自然语言处理从入门到应用——LangChain:记忆(Memory)-[记忆的类型Ⅱ]
分类目录:《自然语言处理从入门到应用》总目录
对话知识图谱记忆(Conversation Knowledge Graph Memory)
这种类型的记忆使用知识图谱来重建记忆:
from langchain.memory import ConversationKGMemory
from langchain.llms import OpenAIllm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
memory = ConversationKGMemory(llm=llm)
memory.save_context({"input": "say hi to sam"}, {"output": "who is sam"})
memory.save_context({"input": "sam is a friend"}, {"output": "okay"})
memory.load_memory_variables({"input": 'who is sam'})
输出:
{'history': 'On Sam: Sam is friend.'}
我们还可以将历史记录作为消息列表获取,如果我们与聊天模型一起使用时,这将非常有用:
memory = ConversationKGMemory(llm=llm, return_messages=True)
memory.save_context({"input": "say hi to sam"}, {"output": "who is sam"})
memory.save_context({"input": "sam is a friend"}, {"output": "okay"})
memory.load_memory_variables({"input": 'who is sam'})
输出:
{'history': [SystemMessage(content='On Sam: Sam is friend.', additional_kwargs={})]}
我们还可以更模块化地从新消息中获取当前实体,这将使用前面的消息作为上下文:
memory.get_current_entities("what's Sams favorite color?")
输出:
['Sam']
我们还可以更模块化地从新消息中获取知识三元组,这也将使用前面的消息作为上下文:
memory.get_knowledge_triplets("her favorite color is red")
输出:
[KnowledgeTriple(subject='Sam', predicate='favorite color', object_='red')]
在链中使用
现在让我们在一个链中使用这个功能:
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
from langchain.prompts.prompt import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import ConversationChaintemplate = """The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know. The AI ONLY uses information contained in the "Relevant Information" section and does not hallucinate.Relevant Information:{history}Conversation:
Human: {input}
AI:"""prompt = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["history", "input"], template=template
)
conversation_with_kg = ConversationChain(llm=llm, verbose=True, prompt=prompt,memory=ConversationKGMemory(llm=llm)
)
conversation_with_kg.predict(input="Hi, what's up?")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context.
If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know. The AI ONLY uses information contained in the "Relevant Information" section and does not hallucinate.Relevant Information:Conversation:
Human: Hi, what's up?
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
" Hi there! I'm doing great. I'm currently in the process of learning about the world around me. I'm learning about different cultures, languages, and customs. It's really fascinating! How about you?"
输入:
conversation_with_kg.predict(input="My name is James and I'm helping Will. He's an engineer.")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context.
If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know. The AI ONLY uses information contained in the "Relevant Information" section and does not hallucinate.Relevant Information:Conversation:
Human: My name is James and I'm helping Will. He's an engineer.
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
" Hi James, it's nice to meet you. I'm an AI and I understand you're helping Will, the engineer. What kind of engineering does he do?"
输入:
conversation_with_kg.predict(input="What do you know about Will?")
输入:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context.
If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know. The AI ONLY uses information contained in the "Relevant Information" section and does not hallucinate.Relevant Information:On Will: Will is an engineer.Conversation:
Human: What do you know about Will?
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
' Will is an engineer.'
对话摘要记忆ConversationSummaryMemory
现在让我们来看一下使用稍微复杂的记忆类型ConversationSummaryMemory。这种类型的记忆会随着时间的推移创建对话的摘要。这对于从对话中压缩信息非常有用。让我们首先探索一下这种类型记忆的基本功能:
from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryMemory, ChatMessageHistory
from langchain.llms import OpenAImemory = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=OpenAI(temperature=0))
memory.save_context({"input": "hi"}, {"output": "whats up"})
memory.load_memory_variables({})
输出:
{'history': '\nThe human greets the AI, to which the AI responds.'}
我们还可以将历史记录作为消息列表获取,如果我们正在与聊天模型一起使用,这将非常有用:
memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=OpenAI(temperature=0), return_messages=True)
memory.save_context({"input": "hi"}, {"output": "whats up"})
memory.load_memory_variables({})
输出:
{'history': [SystemMessage(content='\nThe human greets the AI, to which the AI responds.', additional_kwargs={})]}
我们还可以直接使用predict_new_summary方法:
messages = memory.chat_memory.messages
previous_summary = ""
memory.predict_new_summary(messages, previous_summary)
输出:
'\nThe human greets the AI, to which the AI responds.'
