式和普通函数调用一样,因此取名叫函数对象 (注意operator()先有个括号,接着才是括号(参数…...

Target品质审核零容忍问题点——上篇
【Target品质审核零容忍问题点——上篇】 Target品质验厂审核过程中共有110多个问题点,其中包含零容忍问题12项,审核当天如果出现任何零容忍项或出现很多扣分项,将直接影响最后的结果,极容易导致验厂不通过。建议工厂在遇到Target…...
使用node版本管理器gnvm
目录 一、官网 二、下载 三、查看本机node安装地址 四、将gnvm放到node安装目录 五、安装其他版本node(以管理员身份打开CMD) 六、使用指定版本(以管理员身份打开CMD) 七、查看当前版本(以管理员身份打开CMD&…...
SpringBoot中使用redis事务
本文基于SpringBoot 2.X 事务在关系型数据库的开发中经常用到,其实非关系型数据库,比如redis也有对事务的支持,本文主要探讨在SpringBoot中如何使用redis事务。 事务的相关介绍可以参考: 0、起因 在一次线上事故中,我们…...

2023全网汇总PMP备考攻略(附答题技巧)
一,多复习和学习新版考纲 01《PMBOK》看三遍 这边建议看三遍《PMBOK》,更有利于我们巩固知识,查缺补漏。 第一遍 第一遍是老师带着我们去看。这个时候一定要非常专心,千万不要上课走神或者玩手机。因为这一遍老师会告诉我们&a…...

lightdb/pg reload guc 参数机制
lightdb/pg reload guc 参数机制 本文主要讲述调用pg_reload_conf 后,到guc被真正修改之间发送的故事。(基于pg13) pg_reload_conf 函数实现如下: Datum pg_reload_conf(PG_FUNCTION_ARGS) {if (kill(PostmasterPid, SIGHUP)){ereport(WARNING,(errms…...

E. Archaeology(纯思维)
Problem - E - Codeforces 爱丽丝买了一个刚果总理视频的订阅,正在看一部关于苏格兰卡特林湖的因子岛的考古发现的纪录片。考古学家发现了一本书,其年代和来源都不明。也许爱丽丝可以对它进行一些解释? 这本书包含一串字符 "a"、&…...
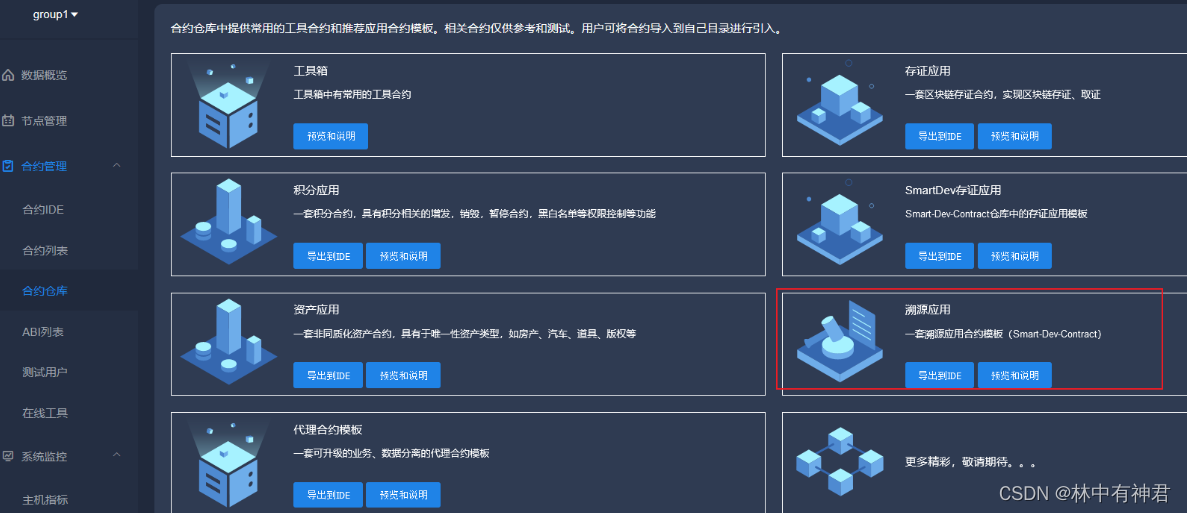
FISCO BCOS(三十四)———商品溯源(智能合约+后端)
FISCO BCOS(三十四)———商品溯源(智能合约+后端) 一、智能合约函数调用流程 注:智能合约来源(官网的合约仓库中) 但是TraceabilityFactory合约有问题,我已经做了修改,可以看原版与我的,只有一个函数不同。 官网上这套合约在TraceabilityFactory这个合约上缺少getGo…...

