How API Gateways handle raw TCP packets
How these gateways actually perform their roles at the HTTP packet level?
Let’s break it down into something more concrete with examples of how these gateways perform their “unique entrance” function by requiring clients to follow specific protocols, often via custom HTTP headers or query parameters.
🔐 1. Unique Entrance via HTTP Headers (or Tokens)
Gateways often serve as the single entry point into your microservice architecture. This is where they inspect incoming requests, enforce rules, and route traffic.
✅ Typical Header-Based Pattern
Clients are expected to add custom headers to each request, like:
GET /api/orders HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR...
X-Client-ID: mobile-app
X-Trace-ID: 93f8de12-312f-4561-abb8-9fe9123345cd
🔧 Gateways Check These Headers:
Authorization: For OAuth2/JWT verification.X-Client-ID: For client identity (mobile, web, internal).X-Trace-ID: For distributed tracing (e.g., with Zipkin).X-VersionorX-Gray-Group: For gray (canary) releases.
If a header is missing or invalid, the gateway can:
- Return
401 Unauthorized - Route to a fallback service
- Log and terminate the request
🚦 2. What Do Gateways Actually Do? (Packet-Level Breakdown)
🛣️ Dynamic Routing
Client:
GET /user-service/profile?id=123 HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.comGateway:
- Inspects path `/user-service/`
- Routes to internal service: `http://user-service.local/profile?id=123`
⚖️ Load Balancing
Gateways maintain a list of backend instances:
"user-service": ["http://10.0.0.2:8080","http://10.0.0.3:8080"
]
And randomly or round-robin routes requests.
🚫 Authentication (JWT)
Gateway verifies the Authorization: Bearer ... token.
If token invalid:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json
{"error": "invalid_token"}
🧯 Circuit Breaker / Degrade
If backend service is down:
GET /product HTTP/1.1→ Circuit breaker detects repeated 5xx
→ Response:
HTTP/1.1 503 Service Unavailable
{"error": "Service temporarily unavailable"}
🧪 Gray (Canary) Release
Clients marked with a special header get routed to new version:
X-Gray-Group: test-users→ Route to v2 instance
Others → Route to stable v1
🛠️ How This Is Implemented in Practice
🔹 Spring Cloud Gateway (Java)
Uses filters + predicates:
routes:- id: user_routeuri: lb://user-servicepredicates:- Path=/user-service/**- Header=X-Client-ID, mobile-appfilters:- AddRequestHeader=X-Trace-ID, #{UUID}- RewritePath=/user-service/(?<segment>.*), /${segment}
🔹 Netflix Zuul (Deprecated)
Java filters (Pre, Post) to intercept requests and do routing.
🔹 Kong (Lua / NGINX)
Can enforce plugin policies:
-- Custom plugin example
if ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Client-ID"] == nil thenreturn kong.response.exit(400, { message = "Client ID required" })
end
🔹 OpenResty (Lua + NGINX)
Lua scripts inspect headers and perform routing:
local client_id = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Client-ID"]
if not client_id thenngx.status = ngx.HTTP_BAD_REQUESTngx.say("Missing Client ID")return ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_BAD_REQUEST)
end
🧪 Real-World Scenario Packet Example
# Client Request:
GET /orders HTTP/1.1
Host: api.myapp.com
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1Ni...
X-Client-ID: ios-app
X-Gray-Group: test# Gateway Inspects:
- Valid JWT? → Yes
- X-Client-ID present? → Yes
- X-Gray-Group: test → Send to beta backend# Routes to:
GET http://orders-v2.internal/orders
Authorization, X-Client-ID, etc. are preserved or rewritten
🧩 Summary
- Gateways do expect clients to include specific headers, tokens, or query params.
