Mybatis 源码 ② :流程分析
文章目录
- 一、前言
- 二、Mybatis 初始化
- 1. AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar
- 2. MapperScannerConfigurer
- 3. ClassPathMapperScanner
- 3.1 ClassPathMapperScanner#scan
- 3.2 ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions
- 4. 总结
- 三、 Mapper Interface 的创建
- 1. MapperFactoryBean
- 1.1 MapperFactoryBean#checkDaoConfig
- 1.2 MapperFactoryBean#getObject
- 2. Configuration
- 2.1 MapperRegistry
- 2.1.1 MapperRegistry#addMapper
- 2.1.2 MapperRegistry#getMapper
- 3. MapperProxy
- 4. MapperMethod
- 4.1 MapperMethod 构造方法
- 4.1.1 SqlCommand
- 4.1.2 MethodSignature
- 4.2 MapperMethod#execute
- 4.2.1 ParamNameResolver
- 4.3 Select 查询
- 4.3.1 MapperMethod#executeWithResultHandler
- 4.3.2 MapperMethod#executeForMany
- 4.3.3 MapperMethod#executeForMap
- 4.3.4 MapperMethod#executeForCursor
- 4.3.5 其他情况
- 四、流程总结
- 1. Mapper 初始化
- 2. Mapper 代理对象的创建
- 3. Mapper 方法的执行
一、前言
Mybatis 官网 以及 本系列文章地址:
- Mybatis 源码 ① :开篇
- Mybatis 源码 ② :流程分析
- Mybatis 源码 ③ :SqlSession
- Mybatis 源码 ④ :TypeHandler
- Mybatis 源码 ∞ :杂七杂八
在 Mybatis 源码 ① :开篇 中 我们整体简单介绍了下Mybatis ,下面我们来对SpringBoot 中 Mybatis 的源码做具体分析
下面我们按照 SpringBoot 自动装配作为入口来进行分析。
二、Mybatis 初始化
我们上面提到过, SpringBoot 通过自动装配会装载 AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 类,下面我们来看:
1. AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar
AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 的会在 容器启动时 扫描所有被 @Mapper 注解修饰的接口(下面我们成为 Mapper Interface),并为其创建 Mybatis 代理对象。
AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 是在 MybatisAutoConfiguration 中注册的, 如下:
// 当容器中没有注入 MapperFactoryBean、MapperScannerConfigurer 时 则引入 AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration@Import(AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar.class)@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ MapperFactoryBean.class, MapperScannerConfigurer.class })public static class MapperScannerRegistrarNotFoundConfiguration implements InitializingBean {@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() {// 日志打印}}
AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 的类图如下 :
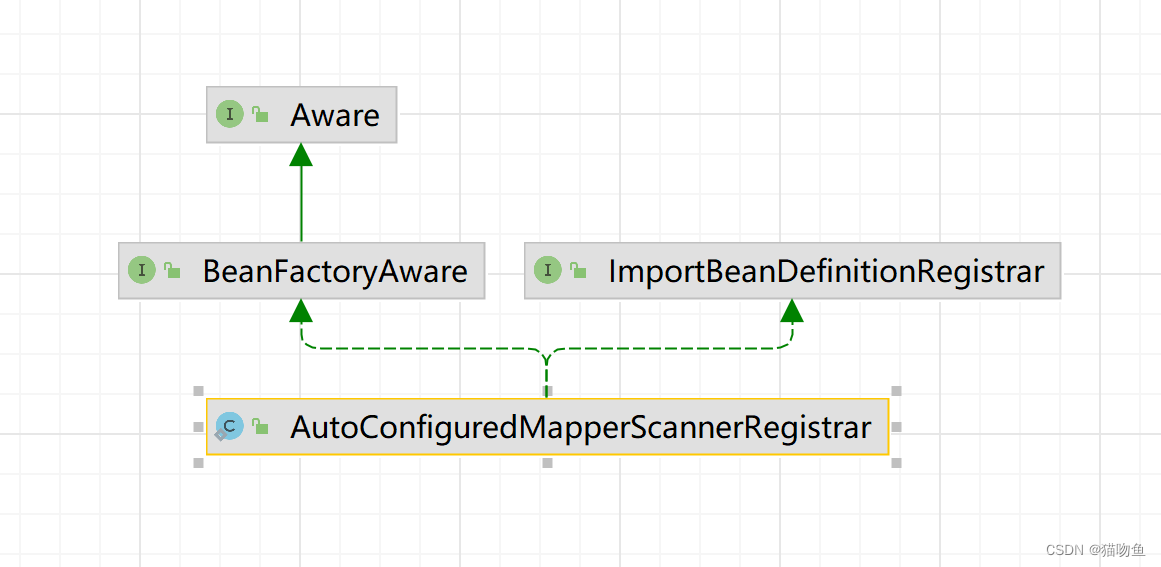
可以看到 AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 是实现了 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口的,所以需要关注AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions 方法的实现,该方法的作用是将 MapperScannerConfigurer 的 BeanDefinition 注册到容器中, 如下 :
@Overridepublic void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {// 是否启用自动装配功能,在 @EnableAutoConfiguration 注解中会通过 AutoConfigurationPackage 注解引入 AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar 来注册该类,有该类存在容器中则说明自动装配启用了if (!AutoConfigurationPackages.has(this.beanFactory)) {return;}// 获取自动装配指定的目录List<String> packages = AutoConfigurationPackages.get(this.beanFactory);// 创建 MapperScannerConfigurer 类的 BeanDefinition 构建器,扫描 packages 目录下的被 @Mapper 注解修饰的 Bean BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);// 是否处理占位符builder.addPropertyValue("processPropertyPlaceHolders", true);// 扫描 Mapper 注解builder.addPropertyValue("annotationClass", Mapper.class);// 设置扫描目录builder.addPropertyValue("basePackage", StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(packages));BeanWrapper beanWrapper = new BeanWrapperImpl(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);Set<String> propertyNames = Stream.of(beanWrapper.getPropertyDescriptors()).map(PropertyDescriptor::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());// 设置一些 Mybatis 属性if (propertyNames.contains("lazyInitialization")) {// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+builder.addPropertyValue("lazyInitialization", "${mybatis.lazy-initialization:false}");}if (propertyNames.contains("defaultScope")) {// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.6+builder.addPropertyValue("defaultScope", "${mybatis.mapper-default-scope:}");}// 将 MapperScannerConfigurer 的 BeanDefinition 注册到容器中。registry.registerBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class.getName(), builder.getBeanDefinition());}
可以看到,这里 AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions 的作用是将 MapperScannerConfigurer 的 BeanDefinition 注册到容器中 (需要注意的是,这里是注入的 BeanDefinition 对象,而非 Bean 对象,因为Spring 容器在创建Bean的时候会先创建Bean 的BeanDefinition ,BeanDefinition 中保存了Bean的各种基本信息,如类名、作用域等,在Spring后续逻辑中会根据 BeanDefinition 创建出对应的Bean),后续Spring 容器会创建 MapperScannerConfigurer 对象。下面我们来看下 MapperScannerConfigurer 的作用。
2. MapperScannerConfigurer
MapperScannerConfigurer 的作用是扫描 被 @Mapper 注解修饰的接口 (Mapper Interface)生成并注册 BeanDefinition。 其类图如下:
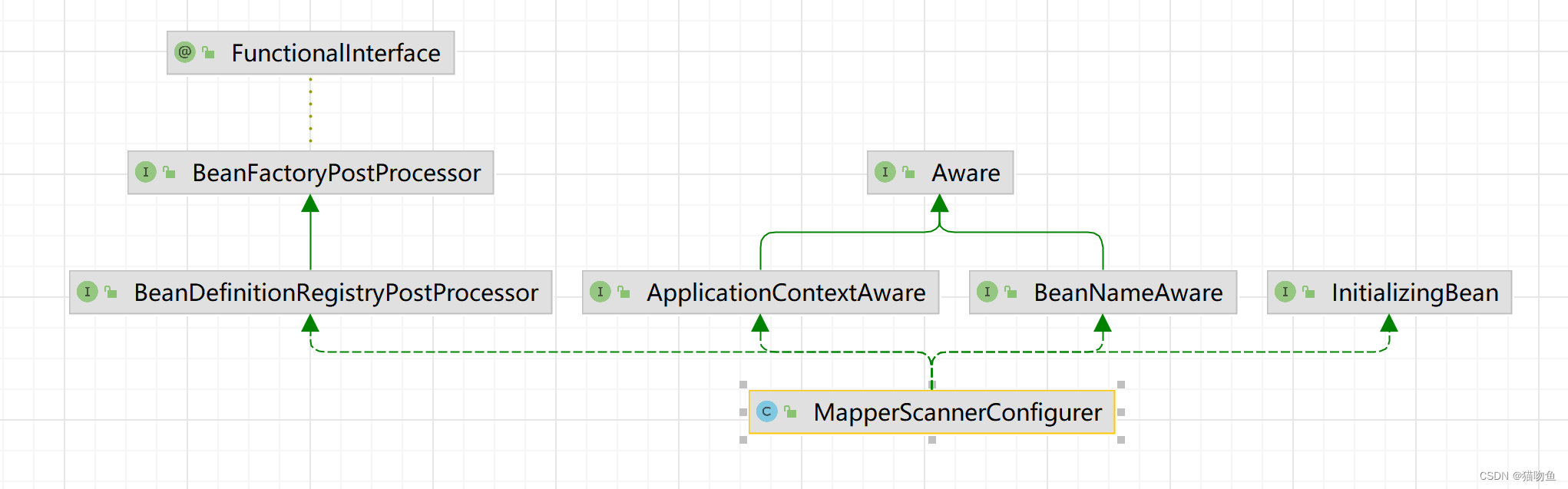
MapperScannerConfigurer 实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,所以我们这里来看下 MapperScannerConfigurer#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法,该方法会从指定目录下扫描被 @Mapper 注解修饰的接口生成BeanDefinition 并注册到容器中,具体实现如下:
@Overridepublic void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {// 1. 如果允许处理占位符,则进行处理if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {processPropertyPlaceHolders();}// 2. 创建 ClassPathMapperScanner 实例,并设置相关属性ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);// 设置相关属性scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);// 设置扫描注解为 @Mapper scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);// 我们可以通过设置 MapperScannerConfigurer 的 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 或 sqlSessionTemplateBeanName 属性来自定义 SqlSessionFactoryscanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);scanner.setMapperFactoryBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);if (StringUtils.hasText(lazyInitialization)) {scanner.setLazyInitialization(Boolean.valueOf(lazyInitialization));}if (StringUtils.hasText(defaultScope)) {scanner.setDefaultScope(defaultScope);}// 3. 注册过滤器scanner.registerFilters();// 4.扫描指定目录scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));}
我们按照上面注释的顺序进行分析:
-
处理占位符:如果 processPropertyPlaceHolders 属性为 true 则会处理占位符 (默认为 true)。官方注释【BeanDefinitionRegistries在应用程序启动的早期,在 BeanFactoryPostProcessors之前被调用。这意味着将不会加载PropertyResourceConfigurers,并且此类属性的任何属性替换都将失败。为了避免这种情况,请找到上下文中定义的任何PropertyResourceConfigurer,并在此类的bean定义上运行它们。然后更新值。】
简单来说当 Spring 容器执行到这里时,还未解析BeanFactoryPostProcessors,所以对于 PropertyResourceConfigurer#postProcessBeanFactory 方法还未执行,导致无法完成对占位符的解析,所以这里如果允许解析占位符,则从容器中获取 PropertyResourceConfigurers 实例并且手动调用 postProcessBeanFactory 方法来支持占位符的解析。MapperScannerConfigurer#processPropertyPlaceHolders 实现如下:
private void processPropertyPlaceHolders() {// 从容器中获取 PropertyResourceConfigurer 实例Map<String, PropertyResourceConfigurer> prcs = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(PropertyResourceConfigurer.class,false, false);if (!prcs.isEmpty() && applicationContext instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {BeanDefinition mapperScannerBean = ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext).getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(beanName);DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();factory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, mapperScannerBean);// 调用 PropertyResourceConfigurer#postProcessBeanFactory 方法for (PropertyResourceConfigurer prc : prcs.values()) {prc.postProcessBeanFactory(factory);}PropertyValues values = mapperScannerBean.getPropertyValues();// 获取并解析指定属性this.basePackage = getPropertyValue("basePackage", values);this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName = getPropertyValue("sqlSessionFactoryBeanName", values);this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName = getPropertyValue("sqlSessionTemplateBeanName", values);this.lazyInitialization = getPropertyValue("lazyInitialization", values);this.defaultScope = getPropertyValue("defaultScope", values);}// 占位符解析,否则为空。this.basePackage = Optional.ofNullable(this.basePackage).map(getEnvironment()::resolvePlaceholders).orElse(null);this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName = Optional.ofNullable(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName).map(getEnvironment()::resolvePlaceholders).orElse(null);this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName = Optional.ofNullable(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName).map(getEnvironment()::resolvePlaceholders).orElse(null);this.lazyInitialization = Optional.ofNullable(this.lazyInitialization).map(getEnvironment()::resolvePlaceholders).orElse(null);this.defaultScope = Optional.ofNullable(this.defaultScope).map(getEnvironment()::resolvePlaceholders).orElse(null);}这里注意,如果手动通过 (如 @Bean 方式)注入 MapperScannerConfigurer 时这里的解析会覆盖在 MapperScannerConfigurer 中人工设置的值。因为 MapperScannerConfigurer创建时会执行 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法,如果 processPropertyPlaceHolders = true,则会解析系统中的变量覆盖自定义的属性。
如下,如果手动注入一个自定义的MapperScannerConfigurer 时, 如果 processPropertyPlaceHolders = true 则会在 MapperScannerConfigurer 中调用 MapperScannerConfigurer#processPropertyPlaceHolders 方法则会覆盖自定义的各种参数。
-
初始化 ClassPathMapperScanner :在 MapperScannerConfigurer#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法中创建了一个ClassPathMapperScanner 实例用于扫描容器中指定注解 (@Mapper)的bean。在这里大部分逻辑都是给 ClassPathMapperScanner 设置相关配置属性,我们挑其中几个属性来说明一下:
-
addToConfig: 是否添加到配置中,为 false 时 Mapper Interface 则必须要在 mybatis-config.xml 中声明。 -
annotationClass:这里的值是 @Mapper 注解,即表明接下来会扫描被 @Mapper 注解修饰的类。 -
sqlSessionFactoryBeanName: 在 ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions 中会根据 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 的值注入到 MapperFactoryBean的SqlSessionTemplate 属性中。该属性值是 MapperScannerConfigurer 的属性,可通过 MapperScan 和 MapperScans 注解指定,或直接往容器中注入 MapperScannerConfigurer 对象来解决赋值。如我们可以通过注解方式指定该属性 :@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.kingfish",sqlSessionFactoryRef = "com.kingfish.config.SqlSessionTemplateWrapper",sqlSessionTemplateRef = "com.kingfish.config.SqlSessionTemplateWrapper") --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 假设我们这里ClassPathMapperScanner#sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 给的值是 `sqlSessionTemplateWrapper`, 那么他在扫描出来 @Mapper修饰的Bean 后在创建对应的该 Bean 的实例, 并指定 Bean 类型为 MapperFactoryBean(确切的说这里仅仅是赋值给了 MapperFactoryBean 的 BeanDefinition ,现在还没真正创建对象), 此时 ClassPathMapperScanner 会将容器中 beanName 为 `sqlSessionTemplateWrapper` 的对象 赋值给 Bean 的 sqlSessionFactory 属性(这里实际上是交由 BeanDefinition ,后面真正创建Bean的时候才会赋值)。 关于这一点我们下面会详述。 -
sqlSessionTemplateBeanName: 与 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 类似,在ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions 中会根据 sqlSessionTemplateBeanName 的值注入到 MapperFactoryBean 的SqlSessionTemplate 属性中。但是优先级低于sqlSessionFactoryBeanName。该属性值是 MapperScannerConfigurer 的属性,可通过 MapperScan 和 MapperScans 注解指定,或直接往容器中注入 MapperScannerConfigurer 对象来解决赋值。
-
-
注册过滤器 : 添加接下来的扫描的过滤器,即被 Mapper 注解修饰的类满足条件。这里不再赘述。
-
扫描指定目录 :开始扫描指定目录的类,并根据过滤器来判断是否符合条件,如果符合条件则将其 BeanDefinition 注册到容器中,后面容器初始化Bean时会创建该 Bean。
我们可以看到 MapperScannerConfigurer#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法主要是为了生成 ClassPathMapperScanner ,并且调用 ClassPathMapperScanner#scan 来进行目录扫描被 @Mapper 注解修饰的类并生成对应的 BeanDefinition。下面我们具体来看:
3. ClassPathMapperScanner
ClassPathMapperScanner 的作用扫描 @Mapper 注解修饰的类并生成BeanDefinition 注册到容器中,类图如下:
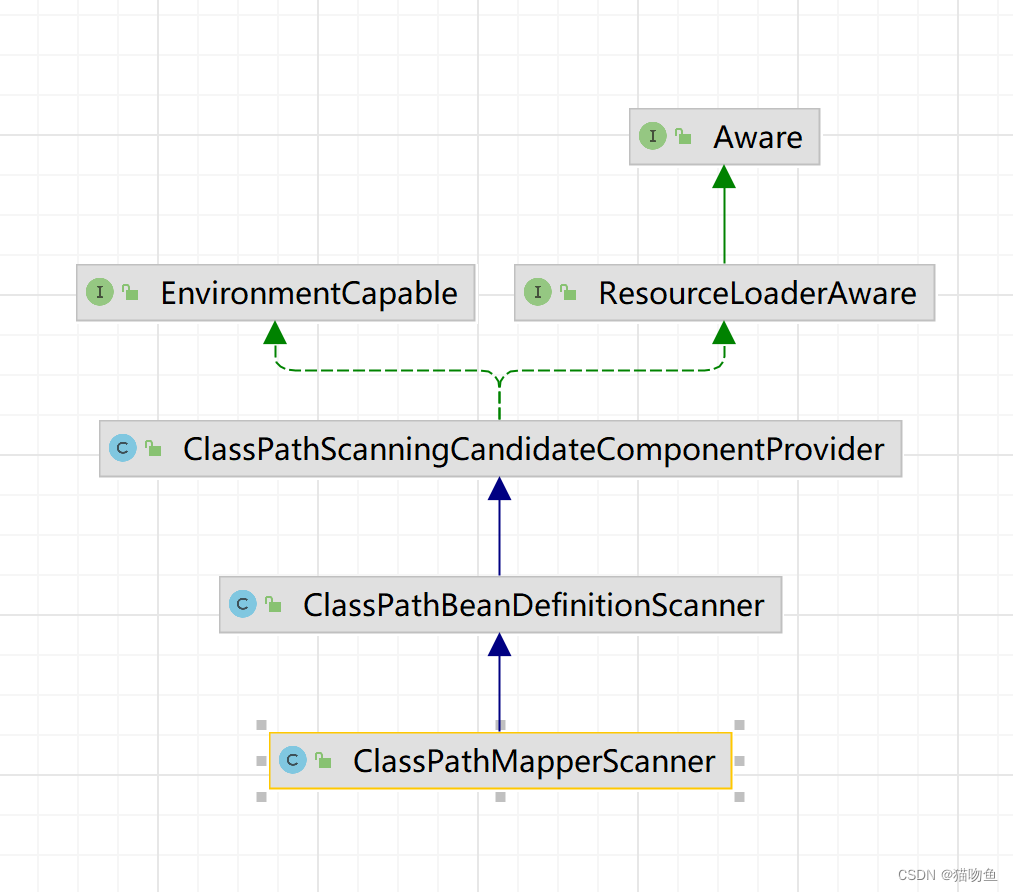
3.1 ClassPathMapperScanner#scan
可以看到 ClassPathMapperScanner 继承了 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,当调用 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#scan 时会调用 doScan 来处理,该方法在 ClassPathMapperScanner 中进行了重写,如下 :
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {// 调用 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan 方法进行扫描,返回扫描后新增的类Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);// 如果没有新增,打印日志if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {LOGGER.warn(() -> "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages)+ "' package. Please check your configuration.");} else {// 处理新增的 Mybatis MapperprocessBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);}return beanDefinitions;}具体的扫描逻辑(super.doScan(basePackages))我们这里无需关注,我们知道,super.doScan(basePackages) 方法返回的 BeanDefinition 都是被 @Mapper 注解修饰的 Mapper Interface,而Mapper Interface 通过 processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions); 方法进行了进一步处理,下面我们来详细看。
3.2 ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions
Mapper Interface 的代理对象不是直接创建的,而是创建一个 MapperFactoryBean ,再通过 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 获得一个代理对象。
ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions 方法会根据 Mapper Interface 的 BeanDefinition 来创建 MapperFactoryBean 的 BeanDefinition(这个 MapperFactoryBean 就专门用来创建当前的 Mapper Interface),而 MapperFactoryBean 实现了 FactoryBean 接口,Spring 容器会通过 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 方法来获取当前 Mapper Interface。在 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 的过程中,Mybatis 进行了进一步的封装,我们后面会详细说明该过程。
首先来看 ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions 方法,其实现如下:
// ClassPathMapperScanner 指定的属性,类型为 MapperFactoryBeanprivate Class<? extends MapperFactoryBean> mapperFactoryBeanClass = MapperFactoryBean.class;// 该方法会创建 MapperFactoryBean 的 BeanDefinition 来代替 Mapper Interface 的 BeanDefinitionprivate void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {AbstractBeanDefinition definition;BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = getRegistry();// 遍历 Mapper Interface 的 BeanDefinitionfor (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {definition = (AbstractBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();boolean scopedProxy = false;// 如果BeanDefinition 类型是 ScopedProxyFactoryBean(目前理解被 @Scope 注解修饰的 dao)// 获取 ScopedProxyFactoryBean 代理的实际 BeanDefinition if (ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class.getName().equals(definition.getBeanClassName())) {definition = (AbstractBeanDefinition) Optional.ofNullable(((RootBeanDefinition) definition).getDecoratedDefinition()).map(BeanDefinitionHolder::getBeanDefinition).orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalStateException("The target bean definition of scoped proxy bean not found. Root bean definition[" + holder + "]"));scopedProxy = true;}// 获取 Dao的 beanNameString beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean// 1. 使用 MapperFactoryBean 替换 Mybatis Dao 的 BeanDefinition// 1.1 设置 MapperFactoryBean 的构造入参类型是 Dao 类型definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // issue #59// 1.2 设置 BeanDefinition 的 BeanClass 是 MapperFactoryBean.class (mapperFactoryBeanClass 是 MapperFactoryBean 的属性)definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);// 设置其他参数definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);// Attribute for MockitoPostProcessor// https://github.com/mybatis/spring-boot-starter/issues/475definition.setAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_OBJECT_TYPE, beanClassName);// 2.下面决定 MapperFactoryBean 的 sqlSessionTemplate 和 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 属性的初始化 : 是通过工厂方法指定的Bean 还是 按照类型 对 MapperFactoryBean 的SqlSessionTemplate 进行注入// 2.1 判断 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 是否指定了 BeanName,指定的话则按照BeanName 注入boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;// 判断是否设值过 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 和 sqlSessionFactory if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory",new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));explicitFactoryUsed = true;} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {// 如果设置了 sqlSessionFactory 实例则直接注入,(该方式已经过时,推荐使用 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName )definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);explicitFactoryUsed = true;}// 如果设置了sqlSessionTemplateBeanName 或 sqlSessionTemplate,则添加至 MapperFactoryBean 属性中, MapperFactoryBean 创建时会根据工厂方法指定的bean 来注入,// 但优先级低于 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 或 sqlSessionFactoryif (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {// 如果已经通过 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 或 sqlSessionFactory 方法注入,则此处忽略处理if (explicitFactoryUsed) {LOGGER.warn(() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");}definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate",new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));explicitFactoryUsed = true;} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {if (explicitFactoryUsed) {LOGGER.warn(() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");}definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);explicitFactoryUsed = true;}// 2.2 没有工厂方法指定,则使用按照类型自动注入if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {LOGGER.debug(() -> "Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);}// 设置是否懒加载definition.setLazyInit(lazyInitialization);if (scopedProxy) {continue;}// 单例情况下,如果设置了作用域则更新为设置的作用域if (ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON.equals(definition.getScope()) && defaultScope != null) {definition.setScope(defaultScope);}// 非单例模式下创建对应的 BeanDefinition if (!definition.isSingleton()) {BeanDefinitionHolder proxyHolder = ScopedProxyUtils.createScopedProxy(holder, registry, true);if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(proxyHolder.getBeanName())) {registry.removeBeanDefinition(proxyHolder.getBeanName());}registry.registerBeanDefinition(proxyHolder.getBeanName(), proxyHolder.getBeanDefinition());}}}
可以看到 ClassPathMapperScanner 的作用是扫描指定目录并根据扫描出来的 BeanDefinition 定义 MapperFactoryBean 的 BeanDefinition 注入容器中。
上面的代码我们需要注意两点:
-
BeanDefinition 的替换 :下面两句将 BeanDefinition 设置为代表 泛型类型为 beanClassName 的 MapperFactoryBean 类。即当前这个 BeanDefinition 是用来创建 MapperFactoryBean 类的。
// 设置当前 BeanDefinition 代表的 Class泛型类型是 beanClassName。 definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // 设置 BeanDefinition 代表的 Class 类型是 MapperFactoryBean definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass); -
MapperFactoryBean#sqlSessionFactory 的初始化 :我们可以通过指定 MapperScannerConfigurer 的 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 和 sqlSessionTemplateBeanName 属性来初始化 MapperFactoryBean 的 sqlSessionTemplate (也可以通过 @MapperScan 和 @MapperScans 注解的对应属性来配置 ) 。如果我们没有指定的,则会从容器中按照类型注入(在 MybatisAutoConfiguration 中如果容器中不存在会自动注入 SqlSessionTemplate 和 SqlSessionFactory 类)。但是需要注意的是, sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 的优先级高于 sqlSessionTemplateBeanName ,如果两个属性都指定,则按照 sqlSessionFactoryBeanName 为准。
指定 SqlSessionTemplate 和 SqlSessionFactory 的方式有如下三种:
- 容器中直接注入 SqlSessionTemplate 和 SqlSessionFactory。
- 容器中注入 MapperScannerConfigurer 类并指定 SqlSessionTemplateBeanName 、SqlSessionFactoryBeanName 属性,此时需要将 ProcessPropertyPlaceHolders 设置为 false,否则容器内部解析会覆盖其他属性(在上面提到过手动注入MapperScannerConfigurer 时属性会在 MapperScannerConfigurer#processPropertyPlaceHolders 方法中被覆盖 )。
- 通过 @MapperScan 和 @MapperScans 注解 sqlSessionTemplateRef 和 sqlSessionFactoryRef 的属性指定 。(需要注意该种方式可以注入多个 MapperScannerConfigurer 实例到容器中)
到这一步,每个 Mapper Interface 对应的实际上是容器中的 MapperFactoryBean ,即Mybatis 为每个 Mapper Interface 接口在容器中实际上是注册了一个对应的 MapperFactoryBean 。而 MapperFactoryBean 实现了 FactoryBean 接口,因此当获取对应 Mapper Interface 的实例时,会通过对应的MapperFactoryBean#getObject 来获取具体的 Mapper Interface 实例。
4. 总结
至此,我们解析出来了 Mybatis 在 Spring容器初始化的时候所做的操作:
- SpringBoot 自动装配会 将 AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 装配到容器中。
- AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 中会将 MapperScannerConfigurer 注册到容器中。(实际上是 MapperScannerConfigurer 的BeanDefinition,后面会利用 BeanDefinition 创建)
- MapperScannerConfigurer 会扫描容器目录下被 @Mapper 注解修饰的 Bean,并为其创建类型为 MapperFactoryBean 的 BeanDefinition 注册到容器中。当容器执行后续流程时会创建 Mapper Interface 时,会根据 BeanDefinition 将 MapperFactoryBean 的实例创建出来,并调用 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 来获取 Mapper Interface 对象。(MapperFactoryBean 会创建 Mapper Interface 代理对象)
三、 Mapper Interface 的创建
1. MapperFactoryBean
通过上面的介绍我们知道,Mapper Interface 在容器中的 BeanDefinition 被 MapperFactoryBean 类型取代。而 MapperFactoryBean 类图如下:
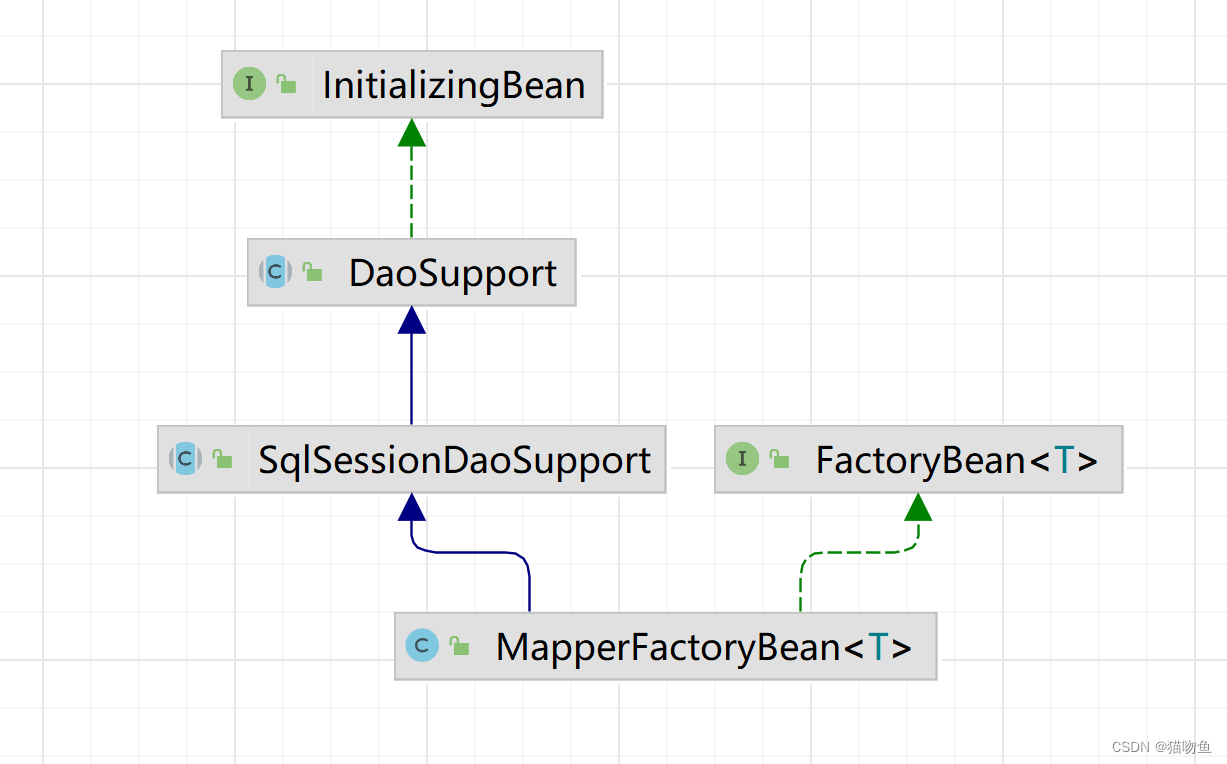
这里需要注意:
- MapperFactoryBean 继承了 SqlSessionDaoSupport :SqlSessionDaoSupport 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,会在Bean初始化时 调用 DaoSupport#afterPropertiesSet,在其中会调用 MapperFactoryBean#checkDaoConfig 方法。
- MapperFactoryBean 实现了 FactoryBean 接口:也即是说容器获取 Mybatis Dao 是通过 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 方法获取的。关于 FactoryBean 的介绍,如有需要详参:Spring 源码分析衍生篇一:FactoryBean介绍
我们来详细看看上面两点的内容 :
1.1 MapperFactoryBean#checkDaoConfig
上面我们知道当Spring 容器初始化该Bean 时会调用 MapperFactoryBean#afterPropertiesSet 方法,如下:
// 这里是在MapperFactoryBean 的父类 DaoSupport#afterPropertiesSet 的实现@Overridepublic final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {// Let abstract subclasses check their configuration.checkDaoConfig();// Let concrete implementations initialize themselves.try {// 留给子类扩展initDao();}catch (Exception ex) {throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);}}
而 MapperFactoryBean 重写了 checkDaoConfig 方法,如下:
@Overrideprotected void checkDaoConfig() {super.checkDaoConfig();notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");// 1. getSqlSession() 获取 SqlSession, 再通过 SqlSession 获取 Configuration Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();// 如果 addToConfig = true 并且 Configuration 中不存在该 mapper 接口,则添加至Configuration 中// 如果 addToConfig 为false则必须Mapper 必须要在 xml 配置文件中声明if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {try {// 2. 添加到 Configuration 中,下面细说configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);} catch (Exception e) {logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e);throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}}这里是调用 getSqlSession() 获取到的SqlSession,具体实现如下(这里可以看到SqlSession已经创建完成,关于SqlSession的创建过程,本文篇幅所限,如有需要详参 Mybatis 源码 ③ :SqlSession 篇):
// org.mybatis.spring.support.SqlSessionDaoSupport#getSqlSessionpublic SqlSession getSqlSession() {return this.sqlSessionTemplate;}
这里我们看到逻辑还是比较简单的 :通过 SqlSession 获取到 Configuration ,判断 Configuration 其是否已经存在当前 Mapper Interface,如果不存在则通过 Configuration#addMapper 方法添加。这里我们注意 getSqlSession() 获取的 SqlSession 实际类型是 SqlSessionTemplate ,因为在默认情况下,MapperFactoryBean#sqlSessionTemplate 属性是按照类型从Spring容器中注入的,而在 MybatisAutoConfiguration 中则注入了 SqlSessionTemplate 。