使用消息进行初始化
如果我们有类似的消息,则可以很容易地使用ChatMessageHistory来初始化这个类,它将会计算一个摘要在加载过程中。
history = ChatMessageHistory()
history.add_user_message("hi")
history.add_ai_message("hi there!")
memory = ConversationSummaryMemory.from_messages(llm=OpenAI(temperature=0), chat_memory=history, return_messages=True)
memory.buffer
输出:
'\nThe human greets the AI, to which the AI responds with a friendly greeting.'
在对话链中使用
让我们通过一个示例来演示在对话链中使用这个功能,同样设置verbose=True以便我们可以看到提示。
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0)
conversation_with_summary = ConversationChain(llm=llm, memory=ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=OpenAI()),verbose=True
)
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="Hi, what's up?")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation:Human: Hi, what's up?
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
" Hi there! I'm doing great. I'm currently helping a customer with a technical issue. How about you?"
输入:
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="Tell me more about it!")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation:The human greeted the AI and asked how it was doing. The AI replied that it was doing great and was currently helping a customer with a technical issue.
Human: Tell me more about it!
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
" Sure! The customer is having trouble with their computer not connecting to the internet. I'm helping them troubleshoot the issue and figure out what the problem is. So far, we've tried resetting the router and checking the network settings, but the issue still persists. We're currently looking into other possible solutions."
输入:
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="Very cool -- what is the scope of the project?")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation:The human greeted the AI and asked how it was doing. The AI replied that it was doing great and was currently helping a customer with a technical issue where their computer was not connecting to the internet. The AI was troubleshooting the issue and had already tried resetting the router and checking the network settings, but the issue still persisted and they were looking into other possible solutions.
Human: Very cool -- what is the scope of the project?
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
" The scope of the project is to troubleshoot the customer's computer issue and find a solution that will allow them to connect to the internet. We are currently exploring different possibilities and have already tried resetting the router and checking the network settings, but the issue still persists."
会话摘要缓冲记忆 ConversationSummaryBufferMemory
ConversationSummaryBufferMemory将ConversationBufferMemory和ConversationSummaryMemory的概念结合起来。它在内存中保留了最近的一些对话交互,并将它们编译成一个摘要。与先前的实现不同,它使用标记长度来确定何时刷新交互,而不是交互数量。
from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryBufferMemory
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
llm = OpenAI()
memory = ConversationSummaryBufferMemory(llm=llm, max_token_limit=10)
memory.save_context({"input": "hi"}, {"output": "whats up"})
memory.save_context({"input": "not much you"}, {"output": "not much"})
memory.load_memory_variables({})
输出:
{'history': 'System: \nThe human says "hi", and the AI responds with "whats up".\nHuman: not much you\nAI: not much'}
我们还可以将历史记录作为消息列表获取,如果我们正在与聊天模型一起使用,将非常有用:
memory = ConversationSummaryBufferMemory(llm=llm, max_token_limit=10, return_messages=True)
memory.save_context({"input": "hi"}, {"output": "whats up"})
memory.save_context({"input": "not much you"}, {"output": "not much"})
我们还可以直接利用predict_new_summary方法:
messages = memory.chat_memory.messages
previous_summary = ""
memory.predict_new_summary(messages, previous_summary)
输出:
'\nThe human and AI state that they are not doing much.'
在链式结构中的使用
让我们通过一个例子来演示在链式结构中的使用ConversationSummaryBufferMemory,我们同样设置verbose=True以便我们可以看到提示信息:
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
conversation_with_summary = ConversationChain(llm=llm, # We set a very low max_token_limit for the purposes of testing.memory=ConversationSummaryBufferMemory(llm=OpenAI(), max_token_limit=40),verbose=True
)
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="Hi, what's up?")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation:Human: Hi, what's up?
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
" Hi there! I'm doing great. I'm learning about the latest advances in artificial intelligence. What about you?"
输入:
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="Just working on writing some documentation!")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation:
Human: Hi, what's up?
AI: Hi there! I'm doing great. I'm spending some time learning about the latest developments in AI technology. How about you?
Human: Just working on writing some documentation!
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
' That sounds like a great use of your time. Do you have experience with writing documentation?'
输入:
# We can see here that there is a summary of the conversation and then some previous interactions
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="For LangChain! Have you heard of it?")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation:
System:
The human asked the AI what it was up to and the AI responded that it was learning about the latest developments in AI technology.
Human: Just working on writing some documentation!
AI: That sounds like a great use of your time. Do you have experience with writing documentation?
Human: For LangChain! Have you heard of it?
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
" No, I haven't heard of LangChain. Can you tell me more about it?"
输入:
# We can see here that the summary and the buffer are updated
conversation_with_summary.predict(input="Haha nope, although a lot of people confuse it for that")
日志输出:
> Entering new ConversationChain chain...
