K8s中的RBAC(Role-Based Access Control)
摘要
RBAC(基于角色的访问控制)是一种在Kubernetes中用于控制用户对资源的访问权限的机制。以下是RBAC的设计实现说明:
- 角色(Role)和角色绑定(RoleBinding):角色定义了一组权限,角色绑定将角色与用户或用户组相关联。通过角色和角色绑定,可以在集群或命名空间级别授予用户或用户组对资源的访问权限。
- 服务账号(ServiceAccount):服务账号是一种专门用于身份认证和授权的账号类型。可以为服务账号分配角色,在应用程序中使用它来访问Kubernetes API。
- ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding:与角色和角色绑定类似,但是ClusterRole和ClusterRoleBinding适用于整个集群而不是单个命名空间。集群级别的角色和角色绑定可以用于集群范围的操作,例如创建命名空间或操作集群配置。
- 命名空间(Namespace)级别的RBAC:通过在命名空间级别定义角色和角色绑定,可以将特定的权限限制在命名空间内。这样,不同命名空间的用户或用户组可以具有不同的权限。
- 细粒度控制:RBAC允许在资源级别进行细粒度的访问控制。可以使用RBAC规则来控制对特定资源类型的创建、查看、修改和删除权限。
- 隐式授权:RBAC支持隐式授权,即如果用户具有访问某个资源的权限,那么他也具有访问该资源子资源的权限。例如,如果用户具有访问Pod的权限,那么他也具有访问该Pod的日志的权限。
- 预定义角色和角色绑定:Kubernetes提供了一些预定义的角色和角色绑定,包括集群管理员、命名空间管理员和只读用户等。这些预定义角色可以用作RBAC的基础,也可以根据需要创建自定义角色。
总的来说,RBAC是通过角色和角色绑定来定义和管理用户对资源的访问权限。它允许细粒度的控制和灵活的配置,以便在Kubernetes中确保安全和权限的管理。通过使用RBAC,可以根据用户或用户组的角色来限制他们对Kubernetes集群中的资源的访问和操作。
Simply put
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) is a mechanism in Kubernetes (K8s) that controls user access to resources. Here is a detailed explanation of RBAC design and implementation in Kubernetes:
- Roles and RoleBindings: Roles define a set of permissions, and RoleBindings associate roles with users or user groups. Roles and RoleBindings are used to grant users or groups access to resources at the cluster or namespace level.
- Service Accounts: Service accounts are dedicated accounts used for authentication and authorization purposes. Roles can be assigned to service accounts, and they can be utilized by applications to access the Kubernetes API.
- ClusterRoles and ClusterRoleBindings: Similar to Roles and RoleBindings, but ClusterRoles and ClusterRoleBindings apply at the cluster level instead of a specific namespace. Cluster-level roles and role bindings can be used for cluster-wide operations, such as creating namespaces or managing cluster configurations.
- Namespace-level RBAC: By defining roles and role bindings at the namespace level, permissions can be restricted within specific namespaces. This allows different users or user groups in different namespaces to have different access permissions.
- Fine-grained control: RBAC allows fine-grained access control at the resource level. RBAC rules can be used to control permissions for creating, viewing, modifying, and deleting specific resource types.
- Implicit authorization: RBAC supports implicit authorization, meaning if a user has access permissions to a resource, they also have access to its subresources. For example, if a user has access to Pods, they also have access to view the logs of that Pod.
