pcl--第十节 点云曲面重建
曲面重建技术在逆向工程、数据可视化、机器视觉、虚拟现实、医疗技术等领域中得到了广泛的应用 。 例如,在汽车、航空等工业领域中,复杂外形产品的设计仍需要根据手工模型,采用逆向工程的手段建立产品的数字化模型,根据测量数据建立人体以及骨骼和器官的计算机模型,在医学、定制生产等方面都有重要意义 。
除了上述传统的行业,随着新兴的廉价 RGBD 获取设备在数字娱乐行业的病毒式扩展,使得更多人开始使用点云来处理对象并进行工程应用 。 根据重建曲面和数据点云之间的关系,可将曲面重建分为两大类:插值法和逼近法。前者得到的重建曲面完全通过原始数据点,而后者则是用分片线性曲面或其他形式的曲面来逼近原始数据点,从而使得得到的重建曲面是原始点集的一个逼近曲面。
关联知识:
Search、KdTree、Octree
基于多项式重构的平滑和法线估计¶
本教程说明如何使用移动最小二乘(MLS)曲面重构方法来平滑和重采样噪声数据。
使用统计分析很难消除某些数据不规则性(由较小的距离测量误差引起)。要创建完整的模型,必须考虑光滑的表面以及数据中的遮挡。在无法获取其他扫描的情况下,一种解决方案是使用重采样算法,该算法尝试通过周围数据点之间的高阶多项式插值来重新创建表面的缺失部分。通过执行重采样,可以纠正这些小的错误,并且可以将多个扫描记录在一起执行平滑操作合并成同一个点云。
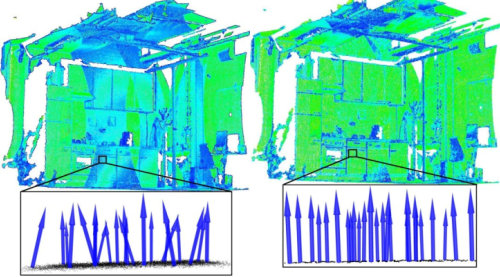
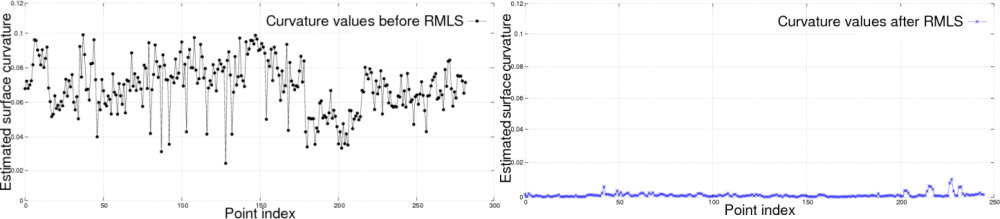
在上图的左侧,我们在包含两个配准点云的数据集中看到了配准后的效果及表面法线估计。由于对齐错误,所产生的法线有噪声。在右侧,使用移动最小二乘法对表面法线估计进行平滑处理后,在同一数据集中看到了该效果。绘制每个点的曲率,作为重新采样前后特征值关系的度量,我们得到:
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
//#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <pcl/surface/mls.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
int
main ()
{// Load input file into a PointCloud<T> with an appropriate typepcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ());// Load bun0.pcd -- should be available with the PCL archive in test pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("table_scene_lms400_downsampled.pcd", *cloud);// Create a KD-Tree//pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>()); // kd树对象// Output has the PointNormal type in order to store the normals calculated by MLSpcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal> mls_points;// Init object (second point type is for the normals, even if unused)pcl::MovingLeastSquares<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointNormal> mls;mls.setComputeNormals (true);// Set parametersmls.setInputCloud (cloud);mls.setPolynomialOrder (2);mls.setSearchMethod (tree);mls.setSearchRadius (0.03);// Reconstructmls.process (mls_points);// Save outputpcl::io::savePCDFile ("table_scene_lms400_downsampled-mls.pcd", mls_points);
}
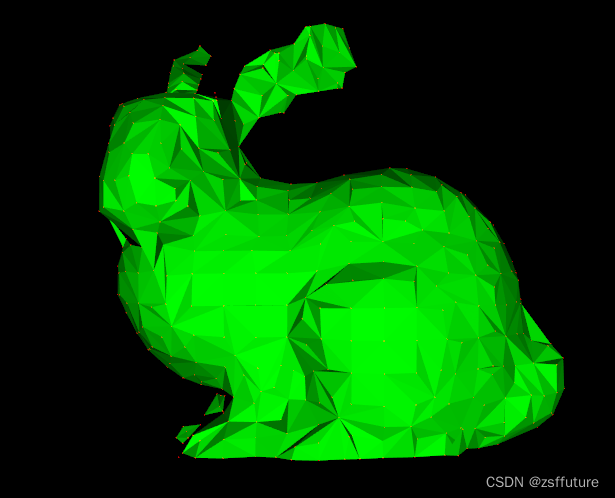
右边是重建后,会发现比左边更平整