1.2 MapperFactoryBean#getObject
上面我们提到MapperFactoryBean 实现了 FactoryBean 接口,因此Spring会调用 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 用来获取 Mapper Interface 的实例,如下:
@Overridepublic T getObject() throws Exception {// 即 SqlSession#getMapper 方法,这里的 SqlSession 也是 SqlSessionTemplatereturn getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);}
这里我们看到是调用 SqlSession#getMapper 来获取 Mapper Interface 的实例,这里最后调用的也是 Configuration#getMapper 方法。这里需要注意 默认情况这里 MapperFactoryBean#getSqlSession 获取到的SqlSession 是 SqlSessionTemplate。在 MapperFactoryBean初始化时会被注入,SqlSessionTemplate 被 Spring管理,事务的提交、回滚等交由 Spring自动完成。
SqlSessionTemplate#getMapper 实现如下:
@Overridepublic <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);}
可以看到,Mapper 的添加和获取是 通过 Configuration#addMapper 和 Configuration#getMapper 来完成的 。我们这里先来对 Mapper Interface 的创建和获取做个小总结 ,如下:
- 每个Mapper Interface 对应Spring容器中的一个 MapperFactoryBean。
- 当 MapperFactoryBean 在创建时会调用 Configuration#addMapper 将自身代表的 Mapper Interface 添加到缓存中。而在这个过程中会为 Mapper Interface 创建一个代理对象缓存。
- 当Spring 容器需要获取 Mapper Interface 时会调用
MapperFactoryBean#getObject -> Configuration#getMapper来获取 代理对象,此时便会获取到Configuration#addMapper这一步创建的缓存的代理对象并返回。
2. Configuration
Configuration#addMapper 和 Configuration#getMapper 这两个方法的具体实现如下:
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);}public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);}
这里可以看到全都是委托给 mapperRegistry属性来处理,而 mapperRegistry 是 Configuration创建时初始化,如下:
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
因此,下面我们需要来看 MapperRegistry#addMapper 和 MapperRegistry#getMapper 方法
2.1 MapperRegistry
MapperRegistry 见名知意,用来注册Mapper Interface,主要依赖于 MapperRegistry#addMapper 和 MapperRegistry#getMapper 两个方法实现:
2.1.1 MapperRegistry#addMapper
MapperRegistry#addMapper 方法会为 Mapper Interface 创建一个 MapperProxyFactory 对象并缓存(当我们通过 MapperRegistry#getMapper 获取Mapper Interface 时会获取缓存的 MapperProxyFactory 对象来创建代理对象,后面细讲),并且会对方法的@Select、@SelectProvider、@ResultMap、@ResultType 等注解进行解析处理,并保存到 Configuration 中。
具体实现如下 :
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {// 判断当前 mapper 是接口if (type.isInterface()) {// 判断当前 mapper 未加载过if (hasMapper(type)) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");}boolean loadCompleted = false;try {// 根据 mapper 类型创建 MapperProxyFactory,并缓存到 knownMappers中knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.// 对 Mapper 上的注解进行解析,如 @Select、@SelectProvider、@ResultMap、@ResultType 等 Mybatis 注解MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);parser.parse();loadCompleted = true;} finally {if (!loadCompleted) {knownMappers.remove(type);}}}}
2.1.2 MapperRegistry#getMapper
MapperRegistry#getMapper 的实现如下,可以看到当调用该方法获取 Mapper Interface 时会通过 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance 创建一个 Mapper Interface Proxy 并返回 :
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {// 尝试从 Mapper 缓存中获取 Mapper final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");}try {// 通过 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance 方法获取 Mapper 代理类return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);} catch (Exception e) {throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);}}
其中MapperProxyFactory#newInstance 实现如下:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);}public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);return newInstance(mapperProxy);}
这里可以看到这里为 mapperInterface 创建一个代理对象,增强类是 MapperProxy,即当调用 mapperInterface 的方法时会被 mapperProxy 拦截并处理。因此下面我们需要来看下MapperProxy 的实现。
3. MapperProxy
MapperProxy 中包含一段静态代码块,主要是根据 privateLookupIn 方法判断当前JDK 版本,如下 :
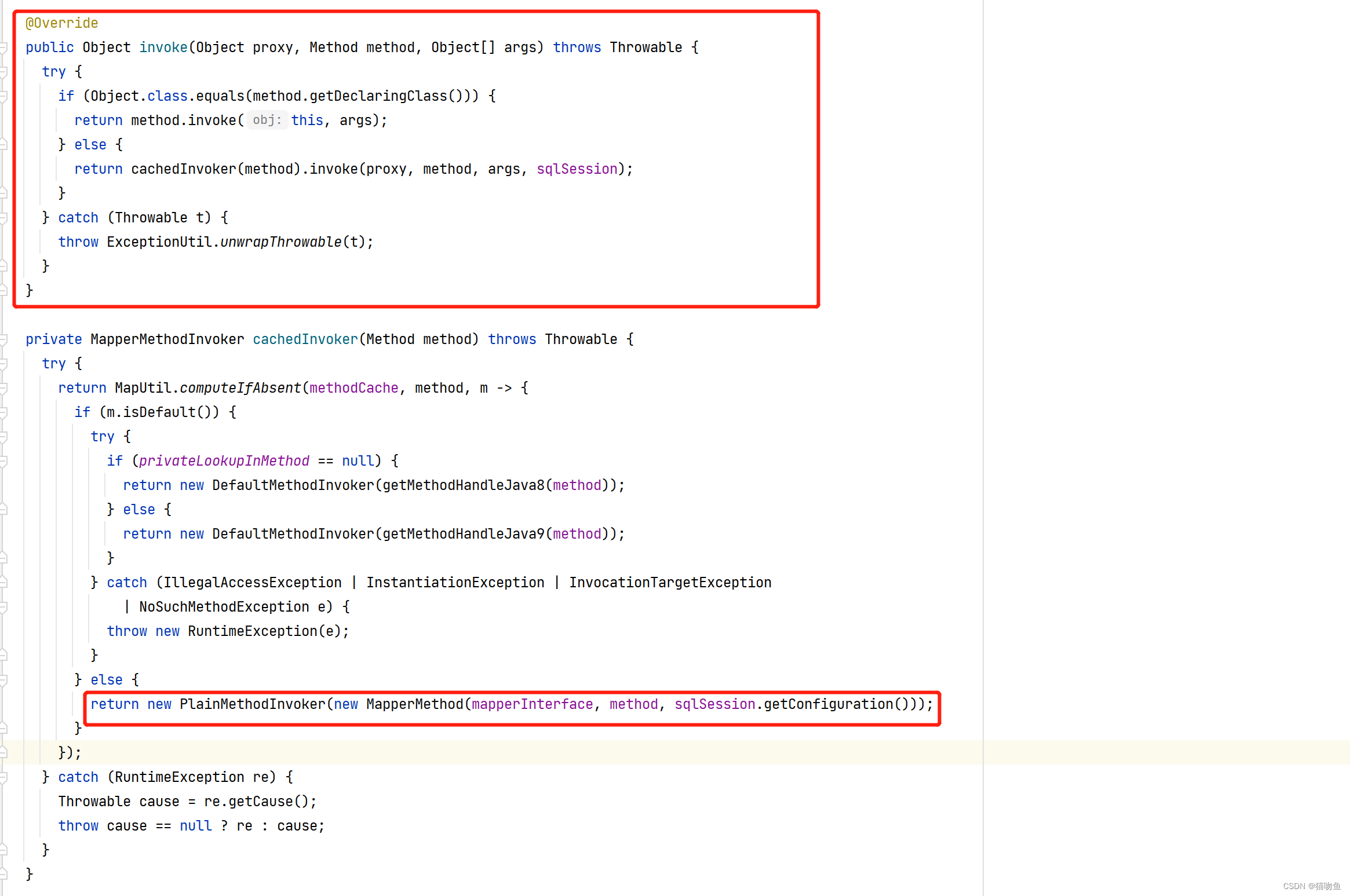
static {Method privateLookupIn;try {// 根据是否包含 privateLookupIn 判断是 jdk 1.8 并对 lookupConstructor 进行赋值privateLookupIn = MethodHandles.class.getMethod("privateLookupIn", Class.class, MethodHandles.Lookup.class);} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {privateLookupIn = null;}privateLookupInMethod = privateLookupIn;Constructor<Lookup> lookup = null;if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {// JDK 1.8try {lookup = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);lookup.setAccessible(true);} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new IllegalStateException("There is neither 'privateLookupIn(Class, Lookup)' nor 'Lookup(Class, int)' method in java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles.",e);} catch (Exception e) {lookup = null;}}lookupConstructor = lookup;}MapperProxy#invoke 方法实现如下,当执行 Mapper Interface 的方法时会通过该方法增强 :
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {// 如果 方法类是 Object 则直接调用,(对 hashCode、equals 等方法做兼容)if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else {// 否则 通过 MapperMethodInvoker#invoke 调用return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}}private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {try {return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {// 如果方法是默认级别if (m.isDefault()) {try {// 对 JDK 1.8 和 1.9 的不同处理if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));} else {return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));}} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException| NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}} else {// 创建 PlainMethodInvoker 并返回 (PlainMethodInvoker#invoke 会调用 MapperMethod#execute 来完成)return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));}});} catch (RuntimeException re) {Throwable cause = re.getCause();throw cause == null ? re : cause;}}
MapperProxy 的作用是为 MapperInterface 创建了一个代理对象,代理增强对象是 MapperProxy, 当调用 MapperInterface 的方法时会通过 MapperProxy#invoke 来增强,而 MapperProxy#invoke 方法中会调用 PlainMethodInvoker#invoke 方法来调用。PlainMethodInvoker 的实现如下:
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {super();this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}}
可以看到 PlainMethodInvoker#invoke 方法会直接调用 MapperMethod#execute 方法来完成调用,因此下面我们直接来看下 MapperMethod 的实现
4. MapperMethod
4.1 MapperMethod 构造方法
上面我们看到 PlainMethodInvoker 构造的时候创建了 MapperMethod 对象,如下:
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
所以我们先看下 MapperMethod 的构造函数,在构造函数中MapperMethod 初始化了Sql命令并且获取到了方法签名,如下:
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {// 1. 初始化Sql命令this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);// 2. 获取方法签名this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);}
下面我们来看下这两个方法的具体实现 :
4.1.1 SqlCommand
SqlCommand 是 MapperMethod 的内部类,其内部保存了Sql 语句id (statementId,生成规则是 {接口全路径名}.{方法名} )和 语句类型(Select、Update、Insert、Delete、Flush),逻辑比较简单,下面我们来看:
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {// 获取方法名和接口路径名final String methodName = method.getName();final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();// 解析 Mapper 语句信息MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,configuration);if (ms == null) {// 如果未获取到语句信息判断当前方法是否被 @Flush 修饰,如果被修饰则标志为 FLUSH 类型。if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {name = null;type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;} else {throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);}} else {name = ms.getId();type = ms.getSqlCommandType();if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);}}}private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {// 生成Sql 语句idString statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;// 从 configuration中根据 id获取具体的语句详情if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {return null;}// 如果当前接口未获取到,则从其父接口进行尝试获取语句信息,因为 Mybatis 的 Mapper Interface 是允许继承的for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,declaringClass, configuration);if (ms != null) {return ms;}}}return null;}}
4.1.2 MethodSignature
MethodSignature 也是 MapperMethod 内部类。作用是获取方法签名,即解析出来方法的各种信息,如 返回类型 (无返回、返回多条、返回游标等、解析 MapKey 注解等)。如下:
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {// 获取方法返回类型Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface);if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) {this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType;} else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType();} else {this.returnType = method.getReturnType();}// 生成对应方法返回类型的参数this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);this.returnsMany = configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray();this.returnsCursor = Cursor.class.equals(this.returnType);this.returnsOptional = Optional.class.equals(this.returnType);// 获取 @MapKey 注解信息this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);this.returnsMap = this.mapKey != null;// 从参数中 获取 RowBounds 类型的参数位置this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);// 从参数中获取 ResultHandler 类型的参数位置this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);// 解析 @Param 注解,并且在后面还会对参数进行处理, 这一块内容我们下面会详细说明this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);}
4.2 MapperMethod#execute
当调用 Mapper Interface Proxy 方法时会委托给 MapperMethod#execute 来处理,因此我们这里来看下 MapperMethod#execute的具体实现:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;// 根据语句类型执行不同的逻辑,如select、update、delete 等switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {// 对参数做处理 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 调用 SqlSession#insert 来处理result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 调用 SqlSession#update来处理result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 调用 SqlSession#delete来处理result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT:// 根据 Select 不同的返回类型做不同的处理,本质还是调用 SqlSession 的方法来处理,在下面有详细分析// 方法返回 void 但是参数中有 ResultHandlerif (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;} else if (method.returnsMany()) {// 方法返回多条记录result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsMap()) {// 方法被 @MapKey 注解修饰,将结果封装成 Map 返回result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {// 方法返回 游标 类型result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);} else {// 方法返回单一结果Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);if (method.returnsOptional()&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {result = Optional.ofNullable(result);}}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());}if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");}return result;}// 对增删改返回类型处理private Object rowCountResult(int rowCount) {final Object result;// 无返回参数if (method.returnsVoid()) {result = null;} else if (Integer.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Integer.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {// 返回参数是 Integer 类型result = rowCount;} else if (Long.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Long.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {// 返回参数是 Long 类型result = (long) rowCount;} else if (Boolean.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Boolean.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {// 返回参数是 Boolean 类型result = rowCount > 0;} else {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + "' has an unsupported return type: " + method.getReturnType());}return result;}
