Go expvar包
介绍与使用
expvar 是 exposed variable的简写
expvar包[1]是 Golang 官方为暴露Go应用内部指标数据所提供的标准对外接口,可以辅助获取和调试全局变量。
其通过init函数将内置的expvarHandler(一个标准http HandlerFunc)注册到http包ListenAndServe创建的默认Server上
如以下案例:
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"expvar"
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"runtime"
"time"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default() //初始化一个gin实例
router.GET("/debug/vars", GetCurrentRunningStats) //接口路由,如果url不是/debug/vars,则用metricBeat去获取会出问题
s := &http.Server{
Addr: ":" + "6666",
Handler: router,
ReadTimeout: 5 * time.Second,
WriteTimeout: 5 * time.Second,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
s.ListenAndServe() //开始监听
}
var CuMemoryPtr *map[string]string
var BTCMemoryPtr *map[string]interface{}
// 开始时间
var start = time.Now()
// calculateUptime 计算运行时间
func calculateUptime() interface{} {
return time.Since(start).String()
}
// currentGoVersion 当前 Golang 版本
func currentGoVersion() interface{} {
return runtime.Version()
}
// getNumCPUs 获取 CPU 核心数量
func getNumCPUs() interface{} {
return runtime.NumCPU()
}
// getGoOS 当前系统类型
func getGoOS() interface{} {
return runtime.GOOS
}
// getNumGoroutins 当前 goroutine 数量
func getNumGoroutins() interface{} {
return runtime.NumGoroutine()
}
// getNumCgoCall CGo 调用次数
func getNumCgoCall() interface{} {
return runtime.NumCgoCall()
}
// 业务特定的内存数据
func getCuMemoryMap() interface{} {
if CuMemoryPtr == nil {
return 0
} else {
return len(*CuMemoryPtr)
}
}
// 业务特定的内存数据
func getBTCMemoryMap() interface{} {
if BTCMemoryPtr == nil {
return 0
} else {
return len(*BTCMemoryPtr)
}
}
var lastPause uint32
// getLastGCPauseTime 获取上次 GC 的暂停时间
func getLastGCPauseTime() interface{} {
var gcPause uint64
ms := new(runtime.MemStats)
statString := expvar.Get("memstats").String()
if statString != "" {
json.Unmarshal([]byte(statString), ms)
if lastPause == 0 || lastPause != ms.NumGC {
gcPause = ms.PauseNs[(ms.NumGC+255)%256]
lastPause = ms.NumGC
}
}
return gcPause
}
// GetCurrentRunningStats 返回当前运行信息
func GetCurrentRunningStats(c *gin.Context) {
c.Writer.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8")
first := true
report := func(key string, value interface{}) {
if !first {
fmt.Fprintf(c.Writer, ",\n")
}
first = false
if str, ok := value.(string); ok {
fmt.Fprintf(c.Writer, "%q: %q", key, str)
} else {
fmt.Fprintf(c.Writer, "%q: %v", key, value)
}
}
fmt.Fprintf(c.Writer, "{\n")
expvar.Do(func(kv expvar.KeyValue) {
report(kv.Key, kv.Value)
})
fmt.Fprintf(c.Writer, "\n}\n")
c.String(http.StatusOK, "")
}
func init() { //这些都是自定义变量,发布到expvar中,每次请求接口,expvar会自动去获取这些变量,并返回
expvar.Publish("运行时间", expvar.Func(calculateUptime))
expvar.Publish("version", expvar.Func(currentGoVersion))
expvar.Publish("cores", expvar.Func(getNumCPUs))
expvar.Publish("os", expvar.Func(getGoOS))
expvar.Publish("cgo", expvar.Func(getNumCgoCall))
expvar.Publish("goroutine", expvar.Func(getNumGoroutins))
expvar.Publish("gcpause", expvar.Func(getLastGCPauseTime))
expvar.Publish("CuMemory", expvar.Func(getCuMemoryMap))
expvar.Publish("BTCMemory", expvar.Func(getBTCMemoryMap))
}
运行程序,并请求127.0.0.1:6666/debug/vars
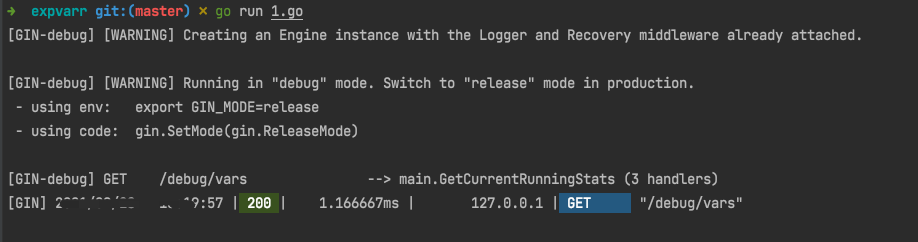
结果如下:
{
"BTCMemory": 0,
"CuMemory": 0,
"cgo": 1,
"cmdline": [
"/var/folders/9t/839s3jmj73bcgyp5x_xh3gw00000gn/T/go-build1753052226/b001/exe/1"
],
"cores": 8,
"gcpause": 0,
"goroutine": 3,
"memstats": {
"Alloc": 1516104,
"TotalAlloc": 1516104,
"Sys": 71961616,
"Lookups": 0,
"Mallocs": 12075,
"Frees": 1237,
"HeapAlloc": 1516104,
"HeapSys": 66650112,
"HeapIdle": 63930368,
"HeapInuse": 2719744,
"HeapReleased": 63930368,
"HeapObjects": 10838,
"StackInuse": 458752,
"StackSys": 458752,
"MSpanInuse": 46376,
"MSpanSys": 49152,
"MCacheInuse": 9600,
"MCacheSys": 16384,
"BuckHashSys": 4156,
"GCSys": 4227128,
"OtherSys": 555932,
"NextGC": 4473924,
"LastGC": 0,
"PauseTotalNs": 0,
"PauseNs": [
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0
],
"PauseEnd": [
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
0
],
"NumGC": 0,
"NumForcedGC": 0,
"GCCPUFraction": 0,
"EnableGC": true,
"DebugGC": false,
"BySize": [
{
"Size": 0,
"Mallocs": 0,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 8,
"Mallocs": 251,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 16,
"Mallocs": 4258,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 24,
"Mallocs": 490,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 32,
"Mallocs": 1194,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 48,
"Mallocs": 745,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 64,
"Mallocs": 572,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 80,
"Mallocs": 72,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 96,
"Mallocs": 84,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 112,
"Mallocs": 2268,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 128,
"Mallocs": 79,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 144,
"Mallocs": 19,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 160,
"Mallocs": 164,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 176,
"Mallocs": 11,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 192,
"Mallocs": 16,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 208,
"Mallocs": 73,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 224,
"Mallocs": 5,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 240,
"Mallocs": 4,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 256,