- Predefined Roles and RoleBindings: Kubernetes provides some predefined roles and role bindings, including cluster-admin, namespace-admin, and read-only user roles. These predefined roles can be used as a foundation for RBAC or custom roles can be created as per requirements.
In summary, RBAC in Kubernetes is implemented using roles and role bindings to define and manage user access to resources. It allows for fine-grained control and flexible configuration to ensure effective security and permissions management within a Kubernetes cluster. By utilizing RBAC, user access and operations on resources can be restricted based on their roles and permissions.
Can-i 命令说明
在Kubernetes(K8s)中,kubectl can-i命令用于检查当前用户对指定资源的操作权限。它可以帮助用户确定他们是否有权限执行某个特定操作。
kubectl can-i命令的语法如下:
kubectl auth can-i VERB RESOURCE其中,VERB表示要执行的操作,例如"get"、“create”、“delete"等,而RESOURCE表示要操作的资源类型,例如"pods”、“deployments”、"services"等。
kubectl can-i命令会在集群中查询当前用户的权限配置,然后确定用户是否具有执行相应操作的权限。如果用户具有权限,则输出"yes";如果用户没有权限,则输出"no"。此外,如果指定的资源类型或操作无效,命令会输出"no (no such resource/group/verb)"。
例如,要检查当前用户是否有权限获取命名空间中的部署(deployments),可以运行以下命令:
kubectl auth can-i get deployments -n <namespace>其中,<namespace>是要检查权限的命名空间。
kubectl can-i命令对于用户在执行操作之前进行权限检查非常有用。它可以帮助用户避免未经授权的操作,并提供更好的安全性和控制。
On the other hand
In the vast world of Kubernetes, where countless containers are orchestrated seamlessly, RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) emerges as a powerful tool to maintain order and security.
In this futuristic realm, organizations have established massive clusters spanning galaxies, each containing a multitude of applications and services. The need for efficient and granular authorization is paramount, ensuring that only the right individuals have access to perform specific actions within the cluster.
Enter RBAC, a system designed to govern access based on predefined roles and permissions. It serves as a protective shield guarding the cluster against unauthorized access and potential malicious activities.
At the core of RBAC lies the concept of roles, which represent a collection of permissions defining what actions can be performed. These roles are meticulously crafted according to the specific needs of each entity within the Kubernetes infrastructure - be it a user, a group, or even a service account.
