Nacos源码—Nacos集群高可用分析(三)
6.CAP原则与Raft协议
(1)CAP分别指的是什么
一.C指的是一致性Consistency
各个集群节点之间的数据,必须要保证一致。
二.A指的是可用性Availability
在分布式架构中,每个请求都能在合理的时间内获得符合预期的响应。
三.P指的是分区容错性Partition Tolerance
当集群节点间出现网络问题,整个系统依然能正常提供服务。
在CAP原则中,我们首先要保证P即分区容错性。
(2)什么是分区以及容错
分区指的是网络分区。如果在分布式架构中,出现了网络通信问题。比如节点A可以和节点B相互通信,但是不能和节点C、D进行通信。但是节点C、D之间是可以通信的,这种情况下就是出现了网络分区。
容错是指在分布式架构中,集群节点出现分区情况时,整个系统仍然要保持对外提供服务的能力,不能因为网络分区而导致整个系统不能对外提供服务。
在CAP原则下:由于P是首要保证的,所以C、A就不能兼得,必须要舍弃其一。因此需要根据业务来权衡,是更注重可用性、还是更加注重一致性。
(3)为什么不能同时满足CAP原则
首先前提条件是,需要满足P。
情况一:假设在分布式集群中选择使用CP架构,更加注重数据的一致性。这时出现了网络分区,节点A、B与节点C之间网络不互通。如果此时向集群写入一个数据,由于节点A、B能够网络互通,所以节点A、B写入的数据可以相互同步,但是节点C没办法做数据同步。那么在这种情况下,如何才能保证数据的一致性呢?
此时只能将节点C暂时看作不可用的状态,等网络恢复和数据同步好了,节点C才能正常地提供服务。否则下一次用户向集群请求获取数据时,请求到了节点C。但由于网络分区导致节点C并未同步数据,那么本次查询就查不到数据,这样就达不到CP架构的一致性要求了。所以肯定需要舍弃节点C的可用性。
情况二:假设在分布式集群中选择使用AP架构,更加注重数据的可用性。这时出现了网络分区,节点A、B与节点C之间网络不互通。虽然节点C暂时由于网络不通的原因,无法进行数据同步。但是由于集群更加注重服务的可用性,所以节点C还是可以正常提供服务。只是节点C和节点A、B之间的数据略有差异,但不影响节点的正常使用。所以就需要舍弃节点C的数据一致性。
在AP架构中,集群节点间的数据也需要同步。集群节点数据的同步一般都是通过一些异步任务来保证数据的最终一致性,只是同步时效没有那么及时。
在CP架构中,可以通过Raft协议实现数据一致性。Raft协议就是在分布式架构下,多节点保证数据一致性的协议。
(4)Raft协议定义节点的三种状态
Raft协议对集群节点定义了三种状态:
一.Follower追随者
这是默认的状态,所有的集群节点一开始都是Follower状态。
二.Candidate候选者
当某集群节点开始发起投票选举Leader时,首先会投给自己一票,这时就会从Follower状态变成Candidate状态。
三.Leader领导者
当某集群节点获得了大多数集群节点的投票,那么就会变成Leader状态。
(5)Raft协议的数据同步流程
一.Raft协议是如何处理数据写入请求
在Raft协议中,只有Leader节点才会处理客户端数据的写入请求。如果非Leader节点收到了写入请求,会转发到Leader节点上进行处理。
数据的写入一共有两个状态:uncommit和commit。这个两个状态对应于两阶段提交,可以保证数据正确写入成功。
当Leader节点接收到一个数据写入请求时:首先会在自身的节点进行数据处理,然后马上同步给集群的其他节点,此时Leader节点的这个数据的状态是uncommit状态。只有当半数以上的其他节点写入成功,Leader节点才会把数据写入成功。当Leader节点最终把数据写入成功后,会通知其他节点进行commit,此时Leader节点的这个数据的状态是commit状态。
二.非Leader节点写入失败如何处理
由于Leader节点只需要有半数以上的节点写入成功即可,所以如果有部分非Leader节点没有写入或写入失败,该如何处理?
Raft协议中的Leader节点和Follower节点会有心跳机制。在心跳传输过程中,Leader节点会把最新的数据传给其他Follower节点,以保证Follower节点中的数据和Leader节点的数据是一致的。
需要注意的是:当Follower节点没有在指定时间内接收到Leader节点发送过来的心跳包,Follower节点就会认为Leader节点挂掉了,此时Follower节点会把自身状态修改为Candidate并且重新发起投票。
https://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft/#homeLet's say we have a single node system.
For this example, you can think of our node as a database server that stores a single value.
We also have a client that can send a value to the server.
Coming to agreement, or consensus, on that value is easy with one node.
But how do we come to consensus if we have multiple nodes?
That's the problem of distributed consensus.
Raft is a protocol for implementing distributed consensus.
Let's look at a high level overview of how it works.A node can be in 1 of 3 states: the Follower state, the Candidate state, or the Leader state.
All our nodes start in the follower state.
If followers don't hear from a leader then they can become a candidate.
The candidate then requests votes from other nodes.
Nodes will reply with their vote.
The candidate becomes the leader if it gets votes from a majority of nodes.
This process is called Leader Election.All changes to the system now go through the leader.
Each change is added as an entry in the node's log.
This log entry is currently uncommitted so it won't update the node's value.
To commit the entry the node first replicates it to the follower nodes...
then the leader waits until a majority of nodes have written the entry.
The entry is now committed on the leader node and the node state is "5".
The leader then notifies the followers that the entry is committed.
The cluster has now come to consensus about the system state.
This process is called Log Replication.(6)Raft协议的Leader选举流程
Leader是如何选举出来的?
一.选举超时时间和选举步骤
假设使用了Raft协议的集群有3个节点:那么一开始,三个节点都会在倒计时中进行等待,此时会有一个称为Election Timeout的随机休眠时间或选举超时时间,该选举超时时间会被随机分配到150ms到300ms之间。
等待超过选举超时时间过后,节点会马上进行投票,投票分为如下几个步骤:
步骤一:先投给自己一票,并且把自己节点状态修改为Candidate
步骤二:向其他集群节点进行投票
步骤三:获取投票结果,如果过半节点投自己,则把状态修改为Leader
一旦Leader节点选举出来,其他节点的数据都要以Leader节点的为准。因此Leader节点会马上通过心跳机制,同步数据给其他节点。
https://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft/#electionIn Raft there are two timeout settings which control elections.First is the election timeout.
The election timeout is the amount of time a follower waits until becoming a candidate.
The election timeout is randomized to be between 150ms and 300ms.
After the election timeout the follower becomes a candidate and starts a new election term...
...votes for itself...
...and sends out Request Vote messages to other nodes.
If the receiving node hasn't voted yet in this term then it votes for the candidate...
...and the node resets its election timeout.
Once a candidate has a majority of votes it becomes leader.
The leader begins sending out Append Entries messages to its followers.Second is the heartbeat timeout.
These messages are sent in intervals specified by the heartbeat timeout.
Followers then respond to each Append Entries message.This election term will continue until a follower stops receiving heartbeats and becomes a candidate.
Let's stop the leader and watch a re-election happen.
Node B is now leader of term 2.
Requiring a majority of votes guarantees that only one leader can be elected per term.If two nodes become candidates at the same time then a split vote can occur.
Let's take a look at a split vote example...
Two nodes both start an election for the same term...