Prompt after formatting:
The following is a friendly conversation between a human and an AI. The AI is talkative and provides lots of specific details from its context. If the AI does not know the answer to a question, it truthfully says it does not know.Current conversation:
System:
The human asked the AI what it was up to and the AI responded that it was learning about the latest developments in AI technology. The human then mentioned they were writing documentation, to which the AI responded that it sounded like a great use of their time and asked if they had experience with writing documentation.
Human: For LangChain! Have you heard of it?
AI: No, I haven't heard of LangChain. Can you tell me more about it?
Human: Haha nope, although a lot of people confuse it for that
AI:> Finished chain.
输出:
' Oh, okay. What is LangChain?'
参考文献:
[1] LangChain官方网站:https://www.langchain.com/
[2] LangChain 🦜️🔗 中文网,跟着LangChain一起学LLM/GPT开发:https://www.langchain.com.cn/
[3] LangChain中文网 - LangChain 是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架:http://www.cnlangchain.com/
相关文章:
-[记忆的类型Ⅱ])
自然语言处理从入门到应用——LangChain:记忆(Memory)-[记忆的类型Ⅱ]
分类目录:《自然语言处理从入门到应用》总目录 对话知识图谱记忆(Conversation Knowledge Graph Memory) 这种类型的记忆使用知识图谱来重建记忆: from langchain.memory import ConversationKGMemory from langchain.llms impo…...
桥接模式-java实现
桥接模式 桥接模式的本质,是解决一个基类,存在多个扩展维度的的问题。 比如一个图形基类,从颜色方面扩展和从形状上扩展,我们都需要这两个维度进行扩展,这就意味着,我们需要创建一个图形子类的同时&#x…...

Linux systemd管理常用的几个小案例
systemd是目前Linux系统上主要的系统守护进程管理工具,配置文件要以.service结尾且放到 /usr/lib/systemd/system/目录下面 1、systemd管理ElasticSearch [Unit] DescriptionElasticsearch Service[Service] Typeforking Userelastic Groupelastic ExecStart/home…...
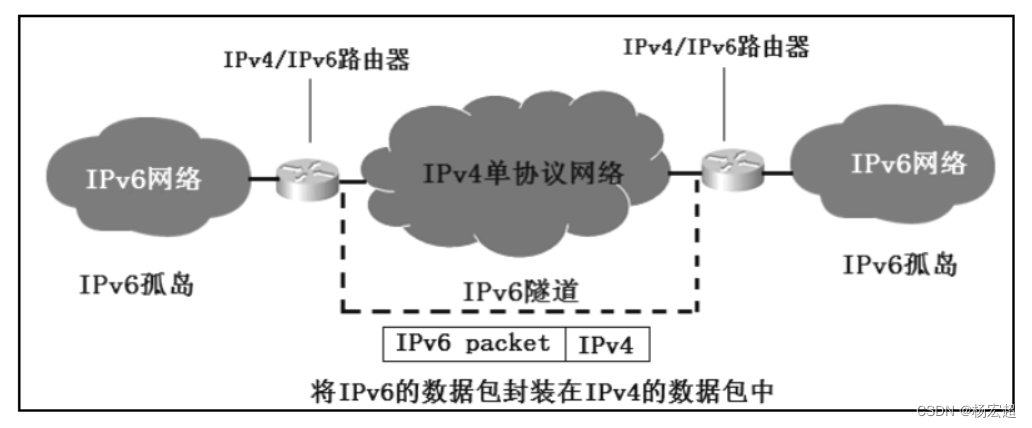
38、IPv6过渡技术
本节内容作为IPv6相关知识的最后一节内容,同时也作为我们本专栏网络层知识的最后一节内容,主要介绍从IPv4地址到IPv6地址过渡的相关技术。在这里我们只学习各类考试中常考的三种技术。 IPv4向IPv6的过渡 在前面的知识中,我们学习到了两种IP地…...

HMMER-序列分析软件介绍
HMMER是一个软件包,它提供了制作蛋白质和DNA序列域家族概率模型的工具,称为轮廓隐马尔可夫模型、轮廓HMM或仅轮廓,并使用这些轮廓来注释新序列、搜索序列数据库以寻找其他同源物,以及进行深度多重序列比对。HMMER是已知蛋白质和DN…...
【项目学习1】如何将java对象转化为XML字符串
如何将java对象转化为XML字符串 将java对象转化为XML字符串,可以使用Java的XML操作库JAXB,具体操作步骤如下: 主要分为以下几步: 1、创建JAXBContext对象,用于映射Java类和XML。 JAXBContext jaxbContext JAXBConte…...

