RustDay05------Exercise[51-60]
51.使用?当作错误处理符
? 是 Rust 中的错误处理操作符。通常用于尝试解析或执行可能失败的操作,并在出现错误时提前返回错误,以避免程序崩溃或出现未处理的错误。
具体来说,? 用于处理 Result 或 Option 类型的返回值。
// errors2.rs
// Say we're writing a game where you can buy items with tokens. All items cost
// 5 tokens, and whenever you purchase items there is a processing fee of 1
// token. A player of the game will type in how many items they want to buy,
// and the `total_cost` function will calculate the total number of tokens.
// Since the player typed in the quantity, though, we get it as a string-- and
// they might have typed anything, not just numbers!// Right now, this function isn't handling the error case at all (and isn't
// handling the success case properly either). What we want to do is:
// if we call the `parse` function on a string that is not a number, that
// function will return a `ParseIntError`, and in that case, we want to
// immediately return that error from our function and not try to multiply
// and add.// There are at least two ways to implement this that are both correct-- but
// one is a lot shorter!
// Execute `rustlings hint errors2` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEuse std::num::ParseIntError;pub fn total_cost(item_quantity: &str) -> Result<i32, ParseIntError> {let processing_fee = 1;let cost_per_item = 5;let qty = item_quantity.parse::<i32>()?;Ok(qty * cost_per_item + processing_fee)
}#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {use super::*;#[test]fn item_quantity_is_a_valid_number() {assert_eq!(total_cost("34"), Ok(171));}#[test]fn item_quantity_is_an_invalid_number() {assert_eq!(total_cost("beep boop").unwrap_err().to_string(),"invalid digit found in string");}
}
52.在main函数中需要对ParseIntError进行Err匹配
这题只能这么理解,具体原理没翻到
// errors3.rs
// This is a program that is trying to use a completed version of the
// `total_cost` function from the previous exercise. It's not working though!
// Why not? What should we do to fix it?
// Execute `rustlings hint errors3` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEuse std::num::ParseIntError;fn main() {let mut tokens = 100;let pretend_user_input = "8";// let cost = total_cost(pretend_user_input)?;// if cost > tokens {// println!("You can't afford that many!");// } else {// tokens -= cost;// println!("You now have {} tokens.", tokens);// }match total_cost(pretend_user_input) {Ok(cost) =>{if cost > tokens {println!("You can't afford that many!");} else {tokens -= cost;println!("You now have {} tokens.", tokens);}}Err(message) => {}}
}pub fn total_cost(item_quantity: &str) -> Result<i32, ParseIntError> {let processing_fee = 1;let cost_per_item = 5;let qty = item_quantity.parse::<i32>()?;Ok(qty * cost_per_item + processing_fee)
}
53.使用if处理不合理的数值范围
// errors4.rs
// Execute `rustlings hint errors4` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONE#[derive(PartialEq, Debug)]
struct PositiveNonzeroInteger(u64);#[derive(PartialEq, Debug)]
enum CreationError {Negative,Zero,
}impl PositiveNonzeroInteger {fn new(value: i64) -> Result<PositiveNonzeroInteger, CreationError> {// Hmm...? Why is this only returning an Ok value?// Ok(PositiveNonzeroInteger(value as u64))if value>0 {Ok(PositiveNonzeroInteger(value as u64))}else if value==0 {Err(CreationError::Zero)}else{Err(CreationError::Negative)}}
}#[test]
fn test_creation() {assert!(PositiveNonzeroInteger::new(10).is_ok());assert_eq!(Err(CreationError::Negative),PositiveNonzeroInteger::new(-10));assert_eq!(Err(CreationError::Zero), PositiveNonzeroInteger::new(0));
}
54.在任意实现了error::Error的类型上处理错误类型
// errors5.rs// This program uses an altered version of the code from errors4.// This exercise uses some concepts that we won't get to until later in the course, like `Box` and the
// `From` trait. It's not important to understand them in detail right now, but you can read ahead if you like.
// For now, think of the `Box<dyn ...>` type as an "I want anything that does ???" type, which, given
// Rust's usual standards for runtime safety, should strike you as somewhat lenient!// In short, this particular use case for boxes is for when you want to own a value and you care only that it is a
// type which implements a particular trait. To do so, The Box is declared as of type Box<dyn Trait> where Trait is the trait
// the compiler looks for on any value used in that context. For this exercise, that context is the potential errors
// which can be returned in a Result.// What can we use to describe both errors? In other words, is there a trait which both errors implement?// Execute `rustlings hint errors5` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEuse std::error;
use std::fmt;
use std::num::ParseIntError;// TODO: update the return type of `main()` to make this compile.
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn error::Error>> {let pretend_user_input = "42";let x: i64 = pretend_user_input.parse()?;println!("output={:?}", PositiveNonzeroInteger::new(x)?);Ok(())
}// Don't change anything below this line.#[derive(PartialEq, Debug)]
struct PositiveNonzeroInteger(u64);#[derive(PartialEq, Debug)]
enum CreationError {Negative,Zero,
}impl PositiveNonzeroInteger {fn new(value: i64) -> Result<PositiveNonzeroInteger, CreationError> {match value {x if x < 0 => Err(CreationError::Negative),x if x == 0 => Err(CreationError::Zero),x => Ok(PositiveNonzeroInteger(x as u64))}}
}// This is required so that `CreationError` can implement `error::Error`.
impl fmt::Display for CreationError {fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {let description = match *self {CreationError::Negative => "number is negative",CreationError::Zero => "number is zero",};f.write_str(description)}
}impl error::Error for CreationError {}
55.通过方法映射错误类型?
这题没太看明白,跟着题目提示和GPT提示做下去的
// errors6.rs// Using catch-all error types like `Box<dyn error::Error>` isn't recommended
// for library code, where callers might want to make decisions based on the
// error content, instead of printing it out or propagating it further. Here,
// we define a custom error type to make it possible for callers to decide
// what to do next when our function returns an error.// Execute `rustlings hint errors6` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEuse std::num::ParseIntError;// This is a custom error type that we will be using in `parse_pos_nonzero()`.
#[derive(PartialEq, Debug)]
enum ParsePosNonzeroError {Creation(CreationError),ParseInt(ParseIntError)
}impl ParsePosNonzeroError {fn from_creation(err: CreationError) -> ParsePosNonzeroError {ParsePosNonzeroError::Creation(err)}// TODO: add another error conversion function here.// fn from_parseint...fn from_parseint(err: ParseIntError) -> ParsePosNonzeroError {ParsePosNonzeroError::ParseInt(err)}
}fn parse_pos_nonzero(s: &str)-> Result<PositiveNonzeroInteger, ParsePosNonzeroError>
{// TODO: change this to return an appropriate error instead of panicking// when `parse()` returns an error.let x: i64 = s.parse().map_err(ParsePosNonzeroError::from_parseint)?;;PositiveNonzeroInteger::new(x).map_err(ParsePosNonzeroError::from_creation)
}// Don't change anything below this line.#[derive(PartialEq, Debug)]
struct PositiveNonzeroInteger(u64);#[derive(PartialEq, Debug)]
enum CreationError {Negative,Zero,
}impl PositiveNonzeroInteger {fn new(value: i64) -> Result<PositiveNonzeroInteger, CreationError> {match value {x if x < 0 => Err(CreationError::Negative),x if x == 0 => Err(CreationError::Zero),x => Ok(PositiveNonzeroInteger(x as u64))}}
}#[cfg(test)]
mod test {use super::*;#[test]fn test_parse_error() {// We can't construct a ParseIntError, so we have to pattern match.assert!(matches!(parse_pos_nonzero("not a number"),Err(ParsePosNonzeroError::ParseInt(_))));}#[test]fn test_negative() {assert_eq!(parse_pos_nonzero("-555"),Err(ParsePosNonzeroError::Creation(CreationError::Negative)));}#[test]fn test_zero() {assert_eq!(parse_pos_nonzero("0"),Err(ParsePosNonzeroError::Creation(CreationError::Zero)));}#[test]fn test_positive() {let x = PositiveNonzeroInteger::new(42);assert!(x.is_ok());assert_eq!(parse_pos_nonzero("42"), Ok(x.unwrap()));}
}
56.为某一种类型实现(impl)共享行为(抽象库)
// traits1.rs
// Time to implement some traits!
