深入理解c++特殊成员函数
深入理解c++特殊成员函数
在c++中,特殊成员函数有下面6个:
- 构造函数
- 析构函数
- 复制构造函数(拷贝构造函数)
- 赋值运算符(拷贝运算符)
- 移动构造函数(c++11引入)
- 移动运算符(c++11引入)
以Widget类为例,其特殊成员函数的签名如下所示:
class Widget{
public:Widget();//构造函数~Widget();//析构函数Widget(const Widget& rhs);//复制构造函数(拷贝构造函数)Widget& operator=(const Widget& rhs);//赋值运算符(拷贝运算符)Widget(Widget&& rhs);//移动构造函数Widget& operator=(Widget&& rhs);//移动运算符
}
每个方法都有哪些作用,又都有哪些注意点?
本文将针对这些方法,进行详细的讲解。
构造函数
构造函数的作用是帮助创建对象的实例,并对实例进行初始化。
在c++中,下面两种形式的语句将会调用类的构造函数:
Widget widget;
Widget *w = new Widget();
调用构造函数将会创建一个类的实例对象。当一个类拥有数据成员时,就需要为该类编写构造函数,在构造函数中对数据成员进行初始化。
对于c++98,如果一个类没有set方法,那么就需要为其创建含参数的构造函数,如下所示:
#include <iostream>class Widget
{
public:Widget(int width, int height):height_(height), width_(width){}
private:int height_;int width_;
};int main()
{Widget w(1,1);return 0;
}
倘若此时不为其创建含参数的构造函数,那么此时创建的对象中的成员的值是随机的,显而易见,这样的创建出的对象是不好的。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Widget
{
public:int getHeight() const{return height_;}int getWidth() const{return width_;}
private:int height_;int width_;
};int main()
{Widget w;std::cout << w.getHeight()<<std::endl;std::cout << w.getWidth()<<std::endl; return 0;
}
但是对于c++11之后的标准,成员的初始值可以在类中定义。
在这种场景下,所有该类创建出的对象将拥有相同的初始值。如果你希望创建出的对象的初始值可以是不相同的,那么还是需要添加含参数的构造函数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;class Widget
{
public:int getHeight() const{return height_;}int getWidth() const{return width_;}
private:int height_{1};int width_{1};
};int main()
{Widget w;std::cout << w.getHeight()<<std::endl;std::cout << w.getWidth()<<std::endl; return 0;
}
析构函数
构造函数的作用是帮助销毁一个实例。
这很好理解,但是合适需要自定义析构函数呢?
首先看下面这个类,这个类需要写自定义析构函数吗?
class Student{
public:Student(std::string name , int age, int id):name_(name), age_(age), id(id_){};//需要析构函数吗?
public:std::string getName() const{return name_;}int getAge() const{return age_;}int getId() const{return id_;}
private:std::string name_;int age_;int id_;
}
答案是否定的,这个Student类只包含了三个成员,默认的析构函数会清理掉这些数据,因此不需要自定义析构函数。
再看看下面这个例子,需要为其自定义析构函数吗?
class Student{
public:Student(const char* s , std::size_t n) :name_(new char[n]);{memcpy(name_, s, n);}//需要析构函数吗?
public:char* getName() const{return name_;}private:char* name_;
}
很显然,该类需要自定义析构函数。默认的析构函数只会将name_置为nullptr,而不会释放new所创建的内存空间。
因此上面的例子需要改造为下面这样的形式:
class Student{
public:Student(const char* s , std::size_t n) :name_(new char[n]);{memcpy(name_, s, n);}~Student(){if(name_){delete[] name_;}}//需要析构函数吗?
public:char* getName() const{return name_;}private:char* name_;
}
其实这个类到目前为止还是有问题的,在下文中会解释为什么。
再看看下面这个例子,需要为其自定义析构函数吗?
class AsyncExec{
public:void exec(std::function<void()>& func){threadPtr_ = new std::thread(func);}//需要析构函数吗?
private:std::thread* threadPtr_{nullptr};
}
很显然,该类也需要自定义析构函数。AsyncExec类的实例在调用完Exec方法后,其内部包含了一个指针,并且其成员是std::thread类型的指针,如果其没有被detach,那么就必须要进行join,否则将会terminate程序。
因此上面的例子需要改造为下面这样的形式:
class AsyncExec{
public~AsyncExec(){if(threadPtr){threadPtr->join;}delete threadPtr;}
public:void exec(std::function<void()>& func){threadPtr_ = new std::thread(func);}//需要析构函数吗?
private:std::thread* threadPtr_{nullptr};
}
通过上面两个例子,也基本可以发现这样的规律:
通常一个类需要管理一些资源时(原始指针,线程,文件描述符等),通常需要为其编写自定义的析构函数,因为此时的默认的析构函数的行为是不正确的。
接下来需要了解一个著名的rule of three定理,如果一个类需要用户定义的析构函数、用户定义的复制构造函数或用户定义的复制赋值运算符三者中的一个,那么它几乎肯定需要这三个函数。
例如下面的例子
#include <cstdint>
#include <cstring>class Student{
public:Student(const char* s , std::size_t n) :name_(new char[n]){memcpy(name_, s, n);}explicit Student(const char* s = ""): Student(s, std::strlen(s) + 1) {}~Student(){if(name_){delete[] name_;}}
public:char* getName() const{return name_;}private:char* name_;
};int main()
{Student s1("shirley");Student s2("tom");Student s3(s1);//(1)s2 = s1;//(2)
}
如果使用默认的复制构造函数,将会出现double free的错误。此时s1和s3的name_成员指向同一处内存,s1和s3析构时将重复析构。
如果使用默认的赋值运算符,不仅会有double free的问题,还会有一处内存泄漏。由于s2被赋值为了s1,因此s2原来的name_指向的内存将不再有指针指向,于是产生了内存泄漏。接下来,同理s1和s2的name_成员指向同一处内存,s1和s2析构时将重复析构。
正确的写法就是在添加自定义析构函数的同时,为其添加自定义的赋值构造函数和自定义的赋值运算符。
#include <cstdint>
#include <cstring>class Student{
public:Student(const char* s , std::size_t n) :name_(new char[n]){memcpy(name_, s, n);}explicit Student(const char* s = ""): Student(s, std::strlen(s) + 1) {}~Student(){if(name_){delete[] name_;}}Student(const Student& other) // II. copy constructor: Student(other.name_) {}Student& operator=(const Student& other) // III. copy assignment{if (this == &other)return *this;std::size_t n{std::strlen(other.name_) + 1};char* new_cstring = new char[n]; // allocatestd::memcpy(new_cstring, other.name_, n); // populatedelete[] name_; // deallocatename_ = new_cstring;return *this;}
public:char* getName() const{return name_;}private:char* name_;
};int main()
{Student s1("shirley");Student s2("tom");Student s3(s1);s2 = s1;
}
赋值运算符中的这段代码的写法,在effective c++中有提到,这样做是为了保证异常安全性,这样的写法可以确保new的失败的情况下,不会对原有对象的数据进行破坏。
std::size_t n{std::strlen(other.name_) + 1};char* new_cstring = new char[n]; // allocatestd::memcpy(new_cstring, other.name_, n); // populatedelete[] name_; // deallocatename_ = new_cstring;
复制构造函数和赋值运算符
复制构造函数的作用是使用一个已经存在的对象去创建一个新的对象。
赋值运算符的作用是将原有对象的所有成员变量赋值给一个已经创建的对象。
二者的区别在于一个是创建一个新对象,一个是赋值给一个已经存在的对象。
在下面的例子中,语法(1)就是调用复制构造函数, 语法(2)就是调用赋值运算符。
{Student s1("shirley");Student s2("tom");Student s3(s1);//(1)复制构造函数s2 = s1;//(2)赋值运算符
}
下面我们回顾下面提到的Student类,看下正确的复制构造函数和赋值运算符的编写需要注意什么。
复制构造函数的功能相对简单,主要是成员的复制,如果存在类管理的指针,则需要进行深拷贝。
Student(const Student& other) // II. copy constructor: Student(other.name_) {}
赋值运算符的编写的注意点相对较多。
首先要添加自我赋值判断。
其次由于赋值运算符是对一个已经存在的对象再次赋值,因此首先需要销毁原有对象的成员。
接着需要处理成员对象的赋值,如果存在类管理的指针,则需要进行深拷贝。
最后需要将*this进行返回,以便进行连续赋值。
