TKernel模块--杂项
TKernel模块–杂项
1.DEFINE_HARRAY1
#define DEFINE_HARRAY1(HClassName, _Array1Type_) \
class HClassName : public _Array1Type_, public Standard_Transient { \public: \DEFINE_STANDARD_ALLOC \DEFINE_NCOLLECTION_ALLOC \HClassName () : _Array1Type_ () {} \HClassName (const Standard_Integer theLower, \const Standard_Integer theUpper) : \_Array1Type_ (theLower,theUpper) {} \HClassName (const Standard_Integer theLower, \const Standard_Integer theUpper, \const _Array1Type_::value_type& theValue) : \_Array1Type_ (theLower,theUpper) { Init (theValue); } \explicit HClassName (const typename _Array1Type_::value_type& theBegin, \const Standard_Integer theLower, \const Standard_Integer theUpper, \const bool) : \_Array1Type_ (theBegin,theLower,theUpper) {} \HClassName (const _Array1Type_& theOther) : _Array1Type_(theOther) {} \const _Array1Type_& Array1 () const { return *this; } \_Array1Type_& ChangeArray1 () { return *this; } \DEFINE_STANDARD_RTTI_INLINE(HClassName,Standard_Transient) \
}; \
DEFINE_STANDARD_HANDLE (HClassName, Standard_Transient)#define IMPLEMENT_HARRAY1(HClassName)
看着是定义一个基于参数2的派生类,提供类似的功能。
2.DEFINE_HASHER
#define DEFINE_HASHER(HasherName, TheKeyType, HashFunctor, EqualFunctor) \
struct HasherName : protected HashFunctor, EqualFunctor \
{ \size_t operator()(const TheKeyType& theKey) const noexcept \{ \return HashFunctor::operator()(theKey); \} \\bool operator() (const TheKeyType& theK1, \const TheKeyType& theK2) const noexcept \{ \return EqualFunctor::operator()(theK1, theK2); \} \
};
集成取哈希值,键比较功能
3.DEFINE_HSEQUENCE
#define DEFINE_HSEQUENCE(HClassName, _SequenceType_) \
class HClassName : public _SequenceType_, public Standard_Transient { \public: \DEFINE_STANDARD_ALLOC \DEFINE_NCOLLECTION_ALLOC \HClassName () {} \HClassName (const _SequenceType_& theOther) : _SequenceType_(theOther) {} \const _SequenceType_& Sequence () const { return *this; } \void Append (const _SequenceType_::value_type& theItem) { \_SequenceType_::Append (theItem); \} \void Append (_SequenceType_& theSequence) { \_SequenceType_::Append (theSequence); \} \_SequenceType_& ChangeSequence () { return *this; } \template <class T> \void Append (const Handle(T)& theOther, \typename opencascade::std::enable_if<opencascade::std::is_base_of<HClassName, T>::value>::type * = 0) { \_SequenceType_::Append (theOther->ChangeSequence()); \} \DEFINE_STANDARD_RTTI_INLINE(HClassName,Standard_Transient) \
}; \
DEFINE_STANDARD_HANDLE (HClassName, Standard_Transient) #define IMPLEMENT_HSEQUENCE(HClassName)
为参数2提供派生类,提供类似功能
4.NCollection_Handle
template <class T>
class NCollection_Handle : public opencascade::handle<Standard_Transient> {
private:class Ptr : public Standard_Transient {public:Ptr (T* theObj) : myPtr (theObj) {}~Ptr () { if ( myPtr ) delete myPtr; myPtr = 0; }protected:Ptr(const Ptr&);Ptr& operator=(const Ptr&);public:T* myPtr; };NCollection_Handle (Ptr* thePtr, int) : opencascade::handle<Standard_Transient> (thePtr) {}public:typedef T element_type;NCollection_Handle () {}NCollection_Handle (T* theObject) : opencascade::handle<Standard_Transient> (theObject ? new Ptr (theObject) : 0) {}T* get () { return ((Ptr*)opencascade::handle<Standard_Transient>::get())->myPtr; }const T* get () const { return ((Ptr*)opencascade::handle<Standard_Transient>::get())->myPtr; }T* operator -> () { return get(); }const T* operator -> () const { return get(); }T& operator * () { return *get(); }const T& operator * () const { return *get(); }static NCollection_Handle<T> DownCast (const opencascade::handle<Standard_Transient>& theOther) {return NCollection_Handle<T>(dynamic_cast<Ptr*>(theOther.get()), 0);}
};
做的还是为原始指针做包装。opencascade::handle<Standard_Transient>已经是一层包装,为原始指针加引用计数管理。这里本质还是在包装。
5.NCollection_Shared
template <class T, typename = typename opencascade::std::enable_if<! opencascade::std::is_base_of<Standard_Transient, T>::value>::type>
class NCollection_Shared : public Standard_Transient, public T {
public:DEFINE_STANDARD_ALLOCDEFINE_NCOLLECTION_ALLOCNCollection_Shared () {}template<typename T1> NCollection_Shared (const T1& arg1) : T(arg1) {}template<typename T1> NCollection_Shared (T1& arg1) : T(arg1) {}template<typename T1, typename T2> NCollection_Shared (const T1& arg1, const T2& arg2) : T(arg1, arg2) {}template<typename T1, typename T2> NCollection_Shared (T1& arg1, const T2& arg2) : T(arg1, arg2) {}template<typename T1, typename T2> NCollection_Shared (const T1& arg1, T2& arg2) : T(arg1, arg2) {}template<typename T1, typename T2> NCollection_Shared (T1& arg1, T2& arg2) : T(arg1, arg2) {}