"Mallocs": 30,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 288,
"Mallocs": 28,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 320,
"Mallocs": 50,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 352,
"Mallocs": 11,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 384,
"Mallocs": 30,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 416,
"Mallocs": 25,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 448,
"Mallocs": 3,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 480,
"Mallocs": 0,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 512,
"Mallocs": 9,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 576,
"Mallocs": 18,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 640,
"Mallocs": 57,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 704,
"Mallocs": 8,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 768,
"Mallocs": 1,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 896,
"Mallocs": 19,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 1024,
"Mallocs": 26,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 1152,
"Mallocs": 23,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 1280,
"Mallocs": 36,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 1408,
"Mallocs": 1,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 1536,
"Mallocs": 3,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 1792,
"Mallocs": 22,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 2048,
"Mallocs": 7,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 2304,
"Mallocs": 3,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 2688,
"Mallocs": 38,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 3072,
"Mallocs": 6,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 3200,
"Mallocs": 2,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 3456,
"Mallocs": 3,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 4096,
"Mallocs": 20,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 4864,
"Mallocs": 2,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 5376,
"Mallocs": 15,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 6144,
"Mallocs": 6,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 6528,
"Mallocs": 1,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 6784,
"Mallocs": 2,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 6912,
"Mallocs": 0,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 8192,
"Mallocs": 3,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 9472,
"Mallocs": 2,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 9728,
"Mallocs": 3,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 10240,
"Mallocs": 8,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 10880,
"Mallocs": 8,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 12288,
"Mallocs": 0,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 13568,
"Mallocs": 0,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 14336,
"Mallocs": 0,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 16384,
"Mallocs": 0,
"Frees": 0
},
{
"Size": 18432,
"Mallocs": 1,
"Frees": 0
}
]
},
"os": "darwin",
"version": "go1.16.7",
"运行时间": "30.037286084s"
}
其中,expvar包会默认携带memstats,该字段内含 各种内存堆栈以及GC的一些信息,具体可见源码注释
src/runtime/mstats.go
src/runtime/mstats.go[2]
// A MemStats records statistics about the memory allocator.
type MemStats struct {
// General statistics.
// Alloc is bytes of allocated heap objects.
//
// This is the same as HeapAlloc (see below).
Alloc uint64
// TotalAlloc is cumulative bytes allocated for heap objects.
//
// TotalAlloc increases as heap objects are allocated, but
// unlike Alloc and HeapAlloc, it does not decrease when
// objects are freed.
TotalAlloc uint64
// Sys is the total bytes of memory obtained from the OS.
//
// Sys is the sum of the XSys fields below. Sys measures the
// virtual address space reserved by the Go runtime for the
// heap, stacks, and other internal data structures. It's
// likely that not all of the virtual address space is backed
// by physical memory at any given moment, though in general
// it all was at some point.
Sys uint64
// Lookups is the number of pointer lookups performed by the
// runtime.
//
// This is primarily useful for debugging runtime internals.
Lookups uint64
// Mallocs is the cumulative count of heap objects allocated.
// The number of live objects is Mallocs - Frees.
Mallocs uint64
// Frees is the cumulative count of heap objects freed.
Frees uint64
// Heap memory statistics.
//
// Interpreting the heap statistics requires some knowledge of
// how Go organizes memory. Go divides the virtual address
// space of the heap into "spans", which are contiguous
// regions of memory 8K or larger. A span may be in one of
// three states:
//
// An "idle" span contains no objects or other data. The
// physical memory backing an idle span can be released back
// to the OS (but the virtual address space never is), or it
// can be converted into an "in use" or "stack" span.
//
// An "in use" span contains at least one heap object and may
// have free space available to allocate more heap objects.
//
// A "stack" span is used for goroutine stacks. Stack spans
// are not considered part of the heap. A span can change
// between heap and stack memory; it is never used for both
// simultaneously.
// HeapAlloc is bytes of allocated heap objects.