在经历过 method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); 处理后,可以看到后面的Sql 操作都委托给 SqlSession 来处理了(如 SqlSession#insert、SqlSession#update、SqlSession#delete 等)。关于SqlSession 的内容,如需详参 Mybatis 源码 ③ :SqlSession
4.2.1 ParamNameResolver
需要注意的是,对于 CURD 操作,在执行前都会通过 method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); 方法来对参数做处理,该方法会调用 ParamNameResolver#getNamedParams 来处理,因此,下面我们来看下 ParamNameResolver 的实现。
// org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod.MethodSignature#convertArgsToSqlCommandParampublic Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {// 调用 ParamNameResolver#getNamedParamsreturn paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);}
ParamNameResolver 是在 MethodSignature 构造函数中初始化,其构造函数如下 :
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {// 是否使用真实参数名称,通过参数 {mybatis.configuration.use-actual-param-name} 指定,默认为true// 如果设为false,则需要为每个 Mapper methods 通过 @Param 注解指定参数名this.useActualParamName = config.isUseActualParamName();final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;// get names from @Param annotationsfor (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {// RowBounds 和 ResultHandler 类型跳过if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {// skip special parameterscontinue;}String name = null;// 获取 @Param 注解标注的参数名for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {if (annotation instanceof Param) {hasParamAnnotation = true;name = ((Param) annotation).value();break;}}if (name == null) {// @Param was not specified.// 当前参数未被 @Param 修饰,如果允许使用真实参数名,则拿真实参数名作为参数名if (useActualParamName) {name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);}// 如果还没获取到,则使用每个参数的顺序作为参数名if (name == null) {// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)// gcode issue #71name = String.valueOf(map.size());}}// 保存到 map 中map.put(paramIndex, name);}// names 为不可变 mapnames = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);}
ParamNameResolver#getNamedParams 实现如下 :
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {final int paramCount = names.size();// Mapper Method 方法无参返回nullif (args == null || paramCount == 0) {return null;} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {// 只有一个参数, 直接构建返回Object value = args[names.firstKey()];// 如果参数类型是 集合 则保存成 Map return wrapToMapIfCollection(value, useActualParamName ? names.get(0) : null);} else {// 到这里说明当前方法 有参数且不止一个final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();int i = 0;for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {// 按照 参数名,值放入 mapparam.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)// 添加泛型参数 param{i},i 为参数顺序,其实相当于给参数起了个别名,为 param1, param2final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param// 确定如果没有覆盖 @param 参数的执行,才添加if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);}i++;}return param;}}
这里注意如果 Mapper Method 参数数量大于一个,则会添加对应的 param{index} 参数, 如下:
// 方法入参为如下两个参数,解析前
{"id": 1,"name": "zhangsan"
}// 解析后, 在 @Param 注解没有指定同名的参数情况下,会追加 名为param{index} 的参数
//(如,如果 @Param 指定了一个参数 名为 param1,则不会再解析出来一个param1 参数),
{"id": 1,"name": "zhangsan","param1": 1,"param2": "zhangsan"
}4.3 Select 查询
上面我们看到 MapperMethod#execute 对 Select 划分了多种情况,其实各种情况核心逻辑都是委托给了 SqlSession 来执行。下面我们就来看看这各种情况
4.3.1 MapperMethod#executeWithResultHandler
当方法无返回参 并且 方法入参中有 ResultHandler 类型的参数时执行该方法
private void executeWithResultHandler(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {// 获取执行语句信息MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(command.getName());// callback 类型判断if (!StatementType.CALLABLE.equals(ms.getStatementType())&& void.class.equals(ms.getResultMaps().get(0).getType())) {throw new BindingException("method " + command.getName()+ " needs either a @ResultMap annotation, a @ResultType annotation,"+ " or a resultType attribute in XML so a ResultHandler can be used as a parameter.");}// 参数处理Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 根据该方法入参是否有 RowBound 调用不同的重载方法if (method.hasRowBounds()) {// 获取 rowBounds 参数RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, rowBounds, method.extractResultHandler(args));} else {sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, method.extractResultHandler(args));}}
4.3.2 MapperMethod#executeForMany
当方法返回参数是 集合 或数组时,即方法会返回多条时调用该方法
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {List<E> result;Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 根据该方法入参是否有 RowBound 调用不同的重载方法if (method.hasRowBounds()) {RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);} else {result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);}// issue #510 Collections & arrays support// 根据返回类型是 数组还是集合进行对应转换if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {return convertToArray(result);} else {return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);}}return result;}
4.3.3 MapperMethod#executeForMap
当调用方法被 @MapKey 修饰时调用该方法.
private <K, V> Map<K, V> executeForMap(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Map<K, V> result;Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 根据该方法入参是否有 RowBound 调用不同的重载方法if (method.hasRowBounds()) {RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);result = sqlSession.selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey(), rowBounds);} else {result = sqlSession.selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey());}return result;}
4.3.4 MapperMethod#executeForCursor
当方法返回类型是游标类型是调用该方法
private <T> Cursor<T> executeForCursor(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Cursor<T> result;Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 根据该方法入参是否有 RowBound 调用不同的重载方法if (method.hasRowBounds()) {RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);result = sqlSession.selectCursor(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);} else {result = sqlSession.selectCursor(command.getName(), param);}return result;}
4.3.5 其他情况
非上述情况下执行下面的代码
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);if (method.returnsOptional()&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {result = Optional.ofNullable(result);}
四、流程总结
上面我们介绍了Mybatis 整个流程,下面我们来总结下:
1. Mapper 初始化
-
SpringBoot 启动后,根据自动装配的原理会加载 MybatisAutoConfiguration 到容器中,而 MybatisAutoConfiguration 中引入了 AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 类,因此会将该类注册到容器中。
-
AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar 实现了 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口,因此具备注册 BeanDefinition 的功能:在 AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar#registerBeanDefinitions 中, 会为 MapperScannerConfigurer 生成 BeanDefinition 并注册到容器中。
-
由于上一步 MapperScannerConfigurer 的 BeanDefinition 注册到了容器中。而 MapperScannerConfigurer 实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,因此在 Spring 容器创建 MapperScannerConfigurer时会 在 MapperScannerConfigurer#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 中会创建 ClassPathMapperScanner,并调用 ClassPathMapperScanner#scan 来扫描所有被 @Mapper 注解修饰的接口,为其创建代理对象注册到容器中。
-
ClassPathMapperScanner 为 Mapper Interface 创建代理的对象的实现在 ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions 方法中,该方法会将扫描出来的 Mapper Interface 的BeanDefinition 的 beanClass 替换为 MapperFactoryBean 类型。至此每个 Mapper Interface 在 Spring 容器中的 BeanDefinition 都被替换为 MapperFactoryBean 的 BeanDefinition。而 MapperFactoryBean 还实现了 InitializingBean 接口,所以在MapperFactoryBean 初始化时会调用 MapperFactoryBean#checkDaoConfig 方法。
-
MapperFactoryBean#checkDaoConfig 会 会调用 org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#addMapper 创建并添加 Mapper 为当前 Mapper Interface 创建一个代理类 并缓存到 Mapper 集合中 (MapperRegistry#knownMappers),这个我们下面细讲。
-
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#addMapper将过程委托给了 MapperRegistry#addMapper。 MapperRegistry#addMapper 会根据当前 Mapper Interface Type 创建一个 MapperProxyFactory 对象并缓存。
-
当Spring 开始根据 BeanDefinition 创建容器中的Bean时,当遇到 MapperFactoryBean 的 BeanDefinition ,发现 MapperFactoryBean 实现了 FactoryBean 接口,因此会调用 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 方法来获取具体的 Bean。 而 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 方法会从Mapper 缓存中(MapperRegistry#knownMappers)获取出创建的 Mapper Interface Proxy。而这一步会调用 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance 来获取 Mapper Interface Proxy。
-
MapperProxyFactory#newInstance 创建的 Mapper Interface Proxy 增强类是 MapperProxy,也即是说当调用 Mapper Interface Proxy 的方法时会调用 MapperProxy#invoke 来增强。如我们调用 SysUserDao.queryById 方法时实际会调用 MapperProxy#invoke 方法。
-
MapperProxy#invoke 方法中会调用 MapperMethodInvoker#invoke 来执行 Mybatis 方法。而这里是实际调用是 PlainMethodInvoker#invoke。
-
PlainMethodInvoker#invoke 委托给了 MapperMethod#execute 来执行增强逻辑。在 MapperMethod#execute 中会根据 SQL 类型执行不同的逻辑,并对结果集进行处理返回。其中具体的DB交互,都是交由 SqlSession 来完成 (SqlSession#insert、SqlSession#update等),默认情况下 SqlSession 的注入类型是 SqlSessionTemplate 。
-
SqlSessionTemplate 也是在 MybatisAutoConfiguration 中通过 sqlSessionTemplate 注入到容器中,该类的创建依赖于 SqlSessionFactory,容器中默认的实现类型是 DefaultSqlSessionFactory,也是在 MybatisAutoConfiguration 中通过 sqlSessionFactory 方法注册。SqlSessionTemplate 本身并没有实现 SqlSession 的功能,而是在构造时创建了一个 SqlSession代理对象 sqlSessionProxy,将具体的逻辑委托给了 sqlSessionProxy,当我们调用 sqlSessionProxy 时会调用其增强方法SqlSessionTemplate.SqlSessionInterceptor#invoke,在该方法中会通过 SqlSession#openSession 方法创建一个 Sql 会话,来执行具体的操作。
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;this.executorType = executorType;this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;// 创建 sqlSession 代理对象,增强类为 SqlSessionInterceptor。this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[] { SqlSession.class }, new SqlSessionInterceptor());} -
也就是说,当我们调用一个 Mapper Interface 的方法时,实际会通过 MapperProxy#invoke -> PlainMethodInvoker#invoke -> SqlSession.methods -> SqlSessionInterceptor#invoke,而 SqlSessionInterceptor#invoke 或通过 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 来创建 DefaultSqlSession 对象,并执行对应的SqlSession.method ,以完成 DB 交互。
下图是 Mapper Interface 代理对象创建过程简单时序图:
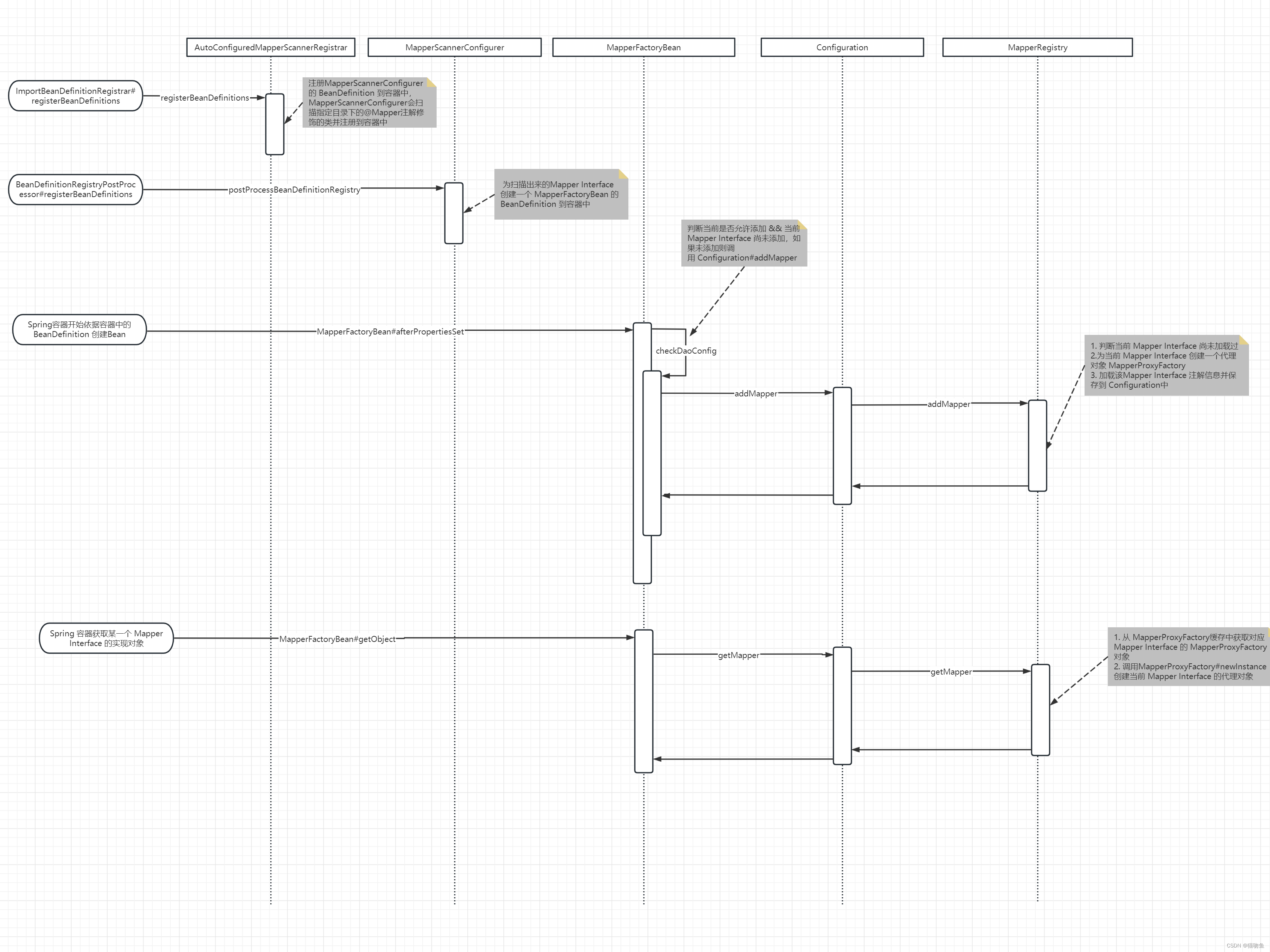
2. Mapper 代理对象的创建
上面提到 MapperFactoryBean#checkDaoConfig 会为当前 Mapper Interface 创建一个代理类 并缓存到 Mapper 集合中 (MapperRegistry#knownMappers),下面我们来总结该过程:
- 从 SqlSession 中获取到 Configuration 配置类,(该类中保存了Mybatis 加载的各种配置信息,包括Mapper 文件,接口、注解信息、扫描目录等)
- 判断 addToConfig = true && 当前 Mapper Interface 未被加载过 (如果addToConfig为false,则映射程序将不会添加到MyBatis。这意味着它必须包含在mybatis-config.xml中)则会调用 org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#addMapper 来加载当前 Mapper Interface,而 org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#addMapper 会调用org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperRegistry#addMapper 来完成添加操作。
- MapperRegistry#addMapper 会判断当前 Mapper Interface 是否已经存在缓存中(已经被解析过),如果没有则为该 Mapper Interface 创建一个 MapperProxyFactory 代理对象,并且会通过 MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse 解析当前 Mapper Interface 的注解信息。
- 当 Spring容器加载 Mapper Interface 对象时,会通过 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 方法获取 Mapper Interfacer 对象,而 MapperFactoryBean#getObject 方法通过
SqlSession#getMapper -> Configuration#getMapper -> MapperRegistry#getMapper的链路来获取对象。 - 在 MapperRegistry#getMapper 中会判断当前Mapper Interface 类型是否已经解析,没有解析则报错,否则通过 MapperProxyFactory#newInstance 方法来创建一个 Mapper Interface 的代理对象,同时会创建一个 MapperProxy 对象作为增强对象,如下图:

3. Mapper 方法的执行
如下: 是一个调用流程的简单时序图:
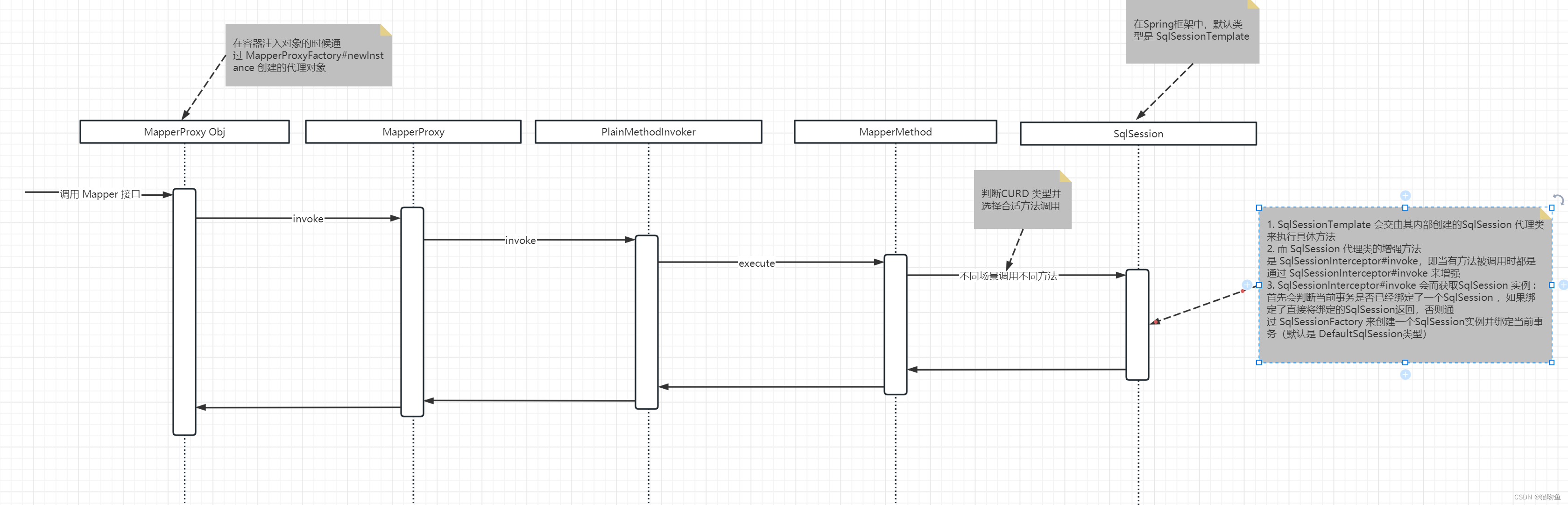
具体流程如下:
-
当 容器中调用 Mapper Interface 的方法时(如add方法),会调用到我们上面说到的 Mapper Interface 的代理对象上,而这个代理对象的增强对象为 MapperProxy,因此实际上会调用 MapperProxy#invoke 方法来执行具体的调用。
-
MapperProxy#invoke 首先会判断是否是 Object 方法,如果不是则创建一个 MapperMethodInvoker 对象,通过 MapperMethodInvoker#invoke 来执行具体的方法。这其中,Mybatis 会为每个 Mapper Interface 缓存一个 MapperMethodInvoker 对象(如果没有缓存则创建,一般创建的都是 PlainMethodInvoker 类型),如下图:
-
上面我们提到,当调用 Mapper Interface 方法时会调用 MapperProxy.PlainMethodInvoker#invoke 来完成,而 MapperProxy.PlainMethodInvoker#invoke 则是直接委托给 MapperMethod#execute来实现,如下:
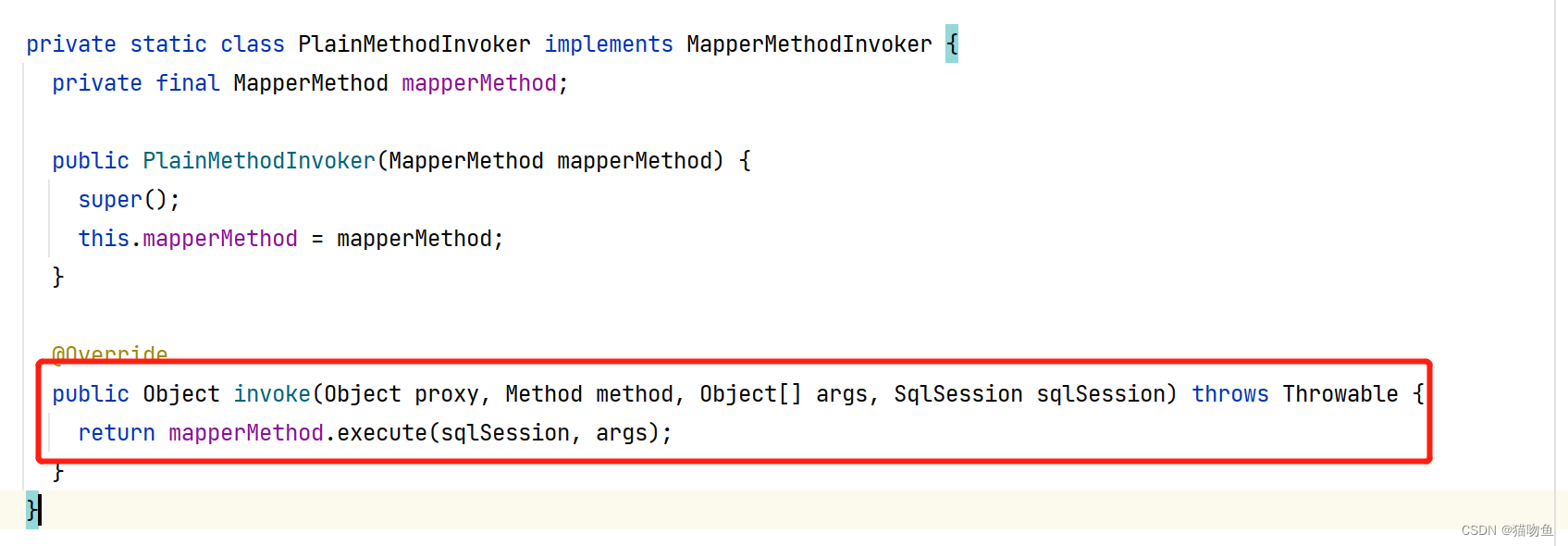
-
因此这里我们需要来看 MapperMethod#execute 方法,这里需要注意 MapperMethod 是在创建 PlainMethodInvoker 时作为构造参数传递进来的,MapperMethod 中保存了要执行的方法的 Sql Id、类型、签名等信息。而 MapperMethod#execute 方法则会根据方法的类型(如INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE 等)来执行不同的逻辑,不过最终都是委托给 SqlSession 来完成与 DB 的交互。如下图:
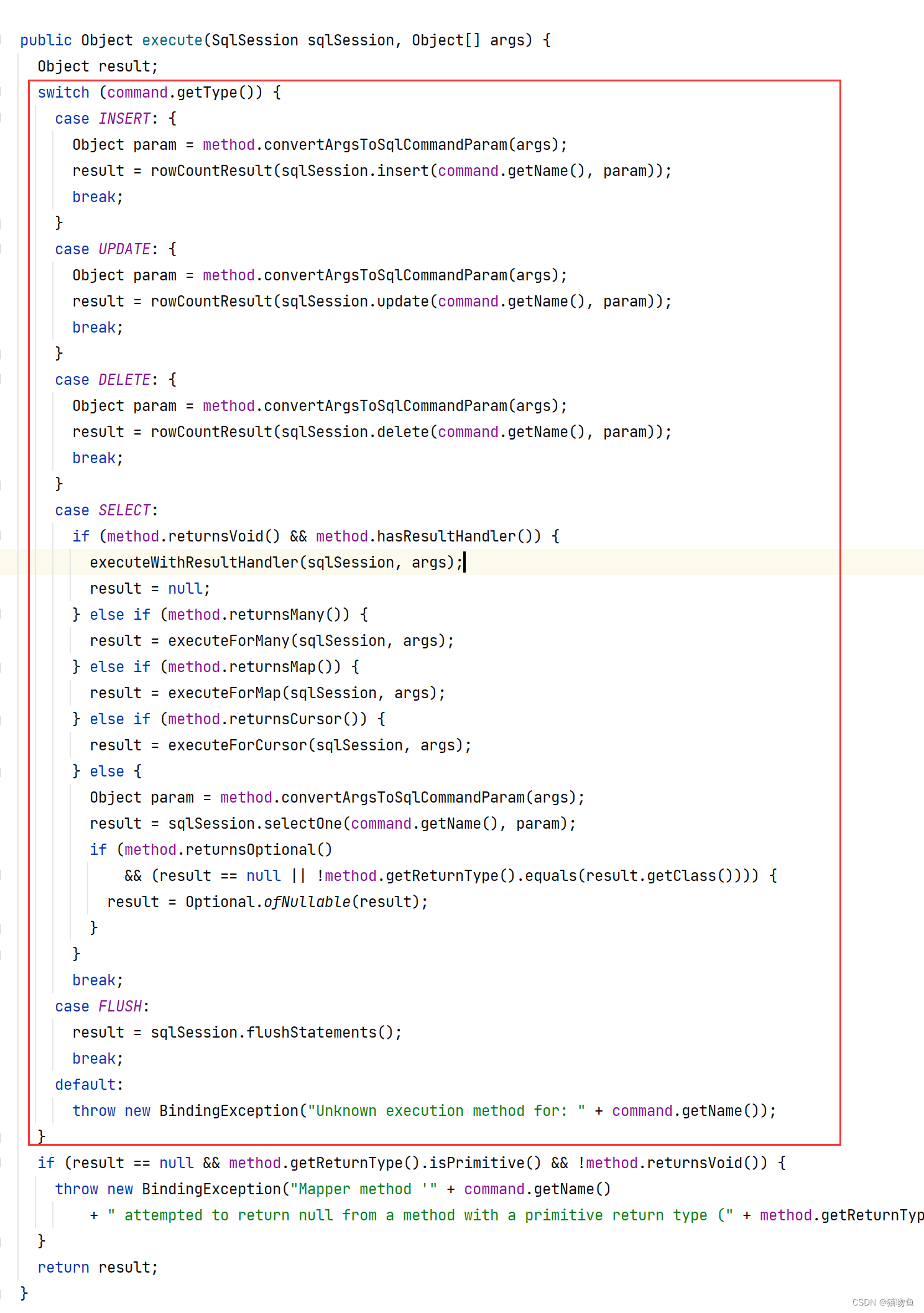
以上:内容部分参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/Liuyunsan/p/15590453.html
如有侵扰,联系删除。 内容仅用于自我记录学习使用。如有错误,欢迎指正
相关文章:

Mybatis 源码 ② :流程分析
文章目录 一、前言二、Mybatis 初始化1. AutoConfiguredMapperScannerRegistrar2. MapperScannerConfigurer3. ClassPathMapperScanner3.1 ClassPathMapperScanner#scan3.2 ClassPathMapperScanner#processBeanDefinitions 4. 总结 三、 Mapper Interface 的创建1. MapperFacto…...
Unity2D RPG开发笔记 P1 - Unity界面基础操作和知识
文章目录 工具选择简单快捷键Game 窗口分辨率检视器Transform 组件Sprite Renderer综合检视器 工具选择 按下 QWERTY 可以选择不同的工具进行 旋转、定位、缩放 简单快捷键 按下 Ctrl D 可以复制物体 Game 窗口分辨率 16:9 为最常见的分辨率 检视器 Transform 组件 物体在…...

聚类与回归
聚类 聚类属于非监督式学习(无监督学习),往往不知道因变量。 通过观察学习,将数据分割成多个簇。 回归 回归属于监督式学习(有监督学习),知道因变量。 通过有标签样本的学习分类器 聚类和…...
了解IL汇编循环
IL代码, .assembly extern mscorlib {}.assembly Test{.ver 1:0:1:0}.module test.exe.method static void main() cil managed{.maxstack 8.entrypoint.locals init (int32, int32)ldc.i4 4stloc.0 //Upper limit of the Loop, total 5 ldc.i4 0 stloc.…...