};
NCollection_Shared 是 OpenCASCADE (OCCT) 中的一个模板类,它提供了一种将非继承自 Standard_Transient 的类包装成可共享对象的方式。
这个类的主要目的是让那些原本不继承 Standard_Transient 的类能够获得引用计数和自动内存管理的功能。这在需要共享对象所有权的情况下非常有用。
6.Standard_MMgrRoot
class Standard_MMgrRoot {
public:Standard_EXPORT virtual ~Standard_MMgrRoot(){}Standard_EXPORT virtual Standard_Address Allocate (const Standard_Size theSize)=0;Standard_EXPORT virtual Standard_Address Reallocate (Standard_Address thePtr, const Standard_Size theSize)=0;Standard_EXPORT virtual void Free(Standard_Address thePtr)=0;Standard_EXPORT virtual Standard_Integer Purge(Standard_Boolean isDestroyed=Standard_False){return 0;}
};
7.Standard_MMgrOpt
if defined(__linux__)#define MMAP_BASE_ADDRESS 0x20000000#define MMAP_FLAGS (MAP_PRIVATE)
end
// 将给定的尺寸向上对齐到页面尺寸倍数
#define PAGE_ALIGN(size,thePageSize) \(((size) + (thePageSize) - 1) & ~((thePageSize) - 1))
// 将给定的尺寸向上对齐到16的倍数
#define ROUNDUP16(size) (((size) + 0xf) & ~(Standard_Size)0xf)
// 将给定的尺寸向上对齐到8的倍数
#define ROUNDUP8(size) (((size) + 0x7) & ~(Standard_Size)0x7)
// 将给定的尺寸向上对齐到4的倍数
#define ROUNDUP4(size) (((size) + 0x3) & ~(Standard_Size)0x3)
// 将给定的尺寸向下对齐到8的倍数
#define ROUNDDOWN8(size) ((size) & ~(Standard_Size)0x7)
// 将给定的尺寸向上对齐到8的倍数
#define ROUNDUP_CELL(size) ROUNDUP8(size)
// 将给定的尺寸向下对齐到8的倍数
#define ROUNDDOWN_CELL(size) ROUNDDOWN8(size)
// 给定尺寸,计算其被8所除的结果整数部分
#define INDEX_CELL(rsize) ((rsize) >> 3)#define BLOCK_SHIFT 1
// 前进一个Standard_Size大小,从块地址得到可用内存地址
#define GET_USER(block) (((Standard_Size*)(block)) + BLOCK_SHIFT)
// 后退一个Standard_Size大小,从可用内存地址得到块地址
#define GET_BLOCK(storage) (((Standard_Size*)(storage))-BLOCK_SHIFT)
class Standard_MMgrOpt : public Standard_MMgrRoot {protected:Standard_Boolean myClear; Standard_Size myFreeListMax; Standard_Size ** myFreeList; Standard_Size myCellSize; Standard_Integer myNbPages; Standard_Size myPageSize; Standard_Size * myAllocList; Standard_Size * myNextAddr; Standard_Size * myEndBlock; Standard_Integer myMMap; Standard_Size myThreshold; Standard_Mutex myMutex; Standard_Mutex myMutexPools;
public:Standard_EXPORT Standard_MMgrOpt(const Standard_Boolean aClear = Standard_True,const Standard_Boolean aMMap = Standard_True, const Standard_Size aCellSize = 200,const Standard_Integer aNbPages = 10000, const Standard_Size aThreshold = 40000){Standard_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(Standard_Size) == sizeof(Standard_Address));myFreeListMax = 0;myFreeList = NULL;myPageSize = 0;myAllocList = NULL;myNextAddr = NULL;myEndBlock = NULL;myClear = aClear;myMMap = (Standard_Integer)aMMap;myCellSize = aCellSize;myNbPages = aNbPages;myThreshold = aThreshold;Initialize(); }
protected:Standard_EXPORT void Initialize(){if ( myNbPages < 100 ) myNbPages = 1000;#ifndef _WIN32myPageSize = getpagesize();if ( ! myPageSize )myMMap = 0;#elseSYSTEM_INFO SystemInfo;GetSystemInfo (&SystemInfo);myPageSize = SystemInfo.dwPageSize;#endifif(myMMap) {myMMap = -1;}myFreeListMax = INDEX_CELL(ROUNDUP_CELL(myThreshold-BLOCK_SHIFT)); // all blocks less than myThreshold are to be recycled// 每个链表负责维护固定尺寸内存块分配和回收?// 链表负责的内存块尺寸以8为刻度递增myFreeList = (Standard_Size **) calloc (myFreeListMax+1, sizeof(Standard_Size *));myCellSize = ROUNDUP16(myCellSize);}
public:Standard_EXPORT virtual Standard_Integer Purge(Standard_Boolean isDestroyed){Standard_Mutex::Sentry aSentry (myMutex);Standard_Integer nbFreed = 0;// 快速定位到myCellSize尺寸最低可分配的链表索引Standard_Size i = INDEX_CELL(ROUNDUP_CELL(myCellSize+BLOCK_SHIFT));// 从该链表到后续各个链表内所有块依次释放for (; i <= myFreeListMax; i++ ) {// 获得链表首个块地址Standard_Size * aFree = myFreeList[i]; while(aFree) {// 保存当前块地址Standard_Size * anOther = aFree;// 移动到下一个块。能如此的原因:每个内存块首个位置存放下一个块的地址。