Roles are then bound to subjects, granting them the authority to execute actions within the cluster. Kubernetes administrators have the power to assign roles to individual users or assign them to groups for convenient management. With RBAC, organizations can enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users only have access to the resources and functions they truly need.
The architecture of RBAC is fortified with additional layers of complexity, introducing role bindings and service accounts. Role bindings establish the association between roles and subjects, ensuring that each entity operates within the boundaries set by their assigned permissions. Service accounts, on the other hand, enable Kubernetes services themselves to securely authenticate and interact with the cluster, further enhancing the system’s flexibility.
But the true power of RBAC shines when combined with the dynamic nature of Kubernetes. Through the utilization of namespaces, RBAC can partition the cluster, confining roles and subjects to specific project boundaries. This enables organizations to maintain isolation and control across a multitude of teams and projects, ensuring that access permissions are carefully curated and enforced.
As the Kubernetes universe continues to expand with new features and evolving demands, RBAC stands as a steadfast guardian. Its flexible and modular design allows it to adapt to the ever-changing needs of organizations, effortlessly regulating access to critical resources, and preserving the cluster’s integrity.
In this dynamic future, where the Kubernetes landscape continuously evolves with technological advancements, RBAC ensures that the intergalactic realm of containers remains secure, regulated, and protected against the unknown forces that may seek to infiltrate and disrupt this intricate web of services.
相关文章:
)
K8s中的RBAC(Role-Based Access Control)
摘要 RBAC(基于角色的访问控制)是一种在Kubernetes中用于控制用户对资源的访问权限的机制。以下是RBAC的设计实现说明: 角色(Role)和角色绑定(RoleBinding):角色定义了一组权限&am…...
)
肖sir__设计测试用例方法之经验测试方法09_(黑盒测试)
设计测试用例方法之经验测试方法 一、经验的测试技术 (1)基于经验的测试技术之错误推测法 错误推测法也叫错误猜测法,就是根据经验猜想,已有的缺陷,测试经验和失败数据等可能有什么问题并依此设计测试用例 ࿰…...
Python爬虫:下载小红书无水印图片、视频
该代码只提供学习使用,该项目是基于https://github.com/JoeanAmier/XHS_Downloader的小改动 1.下载项目 git clone https://github.com/zhouayi/XHS_Downloader.git2.找到需要下载的文章的ID 写入main.py中 3.下载 python main.py最近很火的莲花楼为例<嘿嘿…...
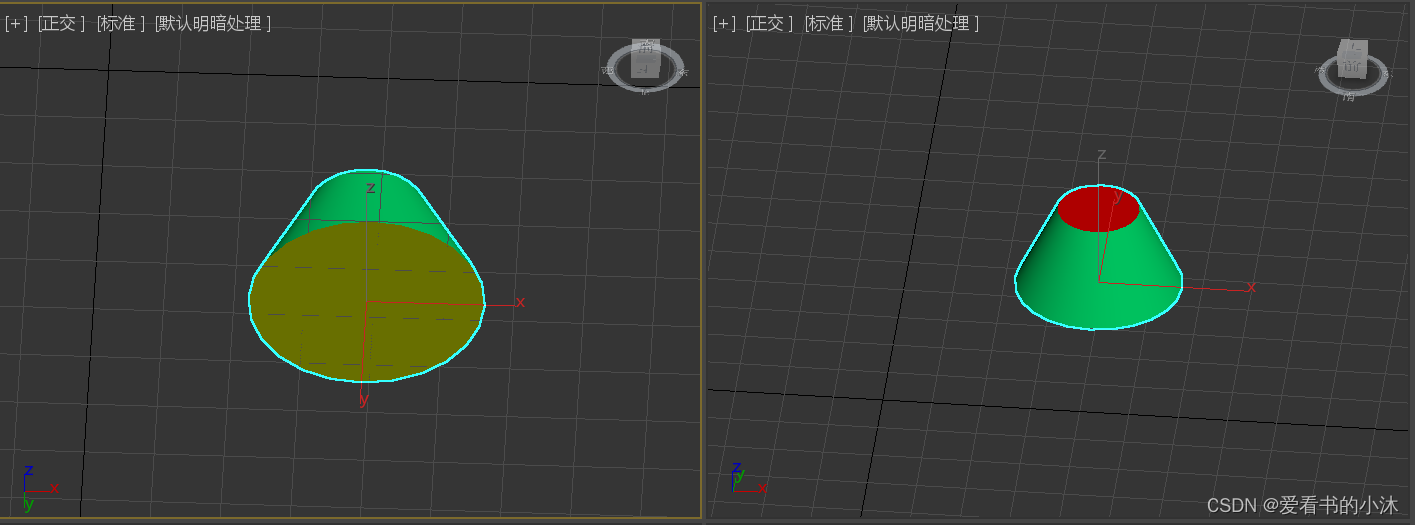
【小沐学Unity3d】3ds Max 多维子材质编辑(Multi/Sub-object)
文章目录 1、简介2、精简材质编辑器2.1 先创建多维子材质,后指定它2.2 先指定标准材质,后自动创建多维子材质 3、Slate材质编辑器3.1 编辑器简介3.2 编辑器使用 结语 1、简介 多维子材质(Multi/Sub-object)是为一个模形࿰…...

