【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_DECIDER
文章目录
- 前言
- SPEED_DECIDER功能简介
- SPEED_DECIDER相关配置
- SPEED_DECIDER流程
- MakeObjectDecision
- GetSTLocation
- Check类函数
- CheckKeepClearCrossable
- CheckStopForPedestrian
- CheckIsFollow
- CheckKeepClearBlocked
- Create类函数
前言
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的PlanOnReferenceLine函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。
在modules/planning/conf/scenario/lane_follow_config.pb.txt配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有task。
stage_config: {stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGEenabled: truetask_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDERtask_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZERtask_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDERtask_type: PATH_DECIDERtask_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZERtask_type: SPEED_DECIDERtask_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDERtask_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZERtask_type: RSS_DECIDER
本文将继续介绍LaneFollow的第11个TASK——SPEED_DECIDER
SPEED_DECIDER功能简介
产生速度决策
 根据粗规划出的速度曲线,依据曲线在障碍物的上方还是下方,采取不同的决策。
根据粗规划出的速度曲线,依据曲线在障碍物的上方还是下方,采取不同的决策。
与路径决策器思路一致,当路径规划器完成路径规划以后,可以得到一条无人车的最优行驶路线,路径决策器就需要对静态障碍物做标签的更新,尤其是那些不在特殊路况下的障碍物,由于缺乏时间信息,路径决策器PathDecider无法对动态障碍物进行标签更新。
而在速度规划器完成未来时间8s或者未来前向距离150m的规划以后,已经得到了一条未来每个时刻无人车出现在参考线上的位置(累积距离s),再配合事先已经规划好的路径,就可以完成对动态障碍物的标签更新,这里仅仅对最近的st障碍物边界框做标签更新,没有对所有的预测时间进行更新。
SPEED_DECIDER相关配置
SPEED_DECIDER流程
SpeedDecider直接继承自Task类,首先构造函数加载相关配置,接着Execute为函数入口,进行具体执行。Execute调用了函数MakeObjectDecision,而整个SpeedDecider的主要逻辑也正在MakeObjectDecision之中。
- 输入:
common::Status SpeedDecider::Execute(Frame* frame, ReferenceLineInfo* reference_line_info) {frame和reference_line_info
因此接下来我们直接来看MakeObjectDecision函数。
主要流程如下图所示:
MakeObjectDecision
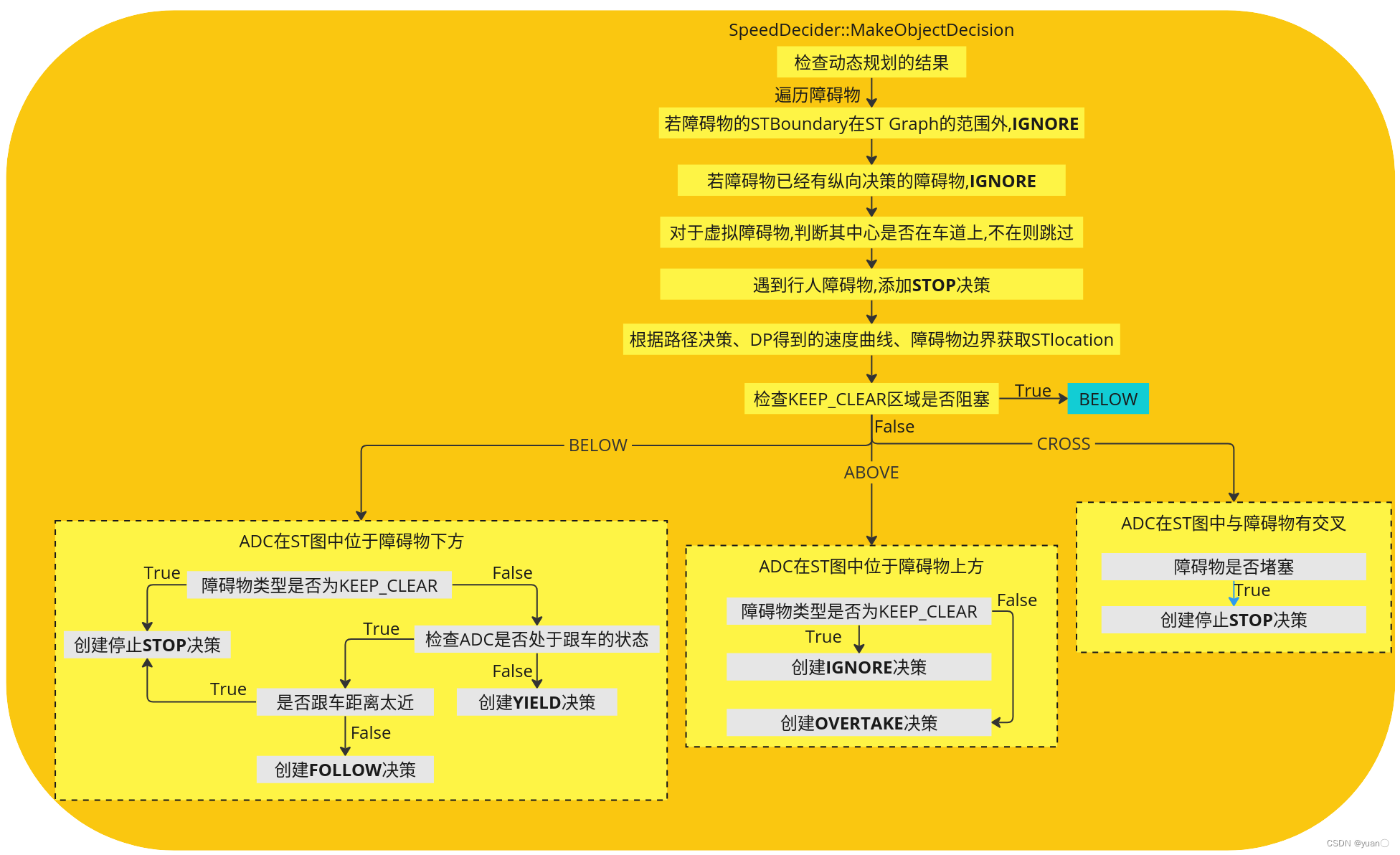
SpeedDecider根据路径决策、DP算法生成的速度曲线和障碍物的STBoundary的位置关系生成Ignore、Stop、Follow、Yield、Overtake的纵向决策。
Status SpeedDecider::MakeObjectDecision(const SpeedData& speed_profile, PathDecision* const path_decision) const {// 检查动态规划的结果if (speed_profile.size() < 2) {const std::string msg = "dp_st_graph failed to get speed profile.";AERROR << msg;return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}// 遍历障碍物for (const auto* obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {auto* mutable_obstacle = path_decision->Find(obstacle->Id());const auto& boundary = mutable_obstacle->path_st_boundary();// 若障碍物的STBoundary在ST Graph的范围内,忽略if (boundary.IsEmpty() || boundary.max_s() < 0.0 ||boundary.max_t() < 0.0 ||boundary.min_t() >= speed_profile.back().t()) {AppendIgnoreDecision(mutable_obstacle);continue;}// 若障碍物已经有纵向决策的障碍物,忽略if (obstacle->HasLongitudinalDecision()) {AppendIgnoreDecision(mutable_obstacle);continue;}// for Virtual obstacle, skip if center point NOT "on lane"// 对于虚拟障碍物,判断其中心是否在车道上,不在则跳过if (obstacle->IsVirtual()) {const auto& obstacle_box = obstacle->PerceptionBoundingBox();if (!reference_line_->IsOnLane(obstacle_box.center())) {continue;}}// always STOP for pedestrian// 遇到行人障碍物,添加stop决策if (CheckStopForPedestrian(*mutable_obstacle)) {ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision,-FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle)) {mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/pedestrian",stop_decision);}continue;}// 根据路径决策、DP得到的速度曲线、障碍物边界获取STlocationauto location = GetSTLocation(path_decision, speed_profile, boundary);// 检查KEEP_CLEAR区域是否阻塞if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {if (CheckKeepClearBlocked(path_decision, *obstacle)) {location = BELOW;}}}switch (location) {case BELOW:// 若障碍物类型为KEEP_CLEAR,创建停止决策if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision, 0.0)) {mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/keep_clear",stop_decision);}// 检查ADC是否处于跟车的状态} else if (CheckIsFollow(*obstacle, boundary)) {// stop for low_speed decelerating// 是否跟车距离太近,if (IsFollowTooClose(*mutable_obstacle)) {ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;// 创建停止决策if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision,-FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle)) {mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/too_close",stop_decision);}} else { // high speed or low speed accelerating// FOLLOW decisionObjectDecisionType follow_decision;if (CreateFollowDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &follow_decision)) {mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph",follow_decision);}}} else {// YIELD decisionObjectDecisionType yield_decision;if (CreateYieldDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &yield_decision)) {mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph",yield_decision);}}break;case ABOVE:if (boundary.boundary_type() == STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {ObjectDecisionType ignore;ignore.mutable_ignore();mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph", ignore);} else {// OVERTAKE decisionObjectDecisionType overtake_decision;if (CreateOvertakeDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &overtake_decision)) {mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/overtake",overtake_decision);}}break;case CROSS:// 障碍物是否堵塞if (mutable_obstacle->IsBlockingObstacle()) {ObjectDecisionType stop_decision;// 建立停止决策if (CreateStopDecision(*mutable_obstacle, &stop_decision,-FLAGS_min_stop_distance_obstacle)) {mutable_obstacle->AddLongitudinalDecision("dp_st_graph/cross",stop_decision);}const std::string msg = absl::StrCat("Failed to find a solution for crossing obstacle: ",mutable_obstacle->Id());AERROR << msg;return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);}break;default:AERROR << "Unknown position:" << location;}AppendIgnoreDecision(mutable_obstacle);}return Status::OK();
}
其中的核心部分就是这一句代码:根据路径决策、DP得到的速度曲线、障碍物边界获取STlocation。
// 根据路径决策、DP得到的速度曲线、障碍物边界获取STlocationauto location = GetSTLocation(path_decision, speed_profile, boundary);
GetSTLocation
接着来看GetSTLocation函数的具体实现:
GetSTLocation依据在ST图中障碍物与速度曲线上的各点之间的位置关系来确定决策。
SpeedDecider::STLocation SpeedDecider::GetSTLocation(const PathDecision* const path_decision, const SpeedData& speed_profile,const STBoundary& st_boundary) const {// 若boundary为空,设置为BELOW;一般情况下这个障碍物直接被跳过,不考虑if (st_boundary.IsEmpty()) {return BELOW;}STLocation st_location = BELOW;bool st_position_set = false;const double start_t = st_boundary.min_t();const double end_t = st_boundary.max_t();// 遍历速度曲线中的每一个点for (size_t i = 0; i + 1 < speed_profile.size(); ++i) {const STPoint curr_st(speed_profile[i].s(), speed_profile[i].t());const STPoint next_st(speed_profile[i + 1].s(), speed_profile[i + 1].t());// 跳过和障碍物不在一个ST范围内的if (curr_st.t() < start_t && next_st.t() < start_t) {continue;}if (curr_st.t() > end_t) {break;}if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {common::math::LineSegment2d speed_line(curr_st, next_st);// 检查是否碰撞if (st_boundary.HasOverlap(speed_line)) {ADEBUG << "speed profile cross st_boundaries.";st_location = CROSS;if (!FLAGS_use_st_drivable_boundary) {// 检查类型是否是KEEP_CLEARif (st_boundary.boundary_type() ==STBoundary::BoundaryType::KEEP_CLEAR) {// 若CheckKeepClearCrossable为false,则设置为BELOWif (!CheckKeepClearCrossable(path_decision, speed_profile,st_boundary)) {st_location = BELOW;}}}break;}}// note: st_position can be calculated by checking two st points once// but we need iterate all st points to make sure there is no CROSSif (!st_position_set) {if (start_t < next_st.t() && curr_st.t() < end_t) {STPoint bd_point_front = st_boundary.upper_points().front();double side = common::math::CrossProd(bd_point_front, curr_st, next_st);st_location = side < 0.0 ? ABOVE : BELOW;st_position_set = true;}}}return st_location;
}Check类函数
Check类函数,这一类函数主要用于对不同障碍物进行判断。
CheckKeepClearCrossable
bool SpeedDecider::CheckKeepClearCrossable(const PathDecision* const path_decision, const SpeedData& speed_profile,const STBoundary& keep_clear_st_boundary) const {bool keep_clear_crossable = true;// 计算最后一点的速度const auto& last_speed_point = speed_profile.back();double last_speed_point_v = 0.0;if (last_speed_point.has_v()) {last_speed_point_v = last_speed_point.v();} else {const size_t len = speed_profile.size();if (len > 1) {const auto& last_2nd_speed_point = speed_profile[len - 2];last_speed_point_v = (last_speed_point.s() - last_2nd_speed_point.s()) /(last_speed_point.t() - last_2nd_speed_point.t());}}static constexpr double kKeepClearSlowSpeed = 2.5; // m/sADEBUG << "last_speed_point_s[" << last_speed_point.s()<< "] st_boundary.max_s[" << keep_clear_st_boundary.max_s()<< "] last_speed_point_v[" << last_speed_point_v << "]";// 若最后一点的s小于KeepClear区域的最大值,且最后一点的速度小于阈值速度,// 则keep_clear_crossable = falseif (last_speed_point.s() <= keep_clear_st_boundary.max_s() &&last_speed_point_v < kKeepClearSlowSpeed) {keep_clear_crossable = false;}return keep_clear_crossable;