aFree = * (Standard_Size **) aFree;// 释放块free(anOther); nbFreed++;}// 释放后链表置空myFreeList[i] = NULL;}Standard_Mutex::Sentry aSentry1 (myMutexPools);#ifndef _WIN32const Standard_Size PoolSize = myPageSize * myNbPages;#else// 内存池大小const Standard_Size PoolSize = PAGE_ALIGN(myPageSize * myNbPages + sizeof(HANDLE), myPageSize) - sizeof(HANDLE);#endif// 向下规整const Standard_Size RPoolSize = ROUNDDOWN_CELL(PoolSize);// 一个池可容纳的Standard_Size对象个数const Standard_Size PoolSizeN = RPoolSize / sizeof(Standard_Size);static const Standard_Integer NB_POOLS_WIN = 512;static Standard_Size* aPools[NB_POOLS_WIN];static Standard_Size aFreeSize[NB_POOLS_WIN];static Standard_Integer aFreePools[NB_POOLS_WIN];Standard_Size * aNextPool = myAllocList;Standard_Size * aPrevPool = NULL;// 给定尺寸得到此尺寸的索引const Standard_Size nCells = INDEX_CELL(myCellSize);Standard_Integer nPool = 0, nPoolFreed = 0;// 每个内存块作为一个Pool?while (aNextPool) {Standard_Integer iPool;for (iPool = 0; aNextPool && iPool < NB_POOLS_WIN; iPool++) {aPools[iPool] = aNextPool;aFreeSize[iPool] = 0;aNextPool = * (Standard_Size **) aNextPool; // get next pool}const Standard_Integer iLast = iPool - 1;(void )nPool; // unused but set for debugnPool += iPool;// 块的个数// 完成小块链表释放for (i = 0; i <= nCells; i++ ) {// 负责小块内存分配的块列表Standard_Size * aFree = myFreeList[i];Standard_Size aSize = BLOCK_SHIFT * sizeof(Standard_Size) + ROUNDUP_CELL(1) * i;while(aFree) {for (iPool = 0; iPool <= iLast; iPool++) {// 若是此个地址块落在内存池块内if (aFree >= aPools[iPool] && aFree < aPools[iPool] + PoolSizeN) {aFreeSize[iPool] += aSize;// 此内存池块内可分配内存增加break;}}aFree = * (Standard_Size **) aFree; // 继续前进到链表下一个小块}}Standard_Integer iLastFree = -1;for (iPool = 0; iPool <= iLast; iPool++) {// 可分配尺寸向上对齐aFreeSize[iPool] = ROUNDUP_CELL(aFreeSize[iPool]);if (aFreeSize[iPool] == RPoolSize)aFreePools[++iLastFree] = iPool;// 得到一个完全空闲的快池}if (iLastFree == -1) {// 无法得到一个完全空闲的块池aPrevPool = aPools[iLast];continue;}Standard_Integer j;for (i = 0; i <= nCells; i++ ) {Standard_Size * aFree = myFreeList[i];Standard_Size * aPrevFree = NULL;while(aFree) {// 若小块落在完全空闲块池for (j = 0; j <= iLastFree; j++) {iPool = aFreePools[j];if (aFree >= aPools[iPool] && aFree < aPools[iPool] + PoolSizeN)break;}if (j <= iLastFree) {// 表示小块落在完全空闲块池// 将此小块从链表移除aFree = * (Standard_Size **) aFree;if (aPrevFree)* (Standard_Size **) aPrevFree = aFree; elsemyFreeList[i] = aFree;nbFreed++;}else {// 表示小块未落在完全空闲块池aPrevFree = aFree;// 取得小块地址aFree = * (Standard_Size **) aFree;// 继续分析下一个小块}}}Standard_Size * aPrev = (aFreePools[0] == 0 ? aPrevPool : aPools[aFreePools[0] - 1]);for (j = 0; j <= iLastFree; j++) {iPool = aFreePools[j];if (j > 0) {if (iPool - aFreePools[j - 1] > 1)aPrev = aPools[iPool - 1];}if (j == iLastFree || aFreePools[j + 1] - iPool > 1) {Standard_Size * aNext = (j == iLastFree && aFreePools[j] == iLast) ? aNextPool : aPools[iPool + 1];if (aPrev)* (Standard_Size **) aPrev = aNext;elsemyAllocList = aNext;}FreeMemory(aPools[iPool], PoolSize);}aPrevPool = (aFreePools[iLastFree] == iLast ? aPrev : aPools[iLast]);(void )nPoolFreed; // unused but set for debugnPoolFreed += iLastFree + 1;}return nbFreed;}void FreeMemory (Standard_Address aPtr, const Standard_Size aSize){if ( myMMap ) {#ifndef _WIN32const Standard_Size AlignedSize = PAGE_ALIGN(aSize, myPageSize);munmap((char*)aBlock, AlignedSize);#elseconst HANDLE * aMBlock = (const HANDLE *)aBlock;HANDLE hMap = *(--aMBlock);UnmapViewOfFile((LPCVOID)aMBlock);CloseHandle (hMap);#endif}elsefree(aBlock);}void FreePools(){Standard_Mutex::Sentry aSentry (myMutexPools);Standard_Size * aFree = myAllocList;myAllocList = 0;while (aFree) {Standard_Size * aBlock = aFree;aFree = * (Standard_Size **) aFree;FreeMemory ( aBlock, myPageSize * myNbPages );}}Standard_EXPORT virtual ~Standard_MMgrOpt(){Purge(Standard_True);free(myFreeList);FreePools();}public:// 分析内存分配实现策略Standard_EXPORT virtual Standard_Address Allocate(const Standard_Size aSize){Standard_Size * aStorage = NULL;// 尺寸向上对齐到倍数volatile Standard_Size RoundSize = ROUNDUP_CELL(aSize);// 可以满足此尺寸的最小索引const Standard_Size Index = INDEX_CELL(RoundSize);// 这里弄了个myFreeListMax这个概念。多级链表,由不同尺寸内存块构成的链表。// myFreeListMax这个概念用于实现小块内存的回收复用。从而避免小块内存分配时执行系统调用malloc/free,提升性能// 系统调用涉及内核态用户态转换,上下文恢复较纯应用层调用耗时会更多if ( Index <= myFreeListMax ) {// 对齐后尺寸能容纳的Standard_Size对象个数const Standard_Size RoundSizeN = RoundSize / sizeof(Standard_Size);// 核心分配过程做了互斥保护myMutex.Lock();// 定位到的链表是否有元素if ( myFreeList[Index] ) {// 取得链表首个元素地址Standard_Size* aBlock = myFreeList[Index];// 将首个元素分配出去,更新链表首个元素地址myFreeList[Index] = *(Standard_Size**)aBlock;myMutex.Unlock();// 基类分配到的内存块尺寸aBlock[0] = RoundSize;// 从块地址得到可用内存地址aStorage = GET_USER(aBlock);if (myClear)memset (aStorage, 0, RoundSize);// 内存部分需要清理}// 对应的小块链表为孔,且对齐后尺寸不超过myCellSizeelse if ( RoundSize <= myCellSize ) {myMutex.Unlock();// 这里使用多个锁,实现细粒度的互斥保护,有利于提升并发性能。