# Go学习-Day8
文章目录 Go学习-Day8单元测试Goroutine进程和线程并发和并行Go协程和主线程MPG模式CPU相关协程并行的资源竞争 Go学习-Day8 个人博客:CSDN博客 单元测试 testing框架会将xxx_test.go的文件引入,调用所有TestXxx的函数 在cal_test.go文件里面写这个 …...
Maven编译java及解决程序包org.apache.logging.log4j不存在问题
1、首先新建一个文件夹,比如hello Hello里新建pom.xml <?xml version"1.0" encoding"UTF-8"?> <project xmlns"http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi…...

【小吉测评】高效简洁的数据库管控平台—CloudQuery
文章目录 🎄CloudQuery是什么🛸CloudQuery支持的数据源类型🍔CloudQuery社区地址🌺如何使用🛸参考官方文档🛸参考视频教程🎈点击免费下载🎈立即下载即可🎈使用服务器完成…...

获取微信小程序二维码的bug
项目场景: 获取微信小程序二维码的bug,原来测试一直是没问题的,上线后也没啥问题,这次突然爆错 问题描述 access_token已失效或已过期 {"errcode":40001,"errmsg":"invalid credential, access_token is invalid…...

Linux之Shell(一)
Linux之Shell Shell概述Linux提供的Shell解析器bash和sh的关系Centos默认的解析器是bash Shell脚本入门脚本格式第一个脚本脚本常用的执行方式 变量系统预定义变量自定义变量特殊变量$n$#\$*、\$$? 运算符条件判断流程控制(▲)if判断case语句for循环while循环 read读取控制台输…...

解决拦截器抛出异常处理类的500状态码Html默认格式响应 !
解决方式 <mvc:annotation-driven><mvc:message-converters><!-- 配置JSON消息转换器 --><bean class"org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"><property name"supportedMediaTypes"&…...

搭建PyTorch神经网络进行气温预测
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torch import torch.optim as optim import warnings warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") %matplotlib inline features pd.read_csv(temps.csv)#看看数据长什么样子 features.he…...

Qt Creato配置PCL库
Qt Creator中使用PCL库_业务不精er的博客-CSDN博客 Qt6.1.0中配置pcl1.11.1_qt6导入pcl库_朽一的博客-CSDN博客 VS2017 中配置QTPCL显示点云或3D图形_pcl显示3d图tiff_桂林巡山的博客-CSDN博客 Windows10下QTVTKPCL环境配置(一次成功)_qt pcl_v俊逸的…...
从阿里到字节跳动,这3年外包做完,我这人生算是彻底废了......
我为什么一直做外包呢,原因是薪资和技术方面。 在阿里做了一年外包,薪资5k,功能测试,接触Linux和网络,但是说实在的技术很难沉淀,就像雾里看花一样,过年之后,想走的人都走了&…...
在汽车行业中如何脱颖而出?使用聊天机器人是关键
汽车行业正在经历一场非凡的技术革命,尖端技术重塑了其本质。汽车中的聊天机器人能作为一种改变游戏规则的技术脱颖而出,推动企业与客户互动甚至吸引新客户的方式的进步。例如SaleSmartly(SS客服)就是一个很优秀的聊天机器人平台。…...

