大模型参数高效微调PEFT的理解和应用
简介
近年的大型语言模型(也被称作基础模型),大多是采用大量资料数据和庞大模型参数训练的结果,比如常见的ChatGPT3有175B的模型参数量。随着Large Language Model(LLM)的横空出世,网络模型对常见问题的解答有了很强的泛化能力。但是如果将LLM应用到特定专业场景,如律师、医生,却仍表现的不尽如人意。即使可以使用few-shot learning或finetuning的技术进行迭代更新,但是模型参数的更新需要昂贵的机器费用。因此近年来,学术界大量研究人员开始从事高效Finetuning的工作,称作Effective Parameter Fine-Tuning(PEFT)。本次从方法构造的区别,可以将现有的PEFT方法分为Adapter、LoRA、Prefix Learning和Soft Prompt。学习过程很大程度上借鉴了李宏毅老师分享的2022 AACL-IJCNLP课件,有兴趣的读者可以翻阅原文链接。
方法
虽然LLM有很好的泛化能力,但如果需要应用到特定的场景任务,常常需要对LLM进行模型微调。问题是LLM的模型参数非常庞大,特定任务的微调需要昂贵的显卡资源,那么如何解决这样的问题呢?很显然,降低微调的模型参数量就是最简单的方法。试验表明,当每个特定任务微调时,只训练模型的一小部分参数,也能得到不错的效果。
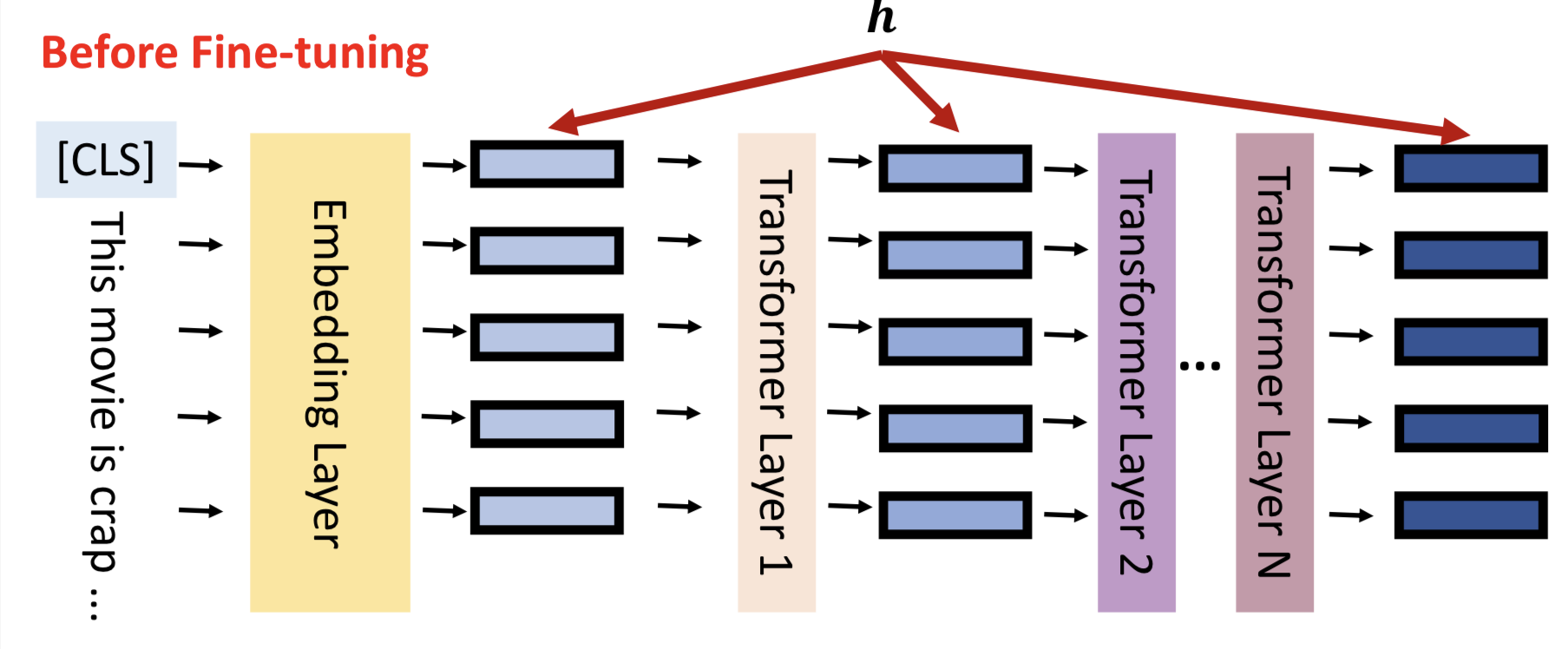
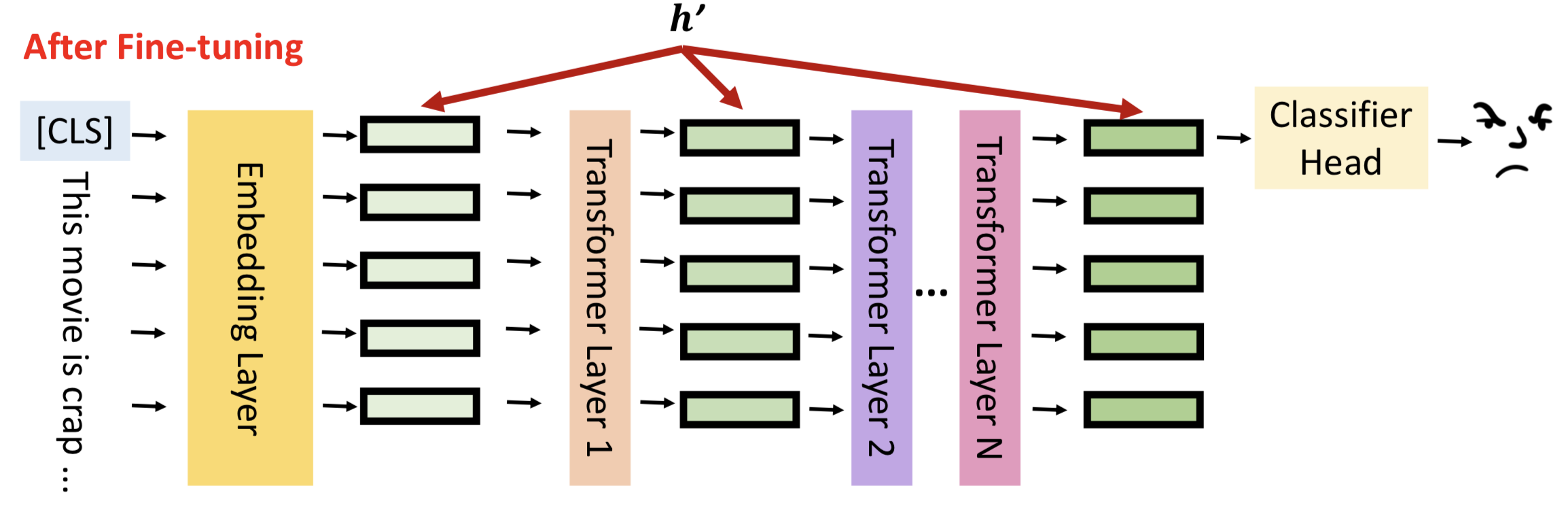
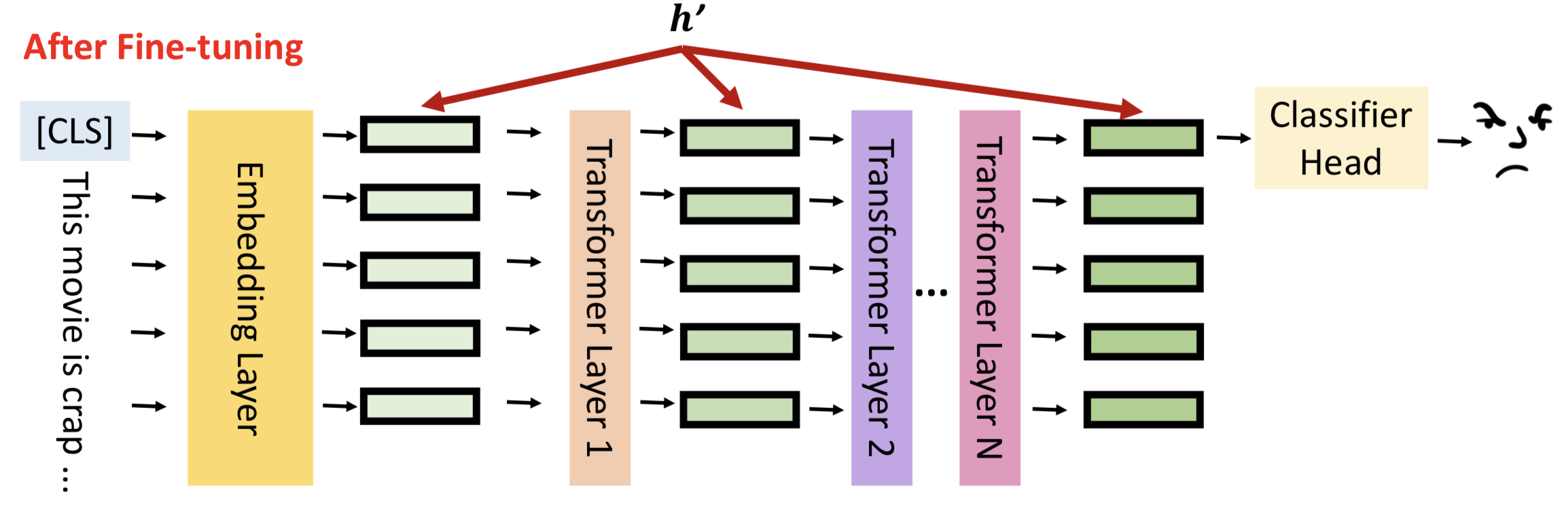
让我们回到模型微调的真实含义,如图所示,h表示每一层隐藏层的输出。