电脑突然黑屏的解决办法
记录一次电脑使用问题 问题描述 基本情况:雷神游戏笔记本 windows10操作系统 64位 使用时间 4年 日期:2023年8月11日 当时 电脑充着电 打开了两个浏览器:edge[页面加载5个左右],火狐[页面加载1个左右] 两个文件夹 一个百度网盘…...

socket练习
socket练习 工具目的代码运行结果 工具 pycharm 目的 使用socket进行图片采集 代码 采集流程: 1 获取url 2 发送请求,获取数据 3 提取数据 4 保存数据 import socket import reurls [https://pic.netbian.com/uploads/allimg/220211/004115-1644511…...
Gitlab CI/CD笔记-第二天-主机套接字进行构建并push镜像。
一、安装gitlab-runner 1.可以是linux也可以是docker的 2.本文说的是docker安装部署的。 二、直接上.gitlab-ci.yml stages: # List of stages for jobs, and their order of execution - build-image build-image-job: stage: build-image image: harbor.com:543/docke…...

nginx服务器报错502 Bad Gateway的原因以及解决办法
服务器报错nginx 502 Bad Gateway的原因以及解决办法_502 bad gateway nginx_主题模板站的博客-CSDN博客...
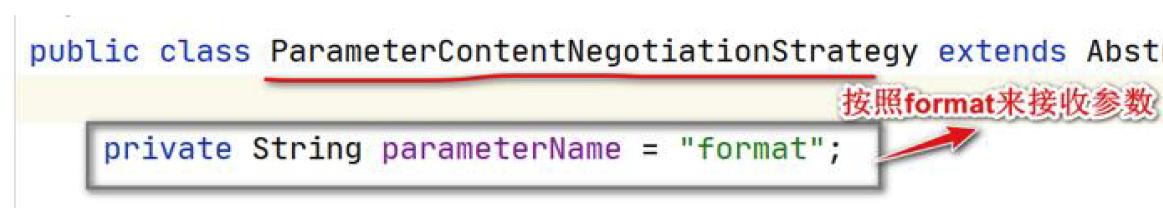
带你了解什么是内容协商---如何返回不同媒体类型的数据
😀前言 本篇博文是关于客户端接收能力不同,SpringBoot 返回不同媒体类型的数据如何处理的说明,希望你能够喜欢😊 🏠个人主页:晨犀主页 🧑个人简介:大家好,我是晨犀&#…...

容器化相关面试题
Docker相关面试题 (1)Docker的组件包含哪些? 客户端:dockerclient服务端:dockerserver## 能看到相关的信息 docker info## docker client向docker daemon发送请求,docker daemon完成相应的任务,并把结果返还给容器 Docker镜像: docker镜像是一个只读的模板,是启动一…...

BIO、NIO、AIO 有什么区别
在Java中,BIO(Blocking I/O)、NIO(Non-blocking I/O)和AIO(Asynchronous I/O)都是用于处理I/O(输入/输出)操作的不同方式。它们在处理I/O时具有不同的特点和适用场景。 B…...

如何构建一个对象池并使用
1.背景 在项目中,如果频繁的通过new 创建对象,之后让gc再去回收,这就很容易造成内存抖动,并且频繁的GC本身也会消耗内存,这样就很容易在一瞬间造成OOM 内存溢出,因为瞬间申请大量内存会造成内存占用突然升…...
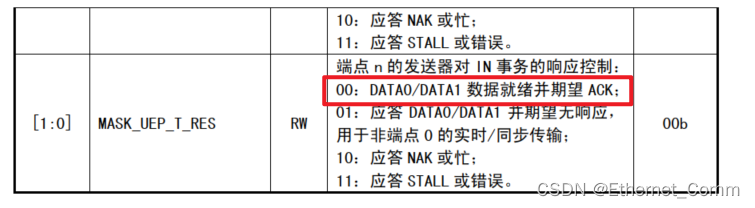
【沁恒蓝牙mesh】CH58x USB功能开发记录(三)
本博文主要记录 ,【沁恒蓝牙mesh】CH58x USB功能开发记录(三),数据收发基于寄存器级别解释 💖 作者简介:大家好,我是喜欢记录零碎知识点的小菜鸟。😎📝 个人主页…...

2023国赛数学建模D题思路分析
文章目录 0 赛题思路1 竞赛信息2 竞赛时间3 建模常见问题类型3.1 分类问题3.2 优化问题3.3 预测问题3.4 评价问题 4 建模资料 0 赛题思路 (赛题出来以后第一时间在CSDN分享) https://blog.csdn.net/dc_sinor?typeblog 1 竞赛信息 全国大学生数学建模…...

linux 学习————LNMP之分布式部署
目录 一、概述 二、LNMP环境部署 三、配置nginx 四、 配置php使nginx能够解析.php 五、配置mysql 六、配置discuz进行登录论坛访问测试 一、概述 LNMP代表 Linux、Nginx、MySQL、PHP,是一种常用的服务器架构。它由以下组件组成: Linux:作…...

第八课 双重所有格和不定代词
系列文章目录 文章目录 系列文章目录前言一、of s 的所有格1、of 有生命的名词 ’s2、of 名词性物主代词3、小结 二、反身代词1、作宾语和介词宾语2、作表语3、作固定惯语 三、相互代词四、指示代词 Such 和 Same 的用法 前言 一、of s 的所有格 1、of 有生命的名词 ’s 2、…...

使用xrdp协议远程桌面控制树莓派,无需公网IP!
远程桌面控制树莓派,我们可以用xrdp协议来实现,它内部使用的是windows远程桌面的协议。我们只需要在树莓派上安装xrdp,就可以在同个局域网下远程桌面控制树莓派。 而如果需要在公网下远程桌面控制树莓派,可以通过cpolar内网穿透&…...
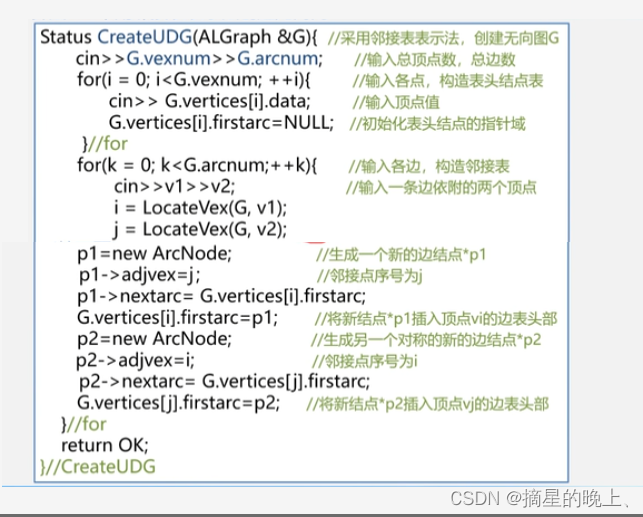
数据结构【图的类型定义和存储结构】
数据结构之图 图的定义和概念图的定义图的术语 图的类型定义图的存储结构数组(邻接矩阵)表示法无向图的邻接矩阵表示法有向图的邻接矩阵表示法网(即有权图)的邻接矩阵表示法 邻接矩阵的ADT定义邻接表(链式)…...

PHP Smarty如何进行调试和错误处理?
欢迎来到PHP Smarty的世界。如果你在这里寻求如何调试和错误处理的方法,那么我可以向你保证,我们会让这个过程尽可能的有趣和轻松。 首先,让我们先来谈谈调试。在Smarty中,你可以使用以下几种方法来进行调试: 使用Sm…...