Standard_Mutex::Sentry aSentry (myMutexPools);// myNextAddr,myEndBlock机制// 在多级小块内存复用链表机制外,对于较小尺寸内存的分配额外引用直接分配机制。// 提供一个较大块,当较小块分配时,定位到其复用块链表为空时,尝试从此较大块直接分配出一个小块。Standard_Size *aBlock = myNextAddr;// 当大块剩余部分不足完成本次分配if ( &aBlock[ BLOCK_SHIFT+RoundSizeN] > myEndBlock ) {// 进入到这里是发现此较大块剩余部分不足完成本次分配。// 采取的策略是重新分配一个较大块Standard_Size Size = myPageSize * myNbPages;aBlock = AllocMemory(Size);// 若当前较大块剩余部分尚有内存空间可供分配if (myEndBlock > myNextAddr) {// 剩余部分中可用内存尺寸const Standard_Size aPSize = (myEndBlock - GET_USER(myNextAddr)) * sizeof(Standard_Size);// 内存尺寸向下对齐const Standard_Size aRPSize = ROUNDDOWN_CELL(aPSize);// 内存尺寸对应的多级小块链表索引const Standard_Size aPIndex = INDEX_CELL(aRPSize);// 若此索引属于合法索引范围if ( aPIndex > 0 && aPIndex <= myFreeListMax ) {myMutex.Lock();// 头插法加入到对应小块链表// 这里的一个灵活多变。// 大尺寸块可分分割为多个小尺寸块。// 大尺寸块的结构是:// 4字节下一个大尺寸块地址+多个小尺寸块// 小尺寸块结构是:// 头4字节+可用内存区域// 在小尺寸块位于回收链表时,其头4字节指向链表下一个小尺寸块的地址// 在小尺寸块被分配出去时,其头4字节存储了此块内已经分配内存尺寸。*(Standard_Size**)myNextAddr = myFreeList[aPIndex];myFreeList[aPIndex] = myNextAddr;myMutex.Unlock();}}// 计算新块的结束位置myEndBlock = aBlock + Size / sizeof(Standard_Size);// 将新的较大块加入myAllocList链表// myAllocList机制:由较大块构成的分配链表。*(Standard_Size**)aBlock = myAllocList;myAllocList = aBlock;// 原始块的布局:// 4字节为下一个块的地址+4字节为本块已经分配出去内存尺寸+可用内存区域aBlock+=BLOCK_SHIFT;}// 记录本块内已经分配内存尺寸aBlock[0] = RoundSize;// 从块得到可用内存区域地址aStorage = GET_USER(aBlock);// 下一个可供分配的地址myNextAddr = &aStorage[RoundSizeN];}// 对应的小块链表为孔,且对齐后尺寸超过myCellSize。// myCellSize属于中尺寸和大尺寸分界线。else {myMutex.Unlock();// 这里相当于处理大尺寸块的分配// 直接通过系统api完成分配Standard_Size *aBlock = (Standard_Size*) (myClear ? calloc( RoundSizeN+BLOCK_SHIFT, sizeof(Standard_Size)) : malloc((RoundSizeN+BLOCK_SHIFT) * sizeof(Standard_Size)) );// 直到无法完成分配时,才执行清理,释放多余空闲内存。// 清理的时机有点晚了。if ( ! aBlock ) {if ( Purge (Standard_False) )aBlock = (Standard_Size*)calloc(RoundSizeN+BLOCK_SHIFT, sizeof(Standard_Size));if ( ! aBlock )throw Standard_OutOfMemory("Standard_MMgrOpt::Allocate(): malloc failed");}// 直接分配的大尺寸块的结构:// 4字节存储块中已经分配内存尺寸+可用内存区域aBlock[0] = RoundSize;// 可用内存区域指针aStorage = GET_USER(aBlock);}}// 索引直接超过了myFreeListMax,属于超大块了。// myFreeListMax构成了大块和超大块的分水岭。else {Standard_Size AllocSize = RoundSize + sizeof(Standard_Size);// 通过AllocMemory完成超大快的分配Standard_Size* aBlock = AllocMemory(AllocSize);aBlock[0] = RoundSize;aStorage = GET_USER(aBlock);}// 每次分配成功都触发一次回调。参数3是对齐后尺寸,参数4是原始尺寸。callBack(Standard_True, aStorage, RoundSize, aSize);return aStorage;}// 释放+重新分配Standard_EXPORT virtual Standard_Address Reallocate (Standard_Address theStorage, const Standard_Size theNewSize){if (!theStorage) {return Allocate(theNewSize);}// 得到块起始地址Standard_Size * aBlock = GET_BLOCK(theStorage);Standard_Address newStorage = NULL;// 块内已经使用内存尺寸Standard_Size OldSize = aBlock[0];if (theNewSize <= OldSize) {// 复用newStorage = theStorage;}else {newStorage = Allocate(theNewSize);memcpy (newStorage, theStorage, OldSize);Free( theStorage );if ( myClear )memset(((char*)newStorage) + OldSize, 0, theNewSize-OldSize);}return newStorage;}Standard_EXPORT virtual void Free (Standard_Address thePtr){if ( ! theStorage )return;Standard_Size* aBlock = GET_BLOCK(theStorage);Standard_Size RoundSize = aBlock[0];// 释放时也触发回调callBack(Standard_False, theStorage, RoundSize, 0);const Standard_Size Index = INDEX_CELL(RoundSize);if ( Index <= myFreeListMax ) {myMutex.Lock();// 头插法加入链表*(Standard_Size**)aBlock = myFreeList[Index];myFreeList[Index] = aBlock;myMutex.Unlock();}else FreeMemory (aBlock, RoundSize);// 直接释放}typedef void (*TPCallBackFunc)(const Standard_Boolean theIsAlloc, const Standard_Address theStorage, const Standard_Size theRoundSize, const Standard_Size theSize);Standard_EXPORT static void SetCallBackFunction(TPCallBackFunc pFunc);// 内存分配Standard_Size* AllocMemory (Standard_Size &aSize){retry:Standard_Size * aBlock = NULL;// 使用内存映射完成分配if (myMMap) {#ifndef _WIN32const Standard_Size AlignedSize = PAGE_ALIGN(Size, myPageSize);aBlock = (Standard_Size * )mmap((char*)MMAP_BASE_ADDRESS, AlignedSize, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MMAP_FLAGS, myMMap, 0);if (aBlock == MAP_FAILED /* -1 */) {int errcode = errno;if ( Purge(Standard_False) )goto retry;throw Standard_OutOfMemory(strerror(errcode));}Size = AlignedSize;#else /* _WIN32 */const Standard_Size AlignedSize = PAGE_ALIGN(Size+sizeof(HANDLE), myPageSize);// 内存映射得到内存HANDLE hMap = CreateFileMapping(INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE, NULL, PAGE_READWRITE, DWORD(AlignedSize / 0x80000000), DWORD(AlignedSize % 0x80000000), NULL); // 获得句柄HANDLE * aMBlock = (hMap && GetLastError() != ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS ? (HANDLE*)MapViewOfFile(hMap,FILE_MAP_WRITE,0,0,0) : NULL);if ( ! aMBlock ) {if ( hMap ) CloseHandle(hMap); hMap = 0;// 无法完成分配时先清理再次尝试if ( Purge(Standard_False) )goto retry;const int BUFSIZE=1024;wchar_t message[BUFSIZE];if ( FormatMessageW (FORMAT_MESSAGE_FROM_SYSTEM, 0, GetLastError(), 0, message, BUFSIZE-1, 0) <=0 )StringCchCopyW(message, _countof(message), L"Standard_MMgrOpt::AllocMemory() failed to mmap");char messageA[BUFSIZE];WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, 0, message, -1, messageA, sizeof(messageA), NULL, NULL);throw Standard_OutOfMemory(messageA);}// 一开始存储hMapaMBlock[0] = hMap;// 块有效区域aBlock = (Standard_Size*)(aMBlock+1);// 有效区域尺寸Size = AlignedSize - sizeof(HANDLE);#endif }else {// 使用api完成分配aBlock = (Standard_Size *) (myClear ? calloc(Size,sizeof(char)) : malloc(Size));if ( ! aBlock ) {if ( Purge(Standard_False) )goto retry;throw Standard_OutOfMemory("Standard_MMgrOpt::Allocate(): malloc failed");}}if (myClear)memset (aBlock, 0, Size);return aBlock;}
};// 源文件
static Standard_MMgrOpt::TPCallBackFunc MyPCallBackFunc = NULL;
Standard_EXPORT void Standard_MMgrOpt::SetCallBackFunction(TPCallBackFunc pFunc) {MyPCallBackFunc = pFunc;
}
inline void callBack(const Standard_Boolean isAlloc,const Standard_Address aStorage, const Standard_Size aRoundSize, const Standard_Size aSize) {if (MyPCallBackFunc)(*MyPCallBackFunc)(isAlloc, aStorage, aRoundSize, aSize);
}
8.Standard_Persistent
class Standard_Persistent : public Standard_Transient {
public:DEFINE_STANDARD_ALLOCStandard_Persistent() : _typenum(0), _refnum(0) {}DEFINE_STANDARD_RTTIEXT(Standard_Persistent,Standard_Transient)Standard_Integer& TypeNum() { return _typenum; }
private:Standard_Integer _typenum;Standard_Integer _refnum;friend class Storage_Schema;
};
9.Standard_Type
class Standard_Type : public Standard_Transient {
public:Standard_CString SystemName() const { return myInfo.name(); }Standard_CString Name() const { return myName; }Standard_Size Size() const { return mySize; }const Handle(Standard_Type)& Parent () const { return myParent; }Standard_EXPORT Standard_Boolean SubType (const Handle(Standard_Type)& theOther) const{return ! theOther.IsNull() && (theOther == this || (! myParent.IsNull() && myParent->SubType (theOther)));}Standard_EXPORT Standard_Boolean SubType (const Standard_CString theOther) const{return theName != 0 && (IsEqual (myName, theName) || (! myParent.IsNull() && myParent->SubType (theName)));}Standard_EXPORT void Print (Standard_OStream& AStream) const{AStream << std::hex << (Standard_Address)this << " : " << std::dec << myName ;}template <class T>static const Handle(Standard_Type)& Instance() {return opencascade::type_instance<T>::get();}Standard_EXPORT static Standard_Type* Register (const std::type_info& theInfo, const char* theName, Standard_Size theSize, const Handle(Standard_Type)& theParent){static Standard_Mutex theMutex;Standard_Mutex::Sentry aSentry (theMutex);registry_type& aRegistry = GetRegistry();Standard_Type* aType = 0;auto anIter = aRegistry.find(theInfo);if (anIter != aRegistry.end())return anIter->second;aType = new Standard_Type (theInfo, theName, theSize, theParent);aRegistry.emplace(theInfo, aType);return aType;}Standard_EXPORT ~Standard_Type (){registry_type& aRegistry = GetRegistry();Standard_ASSERT(aRegistry.erase(myInfo) > 0, "Standard_Type::~Standard_Type() cannot find itself in registry",);}DEFINE_STANDARD_RTTIEXT(Standard_Type,Standard_Transient)
private:Standard_Type (const std::type_info& theInfo, const char* theName, Standard_Size theSize, const Handle(Standard_Type)& theParent);
private:std::type_index myInfo; //!< Object to store system name of the classStandard_CString myName; //!< Given name of the classStandard_Size mySize; //!< Size of the class instance, in bytesHandle(Standard_Type) myParent; //!< Type descriptor of parent class
};
RTTI识别系统识别类型所需的信息。
相关文章:

TKernel模块--杂项
TKernel模块–杂项 1.DEFINE_HARRAY1 #define DEFINE_HARRAY1(HClassName, _Array1Type_) \ class HClassName : public _Array1Type_, public Standard_Transient { \public: …...

充电便捷,新能源汽车移动充电服务如何预约充电
随着新能源汽车的普及,充电便捷性成为影响用户体验的关键因素之一。传统的固定充电桩受限于地理位置和数量,难以完全满足用户需求,而移动充电服务的出现,为车主提供了更加灵活的补能方式。通过手机APP、小程序或在线平台ÿ…...

laya3的2d相机与2d区域
2d相机和2d区域都继承自Sprite。 2d相机必须作为2d区域的子节点,且2d相机必须勾选isMain才能正常使用。 2d区域下如果没有主相机,则他和Sprite无异,他的主要操作皆是针对主相机。 2d相机可以调整自己的移动范围,是否紧密跟随&a…...

2024 CKA模拟系统制作 | Step-By-Step | 19、题目搭建-升级集群
目录 免费获取题库配套 CKA_v1.31_模拟系统 一、题目 二、考点分析 1. Kubernetes 升级策略 2. 节点维护操作 3. 组件升级技术 4. 权限与访问控制 三、考点详细讲解 1. Kubernetes 升级流程 2. 组件版本兼容性 3. drain 操作深度解析 四、实验环境搭建步骤 五、总…...
)
47道ES67高频题整理(附答案背诵版)
1.ES5、ES6(ES2015)有什么区别? ES5(ECMAScript 5)和ES6(也称为ECMAScript 2015)是JavaScript语言的两个版本,它们之间有一些重要的区别和改进: let 和 const 关键字: …...