- These headers are inspected by filters/plugins/scripts.
- Most functionality like auth, circuit breaking, gray release, logging is driven by what’s in these headers.
- Tutorials miss real packet examples because they focus on “what it can do” instead of “how it does it.”
Network service gateways like Spring Cloud Gateway, Netflix Zuul, Kong, and OpenResty are built to handle HTTP(S)-based traffic, not raw TCP packets or non-HTTP protocols (like custom binary protocols or EBCDIC-encoded streams).
✅ What Gateways Can Handle
These gateways operate at Layer 7 (Application Layer) and expect:
- HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2 protocols
- Readable headers and bodies encoded in UTF-8 or ASCII
- JSON, XML, or form data in body
- Sometimes custom headers or cookies
For example:
GET /serviceA/api HTTP/1.1
Host: gateway.company.com
Authorization: Bearer ...
X-Trace-ID: ...
❌ What They Can’t Handle Directly
They cannot natively handle:
- Raw TCP sockets (e.g. telnet-style sessions, legacy protocols)
- Custom binary protocols (e.g. ISO8583, COBOL-style, or EBCDIC)
- Length-prefixed binary streams (where first 8 bytes indicate packet length)
- Protocols requiring byte-level parsing before decoding
For example, this kind of payload:
[00 00 00 2E] [C1 D7 D6 E2 40 D4 D6 D9 E2 C5]...^ ^--- EBCDIC encoded payloadLength = 46
is completely invisible and meaningless to an HTTP-based gateway.
🧱 What Handles This Instead?
You’d need an L4 (Transport Layer) or custom TCP server before the gateway to:
- Accept TCP connection
- Parse the custom binary format (e.g. read first 8 bytes as length, decode EBCDIC)
- Translate it to a valid HTTP request
- Forward it to the gateway
✅ Common Tools for This Purpose:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Custom Java TCP Server | Use java.net.ServerSocket to accept binary TCP streams |
| Netty | Build high-performance custom TCP → HTTP proxies |
| Nginx (stream block) | Works at Layer 4, but still can’t decode binary |
| HAProxy (TCP mode) | Load balancing TCP traffic, but no payload parsing |
| Envoy + Wasm filter | Can parse TCP streams if extended carefully |
| Framing Proxy | Some banks write one that converts ISO8583 → JSON |
🧪 Real-World Example (Banking Context)
A mainframe system sends:
- EBCDIC-encoded binary stream
- First 4 or 8 bytes are a length prefix
- Payload contains financial transaction data (ISO8583)
A custom TCP parser is built in Java or C++:
- Listens on TCP port
- Parses the length-prefixed binary stream
- Converts EBCDIC to UTF-8
- Maps payload to JSON:
{"cardNumber": "12345678","amount": 500,"currency": "USD"
}
- Sends it as HTTP POST to:
POST /processTransaction HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: ...{...}
Then a Spring Cloud Gateway or Kong receives this as a normal HTTP request and can:
- Log
- Route
- Authenticate
- Forward to microservices
🔚 Summary
- ✅ API gateways like Spring Cloud Gateway, Kong, Zuul, and OpenResty only handle HTTP.
- ❌ They do not support raw TCP or binary packet processing, such as reading EBCDIC or length-prefixed binary data.
- 🛠️ You need an intermediary TCP service that converts raw streams into HTTP requests if you’re dealing with legacy systems or custom protocols.
✅ HTTP = Standard Gateway-Friendly Protocol
-
Modern gateways like Spring Cloud Gateway, Netflix Zuul, Kong, OpenResty are designed to handle HTTP/HTTPS traffic only.
-
HTTP includes:
- A request line (e.g.
GET /path HTTP/1.1) - Headers (e.g.
Host,Authorization,X-Custom-Header) - A body (optional, usually JSON, form data, XML, etc.)
- A request line (e.g.