...and each reaches a single follower node before the other.
Now each candidate has 2 votes and can receive no more for this term.
The nodes will wait for a new election and try again.
Node A received a majority of votes in term 5 so it becomes leader.二.不同的选举情况分析
如果集群启动时,节点C率先等待超过了选举超时时间。那么节点C会马上发起投票,并改变它自己的状态变为Candidate。等节点C获取超过半数以上的投票,那么它就会成为Leader节点。
如果在集群运行中,Leader节点突然下线。那么这时候其他的Follower节点会重新进行Leader选举。假设原本的Leader节点是B,但由于B突然下线,节点A、C会重新发起投票,最终节点C成为新的Leader节点。并且重新选举Leader后,Trem(任期)会进行递增。Term可理解为Leader的选举次数,次数越大说明数据肯定是最全的。
如果有四个节点,其中有两个Candidate节点都有2票,没有过半。在这种情况下,则会让全部节点重新进行随机睡眠,重新进行Leader选举。
(7)Raft协议如何解决脑裂问题
在Raft协议的一些情况下,可能会产生多个Leader节点。那么多个Leader节点是如何产生的?多个Leader会不会有冲突?
如果在一个集群下,出现了两个Leader节点,那么这就是脑裂问题。假设集群节点有5个,节点B是Leader,但由于发生了网络分区问题。节点A、B可以相互通信,可是节点C、D、E不能和Leader进行通信。那么节点C、D、E将会重新进行Leader选举,最终节点C也成为了Leader。此时,在原本一个集群下,就会产生两个Leader节点。
此时,如果有客户端来进行写数据:
第一个客户端请求到了节点B,由于节点B所在分区网络只有一个Follower节点,达不到半数以上要求,所以节点B的数据一直处于uncommit状态,数据也不会写入成功。
第二个客户端请求到了节点C,由于节点C所在分区网络有两个Follower节点,有半数以上支持,所以节点C的数据是能够写入成功的。
假如网络突然恢复,5个节点都可以相互通信,那么怎么处理两个Leader。这时两个Leader会相互发送心跳。节点B会发现节点C的Term比自己大,所以会认节点C为Leader并自动转换为Follower节点。
https://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft/#replicationOnce we have a leader elected we need to replicate all changes to our system to all nodes.
This is done by using the same Append Entries message that was used for heartbeats.
Let's walk through the process.First a client sends a change to the leader. Set value by "5".
The change is appended to the leader's log...
...then the change is sent to the followers on the next heartbeat.
An entry is committed once a majority of followers acknowledge it...
...and a response is sent to the client.Now let's send a command to increment the value by "2".
Our system value is now updated to "7".
Raft can even stay consistent in the face of network partitions.Let's add a partition to separate A & B from C, D & E.
Because of our partition we now have two leaders in different terms.
Let's add another client and try to update both leaders.
One client will try to set the value of node B to "3".
Node B cannot replicate to a majority so its log entry stays uncommitted.
The other client will try to set the value of node C to "8".
This will succeed because it can replicate to a majority.Now let's heal the network partition.
Node B will see the higher election term and step down.
Both nodes A & B will roll back their uncommitted entries and match the new leader's log.
Our log is now consistent across our cluster.(8)总结
Raft协议相关论文:
https://raft.github.io/raft.pdfRaft协议详细流程演示:
https://thesecretlivesofdata.com/raft/Nacos既支持AP架构,也支持CP架构。前面介绍的集群源码,是属于AP架构的。在源码中可以看到很多异步任务,说明是比较看重可用性。由于是使用定时任务,那么数据会在某些特定时间出现不一致的情况,但最终还是会保证一致性。
7.Nacos实现的Raft协议是如何写入数据的
(1)Nacos 1.4.1版本实现Raft协议说明
Nacos 1.4.1版本并没有完全按照标准的Raft协议所定义的流程来实现,所以该版本的实现中会存在一些问题。并且Nacos 1.4.1版本,已标注后期会删除这套实现。
Nacos 2.x版本会采用JRaft来实现Raft协议,JRaft就是完全按照Raft协议定义的流程来实现的。所以早期版本实现的Raft协议,没必要仔细研究,大概知道流程即可。
(2)Nacos实现的Raft协议是如何写入数据的
在Raft协议里只有Leader节点才会操作数据,并且会有两阶段提交的动作,所以可以通过服务实例注册的处理为入口进行分析。
在进行服务实例注册时:会通过一个key来选择调用不同ConsistencyService实现类的put()方法。而这个key中会包含一个很关键的属性叫做ephemeral,ephemeral默认是true,所以最终会执行AP架构下的服务注册。我们可以在yml配置文件中,把ephemeral属性设置为false,那么在服务实例注册时,就会执行CP架构下的服务注册。不过,注册中心一般很少使用CP架构。
如果执行的是CP架构下的服务注册,那么最终会调用RaftConsistencyServiceImpl的put()方法,从而触发调用Raft协议的核心方法:RaftCore的signalPublish()方法。
@Component
public class ServiceManager implements RecordListener<Service> {...//Add instance to service. 添加服务实例public void addInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean ephemeral, Instance... ips) throws NacosException {//构建要注册的服务实例对应的服务的keyString key = KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName, ephemeral);//根据命名空间以及服务名获取要注册的服务实例对应的服务Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);//使用synchronized锁住要注册的服务实例对应的服务synchronized (service) {//由于一个服务可能存在多个服务实例,所以需要根据当前注册请求的服务实例ips,获取对应服务的最新服务实例列表List<Instance> instanceList = addIpAddresses(service, ephemeral, ips);//Instances实现了用于在Nacos集群进行网络传输的Record接口Instances instances = new Instances();instances.setInstanceList(instanceList);//执行DelegateConsistencyServiceImpl的put()方法consistencyService.put(key, instances);}}...
}@DependsOn("ProtocolManager")
@Service("consistencyDelegate")
public class DelegateConsistencyServiceImpl implements ConsistencyService { private final PersistentConsistencyServiceDelegateImpl persistentConsistencyService;private final EphemeralConsistencyService ephemeralConsistencyService;public DelegateConsistencyServiceImpl(PersistentConsistencyServiceDelegateImpl persistentConsistencyService, EphemeralConsistencyService ephemeralConsistencyService) {this.persistentConsistencyService = persistentConsistencyService;this.ephemeralConsistencyService = ephemeralConsistencyService;}@Overridepublic void put(String key, Record value) throws NacosException {//如果是临时实例,则调用DistroConsistencyServiceImpl.put()方法//如果是持久化实例,则调用PersistentConsistencyServiceDelegateImpl.put()方法mapConsistencyService(key).put(key, value);}...private ConsistencyService mapConsistencyService(String key) {//根据不同的key选择不同的ConsistencyServicereturn KeyBuilder.matchEphemeralKey(key) ? ephemeralConsistencyService : persistentConsistencyService;}