在平面模型上提取凸(凹)多边形
学习如何为平面模型上的点集提取其对应的凹多边形的例子,该例首先从点云中提取平面模型,再通过该估计的平面模型系数从滤波后的点云投影一组点集形成点云,最后为投影后的点云计算其对应的二维凸(凹)多边形。
#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/filters/project_inliers.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/surface/convex_hull.h>intmain ()
{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_projected (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PCDReader reader;reader.read ("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);// Build a filter to remove spurious NaNs and scene backgroundpcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZ> pass;pass.setInputCloud (cloud);pass.setFilterFieldName ("z");pass.setFilterLimits (0, 1.1);pass.filter (*cloud_filtered);std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->size () << " data points." << std::endl;pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);// Create the segmentation objectpcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;// Optionalseg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);// Mandatoryseg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.01);seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);// Project the model inlierspcl::ProjectInliers<pcl::PointXYZ> proj;proj.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);proj.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);proj.setIndices (inliers);proj.setModelCoefficients (coefficients);proj.filter (*cloud_projected);// Create a Convex Hull representation of the projected inlierspcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_hull (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::ConvexHull<pcl::PointXYZ> chull;chull.setInputCloud (cloud_projected);chull.reconstruct (*cloud_hull);std::cerr << "Convex hull has: " << cloud_hull->size () << " data points." << std::endl;pcl::PCDWriter writer;writer.write ("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_hull.pcd", *cloud_hull, false);return (0);
}

#include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h>
#include <pcl/filters/project_inliers.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/surface/concave_hull.h>int
main ()
{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>), cloud_projected (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PCDReader reader;reader.read ("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);// Build a filter to remove spurious NaNs and scene backgroundpcl::PassThrough<pcl::PointXYZ> pass;pass.setInputCloud (cloud);pass.setFilterFieldName ("z");pass.setFilterLimits (0, 1.1);pass.filter (*cloud_filtered);std::cerr << "PointCloud after filtering has: "<< cloud_filtered->size () << " data points." << std::endl;pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);// Create the segmentation objectpcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;// Optionalseg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);// Mandatoryseg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.01);seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);std::cerr << "PointCloud after segmentation has: "<< inliers->indices.size () << " inliers." << std::endl;// Project the model inlierspcl::ProjectInliers<pcl::PointXYZ> proj;proj.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);// proj.setIndices (inliers);proj.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);proj.setModelCoefficients (coefficients);proj.filter (*cloud_projected);std::cerr << "PointCloud after projection has: "<< cloud_projected->size () << " data points." << std::endl;// Create a Concave Hull representation of the projected inlierspcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_hull (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::ConcaveHull<pcl::PointXYZ> chull;chull.setInputCloud (cloud_projected);chull.setAlpha (0.1);chull.reconstruct (*cloud_hull);std::cerr << "Concave hull has: " << cloud_hull->size ()<< " data points." << std::endl;pcl::PCDWriter writer;writer.write ("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_hull.pcd", *cloud_hull, false);return (0);
}