//
// Your task is to implement the trait
// `AppendBar' for the type `String'.
//
// The trait AppendBar has only one function,
// which appends "Bar" to any object
// implementing this trait.
// Execute `rustlings hint traits1` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEtrait AppendBar {fn append_bar(self) -> Self;
}impl AppendBar for String {//Add your code herefn append_bar(self) -> Self{self+"Bar"}
}fn main() {let s = String::from("Foo");let s = s.append_bar();println!("s: {}", s);
}#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {use super::*;#[test]fn is_foo_bar() {assert_eq!(String::from("Foo").append_bar(), String::from("FooBar"));}#[test]fn is_bar_bar() {assert_eq!(String::from("").append_bar().append_bar(),String::from("BarBar"));}
}
57.自己给Vec写append实现
这道题实际上调用push就可以了
// traits2.rs
//
// Your task is to implement the trait
// `AppendBar' for a vector of strings.
//
// To implement this trait, consider for
// a moment what it means to 'append "Bar"'
// to a vector of strings.
//
// No boiler plate code this time,
// you can do this!
// Execute `rustlings hint traits2` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEtrait AppendBar {fn append_bar(self) -> Self;
}//TODO: Add your code here
impl AppendBar for Vec<String>{fn append_bar(mut self) -> Self{self.push("Bar".to_string());self}
}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {use super::*;#[test]fn is_vec_pop_eq_bar() {let mut foo = vec![String::from("Foo")].append_bar();assert_eq!(foo.pop().unwrap(), String::from("Bar"));assert_eq!(foo.pop().unwrap(), String::from("Foo"));}
}
58.我们不仅可以在impl里面去写具体的实现,也可以在共享行为声明里面完成
// traits3.rs
//
// Your task is to implement the Licensed trait for
// both structures and have them return the same
// information without writing the same function twice.
//
// Consider what you can add to the Licensed trait.
// Execute `rustlings hint traits3` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEpub trait Licensed {fn licensing_info(&self) -> String{String::from("Some information")}
}struct SomeSoftware {version_number: i32,
}struct OtherSoftware {version_number: String,
}impl Licensed for SomeSoftware {} // Don't edit this line
impl Licensed for OtherSoftware {} // Don't edit this line#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {use super::*;#[test]fn is_licensing_info_the_same() {let licensing_info = String::from("Some information");let some_software = SomeSoftware { version_number: 1 };let other_software = OtherSoftware {version_number: "v2.0.0".to_string(),};assert_eq!(some_software.licensing_info(), licensing_info);assert_eq!(other_software.licensing_info(), licensing_info);}
}
59.创建关于共享行为(trait)的两个实例的泛型
这个真的很妙
// traits4.rs
//
// Your task is to replace the '??' sections so the code compiles.
// Don't change any line other than the marked one.
// Execute `rustlings hint traits4` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEpub trait Licensed {fn licensing_info(&self) -> String {"some information".to_string()}
}struct SomeSoftware {}struct OtherSoftware {}impl Licensed for SomeSoftware {}
impl Licensed for OtherSoftware {}// YOU MAY ONLY CHANGE THE NEXT LINE
fn compare_license_types<T:Licensed,U:Licensed>(software: T, software_two: U) -> bool {software.licensing_info() == software_two.licensing_info()
}#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {use super::*;#[test]fn compare_license_information() {let some_software = SomeSoftware {};let other_software = OtherSoftware {};assert!(compare_license_types(some_software, other_software));}#[test]fn compare_license_information_backwards() {let some_software = SomeSoftware {};let other_software = OtherSoftware {};assert!(compare_license_types(other_software, some_software));}
}
60.使用+来放行实现了多种共享行为的类型
// traits5.rs
//
// Your task is to replace the '??' sections so the code compiles.
// Don't change any line other than the marked one.
// Execute `rustlings hint traits5` or use the `hint` watch subcommand for a hint.// I AM NOT DONEpub trait SomeTrait {fn some_function(&self) -> bool {true}
}pub trait OtherTrait {fn other_function(&self) -> bool {true}
}struct SomeStruct {}
struct OtherStruct {}impl SomeTrait for SomeStruct {}
impl OtherTrait for SomeStruct {}impl SomeTrait for OtherStruct {}
impl OtherTrait for OtherStruct {}// YOU MAY ONLY CHANGE THE NEXT LINE
fn some_func<T:SomeTrait+OtherTrait>(item: T) -> bool {item.some_function() && item.other_function()
}fn main() {some_func(SomeStruct {});some_func(OtherStruct {});
}
相关文章:

RustDay05------Exercise[51-60]
51.使用?当作错误处理符 ? 是 Rust 中的错误处理操作符。通常用于尝试解析或执行可能失败的操作,并在出现错误时提前返回错误,以避免程序崩溃或出现未处理的错误。 具体来说,? 用于处理 Result 或 Option 类型的返回值。 // errors2.rs…...
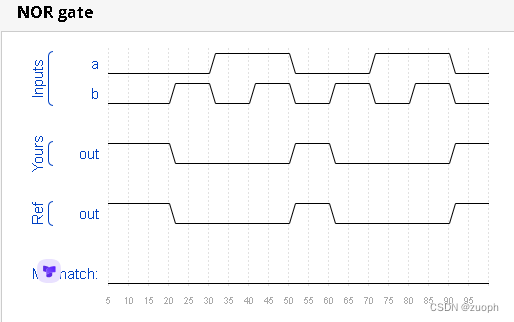
hdlbits系列verilog解答(或非门)-07
文章目录 wire线网类型介绍一、问题描述二、verilog源码三、仿真结果 wire线网类型介绍 wire线网类型是verilog的一种数据类型,它是一种单向的物理连线。它可以是输入也可以是输出,它与reg寄存器数据类型不同,它不能存储数据,只能…...