//
// "Allocated" heap objects include all reachable objects, as
// well as unreachable objects that the garbage collector has
// not yet freed. Specifically, HeapAlloc increases as heap
// objects are allocated and decreases as the heap is swept
// and unreachable objects are freed. Sweeping occurs
// incrementally between GC cycles, so these two processes
// occur simultaneously, and as a result HeapAlloc tends to
// change smoothly (in contrast with the sawtooth that is
// typical of stop-the-world garbage collectors).
HeapAlloc uint64
// HeapSys is bytes of heap memory obtained from the OS.
//
// HeapSys measures the amount of virtual address space
// reserved for the heap. This includes virtual address space
// that has been reserved but not yet used, which consumes no
// physical memory, but tends to be small, as well as virtual
// address space for which the physical memory has been
// returned to the OS after it became unused (see HeapReleased
// for a measure of the latter).
//
// HeapSys estimates the largest size the heap has had.
HeapSys uint64
// HeapIdle is bytes in idle (unused) spans.
//
// Idle spans have no objects in them. These spans could be
// (and may already have been) returned to the OS, or they can
// be reused for heap allocations, or they can be reused as
// stack memory.
//
// HeapIdle minus HeapReleased estimates the amount of memory
// that could be returned to the OS, but is being retained by
// the runtime so it can grow the heap without requesting more
// memory from the OS. If this difference is significantly
// larger than the heap size, it indicates there was a recent
// transient spike in live heap size.
HeapIdle uint64
// HeapInuse is bytes in in-use spans.
//
// In-use spans have at least one object in them. These spans
// can only be used for other objects of roughly the same
// size.
//
// HeapInuse minus HeapAlloc estimates the amount of memory
// that has been dedicated to particular size classes, but is
// not currently being used. This is an upper bound on
// fragmentation, but in general this memory can be reused
// efficiently.
HeapInuse uint64
// HeapReleased is bytes of physical memory returned to the OS.
//
// This counts heap memory from idle spans that was returned
// to the OS and has not yet been reacquired for the heap.
HeapReleased uint64
// HeapObjects is the number of allocated heap objects.
//
// Like HeapAlloc, this increases as objects are allocated and
// decreases as the heap is swept and unreachable objects are
// freed.
HeapObjects uint64
// Stack memory statistics.
//
// Stacks are not considered part of the heap, but the runtime
// can reuse a span of heap memory for stack memory, and
// vice-versa.
// StackInuse is bytes in stack spans.
//
// In-use stack spans have at least one stack in them. These
// spans can only be used for other stacks of the same size.
//
// There is no StackIdle because unused stack spans are
// returned to the heap (and hence counted toward HeapIdle).
StackInuse uint64
// StackSys is bytes of stack memory obtained from the OS.
//
// StackSys is StackInuse, plus any memory obtained directly
// from the OS for OS thread stacks (which should be minimal).
StackSys uint64
// Off-heap memory statistics.
//
// The following statistics measure runtime-internal
// structures that are not allocated from heap memory (usually
// because they are part of implementing the heap). Unlike
// heap or stack memory, any memory allocated to these
// structures is dedicated to these structures.
//
// These are primarily useful for debugging runtime memory
// overheads.
// MSpanInuse is bytes of allocated mspan structures.
MSpanInuse uint64
// MSpanSys is bytes of memory obtained from the OS for mspan
// structures.
MSpanSys uint64
// MCacheInuse is bytes of allocated mcache structures.
MCacheInuse uint64
// MCacheSys is bytes of memory obtained from the OS for
// mcache structures.
MCacheSys uint64
// BuckHashSys is bytes of memory in profiling bucket hash tables.
BuckHashSys uint64
// GCSys is bytes of memory in garbage collection metadata.
GCSys uint64
// OtherSys is bytes of memory in miscellaneous off-heap
// runtime allocations.
OtherSys uint64
// Garbage collector statistics.
// NextGC is the target heap size of the next GC cycle.
//
// The garbage collector's goal is to keep HeapAlloc ≤ NextGC.
// At the end of each GC cycle, the target for the next cycle
// is computed based on the amount of reachable data and the
// value of GOGC.
NextGC uint64
// LastGC is the time the last garbage collection finished, as
// nanoseconds since 1970 (the UNIX epoch).
LastGC uint64
// PauseTotalNs is the cumulative nanoseconds in GC
// stop-the-world pauses since the program started.
//
// During a stop-the-world pause, all goroutines are paused
// and only the garbage collector can run.
PauseTotalNs uint64
// PauseNs is a circular buffer of recent GC stop-the-world
// pause times in nanoseconds.
//
// The most recent pause is at PauseNs[(NumGC+255)%256]. In
// general, PauseNs[N%256] records the time paused in the most
// recent N%256th GC cycle. There may be multiple pauses per
// GC cycle; this is the sum of all pauses during a cycle.
PauseNs [256]uint64
// PauseEnd is a circular buffer of recent GC pause end times,
// as nanoseconds since 1970 (the UNIX epoch).
//
// This buffer is filled the same way as PauseNs. There may be
// multiple pauses per GC cycle; this records the end of the
// last pause in a cycle.
PauseEnd [256]uint64
// NumGC is the number of completed GC cycles.
NumGC uint32
// NumForcedGC is the number of GC cycles that were forced by
// the application calling the GC function.
NumForcedGC uint32
// GCCPUFraction is the fraction of this program's available
// CPU time used by the GC since the program started.