ts体操训练
1 实现pick type MyPick<T, K extends keyof T> {[P in K]: T[P] }2 实现readonly 让interface中所有属性变为可读 type MyReadonly<T> {readonly [K in keyof T]: T[K] }3 TupleToObject 将元组类型转换为对象类型 type tupleToObject<T extends any[]&…...

int指令
格式: int n,n为中断类型码,它的功能是引发中断过程 CPU执行过程 取中断类型码n;标志寄存器入栈,IF0,TF0;CS,IP入栈;(IP)(n4)&…...
Cycling 74 Max for Mac:音乐可视化编程软件
Cycling 74 Max是一款音乐、视觉、互动艺术等领域中广泛使用的编程语言和应用软件,它允许用户创作和控制实时音频和视频效果、交互式应用程序和媒体艺术品等。 Max将程序设计和可视化编程相结合,通过简单的拖拽和连接方式,用户可以将各种功能…...
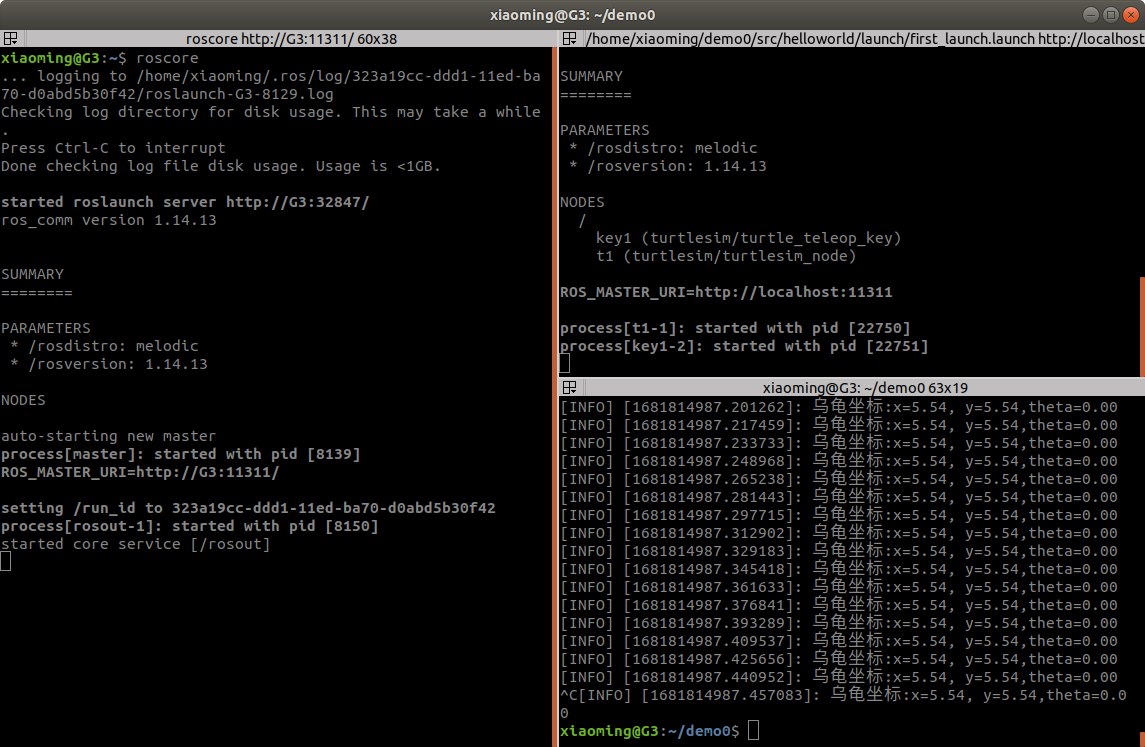
ROS学习第十二节——话题通信控制小乌龟