nginx负载均衡
负载均衡:反向代理来实现 正向代理的配置方法。 1、NGINX的七层代理和四层代理: 七层是最常用的反向代理方式,只能配置在nginx配置文件的http模块。而且配置方法名称:upstream 模块,不能写在server中,也…...
【毕业项目】自主设计HTTP
博客介绍:运用之前学过的各种知识 自己独立做出一个HTTP服务器 自主设计WEB服务器 背景目标描述技术特点项目定位开发环境WWW介绍 网络协议栈介绍网络协议栈整体网络协议栈细节与http相关的重要协议 HTTP背景知识补充特点uri & url & urn网址url HTTP请求和…...
关于安卓jar包修改并且重新发布
背景: 对于某些jar包,其内部是存在bug的,解决的方法无外乎就有以下几种方法: (1)通过反射,修改其赋值逻辑 (2)通过继承,重写其方法 (3࿰…...

Java课题笔记~ AspectJ 对 AOP 的实现(掌握)
AspectJ 对 AOP 的实现(掌握) 对于 AOP 这种编程思想,很多框架都进行了实现。Spring 就是其中之一,可以完成面向切面编程。然而,AspectJ 也实现了 AOP 的功能,且其实现方式更为简捷,使用更为方便,而且还支…...
npm 报错 cb() never called!
不知道有没有跟我一样的情况,在使用npm i的时候一直报错:cb() never called! 换了很多个node版本,还是不行,无法解决这个问题 百度也只是让降低node版本请缓存,gpt给出的解决方案也是同样的 但是缓存清过很多次了&a…...

finally有什么作用以及常用场景
在Java中,finally是一个关键字,用于定义一个代码块,该代码块中的代码无论是否发生异常都会被执行。finally块通常用于确保在程序执行过程中资源的释放和清理。 使用场景: 1. 资源释放:finally块经常用于释放打开的资…...

Python web实战之Django URL路由详解
概要 技术栈:Python、Django、Web开发、URL路由 Django是一种流行的Web应用程序框架,它采用了与其他主流框架类似的URL路由机制。URL路由是指将传入的URL请求映射到相应的视图函数或处理程序的过程。 什么是URL路由? URL路由是Web开发中非常…...
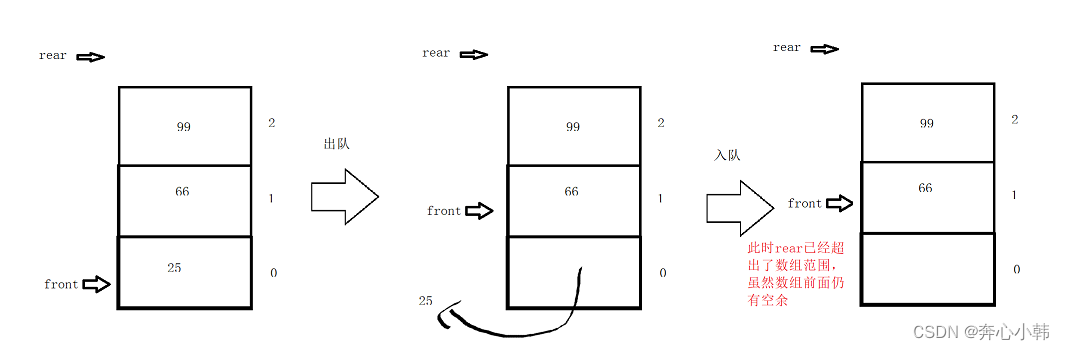
10-数据结构-队列(C语言)
队列 目录 目录 队列 一、队列基础知识 二、队列的基本操作 1.顺序存储 编辑 (1)顺序存储 (2)初始化及队空队满 (3)入队 (4)出队 (5)打印队列 &…...

面试之快速学习C++11 - 右值 移动构造 std::move
C11右值引用 字面意思,以引用传递的方式使用c右值左值和右值,左值是lvalue loactor value 存储在内存中,有明确存储地址的数据, 右值rvalue read value , 指的是那些可以提供数据值的数据(不一定可以寻址,…...
