C++ Primer第五版_第十四章习题答案(21~30)
文章目录
- 练习14.21
- 练习14.22
- 头文件
- CPP文件
- 练习14.23
- 头文件
- CPP文件
- 练习14.24
- 头文件
- CPP文件
- 练习14.25
- 练习14.26
- 练习14.27
- 练习14.28
- 练习14.29
- 练习14.30
练习14.21
编写 Sales_data 类的+ 和+= 运算符,使得 + 执行实际的加法操作而 += 调用+。相比14.3节和14.4节对这两个运算符的定义,本题的定义有何缺点?试讨论之。
缺点:使用了一个 Sales_data 的临时对象,但它并不是必须的。
练习14.22
定义赋值运算符的一个新版本,使得我们能把一个表示 ISBN 的 string 赋给一个 Sales_data 对象。
头文件
#ifndef CP5_ex14_22_h
#define CP5_ex14_22_h#include <string>
#include <iostream>class Sales_data
{friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream&, Sales_data&);friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream&, const Sales_data&);friend Sales_data operator+(const Sales_data&, const Sales_data&);public:Sales_data(const std::string &s, unsigned n, double p) :bookNo(s), units_sold(n), revenue(n*p) {}Sales_data() : Sales_data("", 0, 0.0f) {}Sales_data(const std::string &s) : Sales_data(s, 0, 0.0f) {}Sales_data(std::istream &is);Sales_data& operator=(const std::string&);Sales_data& operator+=(const Sales_data&);std::string isbn() const { return bookNo; }private:inline double avg_price() const;std::string bookNo;unsigned units_sold = 0;double revenue = 0.0;
};std::istream& operator>>(std::istream&, Sales_data&);
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream&, const Sales_data&);
Sales_data operator+(const Sales_data&, const Sales_data&);inline double Sales_data::avg_price() const
{return units_sold ? revenue / units_sold : 0;
}#endif
CPP文件
#include "exercise14_22.h"Sales_data::Sales_data(std::istream &is) : Sales_data()
{is >> *this;
}Sales_data& Sales_data::operator+=(const Sales_data &rhs)
{units_sold += rhs.units_sold;revenue += rhs.revenue;return *this;
}std::istream& operator>>(std::istream &is, Sales_data &item)
{double price = 0.0;is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price;if (is)item.revenue = price * item.units_sold;elseitem = Sales_data();return is;
}std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Sales_data &item)
{os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " " << item.revenue << " " << item.avg_price();return os;
}Sales_data operator+(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs)
{Sales_data sum = lhs;sum += rhs;return sum;
}Sales_data& Sales_data::operator=(const std::string &isbn)
{*this = Sales_data(isbn);return *this;
}
练习14.23
为你的StrVec 类定义一个 initializer_list 赋值运算符。
头文件
#ifndef CP5_STRVEC_H_
#define CP5_STRVEC_H_#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <initializer_list>#ifndef _MSC_VER
#define NOEXCEPT noexcept
#else
#define NOEXCEPT
#endifclass StrVec
{friend bool operator==(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);friend bool operator!=(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);friend bool operator< (const StrVec&, const StrVec&);friend bool operator> (const StrVec&, const StrVec&);friend bool operator<=(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);friend bool operator>=(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);public:StrVec() : elements(nullptr), first_free(nullptr), cap(nullptr) {}StrVec(std::initializer_list<std::string>);StrVec(const StrVec&);StrVec& operator=(const StrVec&);StrVec(StrVec&&) NOEXCEPT;StrVec& operator=(StrVec&&)NOEXCEPT;~StrVec();StrVec& operator=(std::initializer_list<std::string>);void push_back(const std::string&);size_t size() const { return first_free - elements; }size_t capacity() const { return cap - elements; }std::string *begin() const { return elements; }std::string *end() const { return first_free; }std::string& at(size_t pos) { return *(elements + pos); }const std::string& at(size_t pos) const { return *(elements + pos); }void reserve(size_t new_cap);void resize(size_t count);void resize(size_t count, const std::string&);private:std::pair<std::string*, std::string*> alloc_n_copy(const std::string*, const std::string*);void free();void chk_n_alloc() { if (size() == capacity()) reallocate(); }void reallocate();void alloc_n_move(size_t new_cap);void range_initialize(const std::string*, const std::string*);private:std::string *elements;std::string *first_free;std::string *cap;std::allocator<std::string> alloc;
};bool operator==(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);
bool operator!=(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);
bool operator< (const StrVec&, const StrVec&);
bool operator> (const StrVec&, const StrVec&);
bool operator<=(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);
bool operator>=(const StrVec&, const StrVec&);#endif
CPP文件
#include "exercise14_23.h"
#include <algorithm>void StrVec::push_back(const std::string &s)
{chk_n_alloc();alloc.construct(first_free++, s);
}std::pair<std::string*, std::string*>
StrVec::alloc_n_copy(const std::string *b, const std::string *e)
{auto data = alloc.allocate(e - b);return{ data, std::uninitialized_copy(b, e, data) };
}void StrVec::free()
{if (elements){for_each(elements, first_free, [this](std::string &rhs) { alloc.destroy(&rhs); });alloc.deallocate(elements, cap - elements);}
}void StrVec::range_initialize(const std::string *first, const std::string *last)
{auto newdata = alloc_n_copy(first, last);elements = newdata.first;first_free = cap = newdata.second;
}StrVec::StrVec(const StrVec &rhs)
{range_initialize(rhs.begin(), rhs.end());
}StrVec::StrVec(std::initializer_list<std::string> il)
{range_initialize(il.begin(), il.end());
}StrVec::~StrVec()
{free();
}StrVec& StrVec::operator = (const StrVec &rhs)
{auto data = alloc_n_copy(rhs.begin(), rhs.end());free();elements = data.first;first_free = cap = data.second;return *this;
}void StrVec::alloc_n_move(size_t new_cap)
{auto newdata = alloc.allocate(new_cap);auto dest = newdata;auto elem = elements;for (size_t i = 0; i != size(); ++i)alloc.construct(dest++, std::move(*elem++));free();elements = newdata;first_free = dest;cap = elements + new_cap;
}void StrVec::reallocate()
{auto newcapacity = size() ? 2 * size() : 1;alloc_n_move(newcapacity);
}void StrVec::reserve(size_t new_cap)
{if (new_cap <= capacity()) return;alloc_n_move(new_cap);
}void StrVec::resize(size_t count)
{resize(count, std::string());
}void StrVec::resize(size_t count, const std::string &s)
{if (count > size()){if (count > capacity()) reserve(count * 2);for (size_t i = size(); i != count; ++i)alloc.construct(first_free++, s);}else if (count < size()){while (first_free != elements + count)alloc.destroy(--first_free);}
}StrVec::StrVec(StrVec &&s) NOEXCEPT : elements(s.elements), first_free(s.first_free), cap(s.cap)
{// leave s in a state in which it is safe to run the destructor.s.elements = s.first_free = s.cap = nullptr;
}StrVec& StrVec::operator = (StrVec &&rhs) NOEXCEPT
{if (this != &rhs){free();elements = rhs.elements;first_free = rhs.first_free;cap = rhs.cap;rhs.elements = rhs.first_free = rhs.cap = nullptr;}return *this;
}bool operator==(const StrVec &lhs, const StrVec &rhs)
{return (lhs.size() == rhs.size() && std::equal(lhs.begin(), lhs.end(), rhs.begin()));
}bool operator!=(const StrVec &lhs, const StrVec &rhs)
{return !(lhs == rhs);
}bool operator<(const StrVec &lhs, const StrVec &rhs)
{return std::lexicographical_compare(lhs.begin(), lhs.end(), rhs.begin(), rhs.end());
}bool operator>(const StrVec &lhs, const StrVec &rhs)
{return rhs < lhs;
}bool operator<=(const StrVec &lhs, const StrVec &rhs)
{return !(rhs < lhs);
}bool operator>=(const StrVec &lhs, const StrVec &rhs)
{return !(lhs < rhs);
}StrVec& StrVec::operator=(std::initializer_list<std::string> il)
{*this = StrVec(il);return *this;
}
练习14.24
你在7.5.1节的练习7.40中曾经选择并编写了一个类,你认为它应该含有拷贝赋值和移动赋值运算符吗?如果是,请实现它们。
头文件
#ifndef DATE_H
#define DATE_H#ifndef _MSC_VER
#define NOEXCEPT noexcept
#else
#define NOEXCEPT
#endif#include <iostream>
#include <vector>class Date