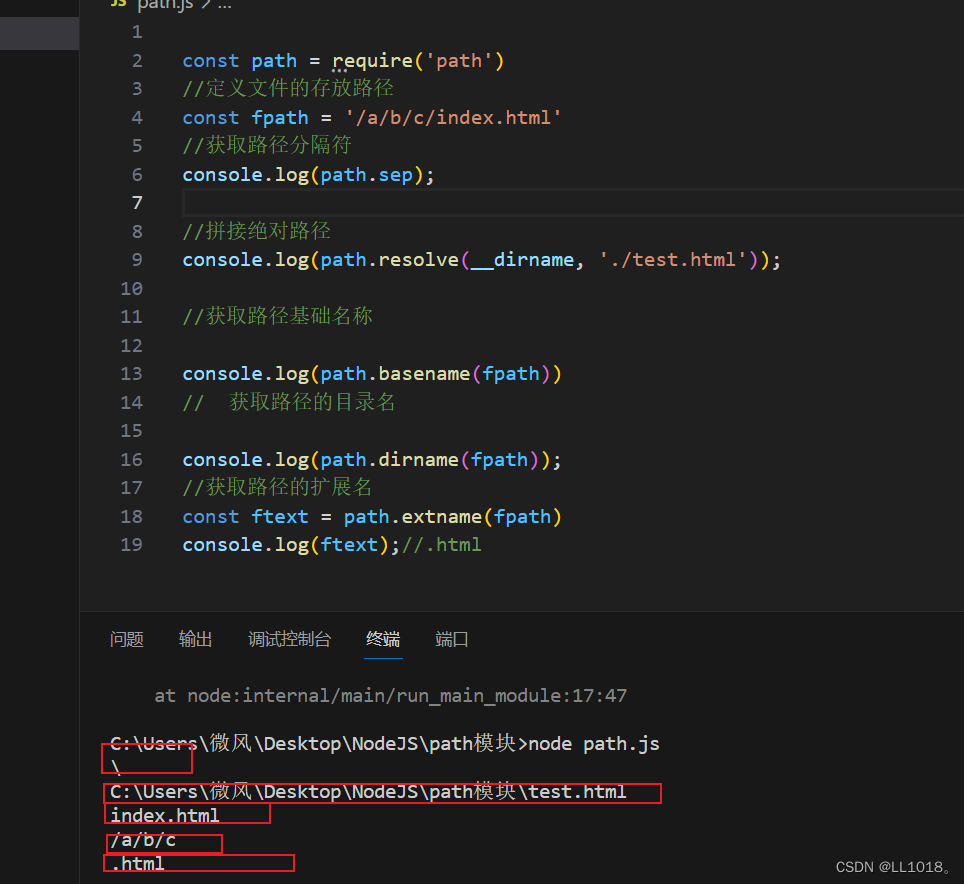
Node学习笔记之path模块
path 模块提供了 操作路径 的功能,我们将介绍如下几个较为常用的几个 API: API 说明 path.resolve 拼接规范的绝对路径常用 path.sep 获取操作系统的路径分隔符 path.parse 解析路径并返回对象 path.basename 获取路径的基础名称 path.dirname…...

使用LangChain与chatGPT API开发故事推理游戏-海龟汤
项目概述 海龟汤简述: 主持人提出一个难以理解的事件,玩家通过提问来逐步还原事件,主持人仅能告知玩家:“是、不是、是也不是、不重要”。引入chatGPT API原因 想通过程序自动化主持人,可通过chatGPT来判断玩家推理正确与否。LangChain是什么 LangChain是一个强大的框架,…...
用ChatGPT编写Excel函数公式进行表格数据处理分析,so easy!
在用Excel进行数据处理分析时,经常需要编写不同的公式,需要了解大量的函数。有了ChatGPT,就很简单了,直接用自然语言描述自己的需求,然后让ChatGPT写出公式就好了。 例子1: Excel某个单元格的内容是&#…...
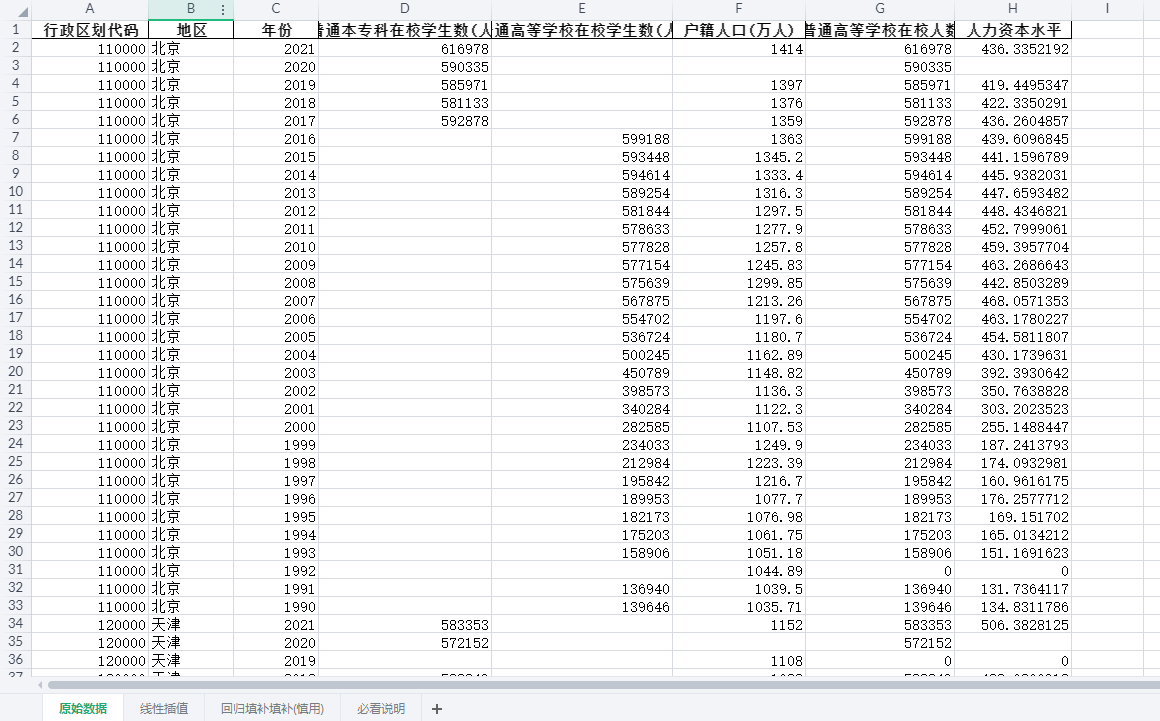
超全全国所有城市人力资本测算数据集(1990-2021年)
参考《管理世界》中詹新宇(2020)的做法,本文对地级市的人力资本水平进行测算,其中人力资本水平用地级市的普通高等学校在校学生数占该地区总人口比重来反映 一、数据介绍 数据名称:地级市-人力资本测算 数据年份&…...

(二)docker:建立oracle数据库mount startup
这章其实我想试一下startup部分做mount,因为前一章在建完数据库容器后,需要手动创建用户,授权,建表等,好像正好这部分可以放到startup里,在创建容器时直接做好;因为setup部分我实在没想出来能做…...