//
// GCCPUFraction is expressed as a number between 0 and 1,
// where 0 means GC has consumed none of this program's CPU. A
// program's available CPU time is defined as the integral of
// GOMAXPROCS since the program started. That is, if
// GOMAXPROCS is 2 and a program has been running for 10
// seconds, its "available CPU" is 20 seconds. GCCPUFraction
// does not include CPU time used for write barrier activity.
//
// This is the same as the fraction of CPU reported by
// GODEBUG=gctrace=1.
GCCPUFraction float64
// EnableGC indicates that GC is enabled. It is always true,
// even if GOGC=off.
EnableGC bool
// DebugGC is currently unused.
DebugGC bool
// BySize reports per-size class allocation statistics.
//
// BySize[N] gives statistics for allocations of size S where
// BySize[N-1].Size < S ≤ BySize[N].Size.
//
// This does not report allocations larger than BySize[60].Size.
BySize [61]struct {
// Size is the maximum byte size of an object in this
// size class.
Size uint32
// Mallocs is the cumulative count of heap objects
// allocated in this size class. The cumulative bytes
// of allocation is Size*Mallocs. The number of live
// objects in this size class is Mallocs - Frees.
Mallocs uint64
// Frees is the cumulative count of heap objects freed
// in this size class.
Frees uint64
}
}
对于各个字段的意义 可参考:
1、Alloc uint64 //Go语言框架 堆空间分配的字节数
2、TotalAlloc uint64 //从服务开始运行至今分配器为分配的堆空间总和,只增加,释放时不减少
3、Sys uint64 //服务现在使用的系统内存
4、Lookups uint64 //被runtime监视的指针数
5、Mallocs uint64 //服务malloc的次数
6、Frees uint64 //服务回收的heap objects的字节数
7、HeapAlloc uint64 //服务分配的堆内存字节数
8、HeapSys uint64 //系统分配的作为运行栈的内存
9、HeapIdle uint64 //申请但未分配的堆内存或者回收了的堆内存(空闲)字节数
10、HeapInuse uint64 //正在使用的堆内存字节数
10、HeapReleased uint64 //返回给OS的堆内存,类似C/C++中的free
11、HeapObjects uint64 //堆内存块申请的量
12、StackInuse uint64 //正在使用的栈字节数
13、StackSys uint64 //系统分配的作为运行栈的内存
14、MSpanInuse uint64 //用于测试用的结构体使用的字节数
15、MSpanSys uint64 //系统为测试用的结构体分配的字节数
16、MCacheInuse uint64 //mcache结构体申请的字节数(不会被视为垃圾回收)
17、MCacheSys uint64 //操作系统申请的堆空间用于mcache的字节数
18、BuckHashSys uint64 //用于剖析桶散列表的堆空间
19、GCSys uint64 //垃圾回收标记元信息使用的内存
20、OtherSys uint64 //golang系统架构占用的额外空间
21、NextGC uint64 //垃圾回收器检视的内存大小
22、LastGC uint64 // 垃圾回收器最后一次执行时间。
23、PauseTotalNs uint64 // 垃圾回收或者其他信息收集导致服务暂停的次数。
24、PauseNs [256]uint64 //一个循环队列,记录最近垃圾回收系统中断的时间
25、PauseEnd [256]uint64 //一个循环队列,记录最近垃圾回收系统中断的时间开始点。
26、NumForcedGC uint32 //服务调用runtime.GC()强制使用垃圾回收的次数。
27、GCCPUFraction float64 //垃圾回收占用服务CPU工作的时间总和。如果有100个goroutine,垃圾回收的时间为1S,那么就占用了100S。
28、BySize //内存分配器使用情况
以上参考golang程序的监控神器----expvar[3]
社区同行开发的expvarmon[4]工具,可以在命令行终端以图形化的方式实时展示特定的指标数据的变化,(expvarmon 即expvar monitor)
go get github.com/divan/expvarmon