Student& operator=(const Student& other) // III. copy assignment
{if (this == &other)return *this;std::size_t n{std::strlen(other.name_) + 1};char* new_cstring = new char[n]; // allocatestd::memcpy(new_cstring, other.name_, n); // populatedelete[] name_; // deallocatename_ = new_cstring;return *this;
}
当你没有提供自定义的复制构造函数和赋值运算符时,编译器将创建默认的复制构造函数和赋值运算符,其将对成员进行浅拷贝。
如果你的类没有管理资源,那么浅拷贝可能是合适的。如果你的类是管理某些资源的(原始指针,线程对象,文件描述符等),那么大概率默认的复制构造函数和赋值运算符是不合适的。
但是要注意有时候,成员虽然有原始指针,但是并不代表该原始指针由该类管理。
例如下面的例子中,Client类中拥有handler_指针,但是该指针的生命周期并不由该类管理,该类仅仅是使用该指针,因此在这种场景下,浅拷贝就没有问题,默认的复制构造函数和赋值运算符就可以满足要求。
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <future>class IHandler
{
public:IHandler() = default;virtual ~IHandler() = default;
public:virtual void connect() = 0;
};class TcpHandler :public IHandler
{
public:TcpHandler() = default;virtual ~TcpHandler() = default;
public:void connect(){std::cout << "tcp connect" << std::endl;}
};class UdpHandler : public IHandler
{
public:UdpHandler() = default;virtual ~UdpHandler() = default;
public:void connect() {std::cout << "udp connect" << std::endl;}
};class Client{
public:Client(IHandler* handler):handler_(handler){};~Client() = default;
public:void connect(){handler_->connect();}
private:IHandler* handler_{nullptr};
};void process(IHandler* handler)
{if(!handler) return;Client client(handler);client.connect();
}
int main()
{IHandler* handler = new TcpHandler();process(handler);delete handler;handler = nullptr;handler = new UdpHandler();process(handler); delete handler;handler = nullptr;
}
因此,在设计类的时候,需要注意类是否是管理资源还是仅仅是使用资源。如果是管理资源,那么大概率你需要自定义复制构造函数和赋值运算符。
这里再次会提到rule of three定理,通常情况下,如果你需要自定义析构函数的时候,大概率你就需要自定义复制构造函数和赋值运算符。
牢记这个点,当你在设计一个类时需要有这样的条件反射。
其实如果当你自定义了析构函数之后,默认的复制构造函数和赋值运算符就可以被delete,但是在c++98年代,这个点还没有被重视。到了c++11年代,因为考虑到旧代码的迁移困难,这个点还是没有继续支持。编译器选择对新支持的移动构造函数和移动运算符支持这个点上的考虑,即如果定义了析构函数,则默认的移动构造函数和移动运算符将会delete,这个点在下面还会继续讲解。
移动构造函数和移动运算符
移动语义在c++11之后大面积使用,它允许将一个对象的所有权从一个对象转移到另一个对象,而不需要进行数据的拷贝。 这种转移可以在对象生命周期的任意时刻进行,可以说是一种轻量级的复制操作。
而移动构造函数和移动运算符就是在类中支持移动语义的二个方法。
关于如何书写移动构造函数和移动运算符,这里参考微软的文档进行理解。
移动构造函数和移动赋值运算符
下面的例子是用于管理内存缓冲区的 C++ 类 MemoryBlock。
// MemoryBlock.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>class MemoryBlock
{
public:// Simple constructor that initializes the resource.explicit MemoryBlock(size_t length): _length(length), _data(new int[length]){std::cout << "In MemoryBlock(size_t). length = "<< _length << "." << std::endl;}// Destructor.~MemoryBlock(){std::cout << "In ~MemoryBlock(). length = "<< _length << ".";if (_data != nullptr){std::cout << " Deleting resource.";// Delete the resource.delete[] _data;}std::cout << std::endl;}// Copy constructor.MemoryBlock(const MemoryBlock& other): _length(other._length), _data(new int[other._length]){std::cout << "In MemoryBlock(const MemoryBlock&). length = "<< other._length << ". Copying resource." << std::endl;std::copy(other._data, other._data + _length, _data);}// Copy assignment operator.MemoryBlock& operator=(const MemoryBlock& other){std::cout << "In operator=(const MemoryBlock&). length = "<< other._length << ". Copying resource." << std::endl;if (this != &other){// Free the existing resource.delete[] _data;_length = other._length;_data = new int[_length];std::copy(other._data, other._data + _length, _data);}return *this;}// Retrieves the length of the data resource.size_t Length() const{return _length;}private:size_t _length; // The length of the resource.int* _data; // The resource.
};
为MemoryBlock创建移动构造函数
- 1.定义一个空的构造函数方法,该方法采用一个对类类型的右值引用作为参数,如以下示例所示:
MemoryBlock(MemoryBlock&& other): _data(nullptr), _length(0)
{
}
- 2.在移动构造函数中,将源对象中的类数据成员添加到要构造的对象:
_data = other._data;
_length = other._length;
- 3.将源对象的数据成员分配给默认值。 这可以防止析构函数多次释放资源(如内存):
other._data = nullptr;
other._length = 0;
为MemoryBloc类创建移动赋值运算符
- 1.定义一个空的赋值运算符,该运算符采用一个对类类型的右值引用作为参数并返回一个对类类型的引用,如以下示例所示:
MemoryBlock& operator=(MemoryBlock&& other)
{
}
- 2.在移动赋值运算符中,如果尝试将对象赋给自身,则添加不执行运算的条件语句。
if (this != &other)
{
}
- 3.在条件语句中,从要将其赋值的对象中释放所有资源(如内存)。
以下示例从要将其赋值的对象中释放 _data 成员:
// Free the existing resource.
delete[] _data;
- 4.执行第一个过程中的步骤 2 和步骤 3 以将数据成员从源对象转移到要构造的对象:
// Copy the data pointer and its length from the
// source object.
_data = other._data;
_length = other._length;// Release the data pointer from the source object so that
// the destructor does not free the memory multiple times.
other._data = nullptr;
other._length = 0;
- 5.返回对当前对象的引用,如以下示例所示:
return *this;
完整的MemoryBlock类如下所示:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>class MemoryBlock
{
public:// Simple constructor that initializes the resource.explicit MemoryBlock(size_t length): _length(length), _data(new int[length]){std::cout << "In MemoryBlock(size_t). length = "<< _length << "." << std::endl;}// Destructor.