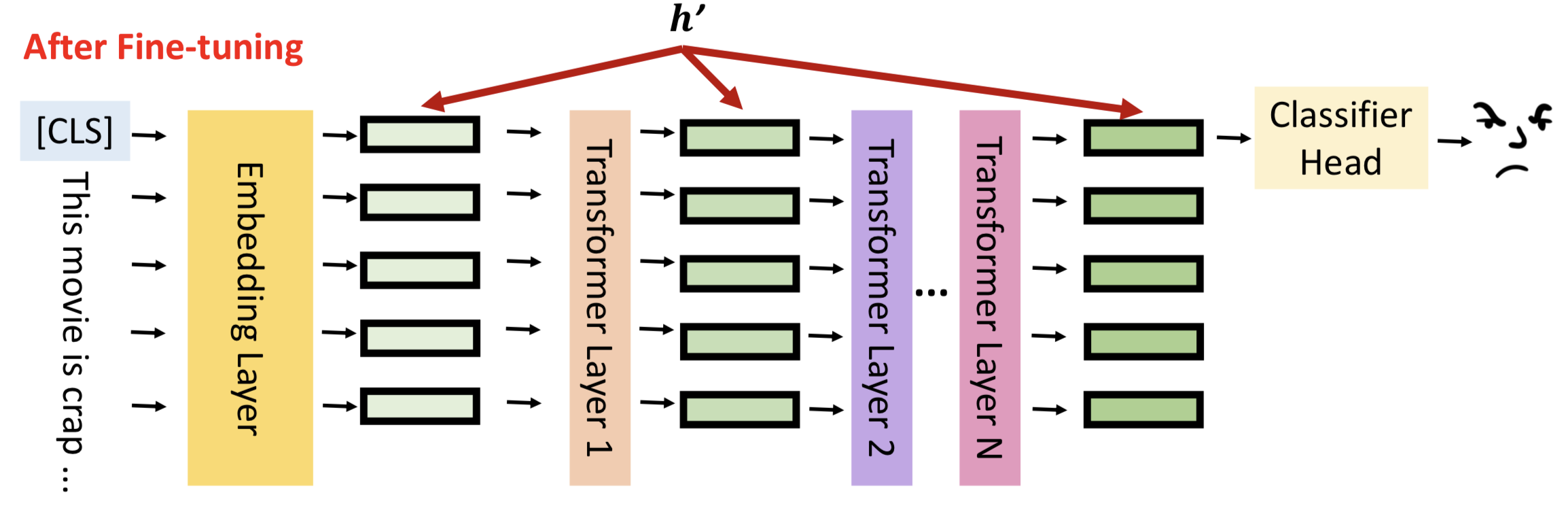
模型微调就是通过数据更新隐藏层的输出结果,更好的拟合输入数据的分布,对下游任务有更佳的表现,我们将隐藏层输出成为hidden representation(h)。
模型微调的结果就是更新hidden representation,用数学语言可以表示为:
h’ = h + 𝚫h
接下来介绍4种不同的方法,通过减少模型参数更新的数量,高效的更新𝚫h。
Adapter方法
Adapter方法通常是在网络模型中增加小型的模型块,通过冻结LLM的参数,仅更新Adapter模块的方式进行模型微调。
如图所示,Adapter应用在Transformer的结构中,在Multi-headed attention和Feed-forward网路层后紧接Adapter子模块,模型训练的时候冻结Transformer的参数,仅更新Adapter的参数。
LoRA方法
LoRA提出的想法是,既然LLM可以泛化用于不同的NLP任务,那么说明不同的任务有不同的神经元来处理,我们只要针对下游任务找到合适的那一批神经元,并对他们的权重进行强化,那么对下游任务也有显著的效果。
LoRA方法假设下游任务只需要低秩矩阵就可以找到大模型中对应的权重,然后仅更新小部分的模型参数,就可以在下游任务中表现不错。
如图所示,LoRA将𝚫h的计算方式更改为两个低秩矩阵的乘法,r表示矩阵秩的大小。那么模型的更新过程可以用数学方式表示为:
W= W + 𝚫W = W + BA, r << min(d_ffw, d_model)
Prefix Learning方法
Prefix Learning方法就是在网络层中,将网络层中扩展可训练的前缀。