1.基操一下 首先打开小乌龟程序和键盘控制程序 rosrun turtlesim turtlesim_node rosrun turtlesim turtle_teleop_key 查看话题列表 rostopic list 打开计算图查看具体是那个话题在起作用 rqt_graph 从上图可以看到两个节点之间的话题是 /turtle1/cmd_vel 使用以下命令获…...
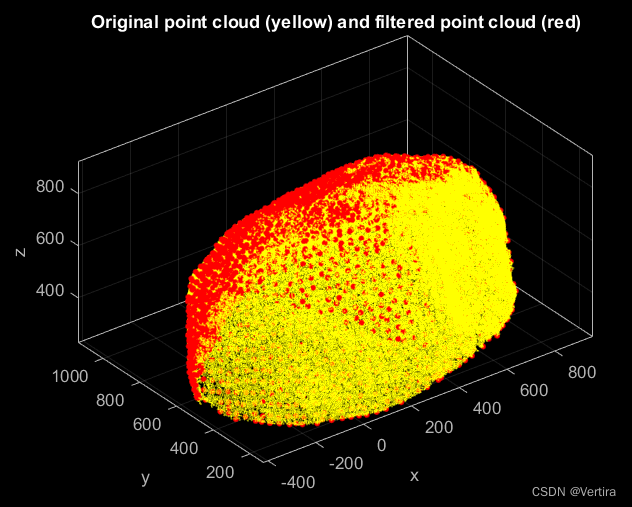
matlab点云的可视化-源码复制粘贴即可(一)
一、导入并可视化一个无属性的点云 clc; clear; close; % clear everything% Import a point cloud from a plain text file (run type(Lion.xyz) to see the contents of the file) pc pointCloud(Lion.xyz);% Generate a z-colored view of the point cloud pc.plot;% Set …...
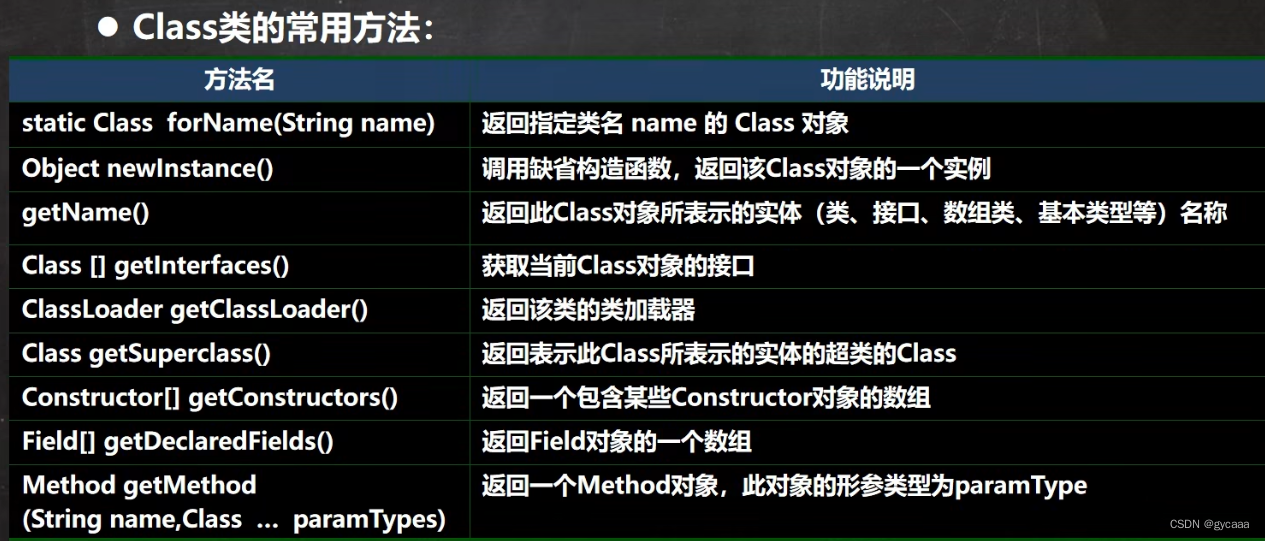
反射-Class类分析
反射相关的主要类 java.lang.Class:代表一个类,Class对象表示某个类加载后在堆中的对象java.lang.reflect.Method:代表类的方法,Method对象表示某个类的方法java.lang.reflect.Field:代表类的成员变量,Fie…...