~MemoryBlock(){std::cout << "In ~MemoryBlock(). length = "<< _length << ".";if (_data != nullptr){std::cout << " Deleting resource.";// Delete the resource.delete[] _data;}std::cout << std::endl;}// Copy constructor.MemoryBlock(const MemoryBlock& other): _length(other._length), _data(new int[other._length]){std::cout << "In MemoryBlock(const MemoryBlock&). length = "<< other._length << ". Copying resource." << std::endl;std::copy(other._data, other._data + _length, _data);}// Copy assignment operator.MemoryBlock& operator=(const MemoryBlock& other){std::cout << "In operator=(const MemoryBlock&). length = "<< other._length << ". Copying resource." << std::endl;if (this != &other){// Free the existing resource.delete[] _data;_length = other._length;_data = new int[_length];std::copy(other._data, other._data + _length, _data);}return *this;}// Move constructor.MemoryBlock(MemoryBlock&& other) noexcept: _data(nullptr), _length(0){std::cout << "In MemoryBlock(MemoryBlock&&). length = "<< other._length << ". Moving resource." << std::endl;// Copy the data pointer and its length from the// source object._data = other._data;_length = other._length;// Release the data pointer from the source object so that// the destructor does not free the memory multiple times.other._data = nullptr;other._length = 0;}// Move assignment operator.MemoryBlock& operator=(MemoryBlock&& other) noexcept{std::cout << "In operator=(MemoryBlock&&). length = "<< other._length << "." << std::endl;if (this != &other){// Free the existing resource.delete[] _data;// Copy the data pointer and its length from the// source object._data = other._data;_length = other._length;// Release the data pointer from the source object so that// the destructor does not free the memory multiple times.other._data = nullptr;other._length = 0;}return *this;}// Retrieves the length of the data resource.size_t Length() const{return _length;}private:size_t _length; // The length of the resource.int* _data; // The resource.
};
值得一提的是,有时候为了减少重复代码,在移动构造函数中也可以调用移动运算符,不过需要确保这样做不会有什么问题。
// Move constructor.
MemoryBlock(MemoryBlock&& other) noexcept: _data(nullptr), _length(0)
{*this = std::move(other);
}
下面要介绍的是,如果一个类自定了析构函数,赋值构造函数,赋值运算符三者之一,则默认的移动构造和移动运算符就会被delete。如果使用一个右值来构造对象,那么编译器将会调用赋值构造函数。
例如,MemoryBlock自定了析构函数,赋值构造函数,赋值运算符,于是默认的移动构造和移动运算符就会被delete。
即便你使用了MemoryBlock m2(std::move(m1));,其仍然调用的是赋值构造函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>class MemoryBlock
{
public:// Simple constructor that initializes the resource.explicit MemoryBlock(size_t length): _length(length), _data(new int[length]){std::cout << "In MemoryBlock(size_t). length = "<< _length << "." << std::endl;}// Destructor.~MemoryBlock(){std::cout << "In ~MemoryBlock(). length = "<< _length << ".";if (_data != nullptr){std::cout << " Deleting resource.";// Delete the resource.delete[] _data;}std::cout << std::endl;}// Copy constructor.MemoryBlock(const MemoryBlock& other): _length(other._length), _data(new int[other._length]){std::cout << "In MemoryBlock(const MemoryBlock&). length = "<< other._length << ". Copying resource." << std::endl;std::copy(other._data, other._data + _length, _data);}// Copy assignment operator.MemoryBlock& operator=(const MemoryBlock& other){std::cout << "In operator=(const MemoryBlock&). length = "<< other._length << ". Copying resource." << std::endl;if (this != &other){// Free the existing resource.delete[] _data;_length = other._length;_data = new int[_length];std::copy(other._data, other._data + _length, _data);}return *this;}// Retrieves the length of the data resource.size_t Length() const{return _length;}private:size_t _length; // The length of the resource.int* _data; // The resource.
};int main()
{MemoryBlock m1(10);MemoryBlock m2(std::move(m1));
}
因此这就诞生了另一个著名定理rule of five定理。即如果你需要自定义移动构造函数和移动运算符,那么大概率你需要自定义5个特殊函数(析构函数,复制构造函数,赋值运算符,移动构造函数,移动运算符)。
这里顺便再提到另一个rule of zero定理,
1.类不应定义任何特殊函数(复制/移动构造函数/赋值和析构函数),除非它们是专用于资源管理的类。
此举为了满足设计上的单一责任原则,将数据模块与功能模块在代码层面分离,降低耦合度。
class rule_of_zero
{std::string cppstring;
public:rule_of_zero(const std::string& arg) : cppstring(arg) {}
};
2.基类作为管理资源的类在被继承时,析构函数可能必须要声明为public virtual,这样的行为会破坏移动复制构造,因此,如果基类在此时的默认函数应设置为default。
此举为了满足多态类在C ++核心准则中禁止复制的编码原则。
class base_of_five_defaults
{
public:base_of_five_defaults(const base_of_five_defaults&) = default;base_of_five_defaults(base_of_five_defaults&&) = default;base_of_five_defaults& operator=(const base_of_five_defaults&) = default;base_of_five_defaults& operator=(base_of_five_defaults&&) = default;virtual ~base_of_five_defaults() = default;
};
关于这个点,还是需要一个例子来加深印象,
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>class A{
public:A() {std::cout << "A()" << std::endl;};~A() = default;A(const A& other){std::cout << "A(const A& other)" << std::endl;}A& operator=(const A& other){std::cout << "operator=(const A& other)" << std::endl;return *this;}A(A&& other){std::cout << "A(A&& other)" << std::endl;}A& operator=(A&& other){std::cout << "operator=(A&& other)" << std::endl;return *this;}
};class DataMgr {
public:DataMgr(){val_.reserve(10);}virtual ~DataMgr() = default;// DataMgr(const DataMgr& other) = default;// DataMgr& operator=(const DataMgr& other) = default;// DataMgr(DataMgr&& other) = default;// DataMgr& operator=(DataMgr&& other) = default;public:void push(A& a){val_.emplace_back(a);}
private:std::vector<A> val_; //同之前一样
};int main()
{A a1, a2;DataMgr s1;s1.push(a1);s1.push(a2);std::cout << "========" << std::endl;DataMgr s2 ;s2 = std::move(s1);
}
这里的运行结果如下所示:
A()
A()
A(const A& other)
A(const A& other)
========
A(const A& other)
A(const A& other)
尽管使用了s2 = std::move(s1)这里使用了移动语义,然而由于定义了析构函数,移动操作被delete,导致了调用了复制构造。试想如果这里的val_的数据量很大,那么程序的运行效率将会相差很大。
总结
- 特殊成员函数是编译器可能自动生成的函数,它包括下面六种默认构造函数,析构函数,复制构造函数,赋值运算符,移动构造函数,移动运算符。
- 对于构造函数而言,如果需要自定义初始化成员的方式,则不能使用默认的构造函数,需要编写自定义构造函数。
- 对于析构函数而言,如果其内部管理了资源(原始指针,文件描述符,线程等等),则通常需要编写自定义的析构函数。如果只是借用资源,通常使用默认析构函数就可以。
- 根据rule of three,析构函数进行了自定义,大概率你也需要自定义复制构造函数和赋值运算符。
- 默认移动操作仅当类没有显式声明移动操作,复制操作,析构函数时才自动生成。如果你定义了析构函数或者复制操作,此时的移动操作会调用复制构造函数。
- 如果一个类没有显示定义复制构造却显示定义了移动构造,则复制构造函数被delete。同理如果一个类没有显示定义赋值运算符却显示定义了移动运算符,则赋值运算符数被delete。
- 日常开发中,尽量显示指明是否使用default的特殊函数以避免某些成员函数被delete。如果某些方法不需要生成,则应该delete掉。
相关文章:

深入理解c++特殊成员函数
深入理解c特殊成员函数 在c中,特殊成员函数有下面6个: 构造函数析构函数复制构造函数(拷贝构造函数)赋值运算符(拷贝运算符)移动构造函数(c11引入)移动运算符(c11引入) 以Widget类为例,其特殊成员函数的签名如下所示: class W…...
RecyclerView面试问答
RecycleView 和 ListView对比: 使用方法上 ListView:继承重写 BaseAdapter,自定义 ViewHolder 与 converView优化。 RecyclerView: 继承重写 RecyclerView.Adapter 与 RecyclerView.ViewHolder。设置 LayoutManager 来展示不同的布局样式 ViewHolder的编写规范化,ListVie…...
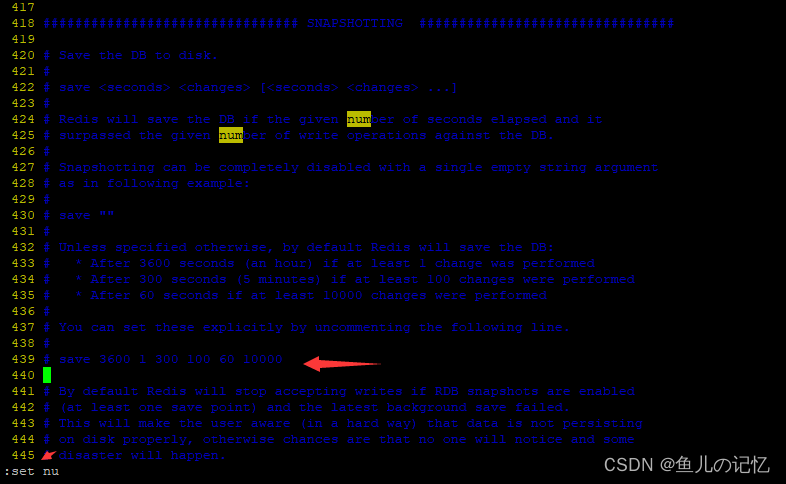
Redis 7 教程 数据持久化
总体 RDB 介绍 RDB 持久化以指定的时间间隔执行数据集的时间点快照 。 把某一时刻的数据和状态以文件的形式写到磁盘上,即使出现故障宕机,快照文件也不会丢失,数据的可靠性得到保证。快照文件就是RDB(Redis DataBase)文件(dump.rdb) 作用 在指定的时间间隔内将内存中的数…...