{friend bool operator ==(const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);friend bool operator < (const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs);friend bool check(const Date &d);friend std::ostream& operator <<(std::ostream& os, const Date& d);
public:typedef std::size_t Size;// default constructorDate() = default;// constructor taking Size as daysexplicit Date(Size days);// constructor taking three SizeDate(Size d, Size m, Size y) : day(d), month(m), year(y) {}// constructor taking iostreamDate(std::istream &is, std::ostream &os);// copy constructorDate(const Date& d);// move constructorDate(Date&& d) NOEXCEPT;// copy operator=Date& operator= (const Date& d);// move operator=Date& operator= (Date&& rhs) NOEXCEPT;// destructor -- in this case, user-defined destructor is not nessary.~Date() { std::cout << "destroying\n"; }// membersSize toDays() const; //not implemented yet.Date& operator +=(Size offset);Date& operator -=(Size offset);private:Size day = 1;Size month = 1;Size year = 0;
};static const Date::Size YtoD_400 = 146097; //365*400 + 400/4 -3 == 146097
static const Date::Size YtoD_100 = 36524; //365*100 + 100/4 -1 == 36524
static const Date::Size YtoD_4 = 1461; //365*4 + 1 == 1461
static const Date::Size YtoD_1 = 365; //365// normal year
static const std::vector<Date::Size> monthsVec_n =
{ 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };// leap year
static const std::vector<Date::Size> monthsVec_l =
{ 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };// non-member operators: << >> - == != < <= > >=
//
std::ostream&
operator <<(std::ostream& os, const Date& d);
std::istream&
operator >>(std::istream& is, Date& d);
int
operator - (const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);
bool
operator ==(const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);
bool
operator !=(const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);
bool
operator < (const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);
bool
operator <=(const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);
bool
operator >(const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);
bool
operator >=(const Date& lhs, const Date& rhs);
Date
operator - (const Date& lhs, Date::Size rhs);
Date
operator +(const Date& lhs, Date::Size rhs);// utillities:
bool check(const Date &d);
inline bool
isLeapYear(Date::Size y);// check if the date object passed in is valid
inline bool
check(const Date &d)
{if (d.month == 0 || d.month >12)return false;else{// month == 1 3 5 7 8 10 12if (d.month == 1 || d.month == 3 || d.month == 5 || d.month == 7 ||d.month == 8 || d.month == 10 || d.month == 12){if (d.day == 0 || d.day > 31) return false;elsereturn true;}else{// month == 4 6 9 11if (d.month == 4 || d.month == 6 || d.month == 9 || d.month == 11){if (d.day == 0 || d.day > 30) return false;elsereturn true;}else{// month == 2if (isLeapYear(d.year)){if (d.day == 0 || d.day >29) return false;elsereturn true;}else{if (d.day == 0 || d.day >28) return false;elsereturn true;}}}}
}inline bool
isLeapYear(Date::Size y)
{if (!(y % 400)){return true;}else{if (!(y % 100)){return false;}elsereturn !(y % 4);}
}
#endif // DATE_H
CPP文件
#include "exercise14_24.h"
#include <algorithm>// constructor taking Size as days
// the argument must be within (0, 2^32)
Date::Date(Size days)
{// calculate the yearSize y400 = days / YtoD_400;Size y100 = (days - y400*YtoD_400) / YtoD_100;Size y4 = (days - y400*YtoD_400 - y100*YtoD_100) / YtoD_4;Size y = (days - y400*YtoD_400 - y100*YtoD_100 - y4*YtoD_4) / 365;Size d = days - y400*YtoD_400 - y100*YtoD_100 - y4*YtoD_4 - y * 365;this->year = y400 * 400 + y100 * 100 + y4 * 4 + y;// check if leap and choose the months vector accordinglystd::vector<Size>currYear= isLeapYear(this->year) ? monthsVec_l : monthsVec_n;// calculate day and month using find_if + lambdaSize D_accumu = 0, M_accumu = 0;// @bug fixed: the variabbles above hade been declared inside the find_if as static// which caused the bug. It works fine now after being move outside.std::find_if(currYear.cbegin(), currYear.cend(), [&](Size m){D_accumu += m;M_accumu++;if (d < D_accumu){this->month = M_accumu;this->day = d + m - D_accumu;return true;}elsereturn false;});
}// construcotr taking iostream
Date::Date(std::istream &is, std::ostream &os)
{is >> day >> month >> year;if (is){if (check(*this)) return;else{os << "Invalid input! Object is default initialized.";*this = Date();}}else{os << "Invalid input! Object is default initialized.";*this = Date();}}// copy constructor
Date::Date(const Date &d) :
day(d.day), month(d.month), year(d.year)
{}// move constructor
Date::Date(Date&& d) NOEXCEPT :
day(d.day), month(d.month), year(d.year)
{ std::cout << "copy moving"; }// copy operator=
Date &Date::operator= (const Date &d)
{this->day = d.day;this->month = d.month;this->year = d.year;return *this;
}// move operator=
Date &Date::operator =(Date&& rhs) NOEXCEPT
{if (this != &rhs){this->day = rhs.day;this->month = rhs.month;this->year = rhs.year;}std::cout << "moving =";return *this;
}// conver to days
Date::Size Date::toDays() const
{Size result = this->day;// check if leap and choose the months vector accordinglystd::vector<Size>currYear= isLeapYear(this->year) ? monthsVec_l : monthsVec_n;// calculate result + days by monthsfor (auto it = currYear.cbegin(); it != currYear.cbegin() + this->month - 1; ++it)result += *it;// calculate result + days by yearsresult += (this->year / 400) * YtoD_400;result += (this->year % 400 / 100) * YtoD_100;result += (this->year % 100 / 4) * YtoD_4;result += (this->year % 4) * YtoD_1;return result;
}// member operators: += -=Date &Date::operator +=(Date::Size offset)
{*this = Date(this->toDays() + offset);return *this;
}Date &Date::operator -=(Date::Size offset)
{if (this->toDays() > offset)*this = Date(this->toDays() - offset);else*this = Date();return *this;
}// non-member operators: << >> - == != < <= > >=std::ostream&
operator <<(std::ostream& os, const Date& d)
{os << d.day << " " << d.month << " " << d.year;return os;
}std::istream&
operator >>(std::istream& is, Date& d)
{if (is){Date input = Date(is, std::cout);if (check(input)) d = input;}return is;
}int operator -(const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs)
{return lhs.toDays() - rhs.toDays();
}bool operator ==(const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs)
{return (lhs.day == rhs.day) &&(lhs.month == rhs.month) &&(lhs.year == rhs.year);
}bool operator !=(const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs)
{return !(lhs == rhs);
}bool operator < (const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs)
{return lhs.toDays() < rhs.toDays();
}bool operator <=(const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs)
{return (lhs < rhs) || (lhs == rhs);
}bool operator >(const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs)
{return !(lhs <= rhs);
}bool operator >=(const Date &lhs, const Date &rhs)
{return !(lhs < rhs);
}Date operator - (const Date &lhs, Date::Size rhs)
{ // ^^^ rhs must not be larger than 2^32-1// copy lhsDate result(lhs);result -= rhs;return result;
}Date operator + (const Date &lhs, Date::Size rhs)
{ // ^^^ rhs must not be larger than 2^32-1// copy lhsDate result(lhs);result += rhs;return result;
}
练习14.25
上题的这个类还需要定义其他赋值运算符吗?如果是,请实现它们;同时说明运算对象应该是什么类型并解释原因。
是。如上题。
练习14.26
为你的 StrBlob 类、StrBlobPtr 类、StrVec 类和 String 类定义下标运算符。
练习14.27
为你的 StrBlobPtr 类添加递增和递减运算符。
练习14.28
为你的 StrBlobPtr 类添加加法和减法运算符,使其可以实现指针的算术运算。
练习14.29
为什么不定义const 版本的递增和递减运算符?
因为递增和递减会改变对象本身,所以定义 const 版本的毫无意义。
练习14.30
为你的 StrBlobPtr 类和在12.1.6节练习12.22中定义的 ConstStrBlobPtr 的类分别添加解引用运算符和箭头运算符。注意:因为 ConstStrBlobPtr 的数据成员指向const vector,所以ConstStrBlobPtr 中的运算符必须返回常量引用。
相关文章:
)
C++ Primer第五版_第十四章习题答案(21~30)
文章目录 练习14.21练习14.22头文件CPP文件 练习14.23头文件CPP文件 练习14.24头文件CPP文件 练习14.25练习14.26练习14.27练习14.28练习14.29练习14.30 练习14.21 编写 Sales_data 类的 和 运算符,使得 执行实际的加法操作而 调用。相比14.3节和14.4节对这两个运…...