}@Component("persistentConsistencyServiceDelegate")
public class PersistentConsistencyServiceDelegateImpl implements PersistentConsistencyService {private final RaftConsistencyServiceImpl oldPersistentConsistencyService;private final BasePersistentServiceProcessor newPersistentConsistencyService;private volatile boolean switchNewPersistentService = false;...@Overridepublic void put(String key, Record value) throws NacosException {switchOne().put(key, value);}private PersistentConsistencyService switchOne() {return switchNewPersistentService ? newPersistentConsistencyService : oldPersistentConsistencyService;}...
}//Use simplified Raft protocol to maintain the consistency status of Nacos cluster.
@Deprecated
@DependsOn("ProtocolManager")
@Service
public class RaftConsistencyServiceImpl implements PersistentConsistencyService {private final RaftCore raftCore;...@Overridepublic void put(String key, Record value) throws NacosException {checkIsStopWork();try {//Raft协议的核心实现raftCore.signalPublish(key, value);} catch (Exception e) {Loggers.RAFT.error("Raft put failed.", e);throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR, "Raft put failed, key:" + key + ", value:" + value, e);}}...
}RaftCore的signalPublish()方法中的逻辑大概分成三部分:
第一部分:方法一开始就会判断自身节点是不是Leader节点,如果不是则会通过HTTP方式转发给Leader节点进行处理。
第二部分:RaftCore的signalPublish()方法中有一行核心代码onPublish(),即如果是Leader节点则会执行RaftCore的onPublish()方法来处理数据。该方法会先把数据写入到本地文件,然后马上同步给内存注册表。
RaftStore的write(datum)方法会把服务实例信息持久化到本地文件,即把Instance服务实例信息以JSON格式持久化到Nacos服务端目录下,并且存储的文件是以命名空间##分组@@服务名来命名的。而持久化的服务实例信息,在下一次服务端重启时会重新加载到内存注册表中。
服务实例信息持久化后,会通过NotifyCenter发布ValueChangeEvent事件更新注册表。RaftCore的init()方法会向NotifyCenter注册一个订阅者PersistentNotifier。所以NotifyCenter发布ValueChangeEvent事件时,就会被PersistentNotifier的onEvent()方法监听到,然后执行PersistentNotifier的notify()方法,最后会执行Service的onChange()方法来更新内存注册表。
第三部分:主要就是遍历集群节点,向每个节点发起通知请求来进行数据同步,这里会使用CountDownLatch闭锁来实现控制集群半数节点同步成功。
在创建CountDownLatch闭锁时,会获取集群半数的数量来创建闭锁。每当有一个集群节点同步成功,就对CountDownLatch闭锁进行减1。最后使用闭锁的await()方法进行等待,直到闭锁减完或超时才继续执行。这样通过CountDownLatch并发工具类就能实现需要过半节点成功的功能。
@Deprecated
@DependsOn("ProtocolManager")
@Component
public class RaftCore implements Closeable {private final RaftProxy raftProxy;private final RaftStore raftStore;public final PersistentNotifier notifier;...@PostConstructpublic void init() throws Exception {...//注册订阅者NotifyCenter.registerSubscriber(notifier);...}...//Signal publish new record. If not leader, signal to leader. If leader, try to commit publish.public void signalPublish(String key, Record value) throws Exception {if (stopWork) {throw new IllegalStateException("old raft protocol already stop work");}//第一部分:判断自己是不是Leader节点if (!isLeader()) {ObjectNode params = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode();params.put("key", key);params.replace("value", JacksonUtils.transferToJsonNode(value));Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<>(1);parameters.put("key", key);//获取Leader节点final RaftPeer leader = getLeader();//将写请求转发给Leader节点raftProxy.proxyPostLarge(leader.ip, API_PUB, params.toString(), parameters);return;}OPERATE_LOCK.lock();try {final long start = System.currentTimeMillis();final Datum datum = new Datum();datum.key = key;datum.value = value;if (getDatum(key) == null) {datum.timestamp.set(1L);} else {datum.timestamp.set(getDatum(key).timestamp.incrementAndGet());}ObjectNode json = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode();json.replace("datum", JacksonUtils.transferToJsonNode(datum));json.replace("source", JacksonUtils.transferToJsonNode(peers.local()));//第二部分:Leader节点会执行到这里进行数据处理,把服务实例信息写入磁盘以及内存onPublish(datum, peers.local());//第三部分:final String content = json.toString();//通过闭锁来控制半数以上节点,peers.majorityCount()就是获取集群半数以上的节点数量final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(peers.majorityCount());//同步给其他节点for (final String server : peers.allServersIncludeMyself()) {if (isLeader(server)) {latch.countDown();continue;}final String url = buildUrl(server, API_ON_PUB);//通过HTTP方式通知其他节点HttpClient.asyncHttpPostLarge(url, Arrays.asList("key", key), content, new Callback<String>() {@Overridepublic void onReceive(RestResult<String> result) {if (!result.ok()) {Loggers.RAFT.warn("[RAFT] failed to publish data to peer, datumId={}, peer={}, http code={}", datum.key, server, result.getCode());return;}//某个节点成功,闭锁-1latch.countDown();}@Overridepublic void onError(Throwable throwable) {Loggers.RAFT.error("[RAFT] failed to publish data to peer", throwable);}@Overridepublic void onCancel() {}});}//通过闭锁的await()方法来等待半数集群节点同步成功if (!latch.await(UtilsAndCommons.RAFT_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {//only majority servers return success can we consider this update successLoggers.RAFT.error("data publish failed, caused failed to notify majority, key={}", key);throw new IllegalStateException("data publish failed, caused failed to notify majority, key=" + key);}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();Loggers.RAFT.info("signalPublish cost {} ms, key: {}", (end - start), key);} finally {OPERATE_LOCK.unlock();}}...