【ArcGIS微课1000例】0072:如何生成空间权重矩阵
严重声明:本文来自专栏《ArcGIS微课1000例:从点滴到精通》,为CSDN博客专家刘一哥GIS原创,原文及专栏地址为:(https://blog.csdn.net/lucky51222/category_11121281.html),谢绝转载或爬取!!! 文章目录 一、空间权重矩阵工具介绍二、ArcGIS生成空间权重矩阵三、注意事项…...

【芯片设计封装与测试】芯片测试目的、方法、分类及案例
目录 1.芯片测试概述(目的、方法) 1.1.测试在芯片产业价值链上的位置 2.测试如何体现在设计的过程中 2.1.半导体测试定义与基本工作机制 2.2.半导体测试环节分类及对应设备 2.3.设计验证 3.测试的各种类型 3.1.抽样测试和生产全测 3.2.测试相关…...

k8s集群证书过期解决
一、k8s集群证书过期解决 问题现象 K8S集群证书过期后,会导无法创建Pod,通过kubectl get nodes也无法获取信息,甚至dashboard也无法访问。 执行命令发现报错: Unable to connect to the server: x509: certificate has expire…...
Linux学习之Ubuntu 20.04在github下载源码安装Openresty 1.19.3.1
参考的博文:《在 Ubuntu 上使用源码安装 OpenResty》 《OpenResty 安装安装详解-Ubuntu》 《Linux学习之CentOS 7源码安装openresty》 https://openresty.org/en/download.html是官网下载网址,页面往下拉有下载的链接。 https://github.com/openresty…...
bootloader串口更新程序[瑕疵学习板]
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档 文章目录 前言一、储备知识二、程序步骤2.程序展示1.bootloader2.然后是主运行函数总结前言 很久没有更新文章了。最近工作太忙,没有学习很多的知识,然后这两天不忙了,就学习了一下bootloader的程序升级…...
浅谈视频汇聚平台EasyCVR视频平台在城市安全综合监测预警台风天气中的重要作用
夏日已至,台风和暴雨等极端天气频繁出现。在城市运行过程中,台风所带来的暴雨可能会导致城市内涝等次生灾害,引发交通瘫痪、地铁停运、管网泄漏爆管、路面塌陷、防洪排涝、燃气爆炸、供热安全、管廊安全、消防火灾等安全隐患,影响…...

GaussDB技术解读系列:高级压缩之OLTP表压缩
8月16日,第14届中国数据库技术大会(DTCC2023)在北京国际会议中心顺利举行。在GaussDB“五高两易”核心技术,给世界一个更优选择的专场,华为云数据库GaussDB首席架构师冯柯对华为云GaussDB数据库的高级压缩技术进行了详…...

管理类联考——英语二——实战篇——大作文——图表——静态图表——第一段
第一句:What is clearly presented in the above 图表类型 is the statistics of 主题词 1. 翻译:从上述图表类型中我们能够清晰地得知有关主题词1的数据。 [备注1]:本句对图表进行整体描述,无需描述具体各项内容所占比例,只需提出主题词的哪方面的有关数据…...
https 的ssl证书过期处理解决方案(lighthttpd)
更换证书:lighthttpd 配置文件位置:/opt/vmware/etc/lighttpd/lighttpd.conf (配置文件的最底部 G快速来到底部) 方案一:阿里云申请免费的证书 这里公司内网环境没有配置域名,可以创建一个临时域名&…...
【java】【idea2023版】Springboot模块没有.iml文件的问题
目录 方法一: 1、首先鼠标选中对应的对应的模块 ,按两下Ctrl键 2、project中选择对应的模块 3、运行mvn idea:module 命令编辑 方法二: 1、可以右键点击open Terminal 2、然后在打开的Terminal里输入 方法一: 1、首先鼠…...

Qt QScrollArea使用
在使用QScrollArea时,有几个注意事项需要考虑: 设置合适的小部件(widget)大小策略: 确保将要放置在QScrollArea中的小部件设置为合适的大小策略。这将确保小部件可以根据需要进行扩展,以适应滚动区域的大小…...
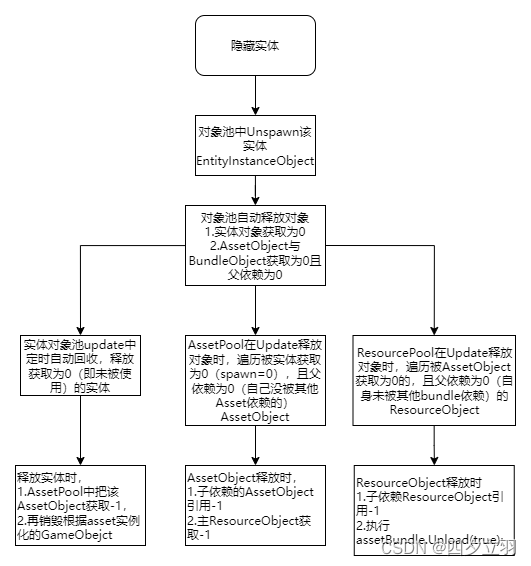
Unity3d:GameFramework解析:实体,对象池,资源管理,获取计数,引用计数,自动释放
基本概念 1.GF万物基于引用池IReference 2.ObjectBase : IReference类的m_Target持有unity中Mono,资源,GameObejct 3.AssetObject : ObjectBase类m_Target持有Assetbundle中的Asset,具有获取,引用两个计数管理释放 4.ResourceObj…...
Django基础6——数据模型关系
文章目录 一、基本了解二、一对一关系三、一对多关系3.1 增删改查3.2 案例:应用详情页3.2 案例:新建应用页 四、多对多关系4.1 增删改查4.2 案例:应用详情页4.3 案例:部署应用页 一、基本了解 常见数据模型关系: 一对一…...