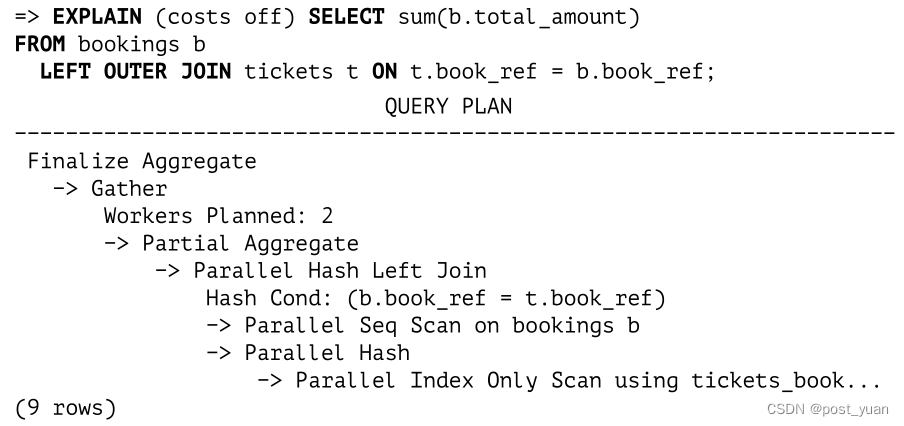
Hash Join(PostgreSQL 14 Internals翻译版)
一阶段哈希连接(One-Pass Hash Joins) 散列连接使用预构建的散列表搜索匹配的行。下面是一个使用这种连接的计划的例子: 在第一阶段,哈希连接节点1调用哈希节点2,哈希节点2从其子节点提取整个内部行集,并将…...
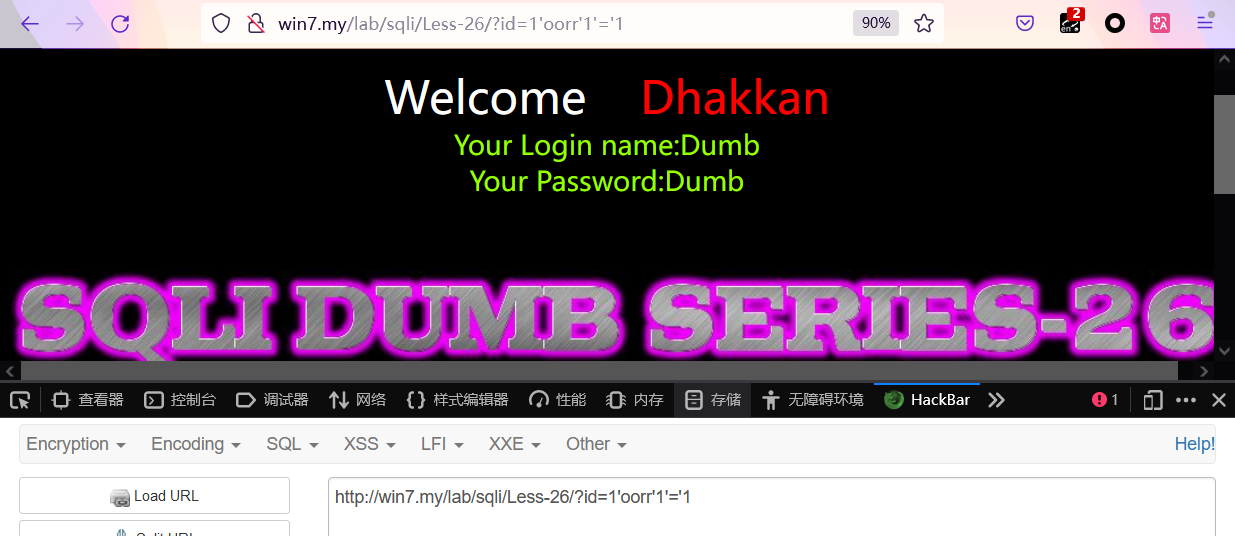
《SQLi-Labs》04. Less 23~28a
title: 《SQLi-Labs》04. Less 23~28a date: 2023-10-19 19:37:40 updated: 2023-10-19 19:38:40 categories: WriteUp:Security-Lab excerpt: 联合注入,注释符过滤绕过之构造闭合,%00 截断、二次注入、报错注入,空格过滤绕过&…...
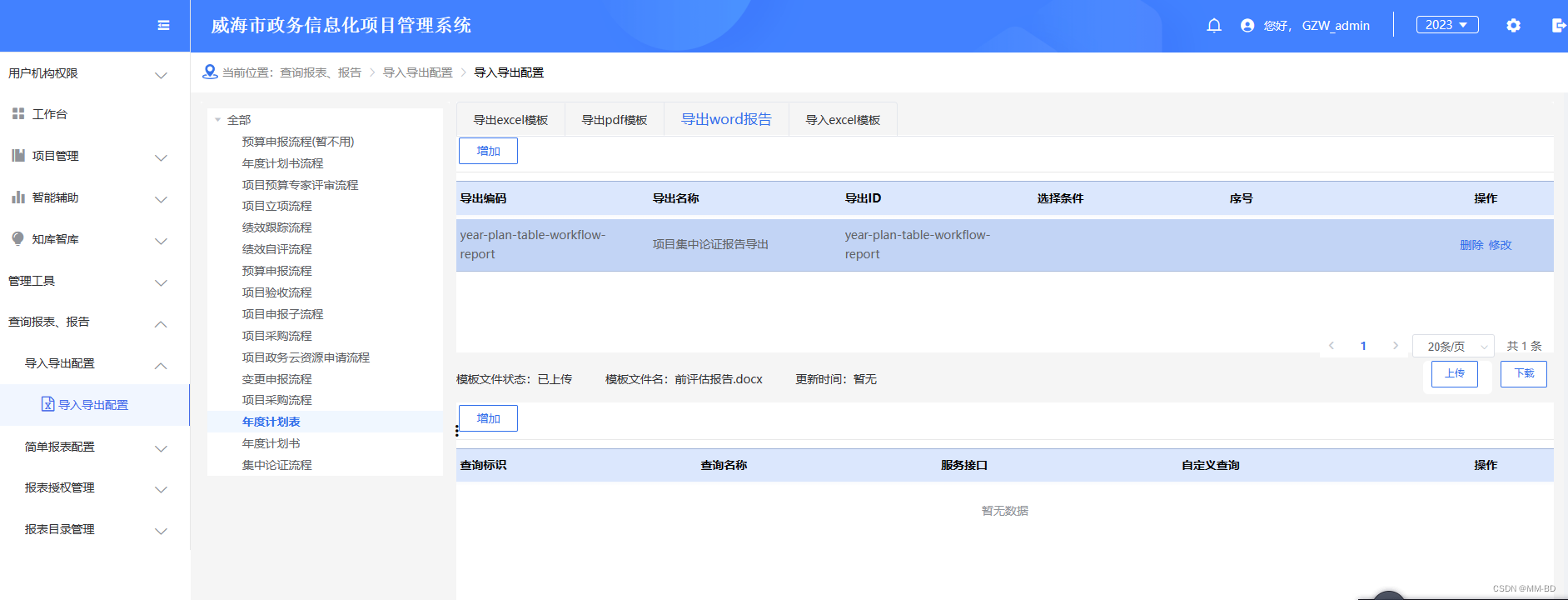
文件打包下载excel导出和word导出
0.文件下载接口 请求 GET /pm/prj/menu/whsj/download/{affixId} 文件affixId多个id以逗号隔开。多个文件会以打包得形式。 1.Excel导出 1.0接口 POST 127.0.0.1:8400/pm/io/exportExcel/year-plan-table-workflow/report 参数 [{"org":"011","re…...