}
CheckStopForPedestrian
bool SpeedDecider::CheckStopForPedestrian(const Obstacle& obstacle) const {const auto& perception_obstacle = obstacle.Perception();// 检查类型是否是行人if (perception_obstacle.type() != PerceptionObstacle::PEDESTRIAN) {return false;}const auto& obstacle_sl_boundary = obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary();// 不考虑在车之后的行人if (obstacle_sl_boundary.end_s() < adc_sl_boundary_.start_s()) {return false;}// read pedestrian stop time from PlanningContextauto* mutable_speed_decider_status = injector_->planning_context()->mutable_planning_status()->mutable_speed_decider();// 用hash表存储停止时间 std::unordered_map<std::string, double> stop_time_map;for (const auto& pedestrian_stop_time :mutable_speed_decider_status->pedestrian_stop_time()) {stop_time_map[pedestrian_stop_time.obstacle_id()] =pedestrian_stop_time.stop_timestamp_sec();}const std::string& obstacle_id = obstacle.Id();// update stop timestamp on static pedestrian for watch timer// check on stop timer for static pedestriansstatic constexpr double kSDistanceStartTimer = 10.0;static constexpr double kMaxStopSpeed = 0.3;static constexpr double kPedestrianStopTimeout = 4.0;bool result = true;if (obstacle.path_st_boundary().min_s() < kSDistanceStartTimer) {const auto obstacle_speed = std::hypot(perception_obstacle.velocity().x(),perception_obstacle.velocity().y());// 如果行人速度超过最大停车速度,则删除行人if (obstacle_speed > kMaxStopSpeed) {stop_time_map.erase(obstacle_id);} else {if (stop_time_map.count(obstacle_id) == 0) {// add timestampstop_time_map[obstacle_id] = Clock::NowInSeconds();ADEBUG << "add timestamp: obstacle_id[" << obstacle_id << "] timestamp["<< Clock::NowInSeconds() << "]";} else {// check timeoutdouble stop_timer = Clock::NowInSeconds() - stop_time_map[obstacle_id];ADEBUG << "stop_timer: obstacle_id[" << obstacle_id << "] stop_timer["<< stop_timer << "]";// 检查其是否已经等待了足够长的时间if (stop_timer >= kPedestrianStopTimeout) {result = false;}}}}// write pedestrian stop time to PlanningContextmutable_speed_decider_status->mutable_pedestrian_stop_time()->Clear();for (const auto& stop_time : stop_time_map) {auto pedestrian_stop_time =mutable_speed_decider_status->add_pedestrian_stop_time();pedestrian_stop_time->set_obstacle_id(stop_time.first);pedestrian_stop_time->set_stop_timestamp_sec(stop_time.second);}return result;
}
CheckIsFollow
bool SpeedDecider::CheckIsFollow(const Obstacle& obstacle,const STBoundary& boundary) const {const double obstacle_l_distance =std::min(std::fabs(obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().start_l()),std::fabs(obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().end_l()));// FLAGS_follow_min_obs_lateral_distance: obstacle min lateral distance to follow; 2.5if (obstacle_l_distance > FLAGS_follow_min_obs_lateral_distance) {return false;}// move towards adcif (boundary.bottom_left_point().s() > boundary.bottom_right_point().s()) {return false;}static constexpr double kFollowTimeEpsilon = 1e-3;static constexpr double kFollowCutOffTime = 0.5;if (boundary.min_t() > kFollowCutOffTime ||boundary.max_t() < kFollowTimeEpsilon) {return false;}// cross lane but be moving to different direction// FLAGS_follow_min_time_sec: // " min follow time in st region before considering a valid follow,"// " this is to differentiate a moving obstacle cross adc's"// " current lane and move to a different direction"// 2.0if (boundary.max_t() - boundary.min_t() < FLAGS_follow_min_time_sec) {return false;}return true;
}
CheckKeepClearBlocked
bool SpeedDecider::CheckKeepClearBlocked(const PathDecision* const path_decision,const Obstacle& keep_clear_obstacle) const {bool keep_clear_blocked = false;// check if overlap with other stop wallfor (const auto* obstacle : path_decision->obstacles().Items()) {if (obstacle->Id() == keep_clear_obstacle.Id()) {continue;}const double obstacle_start_s = obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().start_s();const double adc_length =VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param().length();const double distance =obstacle_start_s - keep_clear_obstacle.PerceptionSLBoundary().end_s();if (obstacle->IsBlockingObstacle() && distance > 0 &&distance < (adc_length / 2)) {keep_clear_blocked = true;break;}}return keep_clear_blocked;
}
Create类函数
建立各类决策。
相关文章:

【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_DECIDER
文章目录 前言SPEED_DECIDER功能简介SPEED_DECIDER相关配置SPEED_DECIDER流程MakeObjectDecisionGetSTLocationCheck类函数CheckKeepClearCrossableCheckStopForPedestrianCheckIsFollowCheckKeepClearBlocked Create类函数 前言 在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算…...
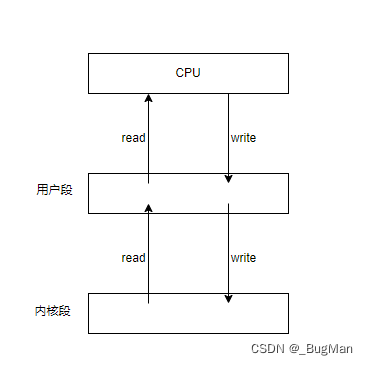
【操作系统】一文快速入门,很适合JAVA后端看
作者简介: 目录 1.概述 2.CPU管理 3.内存管理 4.IO管理 1.概述 操作系统可以看作一个计算机的管理系统,对计算机的硬件资源提供了一套完整的管理解决方案。计算机的硬件组成有五大模块:运算器、控制器、存储器、输入设备、输出设备。操作…...

C++ Primer阅读笔记--allocator类的使用
1--allocator类的使用背景 new 在分配内存时具有一定的局限性,其将内存分配和对象构造组合在一起;当分配一大块内存时,一般希望可以在内存上按需构造对象,这时需要将内存分配和对象构造分离,而定义在头文件 memory 的 …...
【C++历险记】面向对象|菱形继承及菱形虚拟继承
个人主页:兜里有颗棉花糖💪 欢迎 点赞👍 收藏✨ 留言✉ 加关注💓本文由 兜里有颗棉花糖 原创 收录于专栏【C之路】💌 本专栏旨在记录C的学习路线,望对大家有所帮助🙇 希望我们一起努力、成长&…...
【Locomotor运动模块】攀爬
文章目录 一、攀爬主体“伪身体”1、“伪身体”的设置2、“伪身体”和“真实身体”,为什么同步移动3、“伪身体”和“真实身体”,碰到墙时不同步的原因①现象②原因③解决 二、攀爬1、需要的组件:“伪身体”、Climbing、Climbable及Interacto…...
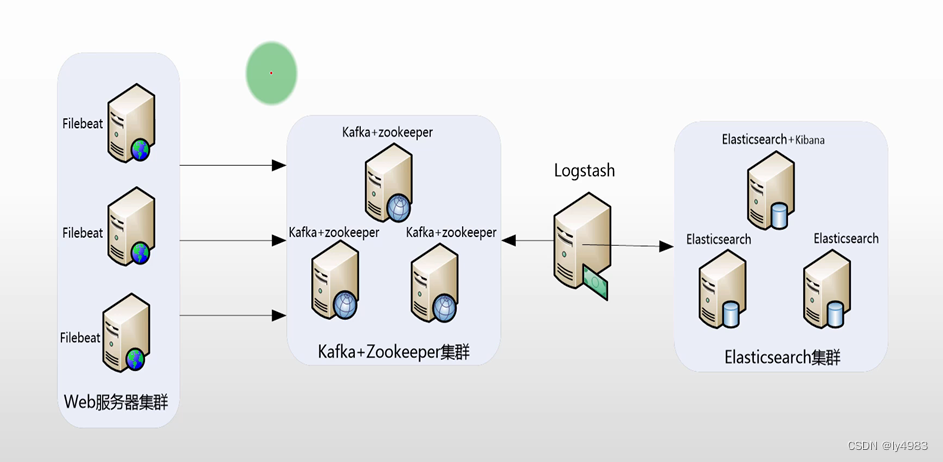
ELK安装、部署、调试(一)设计规划及准备
一、整体规划如图: 【filebeat】 需要收集日志的服务器,安装filebeat软件,用于收集日志。logstash也可以收集日志,但是占用的系统资源过大,所以使用了filebeat来收集日志。 【kafka】 接收filebeat的日志ÿ…...