Let’s Make C++ Great Again——string与常用字符处理函数
文章目录 string使用string类的例子,统计一个字符串中单词的个数:在算法模拟题中翻转字符串:判断回文字符串:字符串查找:字符串替换: 常用字符处理函数strlen()strcpy()strcat()strcmp()toupper() 和 tolow…...

〖Python网络爬虫实战⑰〗- 网页解析利器parsel实战
订阅:新手可以订阅我的其他专栏。免费阶段订阅量1000 python项目实战 Python编程基础教程系列(零基础小白搬砖逆袭) 说明:本专栏持续更新中,目前专栏免费订阅,在转为付费专栏前订阅本专栏的,可以免费订阅付…...
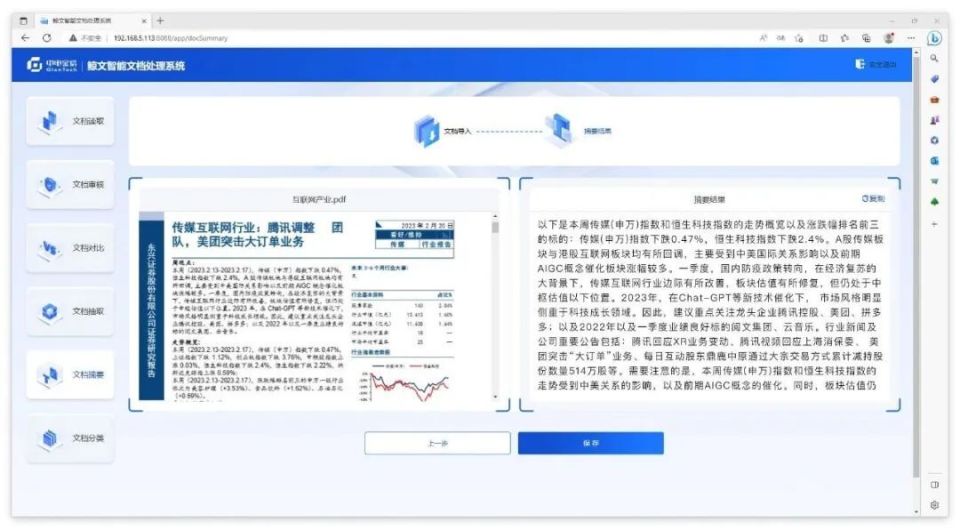
中电金信:生成式AI热潮下,文本智能走向何方?
突破通用人工智能场景,生成式AI正在向全行业应用进攻。 一个脑筋急转弯,几个月前ChatGPT是这样回答的: 然而,仅仅几个月的迭代,它的回答却让人出乎意料。 看似调侃的对比背后实则是无数次模型训练的支撑。基于数据的激…...

探索Linux设备树:硬件描述与驱动程序的桥梁
目录标题 引言:Linux设备树简介 | Introduction: Linux Device Tree Overviewa. 设备树的背景与发展 | Background and Development of Device Treeb. 设备树的作用与意义 | The Role and Significance of Device Tree 设备树语法与结构 | Device Tree Syntax and S…...

UNION ALL用法 以及 UNION ALL和UNION的区别
部分参考自文章: https://blog.csdn.net/a200822146085/article/details/119545374(CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议)CSDN「我心依依旧」 https://www.1keydata.com/cn/sql/sql-unionall.php SQL Union All SQL指令 UNION ALL用法 UNION ALL 这个指令的目的也是要将两个 SQL 语…...

从零实现富文本编辑器#5-编辑器选区模型的状态结构表达
先前我们总结了浏览器选区模型的交互策略,并且实现了基本的选区操作,还调研了自绘选区的实现。那么相对的,我们还需要设计编辑器的选区表达,也可以称为模型选区。编辑器中应用变更时的操作范围,就是以模型选区为基准来…...