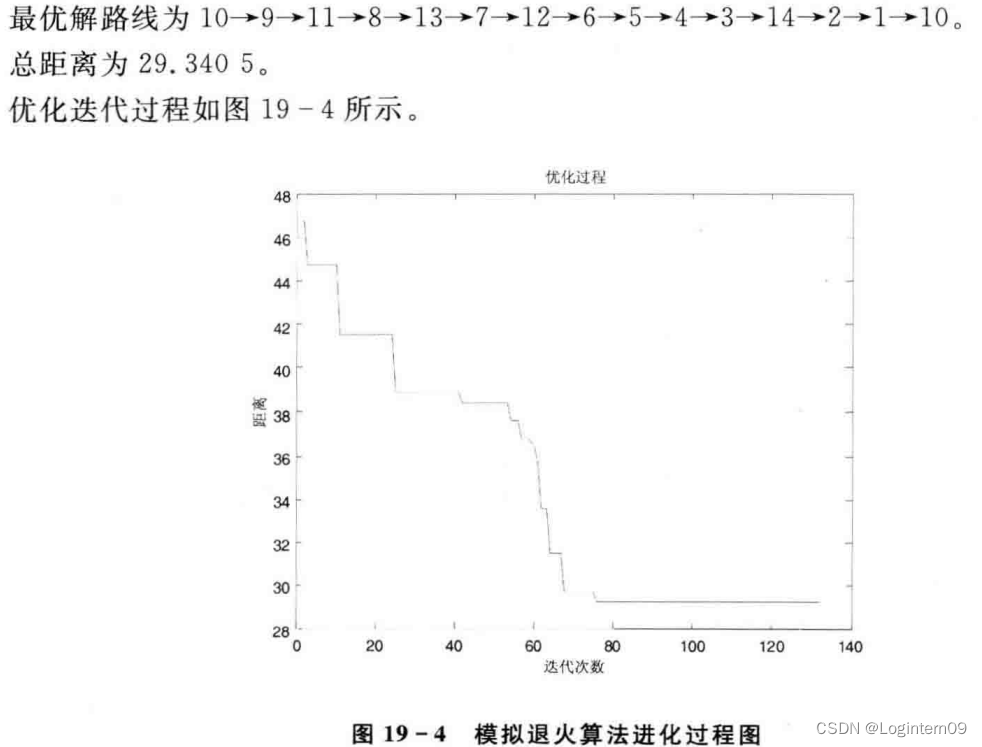
模拟退火算法求解TSP问题(python)
模拟退火算法求解TSP的步骤参考书籍《Matlab智能算法30个案例分析》。 问题描述 TSP问题描述在该书籍的第4章 算法流程 部分实现代码片段 坐标轴转换成两点之间直线距离长度的代码 coordinates np.array([(16.47, 96.10),(16.47, 94.44),(20.09, 92.54),(22.39, 93.37),(2…...

电路基础元件
文章目录 每周电子w5——电路元件基本电路元件电阻元件电容元件电感元件 每周电子w5——电路元件 基本电路元件 电路元件:是电路中最基本的组成单元 电路元件通过其端子与外部相连接;元件的特性则通过与端子有关的物理量描述每一种元件反映某种确定的电…...

百度地图API:JavaScript开源库几何运算判断点是否在多边形内(电子围栏)
百度地图JavaScript开源库,是一套基于百度地图API二次开发的开源的代码库。目前提供多个lib库,帮助开发者快速实现在地图上添加Marker、自定义信息窗口、标注相关开发、区域限制设置、几何运算、实时交通、检索与公交驾车查询、鼠标绘制工具等功能。 判…...
BFS专题8 中国象棋-马-无障碍
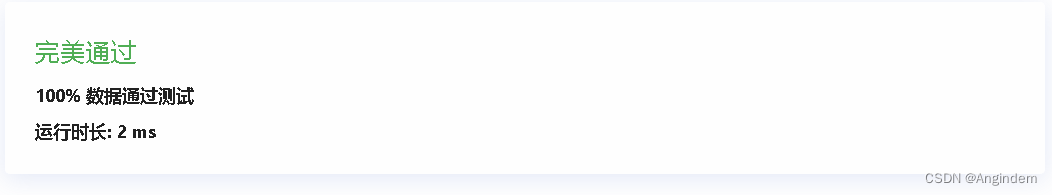
题目: 样例: 输入 3 3 2 1 输出 3 2 1 0 -1 4 3 2 1 思路: 单纯的BFS走一遍即可,只是方向坐标的移动变化,需要变化一下。 代码详解如下: #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include…...
R语言中fread怎么使用?
R语言中 fread 怎么用? 今天分享的笔记内容是数据读取神器fread,速度嘎嘎快。在R语言中,fread函数是data.table包中的一个功能强大的数据读取函数,可以用于快速读取大型数据文件,它比基本的read.table和read.csv函数更…...
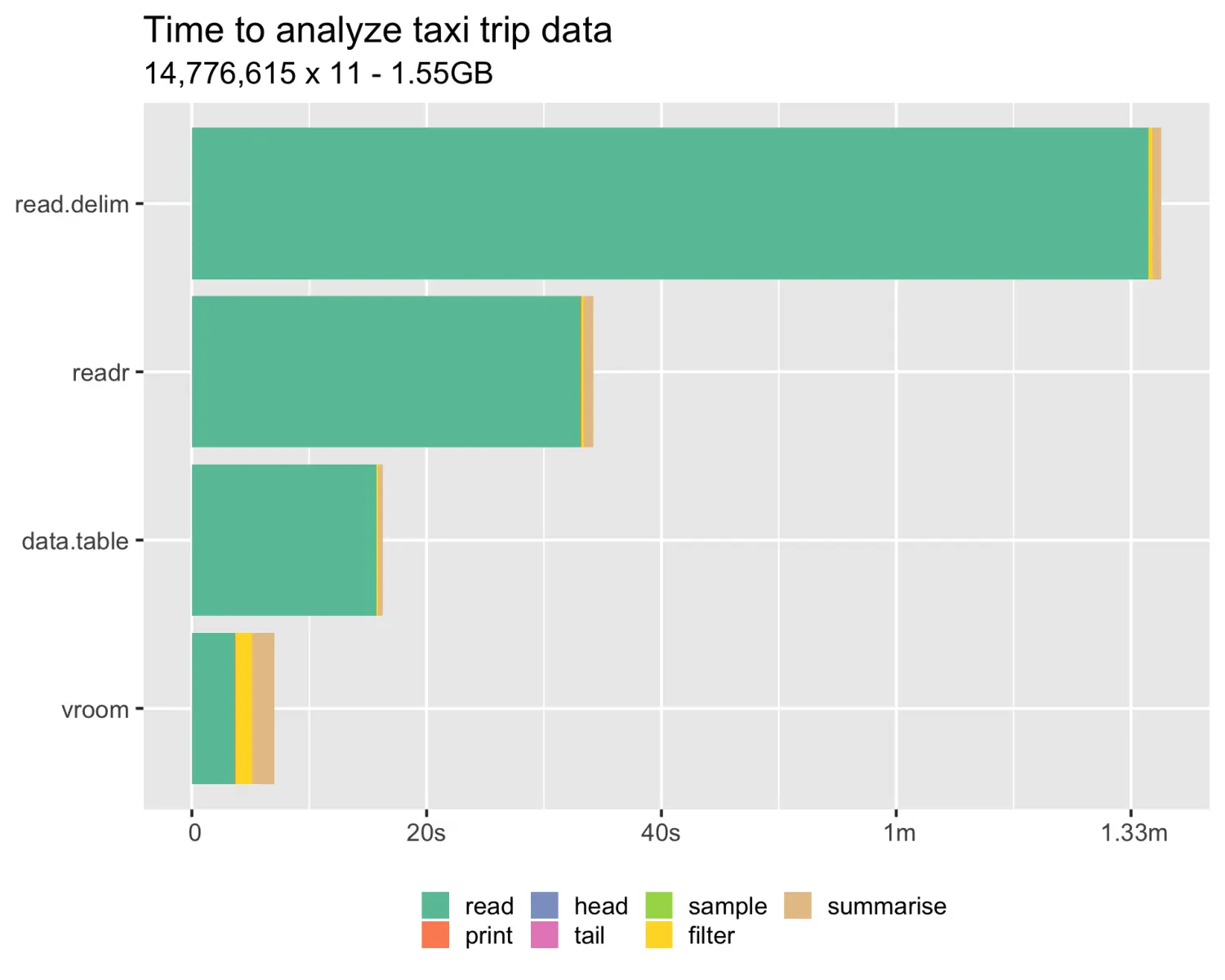
element-plus 表格-自定义样式实现2
<template><h2>表格修改样式利用属性修改</h2><h3>row-style 行样式</h3><h3>row-style header-row-style 不能改背景色</h3><h3>cell-style header-cell-style能改背景色</h3><el-tableref"tableRef":dat…...