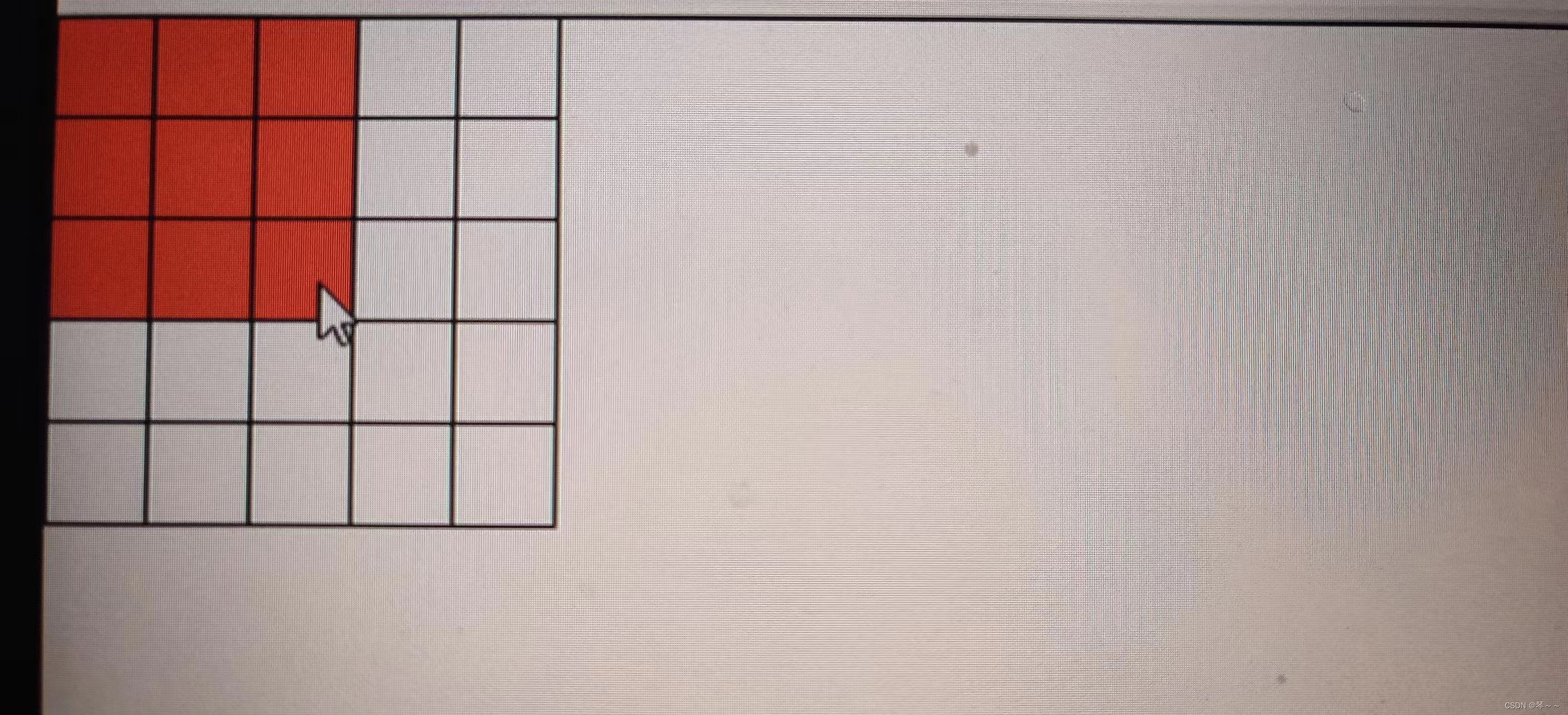
vue实现5*5宫格当鼠标滑过选中的正方形背景颜色统一变色
vue实现5*5宫格当鼠标滑过选中的正方形背景颜色统一变色 1、实现的效果 2、完整代码展示 <template><div id"app" mouseleave"handleMouseLeave({row: 0, col: 0 })"><div v-for"rowItem in squareNumber" :key"rowItem…...

2023-08-09 LeetCode每日一题(整数的各位积和之差)
2023-08-09每日一题 一、题目编号 1281. 整数的各位积和之差二、题目链接 点击跳转到题目位置 三、题目描述 给你一个整数 n,请你帮忙计算并返回该整数「各位数字之积」与「各位数字之和」的差。 示例1: 示例2: 提示: 1 …...
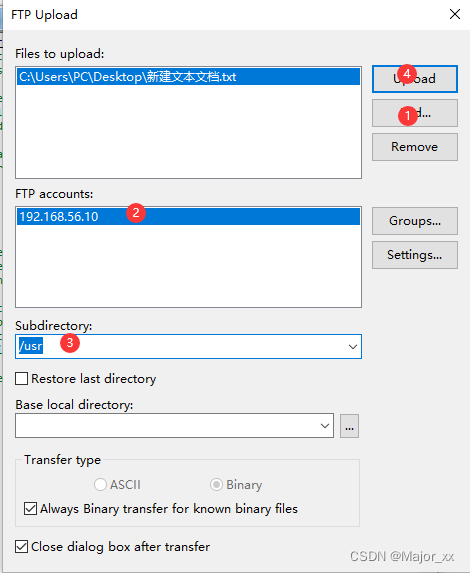
EditPlus连接Linux系统远程操作文件
EditPlus是一套功能强大的文本编辑器! 1.File ->FTP->FTP Settings; 2.Add->Description->FTP server->Username->Password->Subdirectory->Advanced Options 注意:这里的Subdirectory设置的是以后上传文件的默认…...