//Do publish. If leader, commit publish to store. If not leader, stop publish because should signal to leader.public void onPublish(Datum datum, RaftPeer source) throws Exception {if (stopWork) {throw new IllegalStateException("old raft protocol already stop work");}RaftPeer local = peers.local();if (datum.value == null) {Loggers.RAFT.warn("received empty datum");throw new IllegalStateException("received empty datum");}if (!peers.isLeader(source.ip)) {Loggers.RAFT.warn("peer {} tried to publish data but wasn't leader, leader: {}", JacksonUtils.toJson(source), JacksonUtils.toJson(getLeader()));throw new IllegalStateException("peer(" + source.ip + ") tried to publish " + "data but wasn't leader");}if (source.term.get() < local.term.get()) {Loggers.RAFT.warn("out of date publish, pub-term: {}, cur-term: {}", JacksonUtils.toJson(source), JacksonUtils.toJson(local));throw new IllegalStateException("out of date publish, pub-term:" + source.term.get() + ", cur-term: " + local.term.get());}local.resetLeaderDue();//if data should be persisted, usually this is true:if (KeyBuilder.matchPersistentKey(datum.key)) {//先把数据写到本地文件中raftStore.write(datum);}//同步缓存datums.put(datum.key, datum);if (isLeader()) {local.term.addAndGet(PUBLISH_TERM_INCREASE_COUNT);} else {if (local.term.get() + PUBLISH_TERM_INCREASE_COUNT > source.term.get()) {//set leader term:getLeader().term.set(source.term.get());local.term.set(getLeader().term.get());} else {local.term.addAndGet(PUBLISH_TERM_INCREASE_COUNT);}}raftStore.updateTerm(local.term.get());//通过发布ValueChangeEvent事件来同步内存注册表NotifyCenter.publishEvent(ValueChangeEvent.builder().key(datum.key).action(DataOperation.CHANGE).build());Loggers.RAFT.info("data added/updated, key={}, term={}", datum.key, local.term);}
}@Deprecated
@Component
public class RaftStore implements Closeable {...//Write datum to cache file.public synchronized void write(final Datum datum) throws Exception {String namespaceId = KeyBuilder.getNamespace(datum.key);File cacheFile = new File(cacheFileName(namespaceId, datum.key));if (!cacheFile.exists() && !cacheFile.getParentFile().mkdirs() && !cacheFile.createNewFile()) {MetricsMonitor.getDiskException().increment();throw new IllegalStateException("can not make cache file: " + cacheFile.getName());}ByteBuffer data;data = ByteBuffer.wrap(JacksonUtils.toJson(datum).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));try (FileChannel fc = new FileOutputStream(cacheFile, false).getChannel()) {fc.write(data, data.position());fc.force(true);} catch (Exception e) {MetricsMonitor.getDiskException().increment();throw e;}//remove old format file:if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(namespaceId)) {if (datum.key.contains(Constants.DEFAULT_GROUP + Constants.SERVICE_INFO_SPLITER)) {String oldDatumKey = datum.key.replace(Constants.DEFAULT_GROUP + Constants.SERVICE_INFO_SPLITER, StringUtils.EMPTY);cacheFile = new File(cacheFileName(namespaceId, oldDatumKey));if (cacheFile.exists() && !cacheFile.delete()) {Loggers.RAFT.error("[RAFT-DELETE] failed to delete old format datum: {}, value: {}", datum.key, datum.value);throw new IllegalStateException("failed to delete old format datum: " + datum.key);}}}}...
}//事件发布中心:事件发布机制的实现
public class NotifyCenter {...//注册订阅者public static <T> void registerSubscriber(final Subscriber consumer) {...addSubscriber(consumer, subscribeType);}private static void addSubscriber(final Subscriber consumer, Class<? extends Event> subscribeType) {...EventPublisher publisher = INSTANCE.publisherMap.get(topic);//执行DefaultPublisher.addSubscriber()方法publisher.addSubscriber(consumer);}//发布事件public static boolean publishEvent(final Event event) {return publishEvent(event.getClass(), event);}private static boolean publishEvent(final Class<? extends Event> eventType, final Event event) {...EventPublisher publisher = INSTANCE.publisherMap.get(topic);if (publisher != null) {//执行DefaultPublisher.publish()方法return publisher.publish(event);}...}...
}public class DefaultPublisher extends Thread implements EventPublisher {protected final ConcurrentHashSet<Subscriber> subscribers = new ConcurrentHashSet<Subscriber>();...@Overridepublic void addSubscriber(Subscriber subscriber) {subscribers.add(subscriber);}@Overridepublic boolean publish(Event event) {... receiveEvent(event);...}void receiveEvent(Event event) {...for (Subscriber subscriber : subscribers) {...notifySubscriber(subscriber, event);}}@Overridepublic void notifySubscriber(final Subscriber subscriber, final Event event) {final Runnable job = new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {subscriber.onEvent(event);}};final Executor executor = subscriber.executor();if (executor != null) {executor.execute(job);} else {try {job.run();} catch (Throwable e) {LOGGER.error("Event callback exception : {}", e);}}}...
}(3)RaftCore的signalPublish()方法总结
首先会判断自身节点是不是Leader,如果不是,则会转发给Leader处理。如果是Leader,则会对数据进行处理,先是写入到本地文件,然后同步到内存注册表,最后会通知其他Follower节点进行数据同步。
可见Nacos 1.4.1版本在数据的写入实现上,并没有两阶段提交的处理。而是Leader自身处理数据完成后,直接就去同步给其他集群节点。哪怕集群节点同步失败或没有过半节点成功,Leader的数据也不会回滚而只抛出异常。所以,Nacos 1.4.1版本只是实现了Raft的简化版,后续也会被废弃掉的。
文章转载自:东阳马生架构
原文链接:Nacos源码—4.Nacos集群高可用分析二 - 东阳马生架构 - 博客园
体验地址:JNPF快速开发平台
相关文章:
)
Nacos源码—Nacos集群高可用分析(三)
6.CAP原则与Raft协议 (1)CAP分别指的是什么 一.C指的是一致性Consistency 各个集群节点之间的数据,必须要保证一致。 二.A指的是可用性Availability 在分布式架构中,每个请求都能在合理的时间内获得符合预期的响应。 三.P指的是分区容错性Partition To…...