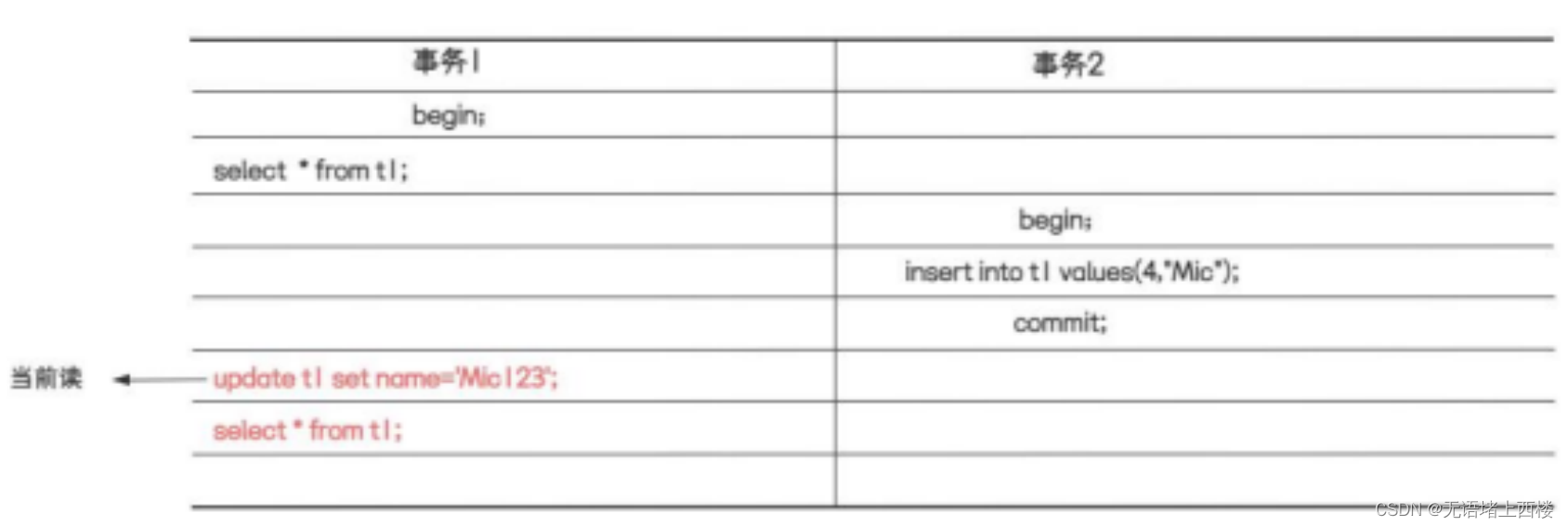
Mysql中的RR 隔离级别,到底有没有解决幻读问题
Mysql 中的 RR 事务隔离级别,在特定的情况下会出现幻读的问题。所谓的幻读,表示在同一个事务中的两次相同条件的查询得到的数据条数不一样。 在 RR 级别下,什么情况下会出现幻读 这样一种情况,在事务 1 里面通过 update 语句触发当…...
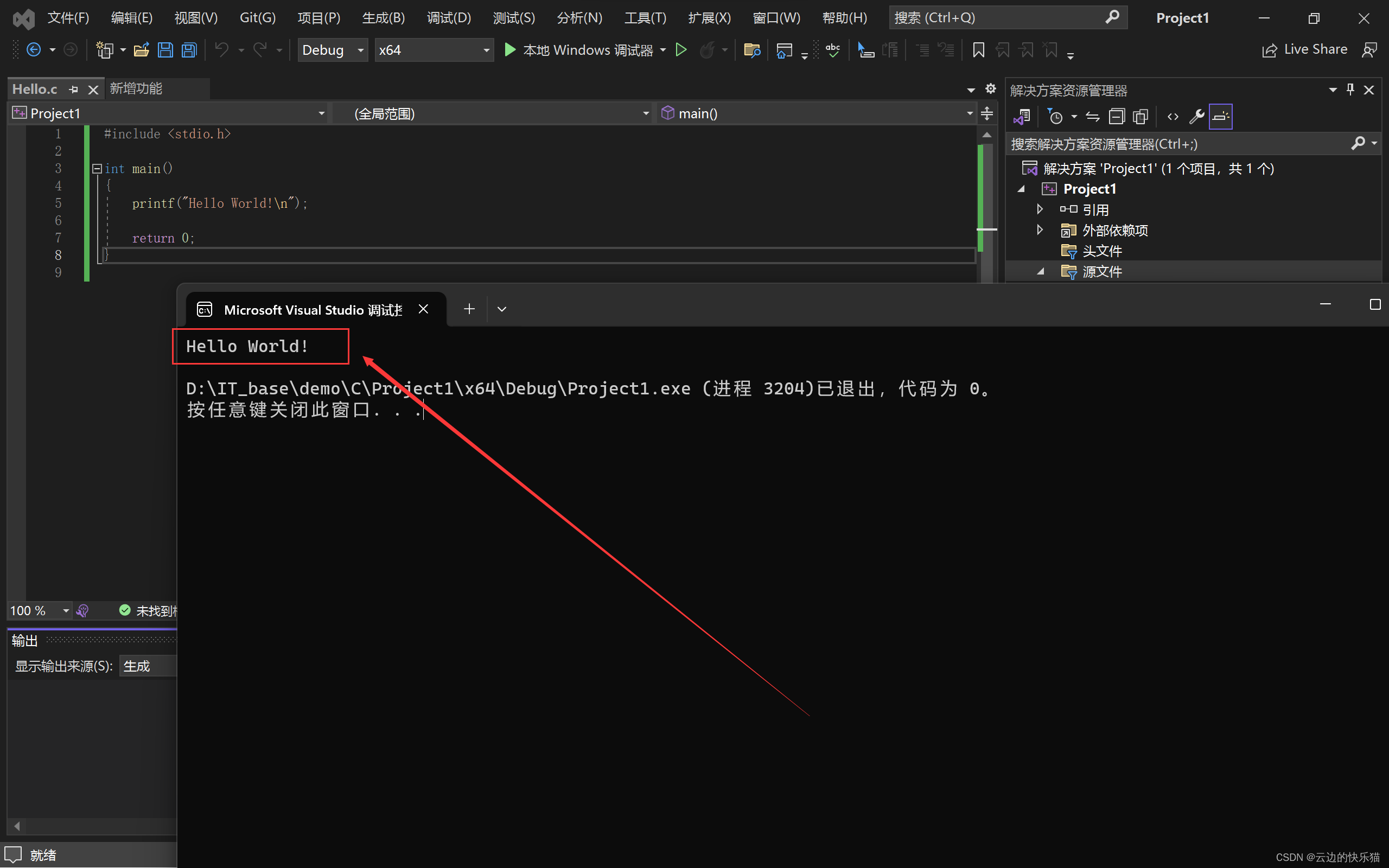
Visual Studio 2022下载安装的详细步骤-----C语言编辑器
目录 一、介绍 (一)和其他软件的区别 (二)介绍编写C语言的编辑器类型 二、下载安装 三、创建与运行第一个C语言程序 (一)创建项目 (二)新建文件 (三)…...