Lauterbach TRACE32专栏
官方培训视频 trace32使用技巧博文 系统崩溃分析 - vmcore 加载到 Trace32 Trace 32 离线 dump 分析环境搭建方法 内核trace分析工具入门 如何用Trace32分析内核死机 trace32调试攻略 TRACE32调试:基础调试技巧之SystemMode、SNOOPer https://cloud.tencent…...

基于 Chrome 浏览器扩展的Chroma简易图形化界面
简介 ChromaDB Manager 是基于 Chrome 浏览器扩展的一款 ChromaDB(一个流行的向量数据库)的数据查询工具。提供了一个用户友好的界面,可以直接从浏览器连接到本地 ChromaDB 实例、查看集合信息和分片数据。本工具特别适合开发人员快速查看和…...

python打卡day41
简单CNN 数据增强卷积神经网络定义的写法batch归一化:调整一个批次的分布,常用与图像数据特征图:只有卷积操作输出的才叫特征图调度器:直接修改基础学习率 一、数据增强 在图像数据预处理环节,为提升数据多样性&#x…...

IM系统的负载均衡
1.IM场景的负载均衡 2.方案总览 SDK层想要连接一个TCP网关或者WebSocket网关的方案 SDK单地址:在SDK中写死某个网关的IP或者域名,缺点是更换地址需要重新打包SDK SDK多地址:防止某一个地址嗝屁了写上多个地址用足保持高可用 暴露接口给客户端:SDK层访问接口动态获得地址 注…...

前端八股 tcp 和 udp
都是传输层协议 udp 数据报协议 不可靠面向数据包对于应用层传递的报文加上UDP首部就传给网络层 tcp 传输控制协议 可靠 会将报文分段进行传输 区别: 1.tcp 可靠 udp 不可靠 2.tcp 面向连接 三握四挥 udp 无连接 3.tcp面向字节流 udp面向报文 4.效率低 效率高…...

使用 Zabbix 监控 MySQL 存储空间和性能指标的完整实践指南
目录 引言 一、最终目标支持功能 二、监控方案设计 2.1 技术选型 2.2 设计思路 三、实现步骤 3.1 准备工作 3.11 创建 MySQL 监控账号 3.12 配置 .my.cnf 文件 3.2 编写统一脚本 3.3 配置 Zabbix Agent UserParameter 3.4 Zabbix 前端配置建议 四、总结 引言 MySQL …...

【技能拾遗】——家庭宽带单线复用布线与配置(移动2025版)
📖 前言:在家庭网络拓扑中,客厅到弱电箱只预埋了一根网线,由于已将广电的有线电视取消并改用IPTV。现在需要解决在客厅布置路由器和观看IPTV问题,这里就用到单线复用技术。 目录 🕒 1. 拓扑规划ὕ…...

异步日志监控:FastAPI与MongoDB的高效整合之道
title: 异步日志监控:FastAPI与MongoDB的高效整合之道 date: 2025/05/27 17:49:39 updated: 2025/05/27 17:49:39 author: cmdragon excerpt: FastAPI与MongoDB整合实现日志监控系统的实战指南。首先配置MongoDB异步连接,定义日志数据模型。核心功能包括日志写入接口、聚合…...

在 Android 上备份短信:保护您的对话
尽管我们的Android手机有足够的存储空间来存储无数的短信,但由于设备故障、意外删除或其他意外原因,您可能会丢失重要的对话。幸运的是,我们找到了 5 种有效的 Android SMS 备份解决方案,确保您的数字聊天和信息保持安全且可访问。…...

标题:2025海外短剧爆发年:APP+H5双端系统开发,解锁全球流量与变现新大陆
描述: 2025年出海新风口!深度解析海外短剧系统开发核心(APPH5双端),揭秘高效开发策略与商业化路径,助您抢占万亿美元市场! 全球娱乐消费模式正在剧变。2025年,海外短剧市场已从蓝海…...

解决RAGFlow(v0.19.0)有部分PDF无法解析成功的问题。
ragflow版本为:v0.19.0 1.解析的时候报错:Internal server error while chunking: Coordinate lower is less than upper。 看报错怀疑是分片的问题,于是把文档的切片方法中的“建议文本块大小”数值(默认512)调小&…...

c#基础08(数组)
文章目录 数组数组概念声明数组初始化数组赋值给数组访问数组元素 集合动态数组(ArrayList)使用foreach循环C#数组细节多维数组传递数组给函数参数数组 数组 数组概念 数组是一个存储相同类型元素的固定大小的顺序集合。数组是用来存储数据的集合,通常认为数组是一…...

嵌入式学习--江协stm32day3
这是我目前为止认为最重要的模块--TIM定时器,这里我们主要学习通用定时器 最小的计数计时单元为时基单元,包括PSC,ARR,CNT CK_PSC(Prescaler,预分频器):作用是对输入时钟信号进行分…...

docker-记录一次容器日志<container_id>-json.log超大问题的处理
文章目录 现象一、查找源头二、分析总结 现象 同事联系说部署在虚拟机里面的用docker启动xxl-job的服务不好使了,需要解决一下,我就登陆虚拟机检查,发现根目录满了,就一层一层的找,发现是<container_id>-json.l…...

4.8.1 利用Spark SQL实现词频统计
在利用Spark SQL实现词频统计的实战中,首先需要准备单词文件并上传至HDFS。接着,可以通过交互式方法或创建Spark项目来实现词频统计。交互式方法包括读取文本文件生成数据集,扁平化映射得到新数据集,然后将数据集转成数据帧&#…...
)
头歌java课程实验(Java面向对象 - 包装类)
第1关:基本数据类型和包装类之间的转换 任务描述 本关任务:实现基本数据类型与包装类之间的互相转换。 相关知识 为了完成本关任务,你需要掌握: 1.什么是包装类; 2.怎么使用包装类。 什么是包装类 在JAVA中&#x…...