服务器性能调优
硬件 如果是硬件瓶颈就换硬件 (包括CPU、内存、网卡) 软件 如果是方案架构设计有问题就换方案,比如mysql、redis方案有问题 建议先 top 看下软件瓶颈在哪,CPU、内存、网络(netstat),哪个进程占…...
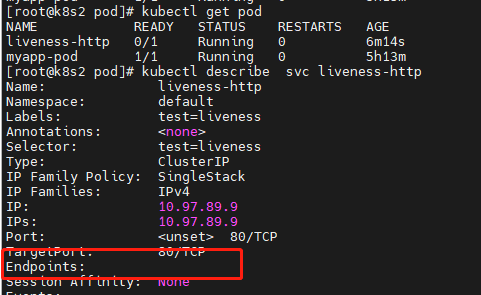
带你深入学习k8s--(三) pod 管理
目录 一、简介 1、什么是pod 2、为什么要有pod 二、pod的分类 0、pod常用命令命令 1、准备镜像 2、自主式pod 3、控制器创建pod 4、扩容pod数量 5、通过service暴露pod(负载均衡,自动发起) 6、更新应用版本 三、编写yaml文件 四、Pod生命周期…...

前端系列11集-ES6 知识总结
ES Module 优点 静态分析 浏览器和 Node 都支持 浏览器的新 API 能用模块格式提供 不再需要对象作为命名空间 export 用于规定模块的对外接口 输出的接口与其对应的值是动态绑定关系可以取到模块内部实时的值 import 用于输入其他模块提供的功能 具有提升效果,会提升…...

连接分析工具箱 | 利用CATO进行结构和功能连接重建
导读 本研究描述了一个连接分析工具箱(CATO),用于基于扩散加权成像(DWI)和静息态功能磁共振成像(rs-fMRI)数据来重建大脑结构和功能连接。CATO是一个多模态软件包,使研究人员能够运行从MRI数据到结构和功能连接组图的端到端重建,定制其分析并…...