无序点云的快速三角化
本小节介绍了怎样使用贪婪投影三角化算法对有向点云进行三角化,具体方法是先将有向点云投影到某一局部二维坐标平面内,再在坐标平面内进行平面内的三角化,再根据平面内三位点的拓扑连接关系获得一个三角网格曲面模型。贪婪投影三角化算法原理是处理一系列可以使网格“生长扩大”的点(边缘点)延伸这些点直到所有符合几何正确性和拓扑正确性的点都被连上。该算法的优点是可以处理来自一个或者多个扫描仪扫描得到并且有多个连接处的散乱点云。但该算法也有一定的局限性,它更适用于采样点云来自于表面连续光滑的曲面且点云密度
变化比较均匀的情况。该算法的三角化过程是局部进行的,首先沿着一点的法线将该点投影到局部二维坐标平面内并连接其他悬空点,然后再进行下一点。所以这里设置如下参数:
- 函数 SetMaximumNearestNeighbors(unsigned)和 SetMu(double),这两个函数的作用是控制搜索邻域大小。前者定义了可搜索的邻域个数,后者规定了被样本点搜索其邻近点的最远距离(是为了适应点云密度的变化),特征值一般是 50~100和2.5~3(或者15每栅格)。
- 函数SetSearchRadius(double),该函数设置了三角化后得到的每个三角形的最大可能边长。
- 函数SetMinimumAngle(double)和 SetMaximumAngle(double),这两个函数是三角化后每个三角形的最大角和最小角。两者至少要符合一个,典型值分别是10和120°(弧度)。
- 函数 SetMaximumSurfaceAgle(double)和 SetNormalConsistency(bool),这两个函数是为了处理边缘或者角很尖锐以及一个表面的两边非常靠近的情况。为了处理这些特殊情况,函数SetMaximumSurfaceAgle(double)规定如果某点法线方向的偏离超过指定角度(注:大多数表面法线估计方法可以估计出连续变化的表面法线方向,即使在尖锐的边缘条件下),该点就不连接到样本点上。该角度是通过计算法向线段(忽略法线方向)之间的角度。函数SetNormalConsistency(bool)保证法线朝向,如果法线方向一致性标识没有设定,就不能保证估计出的法线都可以始终朝向一致。第一个函数特征值为45(弧度)第二个函数默认值为false。
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h> // for KdTree
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/surface/gp3.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <pcl/surface/organized_fast_mesh.h>
int
main ()
{// Load input file into a PointCloud<T> with an appropriate typepcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PCLPointCloud2 cloud_blob;pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("bunny.pcd", cloud_blob);pcl::fromPCLPointCloud2 (cloud_blob, *cloud);//* the data should be available in cloud// Normal estimation*pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> n;pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);tree->setInputCloud (cloud);n.setInputCloud (cloud);n.setSearchMethod (tree);n.setKSearch (20);n.compute (*normals);//* normals should not contain the point normals + surface curvatures// Concatenate the XYZ and normal fields*pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normals (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);pcl::concatenateFields (*cloud, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);//* cloud_with_normals = cloud + normals// Create search tree*pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr tree2 (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>);tree2->setInputCloud (cloud_with_normals);// Initialize objectspcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation<pcl::PointNormal> gp3;pcl::PolygonMesh triangles;// Set the maximum distance between connected points (maximum edge length)gp3.setSearchRadius (0.02);// Set typical values for the parametersgp3.setMu (2.5);gp3.setMaximumNearestNeighbors (100);gp3.setMaximumSurfaceAngle(M_PI/4); // 45 degreesgp3.setMinimumAngle(M_PI/18); // 10 degreesgp3.setMaximumAngle(2*M_PI/3); // 120 degreesgp3.setNormalConsistency(false);// Get resultgp3.setInputCloud (cloud_with_normals);gp3.setSearchMethod (tree2);gp3.reconstruct (triangles);// Additional vertex informationstd::vector<int> parts = gp3.getPartIDs();std::vector<int> states = gp3.getPointStates();// Finishpcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Triangulation");viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);viewer.addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud, "input_cloud");viewer.addPolygonMesh(triangles, "triangles", 0);viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, "input_cloud");viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, "triangles");viewer.spin();return (0);
}

相关文章:

pcl--第十节 点云曲面重建
曲面重建技术在逆向工程、数据可视化、机器视觉、虚拟现实、医疗技术等领域中得到了广泛的应用 。 例如,在汽车、航空等工业领域中,复杂外形产品的设计仍需要根据手工模型,采用逆向工程的手段建立产品的数字化模型,根据测量数据建…...