这里以Self-Attention为例,先回忆一下Self-Attention的结构。
Self-Attention的数学表示为:
A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) = s o f t m a x ( Q K T d k V ) Attention(Q,K,V) = softmax(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}} V) Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(dkQKTV)
首先初始化W_k, W_q, W_v参数,通过 q 1 = x 1 ∗ W q , k 1 = x 1 ∗ W k , v 1 = x 1 ∗ W v q_1=x_1*W_q, k_1=x_1* W_k, v_1=x_1 * W_v q1=x1∗Wq,k1=x1∗Wk,v1=x1∗Wv的方式得到QKV矩阵;
通过 α 1 , 1 = q 1 ∗ k 1 , α 1 , 2 = q 1 ∗ k 2 … \alpha1,1 = q_1 * k_1, \alpha1,2=q_1 * k_2… α1,1=q1∗k1,α1,2=q1∗k2… 的方式获取𝛼矩阵;
通过 z 1 , 1 = s o f t m a x ( α 1 , 1 ∗ v 1 ) … z1,1=softmax(\alpha1,1 * v1)… z1,1=softmax(α1,1∗v1)…的方式得到x1对其他token的注意力
最后累加计算得出 x 1 ′ x'_1 x1′的结果,如此循环计算下一个时刻输出。
PreFix Tuning的做法是对self-attention增加一部分参数,计算𝚫h的结果。
如图所示,增加了3个参数量,模型训练的时候只更新这3个用到的的参数。
Soft Prompt方法
Soft Prompt的做法比较简单,直接在Embedding输出,插入一部分Prefix embedding信息。
Soft Prompt的简化版本是直接在input sequence句首插入文本。
小结
了解4种PEFT的方法后,可以发现PEFT有非常多的好处。
首先,PEFT可以极大的降低finetune的参数量。
如图所示,Adapter训练参数之占模型的5%,LoRa、Prefix Tuning和Soft Prompt的训练参数甚至小于0.1%。
其次,由于训练参数的减少,PEFT更不容易造成模型的过拟合,某种意义也是一种Dropout方法。
最后,由于需要更新的参数少,基础模型在小数据集上有不错的表现。
实践
我们以最受欢迎的LoRA为例,搭建一个简易的demo理解如何使用LoRA微调模型。
Demo的有2个不同分布的数据,分别是均匀分布和高斯分布;然后构造3层的ReLU-MLP对均匀分布数据进行训练;最后通过LoRA的对高斯分布数据进行微调。
首先是构造数据,分别生成均匀分布和高斯分布的数据集,lable范围都是{-1,1}。
import numpy as np
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset, DataLoader
import random
from collections import OrderedDict
import math
import torch.nn.functional as F
random.seed(42)def generate_uniform_sphere(n, d):normal_data = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=[n, d])lambdas = np.sqrt((normal_data * normal_data).sum(axis=1))data = np.sqrt(d) * normal_data / lambdas[:, np.newaxis]return data# data type could be "uniform" or "gaussian"
def data_generator(data_type='uniform', inp_dims=100, sample_size=10000):if data_type == 'uniform':data = generate_uniform_sphere(sample_size, inp_dims)elif data_type == 'gaussian':var = 1.0 / inp_dimsdata = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=var, size=[sample_size, inp_dims])labels = np.sign(np.mean(data, -1))for i in range(sample_size):if labels[i] == 0:labels[i] = 1return data, labels
第二步,构造3层的MLP网络模型,ReLU作为激活函数。
class ReluNN(torch.nn.Module):def __init__(self, inp_dims, h_dims, out_dims=1):super(ReluNN, self).__init__()self.inp_dims = inp_dimsself.h_dims = h_dimsself.out_dims = out_dims# build modelself.layer1 = torch.nn.Linear(self.inp_dims, self.h_dims)self.layer2 = torch.nn.Linear(self.h_dims, self.h_dims)self.last_layer = torch.nn.Linear(self.h_dims, self.out_dims, bias=False)def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1)x = self.layer1(x)x = torch.nn.ReLU()(x)x = self.layer2(x)x = torch.nn.ReLU()(x)x = self.last_layer(x)return xdef calc_loss(logits, labels):return torch.mean(torch.log(1 + torch.exp(-1 * torch.mul(labels.float(), logits.T))))def evaluate(labels, loss=None, output=None, iter=0, training_time=True):correct_label_count = 0for i in range(len(output)):if (output[i] * labels[i] > 0).item():correct_label_count += 1if training_time:print('Iteration: ', iter, ' Loss: ', loss, ' Correct label: ', correct_label_count, '/', len(output))else:print('Correct label: ', correct_label_count, '/', len(output), ', Accuracy: ', correct_label_count / len(output))
第三步,开始训练均匀分布数据。
# input dimensions
inp_dims = 16
# hidden dimensions in our model
h_dims = 32
# training sample size
n_train = 2000
# starting learning rate (I didn't end up using any learning rate scheduler. So this will be constant. )
starting_lr = 1e-4
batch_size = 256# generate data and build pytorch data pipline using TensorDataset module
data_train, labels_train = data_generator(data_type="uniform", inp_dims=inp_dims, sample_size=n_train)
dataset = TensorDataset(torch.Tensor(data_train), torch.Tensor(labels_train))
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, drop_last=True)# Build the model and define optimiser
model = ReluNN(inp_dims, h_dims)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=starting_lr)# ---------------------
# Training loop here
# ---------------------its = 0
epochs = 400
print_freq = 200for epoch in range(epochs):for batch_data, batch_labels in loader:optimizer.zero_grad()output = model(batch_data)loss = calc_loss(output, batch_labels)loss.backward()optimizer.step()if its % print_freq == 0:correct_labels = evaluate(labels=batch_labels, loss=loss.detach().numpy(), output=output, iter=its, training_time=True)its += 1
获取训练输出结果:
Iteration: 0 Loss: 0.6975772 Correct label: 126 / 256
Iteration: 200 Loss: 0.6508794 Correct label: 164 / 256
Iteration: 400 Loss: 0.52307904 Correct label: 215 / 256
Iteration: 600 Loss: 0.34722215 Correct label: 240 / 256
Iteration: 800 Loss: 0.21760023 Correct label: 251 / 256
Iteration: 1000 Loss: 0.19394015 Correct label: 241 / 256
Iteration: 1200 Loss: 0.124890685 Correct label: 250 / 256
Iteration: 1400 Loss: 0.10578571 Correct label: 250 / 256
Iteration: 1600 Loss: 0.07651 Correct label: 252 / 256
Iteration: 1800 Loss: 0.05156578 Correct label: 256 / 256
Iteration: 2000 Loss: 0.045886587 Correct label: 256 / 256
Iteration: 2200 Loss: 0.04692286 Correct label: 256 / 256
Iteration: 2400 Loss: 0.06285152 Correct label: 254 / 256
Iteration: 2600 Loss: 0.03973126 Correct label: 254 / 256
在均匀分布和高斯分布测试集分别进行测试:
print('-------------------------------------------------')
print('Test model performance on uniformly-distributed data (the data we trained our model on)')
data_test, labels_test = data_generator(data_type="uniform", inp_dims=inp_dims, sample_size=1024)
data_test = torch.Tensor(data_test)
labels_test = torch.Tensor(labels_test)output = model(data_test)
correct_labels = evaluate(labels=labels_test, loss=0.0, output=output, iter=0, training_time=False)print('-------------------------------------------------')