中南大学无人机智能体的全面评估!BEDI:用于评估无人机上具身智能体的综合性基准测试
作者:Mingning Guo, Mengwei Wu, Jiarun He, Shaoxian Li, Haifeng Li, Chao Tao单位:中南大学地球科学与信息物理学院论文标题:BEDI: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Embodied Agents on UAVs论文链接:https://arxiv.…...
)
相机Camera日志分析之三十一:高通Camx HAL十种流程基础分析关键字汇总(后续持续更新中)
【关注我,后续持续新增专题博文,谢谢!!!】 上一篇我们讲了:有对最普通的场景进行各个日志注释讲解,但相机场景太多,日志差异也巨大。后面将展示各种场景下的日志。 通过notepad++打开场景下的日志,通过下列分类关键字搜索,即可清晰的分析不同场景的相机运行流程差异…...
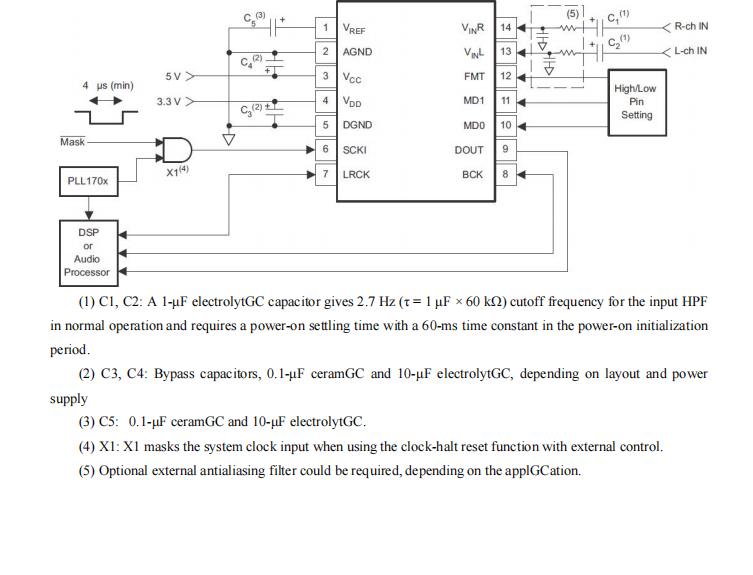