【C语言】程序的预处理,#define详解
一、预定义符号 二、#define 1.#define定义标识符 #define + 自定义名称 + 代替的内容 例: #define MAX 100 #define CASE break;case #define CASE break;caseint main() {int n 0;switch (n){case 1:CASE 2:CASE 3:CASE 4:}return …...
NVM完全指南:安装、配置与最佳实践
发布于 2025年5月7日 • 阅读时间:10分钟 💡 TL;DR: 本文详细介绍了如何完整卸载旧版Node.js,安装NVM,配置阿里云镜像源,以及设置node_global与node_cache目录,打造高效Node.js开发环境。 📋 目…...

(二)毛子整洁架构(CQRS/Dapper/领域事件处理器/垂直切片)
文章目录 项目地址一、Application 层1.1 定义CQRS的接口以及其他服务1. Command2. IQuery查询3. 当前时间服务接口4. 邮件发送服务接口 1.2 ReserveBooking Command1. 处理传入的参数2. ReserveBookingCommandHandler3. BookingReservedDomainEvent 1.3 Query使用Sql查询1. 创…...

基于大核感知与非膨胀卷积的SPPF改进—融合UniRepLK的YOLOv8目标检测创新架构
在当前目标检测领域中,YOLO系列模型因其优异的速度-精度平衡能力而被广泛部署于工业界与科研场景。YOLOv8作为该系列的最新版本,在主干网络与特征金字塔结构上进行了多项优化,进一步提升了其实时性与鲁棒性。然而,其核心组件—SPPF(Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast)模块仍采用…...