【目标检测论文阅读笔记】Detection of plane in remote sensing images using super-resolution
Abstract 由于大量的小目标、实例级噪声和云遮挡等因素,遥感图像的目标检测精度低,漏检率或误检率高。本文提出了一种新的基于SRGAN和YOLOV3的目标检测模型,称为SR-YOLO。解决了SRGAN网络 对超参数的敏感性和模态崩溃问题。同时,Y…...

外卖app开发流程全解析
外卖app开发是现代餐饮业的一个必备部分。在这个数字化时代,人们更愿意使用手机应用程序来订购食品。因此,为了满足客户需求,餐饮企业需要开发自己的外卖app。 第一步:确定目标受众 在开始外卖app的开发之前,需要确定…...

BUUCTF jarvisoj_level0
小白垃圾做题笔记而已,不建议阅读。。。 这道题感觉主要就是64位程序ebp8 题目中给出了shellcode 我们直接将返回地址覆盖就好。 在main函数中调用了vulnerable_function()函数。 vulnerable函数是一个漏洞函数:(存在缓溢出),我们只需要将…...
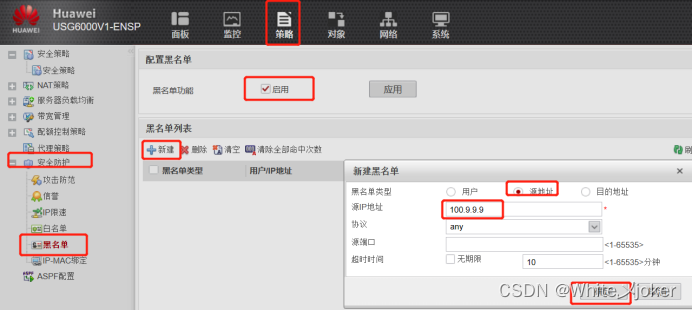
网络安全之入侵检测
目录 网络安全之入侵检测 入侵检测经典理论 经典检测模型 入侵检测作用与原理 意义 异常检测模型(Anomaly Detection) 误用检测模型(Misuse Detection) 经典特征案例 编辑自定义签名 编辑 签名检查过程 检测生命周期…...

元数据管理
1、业务元数据 描述 ”数据”背后的业务含义主题定义:每段 ETL、表背后的归属业务主题。业务描述:每段代码实现的具体业务逻辑。标准指标:类似于 BI 中的语义层、数仓中的一致性事实;将分析中的指标进行规范化。标准维度…...
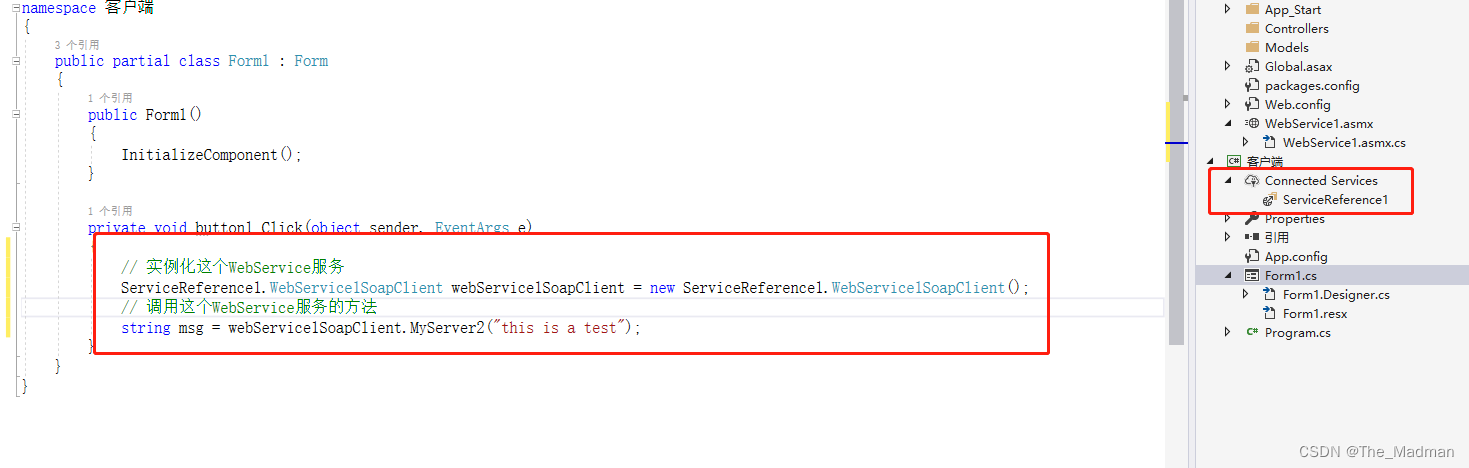
C# WebService的开发以及客户端调用
目录 1、WebService简介 1.1 什么是XML? 1.2 什么是Soap? 1.3 什么是WSDL? 2、WebService与WebApi的区别与优缺点 2.1 WebService与WebApi的区别: 2.2 WebService的优缺点: 2.3 WebApi的优缺点: 3…...

有符号数和无符号数左移和右移
主要是有符号数的左移。 有的说不管符号位,直接左移,所以可以一会正数一会复数 https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/391075092 有的说符号位不动,其他来左移 不明白了。。。。 https://blog.csdn.net/hnjzsyjyj/article/details/119721014 https://…...
Netty小白入门教程
一、概述 1.1 概念 Netty是一个异步的基于事件驱动(即多路复用技术)的网络应用框架,用于快速开发可维护、高性能的网络服务器和客户端。 1.2 地位 Netty在Java网络应用框架中的地位就好比,Spring框架在JavaEE开发中的地位。 以下的框架都使用了Nett…...