GC1808高性能24位立体声音频ADC芯片解析
1. 芯片概述 GC1808是一款24位立体声音频模数转换器(ADC),支持8kHz~96kHz采样率,集成Δ-Σ调制器、数字抗混叠滤波器和高通滤波器,适用于高保真音频采集场景。 2. 核心特性 高精度:24位分辨率,…...
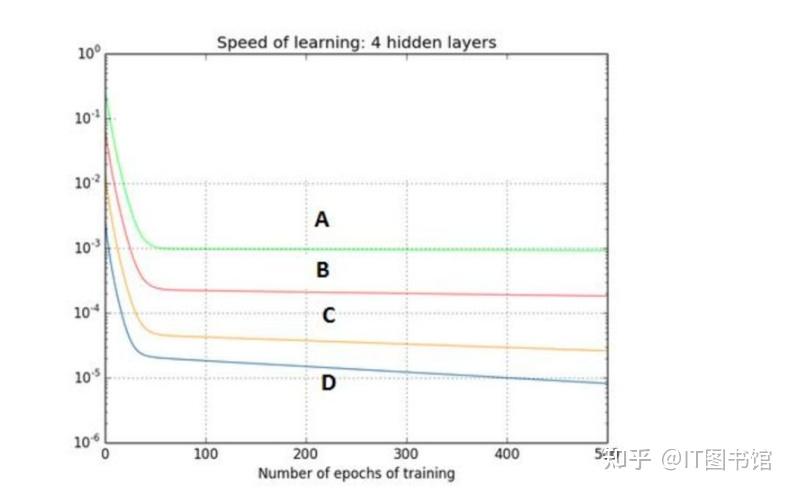
深度学习习题2
1.如果增加神经网络的宽度,精确度会增加到一个特定阈值后,便开始降低。造成这一现象的可能原因是什么? A、即使增加卷积核的数量,只有少部分的核会被用作预测 B、当卷积核数量增加时,神经网络的预测能力会降低 C、当卷…...
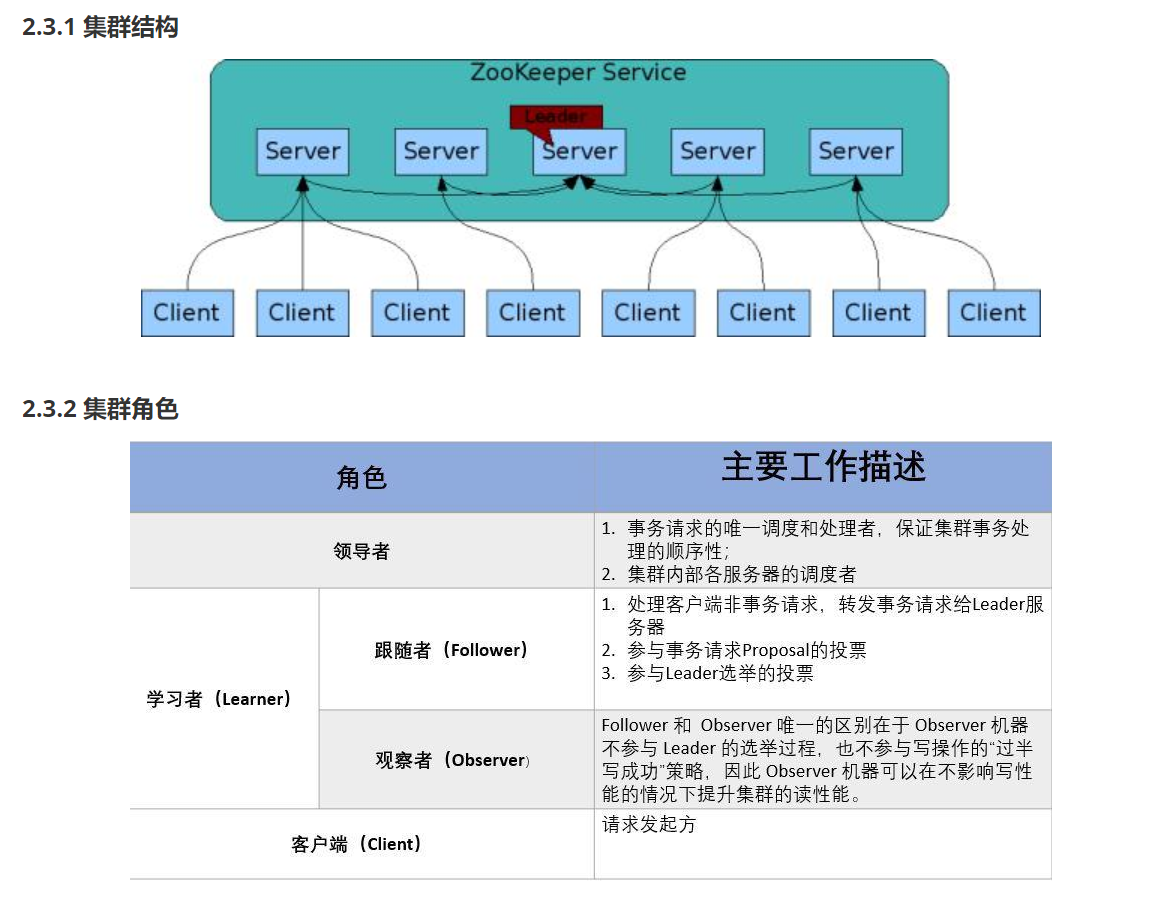
HDFS分布式存储 zookeeper
hadoop介绍 狭义上hadoop是指apache的一款开源软件 用java语言实现开源框架,允许使用简单的变成模型跨计算机对大型集群进行分布式处理(1.海量的数据存储 2.海量数据的计算)Hadoop核心组件 hdfs(分布式文件存储系统)&a…...