【CSS】解决对齐的小问题
问题: 表单或者页面上可能遇到文字无法对平均分,带有冒号的文本无法左右对齐的情况 常见的解决方式: 解决如下图 仍无法解决对齐的问题,还需要考虑字数 解决 这里用css的方式解决 增加 i 标签 固定宽度,设置 i …...
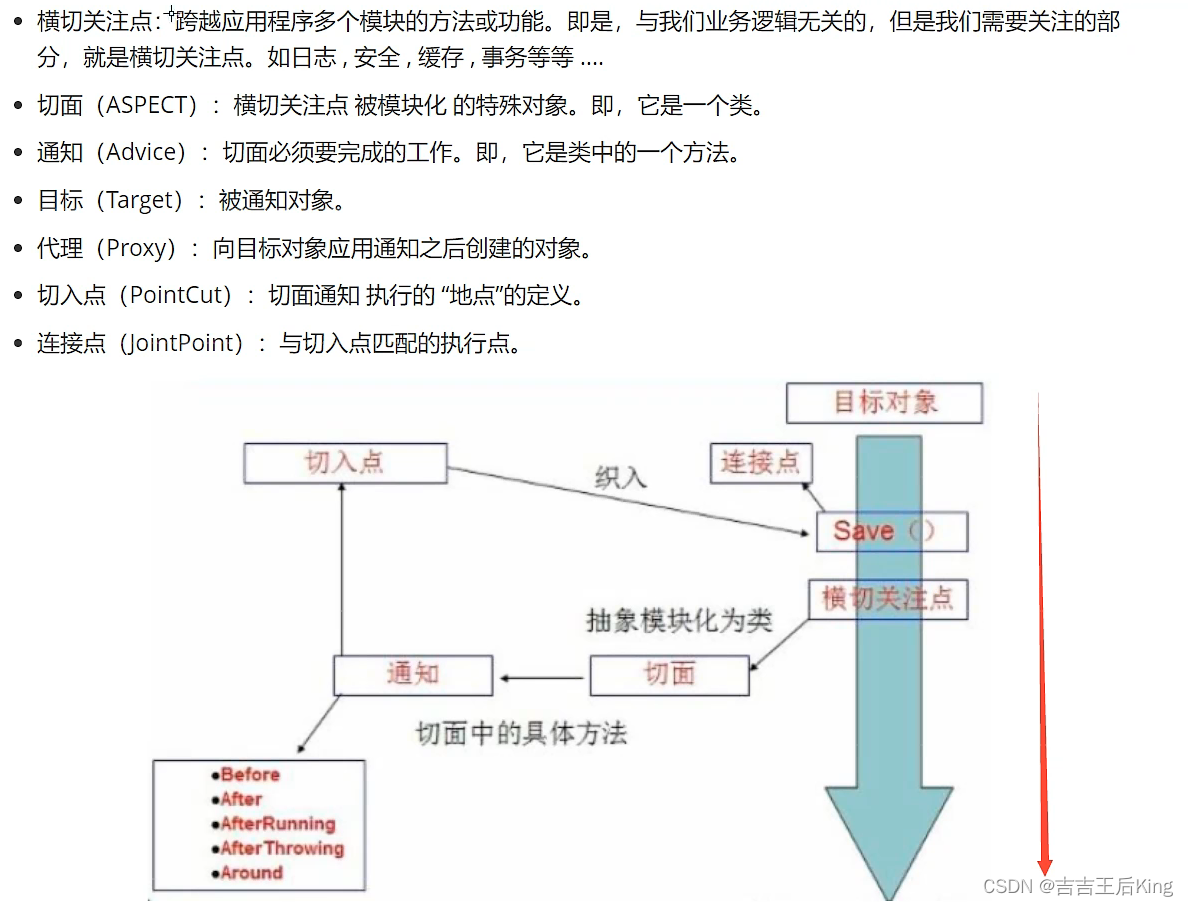
【狂神】Spring5(Aop的实现方式)
今天没有偷懒,只是忘了Mybatis,所以去补课了~ ┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓ NICE PIGGY PIG.. ┗━━━━━━━△━━━━━━━┛ ヽ(・ω・)ノ | / UU 1.Aop实现方式一 1.1、什…...