经济法-7-上市公司首次发行、配股增发条件
一、首次公开发行股票条件 事项 条件存续时间,持续经营能力 持续经营3年以上的股份公司 具有持续经营能力 内部控制制度具备健全且运行良好的组织机构财务最近3年财务会计报告被出具无保留意见审计报告公司治理 1)最近3年内,发行人及…...
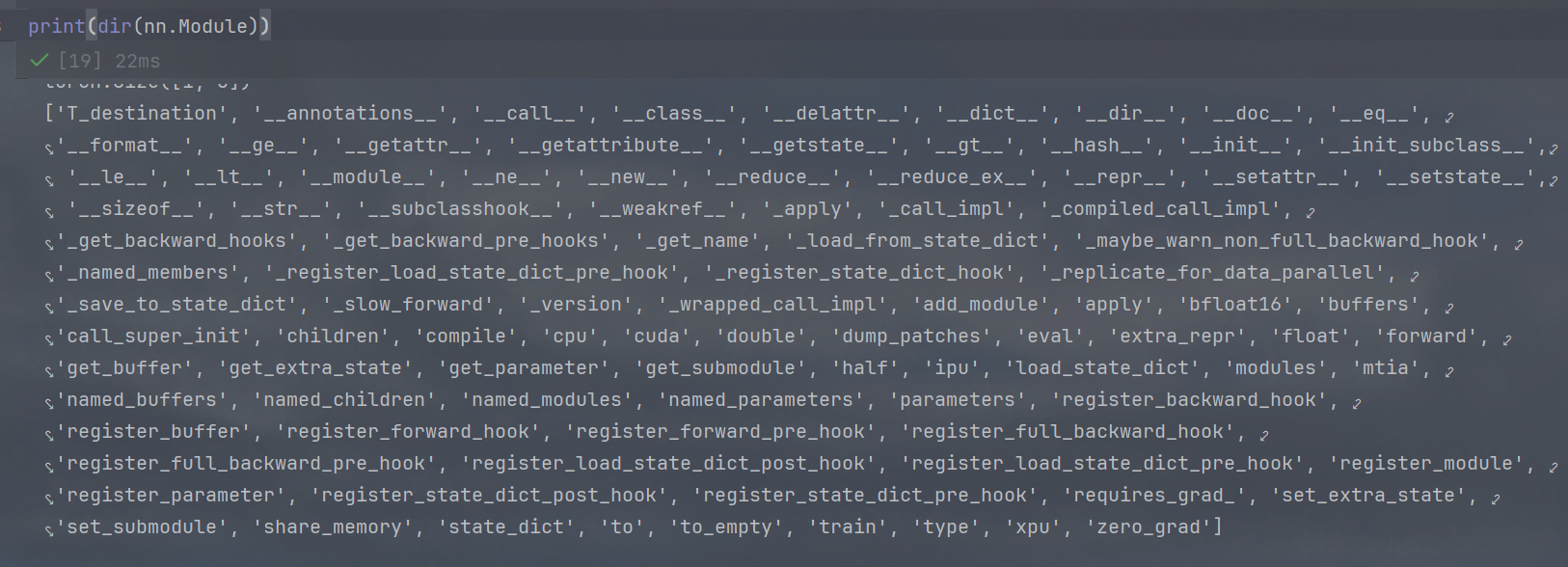
PyTorch中nn.Module详解
直接print(dir(nn.Module)),得到如下内容: 一、模型结构与参数 parameters() 用途:返回模块的所有可训练参数(如权重、偏置)。示例:for param in model.parameters():print(param.shape)named_parameters…...

Mac 每日磁盘写入量异常高
为什么你的 Mac 每日磁盘写入量异常高?深度分析与解决方案 文章目录 为什么你的 Mac 每日磁盘写入量异常高?深度分析与解决方案🔍 问题现象🕵️♂️ 六大罪魁祸首1. 系统日志疯狂输出典型场景: 2. 浏览器缓存3. Ti…...

《深入解析Go语言结构:简洁高效的工程化设计》
《深入解析Go语言结构:简洁高效的工程化设计》 引言 Go语言(Golang)由Google团队于2009年发布,专为现代分布式系统和云计算设计。其核心哲学是"简单性高于一切",通过精简的语法结构和创新的…...

[蓝桥杯]机器人塔
题目描述 X 星球的机器人表演拉拉队有两种服装,A 和 B。 他们这次表演的是搭机器人塔。 类似: A B B A B A A A B B B B B A B A B A B B A 队内的组塔规则是: A 只能站在 AA 或 BB 的肩上。 B 只能站在 AB 或 BA 的肩上。 你的…...

如何将vue2使用npm run build打包好的文件上传到服务器
要将 Vue 2 项目打包并部署到服务器上,并使用 Nginx 作为 Web 服务器,可以按照以下步骤操作: 1. 打包 Vue 2 项目 首先,确保你的 Vue 2 项目已经开发完成,并且可以在本地正常运行。然后使用以下命令进行打包…...

Ubuntu 22.04 系统下 Docker 安装与配置全指南
Ubuntu 22.04 系统下 Docker 安装与配置全指南 一、前言 Docker 作为现代开发中不可或缺的容器化工具,能极大提升应用部署和环境管理的效率。本文将详细介绍在 Ubuntu 22.04 系统上安装与配置 Docker 的完整流程,包括环境准备、安装步骤、权限配置及镜…...

动态表单开发避坑:改变input的值不会触发change事件即时修复策略-WdatePicker ——仙盟创梦IDE
原始传统模式 onchange <input onchange"未来之窗东方仙盟change(this)" oni > <script>function 未来之窗东方仙盟change(onj){console.log("未来之窗东方仙盟change",onj.value)} </script> 测试 原始传统模式 oninput <input …...

10.安卓逆向2-frida hook技术-frida基本使用-frida指令(用于hook)
免责声明:内容仅供学习参考,请合法利用知识,禁止进行违法犯罪活动! 内容参考于:图灵Python学院 工具下载: 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bb8NhJc9eTuLzQr39lF55Q?pwdzy89 提取码࿱…...