【逻辑位移和算数位移】
<< 运算符 && >> 运算符 正数位移 当 x>>n 中 x 为正数时,会将x的所有位右移x位,同时左边高位补0 显而易见,运算结束后,值为1 。 可知右移n位,结果就是 x / 2^n:7 / 2 ^2 1;…...
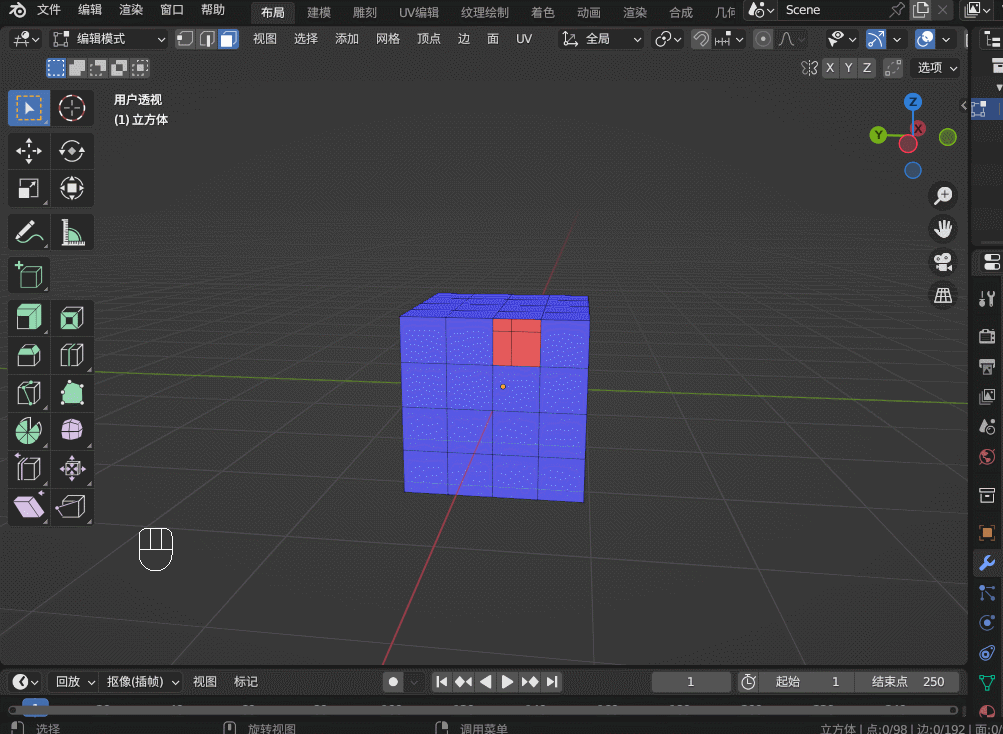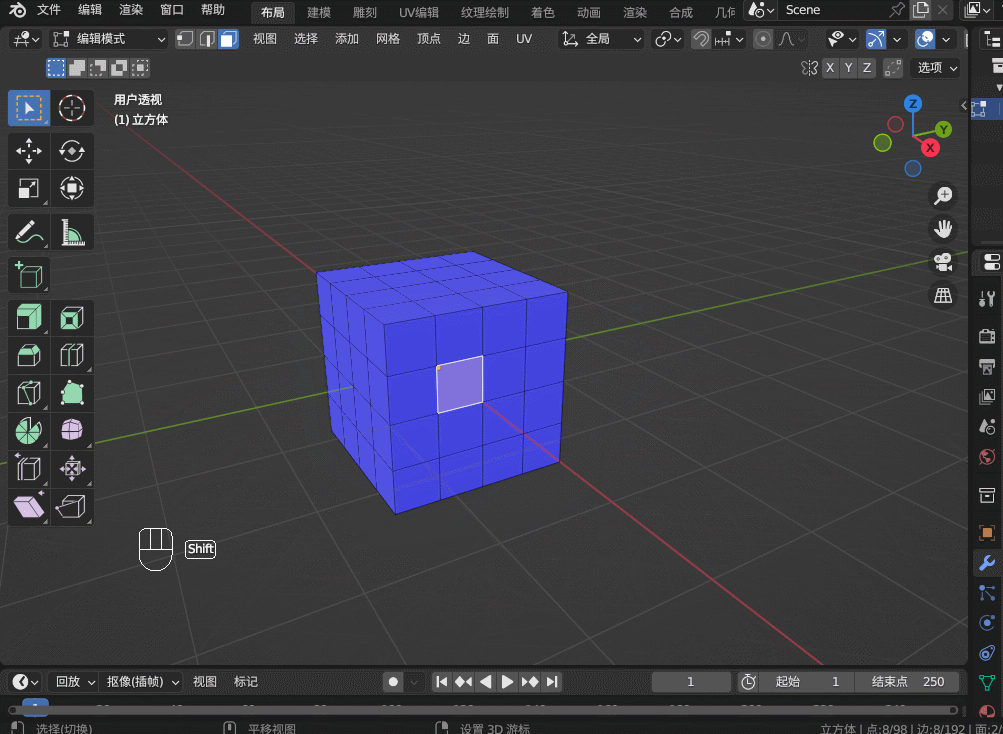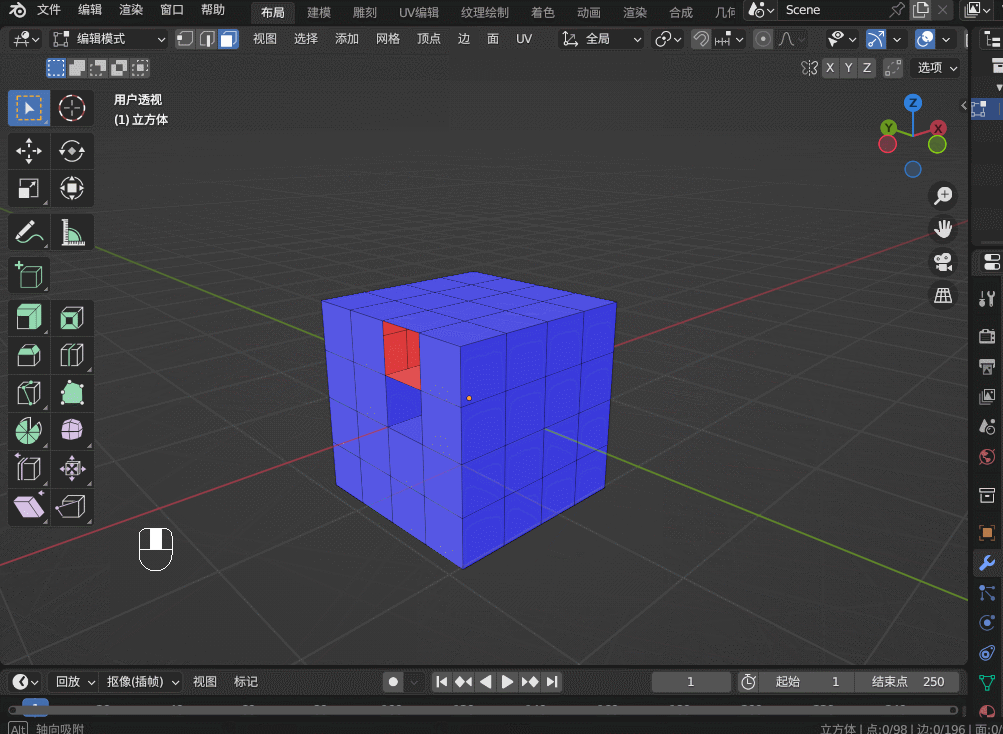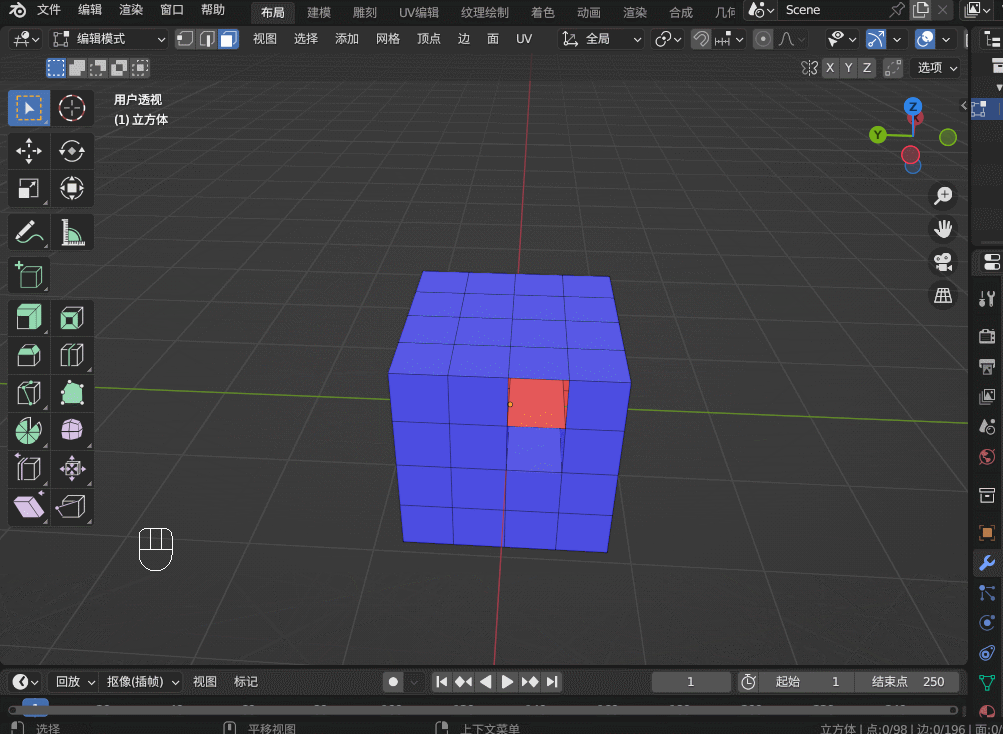
Blender3.5 边的操作
目录 1. 边操作1.1 边的细分 Subdivide1.2 边的滑移 Edge Slide1.3 边的删除1.4 边的溶解 Dissolve1.5 边线倒角 Bevel1.6 循环边 Loop Edges1.7 并排边 Ring Edges1.8 桥接循环边 1. 边操作 1.1 边的细分 Subdivide 在边选择模式,选中一条边,右键&…...