第2章 Linux多进程开发 2.18 内存映射
内存映射:可以进行进程间的通信 1.如果对mmap的返回值(ptr)做操作(ptr), munmap是否能够成功? void * ptr mmap(…); ptr; 可以对其进行操作 munmap(ptr, len); // 错误,要保存地址 2.如果open时O_RDONLY, mmap时prot参数指定PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE会怎样? 错…...

【C++深入浅出】类和对象上篇(类的基础、类的模型以及this指针)
目录 一. 前言 二. 面向对象与面向过程 2.1 面向过程 2.2 面向对象 三. 类的基础知识 3.1 类的引入 3.2 类的定义 3.3 成员变量的命名规则 3.4 封装 3.5 类的访问限定符 3.6 类的作用域 3.7 类的实例化 四. 类的对象模型 4.1 类对象的大小 4.2 类对象的存储方式 …...

气象站在日常生活中的重要性
气象站在我们的日常生活中起着重要的作用,它监测着天气的变化,能够提供及时、准确的天气信息,对我们的生产和生活都有着极大的影响。 一、气象站的工作原理 气象站通过一系列传感器设备,对风速、风向、温度、湿度、气压、雨量等…...

数据结构学习系列之用队列实现栈功能与用栈实现队列功能
队列与栈:队列(Queue)是一种先进先出(FIFO)的线性表;栈(Stack)是一种后进先出(LIFO)的线性表;实例1:用队列实现栈的功能;算…...
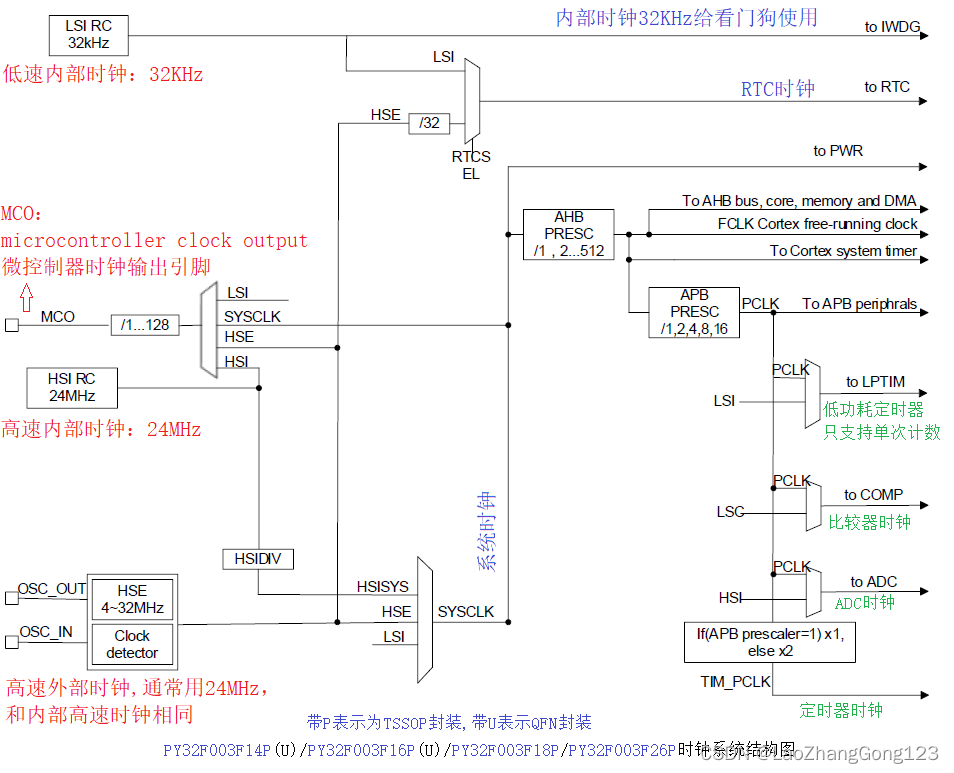
PY32F003F18P单片机概述
PY32F003F18P单片机是普冉的一款ARM微控制器,内核是Cortex-M0。这个单片机的特色,就是价格便宜,FLASH和SRAM远远超过8位单片机,市场竞争力很强大。 一、硬件资源: 1)、FLASH为64K字节; 2)、SRAM为8K字节&…...
查看GPU占用率
如何监控NVIDIA GPU 的运行状态和使用情况_nvidia 85c_LiBiGo的博客-CSDN博客设备跟踪和管理正成为机器学习工程的中心焦点。这个任务的核心是在模型训练过程中跟踪和报告gpu的使用效率。有效的GPU监控可以帮助我们配置一些非常重要的超参数,例如批大小,…...
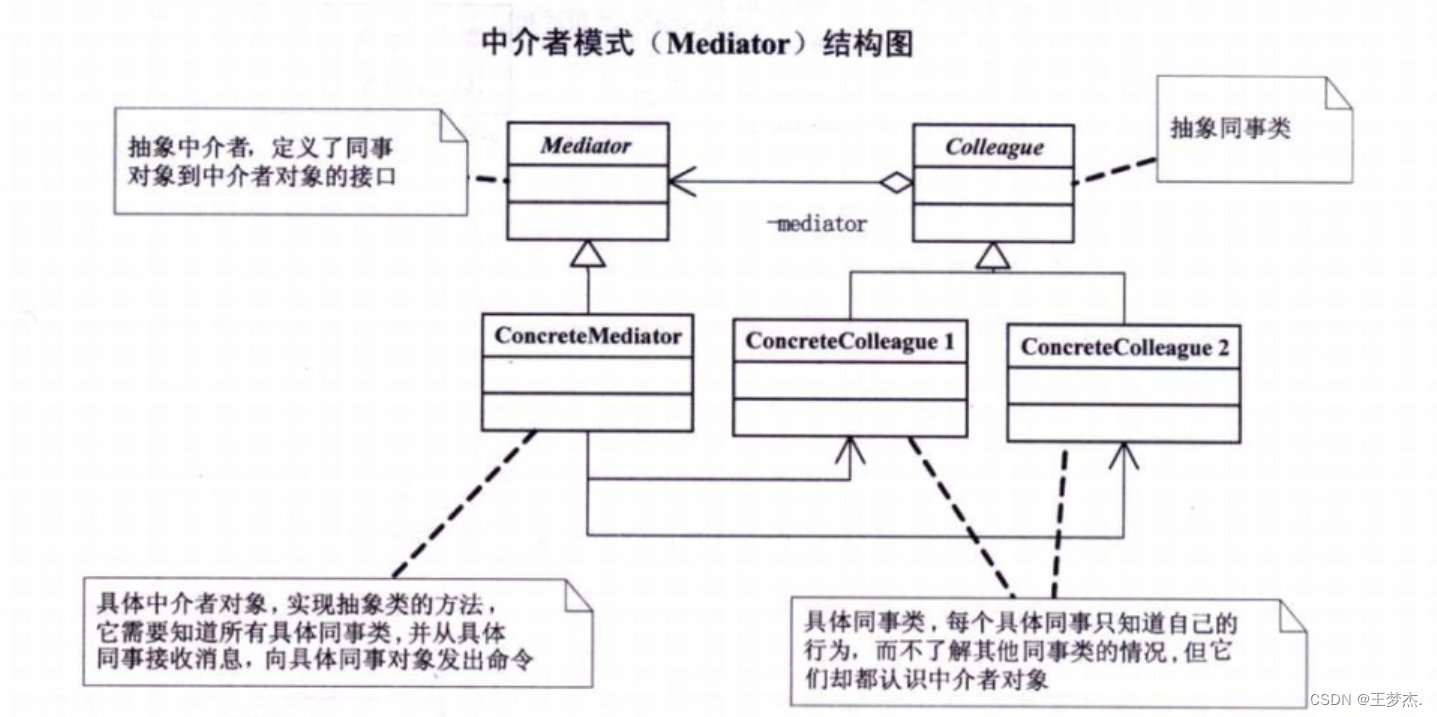
设计模式-中介者模式
文章目录 一、前言二、中介者模式1、定义2、未使用/使用中介者模式对比2.1、未使用中介者模式:2.2、使用中介者模式: 3、角色分析3.1、中介者(Mediator):3.2、同事(Colleague):3.3、…...

react 大杂烩
组件 1.是返回标签的js函数,是可重复利用的UI元素 function test(){ return ( test ); } 2.构建组件: (1)export 导出组件 (2)定义函数,名称必须以大写字母开头 (3)…...
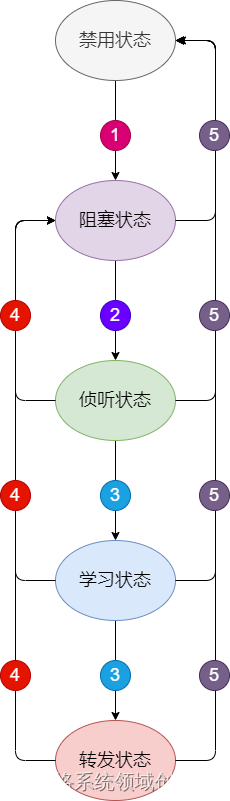
图解 STP
网络环路 现在我们的生活已经离不开网络,如果我家断网,我会抱怨这什么破网络,影响到我刷抖音、打游戏;如果公司断网,那老板估计会骂娘,因为会影响到公司正常运转,直接造成经济损失。网络通信中&…...
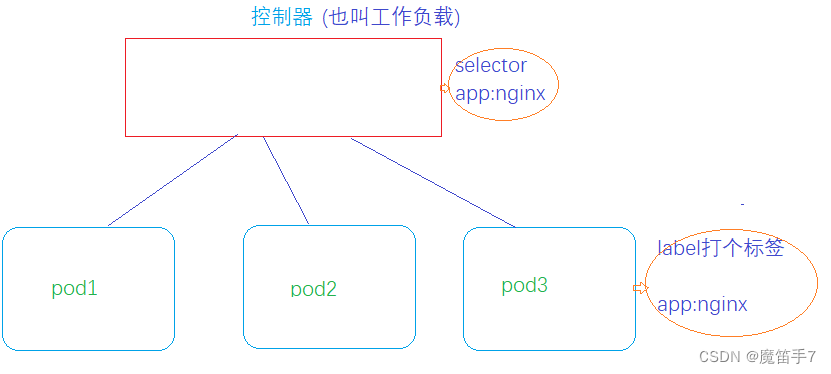
Kubernetes技术--k8s核心技术Controller控制器
1.Controller概述 Controller是在集群上管理和运行容器的对象。是一个实际存在的对象。 2.pod和Controller之间的关系 pod通过controller实现应用的运维,包括伸缩、滚动升级等操作。 这里pod和controller通过label标签来建立关系。如下所示: 3.Deployment控制器应用场景 -1:…...