print('Test model performance on normally-distributed data')
data_test, labels_test = data_generator(data_type="gaussian", inp_dims=inp_dims, sample_size=1024)
data_test = torch.Tensor(data_test)
labels_test = torch.Tensor(labels_test)output = model(data_test)
correct_labels = evaluate(labels=labels_test, loss=0.0, output=output, iter=0, training_time=False)
print('-------------------------------------------------')
获得输出结果为,均匀分布表现远高于高斯分布,这是理所当然的。
-------------------------------------------------
Test model performance on uniformly-distributed data (the data we trained our model on)
Correct label: 1007 / 1024 , Accuracy: 0.9833984375
-------------------------------------------------
Test model performance on normally-distributed data
Correct label: 832 / 1024 , Accuracy: 0.8125
-------------------------------------------------
第四步,实现LoRA改造网络模型,LoRA代码实现来自https://github.com/microsoft/LoRA/tree/main。
class LoRALinear(torch.nn.Linear):def __init__(self, layer: torch.nn.Linear, r: int, lora_alpha: float, in_features: int, out_features: int,**kwargs, ):torch.nn.Linear.__init__(self, in_features, out_features, **kwargs)# trainable parametersself.weight = layer.weightself.r = rif self.r > 0:# lora_A matrix has shape [number of ranks, number of input features]self.lora_A = torch.nn.Parameter(self.weight.new_zeros((in_features, r)))# lora_A matrix has shape [number of output features, number of ranks]self.lora_B = torch.nn.Parameter(self.weight.new_zeros((r, out_features)))self.scaling = lora_alpha / r# Freezing the pre-trained weight matrixself.weight.requires_grad = Falseself.reset_parameters()def reset_parameters(self):if hasattr(self, 'lora_A'):torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(self.lora_A, a=math.sqrt(5))torch.nn.init.zeros_(self.lora_B)def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):if self.r > 0:result = F.linear(x, self.weight, bias=self.bias) result += (x @ self.lora_A @ self.lora_B) * self.scalingreturn resultelse:return F.linear(x, self.weight, bias=self.bias)
改造第二层网络层:
ranks = 2
l_alpha = 1.0# wrap the second layer of the model
lora_layer2 = LoRALinear(model.layer2, r=ranks, lora_alpha=l_alpha, in_features=h_dims, out_features=h_dims)
开始进行微调训练:
# new pipline that contains data generated from Gaussian distribution
ft_data_train, ft_labels_train = data_generator(data_type="gaussian", inp_dims=inp_dims, sample_size=n_train)
ft_data_test, ft_labels_test = data_generator(data_type="gaussian", inp_dims=inp_dims, sample_size=n_train)
dataset = TensorDataset(torch.Tensor(ft_data_train), torch.Tensor(ft_labels_train))
ft_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, drop_last=False)# Adam now takes the 160 trainable LoRA parameters
starting_lr = 1e-3
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(lora_layer2.parameters(), lr=starting_lr)# ---------------------
# Training starts again
# ---------------------its = 0
epochs = 400
print_freq = 200for epoch in range(epochs):for batch_data, batch_labels in ft_loader:optimizer.zero_grad()x = model.layer1(batch_data)x = torch.nn.ReLU()(x)# ---this is the new layer---x = lora_layer2(x)# ---------------------------x = torch.nn.ReLU()(x)output = model.last_layer(x)loss = calc_loss(output, batch_labels)loss.backward()optimizer.step()if its % print_freq == 0:correct_labels = evaluate(labels=batch_labels, loss=loss.detach().numpy(), output=output, iter=its, training_time=True)its += 1
微调输出结果为:
Iteration: 0 Loss: 0.41668275 Correct label: 194 / 256
Iteration: 200 Loss: 0.34483075 Correct label: 249 / 256
Iteration: 400 Loss: 0.28130627 Correct label: 247 / 256
Iteration: 600 Loss: 0.18952605 Correct label: 249 / 256
Iteration: 800 Loss: 0.14345655 Correct label: 249 / 256
Iteration: 1000 Loss: 0.117519796 Correct label: 250 / 256
Iteration: 1200 Loss: 0.100797206 Correct label: 251 / 256
Iteration: 1400 Loss: 0.08887711 Correct label: 252 / 256
Iteration: 1600 Loss: 0.07975915 Correct label: 253 / 256
Iteration: 1800 Loss: 0.07250729 Correct label: 253 / 256
Iteration: 2000 Loss: 0.06658038 Correct label: 253 / 256
Iteration: 2200 Loss: 0.061622016 Correct label: 254 / 256
Iteration: 2400 Loss: 0.057407677 Correct label: 254 / 256
Iteration: 2600 Loss: 0.05379172 Correct label: 254 / 256
Iteration: 2800 Loss: 0.050651148 Correct label: 254 / 256
Iteration: 3000 Loss: 0.04789203 Correct label: 255 / 256
最后一步,再次测试高斯分布的数据集。
data_test, labels_test = data_generator(data_type="gaussian", inp_dims=inp_dims, sample_size=1024)
data_test = torch.Tensor(data_test)
labels_test = torch.Tensor(labels_test)x = model.layer1(data_test)
x = torch.nn.ReLU()(x)
# ---this is the new layer---
x = lora_layer2(x)
# ---------------------------
x = torch.nn.ReLU()(x)
output = model.last_layer(x)
correct_labels = evaluate(labels=labels_test, loss=0.0, output=output, iter=0, training_time=False)
输出结果为:
Correct label: 1011 / 1024 , Accuracy: 0.9873046875
微调效果很明显,准确率从81.2%提升到98.7%。最后再计算LoRA微调的参数量大小。
def count_parameters(model):return sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)print("Original second layer parameters: ", count_parameters(original_layer2))
print("LoRA layer parameters: ", count_parameters(lora_layer2))
输出结果为:
Original second layer parameters: 1056
LoRA layer parameters: 160
通过实验结果发现,原始模型参数量1056,LoRA参数量160,仅为原来的1/10,但是训练效果从81.2%提升到98.7%。
总结
如果对网络层每一层都要重新实现LoRA的方法,是比较复杂的,推荐使用HuggingFace的封装库peft,覆盖基本的网络模型。
- 共用基础LLM是未来的趋势,如果需要快速适应特殊的任务,只需要训练LoRA的参数即可,大大降低了GPU的使用量;
- 当不同任务的切换时,只需要切换不同的LoRA参数;
参考
- Houlsby, Neil, et al. “Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP.” International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019.
- Hu, Edward J., et al. “LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models.” International Conference on Learning Representations. 2021.
- The Power of Scale for Parameter-Efficient Prompt Tuning. Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2021
相关文章:

大模型参数高效微调PEFT的理解和应用
简介 近年的大型语言模型(也被称作基础模型),大多是采用大量资料数据和庞大模型参数训练的结果,比如常见的ChatGPT3有175B的模型参数量。随着Large Language Model(LLM)的横空出世,网络模型对常见问题的解答有了很强的…...
工作游戏时mfc140u.dll丢失的解决方法,哪个方法可快速修复mfc140u.dll问题
在 Windows 操作系统中,mfc140u.dll 文件是非常重要的一个组件,许多基于 MFC(Microsoft Foundation Classes)的程序都需要依赖这个文件。然而,有些用户在运行这些程序时可能会遇到mfc140u.dll丢失的问题,导…...
选择排序——直接选择排序
直接选择排序:(以重复选择的思想为基础进行排序) 1、简述 顾名思义就是选出一个数,再去抉择放哪里去。 设记录R1,R2…,Rn,对i1,2,…,n-1,重复下…...
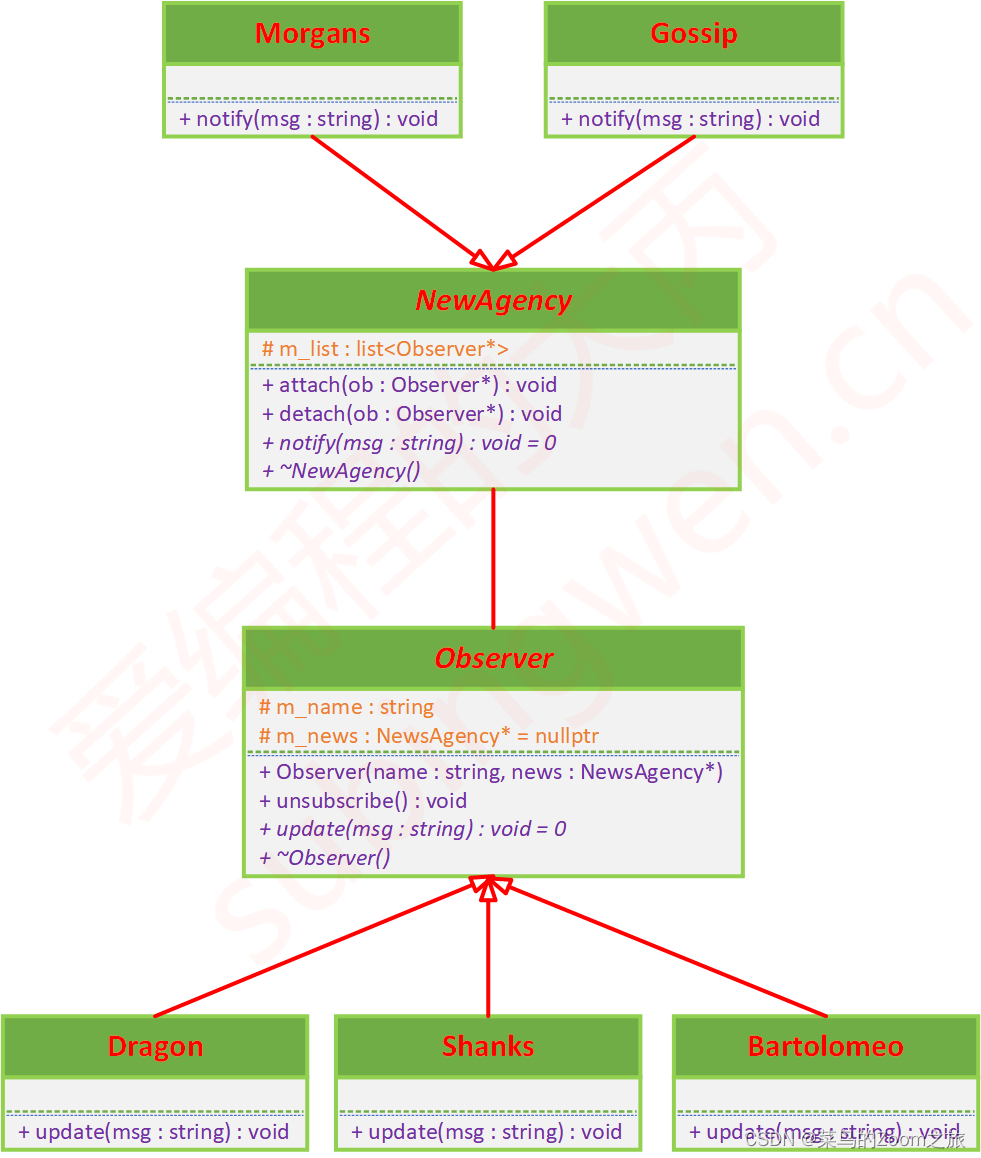
【C++基础】观察者模式(“发布-订阅”模式)
本文参考:观察者模式 - 摩根斯 | 爱编程的大丙 观察者模式允许我们定义一种订阅机制,可在对象事件发生时通知所有的观察者对象,使它们能够自动更新。观察者模式还有另外一个名字叫做“发布-订阅”模式。 发布者: 添加订阅者&…...
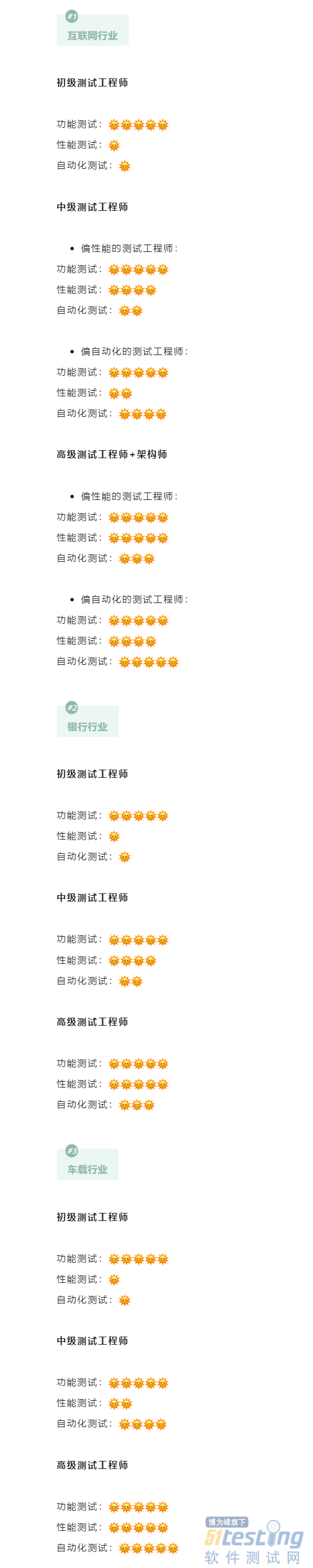
从业多年,我总结出软件测试工程师必须掌握的技能,你不可错过!
经常会有小伙伴询问:“测试工程师有哪些必须要掌握的技能?”这是一个非常大的课题,因为每个人从事的行业不同、岗位不同,需要掌握的技能自然也不一样。 今天小编就从不同岗位、不同行业两个大方面,来讲讲软件测试工程师…...