Because of this, HTTP is the universal entry format for almost all cloud-native microservice infrastructures.
❌ Raw TCP = Incompatible with Application-Layer Gateways
-
Raw TCP packets (like those used in legacy systems, COBOL backends, mainframes, binary protocols) do not have HTTP structure:
- No headers
- No standard request line
- Often have custom formats like
length-prefix + binary body
-
Therefore, HTTP gateways can’t understand or route them.
🔁 TCP-to-HTTP Conversion Pipeline
If your legacy client speaks TCP, and your target services are HTTP-based (behind a gateway), the traffic must go through a conversion layer.
🎯 You need a middle-layer that does:
[RAW TCP Packet] → [Wrap in HTTP format] → [HTTP Gateway] → [Destination Service]or reverse:[Modern HTTP Client] → [Gateway adds header] → [Custom Handler unwraps + sends raw TCP] → [Legacy System]
🧭 Two Common Scenarios
🔹 Scenario 1: Legacy system sends TCP
You want to send legacy packets through a modern API gateway.
You need:
- TCP server (bridge) to read the raw packet
- Add HTTP headers and body (as JSON or binary blob)
- Forward via HTTP to gateway
- Gateway routes to microservice
[Legacy TCP Client] ↓
[TCP-to-HTTP Bridge Server]↓ (HTTP POST)
[API Gateway (Spring Cloud Gateway, Kong, etc.)]↓
[Modern HTTP Microservice]
🔹 Scenario 2: Modern service needs to call a legacy TCP backend
You want to access legacy TCP-based systems from modern HTTP services.
You need:
-
A microservice or sidecar that:
- Receives an HTTP request (via gateway)
- Strips headers and parses JSON
- Converts to a binary TCP format (e.g. EBCDIC, ISO8583)
- Opens a socket to the legacy system
[Modern HTTP Client]↓
[API Gateway]↓
[HTTP-to-TCP Adapter Service]↓
[Legacy Backend (TCP)]
✳️ Think of HTTP as a “Protocol Adapter Format”
HTTP isn’t just a web protocol. It’s become the standard envelope that:
- Lets services be routed
- Carries metadata in headers
- Enables observability (tracing, logging)
- Integrates with API management, firewalls, and security tools
But it’s just a wrapper. The real payload can still be:
- Raw bytes (Base64 or binary)
- Encoded legacy formats
- Anything your adapter logic knows how to parse
🔍 The term “protocol detection” is often misleading.
When API gateways (like Spring Cloud Gateway, Kong, Envoy, etc.) talk about “protocol detection”, they usually mean:
Detecting between different application-layer HTTP protocols, like:
- HTTP/1.1 vs HTTP/2
- gRPC (which runs over HTTP/2)
- WebSocket upgrade
- Possibly TLS sniffing (SNI) if used for routing
But…
❌ They do not mean:
-
Detecting or handling raw non-HTTP binary protocols, like:
- EBCDIC packets
- ISO8583 (banking)
- FIX (finance)
- MQTT, Redis, Telnet
- Custom socket protocols
✅ In practice, all traffic handled by these gateways must already:
-
Start as a valid HTTP request
-
Include all expected parts:
- Method:
GET,POST, etc. - Headers (especially
Host,Content-Type) - Body (optional)
- Method:
Any “detection” happens after the gateway has confirmed it’s dealing with HTTP.
🔁 Real “protocol recognition” (at a raw TCP level) only happens in:
-
L4 proxies like:
- Envoy (L4 sniffing mode)
- NGINX stream module
- HAProxy in TCP mode
-
Custom TCP servers or sidecars you write
Even then, they must read bytes manually to:
- Identify “magic bytes” (e.g., 0x16 for TLS)
- Check headers (e.g.,
GETorPRI * HTTP/2.0) - Do content-based routing
🔄 So, if you hear:
“Our gateway does automatic protocol detection”
You can mentally translate that to:
✅ “It auto-detects HTTP/1 vs HTTP/2 vs gRPC (via headers or ALPN)”
❌ “It does not understand your legacy TCP protocol unless you wrap it in HTTP”
相关文章:

How API Gateways handle raw TCP packets
How these gateways actually perform their roles at the HTTP packet level? Let’s break it down into something more concrete with examples of how these gateways perform their “unique entrance” function by requiring clients to follow specific protocols, …...

芯片配置文件自动化生成
代码的主要功能是将设置了芯片寄存器的Excel表格(.xls或.xlsx)中的特定工作表的数据转换成SVD格式。 步骤 Excel文件读取 使用xlrd库打开Excel文件处理.xls格式的特殊情况(formatting_infoTrue)获取"global"工作表数…...

新能源汽车与油车销量
中国油车与新能源车销量对比(2022-2025年) 1. 市场份额演化(2022-2025年) 年份 新能源车销量 (渗透率) 燃油车销量 (渗透率) 关键事件 2022 688.7万辆…...

LVS-DR 负载均衡集群
目录 一、简介 1.1 LVS-DR工作原理核心特性 1.2 数据包流向深度解析 二、实验环境准备与规划 三、LVS调度器配置实战 3.1 绑定虚拟IP地址(VIP) 3.2 调整内核参数禁用重定向 3.3 配置负载均衡策略 四、真实服务器节点配置 4.1 绑定VIP到lo接口 …...
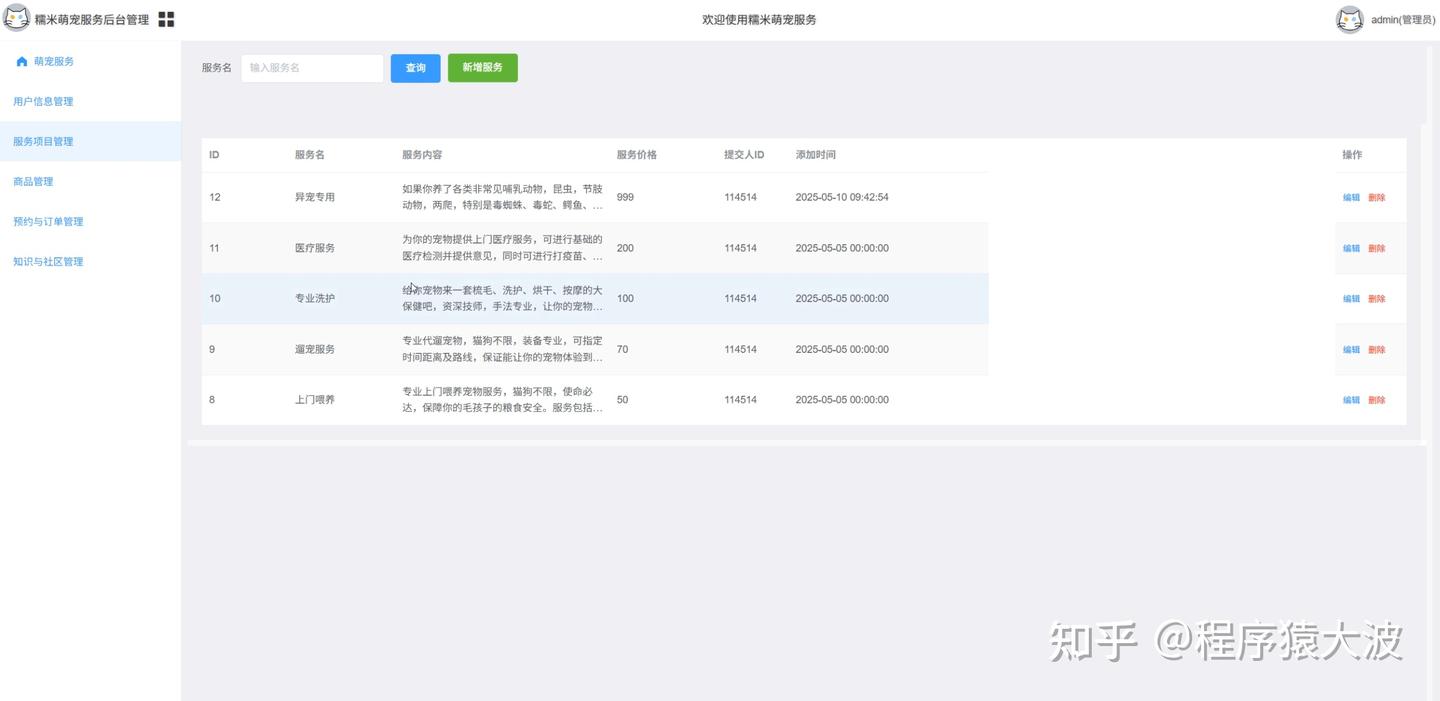
基于Java,SpringBoot,Vue,UniAPP宠物洗护医疗喂养预约服务商城小程序管理系统设计
摘要 随着宠物经济的快速发展,宠物主对宠物服务的便捷性、专业性需求日益增长。本研究设计并实现了一套宠物洗护医疗喂养预约服务小程序系统,采用 Java 与 SpringBoot 构建后端服务,结合 Vue 开发管理后台,通过 UniAPP 实现多端适…...
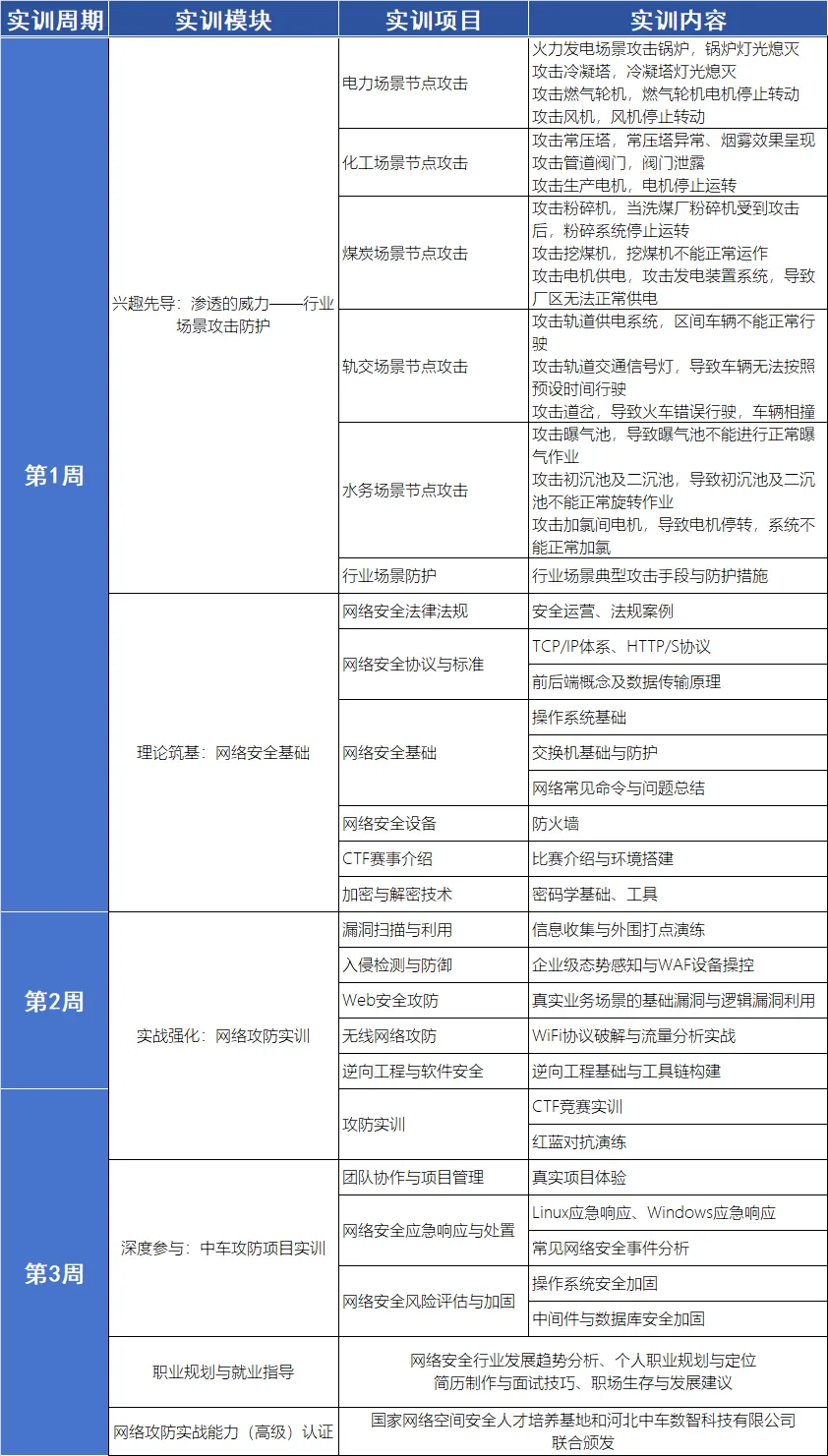
中车靶场,网络安全暑期实训营
不善攻防,何谈就业? 实训目的:提升实战能力,直通就业快道。 实训对象:面向计算机相关专业、有兴趣接触网络攻防、大专及以上学历的学员。 知识准备 为确保高效实训,学员需具备一定的实战基础。报名后&am…...