【力扣-每日一题】2560. 打家劫舍 IV
class Solution { public:bool check(vector<int> &nums,int max_num,int k){//只需要计算可以偷的房间。在满足最大值为max_num下时,能偷的最多的房间,与k值比较//如果大于K,说明max_num还可以缩小//如果小于看,说明ma…...
vue简单案例----小张记事本
小张记事本 具体效果如图所示,这里就简单展示,还有很多不足的地方,希望大家可以对这个小项目进行改进,话不多说可以参考下面的代码 源代码如下 <html lang"en"><head><meta charset"UTF-8"…...
爬虫获取接口数据
上一讲讲的是获取静态网页数据的教程,适用于我们要爬取的数据在网页源代码中出现,但是还是有很多的数据是源代码中没有的,需要通过接口访问服务器来获得,下面我就来讲讲如何爬取这类数据。 以巨潮资讯网爬取比亚迪企业年报为例。…...

私域流量的变现方式,你知道多少?
私域流量的变现方式是指通过有效的管理和运营自有的用户群体,将流量转化为实际收益的过程。私域流量的变现方式多样,下面将介绍其中几种常见的方式。 1. 电商平台入驻 通过将自有流量引导到电商平台,开设店铺进行商品销售,从中获…...
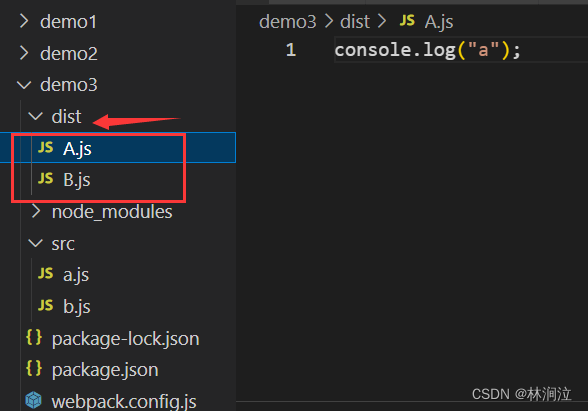
Webpack配置entry修改入口文件或打包多个文件
当我们使用Webpack进行文件打包时,默认打包的文件是src文件下的index.js文件 一、修改Webpack打包入口 如果我们想要在其他文件下打包指定的js文件就需要在webpack.config.js文件中进行entry配置 二、将指定的多个文件打包为一个文件 现在有两个文件,…...
重装回MacOS)
Mac mini2014(装的windows)重装回MacOS
Mac mini2014(装的windows)重装回MacOS 制作macos的启动U盘,我的是32G的 第一步下载你的硬件能使用的系统,建议最好低一个版本,因为我安装的时候出现问题。 下载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/netgc/article/details/130641479下载…...

珠海建筑模板厂家-能强优品木业:为您提供优质建筑模板解决方案
在珠海这座美丽的沿海城市,建筑行业蓬勃发展,对于高质量的建筑模板需求也日益增加。在这里,有一家备受赞誉的建筑模板厂家,那就是能强优品木业。作为一家专业的建筑模板供应商,他们以优质的产品和卓越的服务在业界享有…...

图像识别技术如何改变智能家居的体验?
图像识别技术在智能家居中的应用正在改变我们的生活体验。通过图像识别技术,智能家居可以更准确地识别用户,并自动调整环境以适应用户的需求。以下是图像识别技术在智能家居中的一些应用: 人脸识别:通过人脸识别技术,智…...

前端中blob文件流和base64的区别
在前端中,base64 和 fileBlob 是用于处理文件数据的两种不同方式。 1. Base64 编码 Base64 是一种将二进制数据转换为文本字符串的编码方式。它将文件数据转换为一串由 ASCII 字符组成的字符串。在前端中,可以使用 JavaScript 的 btoa() 和 atob() 函数…...
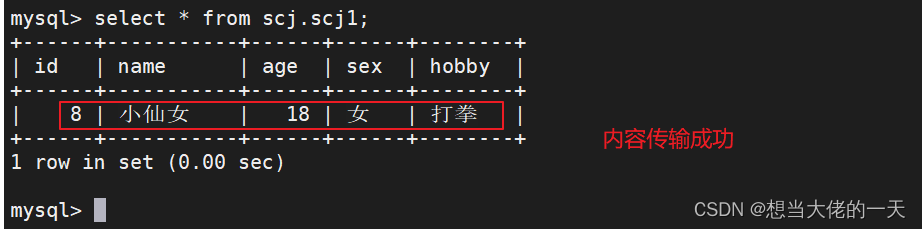
MySQL详解六:备份与恢复
文章目录 1. 数据库备份的分类1.1 从物理和逻辑上分类1.1.1 物理备份1.1.2 逻辑备份 1.2 从数据库的备份策略角度上分类1.2.1 完全备份1.2.2 差异备份1.2.3 增量备份 1.3 常见的备份方法 2. MySQL完全备份2.1 完全备份简介2.2 优点与缺点2.3 实现物理冷备份与恢复2.3.1 实现流程…...