启动刚才的程序,然后执行如下命令,可实时查看应用指标变化 (期间可以进行不同qps的请求)
expvarmon -ports="http://localhost:6666/debug/vars" -i 1s
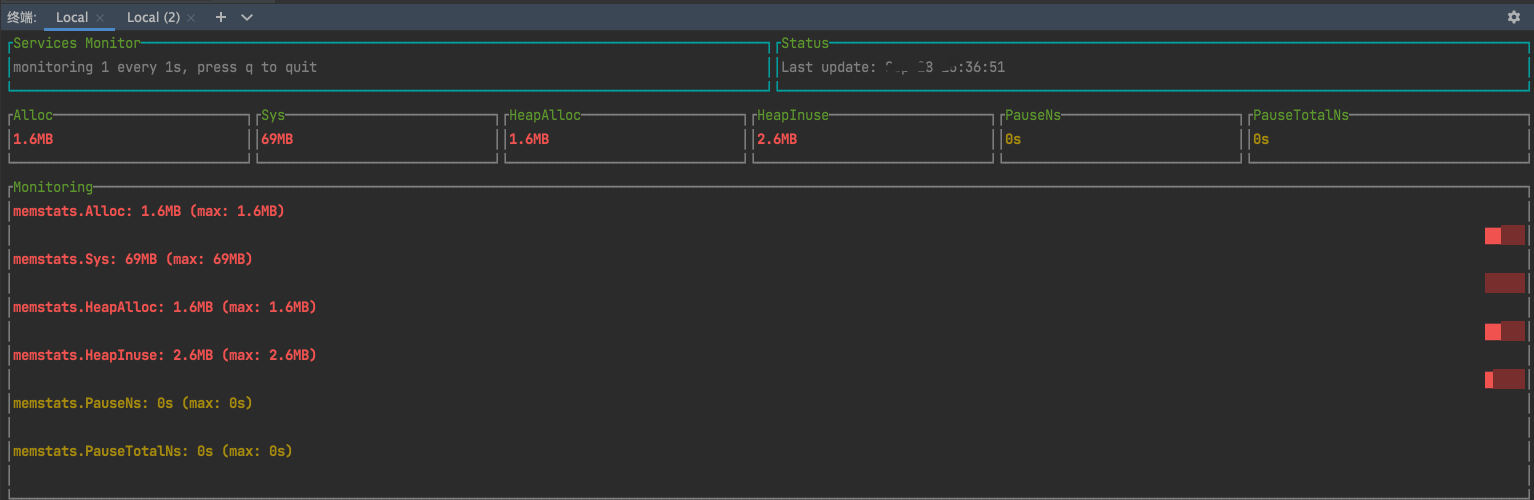
参考 给expvarmon插上数据持久化的“翅膀”[5]
官方库或知名项目中的使用
src/net/http/triv.go[6] 中使用了这个包
另外 golang.org/x/tools@v0.1.6/cmd/godoc/main.go
golang.org/x/tools@v0.1.6/go/internal/gccgoimporter/gccgoinstallation_test.go
go/test/bench/garbage/parser.go
也有使用
以及前面提到的expvarmon[7]
参考资料
expvar包: https://gitee.com/cuishuang/go1.16/tree/master/src/expvar
[2]src/runtime/mstats.go: https://gitee.com/cuishuang/go1.16/blob/master/src/runtime/mstats.go#L107
[3]golang程序的监控神器----expvar: https://blog.csdn.net/jeffrey11223/article/details/78886923/
[4]expvarmon: https://github.com/divan/expvarmon
[5]给expvarmon插上数据持久化的“翅膀”: https://tonybai.com/2021/04/14/expvarmon-save-and-convert-to-xlsx/
[6]src/net/http/triv.go: https://gitee.com/cuishuang/go1.16/blob/master/src/net/http/triv.go
[7]expvarmon: https://github.com/divan/expvarmon
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布
相关文章:

Go expvar包
介绍与使用 expvar 是 exposed variable的简写 expvar包[1]是 Golang 官方为暴露Go应用内部指标数据所提供的标准对外接口,可以辅助获取和调试全局变量。 其通过init函数将内置的expvarHandler(一个标准http HandlerFunc)注册到http包ListenAndServe创建的默认Serve…...

Yolo v8代码逐行解读
train.py文件 1.FILE Path(__file__).resolve() __file__代表的是train.py文件,Path(__file__).resolve()结果是train.py文件的绝对路径。 2.ROOT FILE.parents[0] 获得train.py父目录的绝对路径 3.sys.path 是一个列表list,里面包含了已经添加到系…...

9.18号作业
完善登录框 点击登录按钮后,判断账号(admin)和密码(123456)是否一致,如果匹配失败,则弹出错误对话框,文本内容“账号密码不匹配,是否重新登录”,给定两个按钮…...
)
Spring源码阅读(spring-framework-5.2.24)
spring-aop spring-aspects spring-beans spring-context 等等 第一步: Tags spring-projects/spring-framework GitHub 找到相应的release版本 第二步: 下载相应版本的gardle,如何看版本 spring-framework/gradle/wrapper /gradl…...
【SpringMVC】文件上传与下载、JREBEL使用
目录 一、引言 二、文件的上传 1、单文件上传 1.1、数据表准备 1.2、添加依赖 1.3、配置文件 1.4、编写表单 1.5、编写controller层 2、多文件上传 2.1、编写form表单 2.2、编写controller层 2.3、测试 三、文件下载 四、JREBEL使用 1、下载注册 2、离线设置 一…...

数据结构 第二章作业 线性表 西安石油大学
在顺序表中插入和删除一个结点需平均移动多少个结点?具体的移动次数取决于 哪两个因素? 在顺序表中插入和删除一个结点时,平均移动的结点数量取决于两个因素:插入/删除位置和当前顺序表的长度。 插入/删除位置:如果要…...

vue.mixin全局混合选项
在Vue.js中,Vue.mixin 是一个用来全局混合(mixin)选项的方法。它允许你在多个组件中共享相同的选项,例如数据、方法、生命周期钩子等。这可以用来在组件之间重复使用一些逻辑或共享一些通用的功能 Vue.mixin({// 在这里定义混合的选项data() {return {s…...
VMware Fusion 13+Ubuntu ARM Server 22.04.3在M2芯片的Mac上共享文件夹
因为Server版没有桌面,VMware Tools不能直接装,导致没办法共享文件。 Ubuntu中的包如果需要更新,先执行下面的步骤 sudo apt update 再执行 sudo apt upgrade 不需要更新的话,直接执行下面的步骤 先把open-vm-tools卸载了 …...

PostgreSQL serial类型
serial类型和序列 postgresql序列号(SERIAL)类型包括 smallserial(smallint,short),serial(int)bigserial(bigint,long long int) 不管是smallserial,serial还是bigserial,其范围都是(1,9223372036854775807)&#…...