2.2.2 06年T1
成功的同化机器——美国:2006年考研英语(一)Text 1精析 本文解析2006年考研英语(一)第一篇文章,揭示美国社会强大的文化同化力及其表现。 一、原文与翻译 Paragraph 1:美国社会的同化本质 L1: …...

split_conversion将json转成yolo训练用的txt,在直接按照8:1:1的比例分成训练集,测试集,验证集
第一章 使用说明 类别自己在代码中改,其他四个参数 --json-folder:json文件夹路径 --txt-folder:转换成功后txt的存放路径 --images-dir:图片文件夹路径 --save-dir:转换完成分割后所有文件的路径 终端命令行:p…...

响应式系统与Spring Boot响应式应用开发
响应式系统概述 过去十年间,为应对移动和云计算的需求,软件行业通过改进开发流程来构建更稳定、健壮且灵活的软件系统。这种演进不仅服务于传统用户端(桌面/Web),还需支持多样化设备(手机、传感器等)。为应对这些挑战,多个组织共同制定了《响应式宣言》(2014年发布)…...

【第1章 基础知识】1.8 在 Canvas 中使用 HTML 元素
文章目录 前言示例-橡皮筋式选取框示例代码 前言 尽管我们可以说 Canvas 是 HTML5 之中最棒的功能,不过在实现网络应用程序时,很少会单独使用它。在绝大多数情况下,你都会将一个或更多的 canvas 元素与其他 HTML 控件结合起来使用࿰…...

c++流之sstream/堆or优先队列的应用[1]
目录 c流之sstream 解释 注意事项 215.数据流的第k大 问题分析 修正代码 主要修改点 优先队列的比较规则 代码中的比较逻辑 为什么这样能维护第 k 大元素? 举个例子 总结 Python 实现(使用heapq库) Java 实现(使用P…...

SAR ADC 比较器噪声分析(二)
SAR ADC的比较器是非常重要的模块,需要仔细设计。主要考虑比较器的以下指标: 1)失调电压 2)输入共模范围 3)比较器精度 4)传输延时 5)噪声 6)功耗 这里主要讲一下动态比较器的noise。 动态比较器一般用于高速SAR ADC中,且精度不会超过12bit…...

c#与java的相同点和不同点
C# 和 Java 是两大主流的、面向对象的、托管型编程语言,它们共享许多相似的设计理念和语法,但也在细节、生态系统和运行平台上存在显著差异。以下是它们的相同点和不同点的详细对比: 一、相同点 (核心相似之处) 语法高度相似: 都源…...

phpmyadmin
安装PHPMyAdmin PHPMyAdmin通常可通过包管理器安装或手动部署。对于Linux系统(如Ubuntu),使用以下命令安装: sudo apt update sudo apt install phpmyadmin安装过程中会提示选择Web服务器(如Apache或Nginx࿰…...

机器学习Day5-模型诊断
实现机器学习算法的技巧。当我们训练模型或使用模型时,发现预测误差很 大,可以考虑进行以下优化: (1)获取更多的训练样本 (2)使用更少的特征 (3)获取其他特征 ÿ…...