JVM 垃圾回收
垃圾回收算法 标记-清除算法(Mark and Sweep) 标记-清除算法分为两个阶段。在标记阶段,垃圾收集器会标记所有活动对象;在清除阶段,垃圾收集器会清除所有未标记的对象。标记-清除算法存在的问题是会产生内存碎片&#…...
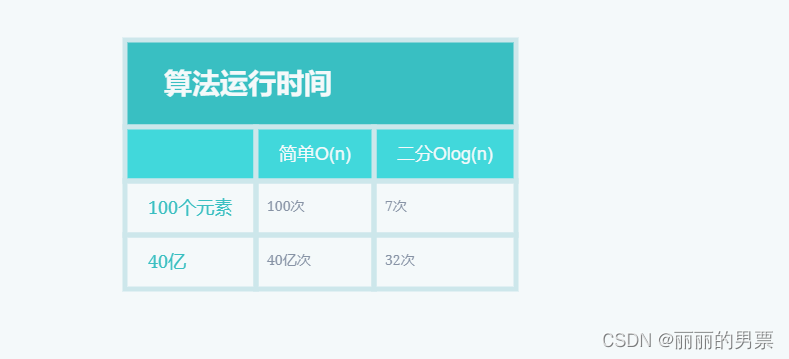
编程中的宝藏:二分查找
二分查找 假设你需要在电话簿中找到一个以字母 “K” 开头的名字(虽然现在谁还在用电话簿呢!)。你可以从头开始翻页,直到进入以 “K” 打头的部分。然而,更明智的方法是从中间开始,因为你知道以 “K” 打头…...
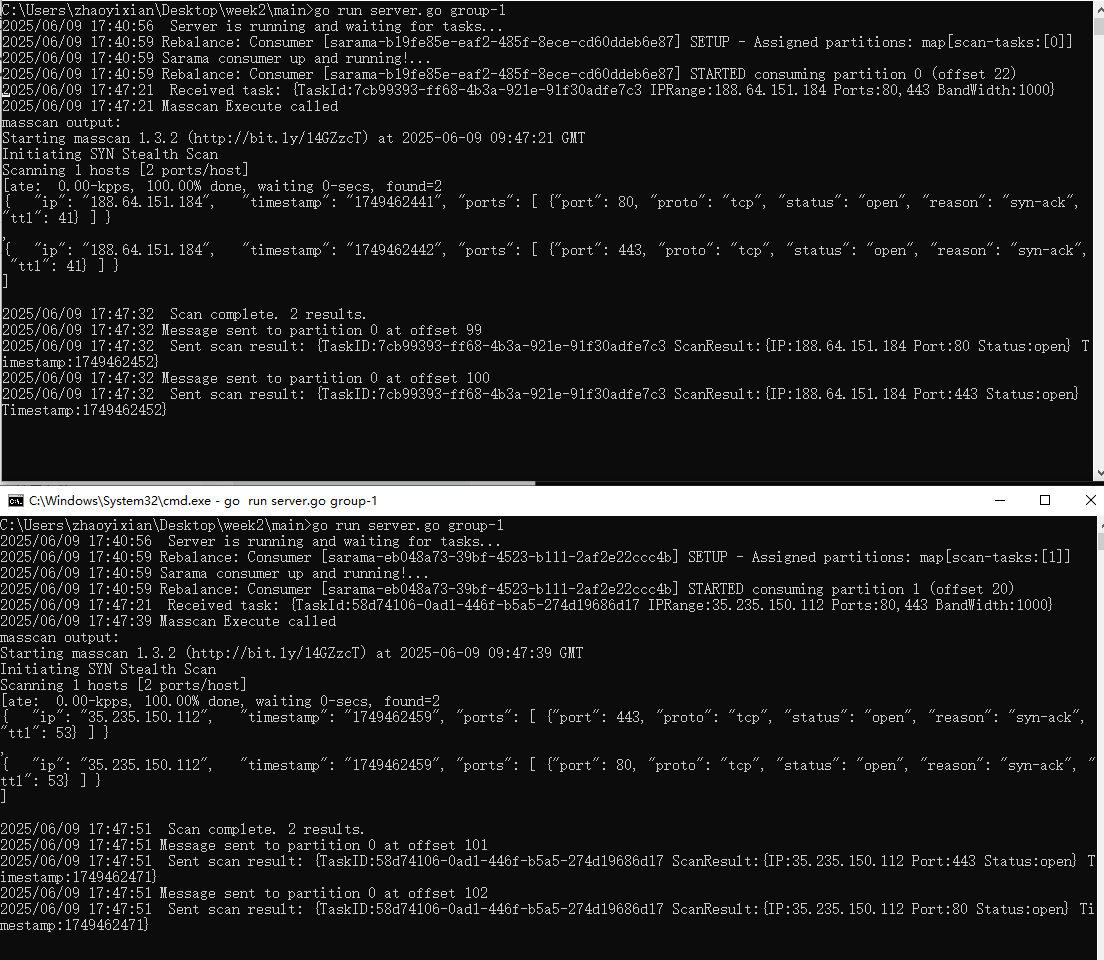
【kafka】Golang实现分布式Masscan任务调度系统
要求: 输出两个程序,一个命令行程序(命令行参数用flag)和一个服务端程序。 命令行程序支持通过命令行参数配置下发IP或IP段、端口、扫描带宽,然后将消息推送到kafka里面。 服务端程序: 从kafka消费者接收…...