【nerfStudio】5-nerfStudio导出3D Mesh模型
几何图形的导出 在这里我们将介绍如何从nerfstudio中导出点云和网格。您将使用的主要命令是ns-export。我们将点云导出为.ply文件,纹理网格导出为.obj文件。 导出网格 1. TSDF融合 TSDF(截断有符号距离函数)融合是一种使用深度图像提取表面网格的算法。此方法适用于所有…...

重要公告|投票委托已经上线,应该如何选择社区代表?
社区代表是Token持有者委托投票权的个人或团体,可以代表Token持有者在Moonbeam治理中投票。委托是可选的,允许代表在治理过程中代表更大比例的Token和Token持有者。相比社区代表,不愿投票的Token持有者可以将投票权委托给社区代表,…...
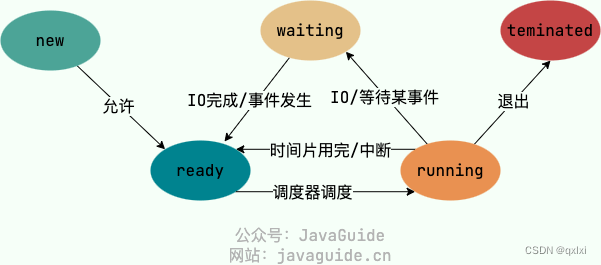
【操作系统】聊聊进程、线程、协程
进程内部有那些数据 为什么创建进程的成本高 进程和线程 进程是资源分配的基本单位,而线程是程序执行的基本单位,一个是从资源分配的角度看,另一个是执行角度。 那么进程和程序的区别是什么? 程序,一段代码ÿ…...