如何将 WSL 的 Ubuntu-24.04 迁移到其他电脑
在使用 Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 时,我们可能会遇到需要将现有的 WSL 环境迁移到其他电脑的情况。无论是为了备份、更换设备,还是在不同电脑之间共享开发环境,掌握迁移 WSL 子系统的方法都是非常有用的。本文将以 Ubuntu-24.04 为例…...

金融欺诈有哪些检测手段
金融欺诈检测是一个多层次的动态防御过程,需要结合技术手段、数据分析、人工智能和人工审核。以下是当前主流的检测手段和技术分类。 ### **一、核心技术手段** 1. **规则引擎(Rule-Based Systems)** - **原理**:预设基于历史…...

HTML5 全面知识点总结
一、HTML 基础概念 HTML:超文本标记语言,用于创建网页和 Web 应用的结构。 超文本:可以包含文字、图片、音频、视频、链接等多种媒体。 标记语言:通过标签标记网页的各个部分。 二、HTML5 的新特性(区别于 HTML4&am…...
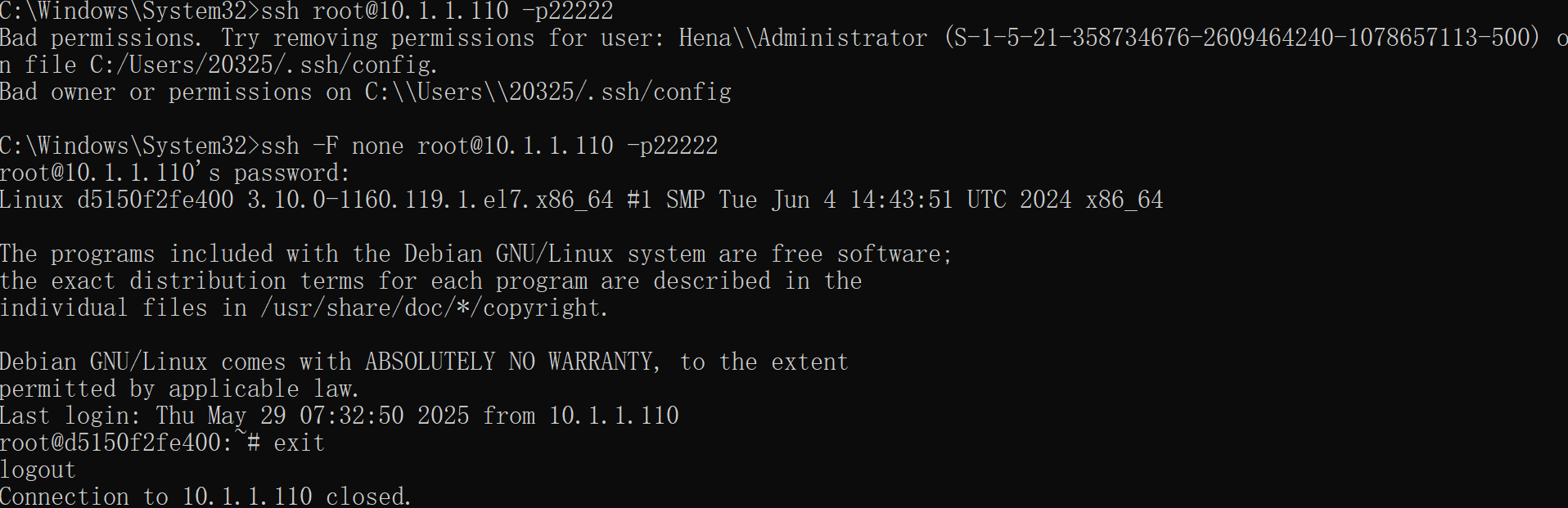
vscode一直连接不上虚拟机或者虚拟机容器怎么办?
1. 检查并修复文件权限 右键点击 C:\Users\20325\.ssh\config 文件,选择 属性 → 安全 选项卡。 确保只有你的用户账户有完全控制权限,移除其他用户(如 Hena\Administrator)的权限。 如果 .ssh 文件夹权限也有问题,同…...