Java与Python、Node.js在人工智能和区块链应用程序开发中的比较
背景 Java、Python和Node.js都是常用的编程语言,它们在不同领域都有广泛的应用。在人工智能和区块链应用程序开发中,这三种语言都具有各自的优势和劣势。 Java的优势 Java在企业级应用中应用广泛,这得益于其跨平台性、安全性和稳定性等特点。在人工智能和区块链应用程序开…...

【计算机是怎么跑起来的】基础:计算机三大原则
【计算机是怎么跑起来的】基础:计算机三大原则 计算机的三个根本性基础1.计算机是执行输入,运算,输出的机器输入,运算,输出 2. 软件是指令和数据的集合指令数据 3. 计算机的处理方式有时与人们的思维习惯不同对计算机来…...
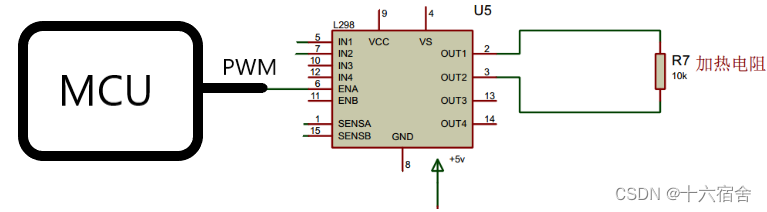
NXP公司LPC21XX+PID实现稳定温度控制
本例使用的是LPC21XX系列芯片提供的PWM功能实现稳定的温度控制。首先我们获得当前环境温度之后,再用设定的温度与当前温度相减,通过PID算法计算出当前输出脉宽,并将其输出到L298N模块中,使加热丝发热,形成闭环…...

【CE实战-生化危机4重置版】实现角色瞬移、飞翔
▒ 目录 ▒ 🛫 导读需求开发环境1️⃣ CE扫描内存,定位坐标地址(加密后的地址)2️⃣ 硬件写入断点,定位真实坐标地址内存写入断点,定位到访问地址分析代码...