什么样的应用程序适合使用Flutter开发桌面?
桌面应用开发的现状 在过去,桌面应用程序的开发通常需要使用特定于操作系统的工具和语言,如C、C#、Java等。这导致了高昂的开发成本和维护困难。尽管有一些跨平台桌面开发工具,如Electron和Qt,但它们在性能、用户体验和开发效率方…...

02强化学习基本概念
强化学习基本概念 前言1、State、Action、Policy等① State② Action③ State transition④ State transition probability⑤ Polity 2、Reward、Return、MDP等① Reward② Trajectory and return③ Discounted return④ Episode⑤ MDP 总结: 前言 本文来自西湖大学…...
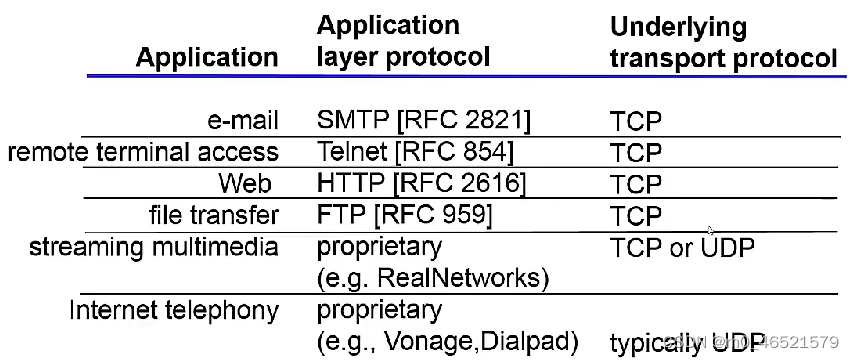
笔记2.2:网络应用基本原理
一. 网络应用的体系结构 (1)客户机/服务器结构(Client-Server, C/S) (2)点对点结构(Peer-to-Peer,P2P) (3)混合结构(Hybrid&#x…...

生活垃圾数据集(YOLO版)
文章目录 1、数据集介绍1.1、数据集图片组成2.1、获取数据集方式 2、扩展代码2.1、文件结构树2.2、划分数据集2.3、获取数据集文件名字2.4、文件成功对应检测 3、其他文章 1、数据集介绍 1.1、数据集图片组成 【有害垃圾】:电池(1 号、2 号、5 号&…...