数据可视化与GraphQL:利用Apollo创建仪表盘
前言 「作者主页」:雪碧有白泡泡 「个人网站」:雪碧的个人网站 「推荐专栏」: ★java一站式服务 ★ ★ React从入门到精通★ ★前端炫酷代码分享 ★ ★ 从0到英雄,vue成神之路★ ★ uniapp-从构建到提升★ ★ 从0到英雄ÿ…...

Java中静态常量和枚举类的区别
在项目中我们有时候会使用常量、静态常量以及枚举,那么他们有什么区别呢?我们先看几个例子: 若依框架中使用的常量: /** 正常状态 */public static final String NORMAL "0";/** 异常状态 */public static final Stri…...
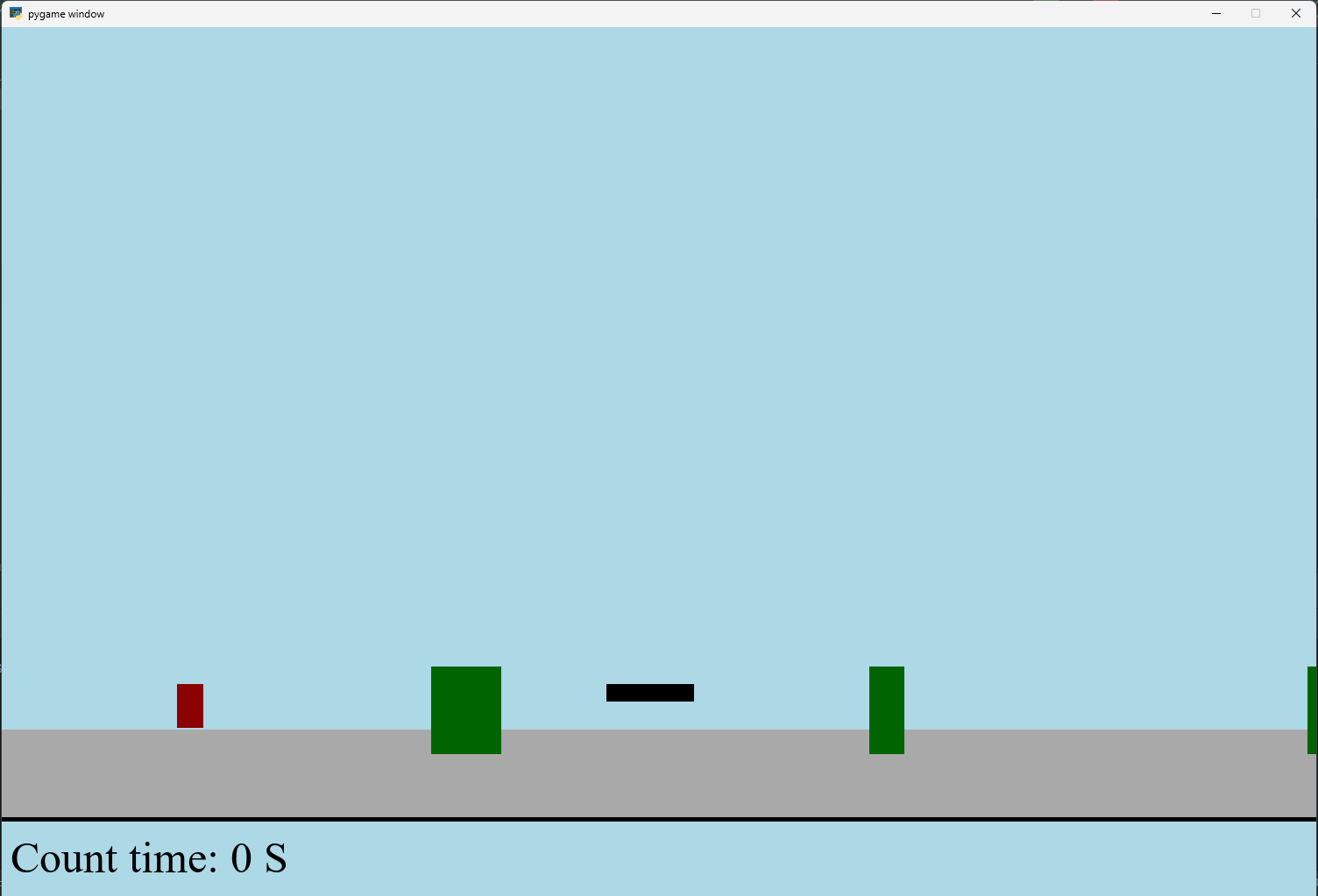
【Python】 -- 趣味代码 - 小恐龙游戏
文章目录 文章目录 00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架代码结构和功能游戏流程总结01 小恐龙游戏程序设计02 百度网盘地址00 小恐龙游戏程序设计框架 这段代码是一个基于 Pygame 的简易跑酷游戏的完整实现,玩家控制一个角色(龙)躲避障碍物(仙人掌和乌鸦)。以下是代码的详细介绍:…...

地震勘探——干扰波识别、井中地震时距曲线特点
目录 干扰波识别反射波地震勘探的干扰波 井中地震时距曲线特点 干扰波识别 有效波:可以用来解决所提出的地质任务的波;干扰波:所有妨碍辨认、追踪有效波的其他波。 地震勘探中,有效波和干扰波是相对的。例如,在反射波…...

利用ngx_stream_return_module构建简易 TCP/UDP 响应网关
一、模块概述 ngx_stream_return_module 提供了一个极简的指令: return <value>;在收到客户端连接后,立即将 <value> 写回并关闭连接。<value> 支持内嵌文本和内置变量(如 $time_iso8601、$remote_addr 等)&a…...