[创业之路-76] - 创业公司如何在长期坚持中顺势而为?诚迈科技参观交流有感
目录 一、创业环境 1.1. VUCA乌卡时代:易变、复杂、不确定性、模糊的时代 1.2. 中国用了四十年的时间完成了三次工业革命:机械化、电气化、数字化 1.3. 中国正在经历着第四次工业革命:智能化、生态化、拟人化 1.4 国产替代:国…...

人脸修复祛马赛克算法CodeFormer——C++与Python模型部署
一、人脸修复算法 1.算法简介 CodeFormer是一种基于AI技术深度学习的人脸复原模型,由南洋理工大学和商汤科技联合研究中心联合开发,它能够接收模糊或马赛克图像作为输入,并生成更清晰的原始图像。算法源码地址:https://github.c…...

linux入门到精通-第三章-vi(vim)编辑器
目录 文本编辑器gedit介绍vi(vim)命令模式命令模式编辑模式末行模式 帮助教程保存文件切换到编辑模式光标移动(命令模式下)复制粘贴删除撤销恢复保存退出查找替换可视模式替换模式分屏其他用法配置文件 文本编辑器 gedit介绍 gedit是一个GNOME桌面环境下兼容UTF-8的文本编辑器…...
)
Mybatis面试题(三)
文章目录 前言一、Xml 映射文件中,除了常见的 select|insert|updae|delete 标签之外,还有哪些标签?二、当实体类中的属性名和表中的字段名不一样,如果将查询的结果封装到指定 pojo?三、模糊查询 like 语句该怎么写四、…...
Qt扩展-KDDockWidgets 简介及配置
Qt扩展-KDDockWidgets 简介及配置] 一、概述二、编译 KDDockWidgets 库1. Cmake Gui 中选择源文件和编译后的路径2. 点击Config,配置好编译器3. 点击Generate4. 在存放编译的文件夹输入如下命令开始编译 三、qmake 配置 一、概述 kdockwidgets是一个由KDAB组织编写…...
Vue3搭配Element Plus 实现候选搜索框效果
直接上代码 <el-col :span"14" class"ipt-col"><el-input v-model"projectName" class"w-50 m-2" input"inputChange" focus"inputFocusFn" blur"inputBlurFn" placeholder"请输入项目名…...
进程间的通信方式
文章目录 1.简单介绍2.管道2.1管道的基础概念**管道读写规则**:**管道特点** 2.2匿名管道匿名管道父子进程间通信的经典案例: 2.3命名管道基本概念:命名管道的创建:命名管道的打开规则:匿名管道与普通管道的区别**例子:用命名管道…...

分类预测 | Matlab实现基于MIC-BP-Adaboost最大互信息系数数据特征选择算法结合Adaboost-BP神经网络的数据分类预测
分类预测 | Matlab实现基于MIC-BP-Adaboost最大互信息系数数据特征选择算法结合Adaboost-BP神经网络的数据分类预测 目录 分类预测 | Matlab实现基于MIC-BP-Adaboost最大互信息系数数据特征选择算法结合Adaboost-BP神经网络的数据分类预测效果一览基本介绍研究内容程序设计参考…...

phpcms v9对联广告关闭左侧广告
修改目录“\caches\poster_js”下的文件“53.js”,修改函数“showADContent()” 将代码: str "<div idPCMSAD_"this.PosID"_"i" style"align_b":"x"px;top:"y"px;width:"this.Width&…...

7.2.4 【MySQL】匹配范围值
回头看我们 idx_name_birthday_phone_number 索引的 B 树示意图,所有记录都是按照索引列的值从小到大的顺序排好序的,所以这极大的方便我们查找索引列的值在某个范围内的记录。比方说下边这个查询语句: SELECT * FROM person_info WHERE nam…...
1400*C. No Prime Differences(找规律数学)
解析: 由于 1 不是质数,所以我们令每一行的数都相差 1 对于行间,分为 n、m之中有存在偶数和都为奇数两种情况。 如果n、m存在偶数,假设m为偶数。 如果都为奇数,则: #include<bits/stdc.h> using name…...

内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc
内存分配函数malloc kmalloc vmalloc malloc实现步骤: 1)请求大小调整:首先,malloc 需要调整用户请求的大小,以适应内部数据结构(例如,可能需要存储额外的元数据)。通常,这包括对齐调整,确保分配的内存地址满足特定硬件要求(如对齐到8字节或16字节边界)。 2)空闲…...
)
Spring Boot 实现流式响应(兼容 2.7.x)
在实际开发中,我们可能会遇到一些流式数据处理的场景,比如接收来自上游接口的 Server-Sent Events(SSE) 或 流式 JSON 内容,并将其原样中转给前端页面或客户端。这种情况下,传统的 RestTemplate 缓存机制会…...
以下是对华为 HarmonyOS NETX 5属性动画(ArkTS)文档的结构化整理,通过层级标题、表格和代码块提升可读性:
一、属性动画概述NETX 作用:实现组件通用属性的渐变过渡效果,提升用户体验。支持属性:width、height、backgroundColor、opacity、scale、rotate、translate等。注意事项: 布局类属性(如宽高)变化时&#…...

边缘计算医疗风险自查APP开发方案
核心目标:在便携设备(智能手表/家用检测仪)部署轻量化疾病预测模型,实现低延迟、隐私安全的实时健康风险评估。 一、技术架构设计 #mermaid-svg-iuNaeeLK2YoFKfao {font-family:"trebuchet ms",verdana,arial,sans-serif;font-size:16px;fill:#333;}#mermaid-svg…...