Kubernetes技术--k8s核心技术 Secret
1.概述 Secret 解决了密码、token、密钥等敏感数据的配置问题,而不需要把这些敏感数据暴露到镜像或者 Pod Spec中。Secret可以以 Volume 或者环境变量的方式使用。 作用 加密数据存储在/etc中,使得pod容器以挂载volume方式进行访问。在进行的数据存储中是以base64加密的方式…...

day27 String类 正则表达式
String类的getBytes方法 String s "腻害"; byte[] bytes s.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); String类的new String方法 String ss "ss我的"; byte[] gbks ss.getBytes("gbk"); String gbk new String(gbks, "gbk"); String类的…...

日语AI面试高效通关秘籍:专业解读与青柚面试智能助攻
在如今就业市场竞争日益激烈的背景下,越来越多的求职者将目光投向了日本及中日双语岗位。但是,一场日语面试往往让许多人感到步履维艰。你是否也曾因为面试官抛出的“刁钻问题”而心生畏惧?面对生疏的日语交流环境,即便提前恶补了…...

【杂谈】-递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战
递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战 文章目录 递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战1、自我改进型人工智能的崛起2、人工智能如何挑战人类监管?3、确保人工智能受控的策略4、人类在人工智能发展中的角色5、平衡自主性与控制力6、总结与…...

Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements
Leetcode 3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路2. 代码实现 题目链接:3576. Transform Array to All Equal Elements 1. 解题思路 这一题思路上就是分别考察一下是否能将其转化为全1或者全-1数组即可。 至于每一种情况是否可以达到…...
1.3 VSCode安装与环境配置
进入网址Visual Studio Code - Code Editing. Redefined下载.deb文件,然后打开终端,进入下载文件夹,键入命令 sudo dpkg -i code_1.100.3-1748872405_amd64.deb 在终端键入命令code即启动vscode 需要安装插件列表 1.Chinese简化 2.ros …...
k8s业务程序联调工具-KtConnect
概述 原理 工具作用是建立了一个从本地到集群的单向VPN,根据VPN原理,打通两个内网必然需要借助一个公共中继节点,ktconnect工具巧妙的利用k8s原生的portforward能力,简化了建立连接的过程,apiserver间接起到了中继节…...

人工智能(大型语言模型 LLMs)对不同学科的影响以及由此产生的新学习方式
今天是关于AI如何在教学中增强学生的学习体验,我把重要信息标红了。人文学科的价值被低估了 ⬇️ 转型与必要性 人工智能正在深刻地改变教育,这并非炒作,而是已经发生的巨大变革。教育机构和教育者不能忽视它,试图简单地禁止学生使…...
论文阅读笔记——Muffin: Testing Deep Learning Libraries via Neural Architecture Fuzzing
Muffin 论文 现有方法 CRADLE 和 LEMON,依赖模型推理阶段输出进行差分测试,但在训练阶段是不可行的,因为训练阶段直到最后才有固定输出,中间过程是不断变化的。API 库覆盖低,因为各个 API 都是在各种具体场景下使用。…...
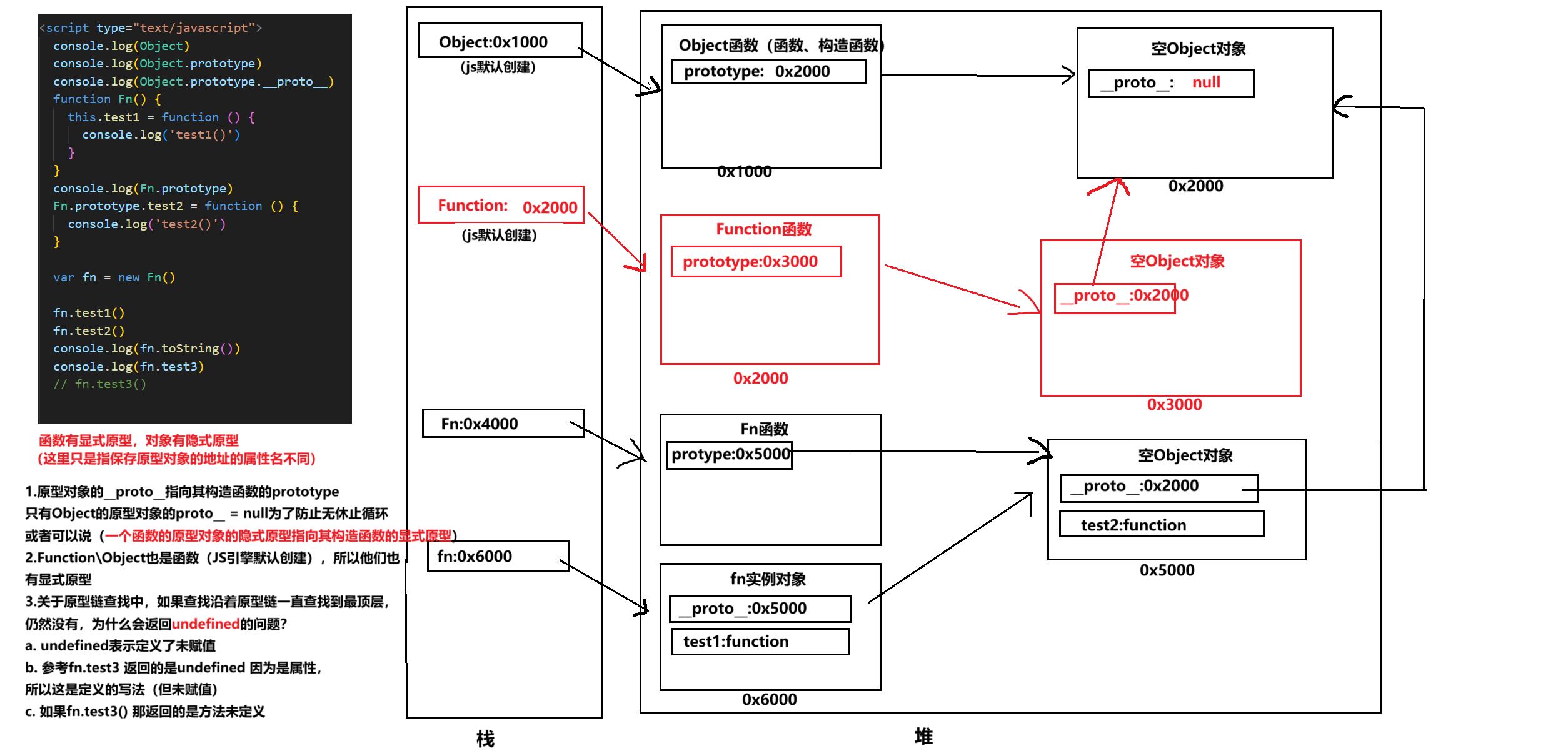
图解JavaScript原型:原型链及其分析 | JavaScript图解
忽略该图的细节(如内存地址值没有用二进制) 以下是对该图进一步的理解和总结 1. JS 对象概念的辨析 对象是什么:保存在堆中一块区域,同时在栈中有一块区域保存其在堆中的地址(也就是我们通常说的该变量指向谁&…...

Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫
Linux安全加固:从攻防视角构建系统免疫 构建坚不可摧的数字堡垒 引言:攻防对抗的新纪元 在日益复杂的网络威胁环境中,Linux系统安全已从被动防御转向主动免疫。2023年全球网络安全报告显示,高级持续性威胁(APT)攻击同比增长65%,平均入侵停留时间缩短至48小时。本章将从…...
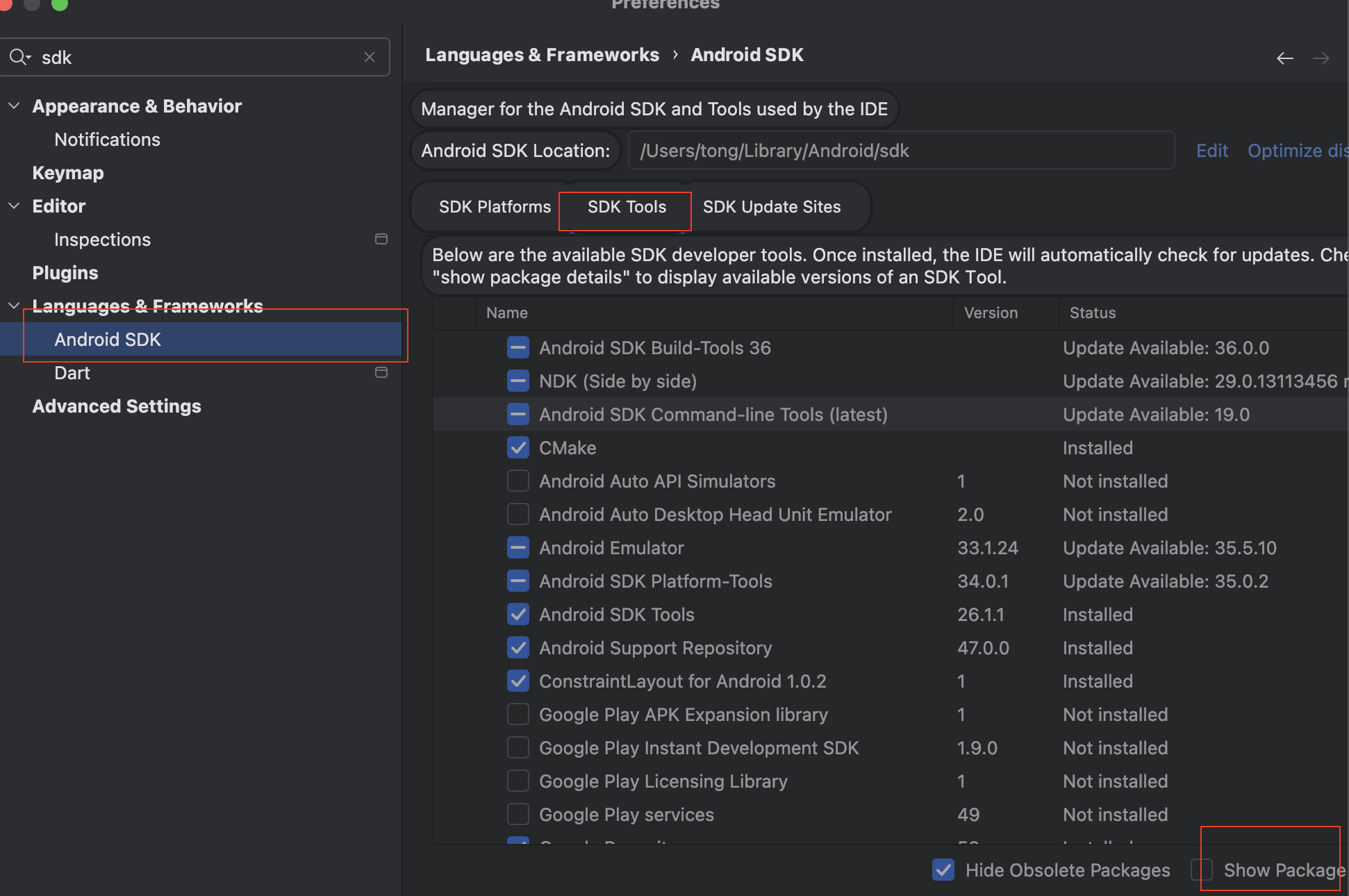
Mac flutter环境搭建
一、下载flutter sdk 制作 Android 应用 | Flutter 中文文档 - Flutter 中文开发者网站 - Flutter 1、查看mac电脑处理器选择sdk 2、解压 unzip ~/Downloads/flutter_macos_arm64_3.32.2-stable.zip \ -d ~/development/ 3、添加环境变量 命令行打开配置环境变量文件 ope…...