操作系统篇之虚拟内存
虚拟内存是什么? 虚拟内存是计算机操作系统中的一种技术,它将每个进程的内存空间划分成若干个固定大小的页,并通过页面映射技术将这些页与物理内存或磁盘上的页面文件进行交换 虚拟内存能干什么? 扩展了实际物理内存容量:虚拟内存使得每个…...
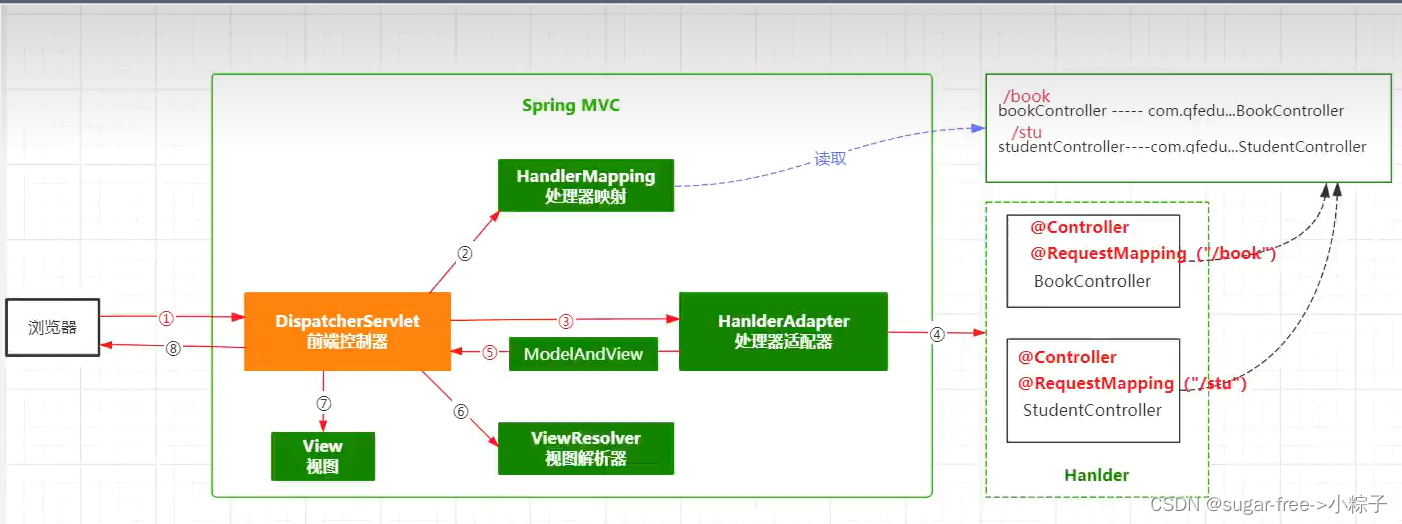
浅谈SpringMVC的请求流程
目录标题 浅谈SpringMVC的请求流程SpringMVC的介绍SpringMVC的逻辑概念运行图解知识总结 浅谈SpringMVC的请求流程 对于SpringMVC而言重点是了解它的底层运行逻辑,从而可以根据其逻辑来进行实际业务的操作或者是利用原理增强业务的功能性,最终达到项目预…...

2309json.nlohmann数格示例1
参考 示例 下面是一些示例,可让你了解如何使用该类. 除了以下示例之外,你可能还需要: ->检查文档 ->浏览独立示例文件 每个API函数(记录在API文档中)都有相应独立示例文件.如,emplace()函数有一个匹配的emplace.cpp示例文件. 从文件中读取JSON json类提供了操作JSON…...

你知道 delete 删除属性时的一些细节吗?
探究 delete 的一些细节,起源于刚刚做过的一道笔试,原题如下: a 1; const b 2; console.log(delete a); console.log(delete b); // 输出结果是? // 答:true false我可从来没用过 delete 的返回值,但凡…...

Blender入门——快捷键
视角控制 旋转视角:鼠标中键摁住即可旋转平移视角:shift中远近视角:中键滚动 物体控制 移动物体:G旋转物体:R缩放物体:S回复变换:AltG,R,S新建物体:shiftA复制物体:shiftD删除物体&a…...