基于SpringBoot网上书店的设计与实现
pom.xml配置文件 1. 项目基本信息(没什么作用) <groupId>com.spring</groupId> <!--项目组织标识,通常对应包结构--> <artifactId>boot</artifactId> <!--项目唯一标识--> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</ve…...

小程序多线程实战
在小程序开发中,由于微信小程序的运行环境限制,原生并不支持传统意义上的多线程编程,但可以通过以下两种核心方案实现类似多线程的并发处理效果,尤其在处理复杂计算、避免主线程阻塞时非常关键: 一、官方方案ÿ…...

如何修改MySQL数据库密码
文章目录 一、忘记数据库密码该如何修改1. 关闭数据库的服务2.跳过安全检查3. 重置密码4.查询用户是否存在5.退出验证密码是否正确 二、未忘记密码该如何修改密码1.直接修改密码2.登录mysql 时间久了,忘记数据库密码了。。。。。 一、忘记数据库密码该如何修改 1. …...

【Python】mat npy npz 文件格式
1、简介 MAT 文件和 NP(.npy 或 .npz)文件是两种不同的格式,用于存储数组数据。它们分别由 MATLAB 和 NumPy 开发,主要用于各自环境中的数据存储和交换。以下是这两种格式的主要区别: 1.1 格式和用途 MAT 文件&…...
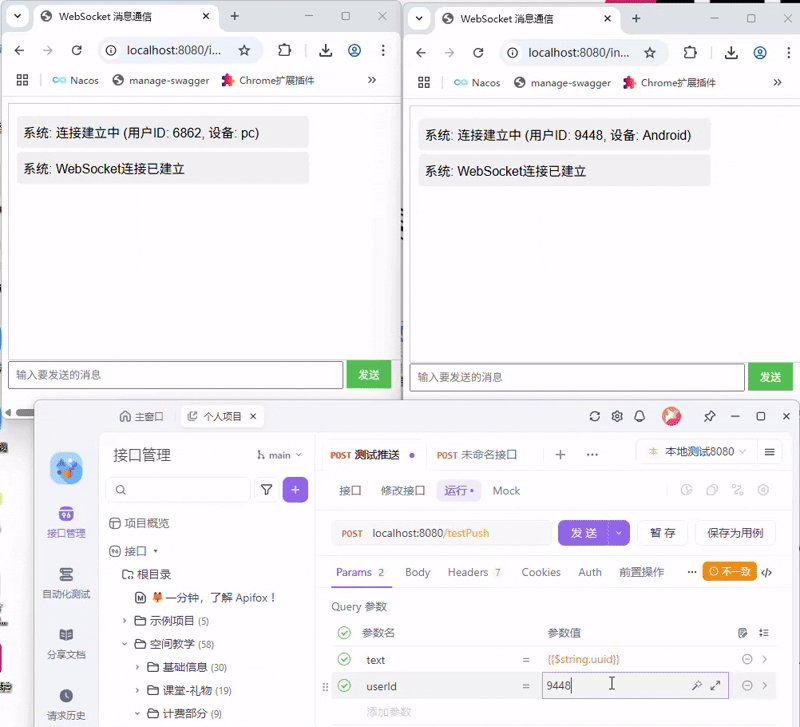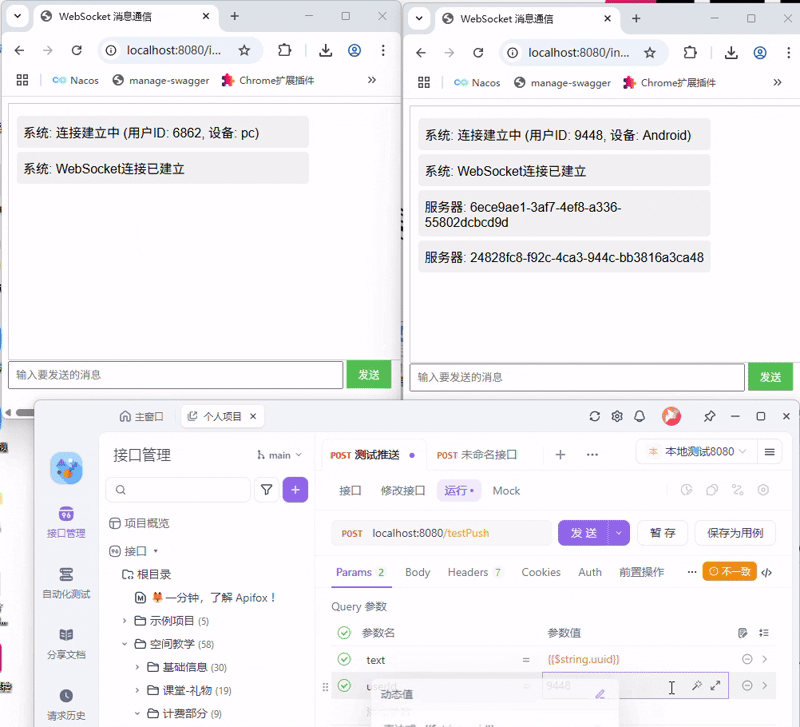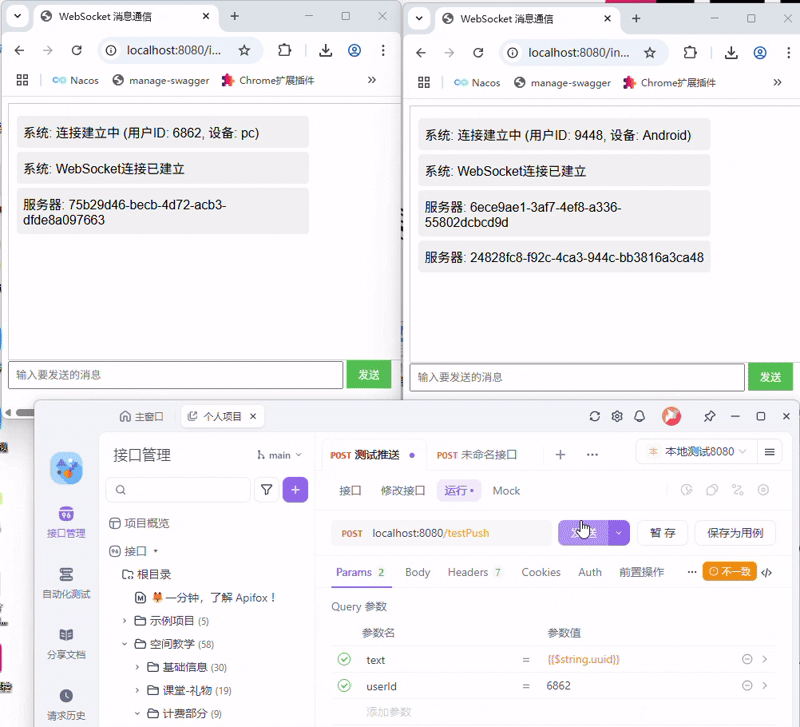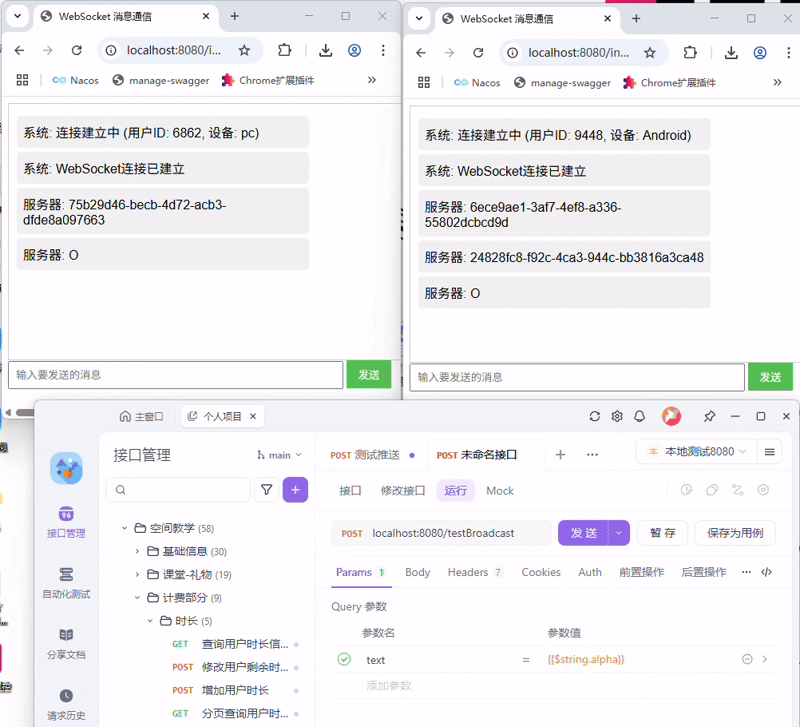
SpringBoot快速入门WebSocket(JSR-356附Demo源码)
现在我想写一篇Java快速入门WebSocket,就使用 JSR-356的websocket,我想分以下几点, 1. websocket介绍, 1.1 介绍 什么是WebSocket? WebSocket 是一种基于 TCP 的全双工通信协议,允许客户端和服务器在单个长连接上实…...