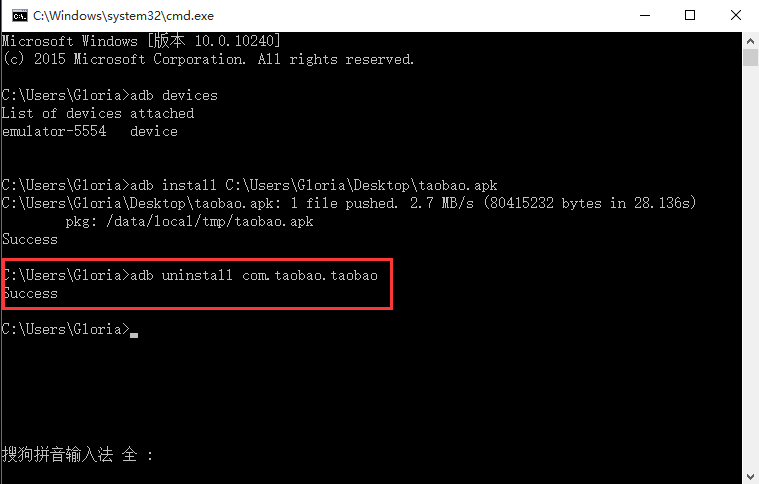
Appium+python自动化(十六)- ADB命令
简介 Android 调试桥(adb)是多种用途的工具,该工具可以帮助你你管理设备或模拟器 的状态。 adb ( Android Debug Bridge)是一个通用命令行工具,其允许您与模拟器实例或连接的 Android 设备进行通信。它可为各种设备操作提供便利,如安装和调试…...

iPhone密码忘记了办?iPhoneUnlocker,iPhone解锁工具Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 高级注册版分享
平时用 iPhone 的时候,难免会碰到解锁的麻烦事。比如密码忘了、人脸识别 / 指纹识别突然不灵,或者买了二手 iPhone 却被原来的 iCloud 账号锁住,这时候就需要靠谱的解锁工具来帮忙了。Aiseesoft iPhone Unlocker 就是专门解决这些问题的软件&…...

HTML 列表、表格、表单
1 列表标签 作用:布局内容排列整齐的区域 列表分类:无序列表、有序列表、定义列表。 例如: 1.1 无序列表 标签:ul 嵌套 li,ul是无序列表,li是列表条目。 注意事项: ul 标签里面只能包裹 li…...

渲染学进阶内容——模型
最近在写模组的时候发现渲染器里面离不开模型的定义,在渲染的第二篇文章中简单的讲解了一下关于模型部分的内容,其实不管是方块还是方块实体,都离不开模型的内容 🧱 一、CubeListBuilder 功能解析 CubeListBuilder 是 Minecraft Java 版模型系统的核心构建器,用于动态创…...
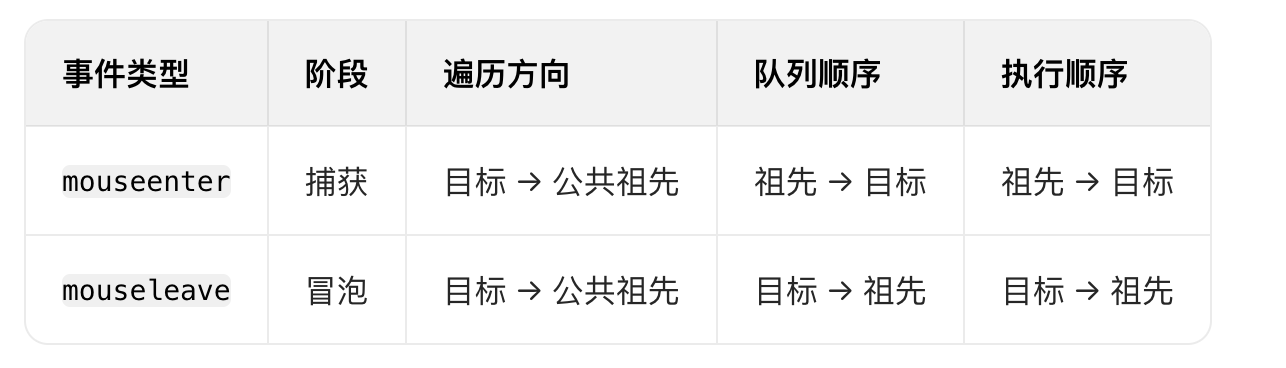
React19源码系列之 事件插件系统
事件类别 事件类型 定义 文档 Event Event 接口表示在 EventTarget 上出现的事件。 Event - Web API | MDN UIEvent UIEvent 接口表示简单的用户界面事件。 UIEvent - Web API | MDN KeyboardEvent KeyboardEvent 对象描述了用户与键盘的交互。 KeyboardEvent - Web…...
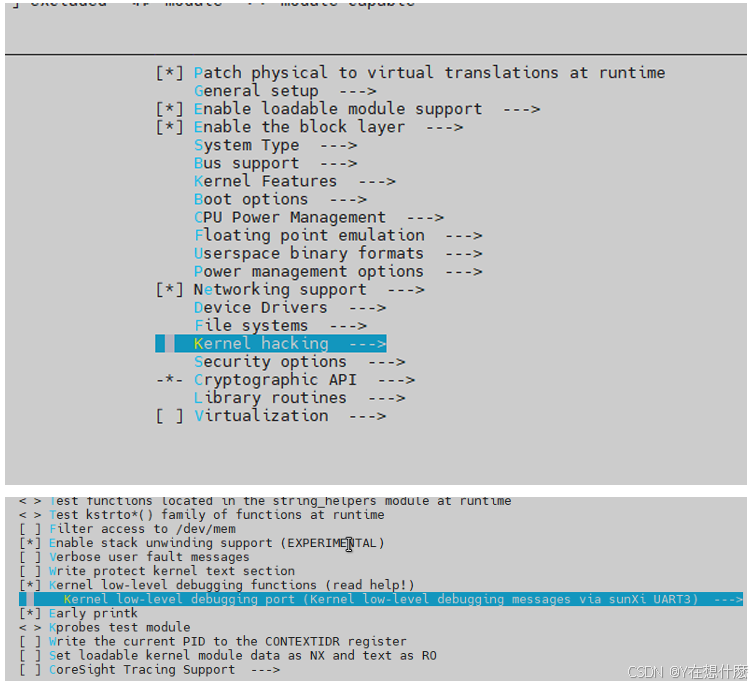
全志A40i android7.1 调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3
一,概述 1. 目的 将调试信息打印串口由uart0改为uart3。 2. 版本信息 Uboot版本:2014.07; Kernel版本:Linux-3.10; 二,Uboot 1. sys_config.fex改动 使能uart3(TX:PH00 RX:PH01),并让boo…...

【碎碎念】宝可梦 Mesh GO : 基于MESH网络的口袋妖怪 宝可梦GO游戏自组网系统
目录 游戏说明《宝可梦 Mesh GO》 —— 局域宝可梦探索Pokmon GO 类游戏核心理念应用场景Mesh 特性 宝可梦玩法融合设计游戏构想要素1. 地图探索(基于物理空间 广播范围)2. 野生宝可梦生成与广播3. 对战系统4. 道具与通信5. 延伸玩法 安全性设计 技术选…...