强烈建议互联网人转战实体和农业,去了就是降维打击!实体太缺人才了,老板也不缺钱!...
大环境不好,互联网人该何去何从? 一位网友提出了一个新思路:强烈建议互联网同学转战实体、农业这些行业。实体真的太缺人才了,目前大部分实体都留下70后、80后在继续奋斗。其实实体老板很多都不缺钱,经过多年积累&…...
)
云计算——弹性云计算器(ECS)
弹性云服务器:ECS 概述 云计算重构了ICT系统,云计算平台厂商推出使得厂家能够主要关注应用管理而非平台管理的云平台,包含如下主要概念。 ECS(Elastic Cloud Server):即弹性云服务器,是云计算…...
:OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下))
脑机新手指南(八):OpenBCI_GUI:从环境搭建到数据可视化(下)
一、数据处理与分析实战 (一)实时滤波与参数调整 基础滤波操作 60Hz 工频滤波:勾选界面右侧 “60Hz” 复选框,可有效抑制电网干扰(适用于北美地区,欧洲用户可调整为 50Hz)。 平滑处理&…...
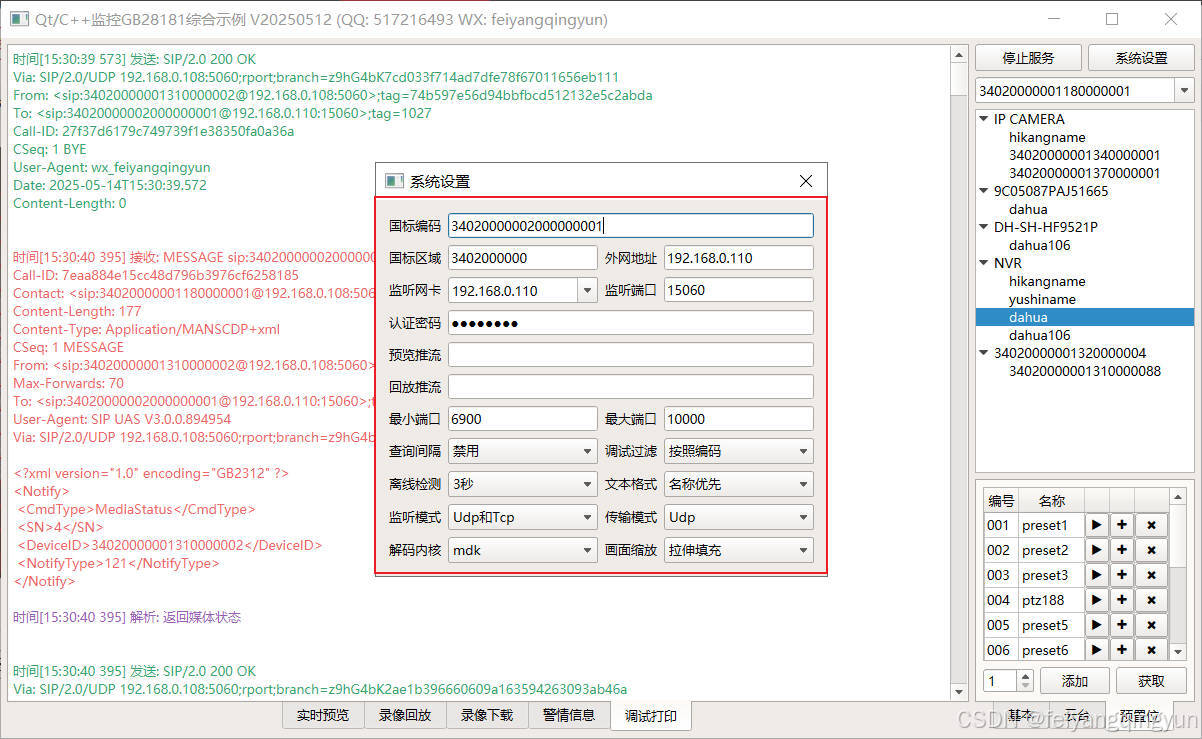
Qt/C++开发监控GB28181系统/取流协议/同时支持udp/tcp被动/tcp主动
一、前言说明 在2011版本的gb28181协议中,拉取视频流只要求udp方式,从2016开始要求新增支持tcp被动和tcp主动两种方式,udp理论上会丢包的,所以实际使用过程可能会出现画面花屏的情况,而tcp肯定不丢包,起码…...

Java 8 Stream API 入门到实践详解
一、告别 for 循环! 传统痛点: Java 8 之前,集合操作离不开冗长的 for 循环和匿名类。例如,过滤列表中的偶数: List<Integer> list Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); List<Integer> evens new ArrayList…...
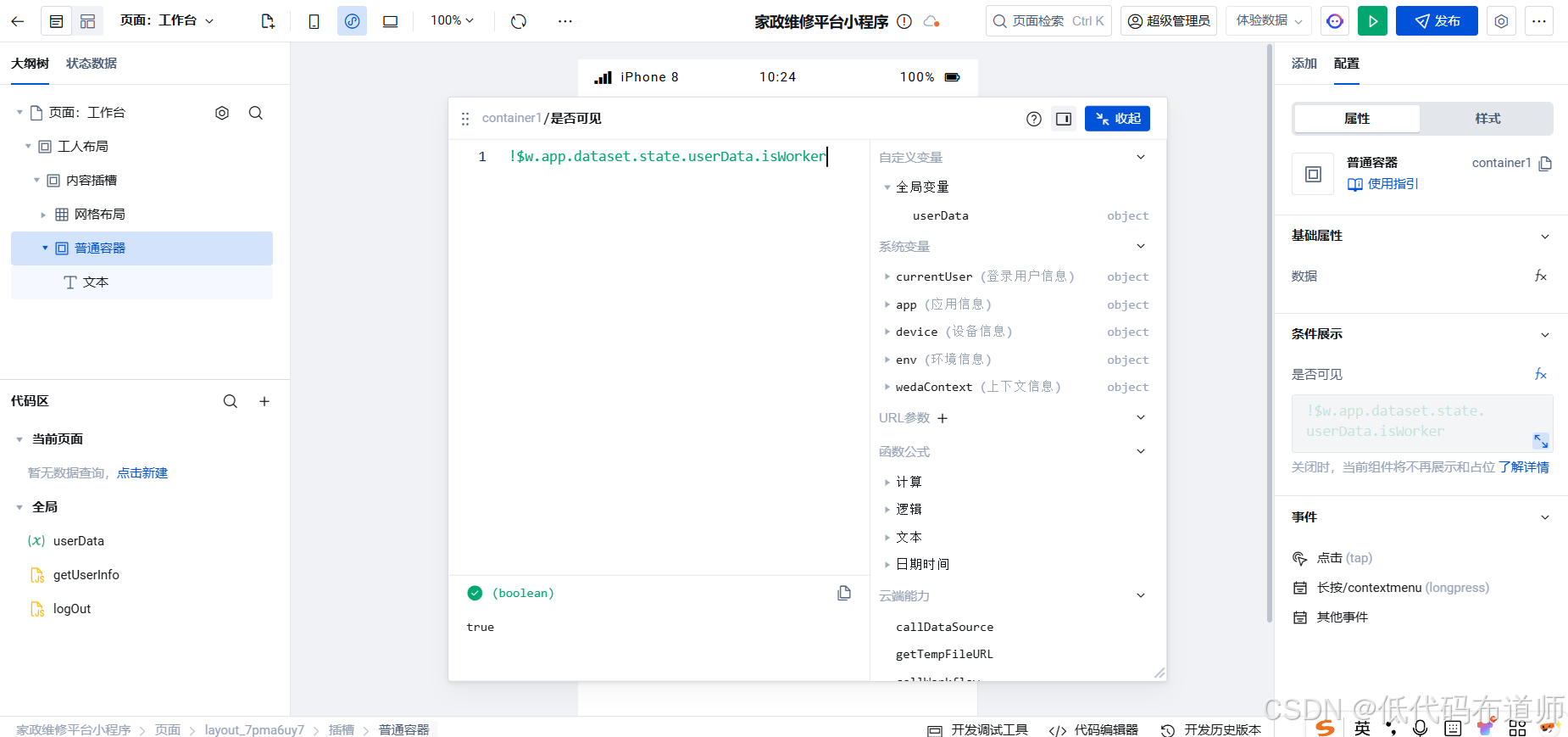
家政维修平台实战20:权限设计
目录 1 获取工人信息2 搭建工人入口3 权限判断总结 目前我们已经搭建好了基础的用户体系,主要是分成几个表,用户表我们是记录用户的基础信息,包括手机、昵称、头像。而工人和员工各有各的表。那么就有一个问题,不同的角色…...
)
postgresql|数据库|只读用户的创建和删除(备忘)
CREATE USER read_only WITH PASSWORD 密码 -- 连接到xxx数据库 \c xxx -- 授予对xxx数据库的只读权限 GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE xxx TO read_only; GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO read_only; GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA public TO read_only; GRANT EXECUTE O…...