JDBC执行sql过程
1. 加载数据库驱动 JDBC 通过 驱动(Driver) 实现与不同数据库的通信。驱动需提前加载到 JVM: 手动加载(JDBC 4.0 前): Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // MySQL 驱…...

VNC windows连接ubuntu桌面
✅ 步骤 1:安装 VNC 服务器 首先,我们需要在 Winux 系统上安装一个 VNC 服务器。这里我们使用 tigervnc 作为例子,它是一个常用的 VNC 服务器软件。 打开终端并更新你的软件包: sudo apt update安装 tigervnc 服务器:…...

CSS中的@import指令
一、什么是import指令? import 是CSS提供的一种引入外部样式表的方式,允许开发者在CSS文件中引入其他CSS文件,或者在HTML的<style>标签中引入外部样式。与常见的<link>标签相比,import 提供了一种更“CSS原生”的样式…...

【安装配置教程】ubuntu安装配置Kodbox
目录 一、引言 二、环境配置 1. 服务器配置 2. 必备组件 三、安装基础环境 1. 安装 PHP 8.1 及扩展 2. 安装 MySQL 数据库 3.安装 Redis(可选,提升缓存性能) 4. 配置nginx文件 4.1. 创建 Kodbox 站点目录 4.2. 编写 Ng…...