springboot 下 activiti 7会签配置与实现
流程图配置 会签实现须在 userTask 节点下的 multi instance 中配置 collection 及 completion condition; collection 会签人员列表;element variable 当前会签变量名称,类似循环中的 item;completion condition: 完成条件。 ${taskExecutionServiceIm…...

RK3399平台开发系列讲解(内核调试篇)spidev_test工具使用
🚀返回专栏总目录 文章目录 一、环境二、执行测试三、回环测试四、字节发送测试五、32位数据发送测试沉淀、分享、成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获!😄 📢 在 Linux 系统上,“spidev_test” 是一个用于测试和配置 SPI(Serial Peripheral Interface)设备的命令行工具。…...
)
点云从入门到精通技术详解100篇-自适应点云局部邻域特征的特征提取与配准(续)
目录 3.4 深度相机误差建模 3.5 实验结果及分析 3.5.1 TOF 相机平面畸变校正 3.5.2 TOF 相机深度误差校正...

VBA技术资料MF52:VBA_在Excel中突出显示前 10 个值
【分享成果,随喜正能量】一言之善,重于千金。善良不分大小,有时候你以为的一句话,小小的举手之劳,也可能就是别人的救赎!不要吝啬你的善良,因为你永远不知道那小小的善良能给多少人带来光明。。…...

leetcode做题笔记134. 加油站
在一条环路上有 n 个加油站,其中第 i 个加油站有汽油 gas[i] 升。 你有一辆油箱容量无限的的汽车,从第 i 个加油站开往第 i1 个加油站需要消耗汽油 cost[i] 升。你从其中的一个加油站出发,开始时油箱为空。 给定两个整数数组 gas 和 cost &…...
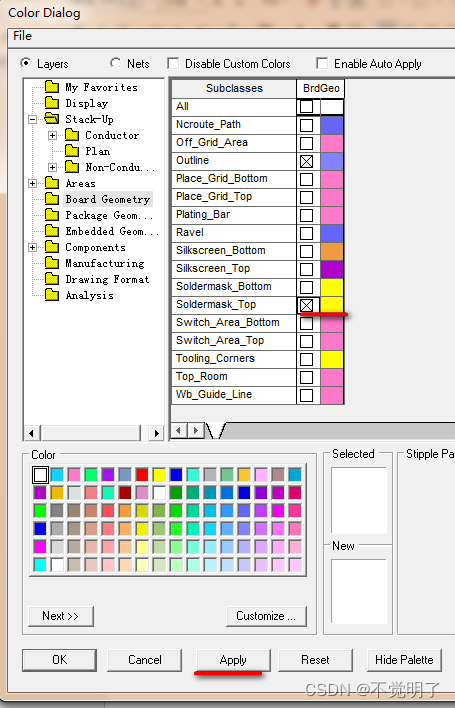
Allegro166版本如何在颜色管理器中实时显示层面操作指导
Allegro166版本如何在颜色管理器中实时显示层面操作指导 在用Allegro166进行PCB设计的时候,需要在颜色管理器中频繁的开关层面。但是166不像172一样在颜色管理器中可以实时的开关层面,如下图 需要打开Board Geometry/Soldermask_top层,首先需要勾选这个层面,再点击Apply即…...

纷享销客入选中国信通院《高质量数字化转型产品及服务全景图》
近期,在中国信息通信研究院主办的“2023数字生态发展大会”暨中国信通院“铸基计划”年中上,重磅发布了《高质量数字化转型产品及服务全景图(2023)》,纷享销客凭借先进的技术能力和十余年客户业务场景应用理解…...

C高级 DAY4
一、分支语句 case ...in语句 shell中的switch语句 case $变量名 in常量1)语句;; ------->类似于C中break的作用,;;除了最后一条分之外,都不能省略常量2)语句;; 常量n)语句;;*) ------->类似于C中default,但…...

C高级day4
作业 实现一个对数组求和的函数,数组通过实参传递给函数 写一个函数,输出当前用户的uid和gid,并使用变量接收结果 思维导图...
Java8-17 --- idea2022
目录 一、idea官网 二、使用idea编写hello world 三、查看工程中的JDK配置信息 四、详细设置 4.1、显示工具栏 4.2、默认启动项目配置 4.3、取消自动更新 4.4、选择整体主体与背景图 4.5、设置编辑器主题样式 4.5.1、编辑器主题 4.5.2、字体大小 4.5.3、修改注…...

Mybatis---增删改查
目录 一、添加用户 (1)持久层接口方法 (2)映射文件 (3)测试方法 二、修改用户 (1)持久层接口方法 (2)映射文件 (3)测试方法 …...
开机性能-如何抓取开机systrace
一、理论 1.背景 抓取开机 trace 需要使用 userdebug 版本,而我们测试开机性能问题时都要求使用 user 版本,否则会有性能损耗问题。因此想要在抓取开机性能trace 时,需要在 user 版本上打开 atrace 功能之后才能抓取 trace,默认 …...

(LeetCode 每日一题) 3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I (哈希、字符串)
题目:3442. 奇偶频次间的最大差值 I 思路 :哈希,时间复杂度0(n)。 用哈希表来记录每个字符串中字符的分布情况,哈希表这里用数组即可实现。 C版本: class Solution { public:int maxDifference(string s) {int a[26]…...

CVPR 2025 MIMO: 支持视觉指代和像素grounding 的医学视觉语言模型
CVPR 2025 | MIMO:支持视觉指代和像素对齐的医学视觉语言模型 论文信息 标题:MIMO: A medical vision language model with visual referring multimodal input and pixel grounding multimodal output作者:Yanyuan Chen, Dexuan Xu, Yu Hu…...