vscode里如何用git
打开vs终端执行如下: 1 初始化 Git 仓库(如果尚未初始化) git init 2 添加文件到 Git 仓库 git add . 3 使用 git commit 命令来提交你的更改。确保在提交时加上一个有用的消息。 git commit -m "备注信息" 4 …...
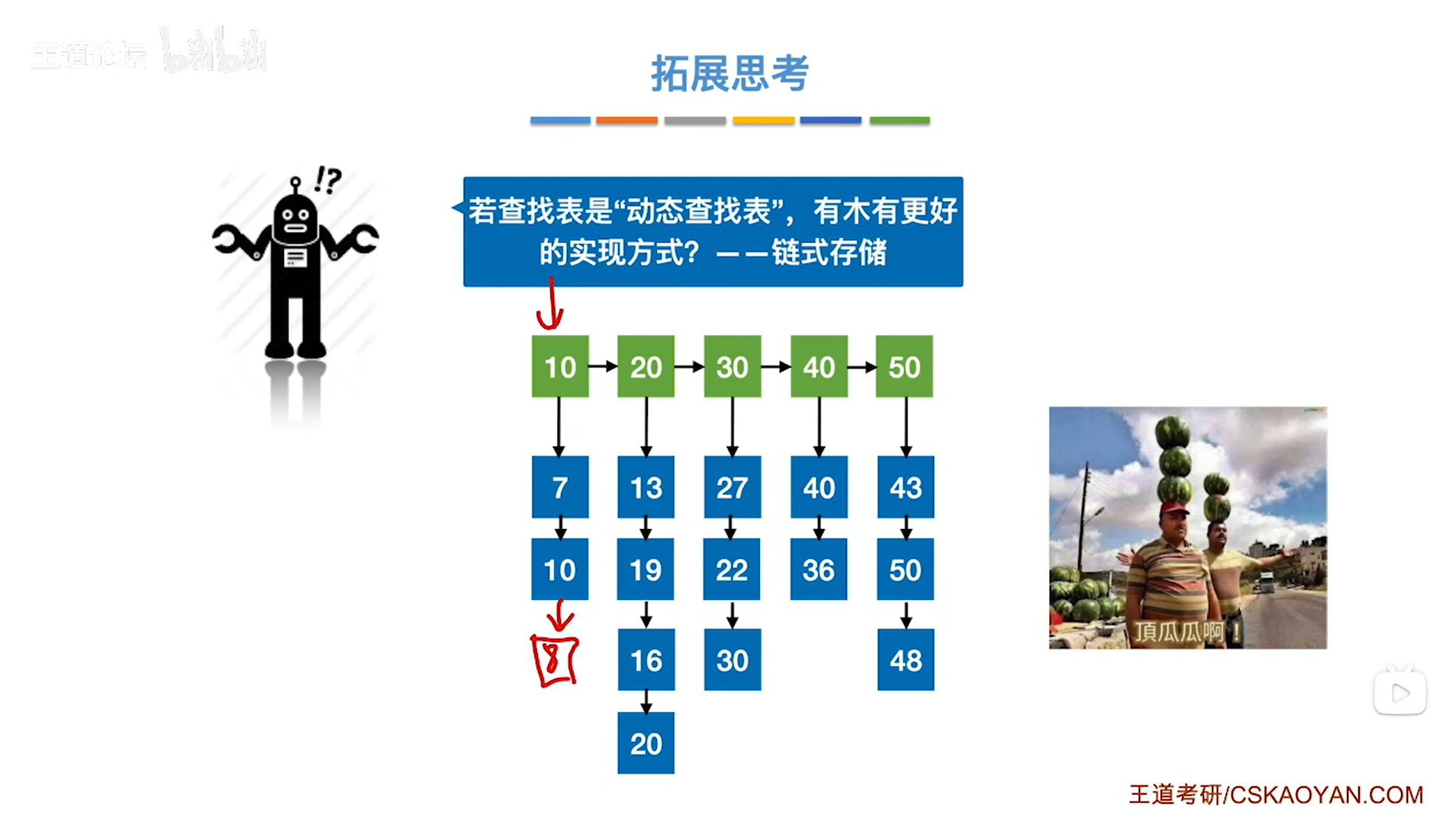
7.4.分块查找
一.分块查找的算法思想: 1.实例: 以上述图片的顺序表为例, 该顺序表的数据元素从整体来看是乱序的,但如果把这些数据元素分成一块一块的小区间, 第一个区间[0,1]索引上的数据元素都是小于等于10的, 第二…...
练习(含atoi的模拟实现,自定义类型等练习)
一、结构体大小的计算及位段 (结构体大小计算及位段 详解请看:自定义类型:结构体进阶-CSDN博客) 1.在32位系统环境,编译选项为4字节对齐,那么sizeof(A)和sizeof(B)是多少? #pragma pack(4)st…...
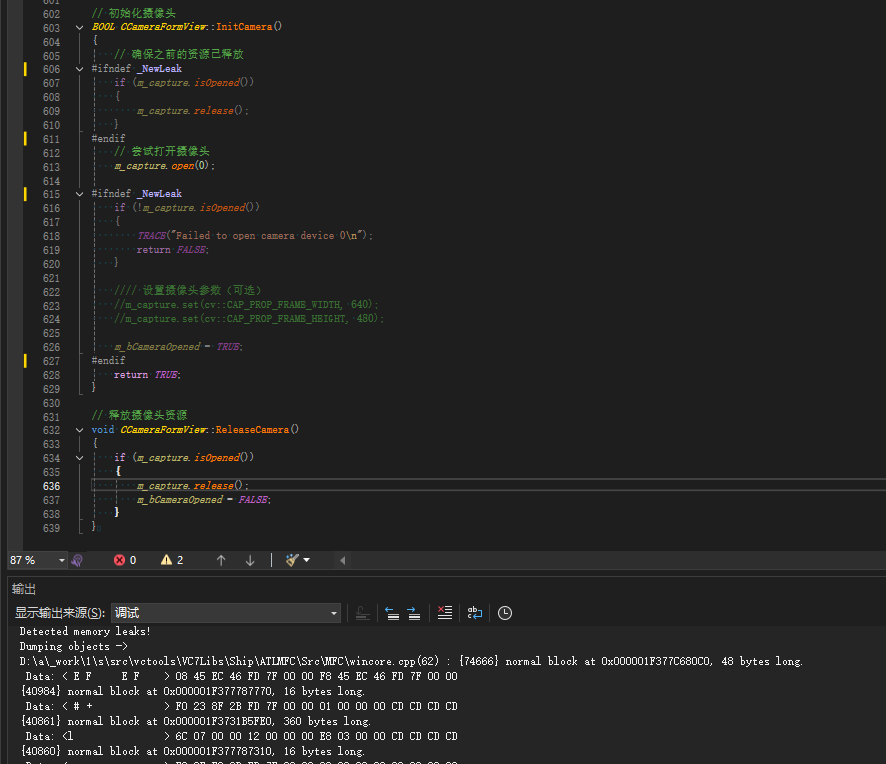
MFC内存泄露
1、泄露代码示例 void X::SetApplicationBtn() {CMFCRibbonApplicationButton* pBtn GetApplicationButton();// 获取 Ribbon Bar 指针// 创建自定义按钮CCustomRibbonAppButton* pCustomButton new CCustomRibbonAppButton();pCustomButton->SetImage(IDB_BITMAP_Jdp26)…...
LeetCode - 394. 字符串解码
题目 394. 字符串解码 - 力扣(LeetCode) 思路 使用两个栈:一个存储重复次数,一个存储字符串 遍历输入字符串: 数字处理:遇到数字时,累积计算重复次数左括号处理:保存当前状态&a…...