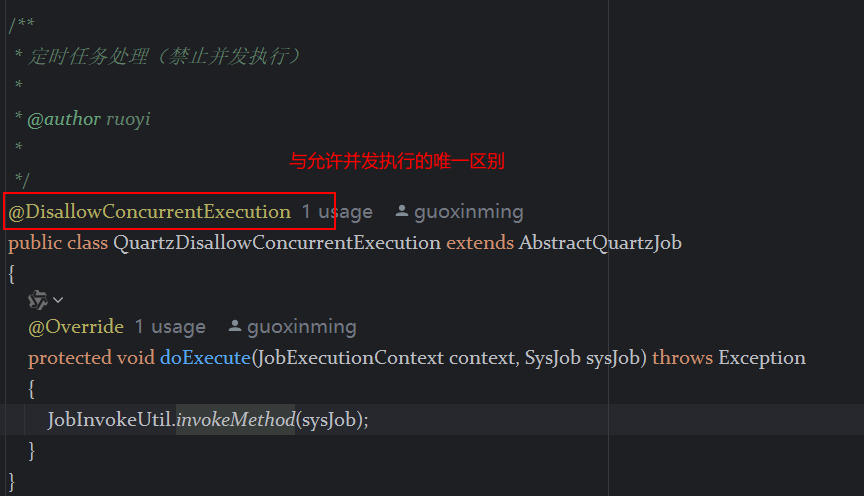
定时器任务——若依源码分析
分析util包下面的工具类schedule utils: ScheduleUtils 是若依中用于与 Quartz 框架交互的工具类,封装了定时任务的 创建、更新、暂停、删除等核心逻辑。 createScheduleJob createScheduleJob 用于将任务注册到 Quartz,先构建任务的 JobD…...
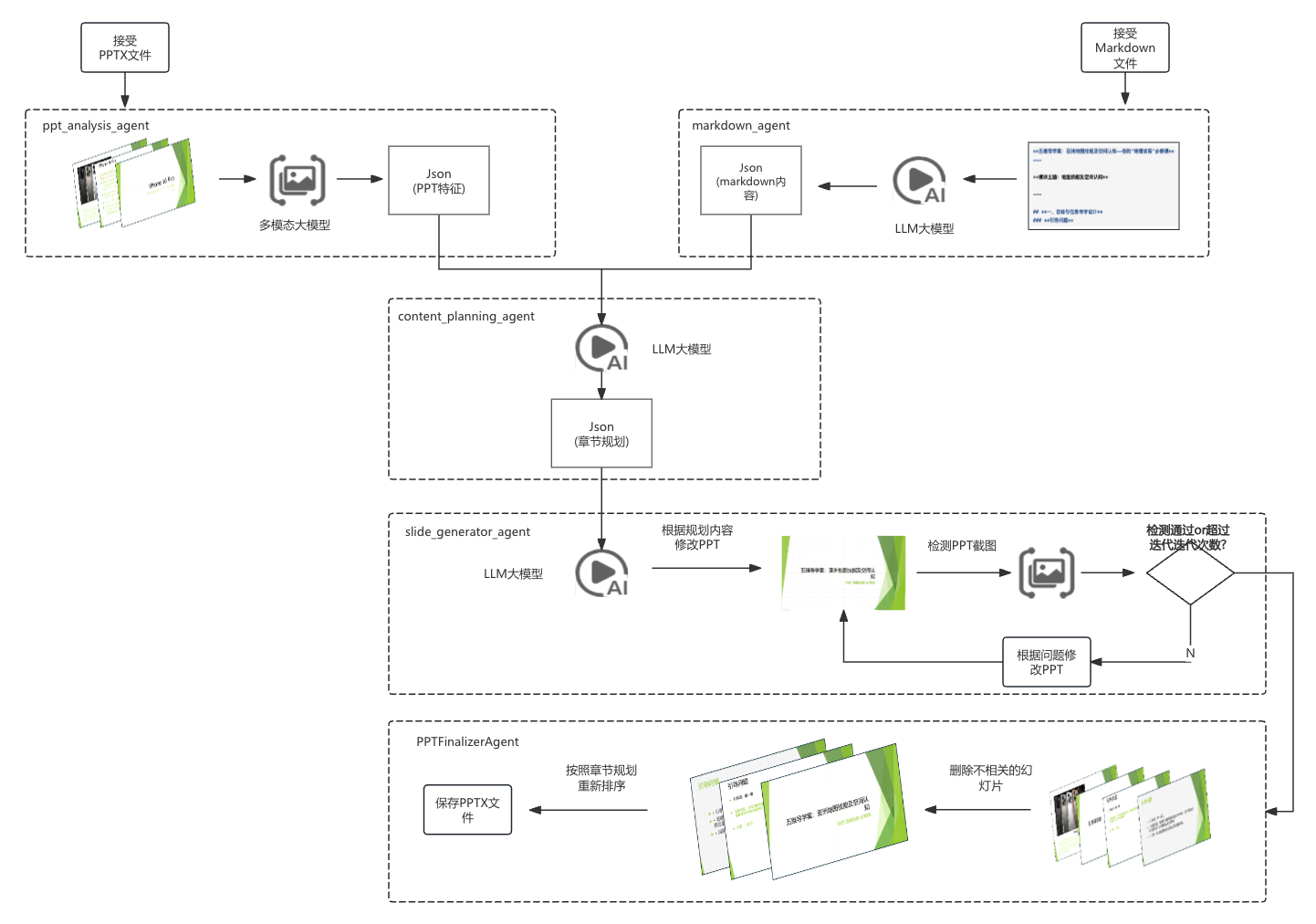
【项目实战】通过多模态+LangGraph实现PPT生成助手
PPT自动生成系统 基于LangGraph的PPT自动生成系统,可以将Markdown文档自动转换为PPT演示文稿。 功能特点 Markdown解析:自动解析Markdown文档结构PPT模板分析:分析PPT模板的布局和风格智能布局决策:匹配内容与合适的PPT布局自动…...