Mysql8 忘记密码重置,以及问题解决
1.使用免密登录 找到配置MySQL文件,我的文件路径是/etc/mysql/my.cnf,有的人的是/etc/mysql/mysql.cnf 在里最后加入 skip-grant-tables重启MySQL服务 service mysql restartShutting down MySQL… SUCCESS! Starting MySQL… SUCCESS! 重启成功 2.登…...

计算机基础知识解析:从应用到架构的全面拆解
目录 前言 1、 计算机的应用领域:无处不在的数字助手 2、 计算机的进化史:从算盘到量子计算 3、计算机的分类:不止 “台式机和笔记本” 4、计算机的组件:硬件与软件的协同 4.1 硬件:五大核心部件 4.2 软件&#…...
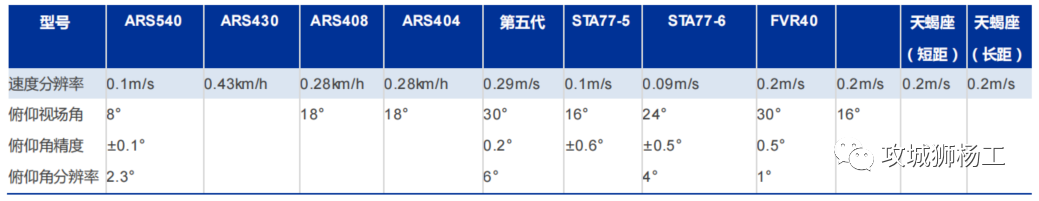
毫米波雷达基础理论(3D+4D)
3D、4D毫米波雷达基础知识及厂商选型 PreView : https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bQkju4r6med7I3TBGJI_bQ 1. FMCW毫米波雷达基础知识 主要参考博文: 一文入门汽车毫米波雷达基本原理 :https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_EN7A5lKcz2Eh8dLnjE19w 毫米波雷达基础…...
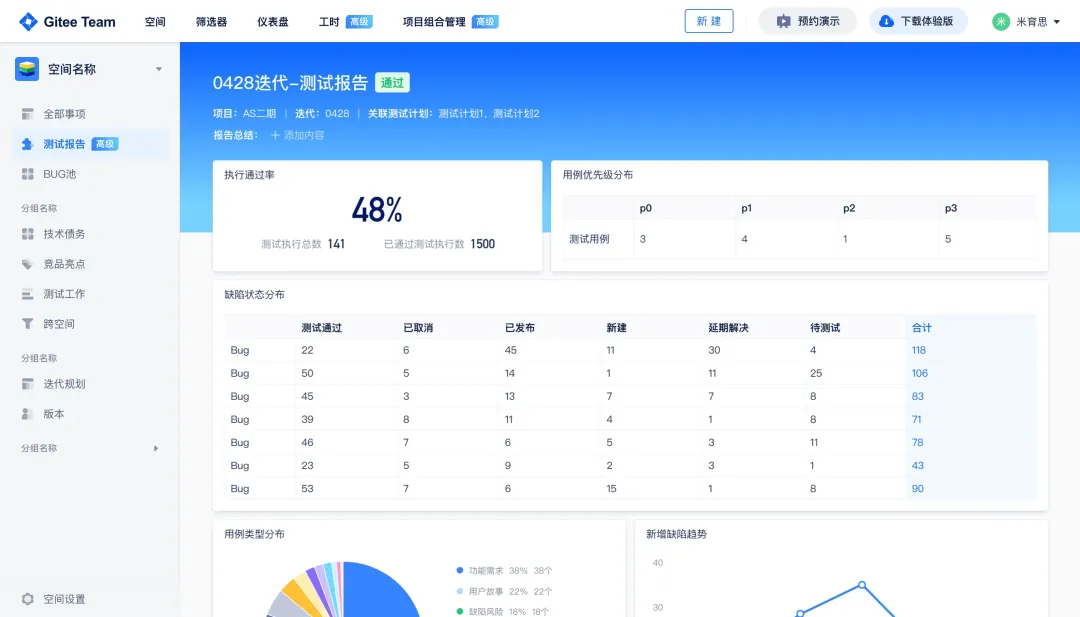
从“安全密码”到测试体系:Gitee Test 赋能关键领域软件质量保障
关键领域软件测试的"安全密码":Gitee Test如何破解行业痛点 在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,软件系统已成为国家关键领域的"神经中枢"。从国防军工到能源电力,从金融交易到交通管控,这些关乎国计民生的关键领域…...