剑指offer20_链表中环的入口节点
链表中环的入口节点 给定一个链表,若其中包含环,则输出环的入口节点。 若其中不包含环,则输出null。 数据范围 节点 val 值取值范围 [ 1 , 1000 ] [1,1000] [1,1000]。 节点 val 值各不相同。 链表长度 [ 0 , 500 ] [0,500] [0,500]。 …...
相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?)
Redis的发布订阅模式与专业的 MQ(如 Kafka, RabbitMQ)相比,优缺点是什么?适用于哪些场景?
Redis 的发布订阅(Pub/Sub)模式与专业的 MQ(Message Queue)如 Kafka、RabbitMQ 进行比较,核心的权衡点在于:简单与速度 vs. 可靠与功能。 下面我们详细展开对比。 Redis Pub/Sub 的核心特点 它是一个发后…...

面向无人机海岸带生态系统监测的语义分割基准数据集
描述:海岸带生态系统的监测是维护生态平衡和可持续发展的重要任务。语义分割技术在遥感影像中的应用为海岸带生态系统的精准监测提供了有效手段。然而,目前该领域仍面临一个挑战,即缺乏公开的专门面向海岸带生态系统的语义分割基准数据集。受…...
MySQL 知识小结(一)
一、my.cnf配置详解 我们知道安装MySQL有两种方式来安装咱们的MySQL数据库,分别是二进制安装编译数据库或者使用三方yum来进行安装,第三方yum的安装相对于二进制压缩包的安装更快捷,但是文件存放起来数据比较冗余,用二进制能够更好管理咱们M…...

Web中间件--tomcat学习
Web中间件–tomcat Java虚拟机详解 什么是JAVA虚拟机 Java虚拟机是一个抽象的计算机,它可以执行Java字节码。Java虚拟机是Java平台的一部分,Java平台由Java语言、Java API和Java虚拟机组成。Java虚拟机的主要作用是将Java字节码转换为机器代码&#x…...