初学c语言21(文件操作)
一.为什么使用文件 之前我们写的程序的数据都是存储到内存里面的,当程序结束时,内存回收,数据丢失, 再次运行程序时,就看不到上次程序的数据,如果要程序的数据一直保存得使用文件 二.文件 文件一般可以…...

数学复习笔记 21
4.15 稍微有点难啊。克拉默法则忘掉了,然后第二类数学归纳法是第一次见。行列式和矩阵,向量和方程组。这是前面四章。现在考研只剩下一个大题。所以就是考最后两章,特征值和二次型。感觉看网课的作用就是辅助理解,自己看书的话&am…...

华为OD机试真题——数据分类(2025B卷:100分)Java/python/JavaScript/C++/C语言/GO六种最佳实现
2025 B卷 100分 题型 本文涵盖详细的问题分析、解题思路、代码实现、代码详解、测试用例以及综合分析; 并提供Java、python、JavaScript、C++、C语言、GO六种语言的最佳实现方式! 本文收录于专栏:《2025华为OD真题目录+全流程解析/备考攻略/经验分享》 华为OD机试真题《数据…...

JavaWeb开发基础Servlet生命周期与工作原理
Servlet生命周期 Servlet的生命周期由Servlet容器(如Tomcat、Jetty等)管理,主要包括以下5个阶段: 加载Servlet类 创建Servlet实例 调用init方法 调用service方法 调用destroy方法 加载(Loading): 当Servlet容器启动或第一次接收到对某个…...

三防平板科普:有什么特殊功能?应用在什么场景?
在数字化浪潮席卷全球的今天,智能设备已成为现代工业、应急救援、户外作业等领域的核心工具。然而,常规平板电脑在极端环境下的脆弱性,如高温、粉尘、水浸或撞击,往往成为制约效率与安全的短板。三防平板(防水、防尘、…...

百度外链生态的优劣解构与优化策略深度研究
本文基于搜索引擎算法演进与外链建设实践,系统剖析百度外链的作用机制与价值模型。通过数据统计、案例分析及算法逆向工程,揭示不同类型外链在权重传递、流量获取、信任背书等维度的差异化表现,提出符合搜索引擎规则的外链建设技术方案&#…...

笔记: 在WPF中ContentElement 和 UIElement 的主要区别
一、目的:简要姐扫在WPF中ContentElement 和 UIElement 的主要区别 ContentElement 和 UIElement 是 WPF 中的两个基类,它们在功能和用途上有显著的区别。 二、主要区别 ContentElement 主要特点: • 没有视觉表示: ContentElement 本身不直接渲染任…...

项目中使用到了多个UI组件库,也使用了Tailwindcss,如何确保新开发的组件样式隔离?
在项目中使用多个组件库,同时使用 TailwindCSS,确保新开发的组件样式隔离是非常重要的。样式隔离可以避免样式冲突、全局污染以及意外的样式覆盖问题。以下是一些常见的策略和最佳实践: 1. 使用 TailwindCSS 的 layer 机制 TailwindCSS 提供…...
高级技巧详解)
AI提示工程(Prompt Engineering)高级技巧详解
AI提示工程(Prompt Engineering)高级技巧详解 文章目录 一、基础设计原则二、高级提示策略三、输出控制技术四、工程化实践五、专业框架应用提示工程是与大型语言模型(LLM)高效交互的关键技术,精心设计的提示可以显著提升模型输出的质量和相关性。以下是经过验证的详细提示工…...

【速写】PPOTrainer样例与错误思考(少量DAPO)
文章目录 序言1 TRL的PPO官方样例分析2 确实可行的PPOTrainer版本3 附录:DeepSeek关于PPOTrainer示例代码的对话记录Round 1(给定模型数据集,让它开始写PPO示例)Round 2 (指出PPOTrainer的参数问题)关键问题…...

5.26 面经整理 360共有云 golang
select … for update 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/goloving/p/13590955.html select for update是一种常用的加锁机制,它可以在查询数据的同时对所选的数据行进行锁定,避免其他事务对这些数据行进行修改。 比如涉及到金钱、库存等。一般这…...