Spring Boot+Neo4j知识图谱实战:3步搭建智能关系网络!
一、引言 在数据驱动的背景下,知识图谱凭借其高效的信息组织能力,正逐步成为各行业应用的关键技术。本文聚焦 Spring Boot与Neo4j图数据库的技术结合,探讨知识图谱开发的实现细节,帮助读者掌握该技术栈在实际项目中的落地方法。 …...

EtherNet/IP转DeviceNet协议网关详解
一,设备主要功能 疆鸿智能JH-DVN-EIP本产品是自主研发的一款EtherNet/IP从站功能的通讯网关。该产品主要功能是连接DeviceNet总线和EtherNet/IP网络,本网关连接到EtherNet/IP总线中做为从站使用,连接到DeviceNet总线中做为从站使用。 在自动…...
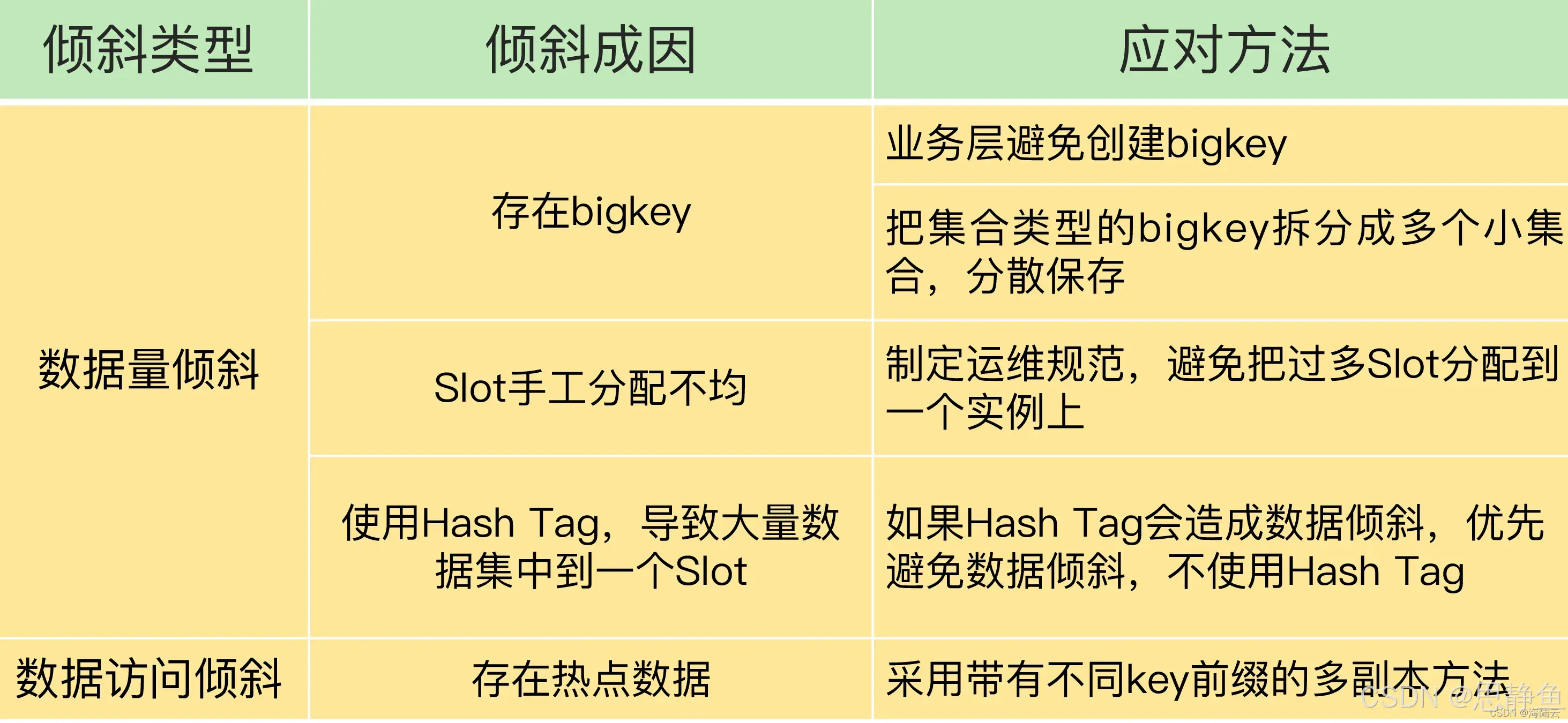
Redis数据倾斜问题解决
Redis 数据倾斜问题解析与解决方案 什么是 Redis 数据倾斜 Redis 数据倾斜指的是在 Redis 集群中,部分节点存储的数据量或访问量远高于其他节点,导致这些节点负载过高,影响整体性能。 数据倾斜的主要表现 部分节点内存使用率远高于其他节…...

MySQL用户和授权
开放MySQL白名单 可以通过iptables-save命令确认对应客户端ip是否可以访问MySQL服务: test: # iptables-save | grep 3306 -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.14.102/32 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 3306 -j ACCEPT -A mp_srv_whitelist -s 172.16.4.16/32 -p tcp -m tcp -…...