安宝特方案丨XRSOP人员作业标准化管理平台:AR智慧点检验收套件
在选煤厂、化工厂、钢铁厂等过程生产型企业,其生产设备的运行效率和非计划停机对工业制造效益有较大影响。 随着企业自动化和智能化建设的推进,需提前预防假检、错检、漏检,推动智慧生产运维系统数据的流动和现场赋能应用。同时,…...
)
是否存在路径(FIFOBB算法)
题目描述 一个具有 n 个顶点e条边的无向图,该图顶点的编号依次为0到n-1且不存在顶点与自身相连的边。请使用FIFOBB算法编写程序,确定是否存在从顶点 source到顶点 destination的路径。 输入 第一行两个整数,分别表示n 和 e 的值(1…...
企业如何增强终端安全?
在数字化转型加速的今天,企业的业务运行越来越依赖于终端设备。从员工的笔记本电脑、智能手机,到工厂里的物联网设备、智能传感器,这些终端构成了企业与外部世界连接的 “神经末梢”。然而,随着远程办公的常态化和设备接入的爆炸式…...
:观察者模式)
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式
JS设计模式(4):观察者模式 一、引入 在开发中,我们经常会遇到这样的场景:一个对象的状态变化需要自动通知其他对象,比如: 电商平台中,商品库存变化时需要通知所有订阅该商品的用户;新闻网站中࿰…...
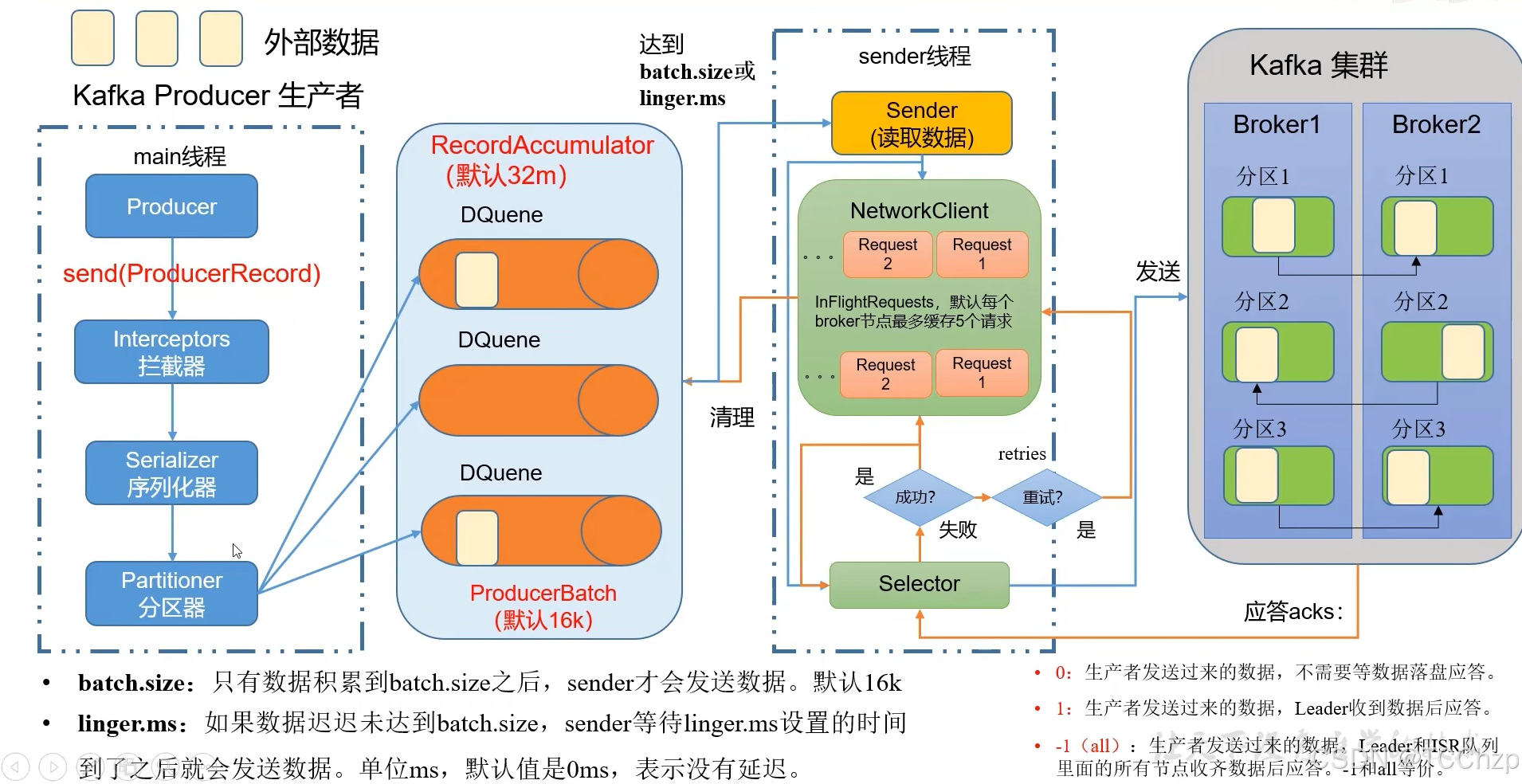
Kafka入门-生产者
生产者 生产者发送流程: 延迟时间为0ms时,也就意味着每当有数据就会直接发送 异步发送API 异步发送和同步发送的不同在于:异步发送不需要等待结果,同步发送必须等待结果才能进行下一步发送。 普通异步发送 首先导入所需的k…...

scikit-learn机器学习
# 同时添加如下代码, 这样每次环境(kernel)启动的时候只要运行下方代码即可: # Also add the following code, # so that every time the environment (kernel) starts, # just run the following code: import sys sys.path.append(/home/aistudio/external-libraries)机…...

从面试角度回答Android中ContentProvider启动原理
Android中ContentProvider原理的面试角度解析,分为已启动和未启动两种场景: 一、ContentProvider已启动的情况 1. 核心流程 触发条件:当其他组件(如Activity、Service)通过ContentR…...

LCTF液晶可调谐滤波器在多光谱相机捕捉无人机目标检测中的作用
中达瑞和自2005年成立以来,一直在光谱成像领域深度钻研和发展,始终致力于研发高性能、高可靠性的光谱成像相机,为科研院校提供更优的产品和服务。在《低空背景下无人机目标的光谱特征研究及目标检测应用》这篇论文中提到中达瑞和 LCTF 作为多…...