Go语言最全面试题,拿offer全靠它,附带免积分下载pdf
面试题文档下链接点击这里免积分下载 go语言入门到精通点击这里免积分下载 文章目录 Go 基础类GO 语言当中 NEW 和 MAKE 有什么区别吗?PRINTF(),SPRINTF(),FPRINTF() 都是格式化输出,有什么不同?GO 语言当中数组和切片的区别是什么…...
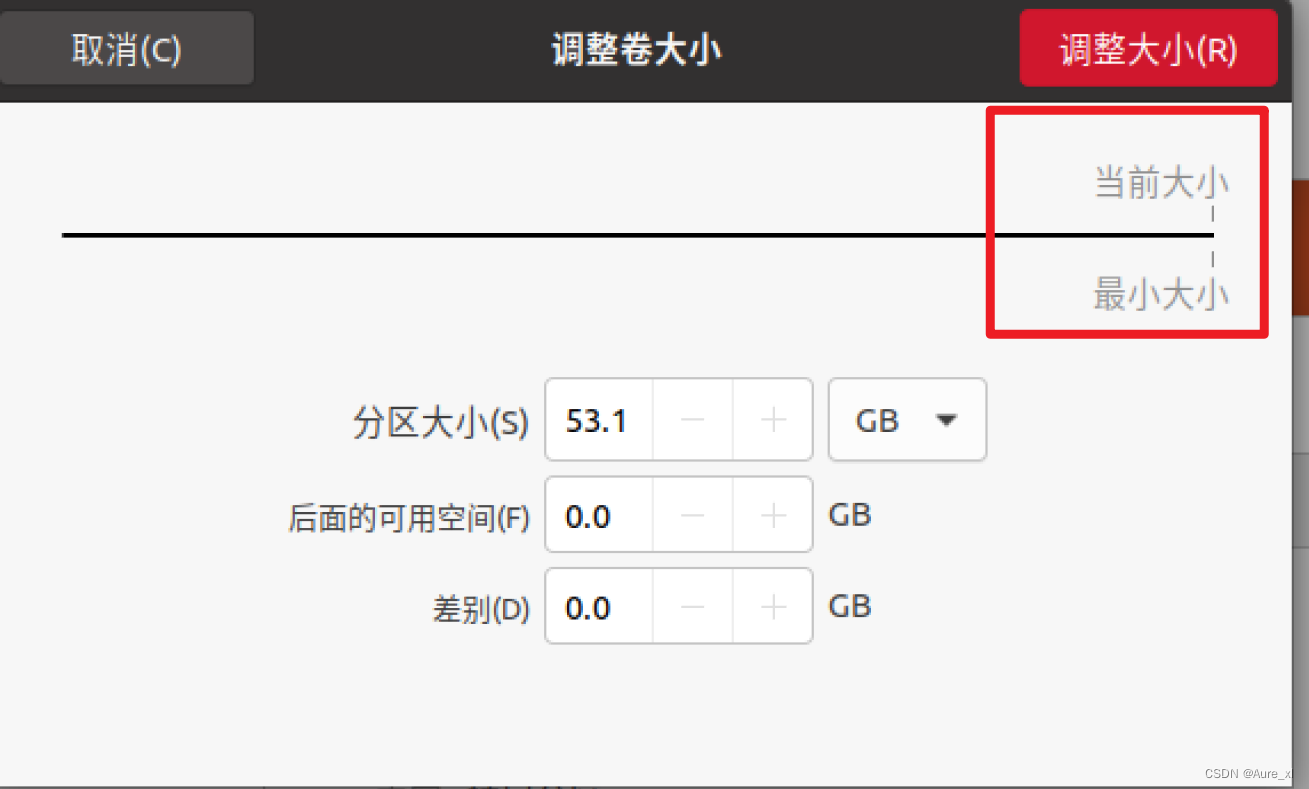
虚拟机Linux20.04磁盘扩展
扩展之前必须要确保!没有快照! ps:先把快照删掉,如果担心弄坏的话可以先克隆一个 如果不删的话就会跟下面一样无法点击扩展: 删除了快照之后就可以点击这个【扩展】,输入你要的磁盘大小即可。 (我这里原…...

类欧几里得算法
求 ∑ i 0 n ⌊ a i b c ⌋ \sum\limits_{i0}^{n}\lfloor \frac{aib}{c} \rfloor i0∑n⌊caib⌋ 推式子步骤: 分类讨论 a 0 a0 a0 是个最简式子 b ≥ c b\ge c b≥c 或 a ≥ c a\ge c a≥c 由 f ( a m o d c , b m o d c , c , n ) f(a\bmod c,b\bmod…...

c++读取和存储文件,对文件操作
#include<bits/stdc.h> using namespace std; int aa[100];//全局变量数组,用来接收我们从文件中读取的数据。 void zhuanhua(string a){//这个函数的作用是转化我们读取的数字,由于我们读取文件时//是按行读取,就是一下读取一行&…...