【chrome扩展开发】如何在项目中判断插件是否已安装
由于安全限制,本文采取间接的方式实现 1、项目部分 比如通过cookie、localStorage等进行状态存储 1.1、初始化判断 function getCookie(name){let arr document.cookie.match(new RegExp("(^| )"name"([^;]*)(;|$)"))if(arr ! null){return u…...
Centos 7.6 安装mongodb
以下是在CentOS 7.6上安装MongoDB的步骤: 打开终端并以root用户身份登录系统。 创建一个新的MongoDB存储库文件 /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-4.4.repo 并编辑它。 sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-4.4.repo在编辑器中,添加下面的内容到文件中并…...
Ubuntu下安装nginx服务,实现通过URL读取ubuntu下图片
1.安装nginx包 sudo apt update sudo apt install nginx 2.安装完成后系统自动启动nginx sudo systemctl status nginx 查看nginx服务的状态 3.开启防火墙上的HTTP服务端口80 sudo ufw allow ‘Nginx HTTP’ 4.在浏览器输入 http://localhost 看到nginx的欢迎界面,…...

本地部署 Stable Diffusion(Mac 系统)
在 Mac 系统本地部署 Stable Diffusion 与在 Windows 系统下本地部署的方法本质上是差不多的。 一、安装 Homebrew Homebrew 是一个流行的 macOS (或 Linux)软件包管理器,用于自动下载、编译和安装各种命令行工具和应用程序。有关说明请访问官…...