在鸿蒙HarmonyOS 5中实现抖音风格的点赞功能
下面我将详细介绍如何使用HarmonyOS SDK在HarmonyOS 5中实现类似抖音的点赞功能,包括动画效果、数据同步和交互优化。 1. 基础点赞功能实现 1.1 创建数据模型 // VideoModel.ets export class VideoModel {id: string "";title: string ""…...
通过Wrangler CLI在worker中创建数据库和表
官方使用文档:Getting started Cloudflare D1 docs 创建数据库 在命令行中执行完成之后,会在本地和远程创建数据库: npx wranglerlatest d1 create prod-d1-tutorial 在cf中就可以看到数据库: 现在,您的Cloudfla…...

Java如何权衡是使用无序的数组还是有序的数组
在 Java 中,选择有序数组还是无序数组取决于具体场景的性能需求与操作特点。以下是关键权衡因素及决策指南: ⚖️ 核心权衡维度 维度有序数组无序数组查询性能二分查找 O(log n) ✅线性扫描 O(n) ❌插入/删除需移位维护顺序 O(n) ❌直接操作尾部 O(1) ✅内存开销与无序数组相…...
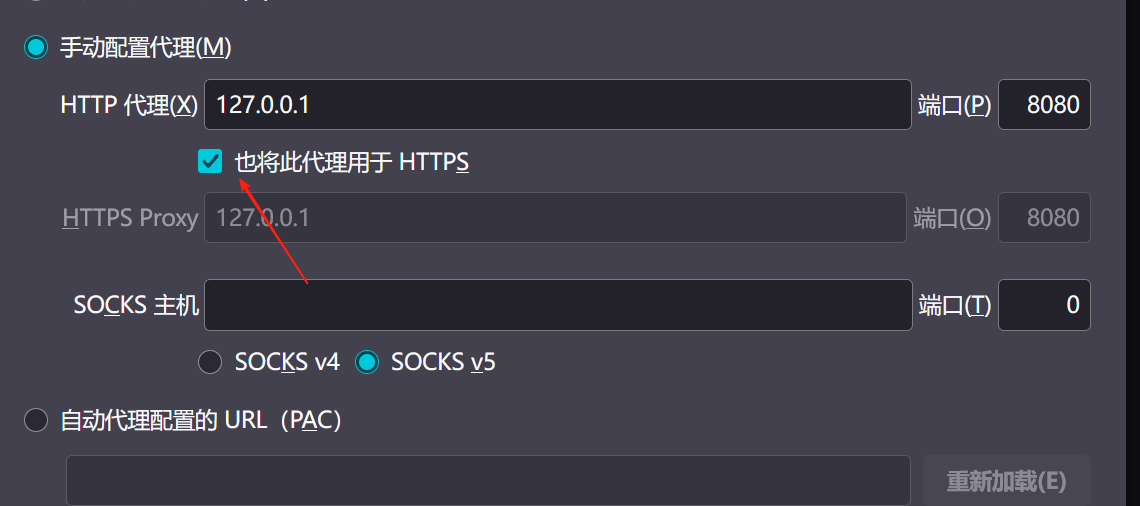
【2025年】解决Burpsuite抓不到https包的问题
环境:windows11 burpsuite:2025.5 在抓取https网站时,burpsuite抓取不到https数据包,只显示: 解决该问题只需如下三个步骤: 1、浏览器中访问 http://burp 2、下载 CA certificate 证书 3、在设置--隐私与安全--…...