InfluxDB API -- InfluxDB笔记四
1.调试工具的安装 ApiPost (类似Postman) 2.InfluxDB v2 API 地址 官方地址: InfluxDB v2 API | InfluxDB OSS 2.7 Documentation 本地文档地址:host1:8086/docs 3.token认证 在web UI 的Load Data -> API Tokens里面可以复制,这个页面也可以创…...
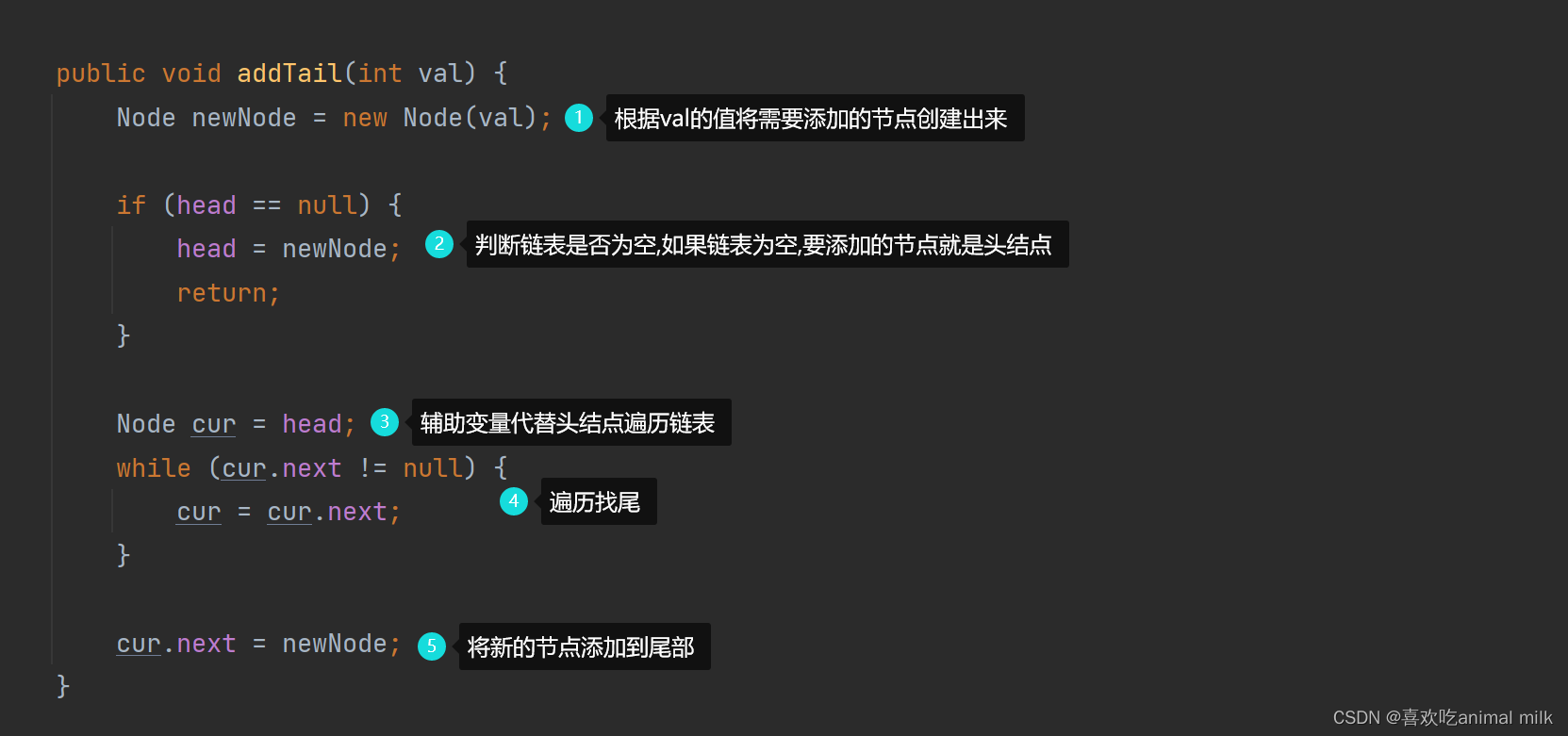
数据结构 - 单链表
文章目录 目录 文章目录 一、什么是链表? 线性表: 顺序表: 二、链表的分类和实现 分类: 实现: 1.创建节点类 2.创建单链表 1.addTail(尾增) 2.删除节点值为key的第一个节点 3.插入节点(在指定位置) 4.获取链表长度 总结 前言 大家好,这篇博客给大家讲一下什么是…...