手搓vue3组件_0,打包配置
打包后引入项目是发现报错: Cannot read properties of null (reading isCE) TypeError: Cannot read properties of null (reading isCE)这个是由于vue版本冲突问题, 这里我引入了自己打包的ui组件库,但是ui组件库中打包进入了自己的vue,那么在此时使用时,如果你引入的自己的组…...
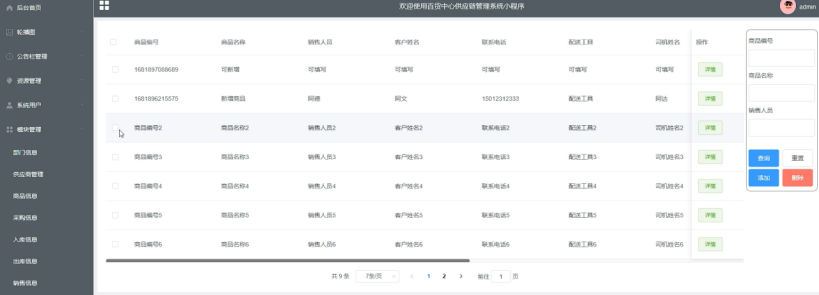
springboot 百货中心供应链管理系统小程序
一、前言 随着我国经济迅速发展,人们对手机的需求越来越大,各种手机软件也都在被广泛应用,但是对于手机进行数据信息管理,对于手机的各种软件也是备受用户的喜爱,百货中心供应链管理系统被用户普遍使用,为方…...
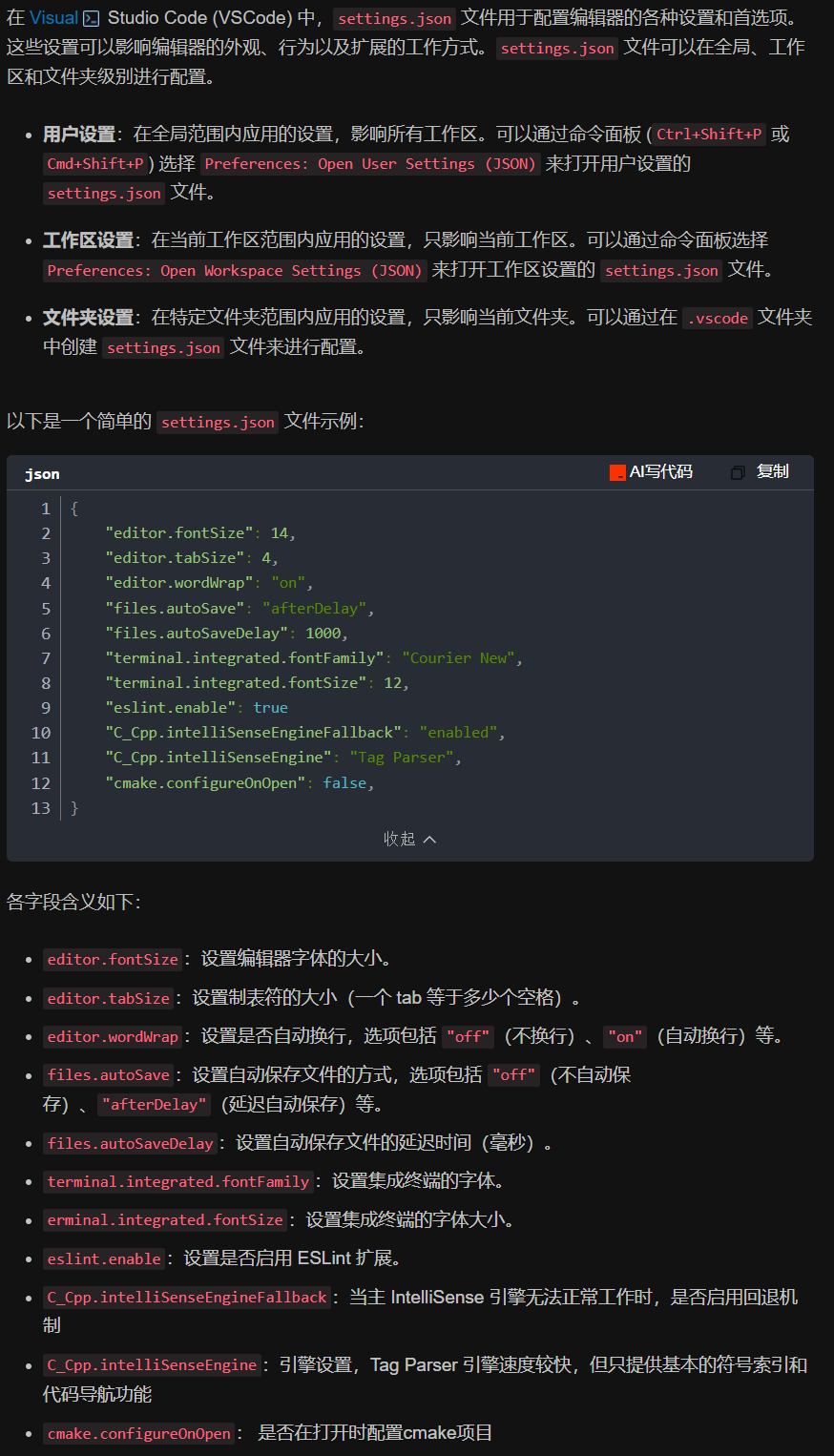
vscode(仍待补充)
写于2025 6.9 主包将加入vscode这个更权威的圈子 vscode的基本使用 侧边栏 vscode还能连接ssh? debug时使用的launch文件 1.task.json {"tasks": [{"type": "cppbuild","label": "C/C: gcc.exe 生成活动文件"…...
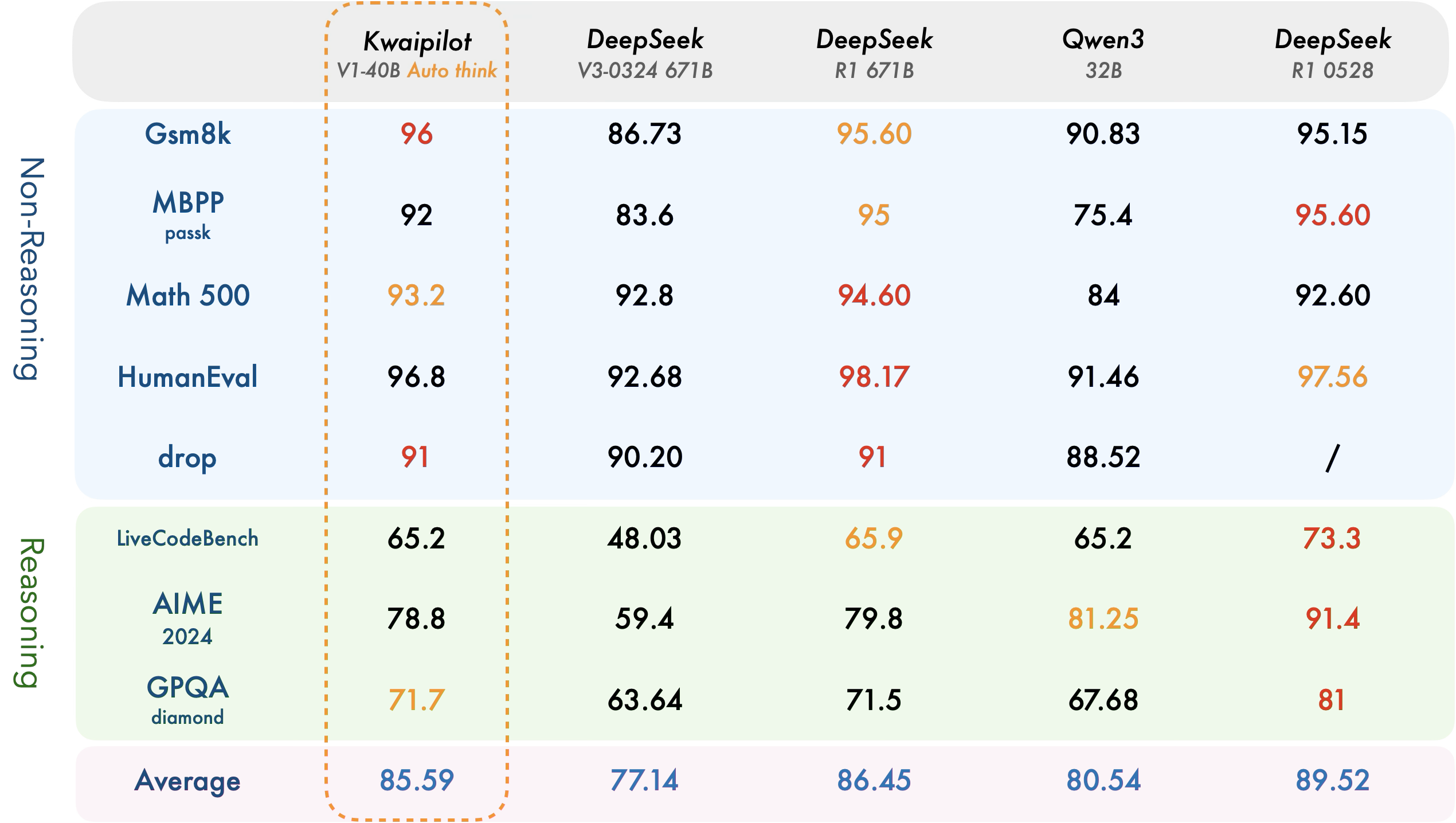
【快手拥抱开源】通过快手团队开源的 KwaiCoder-AutoThink-preview 解锁大语言模型的潜力
引言: 在人工智能快速发展的浪潮中,快手Kwaipilot团队推出的 KwaiCoder-AutoThink-preview 具有里程碑意义——这是首个公开的AutoThink大语言模型(LLM)。该模型代表着该领域的重大突破,通过独特方式融合思考与非思考…...

oracle与MySQL数据库之间数据同步的技术要点
Oracle与MySQL数据库之间的数据同步是一个涉及多个技术要点的复杂任务。由于Oracle和MySQL的架构差异,它们的数据同步要求既要保持数据的准确性和一致性,又要处理好性能问题。以下是一些主要的技术要点: 数据结构差异 数据类型差异ÿ…...
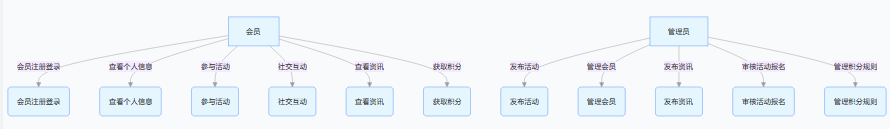
SpringBoot+uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序设计与实现,论文初版实现
摘要 本论文旨在设计并实现基于 SpringBoot 和 uniapp 的 Champion 俱乐部微信小程序,以满足俱乐部线上活动推广、会员管理、社交互动等需求。通过 SpringBoot 搭建后端服务,提供稳定高效的数据处理与业务逻辑支持;利用 uniapp 实现跨平台前…...
指令的指南)
在Ubuntu中设置开机自动运行(sudo)指令的指南
在Ubuntu系统中,有时需要在系统启动时自动执行某些命令,特别是需要 sudo权限的指令。为了实现这一功能,可以使用多种方法,包括编写Systemd服务、配置 rc.local文件或使用 cron任务计划。本文将详细介绍这些方法,并提供…...

CRMEB 框架中 PHP 上传扩展开发:涵盖本地上传及阿里云 OSS、腾讯云 COS、七牛云
目前已有本地上传、阿里云OSS上传、腾讯云COS上传、七牛云上传扩展 扩展入口文件 文件目录 crmeb\services\upload\Upload.php namespace crmeb\services\upload;use crmeb\basic\BaseManager; use think\facade\Config;/*** Class Upload* package crmeb\services\upload* …...
html css js网页制作成品——HTML+CSS榴莲商城网页设计(4页)附源码
目录 一、👨🎓网站题目 二、✍️网站描述 三、📚网站介绍 四、🌐网站效果 五、🪓 代码实现 🧱HTML 六、🥇 如何让学习不再盲目 七、🎁更多干货 一、👨…...

JAVA后端开发——多租户
数据隔离是多租户系统中的核心概念,确保一个租户(在这个系统中可能是一个公司或一个独立的客户)的数据对其他租户是不可见的。在 RuoYi 框架(您当前项目所使用的基础框架)中,这通常是通过在数据表中增加一个…...

Java编程之桥接模式
定义 桥接模式(Bridge Pattern)属于结构型设计模式,它的核心意图是将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使它们可以独立地变化。这种模式通过组合关系来替代继承关系,从而降低了抽象和实现这两个可变维度之间的耦合度。 用例子…...