挑战杯推荐项目
“人工智能”创意赛 - 智能艺术创作助手:借助大模型技术,开发能根据用户输入的主题、风格等要求,生成绘画、音乐、文学作品等多种形式艺术创作灵感或初稿的应用,帮助艺术家和创意爱好者激发创意、提高创作效率。 - 个性化梦境…...
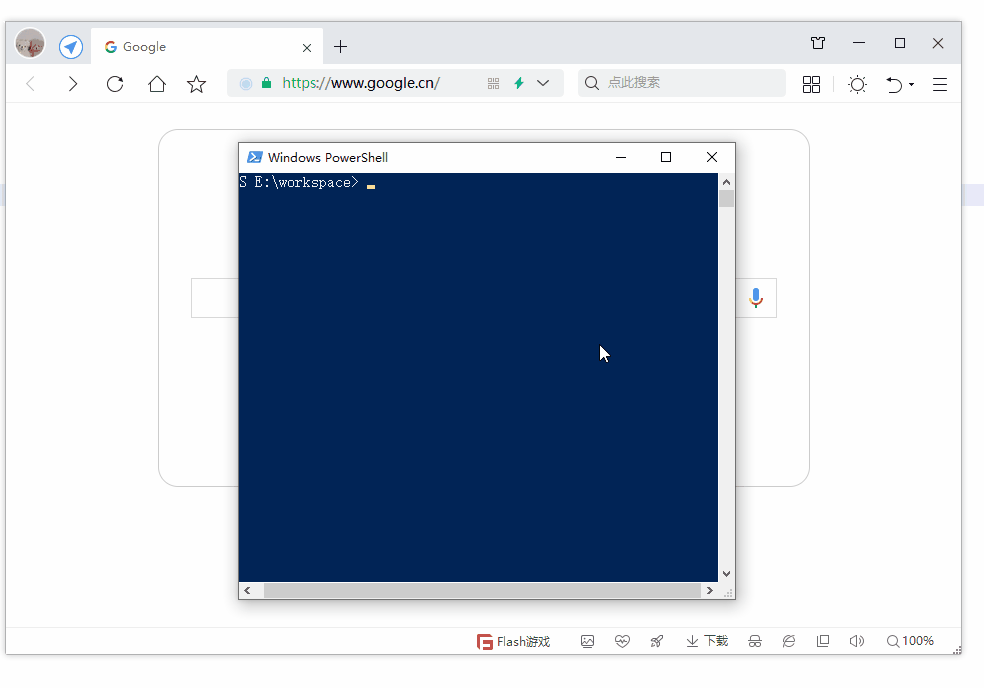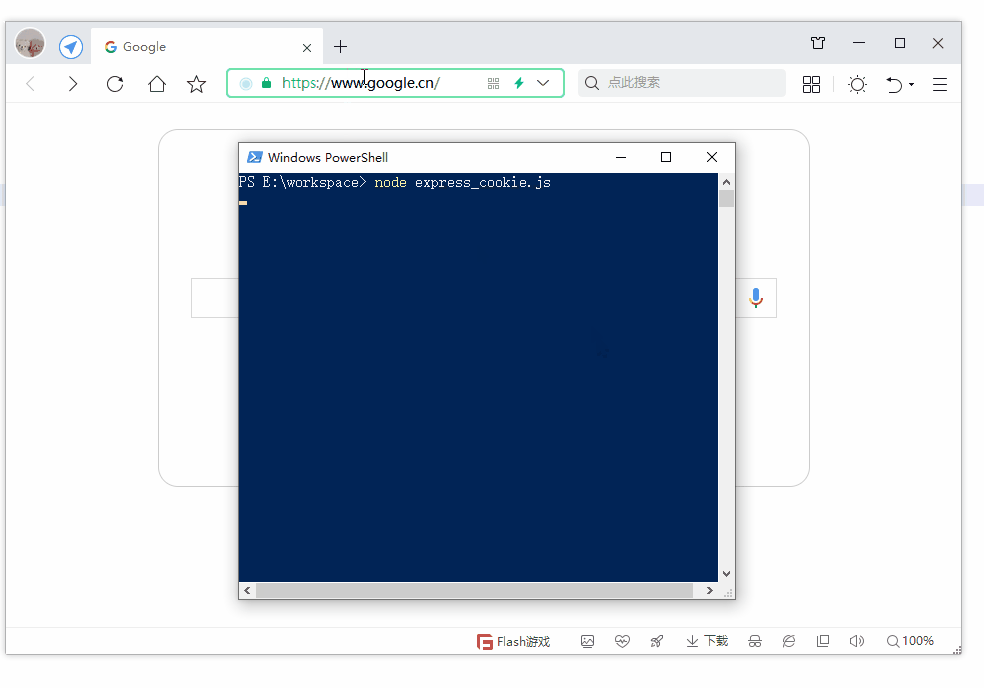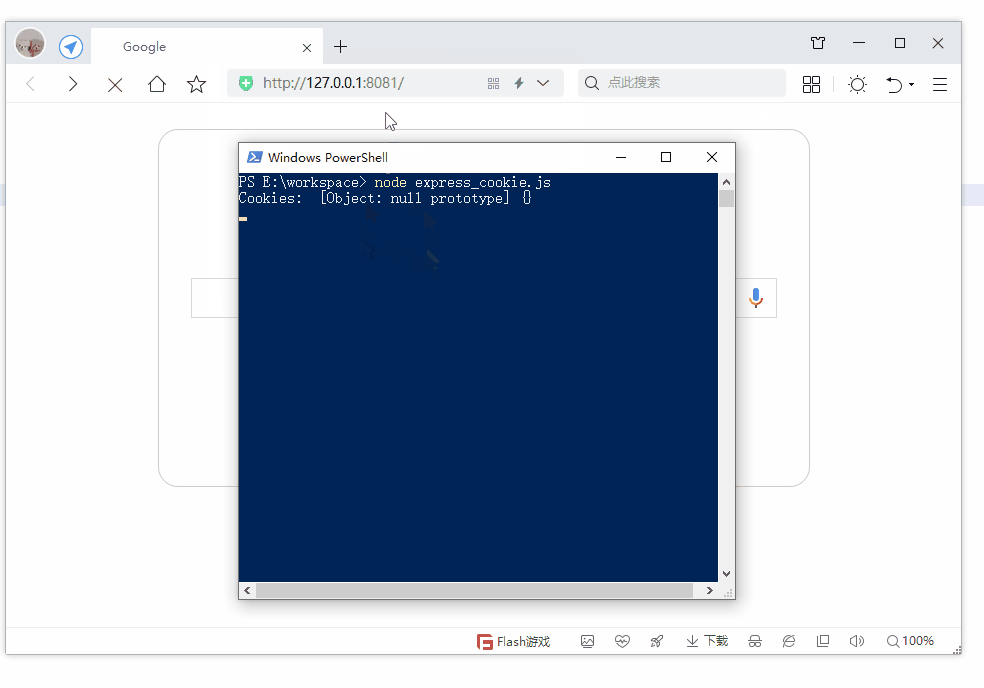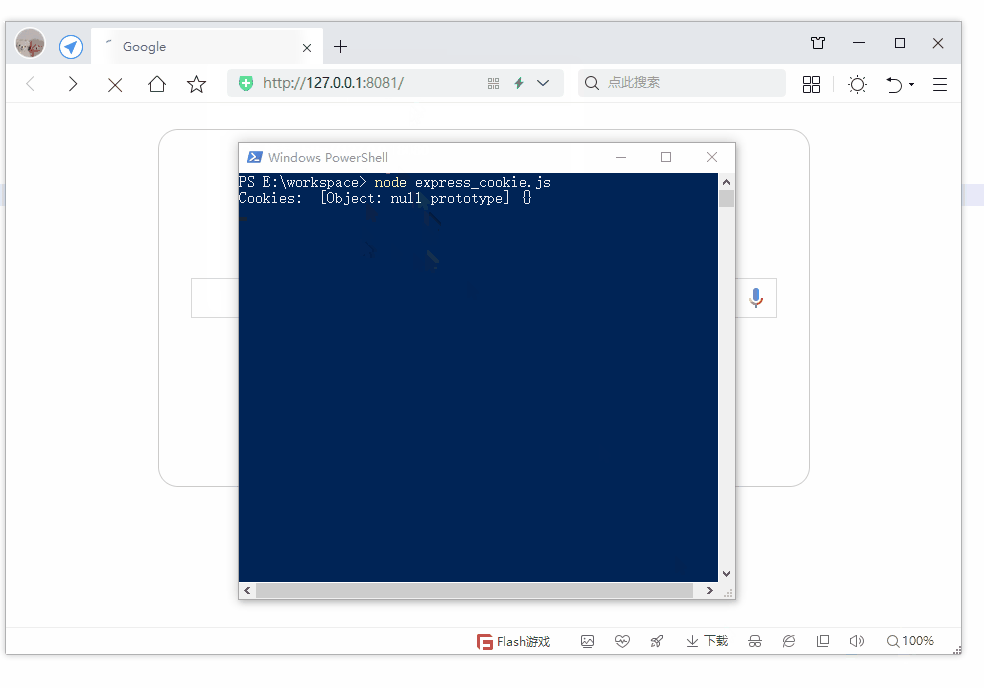
第19节 Node.js Express 框架
Express 是一个为Node.js设计的web开发框架,它基于nodejs平台。 Express 简介 Express是一个简洁而灵活的node.js Web应用框架, 提供了一系列强大特性帮助你创建各种Web应用,和丰富的HTTP工具。 使用Express可以快速地搭建一个完整功能的网站。 Expre…...