Cinnamon修改面板小工具图标
Cinnamon开始菜单-CSDN博客 设置模块都是做好的,比GNOME简单得多! 在 applet.js 里增加 const Settings imports.ui.settings;this.settings new Settings.AppletSettings(this, HTYMenusonichy, instance_id); this.settings.bind(menu-icon, menu…...
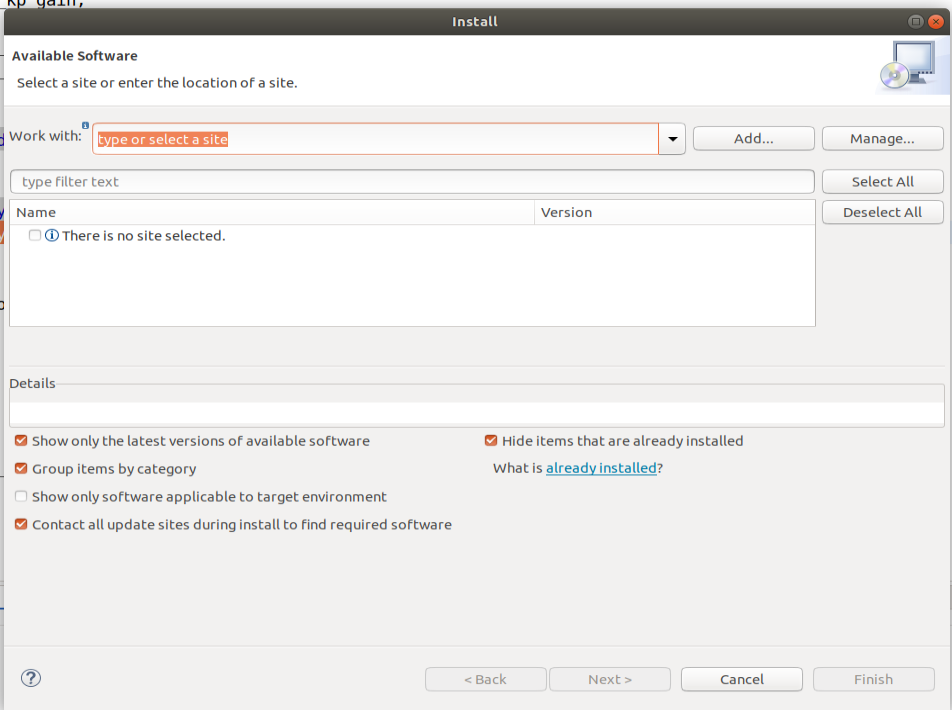
ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++
目录 文章目录 目录摘要1.修复过程摘要 本节主要解决ardupilot 开发环境eclipse 中import 缺少C++,无法导入ardupilot代码,会引起查看不方便的问题。如下图所示 1.修复过程 0.安装ubuntu 软件中自带的eclipse 1.打开eclipse—Help—install new software 2.在 Work with中…...
GC1808高性能24位立体声音频ADC芯片解析
1. 芯片概述 GC1808是一款24位立体声音频模数转换器(ADC),支持8kHz~96kHz采样率,集成Δ-Σ调制器、数字抗混叠滤波器和高通滤波器,适用于高保真音频采集场景。 2. 核心特性 高精度:24位分辨率,…...
以光量子为例,详解量子获取方式
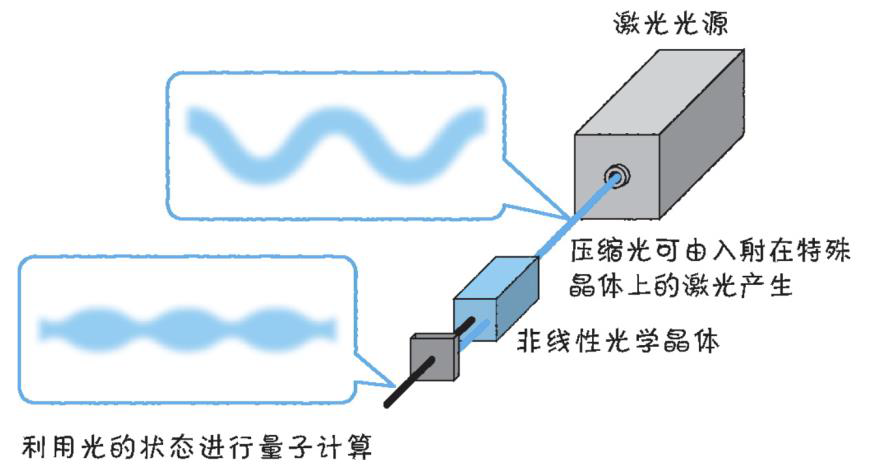
光量子技术获取量子比特可在室温下进行。该方式有望通过与名为硅光子学(silicon photonics)的光波导(optical waveguide)芯片制造技术和光纤等光通信技术相结合来实现量子计算机。量子力学中,光既是波又是粒子。光子本…...