【软件设计师:数据库】13.数据库控制与安全
一、数据库语言SQL SQL是结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language)的缩写,其功能包括数据查询、数据操纵、数据定义和数据控制四个部分。 SQL 语言简洁、方便实用、功能齐全,已成为目前应用最广的关系数据库语言。SQL既是自含式语言(联机交互),又是嵌入式语言(宿主语…...

LabVIEW车牌自动识别系统
在智能交通快速发展的时代,车牌自动识别系统成为提升交通管理效率的关键技术。本案例详细介绍了基于 LabVIEW 平台,搭配大恒品牌相机构建的车牌自动识别系统,该系统在多个场景中发挥着重要作用,为交通管理提供了高效、精准的解决方…...

el-menu 折叠后小箭头不会消失
官方示例 <template><el-radio-group v-model"isCollapse" style"margin-bottom: 20px"><el-radio-button :value"false">expand</el-radio-button><el-radio-button :value"true">collapse</el-ra…...
c语言第一个小游戏:贪吃蛇小游戏01
hello啊大家好 今天我们用一个小游戏来增强我们的c语言! 那就是贪吃蛇 为什么要做一个贪吃蛇小游戏呢? 因为这个小游戏所涉及到的知识有c语言的指针、数组、链表、函数等等可以让我们通过这个游戏来巩固c语言,进一步认识c语言。 一.我们先…...

6. HTML 锚点链接与页面导航
在开发长页面或文档类网站时,锚点链接(Anchor Links)是一个非常实用的功能。通过学习 HTML 锚点技术,将会掌握如何在同一页面内实现快速跳转,以及如何优化长页面的导航体验。以下是基于给定素材的学习总结和实践心得 一、什么是锚点链接? 锚点链接(也称为页面内链接)允…...

[项目总结] 抽奖系统项目技术应用总结
🌸个人主页:https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80050796?spm1000.2115.3001.5343 🏵️热门专栏: 🧊 Java基本语法(97平均质量分)https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80050796/category_12615970.html?spm1001.2014.3001.5482 🍕 Collection与…...

Axios替代品Alova
介绍alova | Alova.JS Multipart 实体请求 | Axios中文文档 | Axios中文网 1. 极致的轻量与性能 Tree-shaking优化:仅打包使用到的功能模块 零依赖:基础包仅 4KB(Axios 12KB) 2. 智能请求管理(开箱即用࿰…...

Python OpenCV性能优化与部署实战指南
在计算机视觉领域,OpenCV作为开源视觉库的标杆,其性能表现直接影响着从工业检测到AI模型推理的各类应用场景。本文结合最新技术趋势与生产实践,系统性梳理Python环境下OpenCV的性能优化策略与部署方案。 一、性能优化核心技术矩阵 1.1 内存…...

k8s的flannel生产实战与常见问题排查
关于 Kubernetes Flannel 插件的详细教程及生产环境实战指南,涵盖核心概念、安装配置、常见问题排查与优化策略 Flannel通信流程 一、Flannel 概述 Flannel 是 Kubernetes 最常用的 CNI(Container Network Interface)插件之一,…...

删除链表倒数第N个节点
Leetcode(19): 给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。 分析: 首要目标就是找到第N个节点的前一个节点,因为只有通过这个节点(cur)才可进行对…...

互联网大厂Java面试实录:Spring Boot与微服务架构在电商场景中的应用解析
💪🏻 1. Python基础专栏,基础知识一网打尽,9.9元买不了吃亏,买不了上当。 Python从入门到精通 😁 2. 毕业设计专栏,毕业季咱们不慌忙,几百款毕业设计等你选。 ❤️ 3. Python爬虫专栏…...

UGUI如何使用EventTrigger
前言 在 Unity 的 UGUI 系统中,EventTrigger 是一个强大的组件,允许开发者监听和处理多种 UI 交互事件。以下是详细的使用方法、示例代码、优缺点分析以及注意事项。 一、EventTrigger 基本用法 1. 添加 EventTrigger 组件 在 Unity 编辑器中选中 UI 对象(如 But…...
PyTorch版)
从代码学习深度学习 - 单发多框检测(SSD)PyTorch版
文章目录 前言工具函数数据处理工具 (`utils_for_data.py`)训练工具 (`utils_for_train.py`)检测相关工具 (`utils_for_detection.py`)可视化工具 (`utils_for_huitu.py`)模型类别预测层边界框预测层连接多尺度预测高和宽减半块基础网络块完整的模型训练模型读取数据集和初始化…...

机器视觉的平板电脑屏幕组件覆膜应用
在现代智能制造业中,平板电脑屏幕组件覆膜工序是确保产品外观和功能完整性的重要环节。随着技术的进步,传统的覆膜方式已经无法满足高速度、高精度的生产需求。而MasterAlign视觉系统的出现,将传统覆膜工艺转变为智能化、自动化的生产流程。在…...

更换内存条会影响电脑的IP地址吗?——全面解析
在日常电脑维护和升级过程中,许多用户都会遇到需要更换内存条的情况。与此同时,不少用户也担心硬件更换是否会影响电脑的网络配置,特别是IP地址的设置。本文将详细探讨更换内存条与IP地址之间的关系,帮助读者理解这两者之间的本质…...
)
SQLite数据库加密(Java语言、python语言)
1. 背景与需求 SQLite 是一种轻量级的关系型数据库,广泛应用于嵌入式设备、移动应用、桌面应用等场景。为了保护数据的隐私与安全,SQLite 提供了加密功能(通过 SQLCipher 扩展)。在 Java 中,可以使用 sqlite-jdbc 驱动与 SQLCipher 集成来实现 SQLite 数据库的加密。 本…...