conda相比python好处
Conda 作为 Python 的环境和包管理工具,相比原生 Python 生态(如 pip 虚拟环境)有许多独特优势,尤其在多项目管理、依赖处理和跨平台兼容性等方面表现更优。以下是 Conda 的核心好处: 一、一站式环境管理:…...
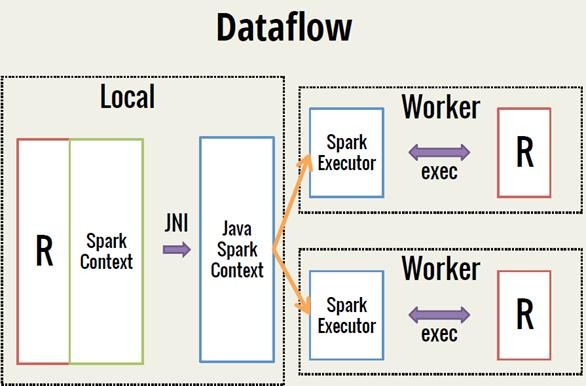
Spark 之 入门讲解详细版(1)
1、简介 1.1 Spark简介 Spark是加州大学伯克利分校AMP实验室(Algorithms, Machines, and People Lab)开发通用内存并行计算框架。Spark在2013年6月进入Apache成为孵化项目,8个月后成为Apache顶级项目,速度之快足见过人之处&…...
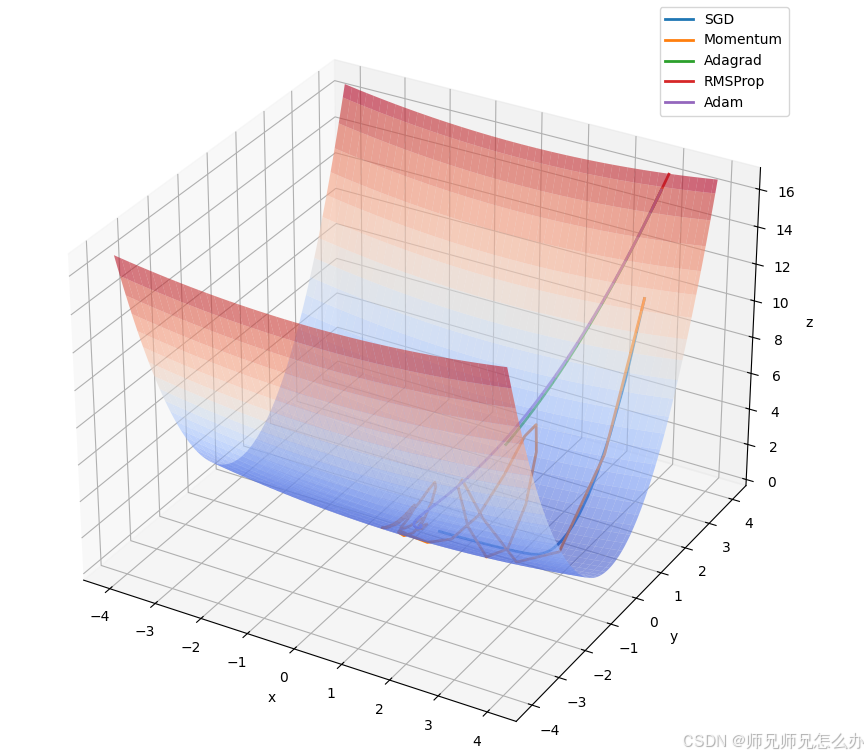
【人工智能】神经网络的优化器optimizer(二):Adagrad自适应学习率优化器
一.自适应梯度算法Adagrad概述 Adagrad(Adaptive Gradient Algorithm)是一种自适应学习率的优化算法,由Duchi等人在2011年提出。其核心思想是针对不同参数自动调整学习率,适合处理稀疏数据和不同参数梯度差异较大的场景。Adagrad通…...

Qt Widget类解析与代码注释
#include "widget.h" #include "ui_widget.h"Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent): QWidget(parent), ui(new Ui::Widget) {ui->setupUi(this); }Widget::~Widget() {delete ui; }//解释这串代码,写上注释 当然可以!这段代码是 Qt …...

Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B深度解析:多语言语义检索的轻量级利器
第一章 引言:语义表示的新时代挑战与Qwen3的破局之路 1.1 文本嵌入的核心价值与技术演进 在人工智能领域,文本嵌入技术如同连接自然语言与机器理解的“神经突触”——它将人类语言转化为计算机可计算的语义向量,支撑着搜索引擎、推荐系统、…...

使用van-uploader 的UI组件,结合vue2如何实现图片上传组件的封装
以下是基于 vant-ui(适配 Vue2 版本 )实现截图中照片上传预览、删除功能,并封装成可复用组件的完整代码,包含样式和逻辑实现,可直接在 Vue2 项目中使用: 1. 封装的图片上传组件 ImageUploader.vue <te…...

涂鸦T5AI手搓语音、emoji、otto机器人从入门到实战
“🤖手搓TuyaAI语音指令 😍秒变表情包大师,让萌系Otto机器人🔥玩出智能新花样!开整!” 🤖 Otto机器人 → 直接点明主体 手搓TuyaAI语音 → 强调 自主编程/自定义 语音控制(TuyaAI…...
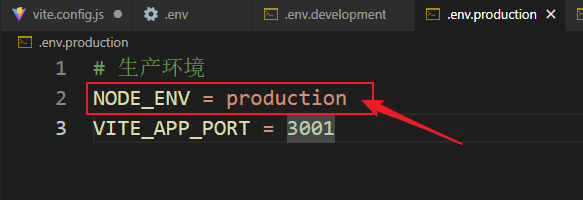
vue3+vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法
vue3vite项目中使用.env文件环境变量方法 .env文件作用命名规则常用的配置项示例使用方法注意事项在vite.config.js文件中读取环境变量方法 .env文件作用 .env 文件用于定义环境变量,这些变量可以在项目中通过 import.meta.env 进行访问。Vite 会自动加载这些环境变…...