解决AndroidX依赖冲突:appcompat-resources版本与compileSdkVersion不兼容问题
1. 从一次真实的构建失败说起 那天下午,我正在给一个老项目添加一个新功能,像往常一样点击了Android Studio那个绿色的“运行”按钮,满心期待地等着应用在模拟器上启动。结果,等来的不是熟悉的启动画面,而是一大段刺眼…...

【实战指南】8D报告全流程解析:从问题识别到标准化落地
1. 8D报告:不只是“填表”,而是解决问题的“作战地图” 如果你在制造业或者涉及产品研发、质量管理的领域工作,大概率听说过“8D报告”。很多朋友一听到这个词,第一反应可能就是:“哦,就是客户投诉了要填的…...

wan2.1-vae开源价值:规避商业模型版权风险,满足国企/政务合规要求
wan2.1-vae开源价值:规避商业模型版权风险,满足国企/政务合规要求 1. 引言:为什么开源模型在今天如此重要? 如果你在国企、事业单位或者任何对数据安全、版权合规有严格要求的机构工作,最近可能正为AI图像生成这件事…...
)
三相三电平整流器仿真:电压电流双闭环控制与SPWM调制效果佳(仅含仿真文件)
三相三电平整流器仿真,采用电压电流双闭环控制方式,SPWM调制。 效果很好。 只有仿真文件。最近在搞三相三电平整流器的仿真项目,用双闭环控制配SPWM调制,效果居然比想象中还要稳。这个拓扑结构天生自带谐波抑制能力,加…...
Gemma-3 Pixel Studio惊艳效果:动态思维链可视化——图文推理过程展示
Gemma-3 Pixel Studio惊艳效果:动态思维链可视化——图文推理过程展示 1. 核心亮点:不只是看图说话 你可能用过不少能“看图说话”的AI工具,上传一张图片,AI给你一段描述。但Gemma-3 Pixel Studio带来的体验完全不同——它不仅能…...

基于LeCroy Xena Edun-224G的1.6T以太网测试方案:从224G SerDes验证到ASIC与光模块全场景测试
1. 为什么我们需要1.6T以太网测试仪? 如果你正在研发下一代数据中心交换机、AI训练集群的网卡,或者高速光模块,那你肯定对“1.6T”这个数字不陌生。它不再是实验室里的概念,而是即将落地的现实。但问题来了,当单端口速…...

GD32F470四驱智能小车:多传感器融合嵌入式控制系统设计
1. 项目概述 本项目是一款基于GD32F470ZGT6高性能微控制器的四驱智能小车平台,面向嵌入式系统学习与工程实践需求设计。系统集成循迹、超声波避障、蓝牙遥控三大核心功能模块,并通过独立按键实现运行模式切换,同时具备电池电量监测、LED车灯模…...

DeOldify多模型效果对比:与原版及主流上色工具横向评测
DeOldify多模型效果对比:与原版及主流上色工具横向评测 老照片承载着记忆,但褪色的黑白影像总让人觉得少了些什么。过去,给老照片上色是件专业且耗时的工作,需要艺术家凭借经验和想象。如今,借助AI技术,我…...

企业数字化转型成熟度评估实战指南:从标准解读到落地应用
1. 别再“摸黑”转型了:为什么你需要一份成熟度“体检报告”? 这几年,我接触了上百家正在搞数字化转型的企业,发现一个特别普遍的现象:很多老板和高管,一提到“转型”就头疼。钱没少花,系统上了…...

CHORD-X创意写作模式展示:生成科幻背景下的“未来科技趋势研究报告”
CHORD-X创意写作模式展示:生成科幻背景下的“未来科技趋势研究报告” 最近在试用各种大模型时,我一直在想,除了写文案、做翻译这些常规操作,它们能不能干点更有想象力的事?比如,让AI基于一套逻辑ÿ…...