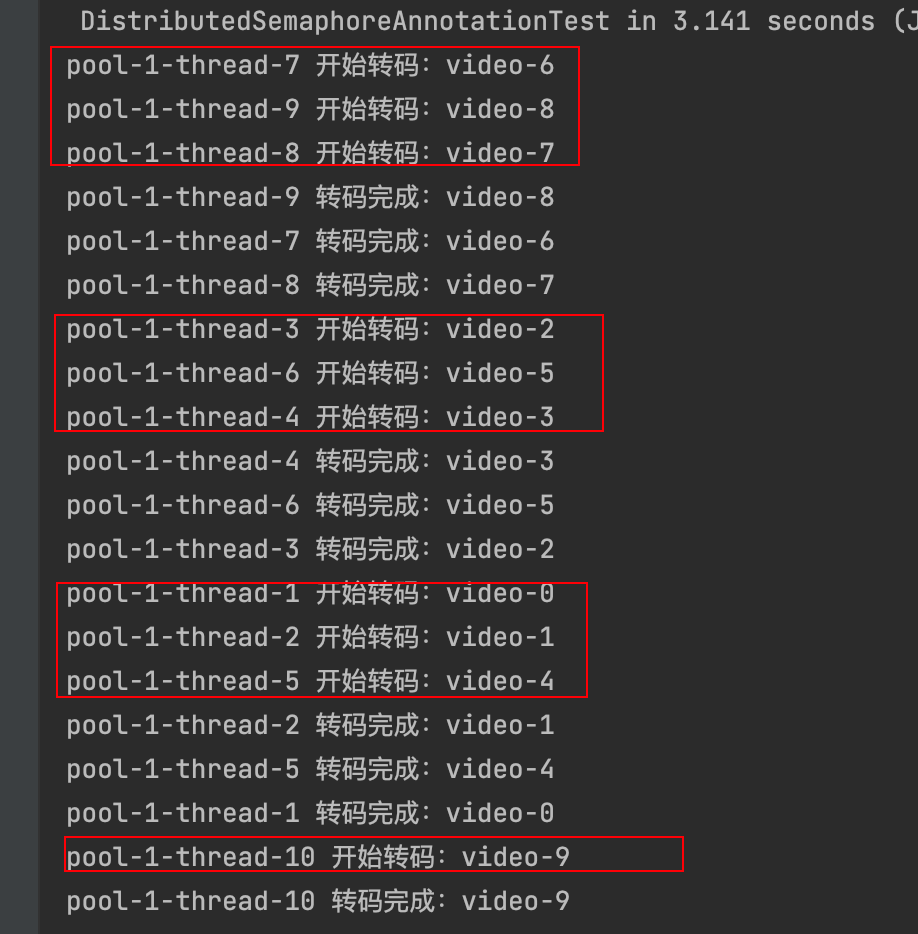
令牌桶 滑动窗口->限流 分布式信号量->限并发的原理 lua脚本分析介绍
文章目录 前言限流限制并发的实际理解限流令牌桶代码实现结果分析令牌桶lua的模拟实现原理总结: 滑动窗口代码实现结果分析lua脚本原理解析 限并发分布式信号量代码实现结果分析lua脚本实现原理 双注解去实现限流 并发结果分析: 实际业务去理解体会统一注…...

HTML前端开发:JavaScript 常用事件详解
作为前端开发的核心,JavaScript 事件是用户与网页交互的基础。以下是常见事件的详细说明和用法示例: 1. onclick - 点击事件 当元素被单击时触发(左键点击) button.onclick function() {alert("按钮被点击了!&…...
免费数学几何作图web平台
光锐软件免费数学工具,maths,数学制图,数学作图,几何作图,几何,AR开发,AR教育,增强现实,软件公司,XR,MR,VR,虚拟仿真,虚拟现实,混合现实,教育科技产品,职业模拟培训,高保真VR场景,结构互动课件,元宇宙http://xaglare.c…...

【学习笔记】erase 删除顺序迭代器后迭代器失效的解决方案
目录 使用 erase 返回值继续迭代使用索引进行遍历 我们知道类似 vector 的顺序迭代器被删除后,迭代器会失效,因为顺序迭代器在内存中是连续存储的,元素删除后,后续元素会前移。 但一些场景中,我们又需要在执行删除操作…...

实战三:开发网页端界面完成黑白视频转为彩色视频
一、需求描述 设计一个简单的视频上色应用,用户可以通过网页界面上传黑白视频,系统会自动将其转换为彩色视频。整个过程对用户来说非常简单直观,不需要了解技术细节。 效果图 二、实现思路 总体思路: 用户通过Gradio界面上…...
